Chaotic Vibration Prediction of a Laminated Composite Cantilever Beam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Beam Model Establishment
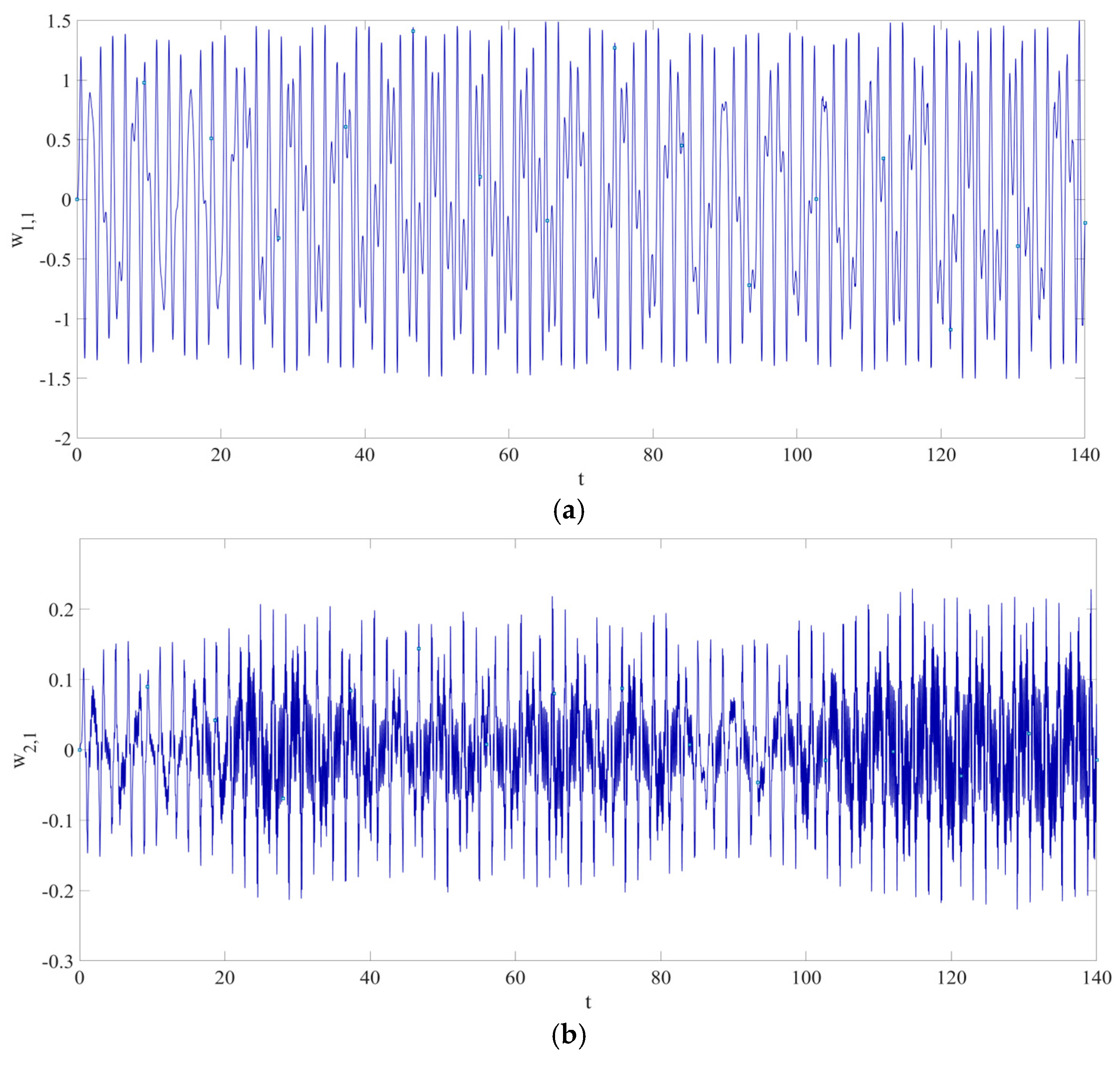
3. RNN Data-Driven Model Establishment
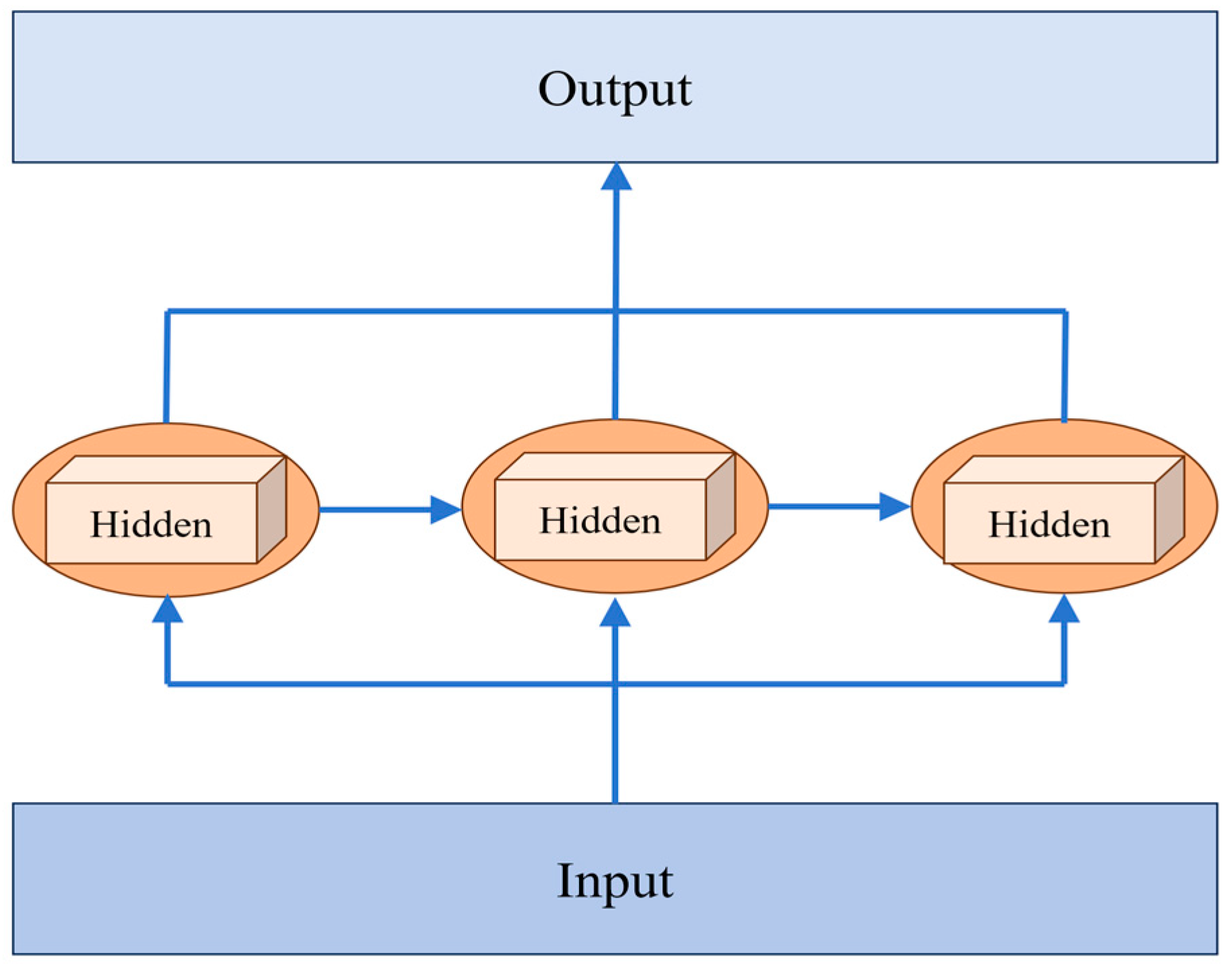
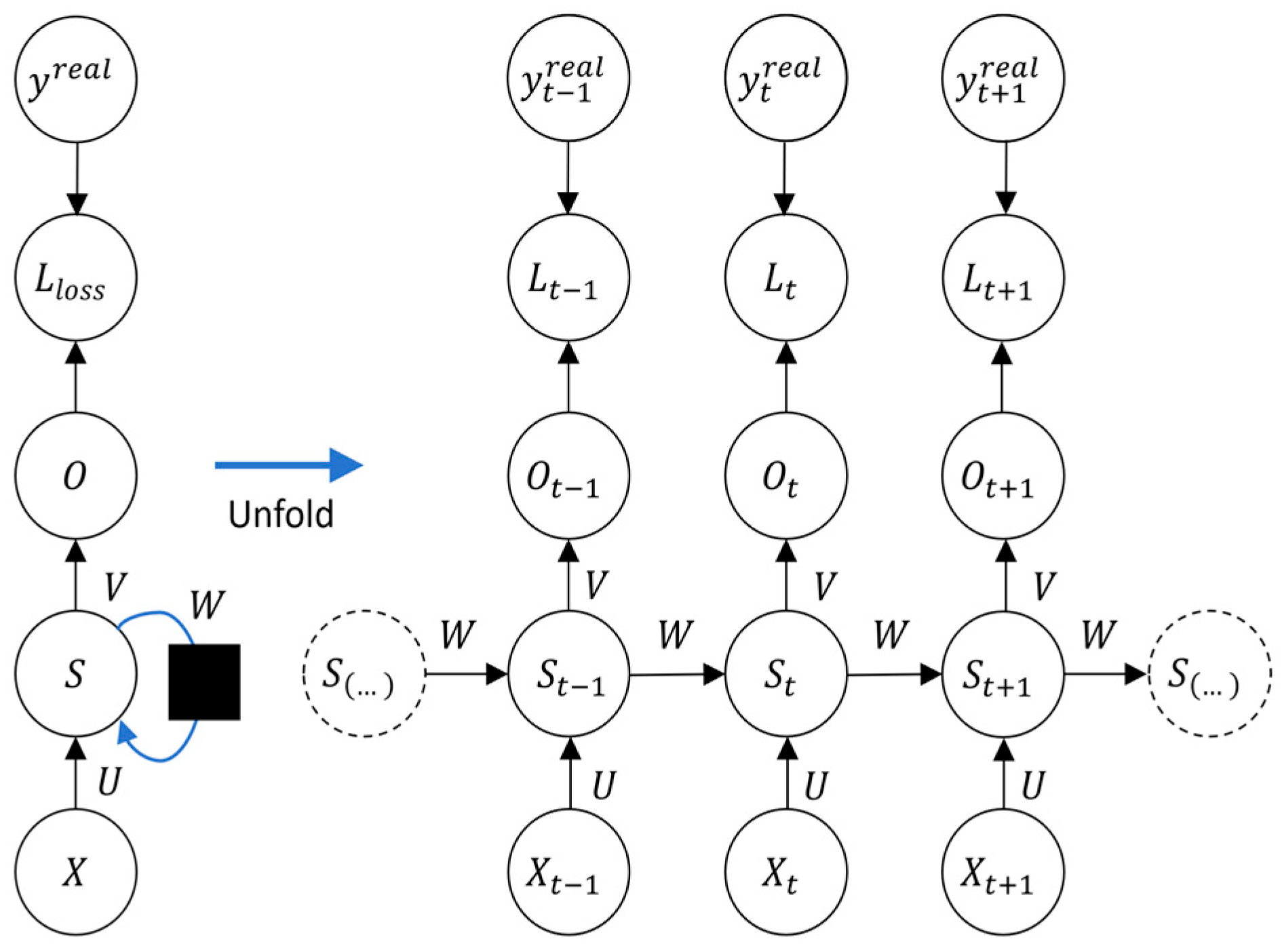
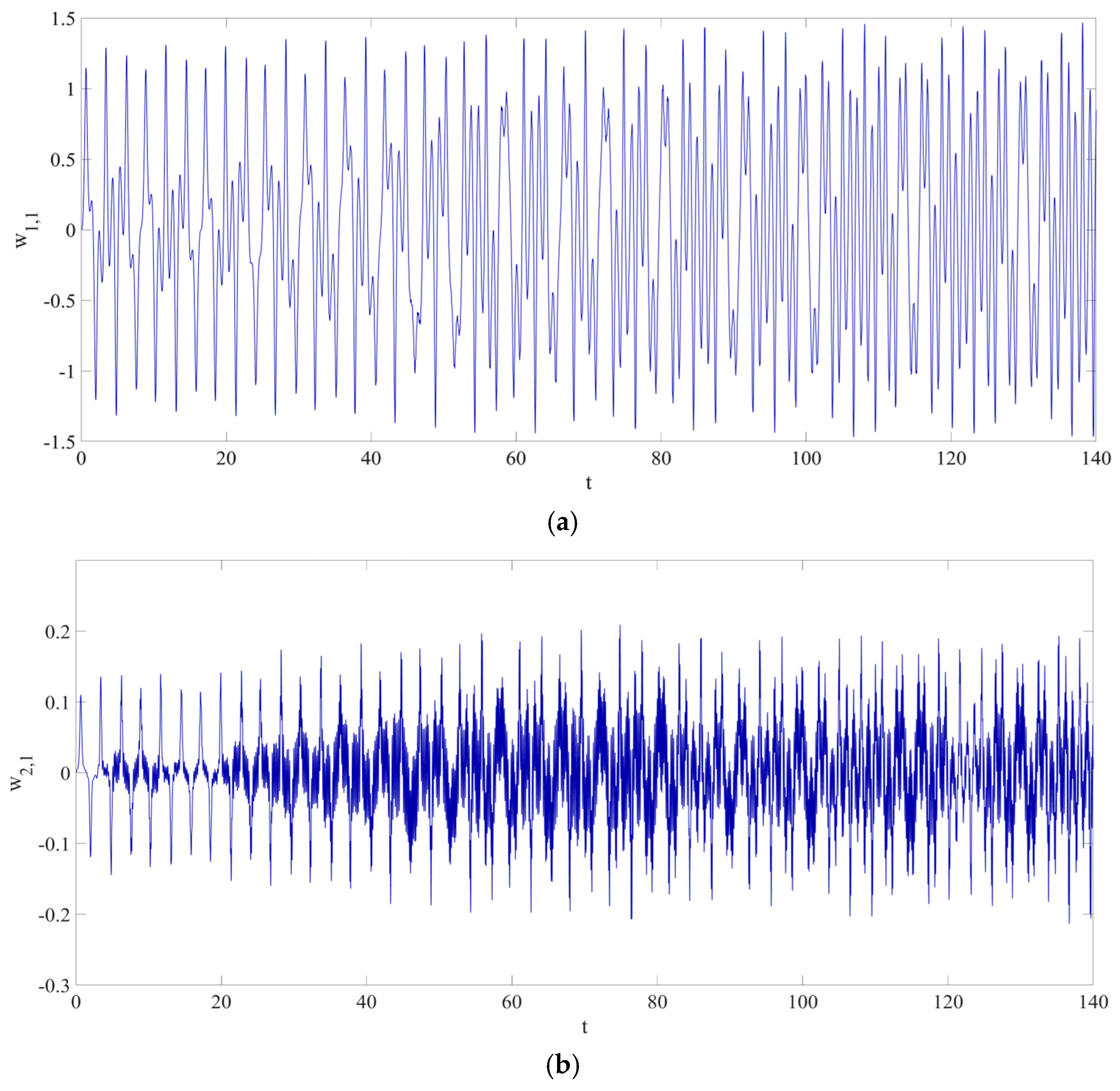
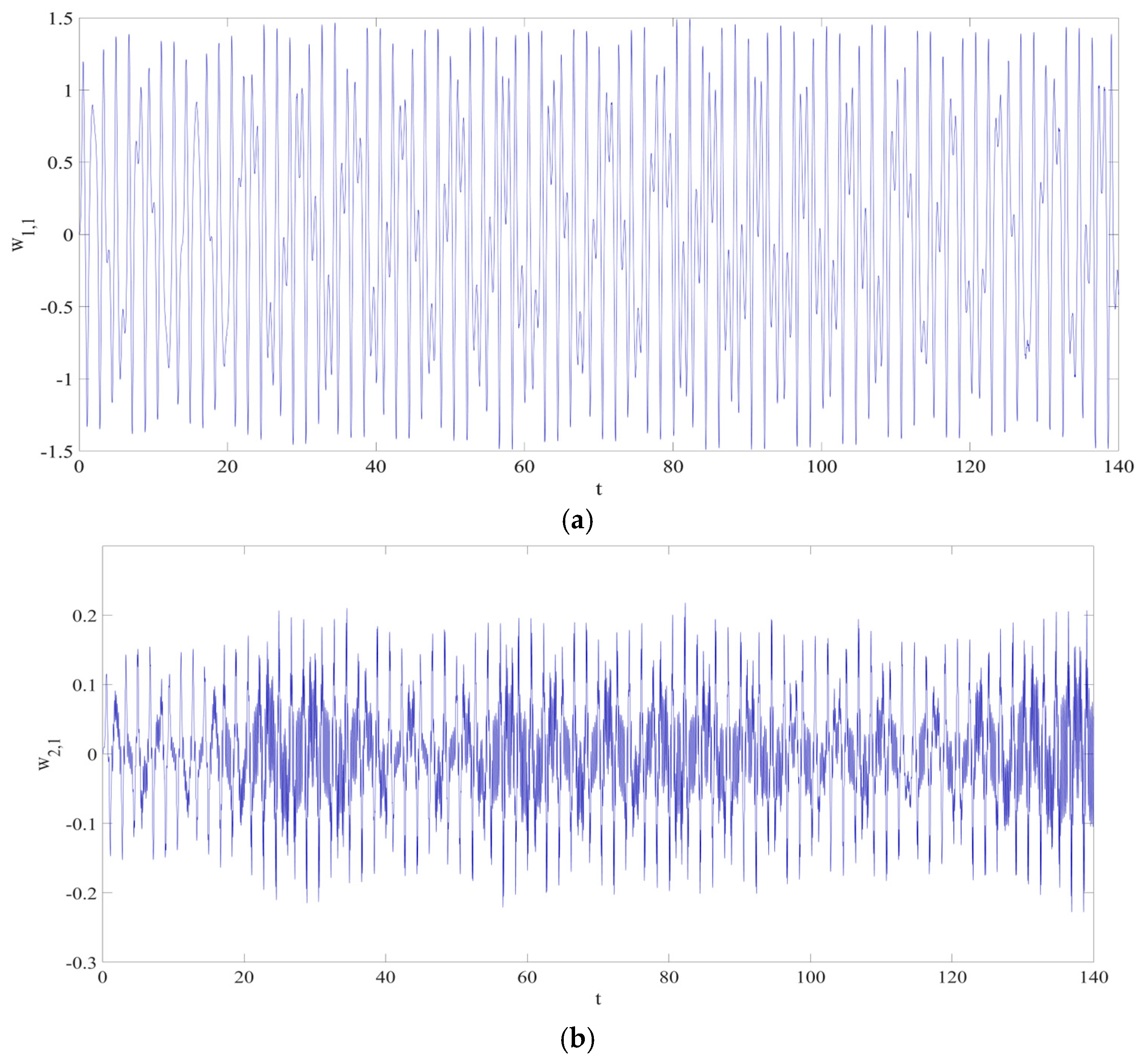
3.1. Architecture of RNN
3.2. Loss Function
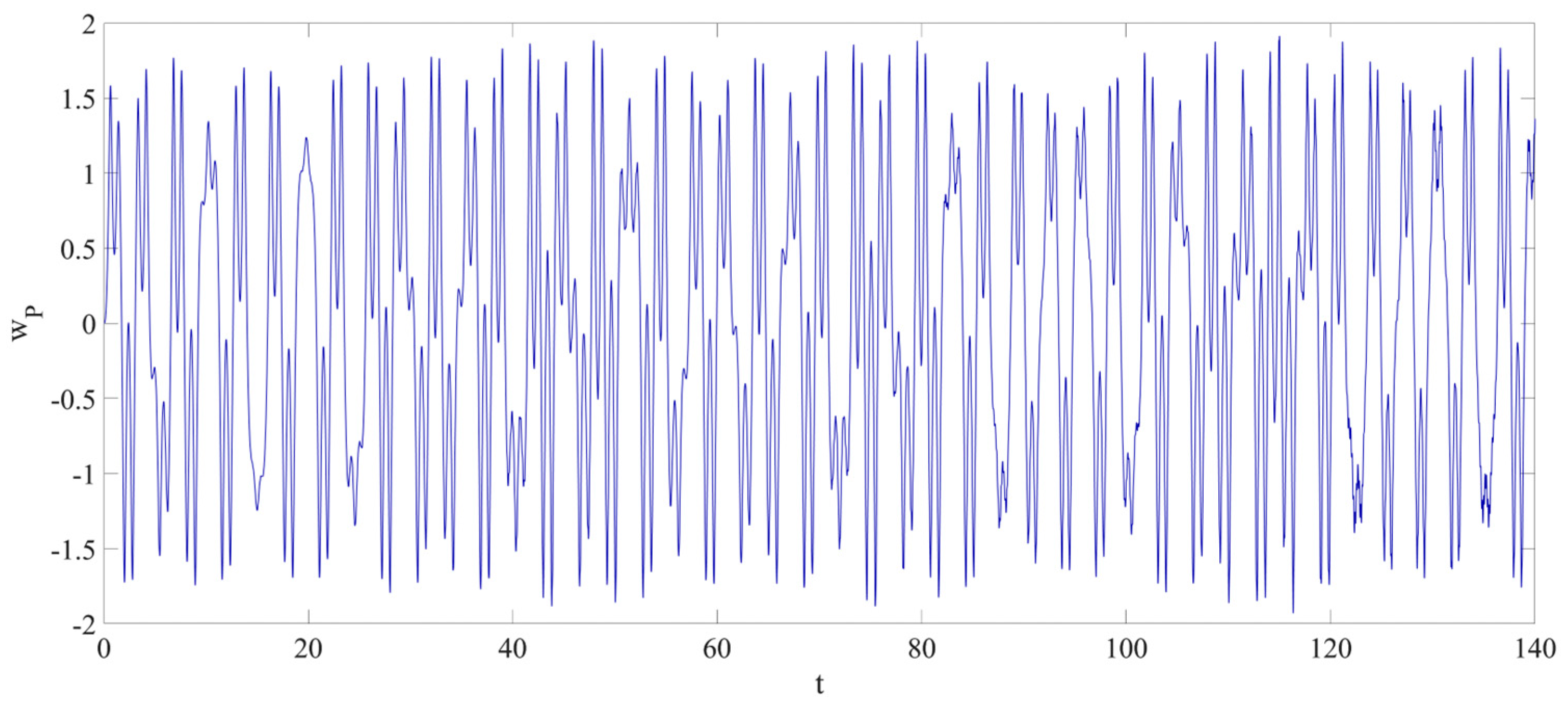
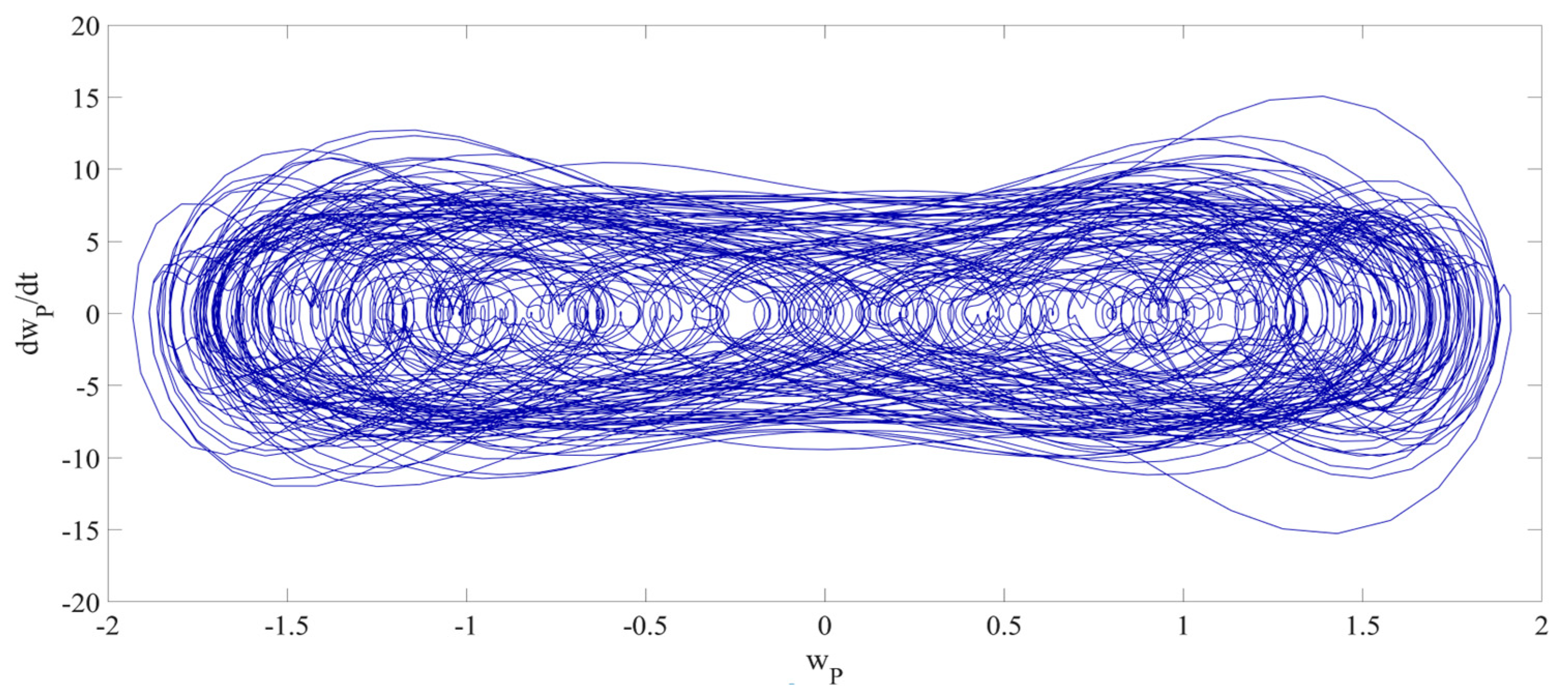
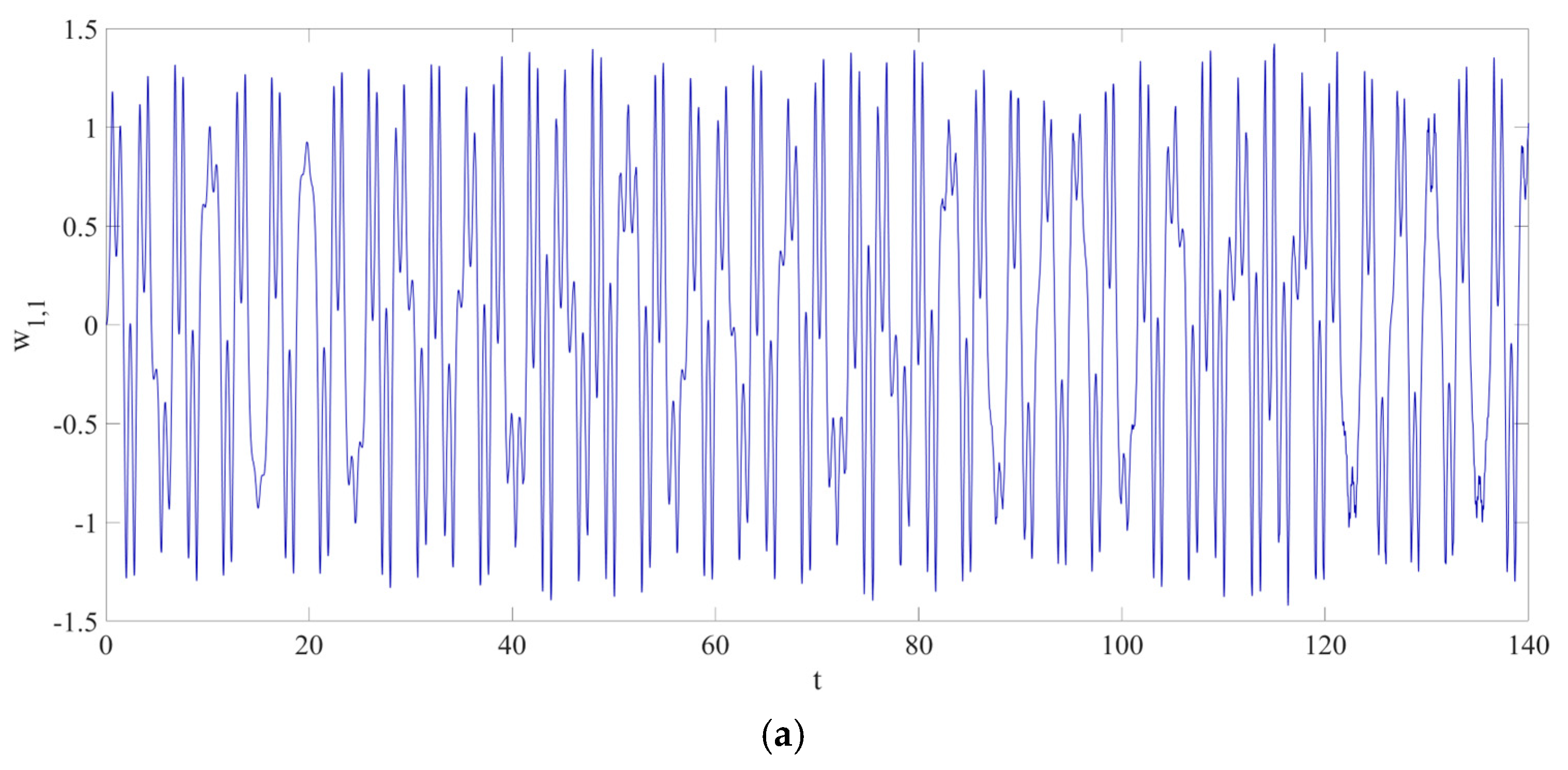
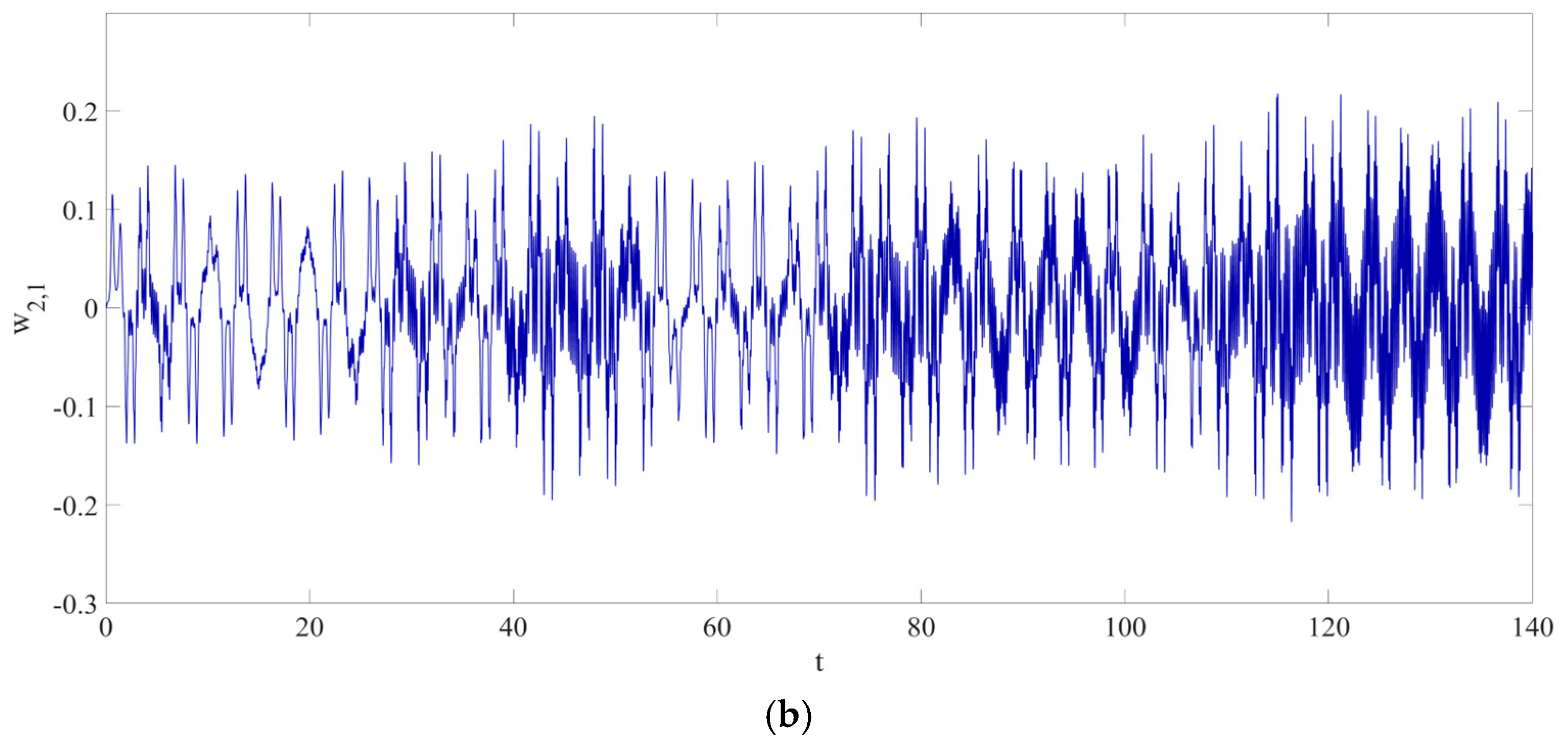
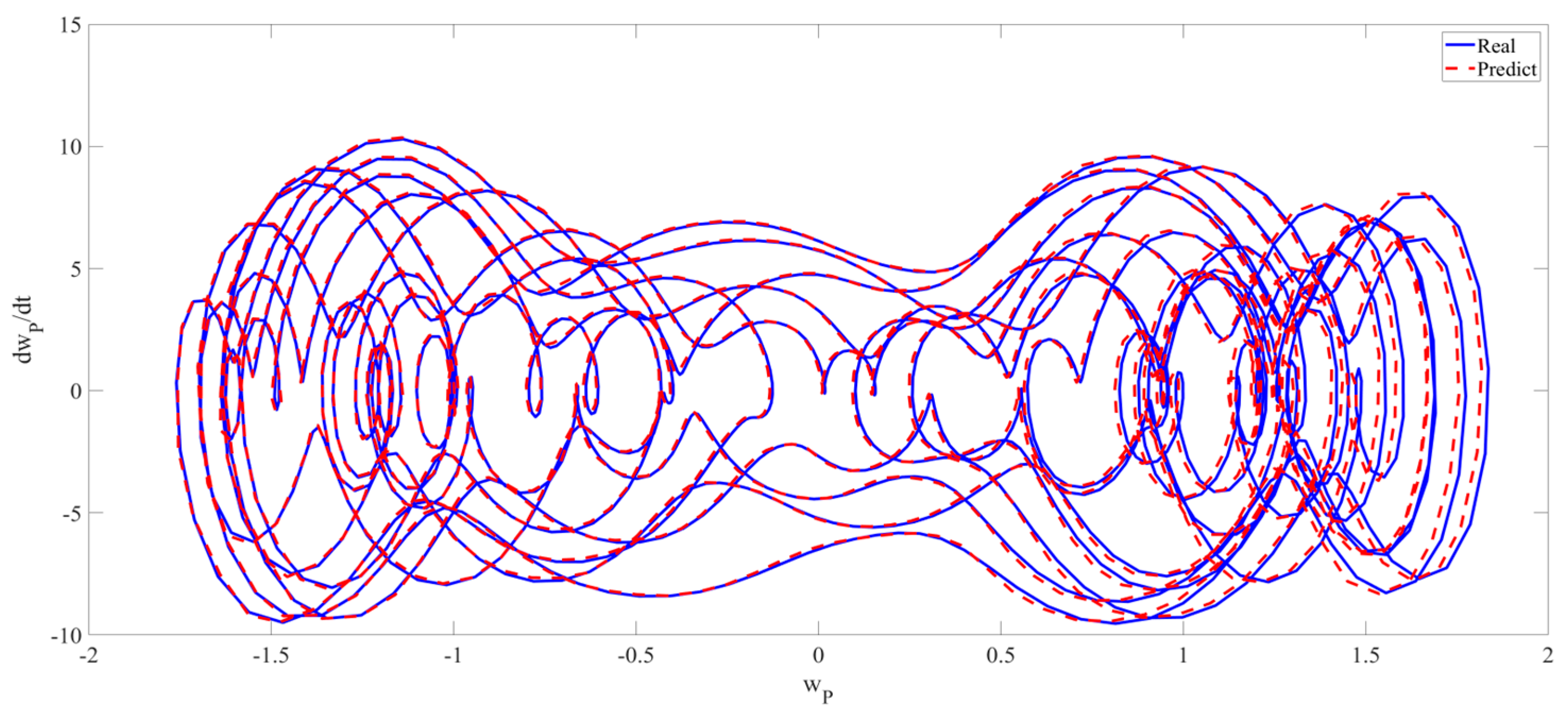
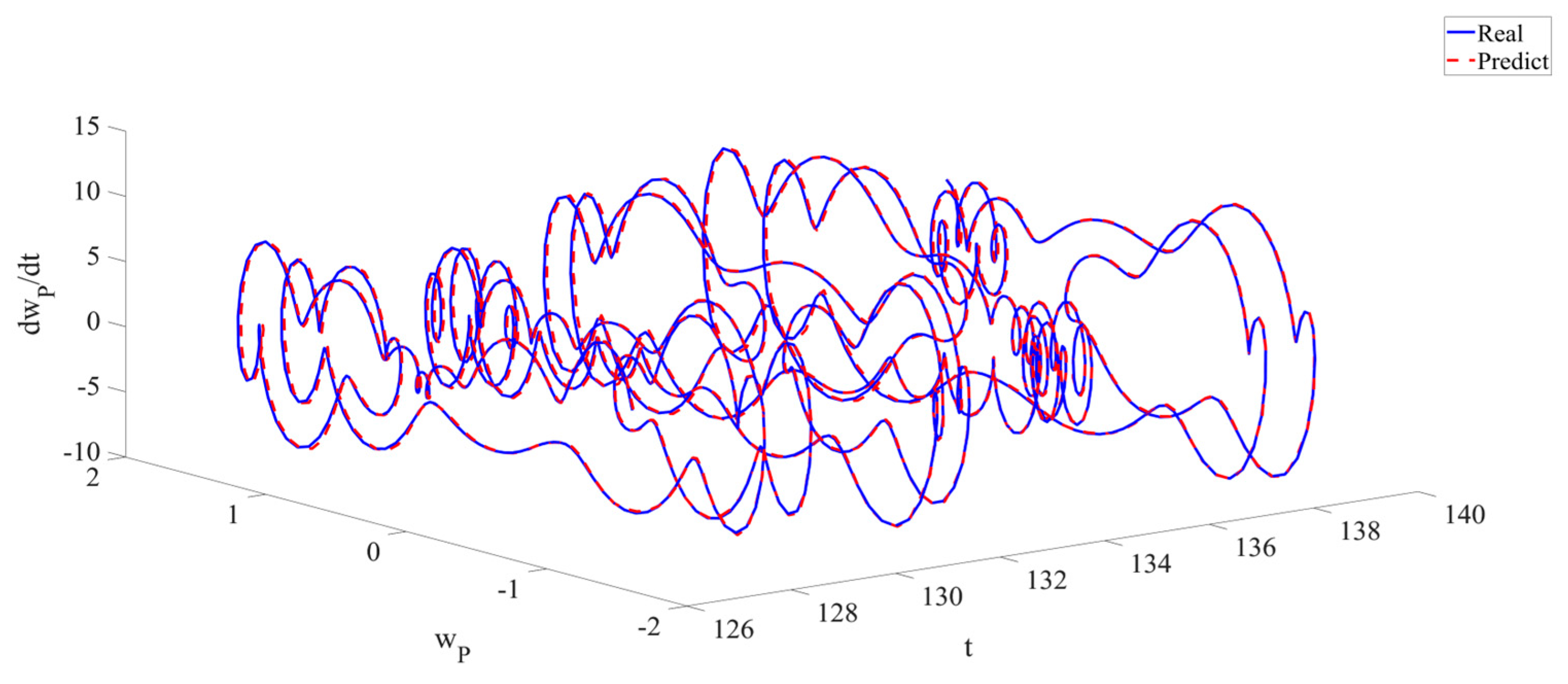
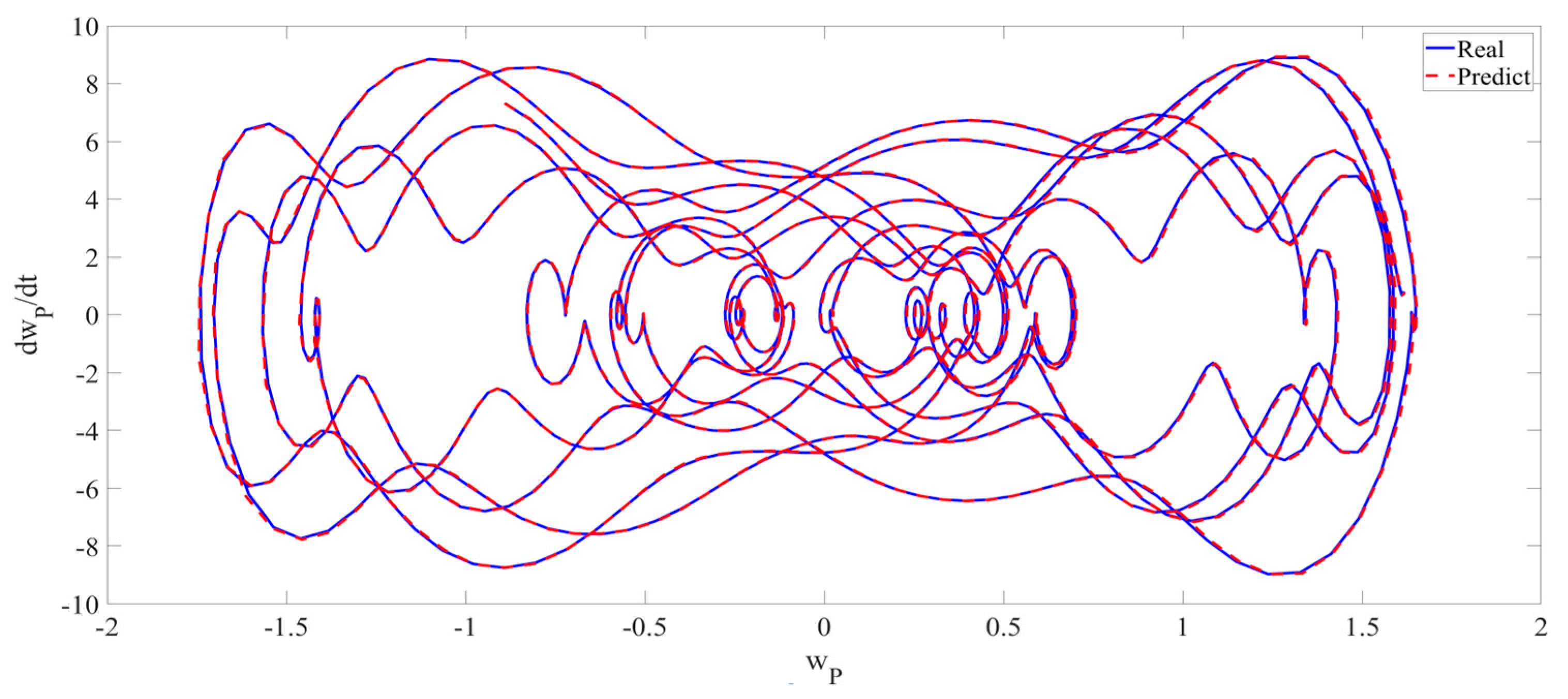
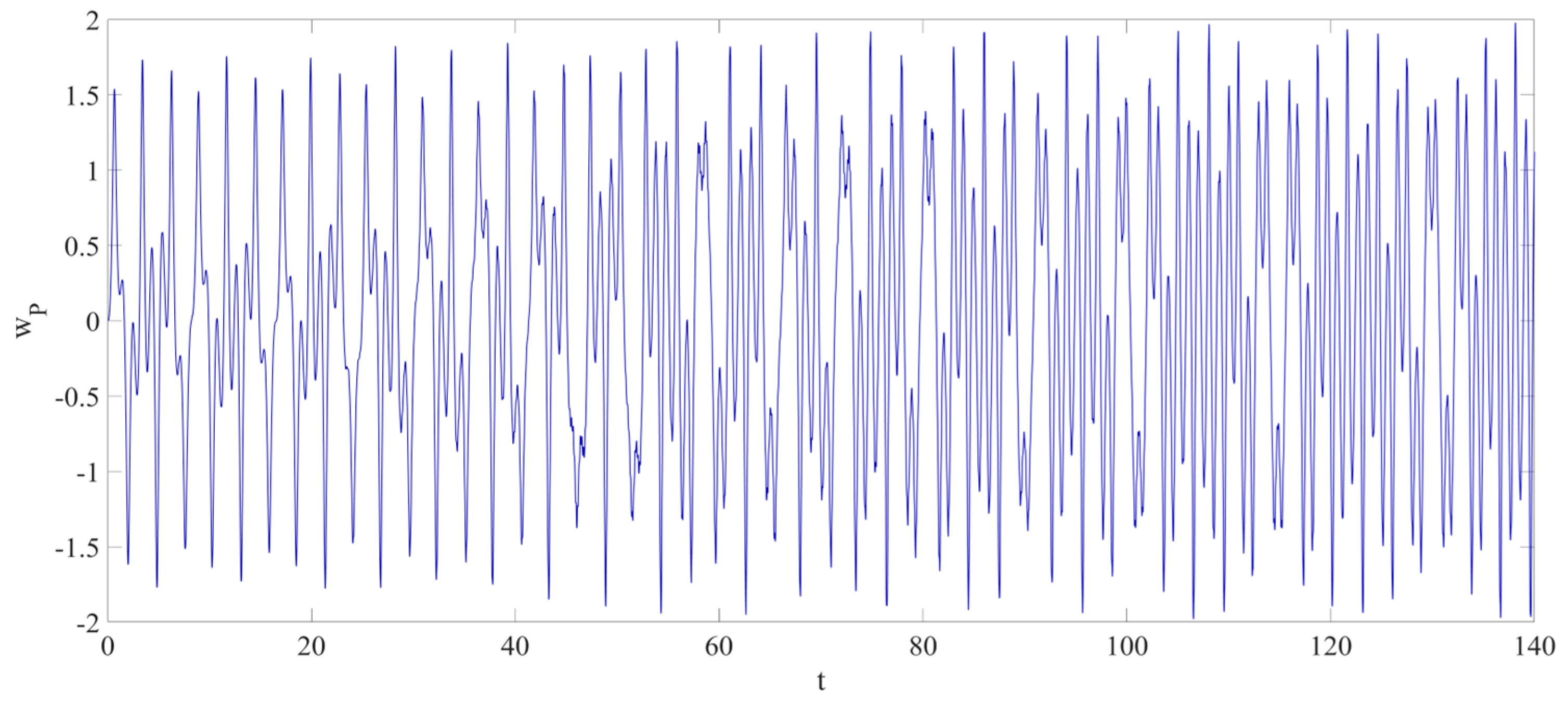
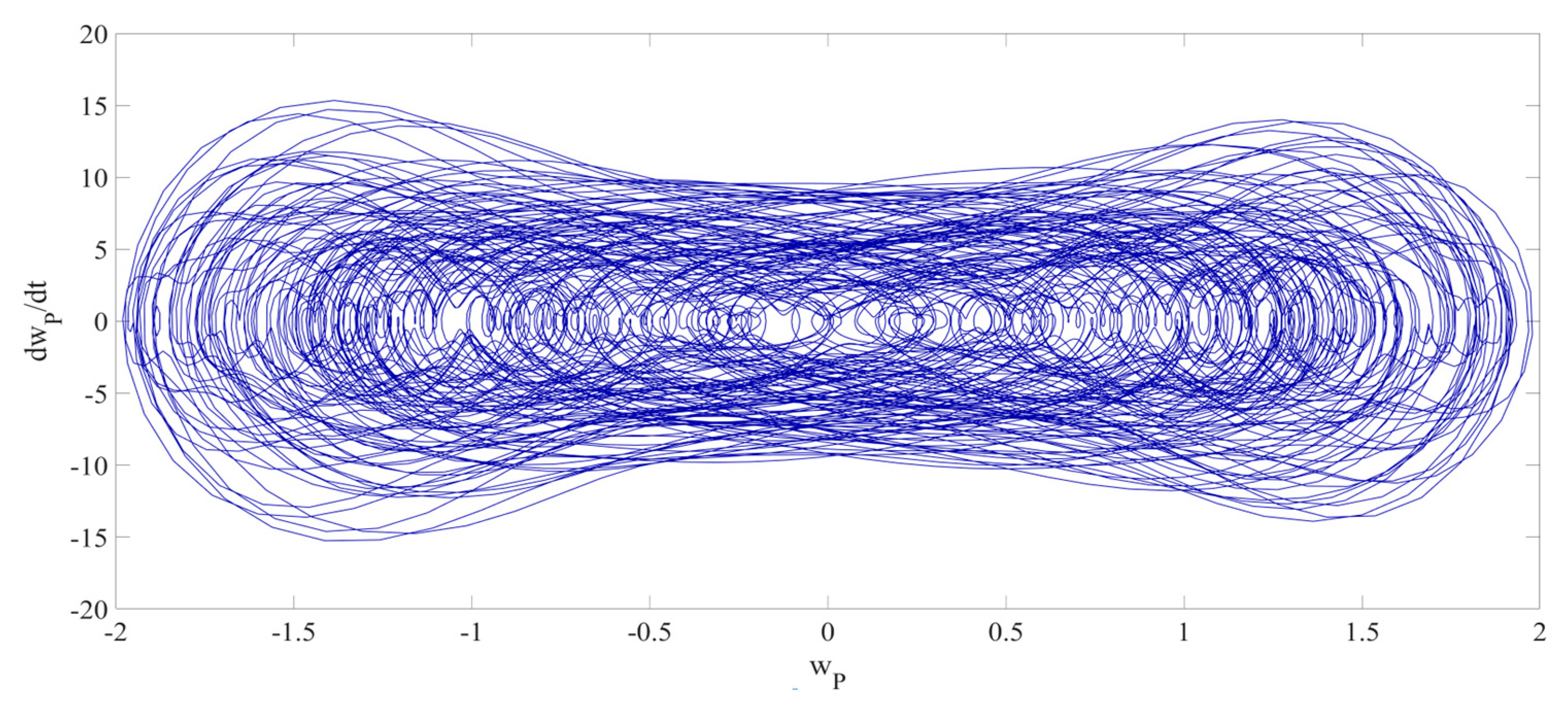
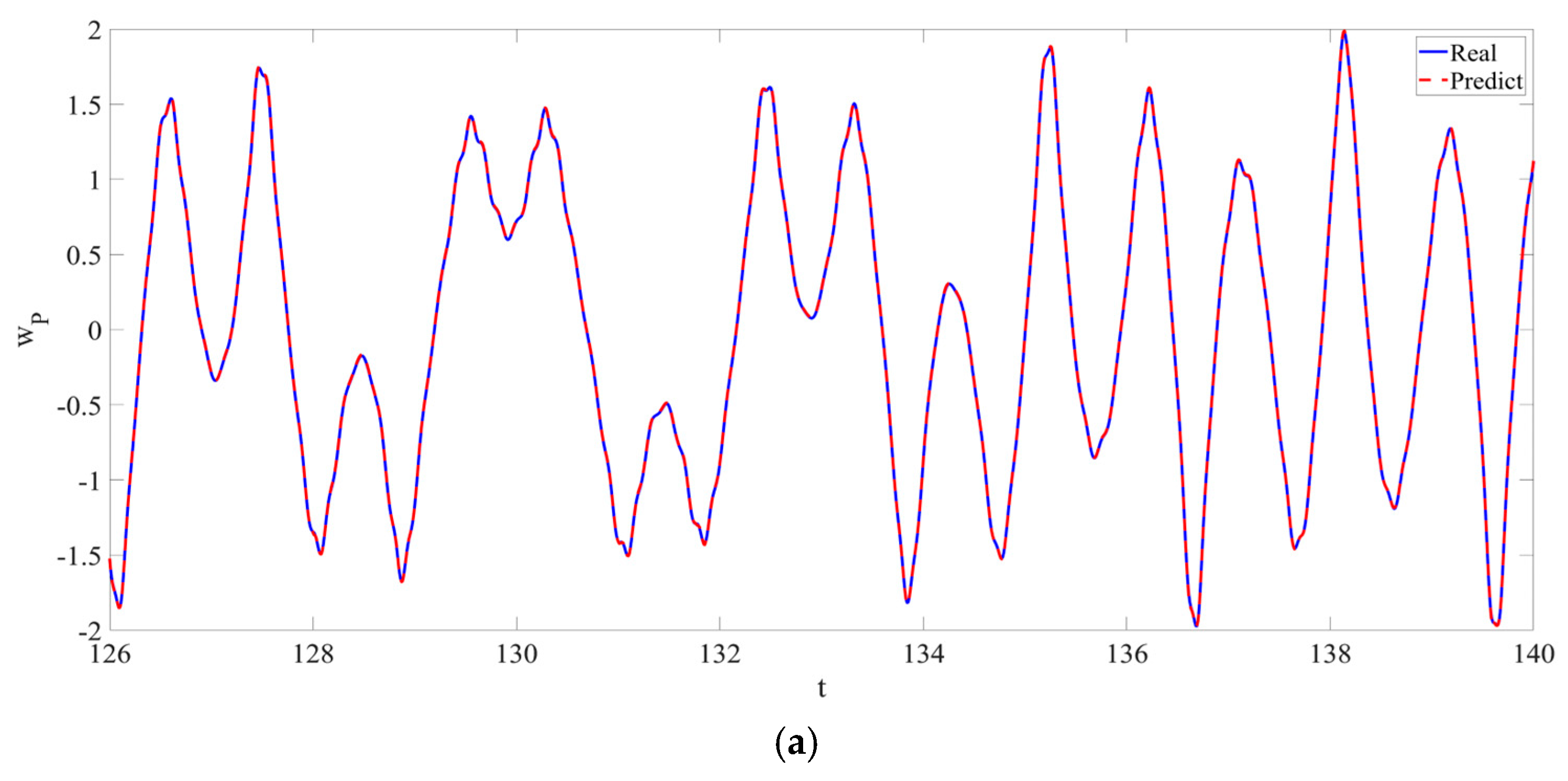
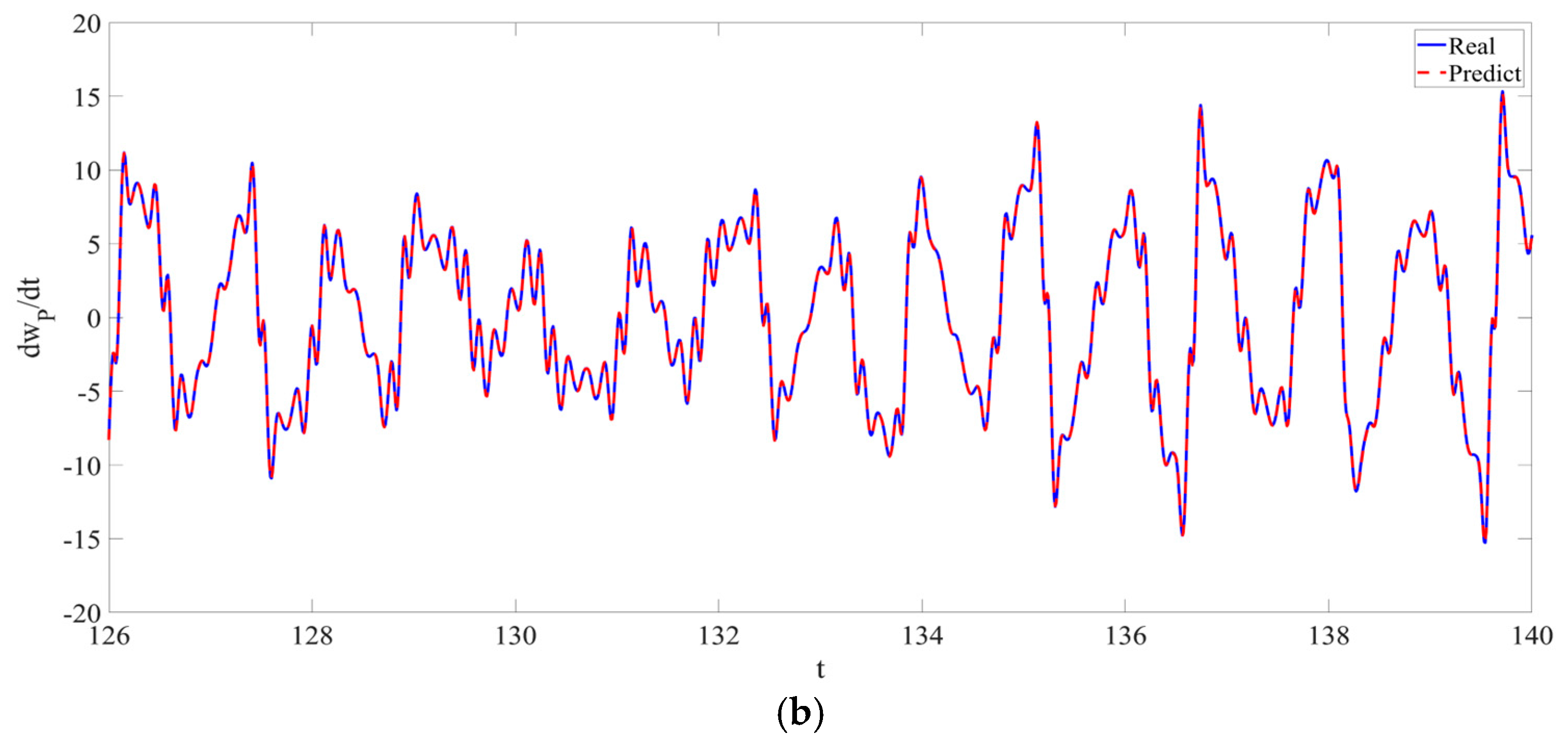
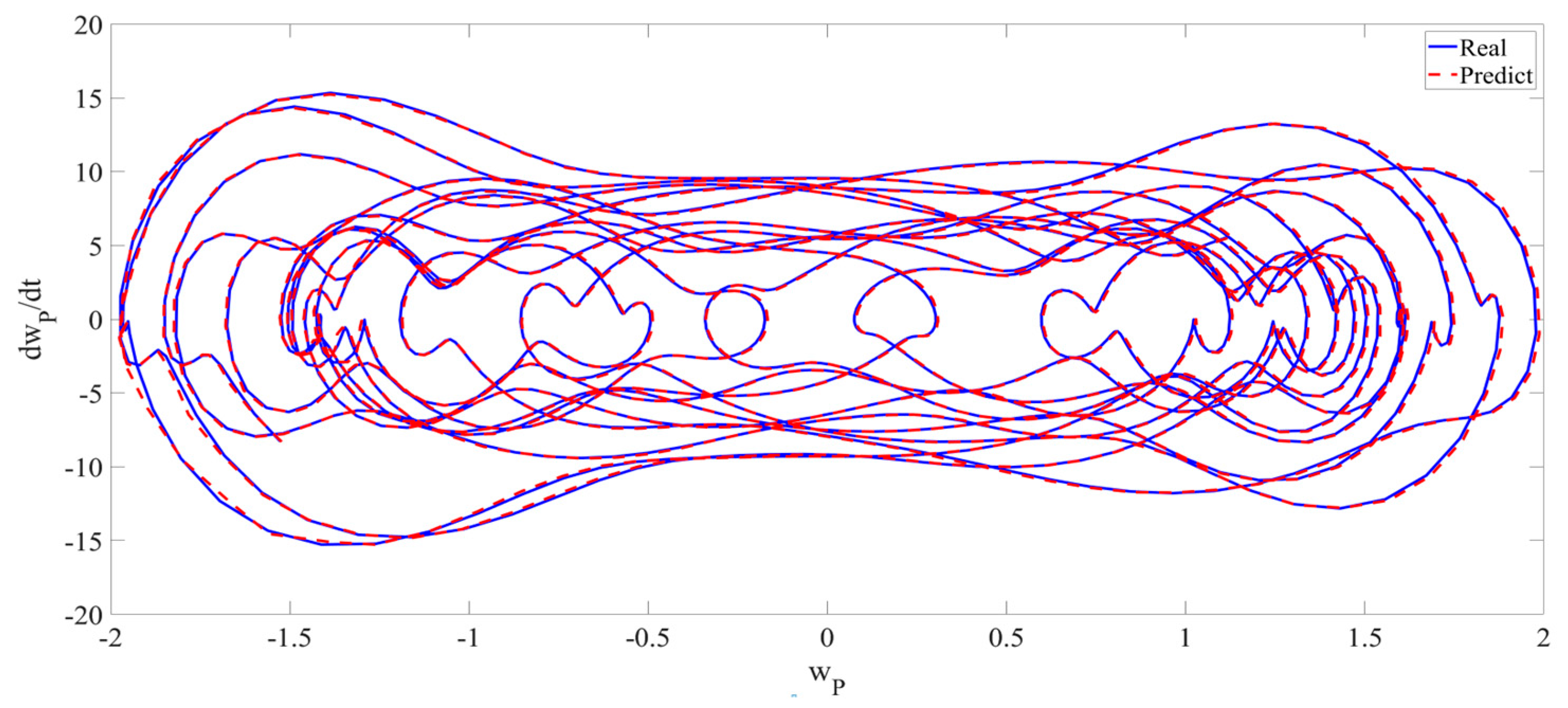
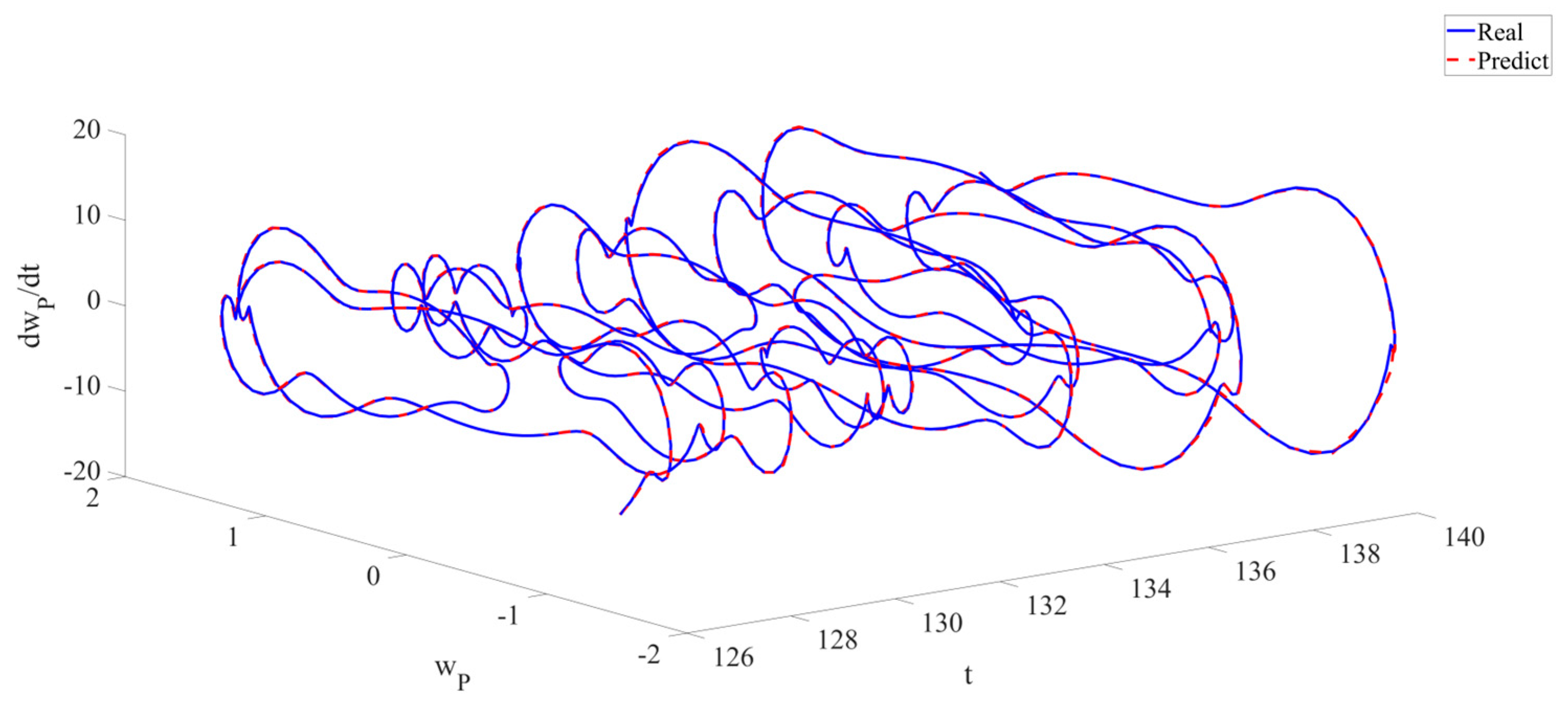
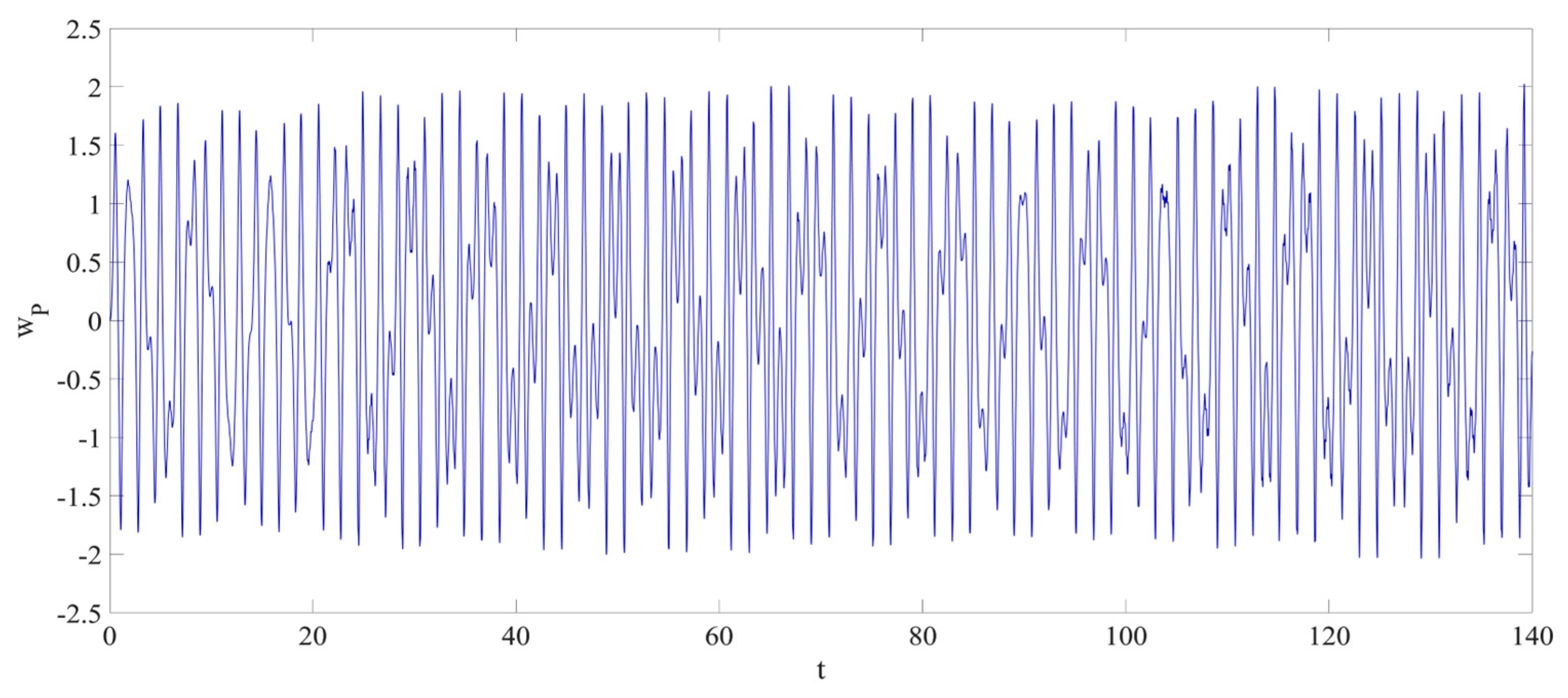
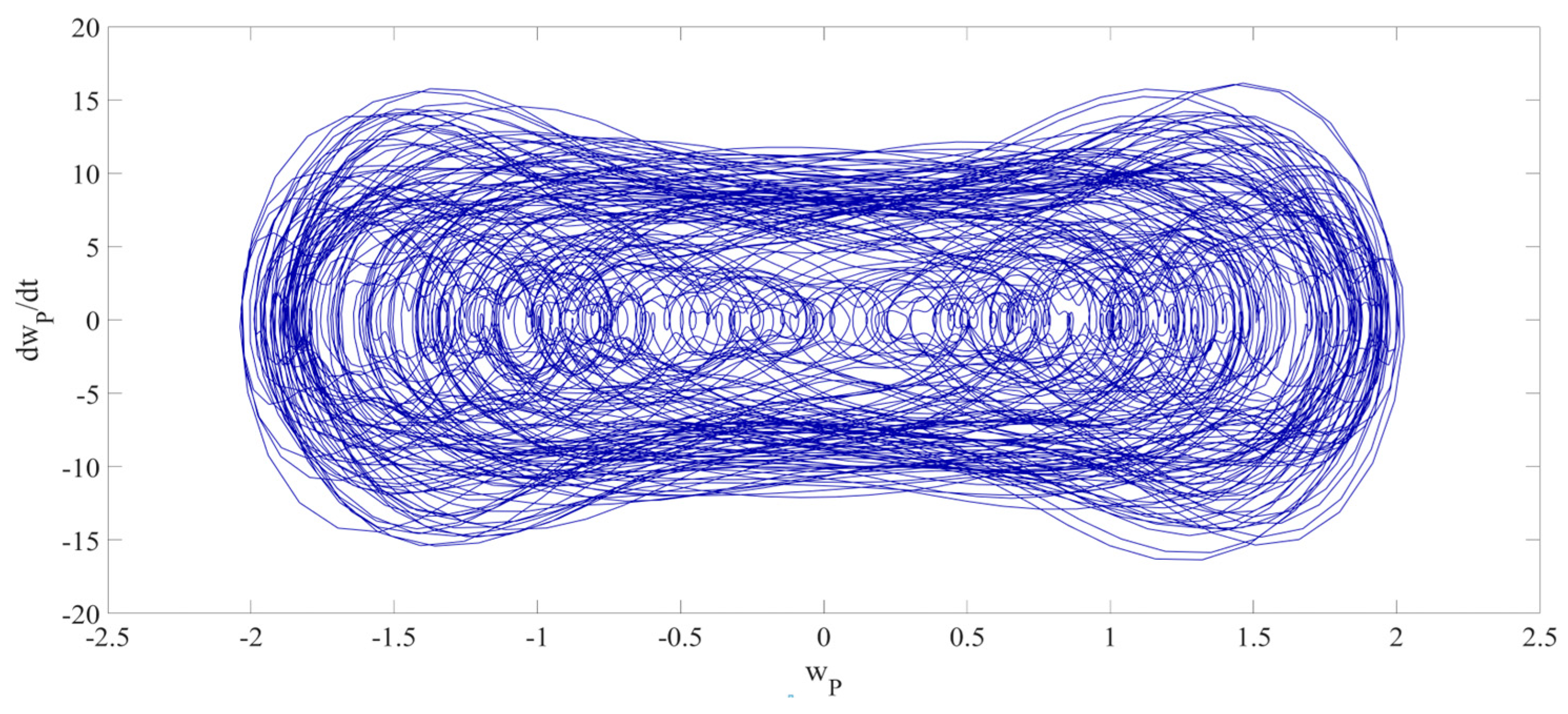
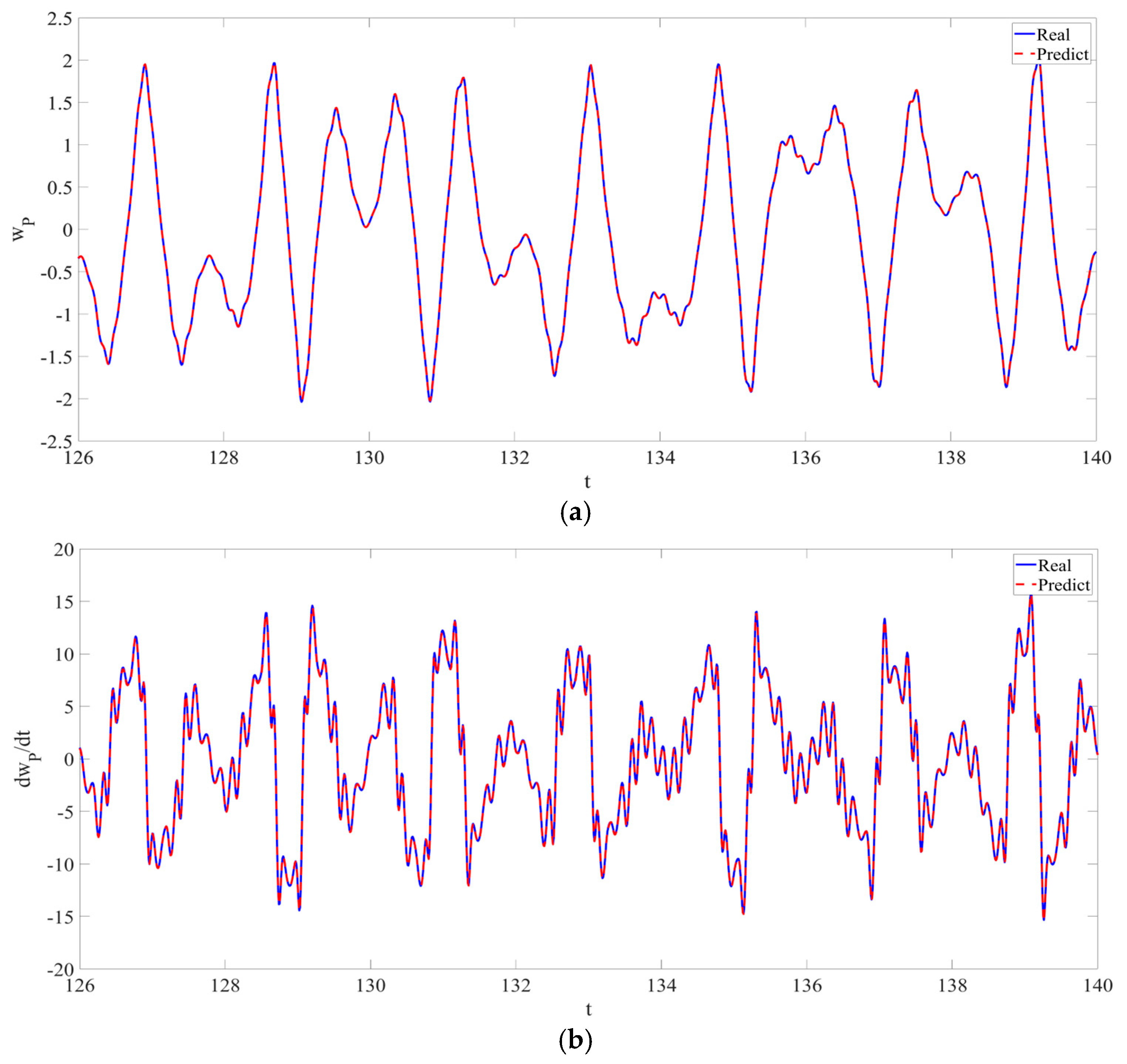
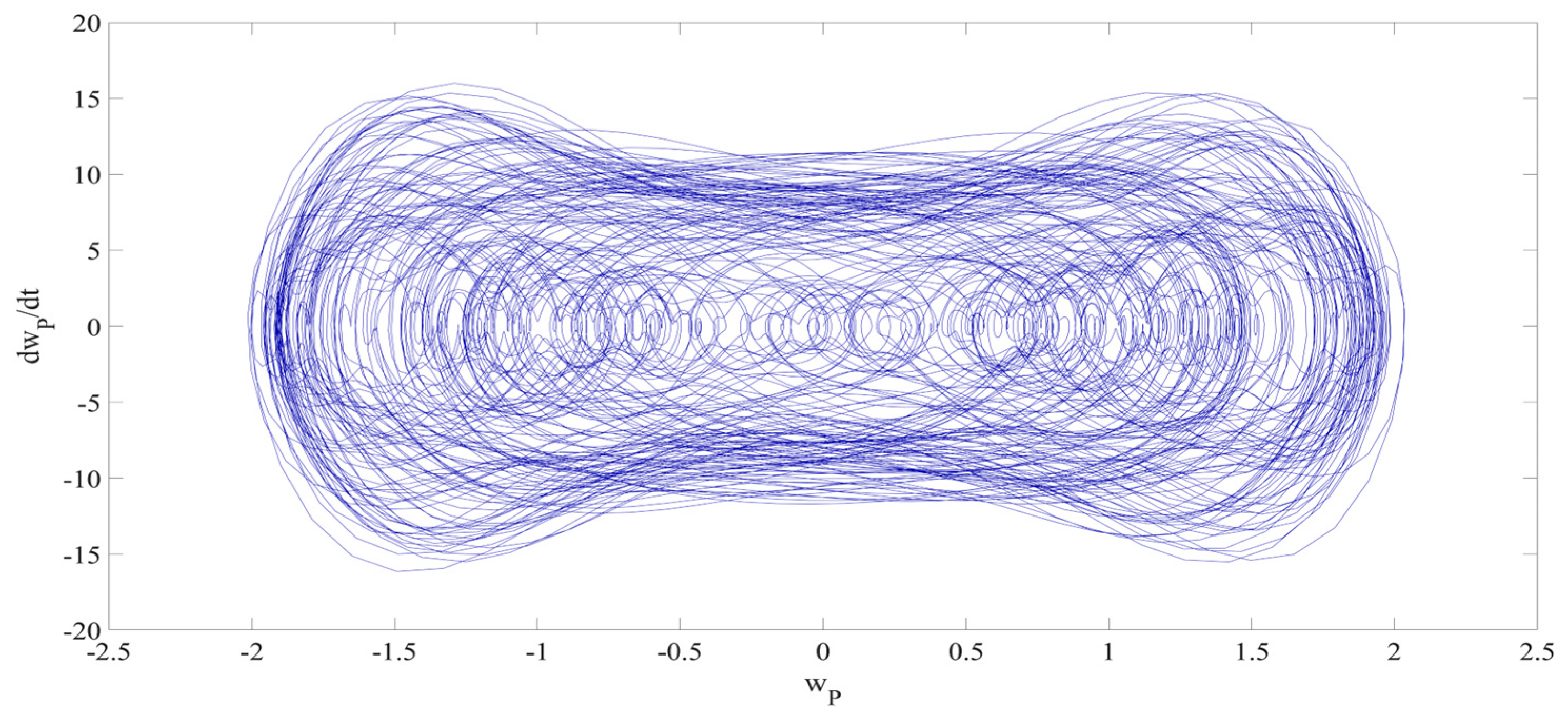
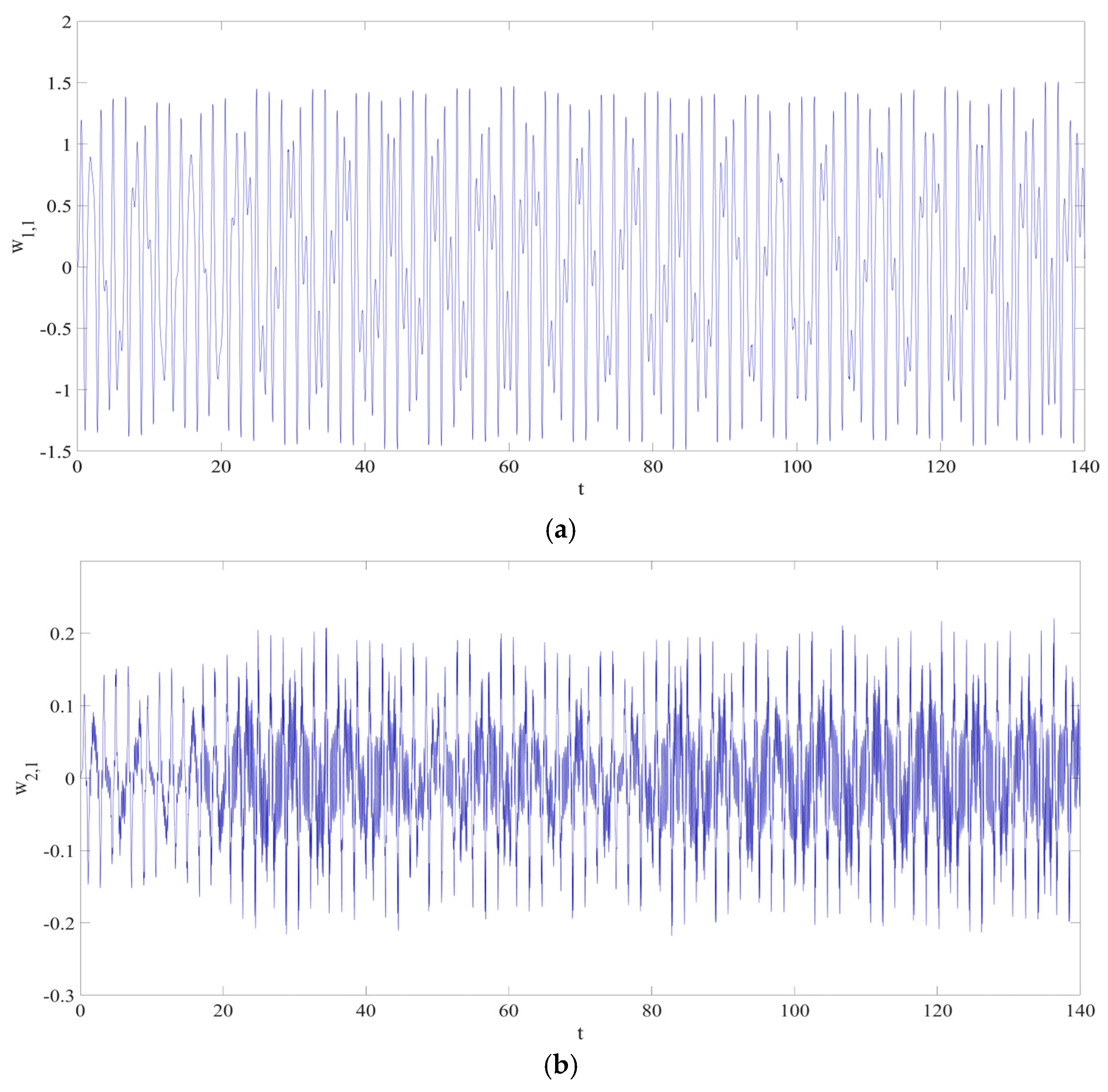
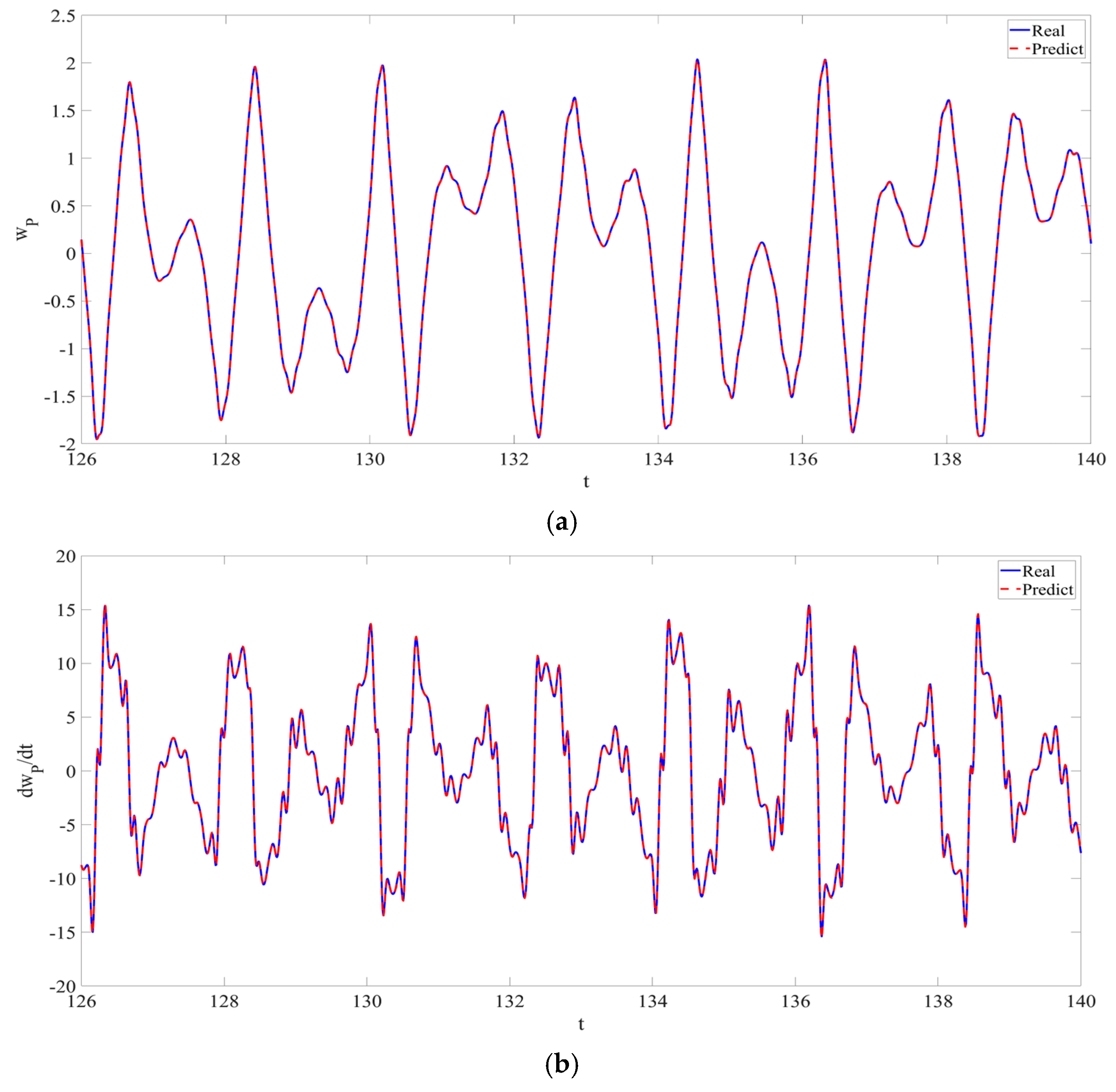
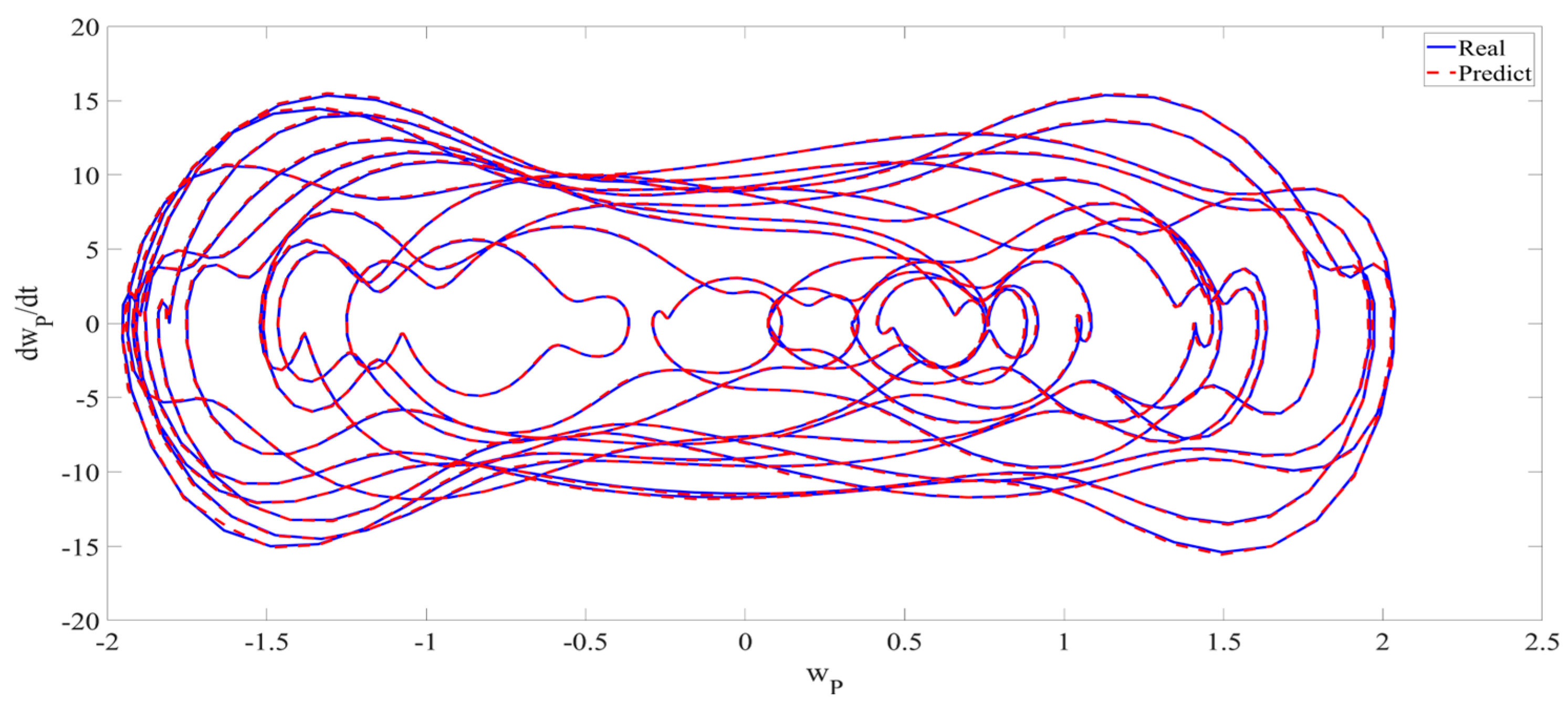
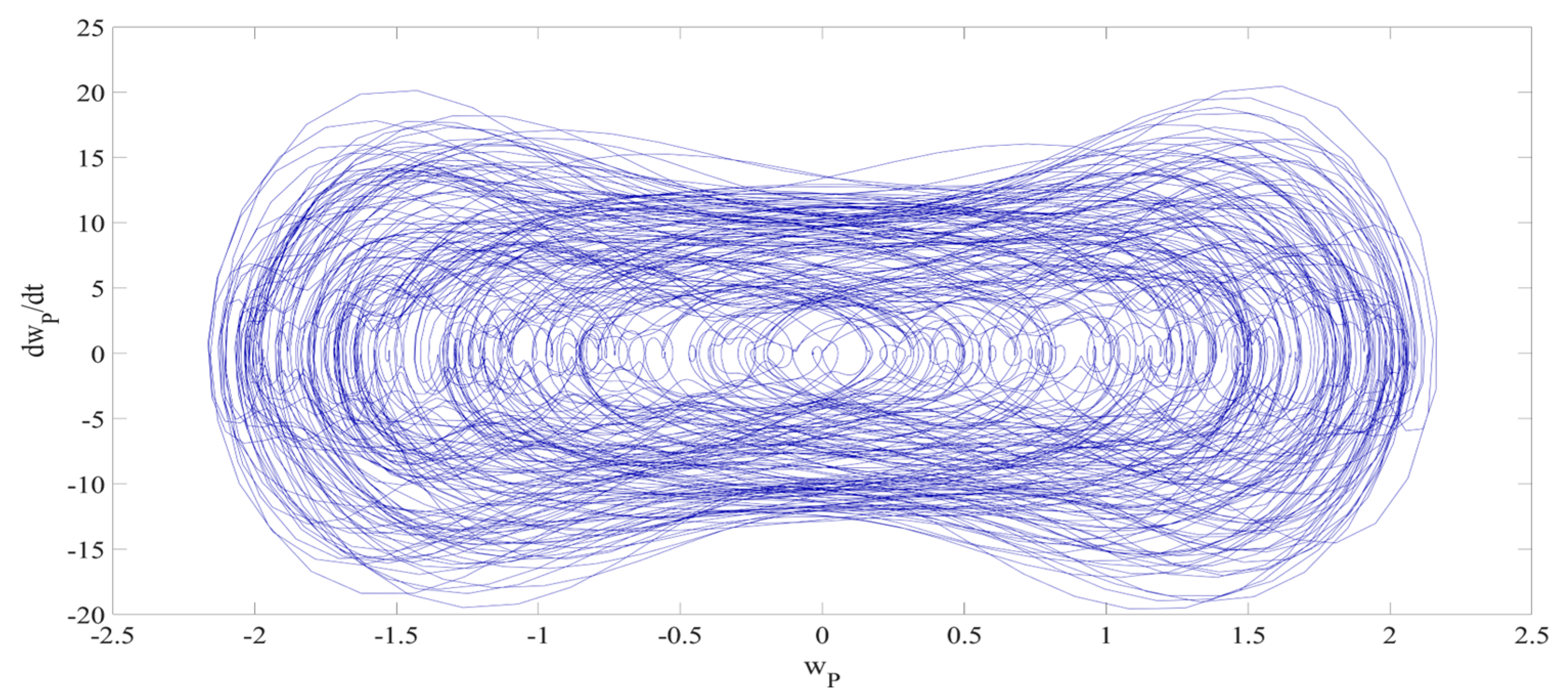
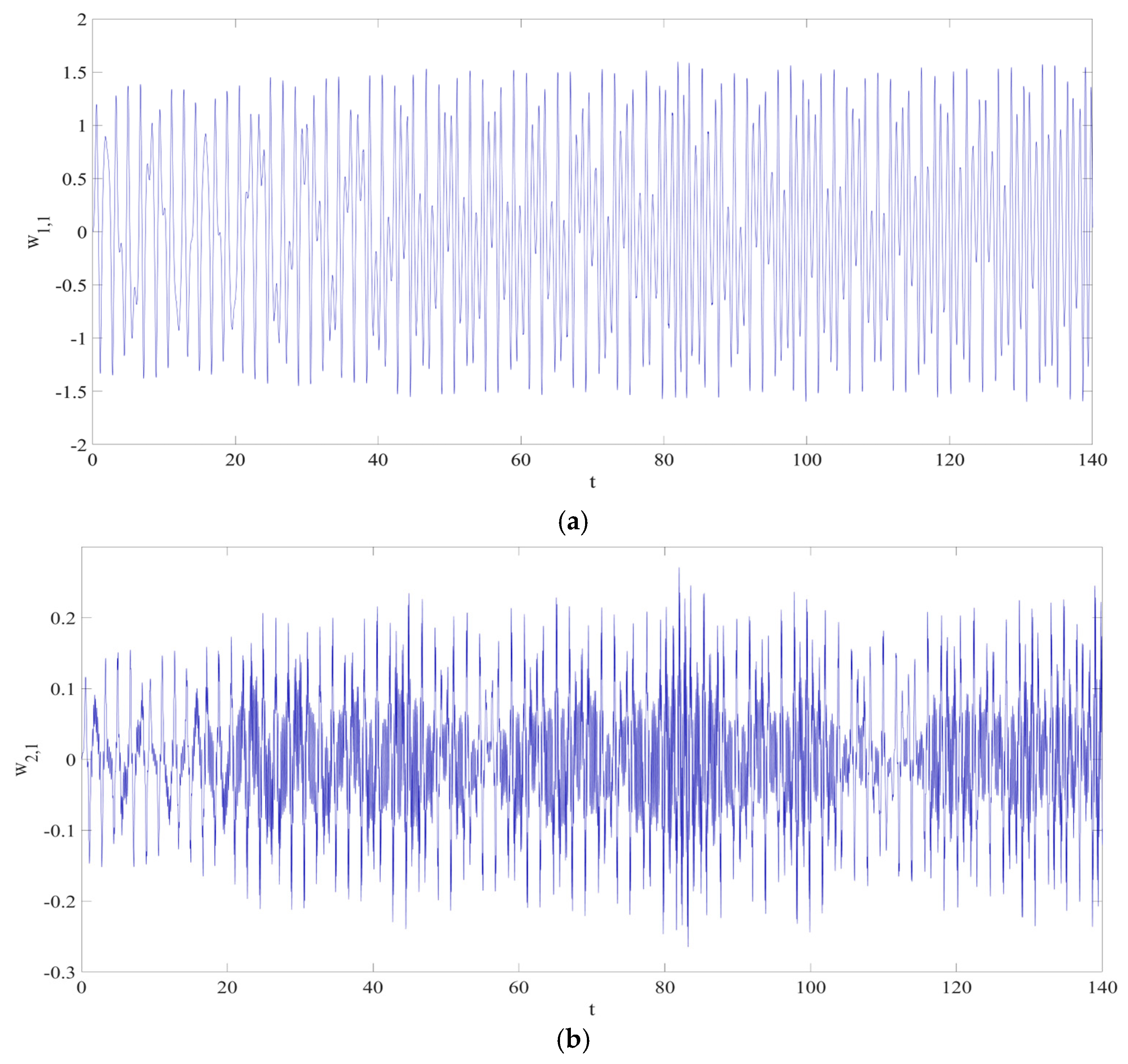
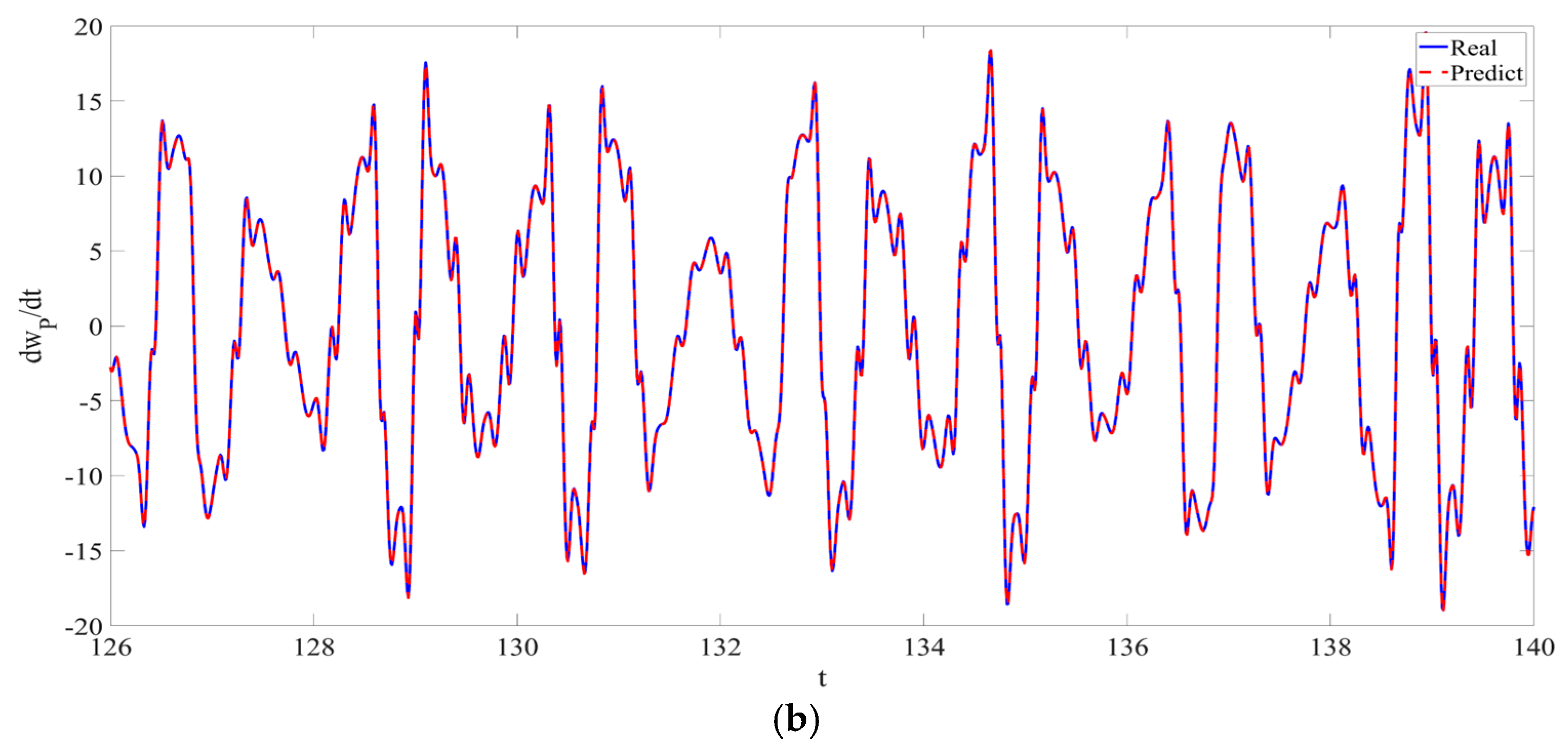
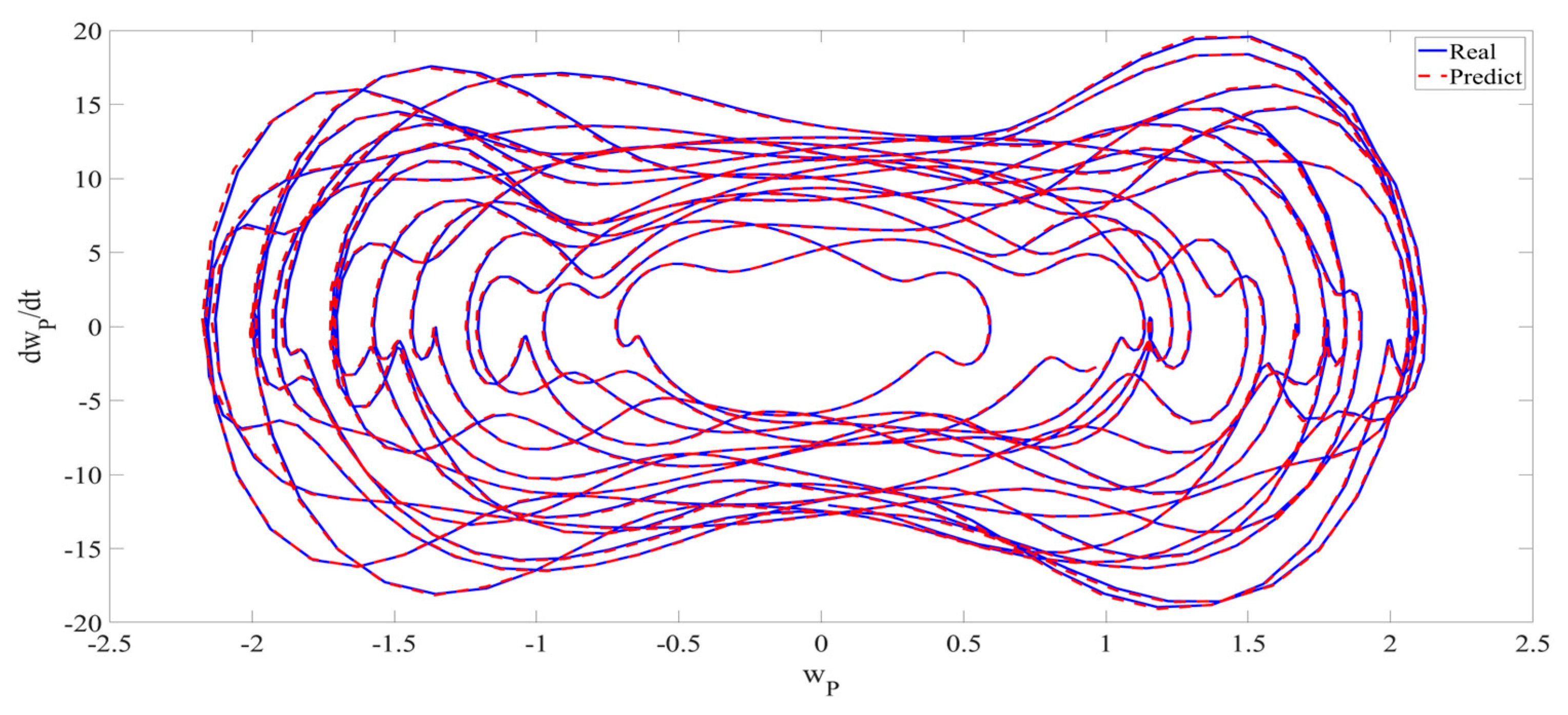
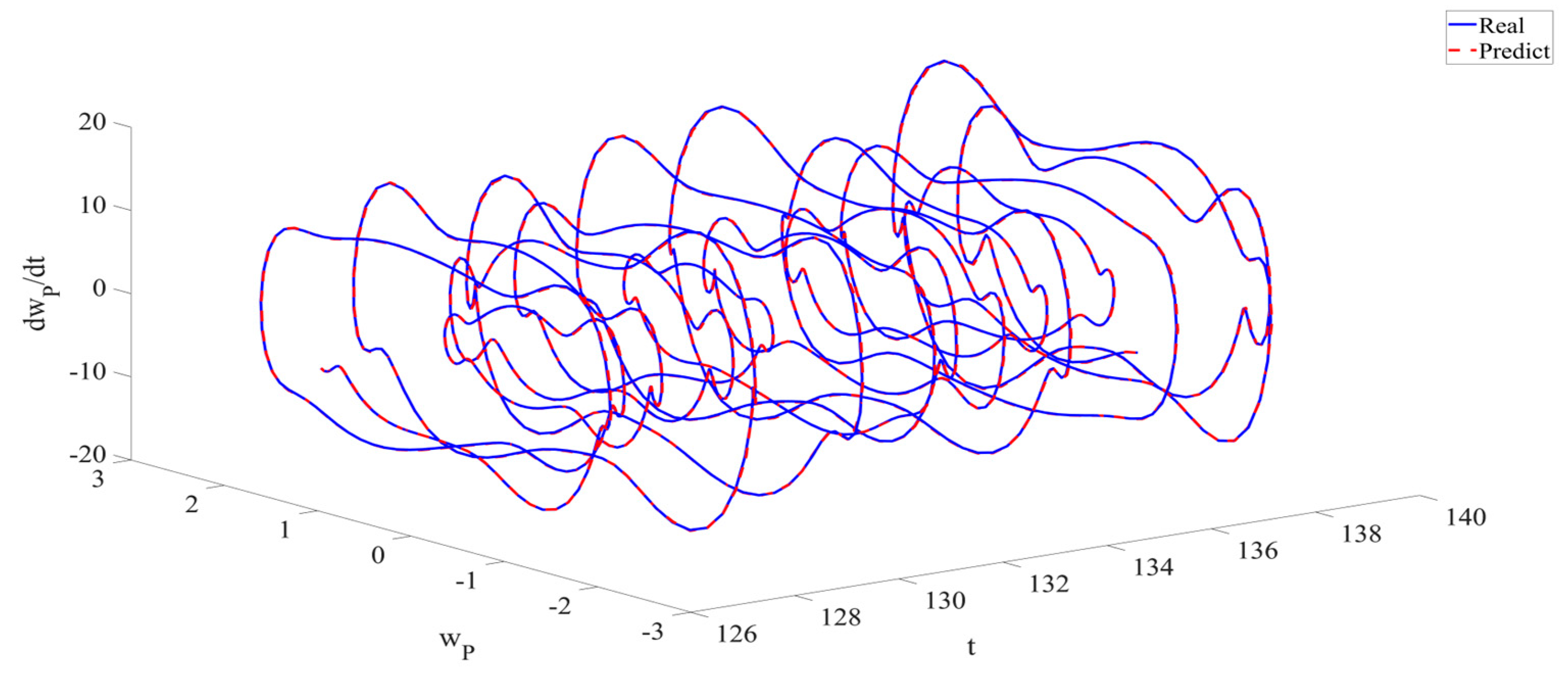
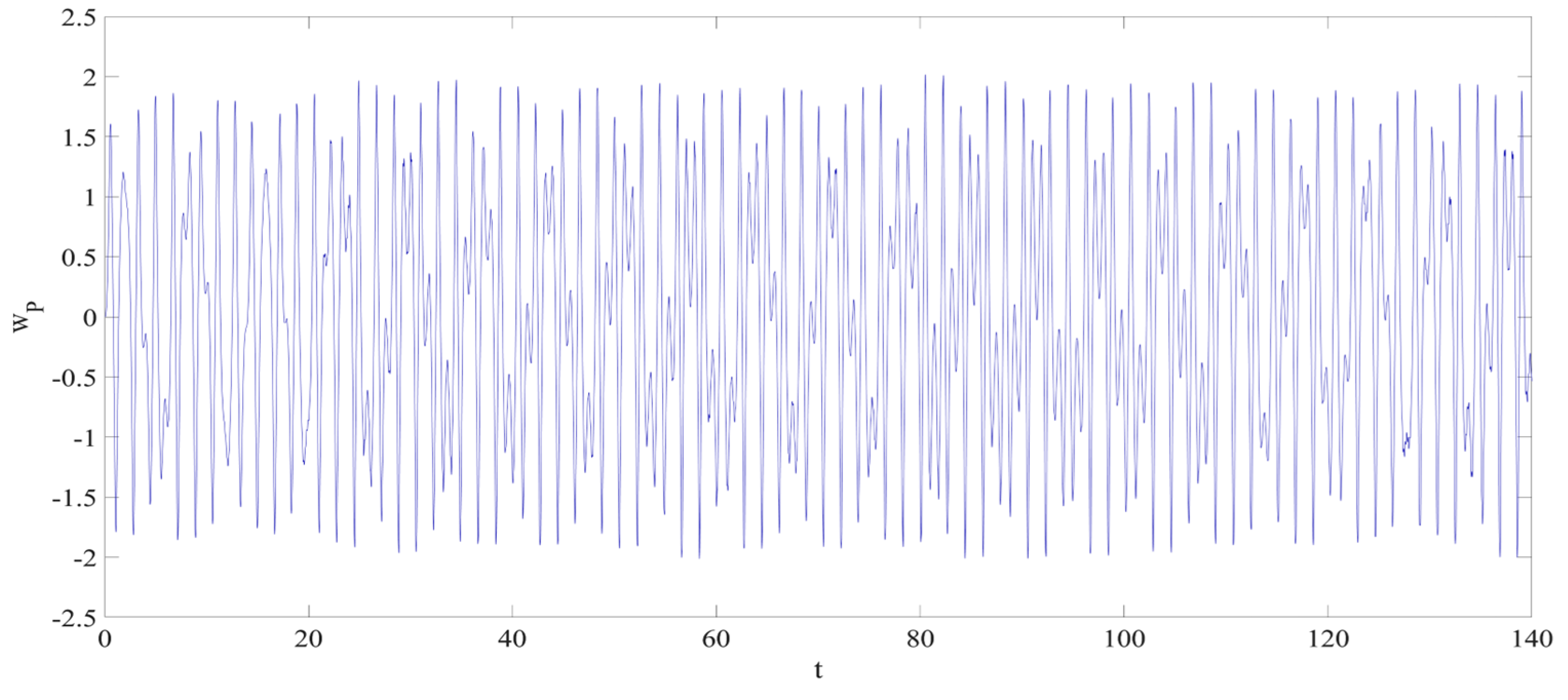
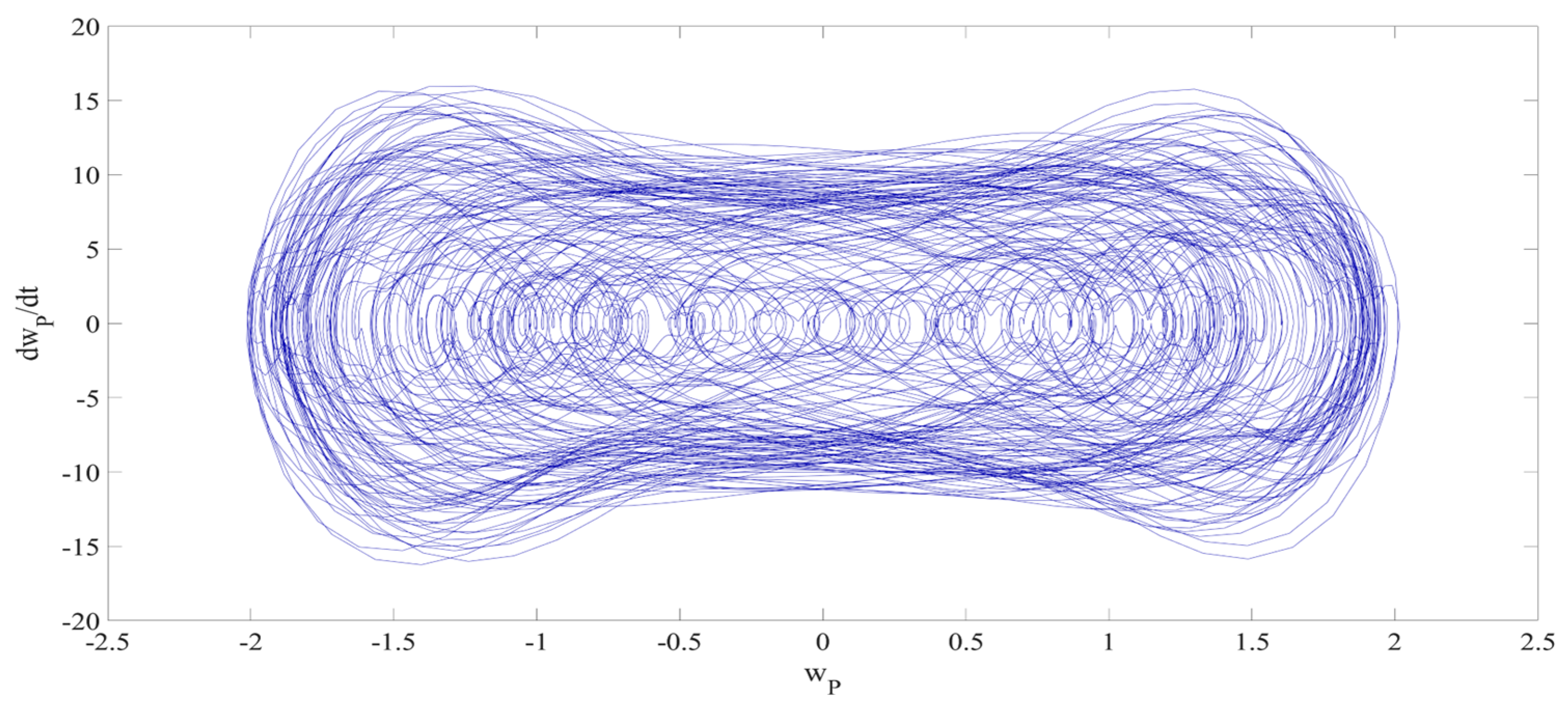
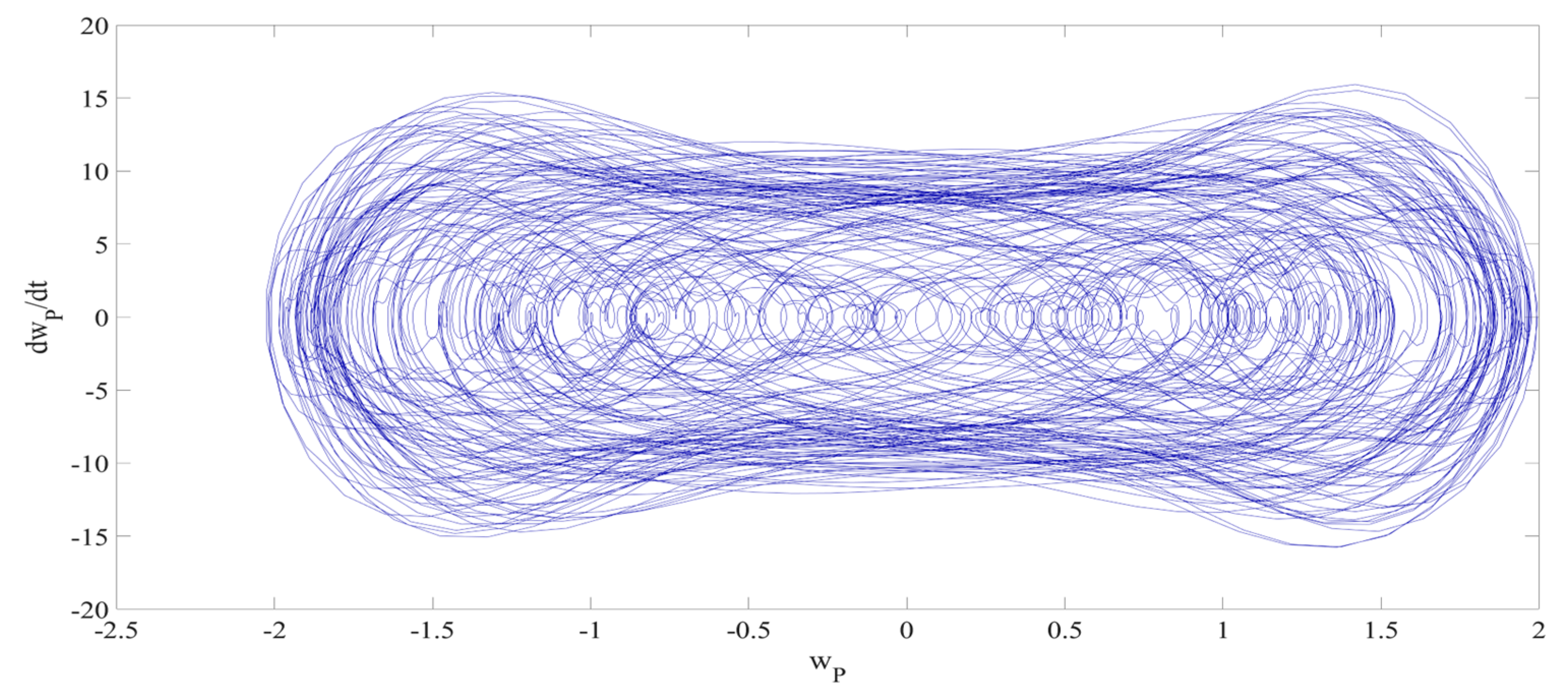
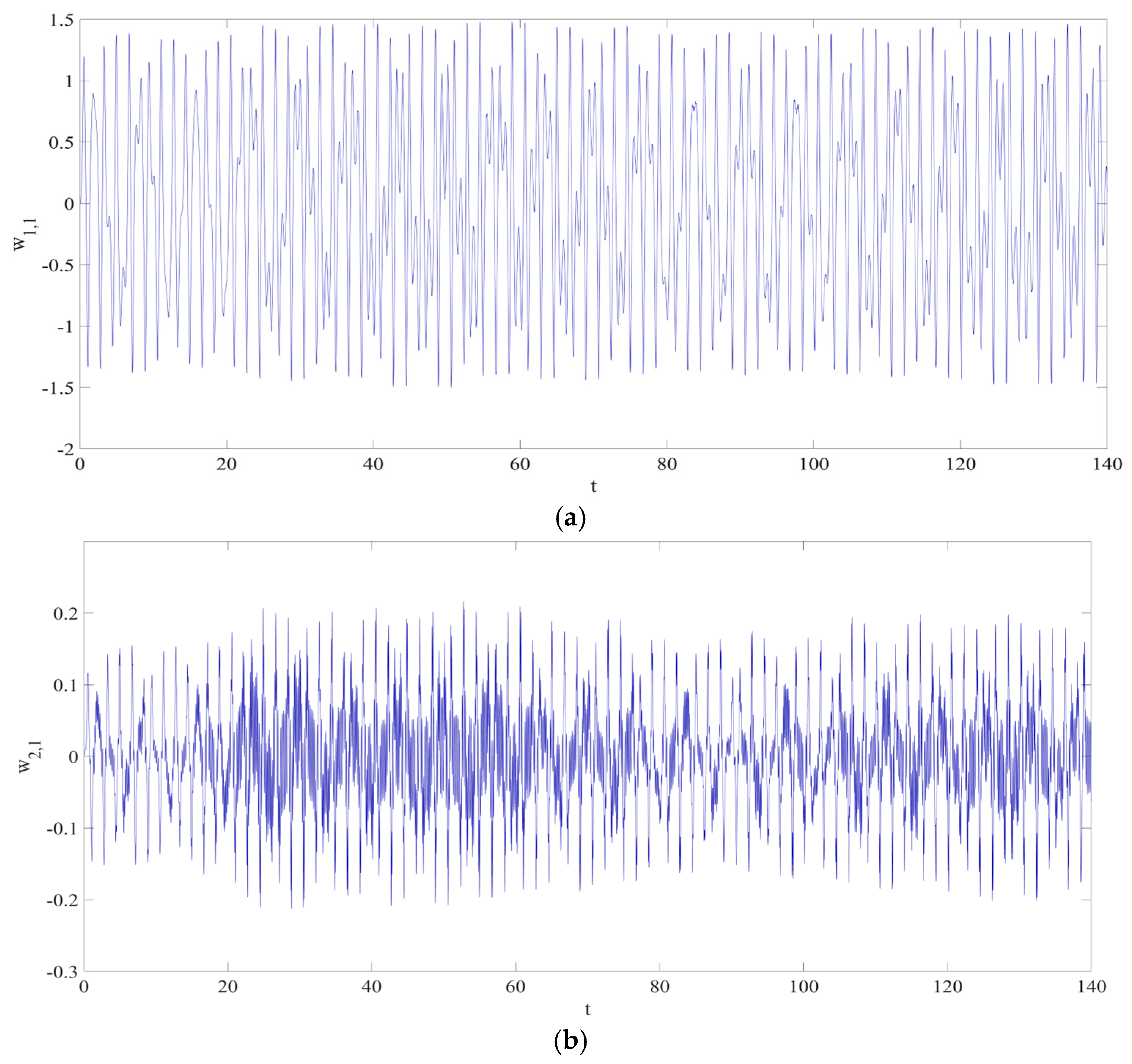
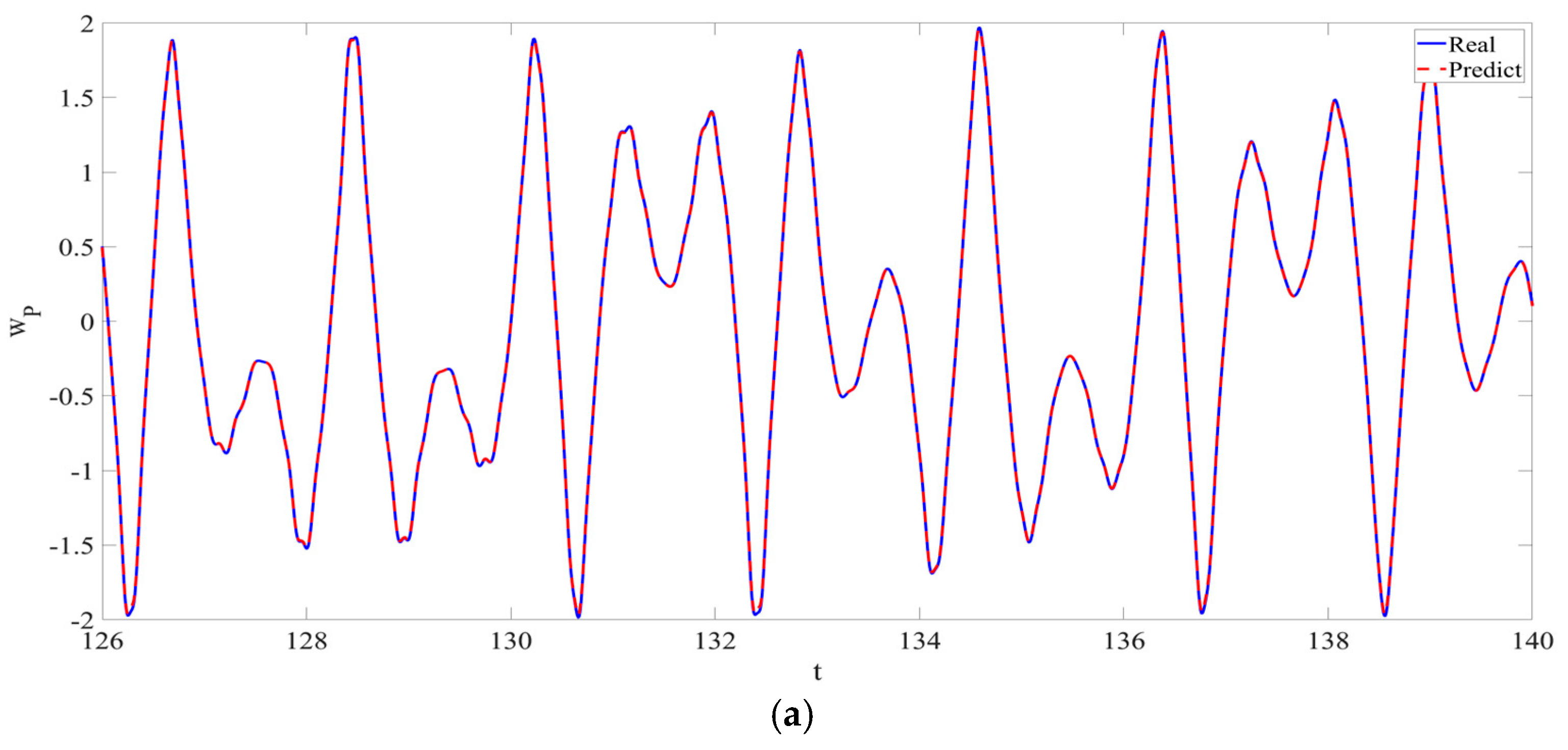
