Abstract
Parameter mismatch in model predictive control (MPC) strategies presents significant challenge in permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) control, often leading to reduced tracking accuracy and compromised system stability under dynamic operating conditions. To address above issue, this article proposes a modified parameter robust FCS-MPC framework that integrates an online learning echo state network (ESN) for real-time compensation of parameter deviations. By leveraging the structural simplicity and application efficiency of ESNs during training, the proposed approach is well-suited to tackling complex parameter variation challenges via online learning. Initially, the ESN is trained offline using data derived from a PMSM-MPC control environment. Subsequently, the trained ESN replaces the predictive model of the MPC controller, enabling online learning under varying PMSM driving conditions. The incorporation of an online ESN allows the proposed controller to achieve real-time adjustments that mitigate the effects of parameter mismatch. Plenty of simulation studies are available and demonstrate that the proposed ESN-MPC controller exhibits enhanced robustness against parameter mismatch compared to the traditional FCS-MPC method.
1. Introduction
Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) are widely used in industrial applications due to their high precision, high efficiency, and excellent control performance. However, PMSM drive systems typically exhibit inherent nonlinearities and variable coupling characteristics, making conventional linear control strategies, such as PI controllers, inadequate to guarantee optimal operational performance. To overcome these nonlinear control challenges, advanced methods including fuzzy logic control, robust control, sliding-mode control, and finite control set model predictive control (FCS-MPC) have been proposed and thoroughly investigated. In particular, FCS-MPC methods enable multivariable optimization, rapid dynamic responses, and flexible handling of system constraints, which are highly suitable to power electronics applications [1,2]. The basic principle of an MPC algorithm is to predict the system’s future outputs corresponding to different inverter voltages. Subsequently, the strategy selects the optimal switching state by minimizing a defined cost function. Although, in theory, FCS-MPC provides superior performance without requiring complex modulation strategies, it is inherently sensitive to parameter uncertainties due to its predictive structure. Specifically, the predictive model relies significantly on accurate system parameters, making parameter accuracy crucial for optimal inverter voltage selection. In practical PMSM systems, critical electromagnetic parameters (such as stator resistance, dq-axis inductances, and flux linkage) experience inevitable fluctuations resulting from magnetic saturation effects and thermal drift, as well as harmonic distortions [3,4,5]. These parameter deviations lead to accumulated prediction errors, consequently degrading overall system control accuracy and causing increased torque ripple, speed oscillations, and efficiency deterioration [6].
To address these challenges, several solutions have been actively explored in prior research. One promising method to enhance the robustness of predictive controllers is to avoid direct dependence on machine parameters, which is known as model-free predictive control. The model-free prediction achieves robustness by directly predicting currents without explicitly relying on PMSM parameters [7,8,9]. However, this approach typically introduces greater sensitivity to measurement noise, particularly under high frequency switching conditions. As an alternative, online parameter identification schemes have demonstrated effectiveness in compensating for parameter variations and improving prediction accuracy [10,11,12,13]. Notable implementations include least-squares estimation for L-type converters, virtual flux-based inductance adaptation, and recursive algorithms for LCL-filter identification. Despite their proven effectiveness, these parameter estimation strategies often incur considerable computational burden due to algorithm complexity, significantly constraining their suitability for practical, real-time control applications [14].
Recent studies have explored integrating artificial neural networks (ANNs) with FCS-MPC to alleviate its intrinsic limitations [15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. For instance, ANN-based implementations have been proposed for real-time adjustment of weighting factors in power converter FCS-MPC schemes [16,17]. These methods effectively address the critical design challenge of balancing reference tracking and switching frequency objectives. Furthermore, experimental validations conducted on DC–DC converters and three-phase inverter systems further confirmed that hybrid ANN-MPC approaches can achieve reduced total harmonic distortion (THD) and superior dynamic response characteristics [18,19]. Additionally, research presented in [20] demonstrated that entirely replacing the traditional MPC structure with an ANN can significantly simplify the computational burden while maintaining comparable or even enhanced performance. However, this complete substitution raises notable concerns, as the prediction model and cost function become “black box” systems, obscuring relationships among internal constraints and significantly limiting their capability for multivariable optimization. As such, it remains questionable whether this ANN-based control approach strictly qualifies as an MPC method. Consequently, further research efforts are still required to explore neural network-based strategies within predictive control architectures, particularly to address parameter sensitivity issues in PMSM drive applications.
