Diversity of Collagen Proteins and Their Biomedical Applications in Drug Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diversity of Collagens
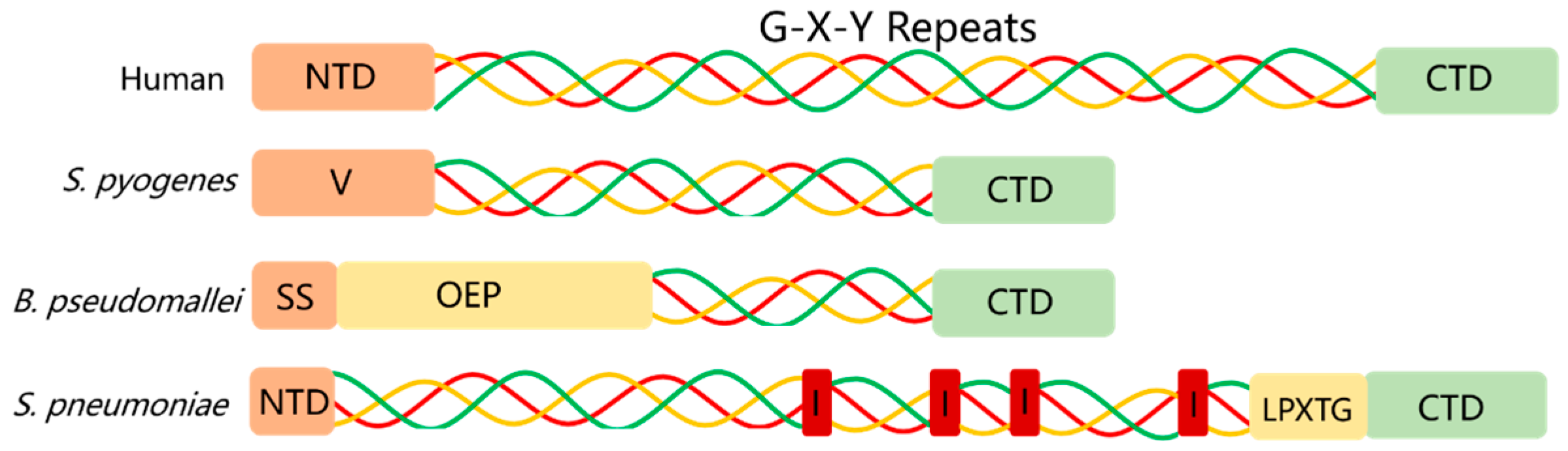
2.1. Prokaryotic Collagen
2.2. Marine Collagen
| Organisms | Species | Tissue Sources | Collagen Content (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea eel | Muraenesox cinereus | Swim bladder | 93.7 | [31] |
| Megalonibea | Megalonibea fusca | Swim bladder | 84.8 | [32] |
| Sea cucumber | Holothuria cinerascens | Body wall | 72.2 | [33] |
| Totoaba | Totoaba macdonaldi | Swim bladder | 65 | [34] |
| Yellowfin tuna | Thunnus albacares | Skin | 61.26 | [35] |
| Asian sea bass | Lates calcarifer | Skin | 59.31 | [35] |
| Mackerel | Scomberomorous niphonius | Skin | 58.62 | [36] |
| Seer fish | Scomberomorus commerson | Skin | 58.21 | [35] |
| Grass carp | Ctenopharyngodon idella | Swim bladder | 38.9 | [37] |
| Sturgeon | Acipenser baeri | cartilage | 28.8 | [38] |
2.3. Mammalian Collagen
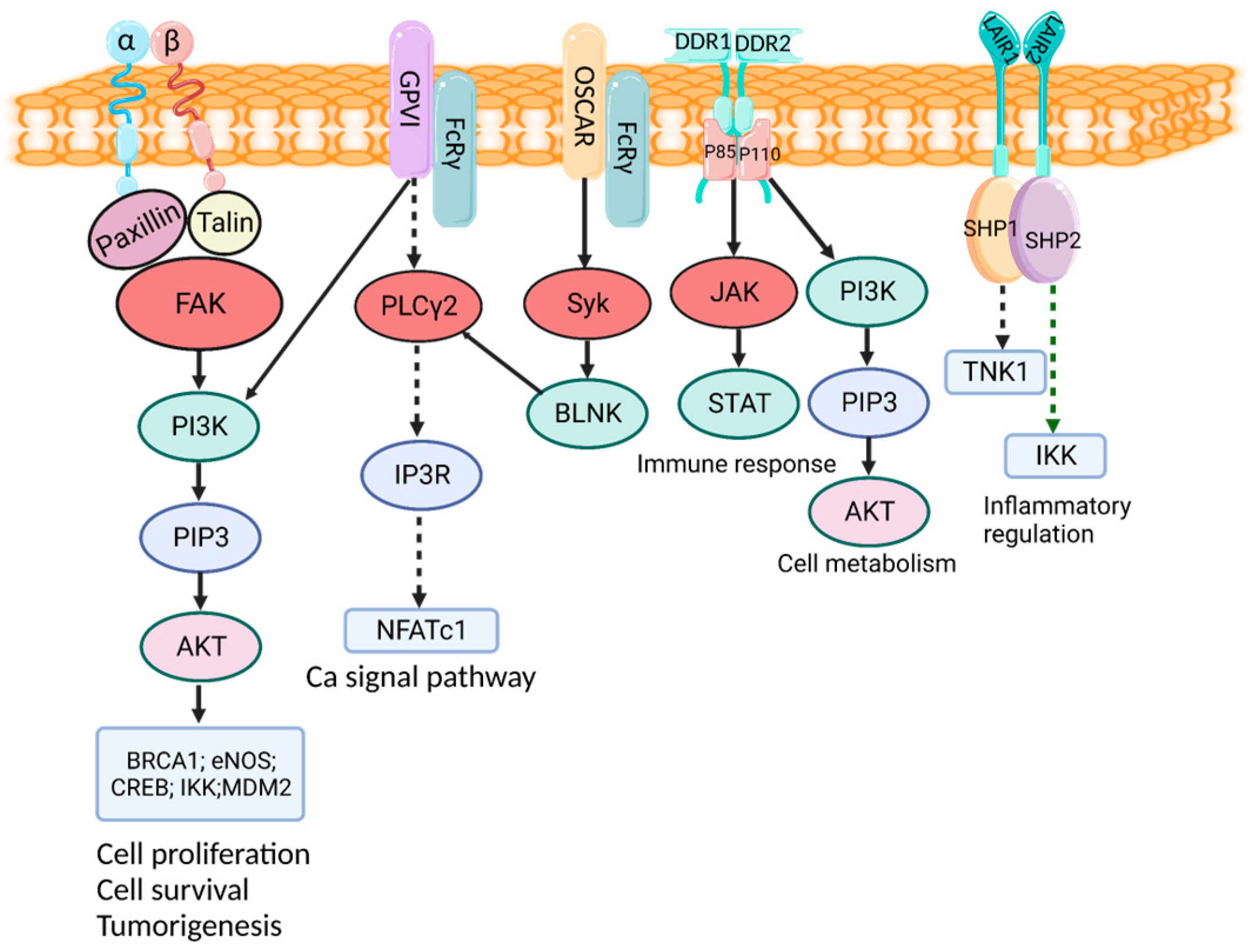
3. Cell Receptor and Function of Collagens
3.1. Integrin Receptor
3.2. DDR
3.3. GPVI Receptor
3.4. OSCAR
3.5. LAIR1 Receptor
3.6. MRC2 Receptor
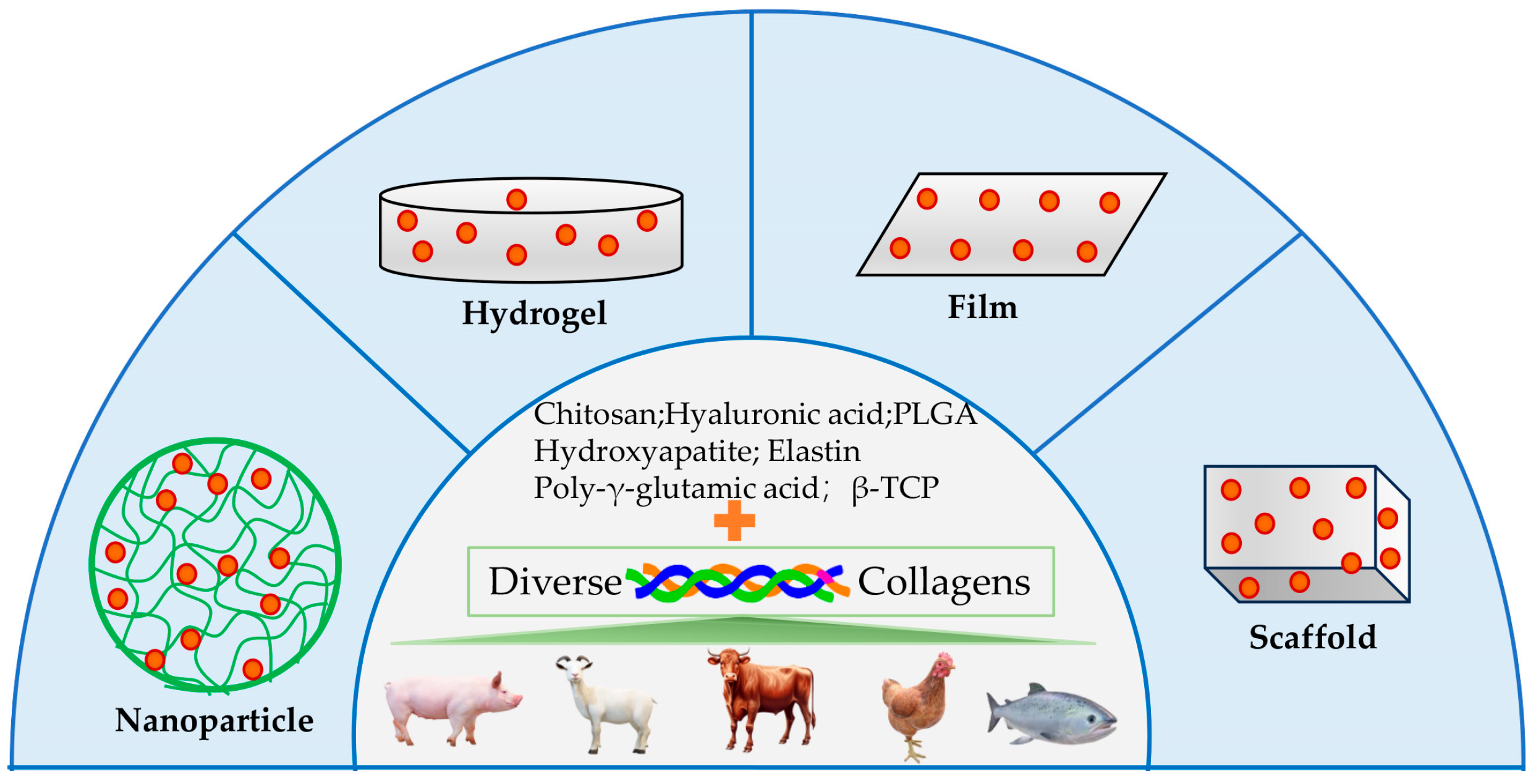
4. Collagen Application for Drug Delivery
4.1. Delivery of Small Molecule Drug
4.2. Delivery of Protein and Peptide Drug
4.3. Delivery of Therapeutic Cells
4.4. Delivery of Gene Drug
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- San Antonio, J.D.; Jacenko, O.; Fertala, A.; Orgel, J.P.R.O. Collagen Structure-Function Mapping Informs Applications for Regenerative Medicine. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exposito, J.Y.; Valcourt, U.; Cluzel, C.; Lethias, C. The Fibrillar Collagen Family. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Lew, J.; Premkumar, J.; Poh, C.L.; Win Naing, M. Production of recombinant collagen: State of the art and challenges. Eng. Biol. 2017, 1, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, B.M.; Keen, J.N.; McPherson, M.J. Collagen-like sequences stabilize homotrimers of a bacterial hydrolase. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 2903–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukomski, S.; Nakashima, K.; Abdi, I.; Cipriano, V.J.; Ireland, R.M.; Reid, S.D.; Adams, G.G.; Musser, J.M. Identification and characterization of the scl gene encoding a group A Streptococcus extracellular protein virulence factor with similarity to human collagen. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6542–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatmore, A.M. Streptococcus pyogenes sclB encodes a putative hypervariable surface protein with a collagen-like repetitive structure. Microbiology 2001, 147, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; St Leger, R.J. A collagenous protective coat enables Metarhizium anisopliae to evade insect immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6647–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro-Guajardo, M.; Olguín-Araneda, V.; Barra-Carrasco, J.; Brito-Silva, C.; Sarker, M.R.; Paredes-Sabja, D. Characterization of the collagen-like exosporium protein, BclA1, of Clostridium difficile spores. Anaerobe 2014, 25, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, G.K.; Nieminen, L.; Jefferies, J.M.C.; Mitchell, T.J. PclA, a pneumococcal collagen-like protein with selected strain distribution, contributes to adherence and invasion of host cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 285, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C.; Prashar, A.; So, J.; Tang, P.; Low Donald, E.; Terebiznik, M.; Guyard, C. Lcl of Legionella pneumophila Is an Immunogenic GAG Binding Adhesin That Promotes Interactions with Lung Epithelial Cells and Plays a Crucial Role in Biofilm Formation. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2168–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, B.A.; Choi, S.J.; Snyder, A.K.; Rio, R.V.M.; Durney, B.C.; Holland, L.A.; Amemiya, K.; Welkos, S.L.; Bozue, J.A.; Cote, C.K.; et al. A Unique Set of the Burkholderia Collagen-Like Proteins Provides Insight into Pathogenesis, Genome Evolution and Niche Adaptation, and Infection Detection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Shang, Q.; Li, Y.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yang, G.; Xie, Z.; Wang, R. Collagen-Like Proteins (ClpA, ClpB, ClpC, and ClpD) Are Required for Biofilm Formation and Adhesion to Plant Roots by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Xiao, F.; Xie, J.; Li, Z.Q.; Gui, J.F. Complete genome sequence of lymphocystis disease virus isolated from China. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6982–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, S.; Lauro, F.M.