The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Corrosion-Resistant Nickel-Based Alloys for Their Application in Nuclear Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
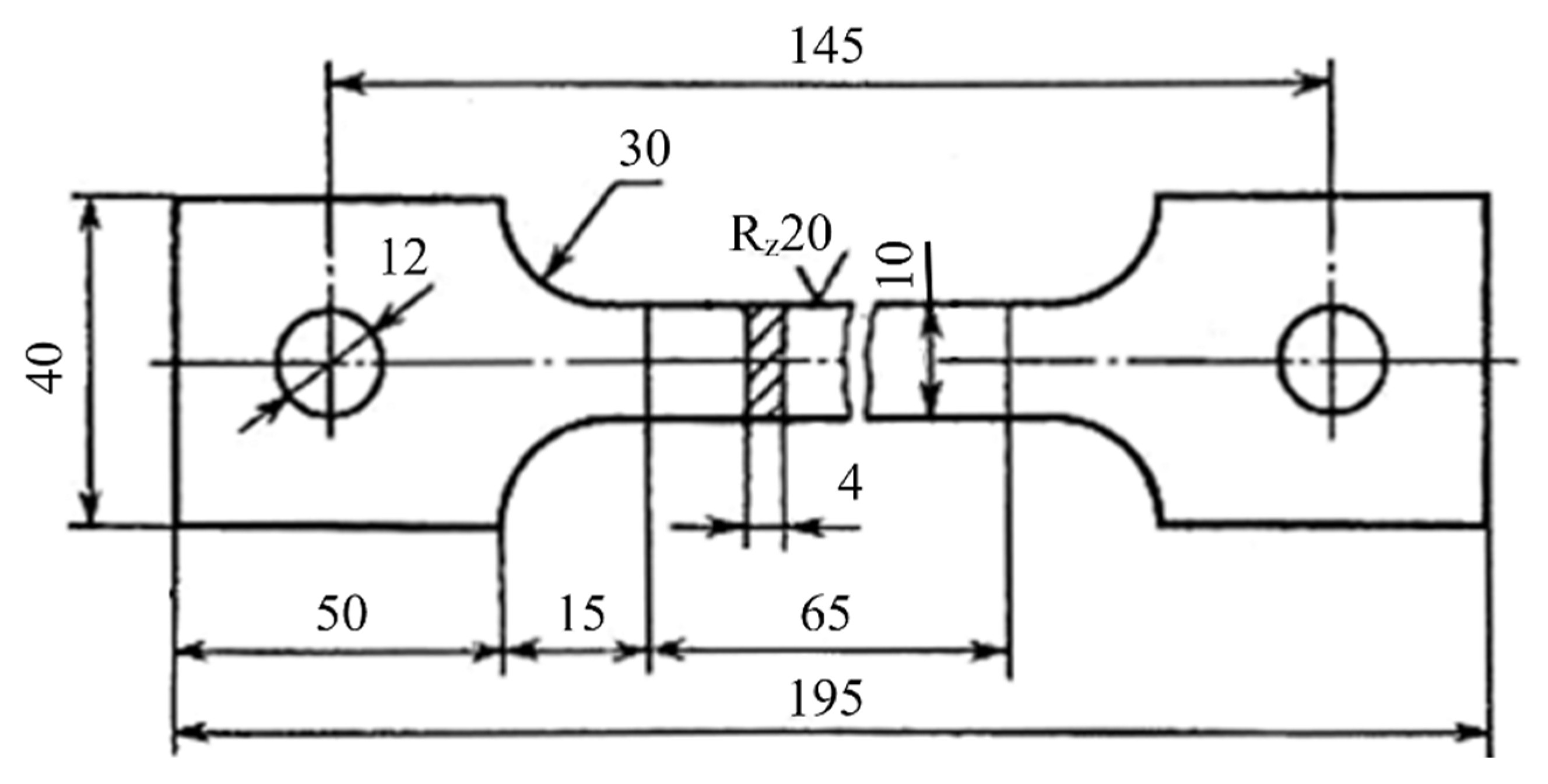
2.1. Equipment and Experimental Methods
2.2. Materials
3. Results
