Abstract
The traditional chemical safety management method mainly relies on manual inspection and empirical judgment, which is incompetent in the face of the increasingly complex production environment and colossal data volume, and there is an urgent need to apply efficient modern emerging technologies to strengthen the safety management of chemical production sites. Therefore, this dissertation researches chemical safety risk factor identification and analysis predicated on improved LDA topic model and Bayesian network. Thirty-three main risk factors are obtained by constructing the LDA topic model, text mining, and thematic analysis of chemical safety accident cases and combining them with the socio-technical system accident model. The correlation and causal relationship between risk factors were revealed based on association rule mining and Bayesian network analysis. Sensitivity and critical causal path analyses were utilized to indicate the possible paths and vital aspects of accident development. The results show that the text mining LDA topic model proposed in the dissertation performs well in analyzing accident reports and can effectively solve the problems of insufficient analyzing ability and high subjectivity of traditional methods. The research method of the thesis can efficiently extract the keywords of accident reports and reveal the correlation and causality between risk factors.
1. Introduction
The raw materials and products involved in the chemical production process are often flammable, explosive, toxic, corrosive, and other characteristics; coupled with the complex and volatile production environment, safety production accidents occur from time to time, endangering both lives and property while threatening social stability. The trend in chemical accidents and resulting deaths in China over the period 2016–2022 is illustrated in Figure 1. These data are from “Southern Metropolis Daily” and “The National Commercial Fire and Safety Association”. There are 1185 chemical accidents with 1477 deaths. Therefore, it is essential to strengthen the management of production safety.
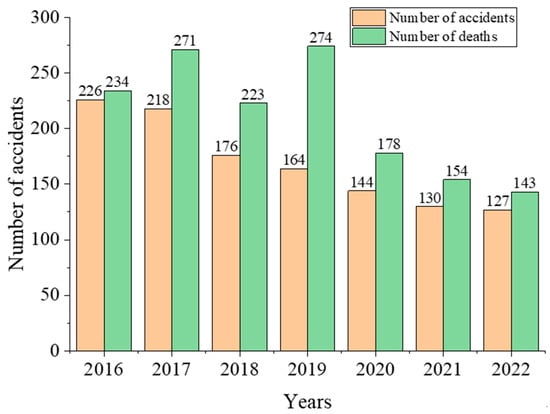
Figure 1.
Chemical accidents and fatalities in China (2016–2022).
Extensive research has been conducted in the field of chemical safety. P. Lassak et al. [1] chose an industrial fixed-bed reactor as the object of study and developed a mathematical model with nine parameters and analyzed the effect of uncertainty on individual model parameters and their combinations using Monte Carlo methods. Building upon traditional safety analysis methods, Rathnayaka et al. [2] introduced a predictive accident model that synergistically combines event tree and fault tree approaches with process historical data and causal analysis. Jain et al. [3] formulated a holistic framework for systematic process safety management and risk assessment tailored to technological applications. Tan [4] achieved basic safety in chemical parks by constructing a capacity assessment model for chemical parks, reduced accident losses, and gave recommendations for expanding the stock of favorable hazards in the development of chemical parks.
These traditional methods need more data collection and analysis capabilities and are highly subjective, unable to fully understand potential safety risks and trends. At the same time, traditional chemical safety management may need to catch up to technological updating and development and is unable to fully utilize new technological means to enhance the efficiency and level of safety management, missing the opportunity to prevent accidents in advance and affecting the effectiveness of safety management.
Text mining can effectively compensate for traditional methods’ shortcomings, extracting useful information from massive text data, discovering hidden knowledge, and making classification predictions, which can help decision-making and applications. Recent developments in text mining include Senave et al.’s [5] systematic examination of text-processing stages, which underscored the significance of keyword extraction. Addressing this critical need, Zhang et al. [6] developed a novel semantic hierarchical graph model that effectively captures keyword contexts and their underlying connection patterns. The hierarchical associations between the words in the semantic graph can be effectively revealed through deep mining of feature item representations. High-probability keyword collection results can be obtained. To optimize news retrieval, Zhang [7] created a text-processing technique that extracts keywords from news articles to obtain their essential information. Text mining sometimes uses clustering methods, and LDA topic modeling is one kind of clustering method. Zhao et al. [8] systematically investigated the privacy preservation of mainstream LDA training algorithms established upon Collapsing Gibbs Sampling (CGS) for the privacy problem in LDA and proposed two LDA algorithms. Among them, the centralized privacy-preserving algorithm (HDP-LDA) prevents the leakage of mid-training statistics in CGS. Unlike conventional LDA, the locally private LDA (LP-LDA) variant incorporates local differential privacy mechanisms to protect each data contributor’s information. Among the LDA variants, Tracer Ratio LDA (TR-LDA) is a classical form given its distinct nature. The algorithm for solving TR-LDA only converges if the sample size is significantly smaller than the dimensionality of the data. To address this problem, Li et al. [9] proposed an adapted form of TR-LDA, which is applied to different datasets through a standardized format. Wu et al. [10] proposed a short text clustering algorithm (SKP-LDA) for LDA using sentiment co-occurrence statistics and extracted knowledge pairs. Among them, the sentiment word co-occurrence considers diverse short texts, and the microblog short texts are also assigned with sentiment polarity. At the same time, the model extracts knowledge pairs (topic-specific words and their relational counterparts) and integrates them into LDA for clustering, significantly enhancing online public opinion analysis accuracy. Jia et al. [11] employed LDA to establish a material cycle safety control system for construction sites, enhancing project safety and offering insights for systematic engineering safety management. Zhang et al. [12] utilized this idea to analyze the research lineage of forestry ecological construction, identifying frontier hotspots and forecasting future trends, thereby contributing valuable guidance for related fields.