In this paper, a specific type of RNN known as the echo state network (ESN) is employed to enhance the parameter robustness of the MPC strategy for PMSM control. Compared with conventional neural networks, the ESN exhibits distinctive advantages in its training mechanism [21]. Structurally, the ESN adopts a three-layer framework consisting of an input/output layer and a dynamic reservoir. The reservoir comprises sparsely interconnected neurons with fixed, randomly initialized weights. The training process only involves linear regression to adjust the output weights for approximating the input–output relationship. This architecture significantly reduces computational complexity compared to back-propagation base neural networks, making it particularly effective for real-time parameter variation compensation through online learning.
Rather than replacing the entire MPC architecture, the proposed ESN-MPC approach substitutes only the predictive model component. This adjustment achieves enhanced performance without sacrificing the inherent advantages of conventional MPC, preserving multivariable constraint handling capability. There are three main contributions in this paper, summarized as follows:
- (1)
- A hybrid ESN-MPC framework is proposed. The trained ESN replaces only the prediction model in the MPC controller framework and maintains the MPC-based cost function by keeping the core MPC structure.
- (2)
- The proposed strategy enhances the robustness of the parameters. The ESN-MPC strategy is initially trained offline using data collected from a real PMSM-MPC control environment. With an online learning algorithm, the proposed controller can make rapid adjustments to mitigate parameter mismatches under real-time deployment.
- (3)
- Compared with traditional MPC, the proposed ESN-MPC approach demonstrates equivalent dynamic performance while achieving superior steady-state performance under parameter mismatch conditions.
The remainder of this article is organized as follows. Section 2 details the implementation of a conventional FCS-MPC strategy in PMSM control. Section 3 details the proposed ESN-MPC strategy. The results of several simulation studies are presented in Section 4, validating the proposed strategy through comparisons with different methods. Finally, conclusions are drawn and suggestions for future work are presented in Section 5.
2. Model Predictive Control for PMSM Drives
Figure 1 presents the topology of the inverter and PMSM system, where a conventional three-phase two-level voltage source inverter (2L-VSI) is employed. The inverter output currents are denoted as ioa, iob, and ioc, with the DC-link voltage denoted as Vdc. The output voltages of the universal bridge, va, vb, and vc, can be expressed as follows:
Here, Sa, Sb, and Sc are the switching states. There are eight switching states, each corresponding to the three-phase universal bridge voltage. By applying the Clarke transformation, the universal bridge voltages can be presented as eight basic voltage vectors at stationary αβ frame:
The eight voltage vectors vn (n = 0, 1, …, 7) and switching states are shown in Figure 2.
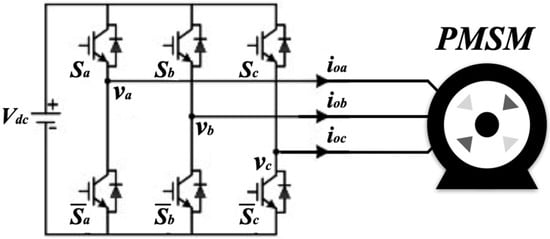
Figure 1.
Topology of the inverter and PMSM system.