3.1. Modeling
3.2. Microstructure and Stress–Strain Behavior of Nickel Alloys in the Initial State
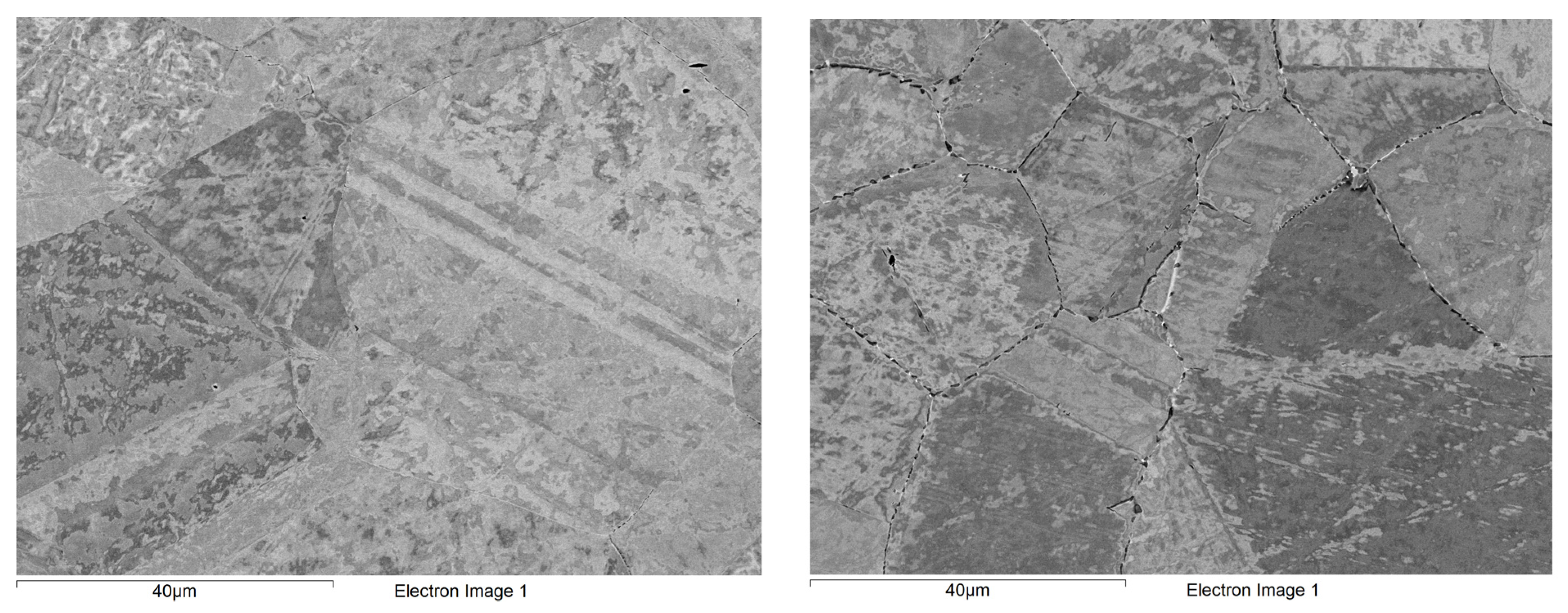