Given the low use of text mining methods in chemical safety, this paper attempts to combine and use text mining, keyword extraction, LDA topic modeling, association rule analysis, and Bayesian networks for chemical accident analysis. Focusing on chemical production safety, this study develops a systematic risk identification and analysis framework tailored to the unique characteristics of chemical production site management. By conducting an in-depth examination of chemical accident investigation reports and leveraging text mining and analytical techniques, the research not only advances the theoretical boundaries of chemical safety management but also demonstrates substantial innovation and practical significance for real-world applications. The objective is to cut down on the frequency of accidents through robust guidance for automated analysis of accident causes and optimization of safety strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset and Data Preprocessing
This study utilizes chemical production accident investigation reports as the primary corpus for analysis, which experts within the safety field make through research, analysis, and writing after an accident. The official websites of China’s Ministry of Emergency Management (MEM) and provincial and municipal emergency management departments have corresponding accident investigation reports. Several websites in China collect and organize accidents regarding chemical production systems, such as the Safety Management Network, China Chemical Safety Association, and Chemical Safety People. To establish robust data provenance, this study downloaded the chemical-related accident investigation reports from these websites from 2013 to 2022, totaling 843 articles. After implementing data cleaning procedures including deduplication and quality filtering, we obtained a final corpus of 514 chemical industry accident reports. The classified distributions of accident severity levels and incident types are visualized in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
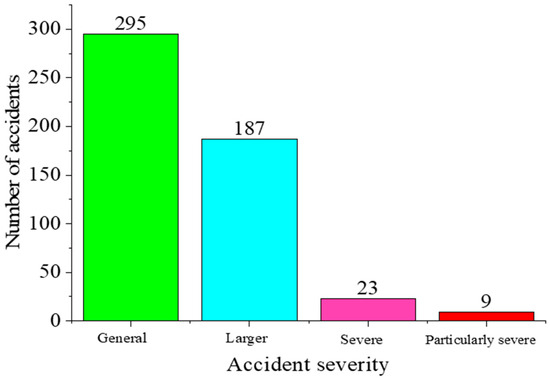
Figure 2.
Number of accidents of different severity.
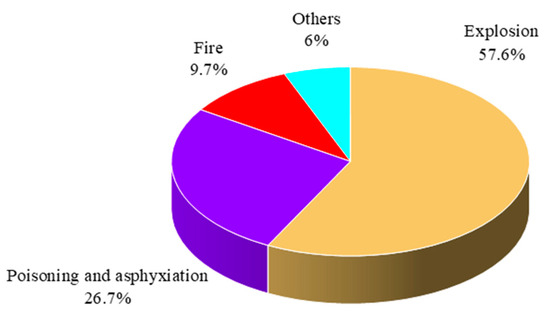
Figure 3.
Percentage of different accident types.
Figure 2 shows that most accidents are general and more significant. Though these accidents caused relatively few casualties or damage, they occur with a high frequency and can still severely impact chemical production. Figure 3 reveals that explosions account for more than 50% of all accidents, while poisoning and asphyxiation incidents represent the second most common type. This pattern primarily stems from the widespread use of combustible, explosive, toxic, and hazardous gases in chemical manufacturing processes, which frequently lead to either mixed-gas explosions or worker exposure resulting in poisoning/asphyxiation cases.
To prevent data redundancy, reduce the workload of text analysis, and minimize the interference of irrelevant information on the analysis, this study further screened out the “Accident History” and “Accident Cause Analysis” in each accident investigation report, which served as the initial corpus for the analysis of this paper. This study further screened out “accident history” and “accident cause analysis” from each accident investigation report as the initial corpus for this paper.
Data preprocessing is an essential yet labor-intensive step, as the raw corpus often includes irregular or irrelevant terms. A key objective involves segmenting the original Chinese text—similar to how English text is divided by spaces—to facilitate subsequent analysis. The text segmentation tool used in this study is the Jieba splitter of python3. Linguistic analysis reveals that the causative factors in chemical accidents predominantly manifest as either nominal phrases or verb–noun constructions, indicating their syntactical simplicity [13], so only common nouns, organization names, other proper names, everyday verbs, and gerunds are selected during the segmentation so that Jieba segmentation will automatically eliminate the rest of the lexical segmentation results during the segmentation.
Jieba participles contain three dictionaries: a domain dictionary, a synonym dictionary, and a deactivation dictionary.
- (1)
- Domain Dictionary: Although the Jieba system comes with a dictionary for splitting words that contain the most common words (e.g., reactor, piping, etc.), current natural language processing systems exhibit significant limitations in recognizing domain-specific terminology, particularly technical terms such as ‘distillation tower’, ‘intermediate chamber’, ‘steam valve’, and ‘gas detector’ that are essential for accurate process industry documentation analysis. When these words are encountered, the Jieba segmentation system may split the entire proprietary word into two or more words, thereby destroying words that would otherwise be highly indicative of safety risk factors. The implementation necessitates constructing a domain-specific lexicon incorporating these industry terms and subsequently integrating this customized dictionary into the segmentation system to the Jieba word-splitting system.
- (2)
- Dictionary of synonyms: The prevalence of synonymous expressions in accident investigation reports introduces lexical variation that adversely affects tokenization consistency, resulting in fragmented segmentation outputs, leading to a significant increase in the difficulty of cluster analysis. Therefore, all the synonyms can be replaced with a word, such as pipeline or steam pipe, which can be substituted with pipeline.
- (3)
- The accident reports contain significant noise elements including non-informative tokens, uncontextualized numerals, and extraneous punctuation marks that require filtration, for instance, yes, 3, “!” etc. The terms demonstrate no statistically significant relevance to the analytical framework and should be incorporated into deactivated word dictionary of the Jieba participle system to be eliminated.
The three lexical databases exert a direct influence on tokenization accuracy, consequently inducing propagation effects throughout downstream analytical processes. Thus, updating these three lexicons several times is necessary to form a Jieba segmentation system that conforms to this study.
A preliminary domain-specific lexicon was constructed prior to text segmentation. For this study, technical terminologies in chemical production were systematically extracted from official web resources of major search engines (Baidu, Sougou, and Google), then standardized and incorporated into the specialized dictionary.
The study adopted the HIT stop-word lexicon as the baseline filtration dictionary. Following corpus segmentation, domain experts conducted rigorous validation of the tokenization results. Identified synonymous expressions were systematically consolidated through incorporation into a synonym repository and subsequent term standardization, while non-content tokens were appended to the enhanced stop-word lexicon. This way, a lexicon that conforms to the textual sub-lexicization of accident investigation reports in chemical safety was obtained. Using this system for the original corpus, the final lexicon results were obtained as data for subsequent analysis.
2.2. Keyword Extraction
Keyword extraction helps to summarize the text content to facilitate users to quickly understand the text topic and main points, but also to improve the accuracy and efficiency of information retrieval, commonly used keyword extraction algorithms are TF-IDF and BM25. While examining lexical-document associations, they overlook the role that word meanings play in extracting keywords. In terms of words indicating security risk factors, longer words usually have more explicit and specialized information. However, the BM25W model [14] is able to extract more accurately words that explicitly indicate safety risk factors. In addition, specialized vocabulary in domain lexicon are carefully screened by domain experts, so their semantic representation is clearer. So the model weights the BM25 model according to the semantics of the words themselves. As shown in Equation (1), the denotes the word the length of the word, and the maximum word length in text . Secondly, weights based on domain dictionary are shown in Equation (2).