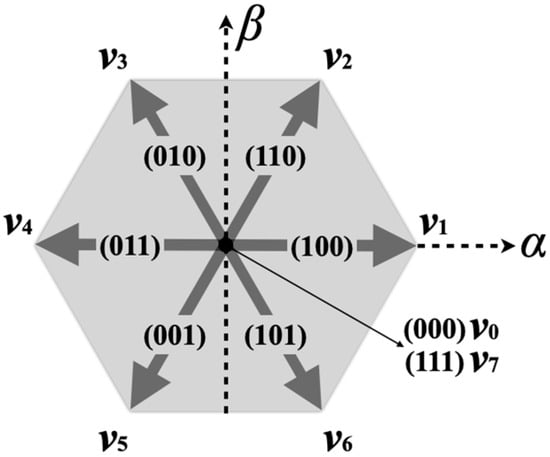
Figure 2.
Switching states and voltage vectors of the inverter.
The stator voltage equation of the PMSM is
where vs = [va vb vc]T and is = [ioa iob ioc]T denote the stator winding voltage and current, respectively. Rs is the stator resistance. The flux linkage is defined by
where ψf denotes the rotor flux linkage. By applying the Clarke and Park transformations, the PMSM voltage and flux linkage equations in the dq-axis can be given as follows:
Based on (5)–(8), the PMSM continuous-time equation can be expressed as
To realize the FCS-MPC strategy, a discrete-time model is employed to predict the system output in the next control period. Based on the Euler approximation formula, the discretized prediction model of the PMSM can be expressed as
where the matrices Ad and Bd are defined as
In MPC strategy, a cost function is used to define the optimal input of the inverter:
Thus, the MPC strategy for the PMSM control can be realized.
3. Proposed ESN-MPC Strategy for PMSM
3.1. Structure of ESN
At each sampling instant, the predictive model utilizes the dq-axis currents (isd(k), isq(k)) and the inverter output voltages (vsd(k), vsq(k)) as inputs, and the outputs are the predicted value in the next control cycle. Therefore, for the ESN, the predictive model of FCS-MPC can be represented as a multivariate function F:
The neural networks, such as ANNs and RNNs, demonstrate excellent performance in addressing nonlinear input–output mapping problems. One of the principal advantages of neural network algorithms lies in their ability to approximate intricate mathematical relationships via multi-layered representations. In the proposed ESN-MPC algorithm, the predictive model of FCS-MPC is replaced with an ESN to achieve real-time parameter adaptation during PMSM drive operation. Thus, the complex algorithm design typically associated with parameter identification techniques is alleviated by the offline training and online learning capabilities of the ESN.
The ESN in this paper includes an input layer with corresponding input vector u, a reservoir with corresponding states x, and an output layer generating the output vector y. A standard tanh(⋅) function is employed as the reservoir’s nonlinear activation. The state and output equations of the ESN can be presented as
In this paper
where Wres, Win, and Wout denote the reservoir, input, and output weight matrices, respectively. Matrices Wres and Win are initialized randomly, while only Wout remains to be determined through the training process. Internal reservoir states and corresponding target outputs are organized into the matrices
The optimal Wout can be determined by solving the following problem:
3.2. Offline Training of ESN
The effectiveness of ESN training largely depends on the quality and diversity of the sample dataset. To ensure the model closely resembles the real practice system, the simulation for generating training data comprehensively incorporates real-world phenomena such as sampling and dead time delays. Specifically, the dataset should span a sufficiently wide range of operational conditions to guarantee satisfactory control performance across various scenarios. The uniform distribution of data points is also critical, as it supports faster and more stable convergence during training. Additionally, careful selection and configuration of the training samples are necessary to prevent both overfitting and underfitting.