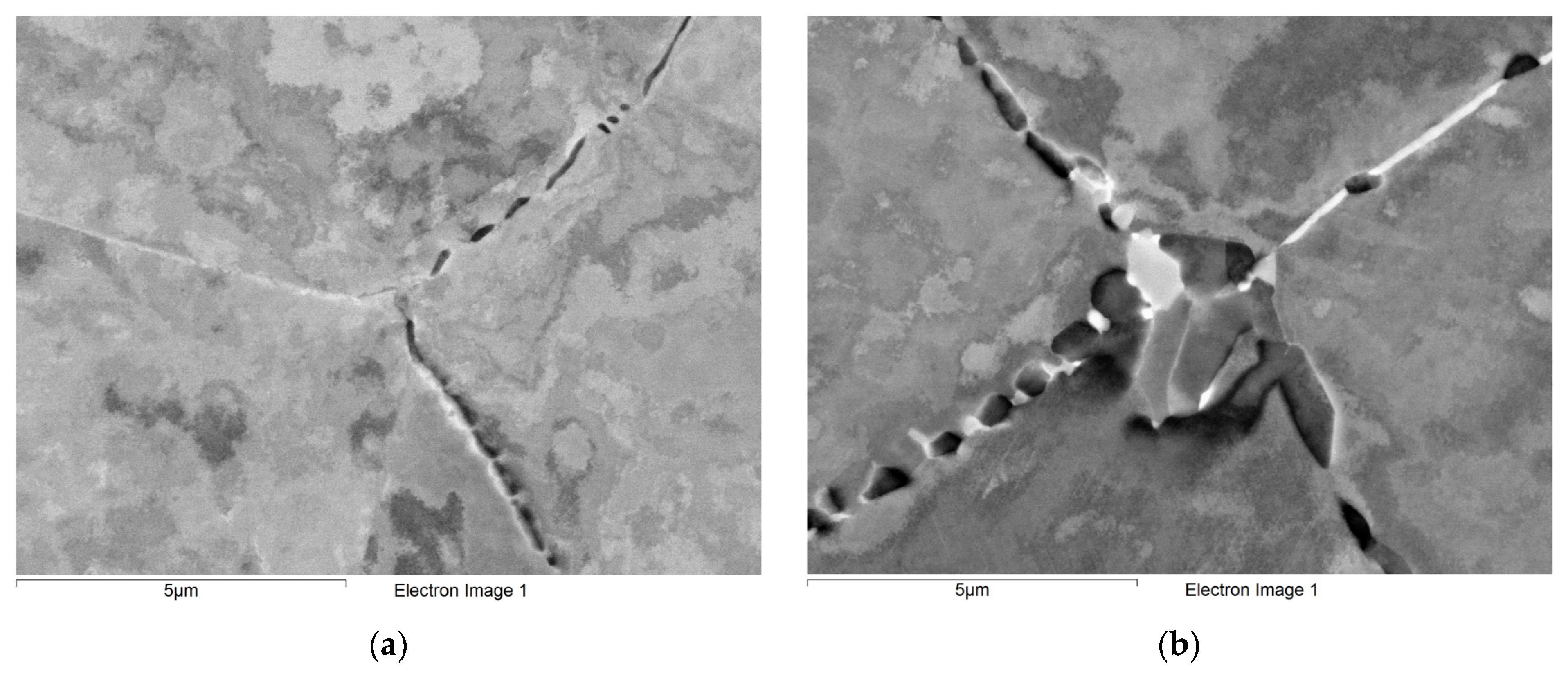
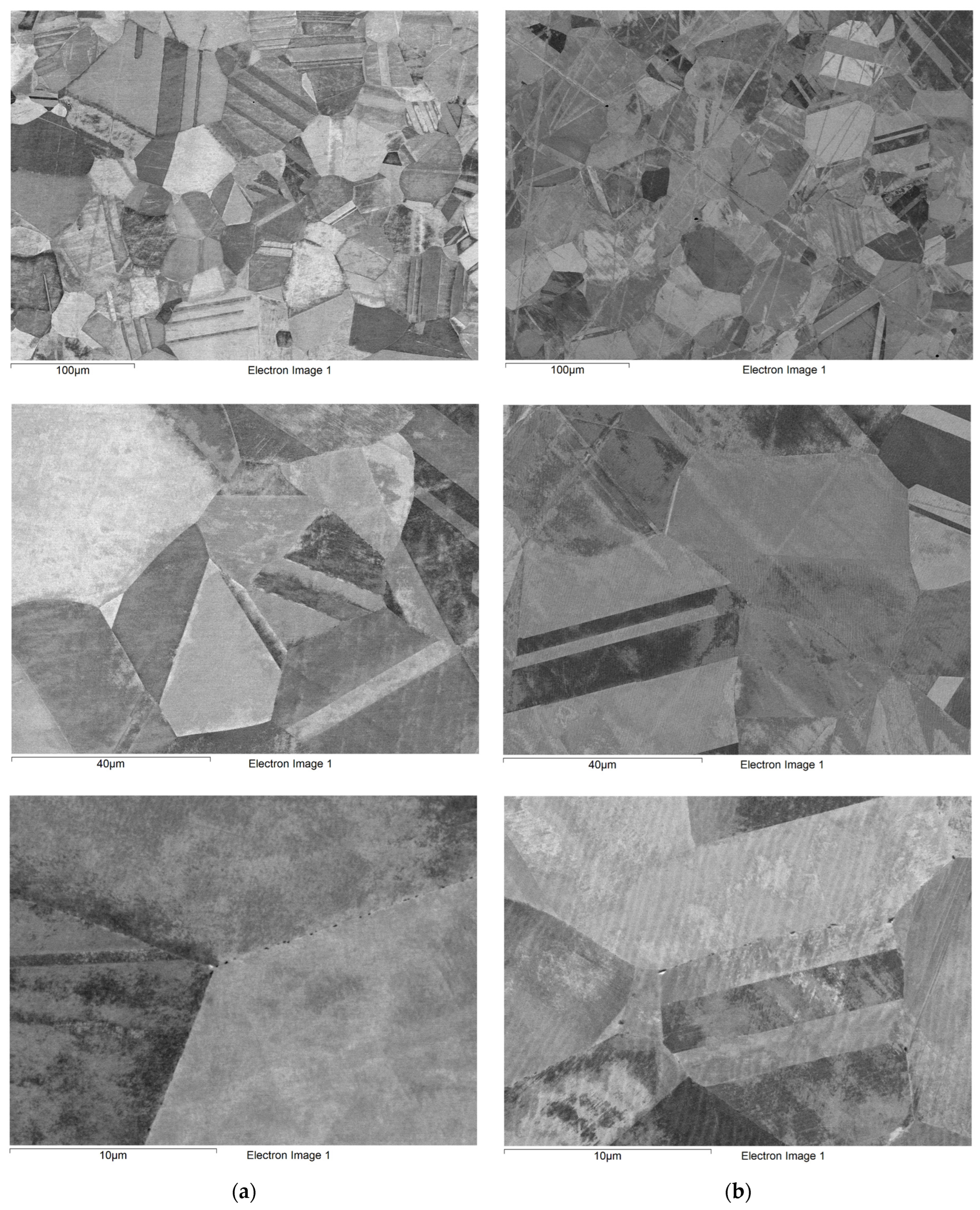
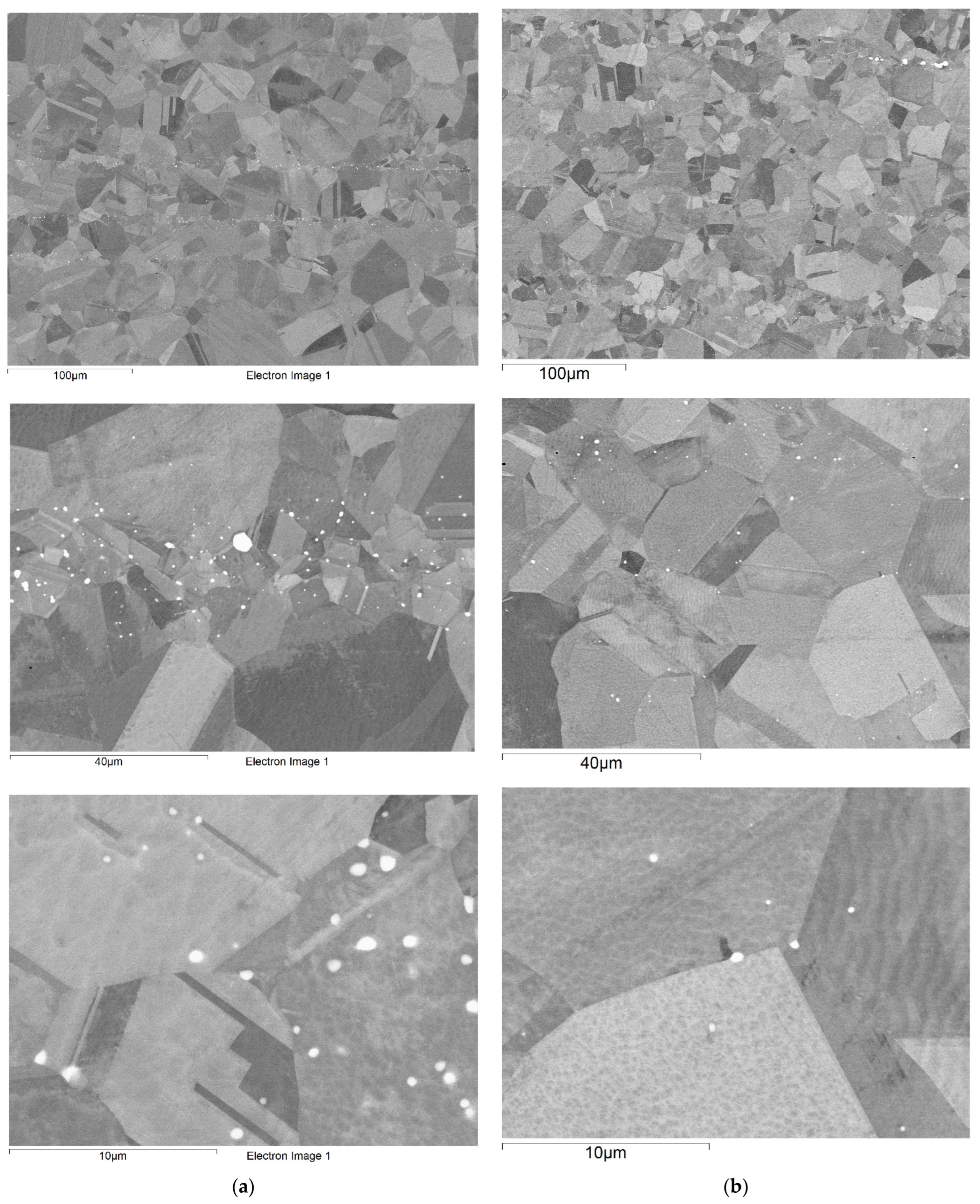
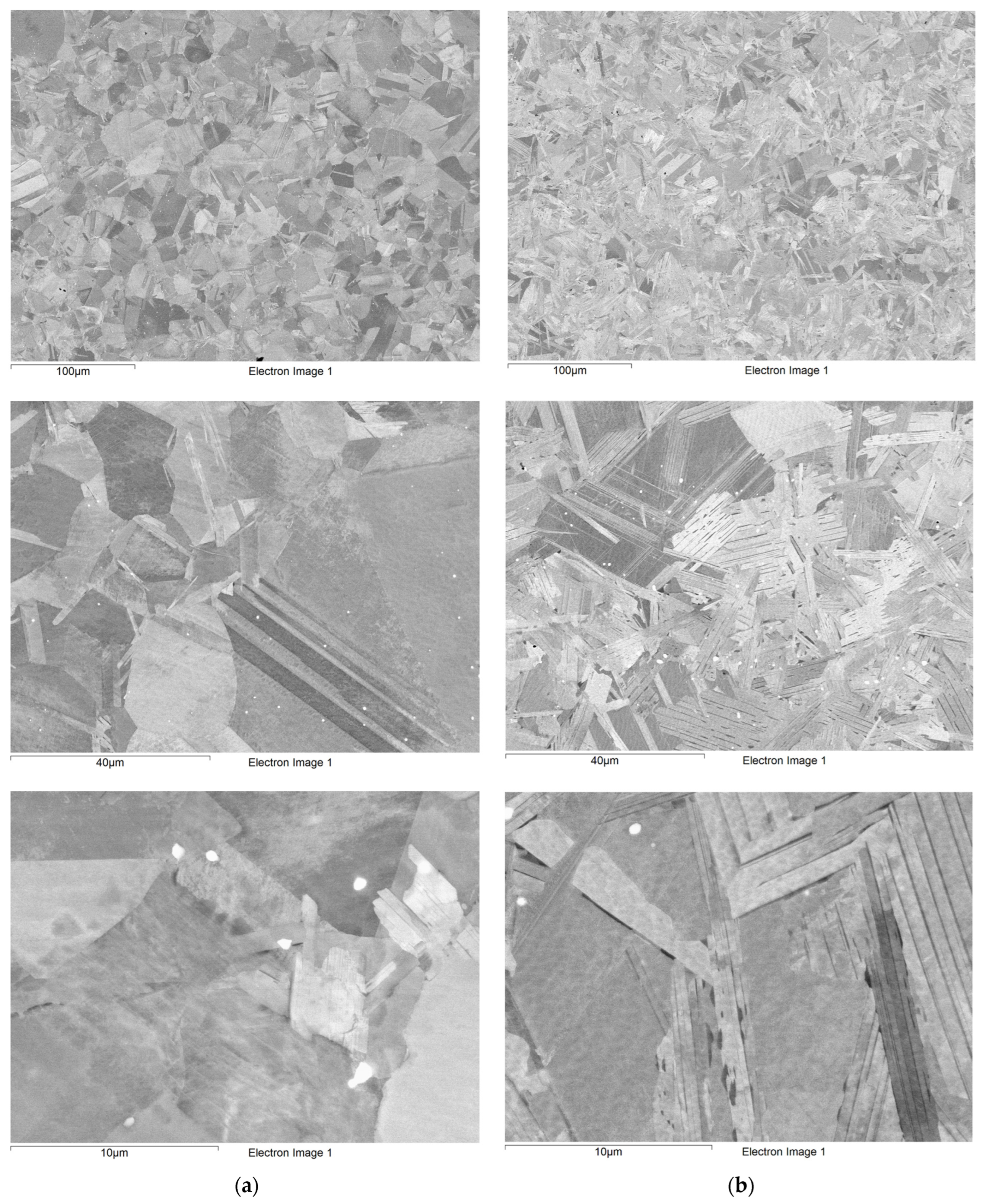