If not present among domain vocabulary, the score is 0. Conversely, if the term exists in the domain dictionary, its initial weight is assigned a value of 0.5 and added to every 100 words to documents ratio of the word to the document. The combined weight of these two components serves as the semantic-based weighting factor, which is subsequently incorporated into the BM25 scoring formula as presented in Equation (3).
2.3. LDA Subject Modeling
LDA is generative probabilistic model [15] pioneered by David Blei, Andrew Ng, and Michael Jordan in 2003 for revealing potential topics in textual data. The creation of LDA has brought significant progress in textual topic modeling. With the popularity of social media, the importance of textual data is increasing, posing new challenges to social science researchers. LDA models are widely used in social science research, including topic discovery and document categorization, due to their ability to extract topics from large amounts of text effectively.
Figure 4 depicts the LDA topic model framework.
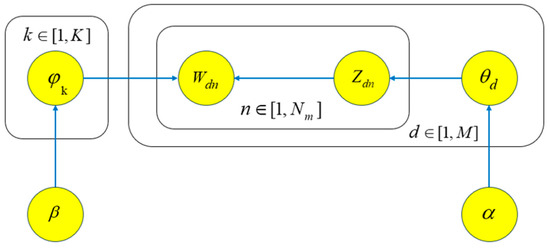
Figure 4.
Diagram of LDA subject model.
The LDA model corresponding to Figure 4 has two main generative processes:
- (1)
- : In the LDA model, this process describes the generation process of the th word in document . First, the topic distribution of document is extracted from the Dirichlet distribution based on the hyperparameter , which represents the mixture of document topics. Then, the th word in document is assigned its attributable topic based on . This process synthesizes the distribution of document topics and the distribution of vocabulary under each topic to ensure the appropriate matching of vocabulary and topic.
- (2)
- : In the LDA model, this process describes the generation of the th word in a document . First, topic-word distributions are obtained by sampling from the Dirichlet distribution based on the hyperparameter . Subsequently, the topic of the th word in document is determined, and the appropriate vocabulary is generated for the word based on the corresponding topic-word distribution . This process effectively captures the association between vocabulary and topic and realizes the topic modeling of textual data. The key point is to determine the topic for each word in the document through the topic-word distribution and then generate the corresponding words.
Where the joint distribution of all variables is shown in Equation (4):
in Equation (4) represents the th word in the th document, which is a key concept in text data analysis. Text data is the object we want to analyze and mine, while the parameters and are pre-set values that have a guiding role and affect the generation of topics and vocabulary. Except for the observable lexical variable and the a priori parameters and , other variables in the LDA model are hidden. Among these hidden variables, denotes the topic to which the th word in a document belongs, denotes the topic distribution of document , and denotes the vocabulary distribution of the th topic. LDA establishes the link between a document and a topic by inferring these hidden variables through analyzing textual data [16]. The model uses methods such as Bayesian inference for parameter estimation and learning to capture the topic structure and semantics of text to support text analysis and applications.
The most commonly used parameter estimation methods for LDA probabilistic subject models include Gibbs Sampling [17] and Variational Inference [18]. Compared to Variational Inference, Gibbs Sampling is a simple and intuitive Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method [19] for sampling hidden variables and parameters from a joint distribution, which can accurately sample from the posterior distribution to obtain accurate parameter estimates. In the LDA model, Gibbs sampling can update the estimates of the model parameters step by step by sampling each variable given the other variables. Therefore, Gibbs sampling is used in this paper to construct the LDA model.
2.4. Association Rule Analysis
Initially introduced by Agrawal et al. [20] for market basket analysis, association rule mining serves as a computational method for discovering hidden relationships among item sets within transactional databases. As an important data mining technique, it effectively analyzes accident data, reveals accident-related patterns and causal relationships, and aids managerial decision-making, with proven applications in diverse fields [21,22].
Apriori, as a classical algorithm in association rule mining, has a solid theoretical foundation and a wide range of applications. It applies to various datasets and is easy to understand and implement. Although the Apriori algorithm is less efficient when dealing with large-scale datasets, it still performs well when the data size is not particularly large or the set of frequent items is small. The setting of the support and confidence parameters makes the results tunable and interpretable, which can meet the needs of different scenarios. The causal interdependencies among security risk factors exhibit a high degree of complexity and non-linearity, and there are many association rules with multiple sets, so this study uses the Apriori algorithm for association rule mining.
2.5. Bayesian Network Analysis
Bayesian networks provide a graphical representation of how random variables probabilistically influence one another, combining graph theory with probability theory. In the network structure, vertices correspond to random variables, while directed edges signify conditional dependency relationships between them, and the probability distribution of a node takes into account the conditional probability distribution of that node given its parent. Bayesian networks can effectively deal with uncertainty, provide flexible and accurate modeling for many practical problems, help to understand the probabilistic dependencies of complex systems and support inference and decision-making.
The 3 fundamental topological configurations of Bayesian networks are illustrated in Figure 5.
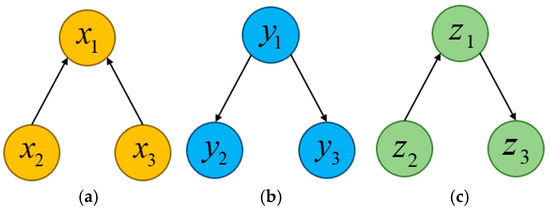
Figure 5.
The 3 basic structures of Bayesian networks: (a) V-structure; (b) same parent structure; (c) sequential structure.
Where in the V-shaped structure of Figure 5a, one feature is dependent on the others, i.e., is dependent on with . When the values of the sub-features are unknown, the parent features are statistically independent, i.e., when is unknown, is independent of , with the following equation:
In the same parent structure of Figure 5b, multiple features depend on one feature, i.e., and depend on . is independent of when is known, as in Equation (7):
In the sequential structure of Figure 5c, the first feature depends on the second feature, and the second feature depends on the third feature, i.e., depends on , and depends on . is independent of when is known as in Equation (8):
The Bayesian network constructed in this paper basically consists of these 3 basic structures.
3. Results
3.1. Data Preprocessing and Keyword Extraction
The raw corpus was subdivided using the subdividing algorithm of the Python 3.7 program, and from the acquired English text corpus (words separated by spaces), we identified 2898 distinct word features, a selection of which appears in Table 1. The standardized text format facilitates efficient keyword extraction computational processing in subsequent steps.

Table 1.
Results of partial partitioning.
In this study, the BM25W model was used to obtain the importance scores of all feature words in the partitioning results, and some of the high-scoring feature words are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Characterization words for some high BM25W scores.