The overall data generation and offline training procedure for the ESN are depicted in Figure 3. The dataset for ESN training is collected using the FCS-MPC model for PMSM drives, as discussed in Section 2. While the reference for isd is fixed at zero, the reference for isq can be determined via a PI controller. Based on the prediction model (10), the predicted values of the dq-axis currents corresponding to all possible input voltage are calculated. The optimal switching state is then selected and applied by evaluating the cost function. The input and output state datasets are obtained through sensor sampling and the prediction block of the FCS-MPC. Before training, the dataset is normalized to improve the convergence speed and accuracy of the algorithm. The normalization process is as follows:
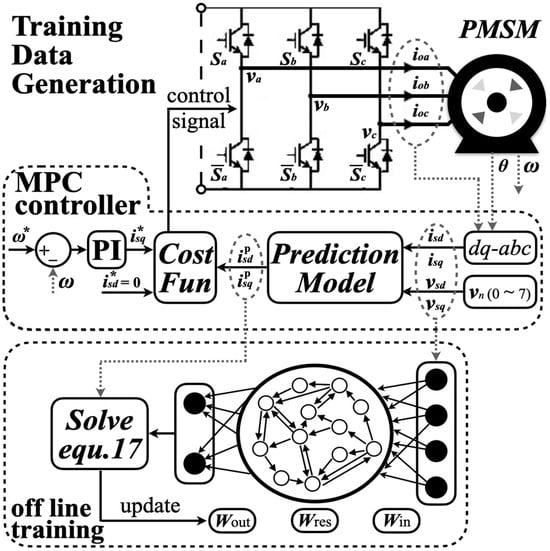
Figure 3.
The process of ESN training data generation of proposed strategy.
The training data spans various operating conditions, including wide ranges of dq-axis inductance values (Ld, Lq), speed (ωr), and load torque (Te). Both the input and output state data from the FCS-MPC controller are stored for training purposes.
3.3. Proposed ESN-MPC Controller and Online Learning Process
To improve the robustness of the ESN-MPC controller in response to PMSM model parameter mismatch, an efficient online learning mechanism is developed to enable adaptive processing of new input–output samples collected from the control system. Inspired by the methodology described in [22], this paper integrates an online learning scheme called the Woodbury Online Learning Echo State Network (WOLESN). As described in Section 3.1, given a historical dataset [Zi, Yi], I = 1, 2, …, k − 1, the goal is to determine an appropriate matrix W by minimizing the following objective function:
Taking the objective function’s partial derivative with respect to W and solving for zero yields the following expression:
Assuming k − 1 samples are accumulated, the previously computed Wold satisfies the solution below:
where
When encountering a new data sample [Zk, Yk] at k, the updated matrices Γnew and Anew become
The updated Wnew also satisfies the following relation:
To alleviate computational burdens associated with direct matrix inversion, the online updating can be efficiently calculated via the Sherman–Morrison formula. Specifically, the new updated Wnew is given by
Here, Kk represents the inverse of Γnew, computed recursively by
As depicted in Figure 4, the prediction part is now replaced by the trained ESN, and the predicted current value at k + 1 is used to evaluate the optimal switching state and implement online learning. At each control instant k, the controller stores the predicted output and activates the online learning block once the actual system response has been sampled at step k + 1. The newly updated output matrix Wout is then employed to guide inverter actions in the subsequent control cycle prediction. In this manner, the proposed ESN-MPC strategy exhibits improved adaptive capabilities, effectively addressing the model mismatches.
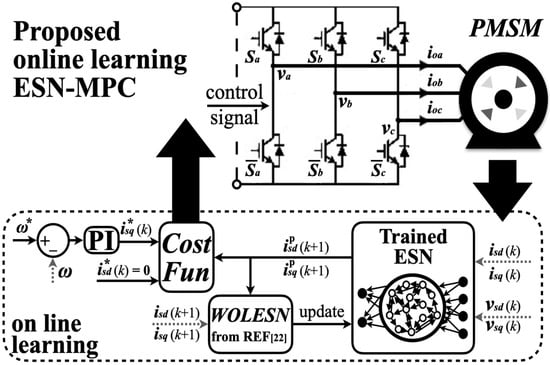
Figure 4.
Control and online learning process of proposed ESN-MPC.