3.2.1. Initial Microstructure of Materials
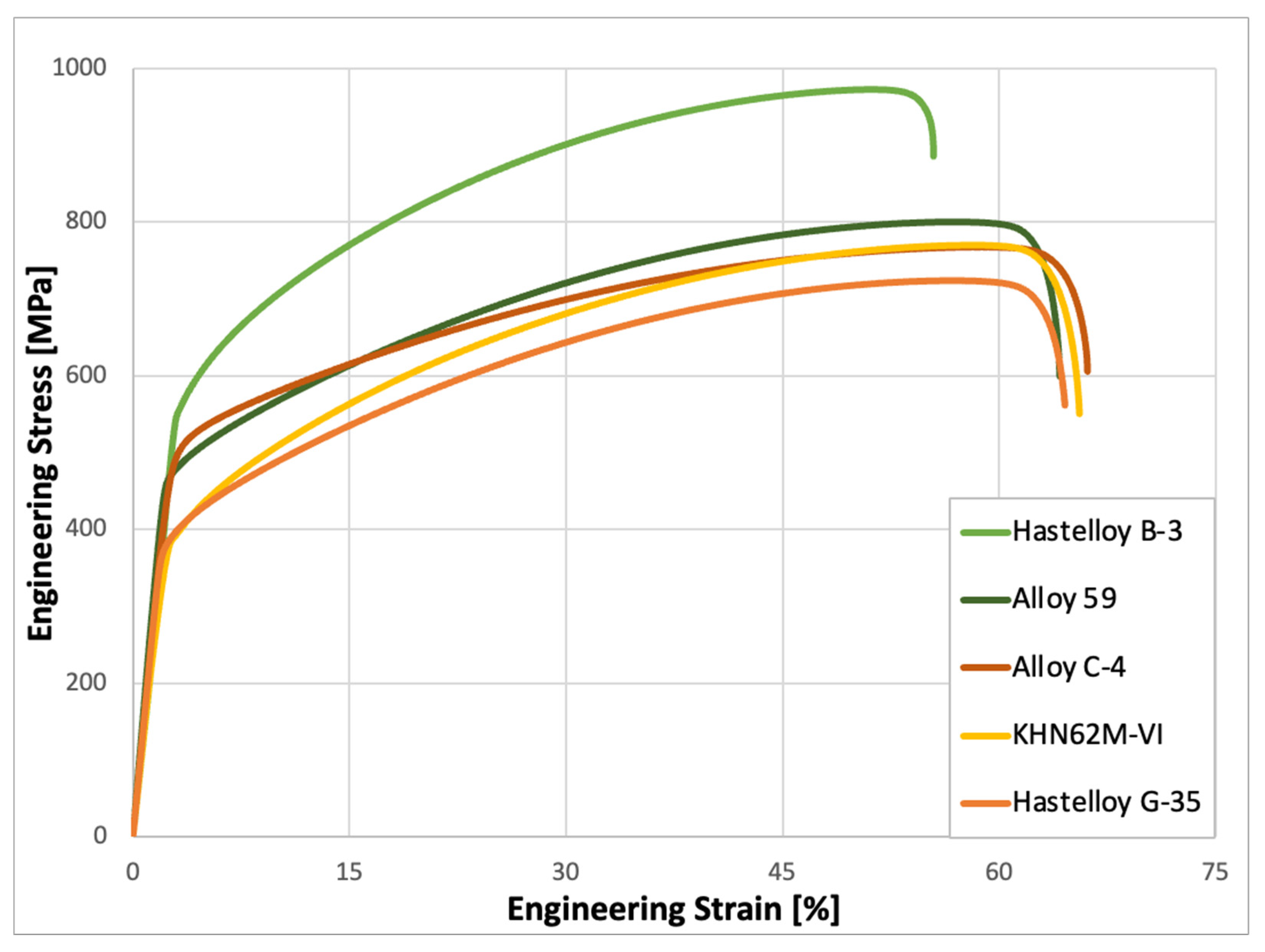
3.2.2. Deformation Behavior of Alloys in the Initial State