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Brown, M.V.; Thomas, T.; Raftery, M.J.; Andrews-Pfannkoch, C.; Lewis, M.; Hoffman, J.M.; Gibson, J.A.; et al. Virophage control of antarctic algal host-virus dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6163–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetefeld, J.; Frank, S.; Jenny, M.; Schulthess, T.; Kammerer, R.A.; Boudko, S.; Landwehr, R.; Okuyama, K.; Engel, J. Collagen Stabilization at Atomic Level: Crystal Structure of Designed (GlyProPro)10foldon. Structure 2003, 11, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berisio, R.; Vitagliano, L.; Mazzarella, L.; Zagari, A. Crystal structure of the collagen triple helix model [(Pro-Pro-Gly)(10)](3). Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxey, A.C.; McConkey, B.J. Prediction of molecular mimicry candidates in human pathogenic bacteria. Virulence 2013, 4, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; McKillop, T.J.; Jowitt, T.A.; Howard, M.; Davies, H.; Holmes, D.F.; Roberts, I.S.; Bella, J. Collagen-Like Proteins in Pathogenic E. coli Strains. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhai, C.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Yeo, J. Current Insights on the Diverse Structures and Functions in Bacterial Collagen-like Proteins. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 3778–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukomski, S.; Bachert, B.A.; Squeglia, F.; Berisio, R. Collagen-like proteins of pathogenic streptococci. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 103, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grund, M.E.; Choi, S.J.; McNitt, D.H.; Barbier, M.; Hu, G.; LaSala, P.R.; Cote, C.K.; Berisio, R.; Lukomski, S. Burkholderia collagen-like protein 8, Bucl8, is a unique outer membrane component of a putative tetrapartite efflux pump in Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia mallei. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnicker, N.J.; Dey, M. Bacillus anthracis Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase Modifies Collagen-like Substrates in Asymmetric Patterns. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13360–13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, A.L.; Darris, C.E.; Chetyrkin, S.V.; Pedchenko, V.K.; Boudko, S.P.; Brown, K.L.; Gray Jerome, W.; Hudson, J.K.; Rokas, A.; Hudson, B.G. Collagen IV and basement membrane at the evolutionary dawn of metazoan tissues. eLife 2017, 6, e24176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Bové, X.; Torruella, G.; Donachie, S.; Suga, H.; Leonard, G.; Richards, T.A.; Ruiz-Trillo, I. Dynamics of genomic innovation in the unicellular ancestry of animals. eLife 2017, 6, e26036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, M.H.; Hall, B.; Hofman, K. Isolation and Characterisation of Major and Minor Collagens from Hyaline Cartilage of Hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae). Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, F.; Ikram, M.; Shehzad, A.; Ghafoor, A. Marine Collagen: An Emerging Player in Biomedical applications. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4703–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, P.; Ridzwan, M.S.M.; Bakar, J.; Hashim, D.M. Collagen in food and beverage industries. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.S.; Ok, Y.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kwak, J.Y.; Yoon, S. Marine Collagen as A Promising Biomaterial for Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, I.R.; Ganesh, K.N. Enhanced triple helix stability of collagen peptides with 4R-aminoprolyl (Amp) residues: Relative roles of electrostatic and hydrogen bonding effects. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 2079–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tian, J.; Cao, H.; Tang, Y.; Huang, F.; Yang, Z. Preparation of Enzyme-Soluble Swim Bladder Collagen from Sea Eel (Muraenesox cinereus) and Evaluation Its Wound Healing Capacity. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; Dong, W.; Liang, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Extraction and Characterization of Pepsin- and Acid-Soluble Collagen from the Swim Bladders of Megalonibea fusca. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.H.; Lu, W.C.; Chan, Y.J.; Ko, W.C.; Jung, C.C.; Huynh, D.T.L.; Ji, Y.X. Extraction and characterization of collagen from sea cucumber (Holothuria cinerascens) and its potential application in moisturizing cosmetics. Aquaculture 2020, 515, 734590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-López, H.; Rodríguez-Morales, S.; Enríquez-Paredes, L.M.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; True, C.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; Fernández-Velasco, D.A.; López, L.M. Swim Bladder of Farmed Totoaba macdonaldi: A Source of Value-Added Collagen. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampitiya, A.; Gonapinuwala, S.T.; Fernando, C.A.N.; de Croos, M.D.S.T. Extraction and characterisation of type I collagen from the skin offcuts generated at the commercial fish processing centres. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-R.; Wang, B.; Chi, C.-F.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Gong, Y.-D.; Tang, J.-J.; Luo, H.-Y.; Ding, G.-F. Isolation and characterization of acid soluble collagens and pepsin soluble collagens from the skin and bone of Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorous niphonius). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Dai, Z. Physicochemical, Structural and Antioxidant Properties of Collagens from the Swim Bladder of Four Fish Species. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.-M.; Qiu, Y.-T.; Chi, C.-F.; Luo, H.-Y.; Wang, B. Gelatin From Cartilage of Siberian Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii): Preparation, Characterization, and Protective Function on Ultraviolet-A-Injured Human Skin Fibroblasts. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 925407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamito, M.; Nauroy, P.; Ruggiero, F. The Collagen Superfamily: Everything You Always Wanted to Know. In The Collagen Superfamily and Collagenopathies; Ruggiero, F., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Alcaide-Ruggiero, L.; Molina-Hernández, V.; Granados, M.M.; Domínguez, J.M. Main and Minor Types of Collagens in the Articular Cartilage: The Role of Collagens in Repair Tissue Evaluation in Chondral Defects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuivaniemi, H.; Tromp, G. Type III collagen (COL3A1): Gene and protein structure, tissue distribution, and associated diseases. Gene 2019, 707, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianakas, C.A.; Keeley, D.P.; Ramos-Lewis, W.; Park, K.; Jayadev, R.; Kenny, I.W.; Chi, Q.; Sherwood, D.R. Hemicentin-mediated type IV collagen assembly strengthens juxtaposed basement membrane linkage. J. Cell Biol. 2023, 222, e202112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indarwulan, N.; Savitri, M.; Ashariati, A.; Bintoro, S.U.Y.; Diansyah, M.N.; Amrita, P.N.A.; Romadhon, P.Z. Bone Mineral Density, C-Terminal Telopeptide of Type I Collagen, and Osteocalcin as Monitoring Parameters of Bone Remodeling in CML Patients Undergoing Imatinib Therapy: A Basic Science and Clinical Review. Diseases 2024, 12, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Jin, M.; Mu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ma, C.; Ma, L.; Liu, B.; Yao, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. Collagen Type II-Based Injectable Materials for In situ Repair and Regeneration of Articular Cartilage Defect. Biomater. Res. 2024, 28, 0072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, O.; Tham, S.K.; Morrison, W.; Ek, E.T.; Palmer, J.; McCombe, D. Collagen and Vascular Changes in the Scapholunate Ligament Following Injury: An Immunohistochemical Study. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, P.; Alanazi, A.; Kwok, B.; Li, Q.; Viraraghavan, G.; Balasubramanian, S.; Frank, D.B.; Lu, X.L.; Birk, D.E.; Mauck, R.L.; et al. Type V collagen exhibits distinct regulatory activities in TMJ articular disc versus condylar cartilage during postnatal growth and remodeling. Acta Biomater. 2024, 189, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Chou, C.Y. Collagen XI Alpha 1 Chain, a Novel Therapeutic Target for Cancer Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 925165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, H.E.; Lang, M.R.; Pace, J.M.; Parichy, D.M. Critical early roles for col27a1a and col27a1b in zebrafish notochord morphogenesis, vertebral mineralization and post-embryonic axial growth. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plumb, D.A.; Ferrara, L.; Torbica, T.; Knowles, L.; Mironov, A., Jr.; Kadler, K.E.; Briggs, M.D.; Boot-Handford, R.P. Collagen XXVII organises the pericellular matrix in the growth plate. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, H.; He, Y.; Karsdal, M.A.; Madsen, E.A.; Bay-Jensen, A.-C.; Willumsen, N.; Nielsen, S.H. Type IX Collagen Turnover Is Altered in Patients with Solid Tumors. Cancers 2024, 16, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Tartaglia, G.; Alexander, M.; Park, P.H.; Poojan, S.; Farshchian, M.; Fuentes, I.; Chen, M.; McGrath, J.A.; Palisson, F.; et al. Collagen VII maintains proteostasis in dermal fibroblasts by scaffolding TANGO1 cargo. Matrix Biol. Plus 2022, 111, 226–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubost, A.; Micol, D.; Lethias, C.; Listrat, A. New insight of some extracellular matrix molecules in beef muscles. Relationships with sensory qualities. Animal 2016, 10, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratzinger, S.; Grässel, S.; Dowejko, A.; Reichert, T.E.; Bauer, R.J. Induction of type XVI collagen expression facilitates proliferation of oral cancer cells. Matrix Biol. 2011, 30, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, A.C.; Moreno, L.; Moreno, L.; Toivonen, J.M.; Manzano, R.; Molina, N.; de la Torre, M.; López, T.; Miana-Mena, F.J.; Muñoz, M.J.; et al. Type XIX collagen: A promising biomarker from the basement membranes. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorlacius-Ussing, J.; Jensen, C.; Madsen, E.A.; Nissen, N.I.; Manon-Jensen, T.; Chen, I.M.; Johansen, J.S.; Diab, H.M.H.; Jørgensen, L.N.; Karsdal, M.A.; et al. Type XX Collagen Is Elevated in Circulation of Patients with Solid Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.Y.; Li, H.C. Genomic organization and characterization of the human type XXI collagen (COL21A1) gene. Genomics 2002, 79, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, E.A.; Thorlacius-Ussing, J.; Nissen, N.I.; Jensen, C.; Chen, I.M.; Johansen, J.S.; Diab, H.M.H.; Jørgensen, L.N.; Hansen, C.P.; Karsdal, M.A.; et al. Type XXII Collagen Complements Fibrillar Collagens in the Serological Assessment of Tumor Fibrosis and the Outcome in Pancreatic Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyhan, A.B.; Kaynar, A.; Altay, O.; Zhang, C.; Temel, S.G.; Turkez, H.; Mardinoglu, A. Identifying Hub Genes and Metabolic Pathways in Collagen VI-Related Dystrophies: A Roadmap to Therapeutic Intervention. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, H.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshihara, S.; Fukuda, H.; Tomono, Y.; Tometsuka, C.; Mizuno, K.; Nishiyama, T.; Hattori, S. Laminin 511 E8 fragment promotes to form basement membrane-like structure in human skin equivalents. Regen. Ther. 2024, 26, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, R. A novel function of membrane-associated collagen in cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2577–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Sun, R.; Xu, K.; Wang, K.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Tao, W.; Yu, S.; Linghu, K.; et al. Identification of a human type XVII collagen fragment with high capacity for maintaining skin health. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2024, 9, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyard, J.; Bao, L.; Zetter, B.R. Type XXIII collagen, a new transmembrane collagen identified in metastatic tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20989–20994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, C.R.; Ruud, K.F.; Martinez, S.R.; Li, W. Identification of the Collagen Types Essential for Mammalian Breast Acinar Structures. Gels 2022, 8, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Pan, X.; Mi, J. Fiber anatomy and histological characteristics of the innervation of the triangular fibrocartilage complex. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2024, 46, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretaud, S.; Guillon, E.; Karppinen, S.M.; Pihlajaniemi, T.; Ruggiero, F. Collagen XV, a multifaceted multiplexin present across tissues and species. Matrix Biol. Plus 2020, 15, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randles, M.J.; Lausecker, F.; Kong, Q.; Suleiman, H.; Reid, G.; Kolatsi-Joannou, M.; Davenport, B.; Tian, P.; Falcone, S.; Potter, P.; et al. Identification of an Altered Matrix Signature in Kidney Aging and Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 1713–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohabeer, A.L.; Kroetsch, J.T.; McFadden, M.; Khosraviani, N.; Broekelmann, T.J.; Hou, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wang, M.; Gramolini, A.O.; et al. Deletion of type VIII collagen reduces blood pressure, increases carotid artery functional distensibility and promotes elastin deposition. Matrix Biol. Plus 2021, 12, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, X.; Yang, K.; Zhong, J. Oncogenic mechanisms of COL10A1 in cancer and clinical challenges (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2024, 52, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidler, A.L.; Boudko, S.P.; Rokas, A.; Hudson, B.G. The triple helix of collagens—An ancient protein structure that enabled animal multicellularity and tissue evolution. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs203950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitinger, B.; Hohenester, E. Mammalian collagen receptors. Matrix Biol. 2007, 26, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, D.V.; Calderwood, D.A. Regulation of integrin-mediated adhesions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 36, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labus, J.; Tang, K.; Henklein, P.; Krüger, U.; Hofmann, A.; Hondke, S.; Wöltje, K.; Freund, C.; Lucka, L.; Danker, K. The α(1) integrin cytoplasmic tail interacts with phosphoinositides and interferes with Akt activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2024, 1866, 184257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockhaus, K.; Hemsen, I.; Jauch-Speer, S.L.; Niland, S.; Vogl, T.; Eble, J.A. Integrin α2 is an early marker for osteoclast differentiation that contributes to key steps in osteoclastogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1448725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Wei, M.; Bao, B.; Pan, Z.; Elango, J.; Wu, W. The Role of Integrin Receptor’s α and β Subunits of Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cells on the Interaction of Marine-Derived Blacktip Reef Shark (Carcharhinus melanopterus) Skin Collagen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiime, M.; Erusappan, P.M.; Cukierman, E.; Chang, J.; Molven, A.; Hansen, U.; Zeltz, C.; Gullberg, D. Fibroblast integrin α11β1 is a collagen assembly receptor in mechanoregulated fibrillar adhesions. Matrix Biol. 2024, 134, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Karimpour, P.A.; Elliott, A.; He, D.; Knifley, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; O’Connor, K.L. Integrin α6β4 Upregulates PTPRZ1 Through UCHL1-Mediated Hif-1α Nuclear Accumulation to Promote Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Invasive Properties. Cancers 2024, 16, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeltz, C.; Kusche-Gullberg, M.; Heljasvaara, R.; Gullberg, D. Novel roles for cooperating collagen receptor families in fibrotic niches. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2023, 85, 102273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, R.T.; Hallett, S.A.; Ge, C. Discoidin domain receptors; an ancient family of collagen receptors has major roles in bone development, regeneration and metabolism. Front. Dent. Med. 2023, 4, 1181817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, L.K.; Luczynski, M.T.; Huang, P.H. Discoidin domain receptors: A proteomic portrait. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 3269–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariadoss, A.V.A.; Wang, C.Z. Exploring the Cellular and Molecular Mechanism of Discoidin Domain Receptors (DDR1 and DDR2) in Bone Formation, Regeneration, and Its Associated Disease Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trono, P.; Ottavi, F.; Rosano, L. Novel insights into the role of Discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) in cancer progression: A new avenue of therapeutic intervention. Matrix Biol. 2024, 125, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ding, Z.; Lu, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lu, S. DDR1-targeted therapies: Current limitations and future potential. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.R.; Yeh, Y.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Lo, F.Y.; Tang, M.J.; Wang, Y.K. DDR1 promotes E-cadherin stability via inhibition of integrin-β1-Src activation-mediated E-cadherin endocytosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmens, T.P.; Luo, Q.; Wielders, S.J.H.; Scheijen, J.; Al-Nasiry, S.; Koenen, R.R.; Wenzel, P.; Cosemans, J. Platelet collagen receptors and their role in modulating platelet adhesion patterns and activation on alternatively processed collagen substrates. Thromb. Res. 2024, 244, 109201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.P.; Herbert, J.M.J.; Pollitt, A.Y. GPVI and CLEC-2 in hemostasis and vascular integrity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, H.S.; Nitze, L.M.; Zeuthen, L.H.; Keller, P.; Gruhler, A.; Pass, J.; Chen, J.; Guo, L.; Fleetwood, A.J.; Hamilton, J.A.; et al. Collagen induces maturation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells by signaling through osteoclast-associated receptor. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 3169–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeva, I.R.; Vitale, M.; Elson, A.; Hoyland, J.A.; Bella, J. Role of OSCAR Signaling in Osteoclastogenesis and Bone Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 641162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achieng, A.O.; Guyah, B.; Cheng, Q.; Ong’echa, J.M.; Ouma, C.; Lambert, C.G.; Perkins, D.J. Molecular basis of reduced LAIR1 expression in childhood severe malarial anaemia: Implications for leukocyte inhibitory signalling. EBioMedicine 2019, 45, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Zhang, K.; Gao, X.; Lv, M.; Luan, J.; Hu, Z.; Li, A.; Gou, X. Role and mechanism of LAIR-1 in the development of autoimmune diseases, tumors, and malaria: A review. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2020, 68, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelholm, L.H.; Melander, M.C.; Hald, A.; Persson, M.; Madsen, D.H.; Jürgensen, H.J.; Johansson, K.; Nielsen, C.; Nørregaard, K.S.; Ingvarsen, S.Z.; et al. Targeting a novel bone degradation pathway in primary bone cancer by inactivation of the collagen receptor uPARAP/Endo180. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, W.; Guo, R.; Wu, H.; Huang, S.; Xu, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wei, B.; et al. Unraveling the role of integrating signal peptides into natural collagen on modulating cancer cell adhesion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andonegi, M.; Carranza, T.; Etxabide, A.; de la Caba, K.; Guerrero, P. 3D-Printed Mucoadhesive Collagen Scaffolds as a Local Tetrahydrocurcumin Delivery System. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandhakumar, S.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Ramkumar, K.M.; Raichur, A.M. Preparation of collagen peptide functionalized chitosan nanoparticles by ionic gelation method: An effective carrier system for encapsulation and release of doxorubicin for cancer drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 70, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, A.; Drannikov, A.; Surgutskaia, N.S.; Ozaltin, K.; Postnikov, P.S.; Marina, T.E.; Sedlarik, V. Chitosan-collagen based film for controlled delivery of a combination of short life anesthetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Mou, S.; Yang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Guo, L.; Zhong, A.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z. Sustained delivery of alendronate by engineered collagen scaffold for the repair of osteoporotic bone defects and resistance to bone loss. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2020, 108, 2460–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, P.; Arora, I.; Rastogi, S.; Akhtar, M.; Singh, S.; Samim, M. Collagen Nanoparticle-Mediated Brain Silymarin Delivery: An Approach for Treating Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion-Induced Brain Injury. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 538404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Huang, H.; Sullivan, M.O.; Kiick, K.L. Controlled Delivery of Vancomycin from Collagen-tethered Peptide Vehicles for the Treatment of Wound Infections. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Liu, C.J.; Chung, R.J. Integrated Oxidized-Hyaluronic Acid/Collagen Hydrogel with β-TCP Using Proanthocyanidins as a Crosslinker for Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, A.; Shin, W.; Heo, M.B.; Noh, H.J.; Hong, K.S.; Cho, J.H.; Lim, Y.T. Photothermal-modulated drug delivery and magnetic relaxation based on collagen/poly(γ-glutamic acid) hydrogel. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2607–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, W.; Tang, C.; Huang, J.; Fan, C.; Yin, Z.; Hu, Y.; Chen, W.; Ouyang, H.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Targeted pathological collagen delivery of sustained-release rapamycin to prevent heterotopic ossification. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay9526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; David, M.A.; Dunshee, L.C.; Scott, R.A.; Urello, M.A.; Price, C.; Kiick, K.L. Thermoresponsive Elastin-b-Collagen-Like Peptide Bioconjugate Nanovesicles for Targeted Drug Delivery to Collagen-Containing Matrices. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2539–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Fu, L.; Gu, C.; Wang, H.; Yu, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhao, D.; Ge, B.; Zhang, N. Delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2 by crosslinking heparin to nile tilapia skin collagen for promotion of rat calvaria bone defect repair. Prog. Biomater. 2023, 12, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, C.M.A.P.; Aguayo, S.; Zavala, G.; Khoury, M. Exosome-like vesicles in Apis mellifera bee pollen, honey and royal jelly contribute to their antibacterial and pro-regenerative activity. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb208702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, O.J.; Alvarez, S.; Contreras-Kallens, P.; Barrera, N.P.; Aguayo, S.; Schuh, C. Type I collagen hydrogels as a delivery matrix for royal jelly derived extracellular vesicles. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Wufuer, M.; Kim, I.; Choi, T.H.; Kim, B.J.; Jung, H.G.; Jeon, B.; Lee, G.; Jeon, O.H.; Chang, H.; et al. Sequential dual-drug delivery of BMP-2 and alendronate from hydroxyapatite-collagen scaffolds for enhanced bone regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Puthia, M.; Sheehy, E.J.; Ambite, I.; Petrlova, J.; Prithviraj, S.; Oxborg, M.W.; Sebastian, S.; Vater, C.; Zwingenberger, S.; et al. Sustained delivery of a heterodimer bone morphogenetic protein-2/7 via a collagen hydroxyapatite scaffold accelerates and improves critical femoral defect healing. Acta Biomater. 