3.4. Computational Complexity Analyze
In conventional FCS-MPC strategies, the computational burden primarily depends on the complexity of the system model, prediction horizon length S, the number of candidate switching states, and the cost function. In this paper, the inverter has eight candidate switching states. The computational complexities attributable to the prediction model and the cost function evaluation are denoted as CP and CCF, respectively (in this paper, CP = 30 and CCF = 4). Thus, at each control cycle, the computational burden of conventional FCS-MPC with prediction horizon S can be expressed as
For the proposed ESN-MPC controller, the computational complexity consists of two main parts. The first is associated with reproducing the mathematical relationship through the trained ESN model. The complexity of the ESN primarily depends upon the network structure (layer number and neuron quantities) and the activation function complexity, denoted Ctanh (Ctanh = 4 in this paper). This article defines the size of the input layer, reservoir, and output layer as NI, NH, and NO, respectively (NI = 4, NO = 2 in this paper). Moreover, in practical implementation, the number of candidate switching states can easily be pre-selected and reduced to 3 according to the error between reference and current value. In this way, the computational complexity of the ESN can considerably simplify and expressed as
Activating the online learning algorithm introduces an additional computation burden, related primarily to the network reservoir size NH. While increasing the reservoir size may enhance modeling and prediction accuracy, it will increase the complexity, potentially hindering real-time applications. Hence, properly determining the reservoir size is crucial for effectively balancing computational efficiency and prediction performance. Table 1 compared the estimated computational complexity during the implementation of conventional FCS-MPC and the proposed ESN-MPC. Considering a comprehensive trade-off between simplicity and prediction accuracy, the reservoir size is eventually set to NH = 15 in the succeeding tests. In this reservoir size, the proposed ESN-MPC can achieve a modeling accuracy of approximately 90.2%. The following section will verify the control performance of the proposed strategy and parameter robustness under changing load and reference tracking conditions.

Table 1.
Comparison on computation burden of different strategies.
4. Simulation Validation
This section presents a comprehensive evaluation and comparative analysis of the control results of the proposed ESN-MPC and the traditional FCS-MPC under different operating conditions. Table 2 lists the parameters utilized in the test system. At the first step, a conventional FCS-MPC controller with stable performance is developed for the PMSM drive control. A dataset containing over million samples, obtained through extensive experimental trials, is employed for ESN training and validation. Specifically, 80% of the collected data are used for training, while the remaining 20% serve as a validation set. Importantly, the test dataset comprises samples different from those in the training, allowing effective performance verification of the proposed strategy beyond the training scenario.

Table 2.
System parameters.
4.1. Dynamic Response to Torque Load Change
This subsection provides detailed comparisons of the control performance between conventional FCS-MPC and the proposed ESN-MPC under nominal conditions. Figure 5a,b depict the dynamic response of the PMSM when subjected to a step change in load torque. Initially, the PMSM operates at a stable speed of 2100 rpm with a load of 40 N·m, and the torque is subsequently stepped up to 80 N·m at 0.5 s. The waveform reveals that the proposed ESN-MPC achieves comparable steady state performance to the conventional FCS-MPC and superior transient performance, exhibiting an improved transient time (Ts = 4.64 ms vs. 6.28 ms in FCS-MPC). The transient superiority is further corroborated by a smaller speed deviation (42.6 rpm drop vs. 67.1 rpm in FCS-MPC) during load transitions. This improved transient performance results primarily from the reservoirs in ESNs that enable the ESN to effectively adapt to abrupt disturbances. Furthermore, steady-state torque ripple and current THD for both methods remain nearly identical, highlighting that the proposed ESN-MPC transient improvements are achieved without compromising steady-state waveform quality.