Word cloud analysis can quickly and intuitively show critical information; this paper will BM25W score of the top 100 keywords for visual display, as shown in Figure 6. In Figure 6, the larger the shape of a word, the more critical it is in the accident investigation report, and we observe that “equipment and facilities”, “supervision and management”, “safety education and training”, etc., have a significant position in the accident investigation report. It can be found that “equipment and facilities”, “supervision and management”, “safety education and training”, and so on have a significant position in the accident investigation report.

Figure 6.
Visualized word cloud of the top 100 keywords.
By comparing the BM25W scores of feature words, it is possible to identify those words that are more thematically relevant. This feature word screening method based on the BM25W algorithm not only considers the word frequency but also the importance and contextual relevance of the words in the text, thus more accurately reflecting the degree of contribution of the feature words to the text topic. By deleting those feature words with lower scores, noise, and irrelevant information can be reduced, which improves the performance and explication ability of the LDA topic model and aids in enhancing the effectiveness of the topic model in practical applications.
3.2. LDA Topic Model Analysis
3.2.1. Estimation of the Optimal Number of Topics
Determining the number of topics in an LDA model is critical to data interpretation and clustering effectiveness. Too many issues may lead to overfitting of the model, introducing noise and reducing interpretability; too few may ignore essential information, resulting in underfitting and failing to capture the deep structure of the data. In large-scale corpora, it is unclear how many topics there are only by experience and scientific estimation is needed to find the optimal number.
Established methodologies for determining the most suitable number of topics for LDA are perplexity and thematic coherence. Perplexity reflects article categorization certainty and decreases with increasing topics, but too many issues may lead to overfitting. Thematic coherence measures inter-topic correlation and is another indicator to assess the strength of a model. Many empirical studies have demonstrated the effect of thematic coherence [23]. Generally, the higher a thematic coherence score is, the better the topic model is. Therefore, this paper adopts the two methods of perplexity and thematic coherence at the same time to comprehensively determine the optimum count of themes established by calculating the scores of perplexity and theme coherence under different numbers of themes. This method balances model predictability and the quality of the themes to achieve the best results for the theme model. This method has been widely used in many studies [24,25,26,27,28] to help researchers more accurately select the LDA model parameters suitable for the data, and then improve the performance and explanatory power of the topic model. The formula calculates the confusion degree:
where denotes the set of all documents in the corpus, the full set of these records is , the word count of each record is denoted by , denotes the word in document , and denotes the probability that the word is produced.
In this paper, we first set a maximum value of n_max_topics that the total number of topics may be taken, i.e., in general, the overall topic count in the text of the accident investigation report of the chemical enterprise exceeds this maximum value, which is not in line with the actual situation. In this study, n_max_topics = 100, that is, the overall topic count of the LDA topic model takes the value of the range 1~100 (take an integer) and then lets the Python program traverse all the number of topics to take the value of each traversal, each traversal of the other parameter α to take the empirical value, that is, the inverse of the overall topic count of the current traversal of count of β 0.01, the number of sampling iterations to choose 1000 times. This yields the topic models and their corresponding perplexity and consistency scores for each topic under the total number of topics in the range of values taken. An image of the variation of perplexity and topic consistency with the number of topics is plotted, as shown in Figure 7. In the figure, when the number of topics is 50, the perplexity is at the inflection point, the value is the smallest, and the topic consistency is the largest. The number of topics at this time is the best estimate.
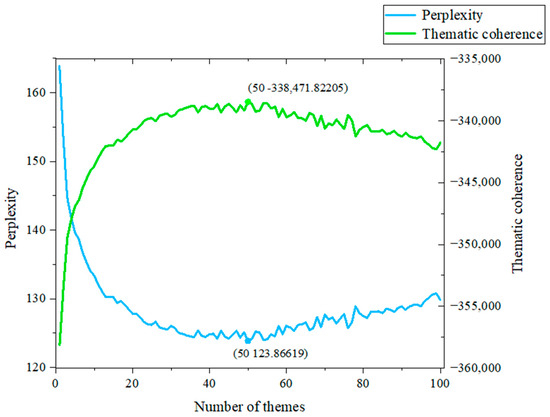
Figure 7.
Perplexity and thematic coherence curves.
3.2.2. Thematic Analysis
In this paper, we use LDA theme analysis to obtain 50 highly clustered feature phrases, and then according to the expert experience and analysis of each feature phrase corresponding to the risk factor theme. Still, the number of themes is also an estimate; the results will inevitably have some unrealistic themes, which require further screening manually. After screening and removing the four noisy themes that do not conform to reality, 46 themes were finally analyzed, as presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Theme mining results of accident risk factors in chemical enterprises.
In this paper, the risk management framework based on the socio-technical systems theory proposed by Rasmussen [29] is used to analyze the risk factors of chemical safety accidents, which helps to analyze the relevant correlations between macro- and micro-level factors in the chemical production system. Combining this risk management framework with the actual situation of the chemical industry, this study proposes five levels to categorize the risk causation of chemical accidents, including regulatory authorities, chemical enterprises, site management, operators, environment and equipment. It should be emphasized that because the risk factor themes are manually summarized and derived from the integration of feature words under each theme, some of the summarized risk factor themes cover more than one of the original themes to maintain the consistency of the dimensions of each risk factor theme and to prevent significant errors due to inconsistencies in the magnitude of the subsequent calculations. These risk factor themes were integrated and de-weighted, and the final classification results are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Safety risk factors in chemical enterprises.
After obtaining all the themes, the LDA modeling enables the computation of topic probability distributions in all the accident investigation reports, marking the accident investigation reports that contain the risk factor theme as one and those that do not include the risk factor theme as 0. This way, a structured Boolean dataset of “0–1” can be obtained and analyzed using association rule mining and Bayesian network analysis in the following section, as presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Boolean dataset of accident risk causation in chemical companies.
3.3. Association Rule Analysis
The accident level information is added to the Boolean dataset of chemical enterprise accident risk causation information to obtain an adaptive data format for association rule mining. In this paper, the accident level is categorized into general accidents (G), significant accidents (L), and significant and above accidents (MS), which corresponds to each accident investigation report and combines with the Boolean dataset of accident risk causation information of chemical enterprises obtained above to obtain the primary dataset of association rule mining, as detailed in Table 6.

Table 6.
Association rule mining base dataset.