2023, 162, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Z.; Islam, A.; Sherrell, P.; Le-Moine, M.; Lolas, G.; Syrigos, K.; Rafat, M.; Jensen, L.D. Adjustable delivery of pro-angiogenic FGF-2 by alginate:collagen microspheres. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio027060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Lee, K.I.; Ra, H.J.; Lotz, M.K.; D’Lima, D.D. Collagen fibrous scaffolds for sustained delivery of growth factors for meniscal tissue engineering. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Liang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, F.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Song, H.; Bao, Z.; Nian, R. Development of tilapia collagen and chitosan composite hydrogels for nanobody delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 195, 111261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humpel, C. Intranasal Delivery of Collagen-Loaded Neprilysin Clears Beta-Amyloid Plaques in a Transgenic Alzheimer Mouse Model. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 649646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Y.H.; Jubin, K.; Smalley, S.; Wong, J.P.F.; Brown, R.A.; Metcalfe, A.D. A novel system for expansion and delivery of human keratinocytes for the treatment of severe cutaneous injuries using microcarriers and compressed collagen. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 3124–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, D.; Lin, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X. Cellulose Nanocrystal Reinforced Collagen-Based Nanocomposite Hydrogel with Self-Healing and Stress-Relaxation Properties for Cell Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Kong, W.; Yuan, L.; Guo, L.; Li, C.; Fan, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X. Injectable and self-crosslinkable hydrogels based on collagen type II and activated chondroitin sulfate for cell delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 2014–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.S.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Chu, A.M.W.; Chan, B.P.; Yao, K.M.; Lo, A.C.Y. Injectable cell-encapsulating composite alginate-collagen platform with inducible termination switch for safer ocular drug delivery. Biomaterials 2019, 201, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simorgh, S.; Milan, P.B.; Saadatmand, M.; Bagher, Z.; Gholipourmalekabadi, M.; Alizadeh, R.; Hivechi, A.; Arabpour, Z.; Hamidi, M.; Delattre, C. Human Olfactory Mucosa Stem Cells Delivery Using a Collagen Hydrogel: As a Potential Candidate for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials 2021, 14, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davaa, G.; Hong, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.S.; Buitrago, J.O.; Li, Y.M.; Lee, H.H.; Han, D.W.; Leong, K.W.; Hyun, J.K.; et al. Delivery of Induced Neural Stem Cells Through Mechano-Tuned Silk-Collagen Hydrogels for the Recovery of Contused Spinal Cord in Rats. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2201720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourgiantaki, A.; Tzeranis, D.S.; Karali, K.; Georgelou, K.; Bampoula, E.; Psilodimitrakopoulos, S.; Yannas, I.V.; Stratakis, E.; Sidiropoulou, K.; Charalampopoulos, I.; et al. Neural stem cell delivery via porous collagen scaffolds promotes neuronal differentiation and locomotion recovery in spinal cord injury. NPJ Regen. Med. 2020, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Cabrerizo, P.; Saludas, L.; Prósper, F.; Abizanda, G.; Echanove-González de Anleo, M.; Ruiz-Villalba, A.; Garbayo, E.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J. Development of an injectable alginate-collagen hydrogel for cardiac delivery of extracellular vesicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 629, 122356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isali, I.; McClellan, P.; Wong, T.R.; Cingireddi, S.; Jain, M.; Anderson, J.M.; Hijaz, A.; Akkus, O. In Vivo Delivery of M0, M1, and M2 Macrophage Subtypes via Genipin-Cross-Linked Collagen Biotextile. Tissue Eng. 2022, 28, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urello, M.A.; Kiick, K.L.; Sullivan, M.O. ECM turnover-stimulated gene delivery through collagen-mimetic peptide-plasmid integration in collagen. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekoura, E.K.; Dick, T.; Pankongadisak, P.; Graf, D.; Boluk, Y.; Uludağ, H. Delivery of Bioactive Gene Particles via Gelatin-Collagen-PEG-Based Electrospun Matrices. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, C.; Abbah, S.A.; Bhowmick, S.; Collin, E.; Pandit, A. Localized temporal co-delivery of interleukin 10 and decorin genes using amediated by collagen-based biphasic scaffold modulates the expression of TGF-β1/β2 in a rabbit ear hypertrophic scarring model. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 3136–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackington, W.A.; Gomez-Sierra, M.A.; González-Vázquez, A.; O’Brien, F.J.; Stoddart, M.J.; Thompson, K. Non-viral Gene Delivery of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Using Collagen-Hydroxyapatite Scaffold Protects Rat BM-MSCs From IL-1β-Mediated Inhibition of Osteogenesis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 582012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badieyan, Z.S.; Berezhanskyy, T.; Utzinger, M.; Aneja, M.K.; Emrich, D.; Erben, R.; Schüler, C.; Altpeter, P.; Ferizi, M.; Hasenpusch, G.; et al. Transcript-activated collagen matrix as sustained mRNA delivery system for bone regeneration. J. Control Release 2016, 10, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Supra Structure | Types | Polypeptide Chains | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibril | I | α1(I) × 2 + α2(I); α1(I) × 3 | Providing three-dimensional scaffolds for tissues and organs | [43] |
| II | α1(II) × 3 | [44] | ||
| III | α1(III) × 3 | [45] | ||
| V | α1(V) × 2 + α2(V); α1(V) + α2(V) + α3(V); α1(V) × 3 | [46] | ||
| XI | α1(XI) + α2(XI) + α3(XI) | [47] | ||
| XXIV | α1(XXIV) × 3 | [48] | ||
| XXVII | α1(XXVII) × 3 | [49] | ||
| Fibril associated (FACIT) | IX | α1(IX) + α2(IX) + α3(IX) | Forming a molecular bridge to enhance the organization and stability of ECM Promoting the adhesion and interactions between collagens Regulating the properties of collagens | [50] |
| XII | α1(XII) × 3 | [51] | ||
| XIV | α1(XIV) × 3 | [52] | ||
| XVI | α1(XII) × 3 | [53] | ||
| XIX | α1(XIX) × 3 | [54] | ||
| XX | α1(XX) × 3 | [55] | ||
| XXI | α1(XXI) × 3 | [56] | ||
| XXII | α1(XXII) × 3 | [57] | ||
| Microfibril | VI | α1(VI) + α2(VI) + α3(VI) | Interacting with fibrils and cells | [58] |
| Anchoring fibrils | VII | α1(VII) × 3 | Guaranteeing the integrity and stability of the basement membrane | [59] |
| Transmembrane collagen | XIII | α1(XIII) × 3 | Participating in cell adhesion, migration, and immune response | [60] |
| XVII | α1(XVII) × 3 | [61] | ||
| XXIII | α1(XXIII) × 3 | [62] | ||
| XXV | α1(XXV) × 3 | [63] | ||
| Basement membrane collagen | IV | α1(IV) × 2 + α2(IV); α3(IV) + α4(IV) + α5(IV) + α6(IV) | Enforcing tensile strength and anchoring to the laminin network | [64] |
| XV | α1(XV) × 3 | [65] | ||
| XVIII | α1(XVIII) × 3 | [66] | ||
| Short chains collagen | VIII | α1(VIII) × 2 + α2(VIII) | Involving in the calcification | [67] |
| X | α1(X) × 3 | [68] |
| Tissues or Organs | Collagen Types | Diseases |
|---|---|---|
Bone | I | Osteogenesis imperfecta |
| II | Dysplasias, achondrogenesis, kniest dysplasia | |
| XI | Stickler syndrome | |
| XXVII | Steel syndrome | |
Brain | IV | Porencephaly, schizencephaly |
Cartilage | II | Chondrodysplasias, achondrogenesis |
| IX | Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia | |
| XI | Fibrochondrogenesis, chondrodysplasias | |
Eye | I | Osteogenesis imperfecta |
| II | Dysplasias, stickler syndrome | |
| IV | Alport syndrome | |
| XI | Stickler syndrome | |
| XXV | Congenital cranial dysinnervation | |
Inner ear | I | Osteogenesis imperfecta |
| II | Stickler syndrome | |
| IV | Alport syndrome, X-linked deafness | |
| XI | Deafness | |
Joint | II | Stickler syndrome |
| III | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome | |
| V | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome | |
| IX | Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia | |
| XI | Stickler syndrome | |
Kidney | IV | Alport syndrome, hereditary angiopathy with nephropathy |
Muscle | IV | Hereditary angiopathy with nephropathy |
| VI | Bethlem myophthy, Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy | |
| XII | Bethlem myophthy | |
Skin | III | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome |
| V | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome | |
| VII | Epidermolysis bullosa | |
| XVI | Epidermolysis bullosa | |
Teeth | I | Osteogenesis imperfecta, dentinogenesis imperfecta |
Vasculature | III | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome |
| IV | Cerebral small-vessel disease, Hereditary angiopathy with nephropathy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Cao, R.; Dong, H. Diversity of Collagen Proteins and Their Biomedical Applications in Drug Delivery. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126472
Wang K, Cao R, Dong H. Diversity of Collagen Proteins and Their Biomedical Applications in Drug Delivery. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126472
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kuiming, Rui Cao, and Huijun Dong. 2025. "Diversity of Collagen Proteins and Their Biomedical Applications in Drug Delivery" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126472
APA StyleWang, K., Cao, R., & Dong, H. (2025). Diversity of Collagen Proteins and Their Biomedical Applications in Drug Delivery. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126472