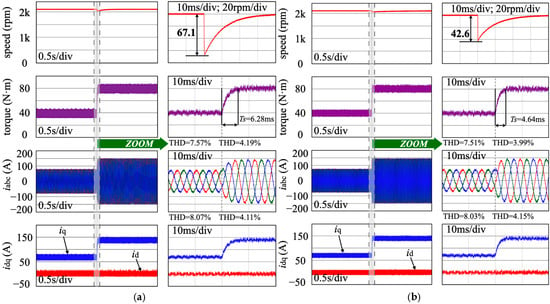
Figure 5.
Control performance using (a) conventional FCS-MPC and (b) proposed ESN-MPC.
4.2. Inductance Parameter Mismatch Investigation
In practical PMSM drive applications, inductance values may vary considerably due to magnetic saturation during high current injections. To fully emulate the actual scenario, a 50% reduction in inductance and the realistic error factors including dead time and sampling delay presented in Table 2 are considered in the simulation modeling. The results in Figure 6 clearly illustrate the performance differences across three scenarios: (a) FCS-MPC with mismatched model, (b) FCS-MPC with accurate model, and the (c) proposed ESN-MPC, which is not trained under this set of parameters.
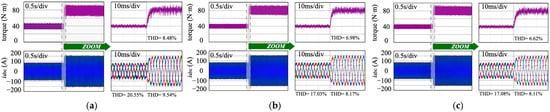
Figure 6.
Test results with −50% to the nominal inductance under (a) a conventional FCS-MPC with mismatched model, (b) a conventional FCS-MPC with accurate model, and (c) the proposed ESN-MPC (not trained with this test set).
The waveform results show that when the inductance is mismatched, the traditional FCS-MPC is significantly affected and the ripple increases (up to 30 N·m). In contrast, the FCS-MPC strategy with an accurate model reduces this ripple notably to 21.5 N·m. In the test, the proposed ESN-MPC activates the online learning block to adapt to parameter variations and stops it at 0.1 s after the load step. After online learning, the proposed ESN-MPC achieves a reduced ripple level (approximately 22 N·m), even without prior training samples from the mismatch scenario.
A more extensive investigation, depicted in Figure 7, was conducted by varying inductance values over a wide range. The test involved performing approximately 1000 simulations to comprehensively assess the system behavior. As shown in Figure 7a, the output current THD with conventional FCS-MPC exhibits large fluctuations, ranging notably from 4.11% to 9.48%, which indicates considerable sensitivity to parameter mismatch. These prominent THD variations mainly result from nonlinearities in the system, sampling errors, and dead-time influences. With a perfectly modeled FCS-MPC (Figure 7b), a relatively low current THD value can be obtained (4.11–7.93%). Furthermore, the proposed ESN-MPC (Figure 7c) effectively compensates for model uncertainties and improves robustness against inductance variations via online learning. It consistently achieves lower current THD values (4.15–7.79%).
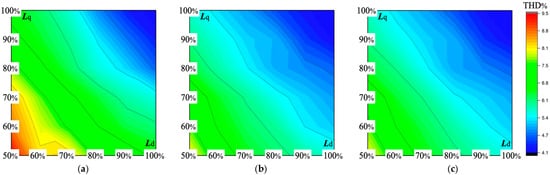
Figure 7.
Variation in the current THD relative to the inductance value change under (a) conventional FCS-MPC with mismatched model, (b) conventional FCS-MPC with accurate model, and (c) proposed ESN-MPC (not trained with these test sets).
4.3. Flux and Resistance Parameter Mismatch Investigation
Flux linkage may considerably vary with rising magnet temperatures. Hence, flux parameter mismatch scenarios (−20% to +20% variation) are investigated in the tests. Figure 8 compares torque ripple vs. flux parameter mismatch under three control strategies. The results confirm that flux mismatch generally causes increased prediction error and torque ripple. Compared to the performance with a torque ripple close to 8 N·m at nominal flux settings, the FCS-MPC under a −20% flux mismatch exhibits a torque ripple rising to around 16 N·m. Although flux deviations slightly elevate torque ripple in ESN-MPC, the rise remains limited, reflecting the robustness of the ESN in handling flux uncertainties.