Each entry in Table 6 corresponds to a textual record from an accident investigation report, i.e., an accident, and a “1” indicates that the risk factor in the corresponding column appeared in the accident. In contrast, a “0” means that it did not appear in the accident, as shown in Table 6; the C1 risk factor appeared in the accident investigation report with serial number 5 and did not appear in the accident investigation report with serial number 4. As shown in Table 6, risk factor C1 appeared in the accident investigation report with serial number 5, while it did not appear in the accident investigation report with serial number 4. The rightmost column shows the accident level corresponding to each accident, forming a 514 × 34-dimensional dataset for association rule mining.
Support, Confidence, and Lift are three critical metrics to measure association rules, and strong association rules can be filtered based on these metrics [30].
Assuming that each accident investigation report is regarded as a “transaction”, denoted as , then the set of transactions in this paper is expressed as . Assuming that each safety risk factor in the accident investigation report is regarded as a “project”, denoted by , then the project set of this paper is denoted as .
The Support is the ratio of the number of transactions containing both itemsets and to the gross amount of transactions, and is calculated as shown in Equation (10):
The Confidence is the existence of the itemset in the transaction of the simultaneous existence of the term set of the transaction, which is calculated as shown in Equation (11):
The Lift reflects the fact that the association rules in and correlations, and is calculated as shown in Equation (12):
For , its value less than 1 indicates that has little influence on ; conversely, it indicates that the rule is of practical significance, suggesting that the appearance of largely leads to the appearance of ; and its value equal to 1 indicates independence from each other.
According to the above principle, to obtain more valuable and higher correlation rules between safety risk factors in chemical enterprises, after several experiments, the minimum Support is set to 5%, the minimum Confidence is set to 20%, and the enhancement threshold is set to 1.2. Finally, 53 strong correlation rules can be obtained, as shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Strong correlation rules for safety risk factors in chemical enterprises.
The high-frequency risk factors obtained through association rule mining analysis can be regarded as nodes in a Bayesian network. In contrast, the significant association relationships between risk factors correspond to edges in a Bayesian network. The topology of the Bayesian network can be constructed based on these correlations better to describe the dependencies and probability distributions among risk factors. In addition, the Bayesian network can incorporate information such as accident levels, which can be used as observation nodes or implied nodes to improve the model’s accuracy and practicality.
4. Discussion
The Bayesian network is constructed by using the antecedent and consequent of the association rules as nodes, with directed edges pointing from the antecedent to the consequent. The framework undergoes expert validation to filter out non-viable connections, ultimately producing the security risk factor Bayesian network topology depicted in Figure 8. Among them, “Accident” is not a node in the association rule mining but a new node representing chemical production accidents.
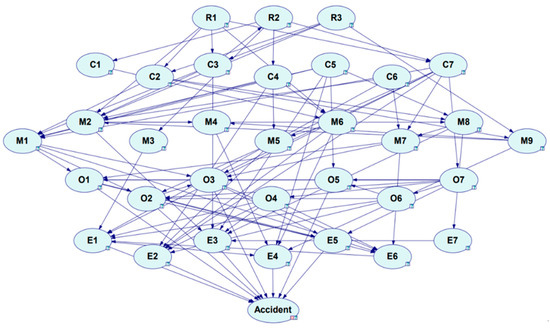
Figure 8.
Bayesian network structure of chemical company accidents.
4.1. Sensitive Risk Factor Analysis
Sensitivity analysis is a tool for assessing the sensitivity of a model to parameter changes and is categorized into univariate and multivariate analysis. In the chemical safety field, it helps identify key risk factors, assess their impact on safety, guide resource optimization, and process improvement, and reduce the risk of accidents. Univariate analysis measures the sensitivity of each factor to the model, while multivariate analysis integrates the effects of multiple parameters. In addition, parametric and interval sensitivity analyses enhance model robustness and support decision-making. Sensitivity analysis provides a scientific basis for chemical safety, identifies risk factors, optimizes safety management, and reduces accidents.
This paper involves multiple risk factors of Bayesian network structure, so multivariate sensitivity analysis is used. The sensitivity factor between two nodes in Bayesian network structure is calculated:
In the above equation, the is a child node and is its state; is the child node of the parent node, and is the state of each parent node. denotes the parent node ‘s risk expansion performance, and denotes its risk-reducing performance, and the average of the two, is the sensitivity coefficient between the parent node and the child node .
In this paper, we hope to discover the sensitive factors affecting the accident (“Accident” node) through sensitivity analysis. Therefore, sensitivity analysis is performed on the Bayesian network using GeNIe 4.0, with ‘Accident’ selected as the target node. As shown in Figure 9, nodes with darker colors exhibit greater sensitivity.
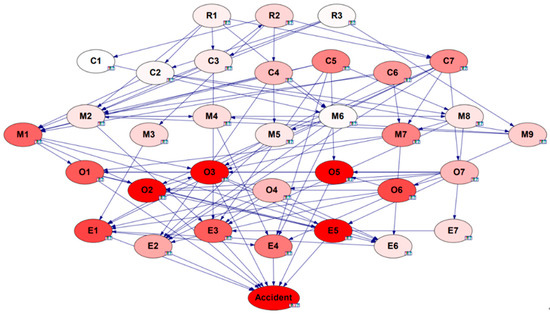
Figure 9.
Results of Bayesian network sensitivity analysis.
The computed sensitivity values of the complete set of safety risk factors are visualized in Figure 10. In this paper, those greater than 0.01 are regarded as the susceptible factors of accidents. In descending order, they are non-compliant operation O5, inadequate equipment maintenance and management E5, operators not licensed or not accompanied by supervisors O2, inadequate risk identification for special operations O3, unreliable equipment and facilities E1, adventure organization operations O6, failure to wear protective equipment O1, abnormal pressure/temperature values E3, careless or misrepresentation of the work site inspection M1. Analysis reveals that while numerous critical factors contribute to chemical production accidents, susceptible factors are principally concentrated in the operating personnel, especially the sensitivity value of O5, which exceeds the sensitivity value of M1 by 166.83%. The sensitivity value of E5 exceeds that of M1 by 4.04%.
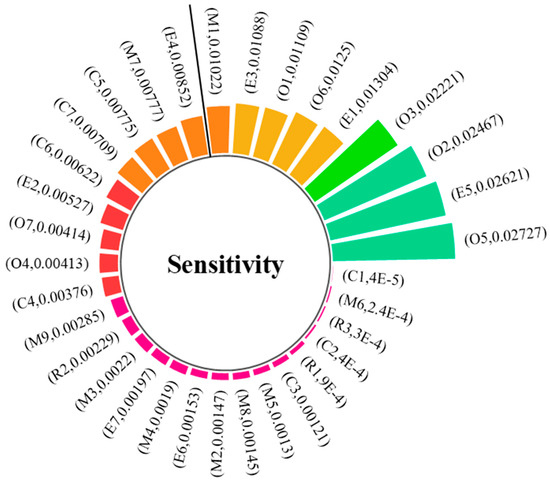
Figure 10.