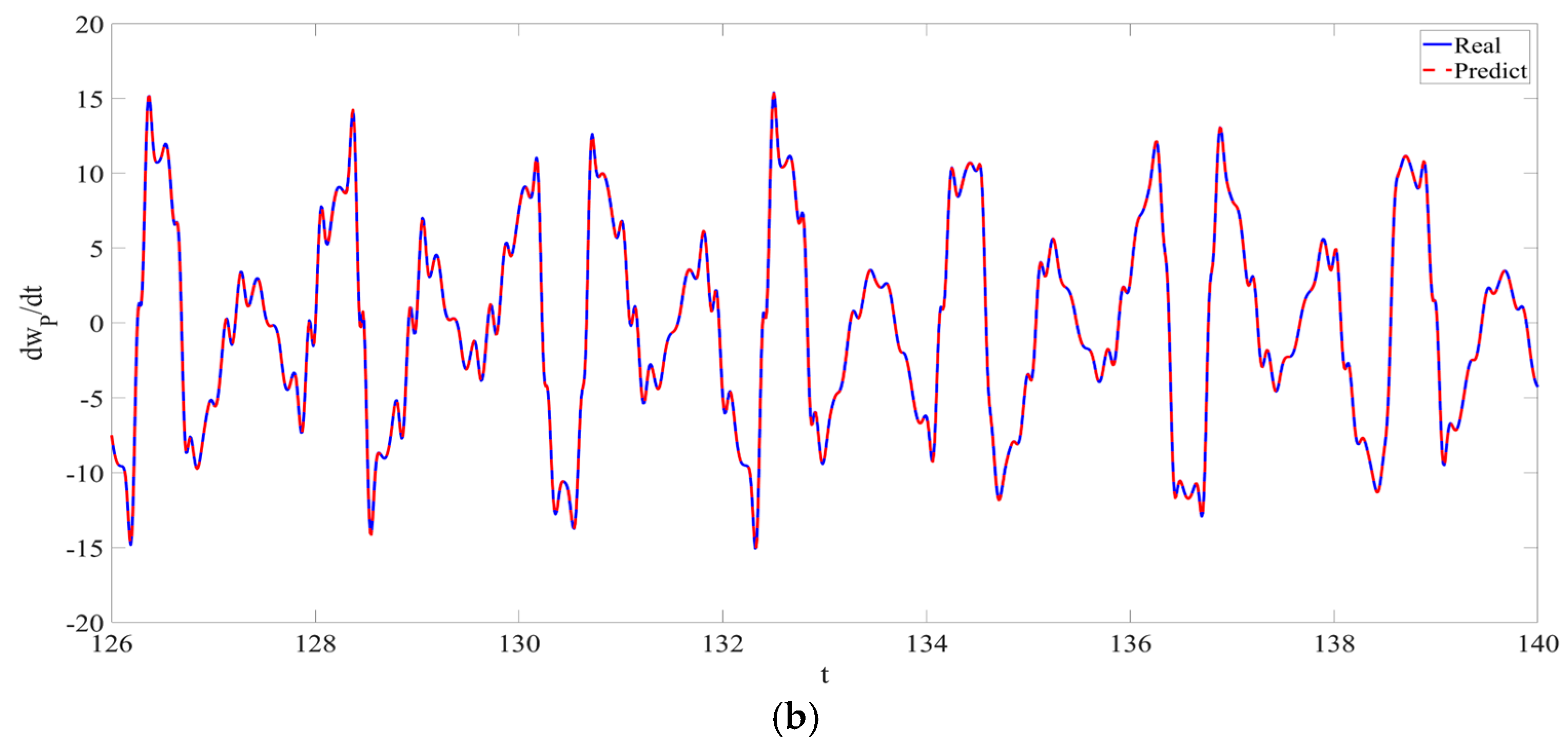
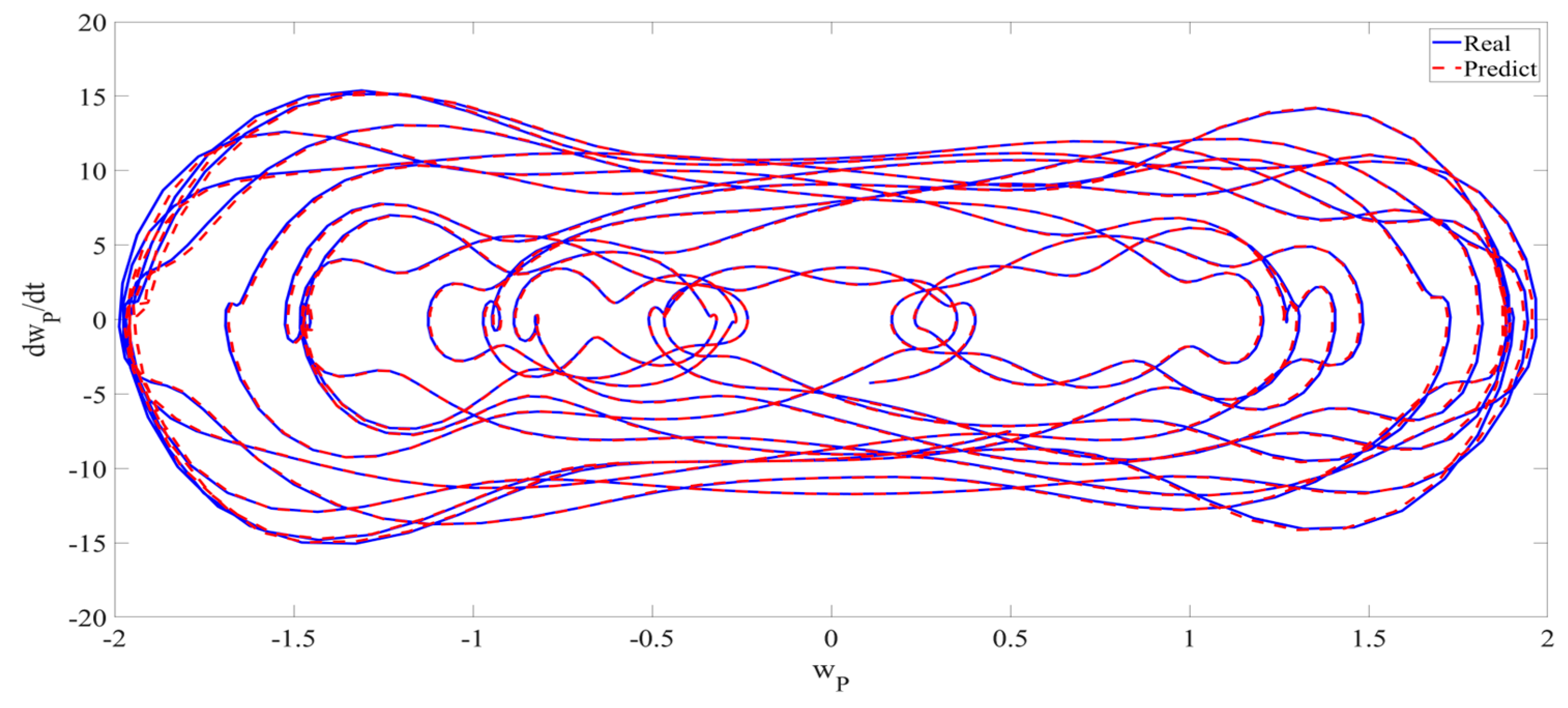
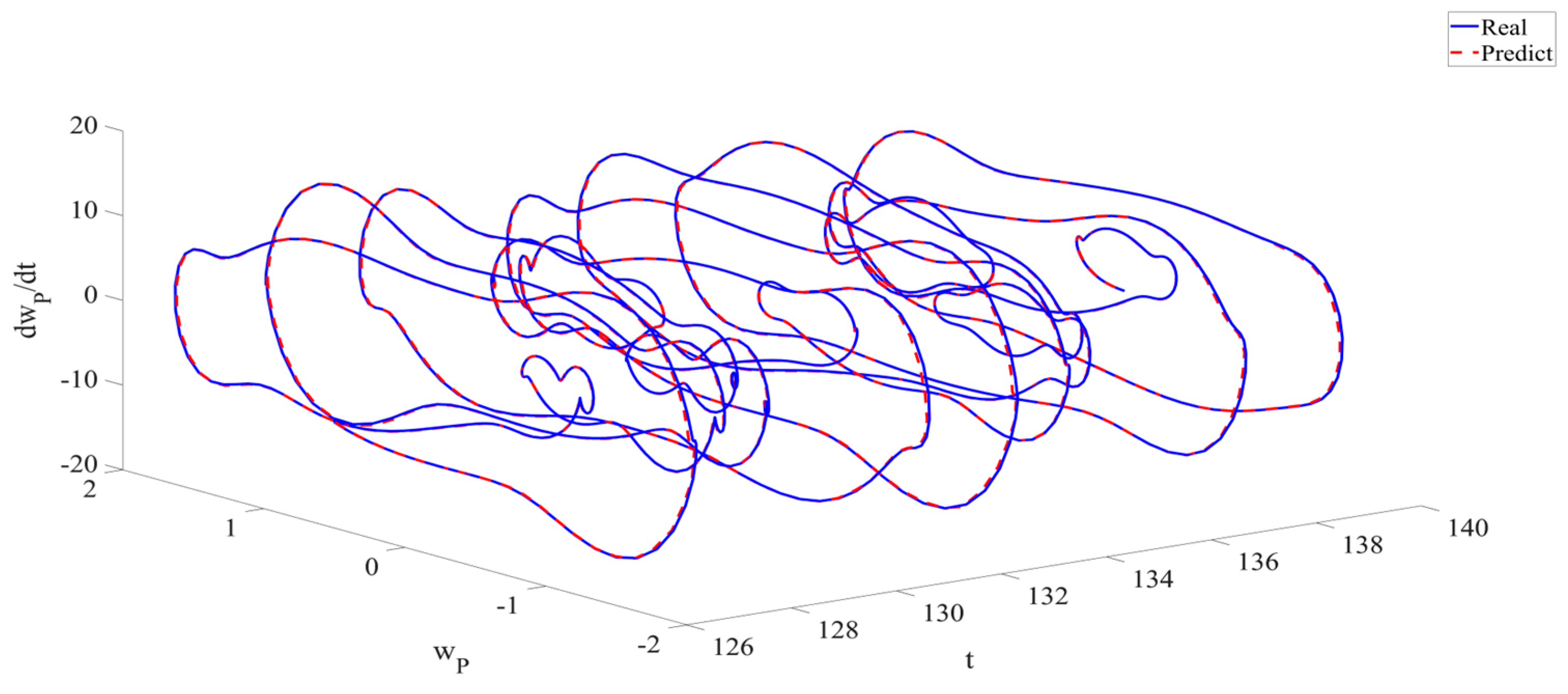
4. Numerical Simulation
4.1. Predictions Corresponding to Different
4.2. Prediction Corresponding to Different
4.3. Prediction Corresponding to Different Initial Conditions
5. Conclusions
6. Future Development
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jin, F.; Zhao, C.; Xu, P.; Xue, J.; Xia, F. Nonlinear eccentric bending and buckling of laminated cantilever beams actuated by embedded pre-stretched SMA wires. Compos. Struct. 2022, 284, 115211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, L.; Yang, X.D.; Jia, P. Nonlinear dynamic behaviors of a deploying-and-retreating wing with varying velocity. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 6785–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yao, D.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Jin, X. Sound-insulation prediction model and multi-parameter optimisation design of the composite floor of a high-speed train based on machine learning. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 200, 110631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormanikova, E.; Kotrasova, K.; Melcer, J.; Valaskova, V. Numerical investigation of the dynamic responses of fibre-reinforced polymer composite bridge beam subjected to moving vehicle. Polymers 2022, 14, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Kong, Q.; Ji, K.; Xiong, Q.; Yuan, C. Deep learning-based analysis of interface performance between brittle engineering materials and composites. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, V. Predictability of weather and climate. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihlo, A. A generative adversarial network approach to (ensemble) weather prediction. Neural Netw. 2021, 139, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Yao, M. Global bifurcations and chaotic dynamics in nonlinear nonplanar oscillations of a parametrically excited cantilever beam. Nonlinear Dyn. 2005, 40, 251–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouadjadja, S.; Tati, A.; Guerira, B. Analytical and experimental investigations on large deflection analysis of composite cantilever beams. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, Q.M.; Lv, Z. Theoretical and experiment optimization research of a frequency up-converted piezoelectric energy harvester based on impact and magnetic force. Eng. Res. Express 2024, 6, 035314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Kitipornchai, S.; Yang, J. Thermal buckling and postbuckling of functionally graded graphene nanocomposite plates. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, B.; Cao, D.; Sun, L. Influence of nonlinear terms on dynamical behavior of graphene reinforced laminated composite plates. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 78, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Viet, N.; Zaki, W.; Umer, R. Bending theory for laminated composite cantilever beams with multiple embedded shape memory alloy layers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 30, 1549–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, L.; Xiaobin, L.; Hongxing, H. Free vibration analysis of third-order shear deformable composite beams using dynamic stiffness method. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2009, 79, 1083–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amabili, M.; Ferrari, G.; Ghayesh, M.H.; Hameury, C.; Zamal, H.H. Nonlinear vibrations and viscoelasticity of a self-healing composite cantilever beam: Theory and experiments. Compos. Struct. 2022, 294, 115741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, M.H.; Guo, X.Y. Nonlinear responses of a symmetric cross-ply composite laminated cantilever rectangular plate under in-plane and moment excitations. Compos. Struct. 2013, 100, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, L. Chaotic vibration control of a composite cantilever beam. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, P.; Cao, D. Influence of piezoelectric performance on nonlinear dynamic characteristics of MFC shells. Complexity 2019, 2019, 1970248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ren, L.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Guo, X.T. Chaotic snap-through vibrations of bistable asymmetric deployable composite laminated cantilever shell under foundation excitation and application to morphing wing. Compos. Struct. 2024, 343, 118261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, X.D.; Liu, X. Control of large amplitude limit cycle of a multi-dimensional nonlinear dynamic system of a composite cantilever beam. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazoul, T.; Benatta, M.A.; Khatir, A.; Beldjelili, Y.; Krour, B.; Bouiadjra, M.B. Analytical investigation on the buckling and free vibration of porous laminated FG-CNTRC plates. Vojnoteh. Glas. 2024, 72, 1242–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.; Cuccurullo, S.; Perli, F.P.; Maspero, F.; Corigliano, A.; Ardito, R. A