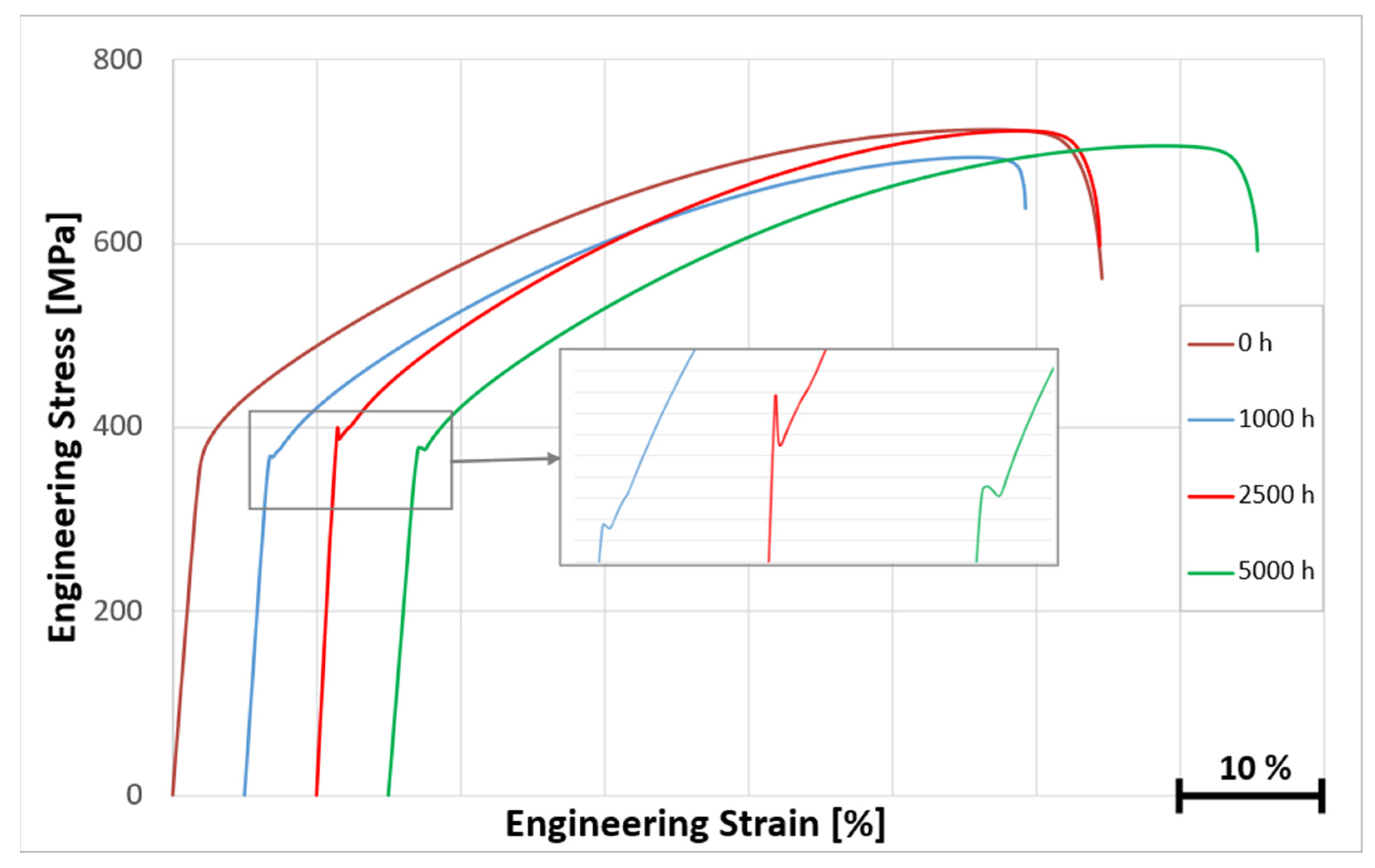
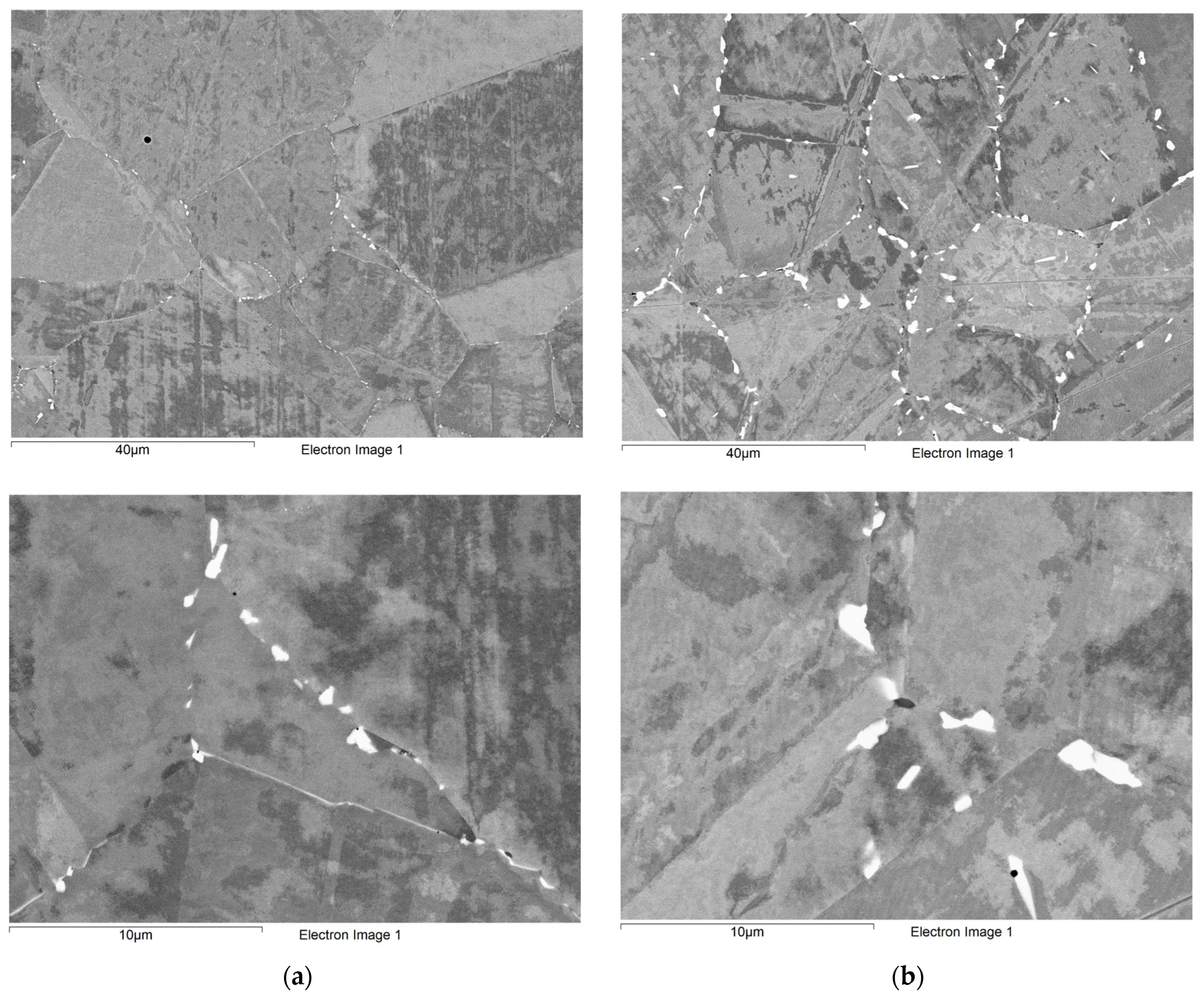
3.3. Microstructure and Stress–Strain Curves of Nickel Alloys After Long-Term Aging