Sensitivity values for security risk factors.
According to Human Factors Engineering (HFE) and High-Reliability Organizing (HRO) theories, it is known that in a high-risk organization, the operating personnel are critical because they are directly involved in the operation, and they can quickly respond to accidents and prevent deterioration. High-risk operations in chemical production, such as fire and elevated work, require operators to have specialized skills and mental qualities, including chemical knowledge, equipment operation, and emergency response capabilities. They must be alert, make quick decisions, and respond effectively to emergencies. In addition, continuous training and education are vital to upgrading the quality of operators and keeping up with safety standards. The chemical industry requires operators to be fully competent technically and psychologically in dealing with challenges. Safety managers should optimize safety inputs, control susceptible factors, prevent accidents, and improve safety production.
4.2. Critical Causal Path Analysis
The research proceeded with Bayesian network diagnostic analysis through GeNIe 4.0 subsequent to sensitivity testing. The diagnostic approach reconstructs the most credible accident causation chain through upward reasoning in the Bayesian network framework. Then, the last possible path that caused the accident can be found. First, clear all object nodes, and start from “Accident” to “set evidence”, and then use the computer to calculate the inferred probability of parent nodes of node; for node A (accident node), the a posteriori probability of node A (accident node) is calculated by the computer, assuming that the probability of occurrence of the general accident is 100%, i.e., , and its parent node is set as . The a posteriori probability of the parent node of A is calculated as detailed in Equation (16):
According to Equation (16), a parent node with the largest a posteriori probability is identified, and then “set evidence” is performed, and so on, until the root node is reached. Consequently, the critical causal pathways for general accidents, larger-scale accidents, and major/severe accidents were successfully identified, as illustrated in Figure 11a–c.
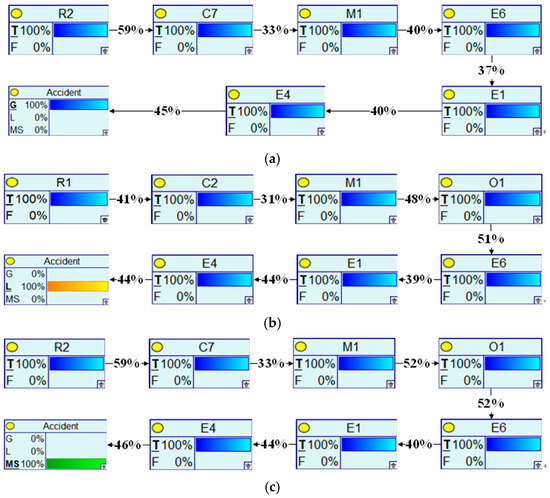
Figure 11.
Critical causal transmission pathways for different classes of accidents: (a) critical causal transmission pathways for general accidents; (b) critical causal transmission pathways for larger accidents; (c) critical causal transmission pathways for major and above accidents.
As can be seen in Figure 11, despite the various accident categories and probability of propagation of the key causal factors, the second half of the path that leads to all kinds of accidents is the same, which is the failure of the safety monitoring and surveillance equipment, which may include the failure of sensors, instruments, or monitoring systems, which results in the impact on the real-time monitoring and detection function of the production process or equipment status. In contrast, the failure of the safety monitoring and surveillance equipment makes the related equipment and facilities unreliable. Because the role of monitoring equipment is to detect and correct potential problems promptly, when monitoring fails, it may result in the equipment failing to be informed of the problem or to take the necessary action promptly. This may leave the entire production system in an unreliable state, and further unreliable equipment and facilities may cause problems in the production process, one of which is the possibility of leakage. With adequate monitoring and control, it may be possible to detect, isolate, or repair potential sources of leakage in time. This can increase the risk of leaks of hazardous substances, which may involve chemicals, gases, or other dangerous substances. Ultimately, these leaks can lead to accidents, which demonstrate dependence on the specific category and size of spilled substance, including fires, explosions, and chemical spills, posing a potential threat to the safety of people and the environment. In the previous accident type statistics, it was also found that the number of accident types such as explosions, fires, poisoning, and asphyxiation, etc., which are closely related to the leakage problems, accounted for 94% of the total number of accidents, which inversely confirms the validity of the accident causation chain.
Inadequate regulation is the root cause of both general and significant accidents. Negligence on the part of the regulator may lead to irregular contracting and the involvement of unqualified firms in production, resulting in safety management deficiencies and non-compliance issues. This may lead to lax or false site inspections and affect the maintenance of safety management equipment, such as safety monitoring equipment, that may fail. Failure to wear protective equipment is particularly prominent in significant accidents. This may be due to lax inspections or misrepresentation leading to the inability to implement emergency rescue and drills effectively, and rescue workers may have expanded the accident in the early stages because they needed to wear protective equipment or blindly performed the rescue.
More significant accidents are often triggered by poor tracking of hidden dangers and corrections, leading to inadequate safety systems, including failure to correct hidden safety problems promptly, insufficient training, and loopholes in management systems. This results in poorly detailed on-site inspections and inaccurate risk and hazard identification and assessment. A sufficient safety management framework may also lead to misrepresenting inspection results and covering up problems, leading to accidents.
In the domino theory, improving these issues can effectively prevent accidents by cutting off the most likely pathways leading to accidents. However, this does not mean focusing only on the critical causal pathways; ignoring other safety risk factors is necessary. Given the structural complexity inherent in Bayesian networks and the interconnected nature of safety factors, accidents may occur through other paths after cutting off a node. Therefore, in enterprise safety management, it is necessary to focus on cutting off critical causal paths and creating new paths simultaneously and continuously adjusting the safety governance strategy according to the changes in critical paths.
4.3. Statistical Analysis of Frequency
Statistical frequency-based accident risk causation analysis can provide a comprehensive understanding and analysis of historical accident data, revealing potential patterns and regularities in accident occurrence. Through extensive collection of accident data, high-frequency causal factors can be identified, and their relevance and impact can be analyzed.
The formula for calculating the frequency of security risk factors is as follows:
where denotes the total number of accident investigation reports, refers to 33 safety risk factors, and denotes the number of accident investigation reports that contain risk factor . The results of frequency statistics are detailed in Figure 12.