method to enhance the nonlinear magnetic plucking for vibration energy harvesters. Meccanica 2024, 59, 1577–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.X.; Sun, K.C.; Li, H. Nonlinear dynamics of the GPR porous cantilever twisted plate near veering regions. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2025, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Gao, F.; Li, H.-X.; Zhao, X.; Deng, L. A neural network-based distributed parameter model identification approach for microcantilever. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C 2015, 230, 3663–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Mahadevan, S. Bayesian estimation of discrepancy in dynamics model prediction. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 123, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Q.; Zhang, L. Data driven nonlinear dynamical systems identification using multi-step CLDNN. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 085311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestnik, R.; Abel, M. Inferring the dynamics of oscillatory systems using recurrent neural networks. Chaos 2019, 29, 063128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zheng, H.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X. A Novel Model Based on DA-RNN Network and Skip Gated Recurrent Neural Network for Periodic Time Series Forecasting. Sustainability 2022, 14, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribarri, G.; Mindlin, G.B. Dynamical time series embeddings in recurrent neural networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 154, 111612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudukcu, H.V.; Taskiran, M.; Cam Taskiran, Z.G.; Yildirim, T. Temporal convolutional networks with RNN approach for chaotic time series prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 133, 109945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiorgio, M.; Dercole, F.; Guariso, G. Forecasting of noisy chaotic systems with deep neural networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 153, 111570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yao, M. Chaotic time series prediction of nonlinear systems based on various neural network models. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 175, 113971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Ng, W.W.Y. Robust recurrent neural networks for time series forecasting. Neurocomputing 2023, 526, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatir, A.; Capozucca, R.; Khatir, S.; Magagnini, E.; Benaissa, B.; Thanh, C.L.; Wahab, M.A. A new hybrid PSO-YUKI for double cracks identification in CFRP cantilever beam. Compos. Struct. 2023, 311, 116803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatir, A.; Capozucca, R.; Khatir, S.; Magagnini, E.; Benaissa, B.; Cuong-le, T. An efficient improved Gradient Boosting for strain prediction in Near-Surface Mounted fiber-reinforced polymer strengthened reinforced concrete beam. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2024, 18, 1148–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dai, L.; Sun, L. ConvLSTM-based spatiotemporal and temporal processing models for chaotic vibration prediction of a microbeam. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2025, 140, 108411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatir, A.; Capozucca, R.; Khatir, S.; Magagnini, E.; Cuong-le, T. Enhancing damage detection using reptile search algorithm-optimized neural network and frequency response function. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2025, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmani, A.; Shamass, R.; Tsavdaridis, K.D.; Ferreira, F.P.V.; Khatir, A. Deflection predictions of tapered cellular steel beams using analytical models and an artificial neural network. Buildings 2025, 15, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.N. Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plates and Shells: Theory and Analysis; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Hou, F.L.; Liu, X.P. Nonlinear vibration control of a high-dimensional nonlinear dynamic system of an axially-deploying elevator cable. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yang, S.W. Nonlinear transverse vibrations of angle-ply laminated composite piezoelectric cantilever plate with four-modes subjected to in-plane and out-of-plane excitations. Eng. Struct. 2019, 198, 109501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Luo, Z.; Cao, D.X. Nonlinear dynamics analysis of a graphene laminated composite plate based on an extended Rayleigh–Ritz method. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 186, 110673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khennour, M.E.; Bouchachia, A.; Kherfi, M.L.; Bouanane, K. Randomising the Simple Recurrent Network: A lightweight, energy-efficient RNN model with application to forecasting problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 19707–19718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



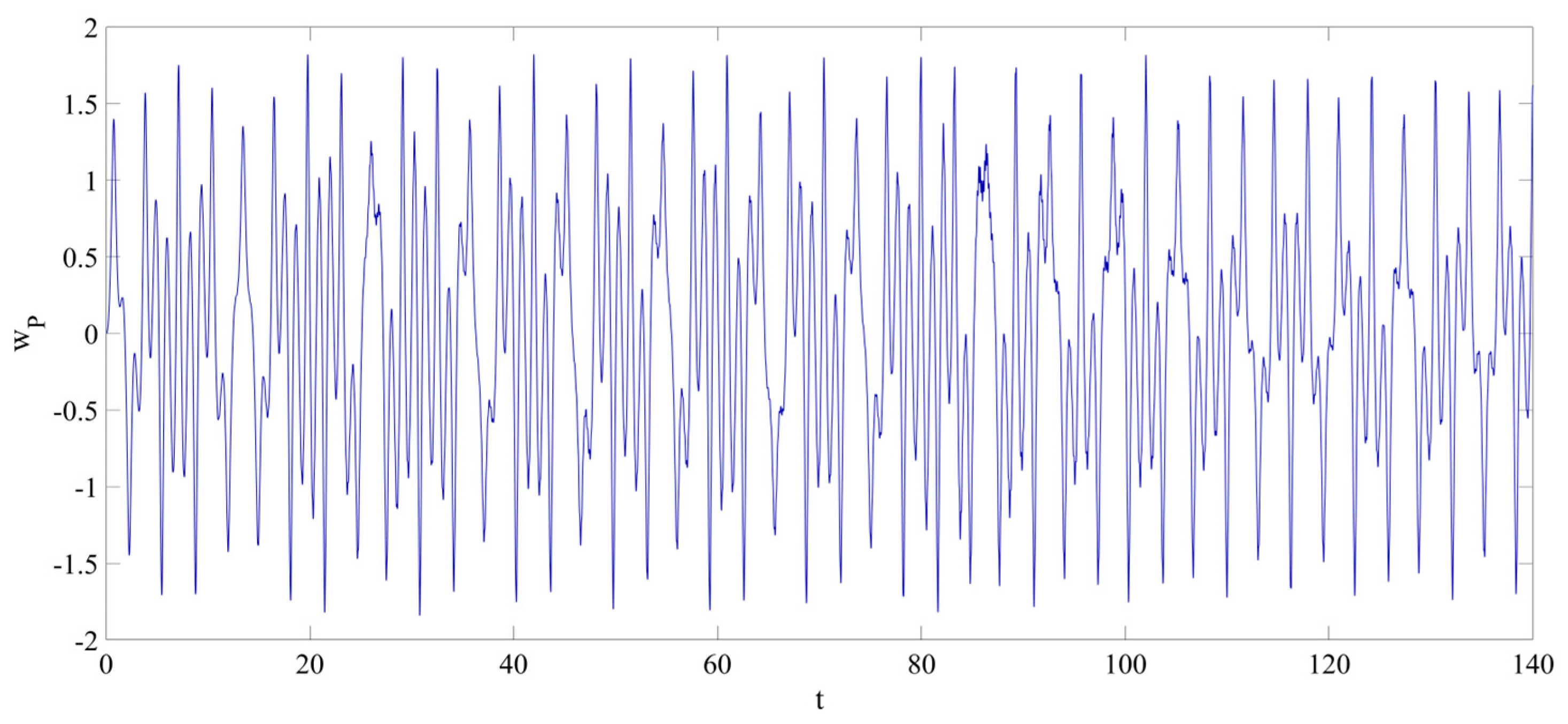
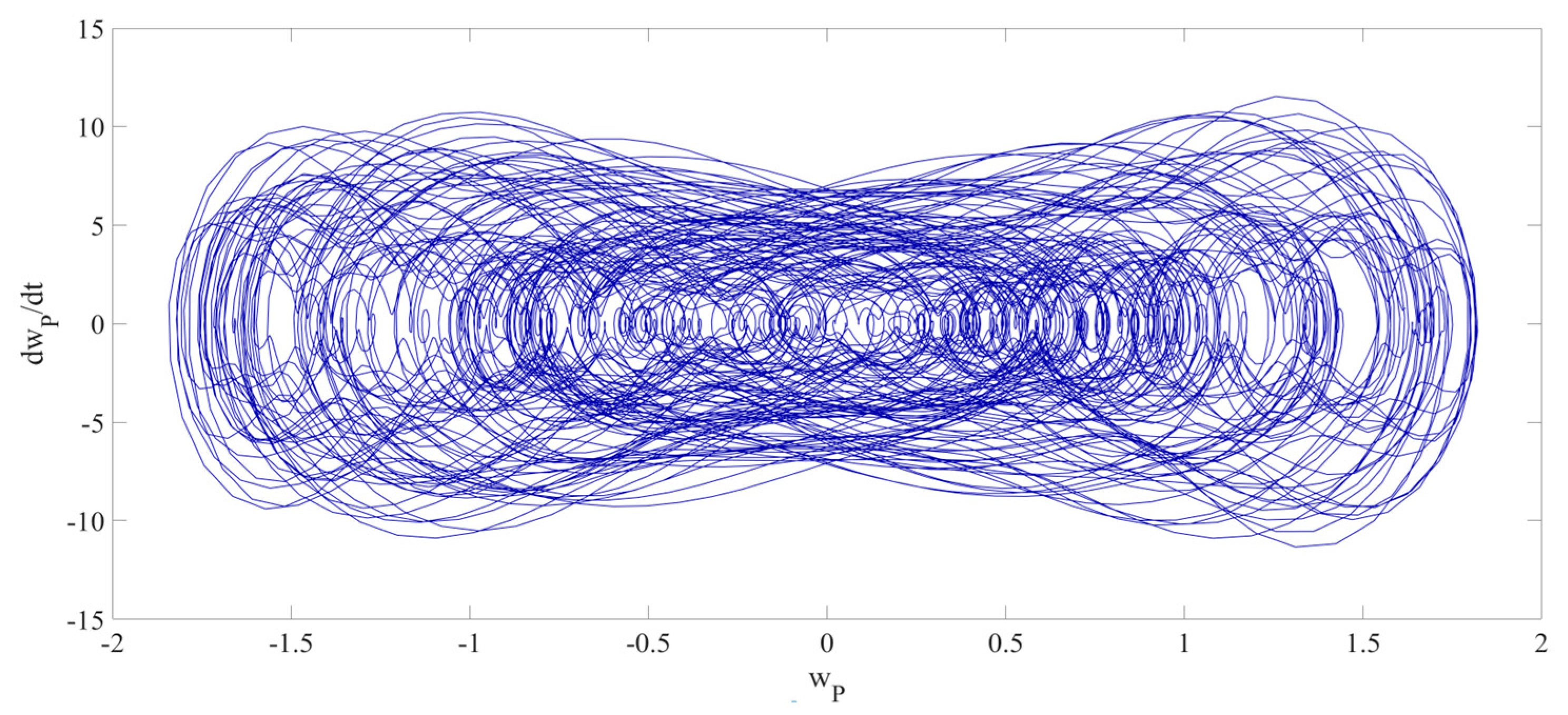
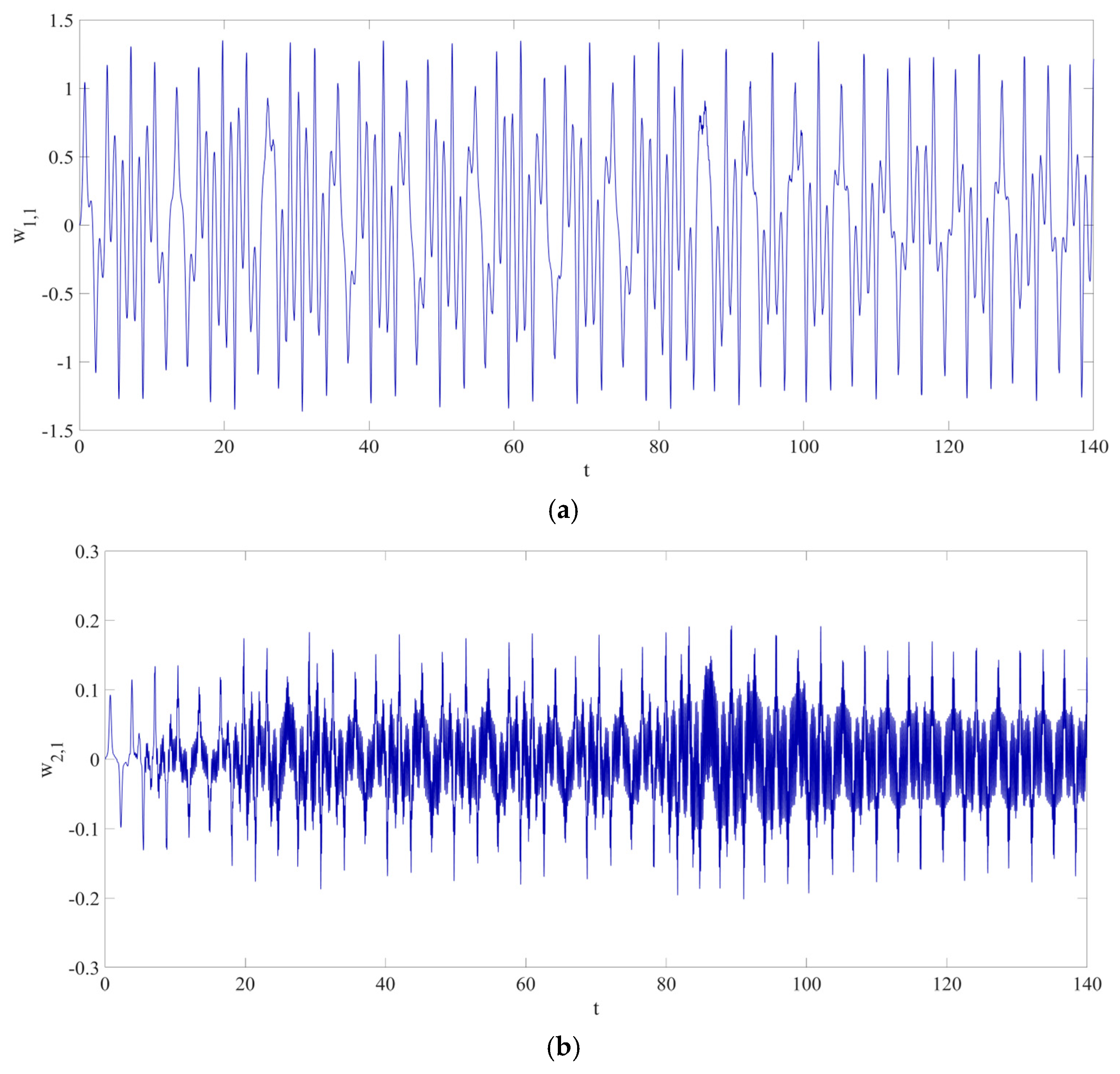
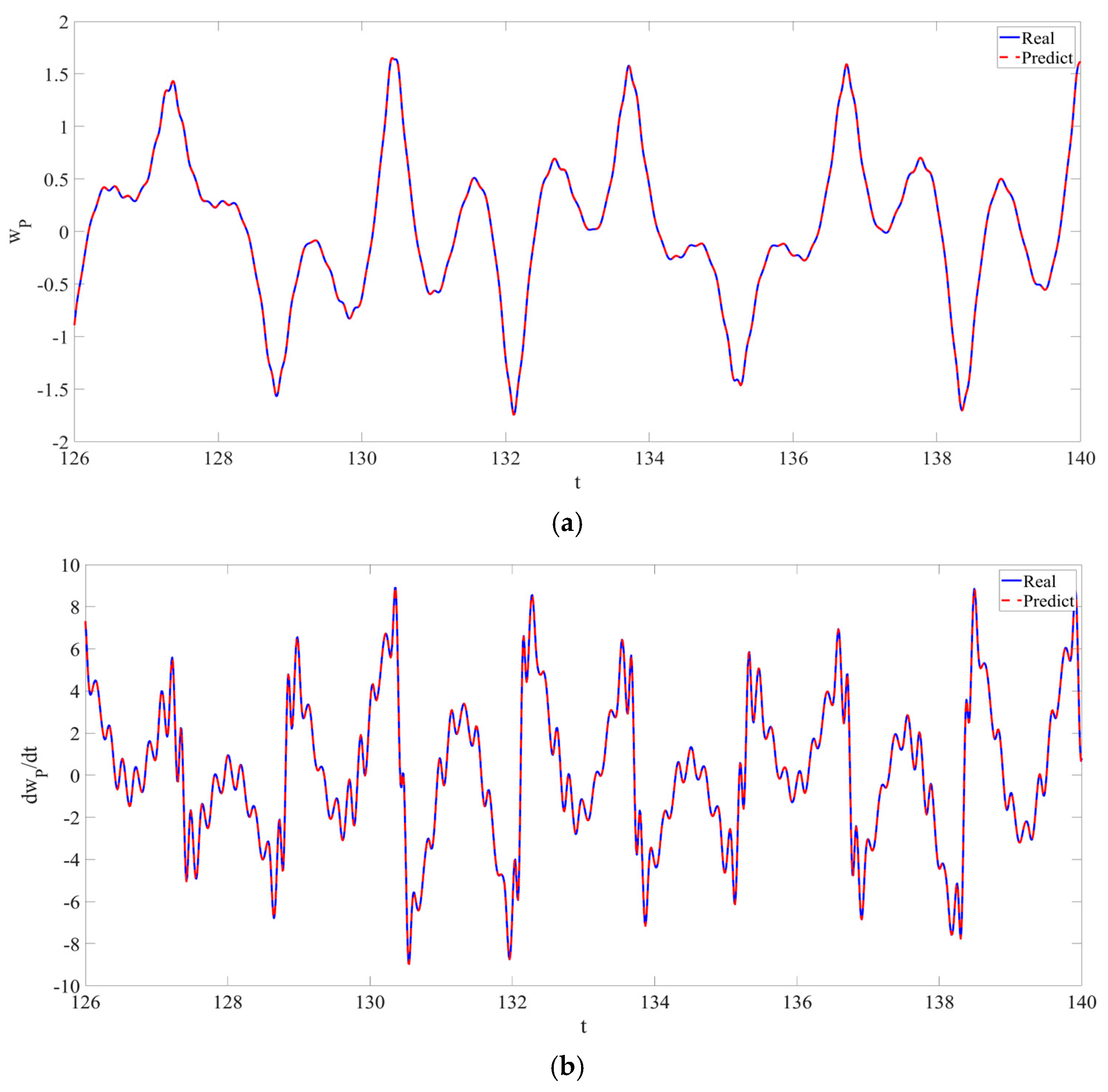







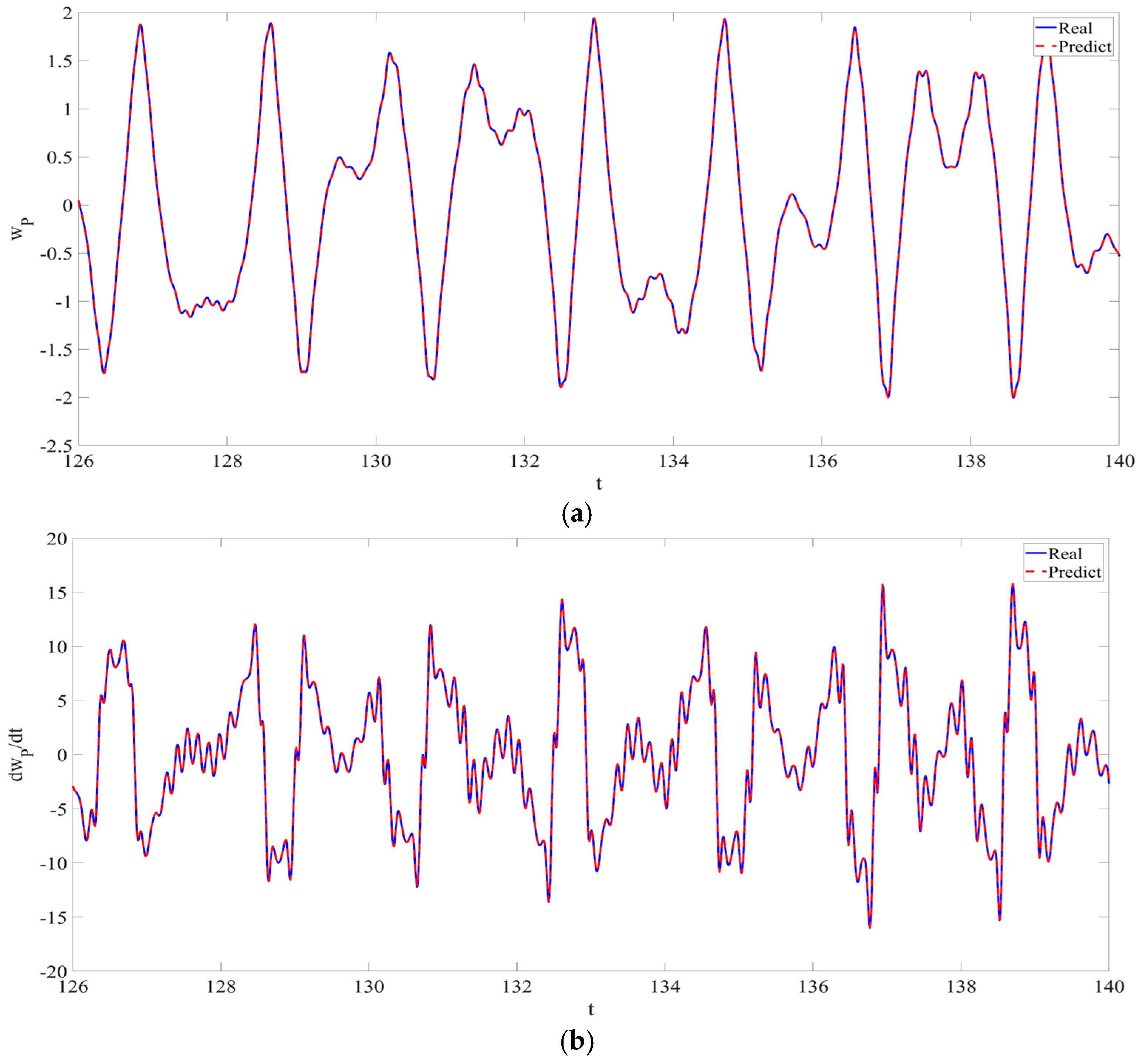
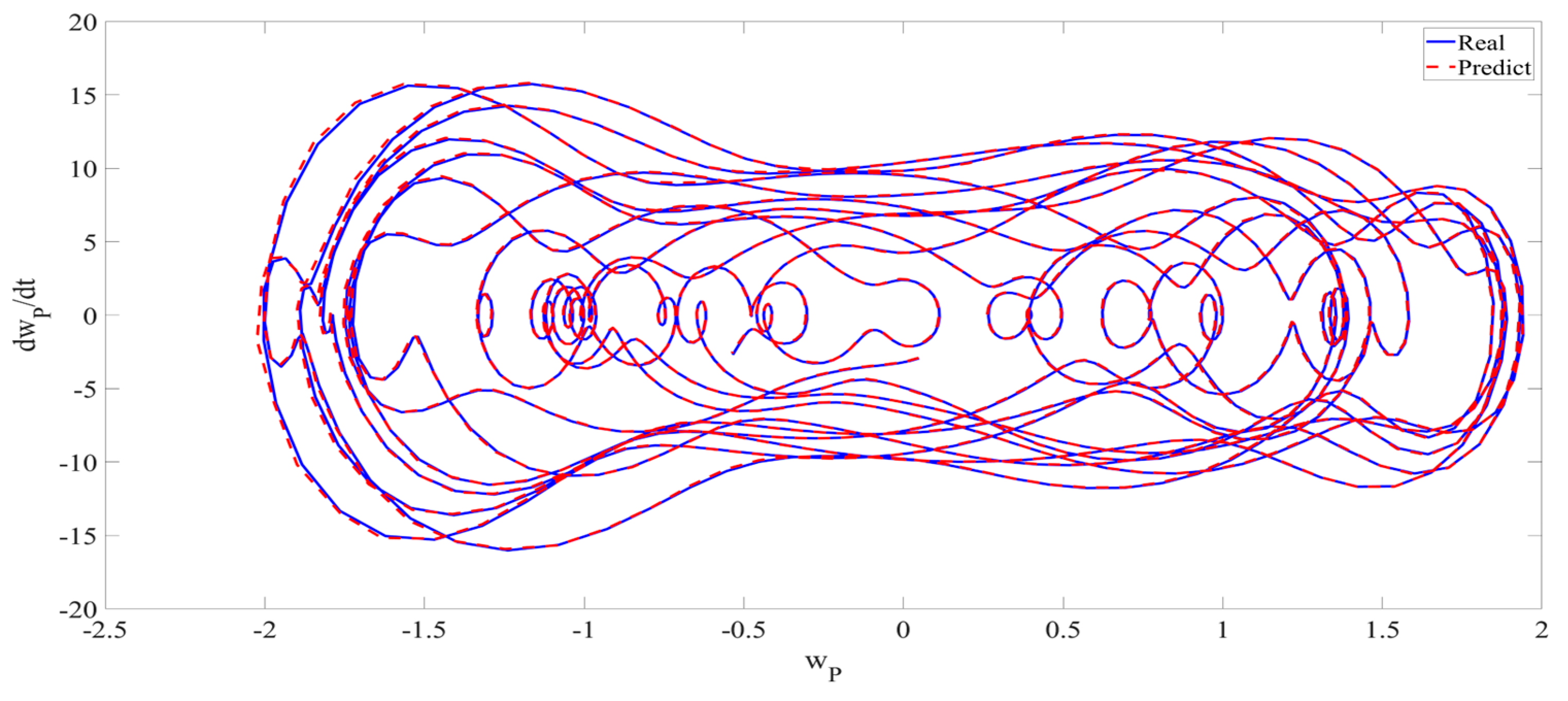
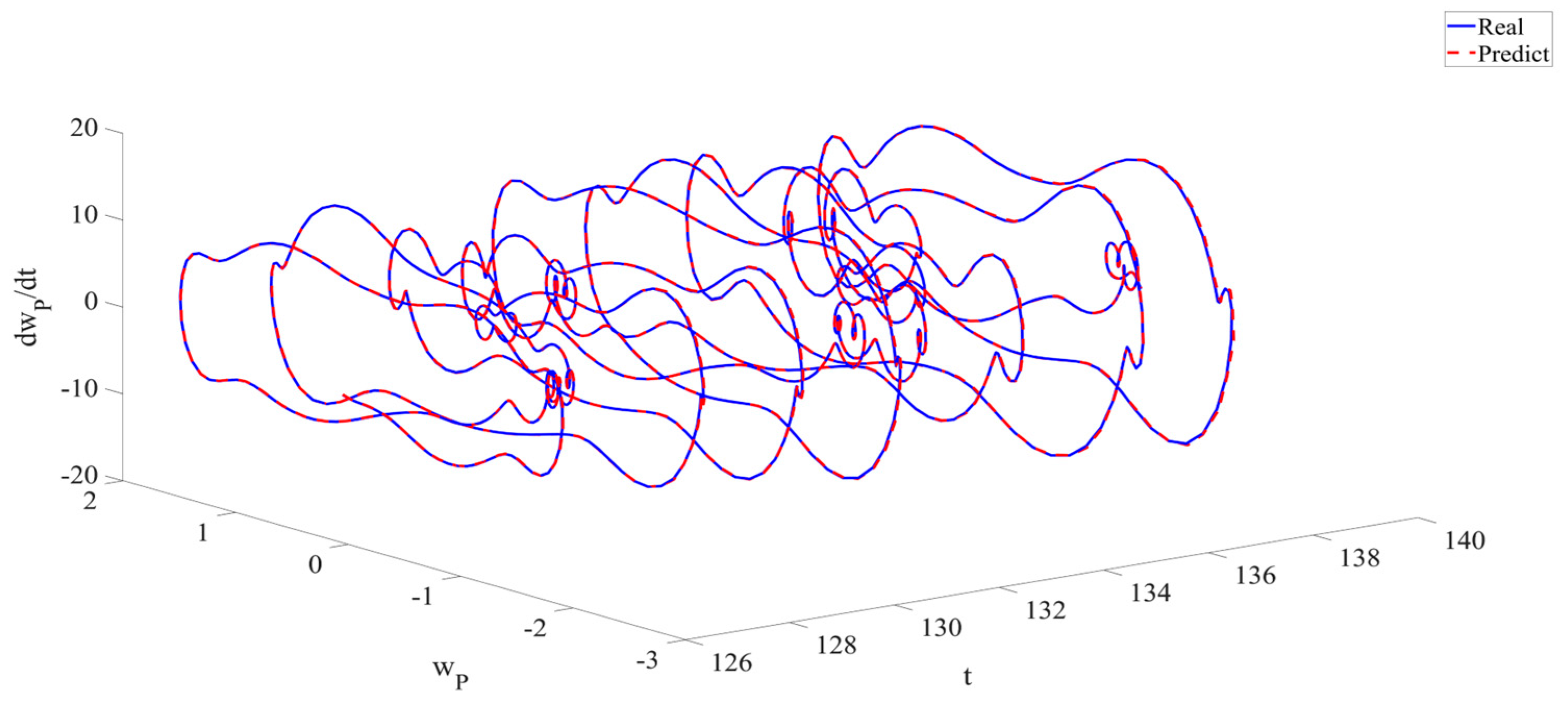
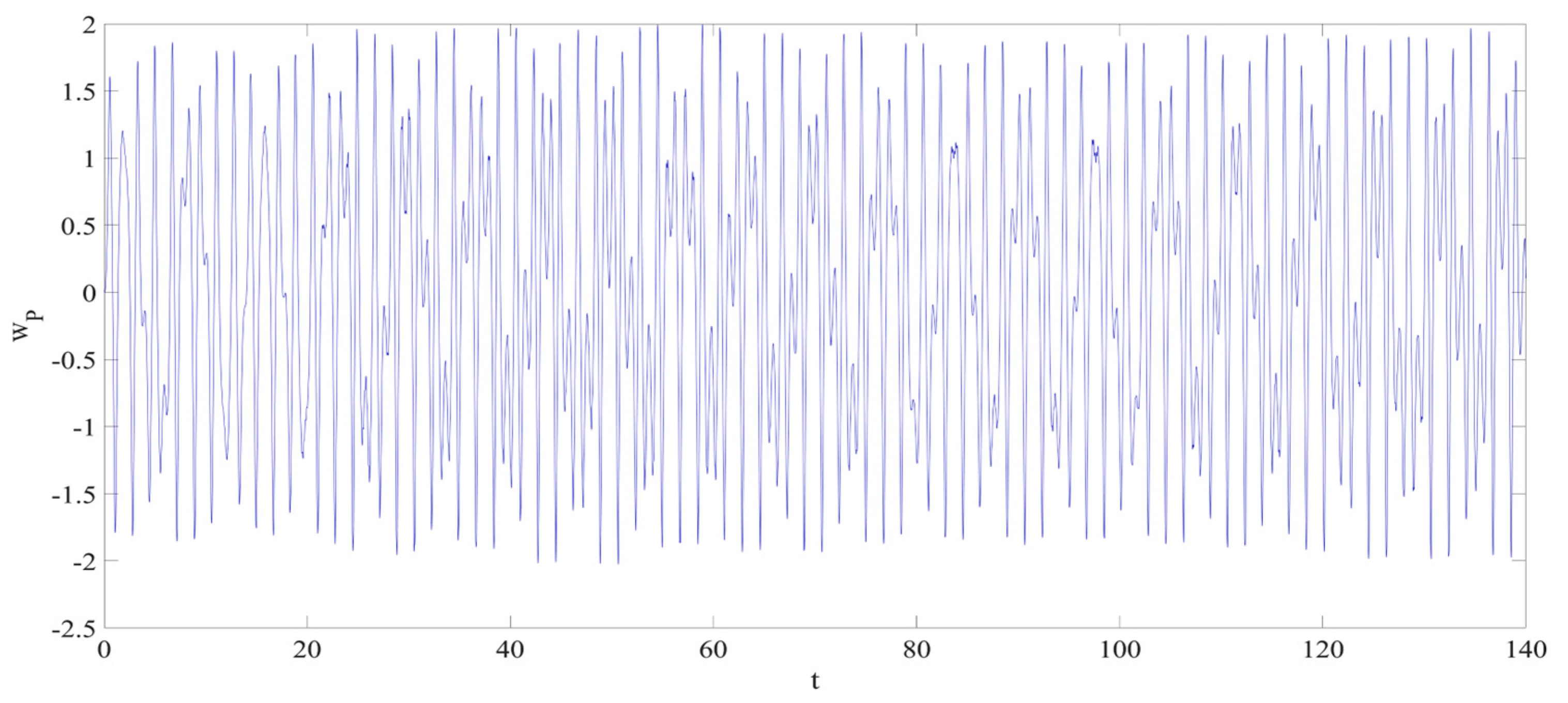
| MAE | 0.030 | 0.010 | 0.024 | 0.041 |
| 0.053 | 0.018 | 0.043 | 0.080 | |
| 0.008 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.003 | |
| RMSE | 0.050 | 0.019 | 0.039 | 0.067 |
| 0.070 | 0.026 | 0.055 | 0.095 | |
| 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.004 |
| MAE | 0.022 | 0.019 | 0.017 | 0.013 |
| 0.042 | 0.034 | 0.031 | 0.022 | |
| 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.005 | |
| RMSE | 0.038 | 0.032 | 0.029 | 0.021 |
| 0.054 | 0.045 | 0.041 | 0.029 | |
| 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, X.; Duo, Y. Chaotic Vibration Prediction of a Laminated Composite Cantilever Beam. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126403
Li X, Sun L, Liu X, Duo Y. Chaotic Vibration Prediction of a Laminated Composite Cantilever Beam. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126403
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xudong, Lin Sun, Xiaopei Liu, and Yili Duo. 2025. "Chaotic Vibration Prediction of a Laminated Composite Cantilever Beam" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126403
APA StyleLi, X., Sun, L., Liu, X., & Duo, Y. (2025). Chaotic Vibration Prediction of a Laminated Composite Cantilever Beam. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6403. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126403