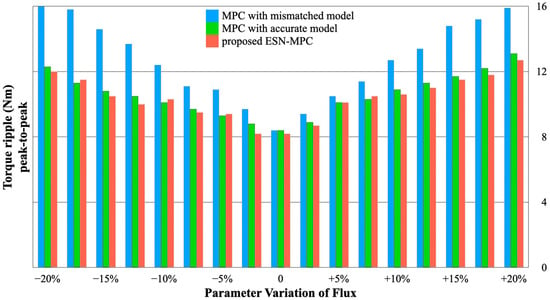
Figure 8.
Test results under flux parameter mismatch with three control strategies.
Lastly, variations in stator resistance, often impacted by temperature increases in high-current operating conditions (e.g., EV applications), were investigated in Figure 9. The stator resistance was varied between 60% and 200% of its nominal value. Interestingly, test results indicate nearly negligible discrepancies in output current THD across the three evaluated strategies. The relatively small influence might possibly be the fact that under steady-state load conditions, the prediction error caused by resistance mismatch has a limited impact on FCS-MPC. Thus, the proposed ESN-MPC and conventional FCS-MPC can achieve a similar performance in this scenario. However, it may still introduce a significant impact on those strategies that requires more precise prediction (e.g., deadbeat control).
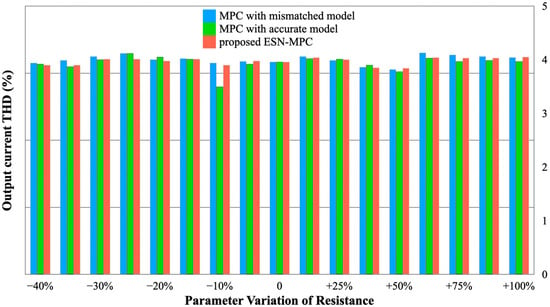
Figure 9.
Test results under resistance parameter mismatch with three control strategies.
Overall, the presented simulation validations indicate that the proposed ESN-MPC achieves enhanced robustness and transient response under parameter mismatch compared to conventional FCS-MPC approaches.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents an ESN-MPC control strategy to enhance parameter robustness and control performance in PMSM drives. Initially, a conventional MPC-based PMSM control model is established to generate representative training data. Subsequently, the ESN is trained offline using extensive data samples and replaces the predictive model of the MPC by incorporating adaptive online learning capabilities. The main advantage of the proposed ESN-MPC method is that it can compensate for various system parameter mismatches while preserving excellent transient and steady-state control performance. Simulation studies indicate that the proposed ESN-MPC achieves performance that closely matches that of an FCS-MPC with accurate model parameters. However, the concept of integrating neural networks into the MPC method also has certain limitations. Although the proposed strategy can maintain acceptable resource utilization, the online learning process still introduces a considerable computation burden, particularly when a large reservoir size is required. This issue can possibly be mitigated by updating only a separated part of the matrix at each time step, thereby reducing the computational burden per control cycle. Future research directions can include developing efficient ESN simplification methods to further reduce the computational load, as well as conducting experimental verification under extreme working conditions of actual PMSM drive systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z., J.L. and P.Y.; Methodology, X.Z. and H.C.; Software, X.Z.; Validation, X.Z.; Formal analysis, X.Z.; Investigation, X.Z., J.L., P.Y., H.C. and D.L.; Resources, J.L.; Data curation, J.L. and Y.Z.; Writing—original draft, H.C. and D.L.; Visualization, P.Y.; Project administration, D.L.; Funding acquisition, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Smart Grid-National Science and Technology Major Project under Grant 2024ZD0800300 and in part by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. LQN25E070005.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Daren Li was employed by the company State Grid Zhejiang Power Co., Ltd., Wenzhou Power Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Tu, W.; Luo, G.; Chen, Z.; Cui, L.; Kennel, R. Predictive cascaded speed and current control for PMSM drives with multi-timescale optimization. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 11046–11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanakos, P.; Liegmann, E.; Geyer, T.; Kennel, R. Model predictive control of power electronic systems: Methods, results, and challenges. IEEE Open J. Ind. Appl. 2020, 1, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Feng, G.; Mukherjee, K.; Kar, N.C. Investigations of the influence of PMSM parameter variations in optimal stator current design for torque ripple minimization. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Wang, G.; Kong, Q. Study on the influence of ultra-thin non-oriented silicon steel sheet on the performance of ultra-high-speed permanent magnet motor. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 065307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukundan, M.S.; Dhulipati, H.; Tjong, J.; Kar, N.C. Parameter Determination of PMSM Using Coupled Electromagnetic and Thermal Model Incorporating Current Harmonics. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.A.; Perez, M.A.; Rodriguez, J. Analysis of finite-controlset model predictive current control with model parameter mismatch in a three-phase inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 31003107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerten, J.; Verveckken, J.; Driesen, J. Predictive direct torque control for flux and torque ripple reduction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-K.; Liu, T.-H.; Yu, J.-T.; Fu, L.-C.; Hsiao, C.-F. Model-Free Predictive Current Control for Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Based on Current Difference Detection Technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, X.; Su, X.; Shen, Y.; Xiao, D.; Zhao, H. A Switched Ultra-Local Model-Free Predictive Controller for PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 10665–10669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Yang, M.; Xu, D. An adaptive robust predictive current control for PMSM with online inductance identification. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2012, 7, 3845–3856. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Wang, M.; Song, Z.; Liu, T. Robust model predictive current control of three phase voltage source PWM rectifier with online disturbance observation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2012, 8, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.; Moon, U.; Park, J. Predictive-Control-Based direct power control with an adaptive parameter identification technique for improved AFE performance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 6178–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirsto, V.; Kukkola, J.; Rahman, F.M.M.; Hinkkanen, M. Real-Time identification of LCL filters employed with grid converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 5158–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcari, E.; Iannelli, A.; Carron, A.; Zeilinger, M.N. Stochastic MPC With Robustness to Bounded Parameteric Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 68, 7601–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzgec, U.; Becerikli, Y.; Turker, M. Dynamic Neural-Network-Based Model-Predictive Control of an Industrial Baker’s Yeast Drying Process. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2008, 19, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, S.; Marino, D.; Zafra, E.; Peña, M.D.V.; Rodríguez-Andina, J.J.; Franquelo, L.G.; Manic, M. An Artificial Intelligence Approach for Real-Time Tuning of Weighting Factors in FCS-MPC for Power Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 11987–11998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Ma, G.; Sun, Z.; Luo, J.; Ren, G.; Xu, S. Weighting Factors Optimization for FCS-MPC in PMSM Drives Using Aggregated Residual Network. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 1292–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.V.S.; Suprabhath, K.S.; Madichetty, S.; Mishra, S.; El Kamel, A. Design and Implementation of Model Parameter Independent Robust Current Control Scheme of Three-Phase Inverter—A Neural Network-Based Classification Approach. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2024, 9, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bana, P.R.; Amin, M.; Molinas, M. ANN-Based Surrogate PI and MPC Controllers for Grid-Connected VSC System: Small-Signal Analysis and Comparative Evaluation. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huangfu, Y.; Li, X.; Tan, B.; Li, P.; Tian, C.; Quan, S. A Virtual MPC-Based Artificial Neural Network Controller for PMSM Drives in Aircraft Electric Propulsion System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 3603–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenio, L.B.; Terzi, E.; Farina, M.; Scattolini, R. Echo State Networks: Analysis, training and predictive control. In Proceedings of the 2019 18th European Control Conference (ECC), Naples, Italy, 25–28 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Jin, L.; Li, S. An Online Learning Strategy for Echo State Network. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).