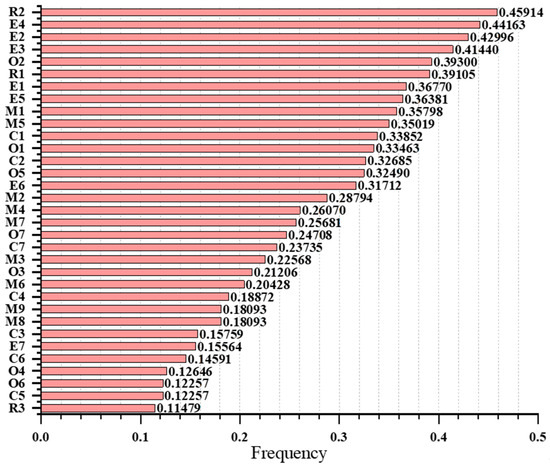
Figure 12.
Statistical frequency of accident safety risk factors.
As can be seen from Figure 12, the statistical frequency of the first 15 items is more significant than 0.3, and with the rest of the items there is a frequency fault, these 15 items are: failure to conscientiously fulfill the responsibility of safety supervision R2, leakage problems E4, abnormal concentration of hazardous gases E2, abnormal pressure/temperature values E3, operators not licensed or not accompanied by supervisors O2, hidden dangers rectification and tracking is not in place R1, unreliable equipment and facilities E1, inadequate equipment maintenance and management E5, careless or misrepresentation of the work site inspection M1, inadequate fire and explosion prevention measures M5, inadequate safety education and training C1, failure to wear protective equipment O1, inadequate safety system C2, non-compliant operation O5, failure of safety monitoring and control equipment E6.
It can be found that the environmental and equipment factors are basically in the top 15 of the frequency faults. This also proves that no matter what the initial cause of the accident is and what triggers it, the accident will eventually manifest itself in these environmental and equipment factors, which reveals that the safety management personnel, in the daily risk warning work, need to focus on these aspects to strengthen the monitoring, so as to achieve early warning and nip the accident in the bud. In addition to the environment and equipment factors, the frequency of the top 15 is also more evenly distributed among the other four types of risk factors, which indicates that the environment and equipment factors are not the root cause of accidents; the root cause often comes from the people and management.
After obtaining the results of sensitive risk factor analysis, critical causal path analysis, and frequency statistical analysis, the investigation established that some factors existed in a set of factors of these three analyses, indicating these factors are critical in chemical enterprise accidents. These three results intersect and determine the essential risk factors leading to chemical enterprise accidents. In contrast, the non-intersecting part of the results of the three analyses belongs to the critical risk factors, and the remaining ones are the general risk factors with the following formula:
where , , and refer to sensitive factors, causal path factors, and high-frequency factors, respectively. , , and refer to critical, important, and general factors, respectively, and is the set of all risk factors in the structure of the Bayesian network. The results are detailed in Table 8.

Table 8.
Critical, important and general factors for accidents in chemical enterprises.
Through comprehensive analysis, the general factors have less influence on chemical enterprise accidents, so the main critical and important factors are analyzed and the corresponding control scheme is constructed, i.e., unreliable equipment and facilities E1, failure to wear protective equipment O1, careless or misrepresentation of the work site inspection M1, non-compliant operation O5, inadequate equipment maintenance and management E5, operators not licensed or not accompanied by supervisors O2, inadequate risk identification for special operations O3, adventure organization operations O6, abnormal pressure/temperature values E3, leakage problems E4, failure to conscientiously fulfill the responsibility of safety supervision R2, abnormal concentration of hazardous gases E2, hidden dangers rectification and tracking is not in place R1, inadequate fire and explosion prevention measures M5, inadequate safety education and training C1, inadequate safety system C2, failure of safety monitoring and control equipment E6, and illegalized contracting C7.
This paper found that in these risk factors, E1, O5, O1, and E4, the characterization of the modality is often a visual form of information; for example, the specific performance of not wearing protective equipment O1 may be in the case of poisoning, on-site personnel in the absence of effective protective equipment to rescue the case, can be detected in the face of the rescuers if they do not have masks, gas masks or other masks, leakage problems E4, specific performance where a pipeline or plant at a location suddenly appeared to produce a large amount of visible gas or even began to produce open flames, and so on.
As for the unreliable equipment and facilities E1, the most common manifestations in the chemical enterprise site are frequent failures and shutdowns, equipment aging and wear and tear, unqualified maintenance and repair, missing or damaged parts, inefficient automation and control systems and so on, through the trajectory intersecting theory (Trace Intersecting Theory) to know when the equipment and facilities appear to be unreliable. If the person appears in the same position, it is very likely to cause casualties, and if the person does not appear in the surroundings, according to the theory, it will be able to effectively avoid the occurrence of casualties.
The chemical production site environment is complex, the incidence of accidents is high, and personnel intrusion into the hazardous area is the direct cause of accidents; based on the computer vision of the personnel hazardous area intrusion detection method can effectively make up for the defects of the chemical safety management of manual supervision, so as to reduce the probability of accidents.
The rest of the risk factors are often characterized by the modality of textual information, such as the operation site inspection is not detailed or misrepresentation of the specific performance of M1 may be the operation site of the enterprise’s safety checklist is not filled out on time, hazardous operations management review checklist content, etc., safety education and training is insufficient C1 meaning the enterprise did not regularly arrange for staff safety education training courses and, therefore, there is no corresponding intervention. The specific manifestation of insufficient safety education and training C1 may be that the enterprise has not arranged regular safety education training courses for its employees and, therefore, does not have the corresponding class schedules and course materials, or has not carried out regular safety examinations and, therefore, does not have the examination papers and transcripts for examining its employees.
This visual and textual modal information together characterize the above risk factors, which can further reflect the safety management level of the enterprise. Therefore, it is proposed to establish a safety production platform that integrates textual and visual information, which can capture potential risks and hidden dangers in chemical production more clearly by integrating visual images and textual information and provide more timely and effective early warnings and countermeasures for the relevant departments, so as to minimize the safety risks in the process of chemical production and safeguard the safety of people’s lives and properties.
5. Conclusions
Due to the flammable, explosive, and toxic substances involved in its production process and the complex and changeable production environment, the chemical industry has led to frequent safety accidents, which pose a severe threat to human life, property, and social stability. To address the inherent constraints of conventional chemical safety management approaches, this study presents a modern, data-driven, technology-based approach to improve efficiency and safety management.
For data preprocessing, the text segmentation of the chemical safety accident investigation report was performed using the Jieba participle, and the accuracy of the participle was improved by using a domain dictionary, synonym dictionary, and deactivation dictionary. The BM25W algorithm was used for keyword extraction to extract critical information in the text to provide input for the LDA model. Next, the chemical safety accident cases were thematically analyzed using the LDA model to identify major risk factors. In addition, the Apriori algorithm is used in association rule analysis to mine the association relationship between risk factors. Finally, a Bayesian network model analyzes the causal relationship between risk factors. The approach established in the current research, which combines an improved LDA topic model and the Bayesian network, aims to improve the identification and analysis of chemical safety risks. Thirty-three major risk factors were identified and categorized through text mining and model analysis.
For model evaluation, the model’s sensitivity to each risk factor was assessed through sensitivity analysis to identify the key risk factors. The possible paths of accident development were inferred through critical causal path analysis combined with Bayesian network diagnosis. The importance of recognizing and preventing common risk factors in chemical safety accidents and the necessity of taking targeted measures in safety management are emphasized through frequency statistical analysis. The findings of this paper not only reveal the potential causes and patterns of chemical safety accidents but also furnish a theoretical framework for optimizing chemical plant safety management, helping them to optimize the allocation of resources and improve the level of safety management.
The method proposed in this paper can effectively extract keywords from chemical safety accident reports and reveal the correlation and causality between risk factors; at the same time, it provides a new analytical tool for the chemical safety field, which helps to identify and prevent potential safety risks in advance, enhances the scientific and systematic nature of safety management, and protects the safety of personnel and property to a greater extent, and is of great significance for promoting the sustainable development of the chemical industry. It can effectively deal with the complexity of the chemical production site and provides an innovative solution for the intelligent and automated development of chemical safety management tools in the future. Through effective processing of unstructured data, it no longer relies only on limited experience and one-sided information to cope with chemical safety risks but can establish more comprehensive and accurate risk identification based on a large amount of data analysis, greatly enriching and improving chemical safety risk management theories and methods and promoting the transformation of chemical safety management to intelligence. Meanwhile, this paper also has some limitations, the chemical industry is diverse and the types of hazardous chemicals involved are also very complex; future studies will refine the study of the chemical industry, distinguishing between different sub-industries of the chemical industry and their different types of hazardous chemical safety risk identification and analysis, so as to make the model more versatile.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z.; methodology, Z.Z. and J.G.; software, Z.Z. and J.G.; validation, Z.Z., J.G. and J.H.; formal analysis, Z.Z. and J.G.; investigation, Z.Z. and J.G.; resources, Z.Z.; data curation, Z.Z., J.G. and J.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z., J.G. and J.H.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z. and J.G.; visualization, Z.Z. and J.G.; supervision, J.H.; project administration, Z.Z.; funding acquisition, Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CGS | Collapsing Gibbs Sampling |
| LDA | Latent Dirichlet Allocation |
| MCMC | Markov Chain Monte Carlo |
| HFE | Human Factors Engineering |
References
- Lassak, P.; Labovsky, J.; Jelemensky, L. Influence of parameter uncertainty on modeling of industrial ammonia reactor for safety and operability analysis. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2010, 23, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayaka, S.; Khan, F.; Amyotte, P. SHIPP methodology: Predictive accident modeling approach (Part I: Methodology and model description). Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2011, 89, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Pasman, H.J.; Waldram, S.P.; Rogers, W.J.; Mannan, M.S. Did we learn about risk control since Seveso? Yes, we surely did, but is it enough? An historical brief and problem analysis. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2017, 49, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.Q. Research on Evaluation Model for Safety Capacity of Chemical Industrial Park Based on Regional Risk and Its Application in Chemical Industrial Park. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Senave, E.; Jans, M.J.; Srivastava, R.P. The application of text mining in accounting. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2023, 50, 100624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Chen, K.; Li, B.Z. Document keyword extraction based on semantic hierarchical graph model. Scientometrics 2023, 128, 2623–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K. Web News Data Extraction Technology Based on Text Keywords. Complexity 2021, 2021, 5529447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Y.; Ren, X.B.; Yang, S.S. Latent Dirichlet Allocation Model Training With Differential Privacy. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 1290–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Nie, F.P.; Wang, R. A Revised Formation of Trace Ratio LDA for Small Sample Size Problem. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 5803–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Yang, R.X.; Shen, C. Sentiment word co-occurrence and knowledge pair feature extraction based LDA short text clustering algorithm. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2021, 56, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.R.; Pang, Y.C. Analysis of the Causes of Construction Safety Accidents Based on LDA Modelling. Eng. Constr. 2025, 57, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Sun, H. Analysis of Knowledge Mapping and LDA Topic Modelling of Forestry Ecological Construction in China. China For. Spec. Prod. 2025, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. Causation Analysis and Risk Study of Rail Transportation Accidents Based on Text Data. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Lu, Y. A new text mining-Bayesian network approach for identifying chemical safety risk factors. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Gao, C.; Chen, X.M. Text clustering study based on LDA model. Intell. Sci. 2015, 33, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, T.L.; Steyvers, M. Finding scientific topics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 1, 5228–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, N.; William, C.; John, L. Parallelized Variational EM for Latent Dirichlet Allocation: An Experimental Evaluation of Speed and Scalability. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW 2007), Omaha, NE, USA, 28–31 October 2007; pp. 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, S. Markov chain Monte Carlo method and its application. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D (Stat.) 1998, 47, 69–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Imielinski, T.; Swami, A. Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases. In Proceedings of the 1993 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Washington, DC, USA, 25–28 May 1993; pp. 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.S.; Han, J.W.; Yu, P.S. Data mining: An overview from a database perspective. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 1996, 8, 866–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.J. Research on Coal Mine Safety Risk Identification and Evaluation Based on Text Mining. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Roder, M.; Both, A.; Hinneburg, A. Exploring the Space of Topic Coherence Measures; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 399–408. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Xia, T.; Li, J.T. A density-based method for adaptive LDA model selection. Neurocomputing 2009, 72, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggers, L.R.; Bocovich, C.; Capshaw, R. Configuring latent Dirichlet allocation based feature location. Empir. Softw. Eng. 2014, 19, 465–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.Z. A framework for analyzing technology evolution based on a two-layer thematic model and its application. Data Anal. Knowl. Discov. 2022, 6, 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H. A Study on Discovery of Hot Topics in Microblogs Based on the Improved Algorithm of Burst Word to Topic Modeling. Intell. J. 2022, 41, 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sievert, C.; Shrley, K.E.; Davis, L. A method for visualizing and interpreting topics. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Baltimore, MD, USA, 22–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, J. Risk management in a dynamic society: A modelling problem. Saf. Sci. 1997, 27, 183–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenonen, N. Analysing factors related to slipping, stumbling, and falling accidents at work: Application of data mining methods to Finnish occupational accidents and diseases statistics database. Appl. Ergon. 2012, 44, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).