3.3.1. Microstructure and Stress–Strain Curves of Hastelloy® G-35® After Long-Term Aging at 500 °C
3.3.2. Microstructure and Stress–Strain Curves of Hastelloy® G-35® After Long-Term Aging at 650 °C
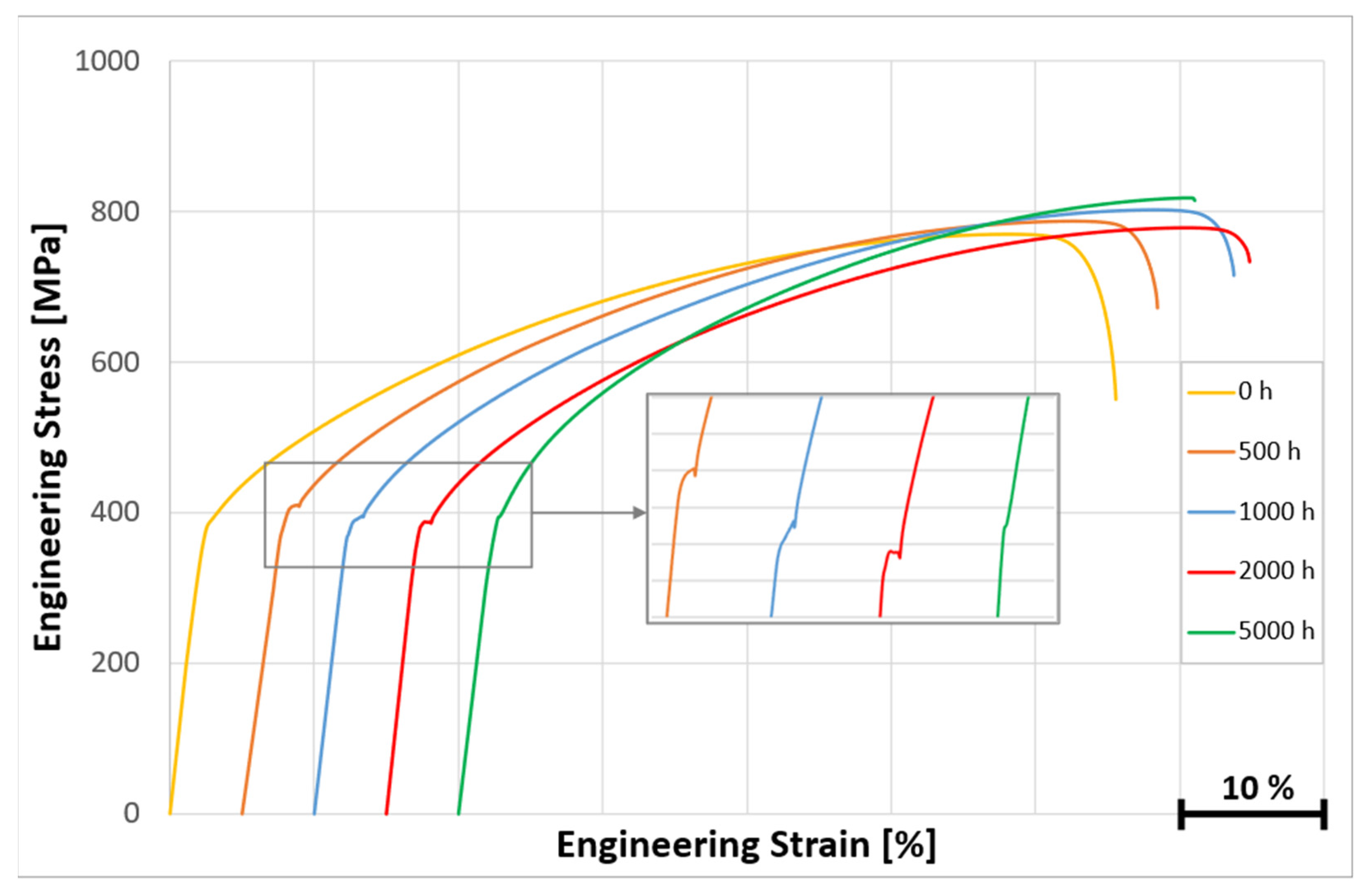
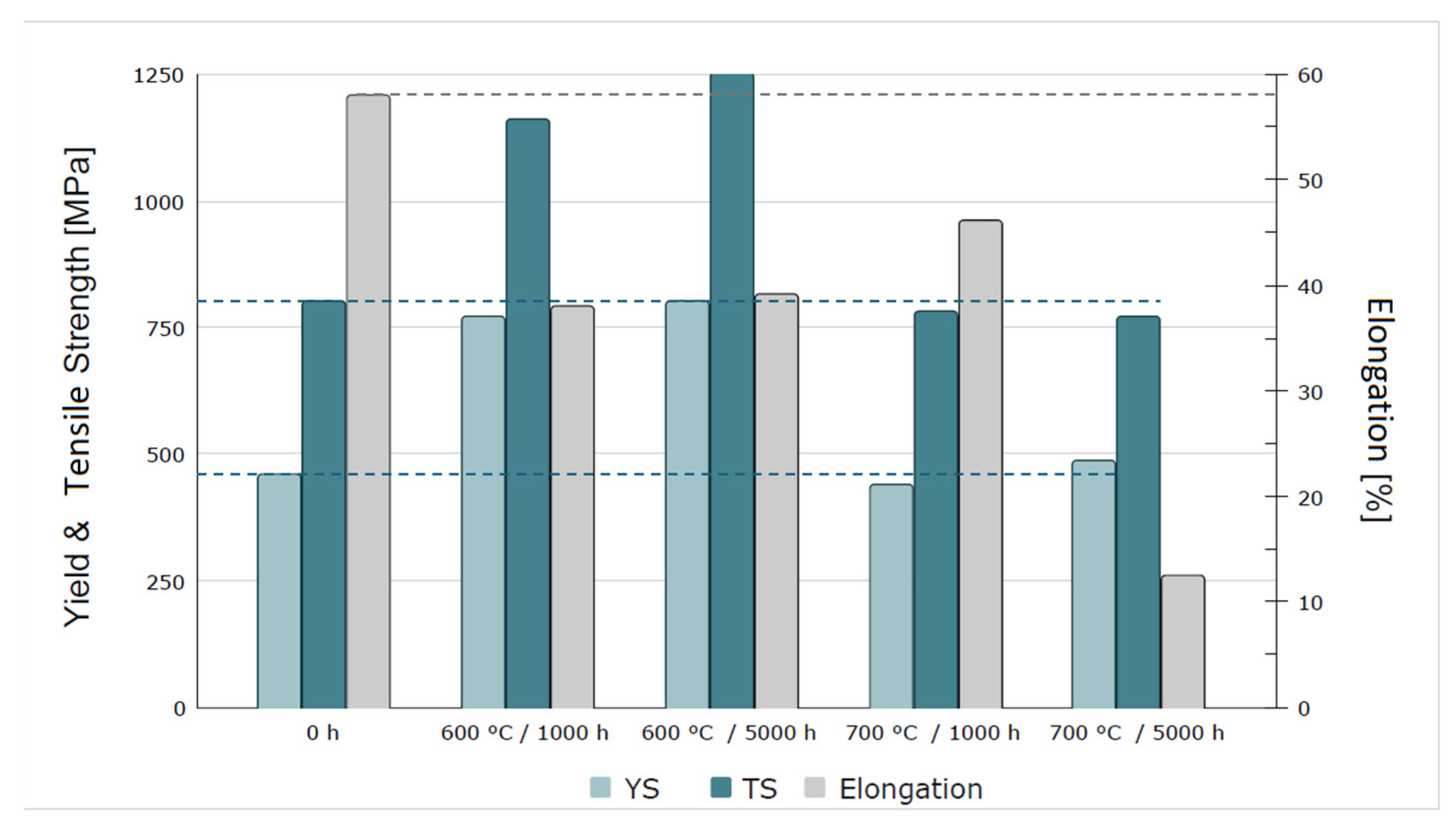
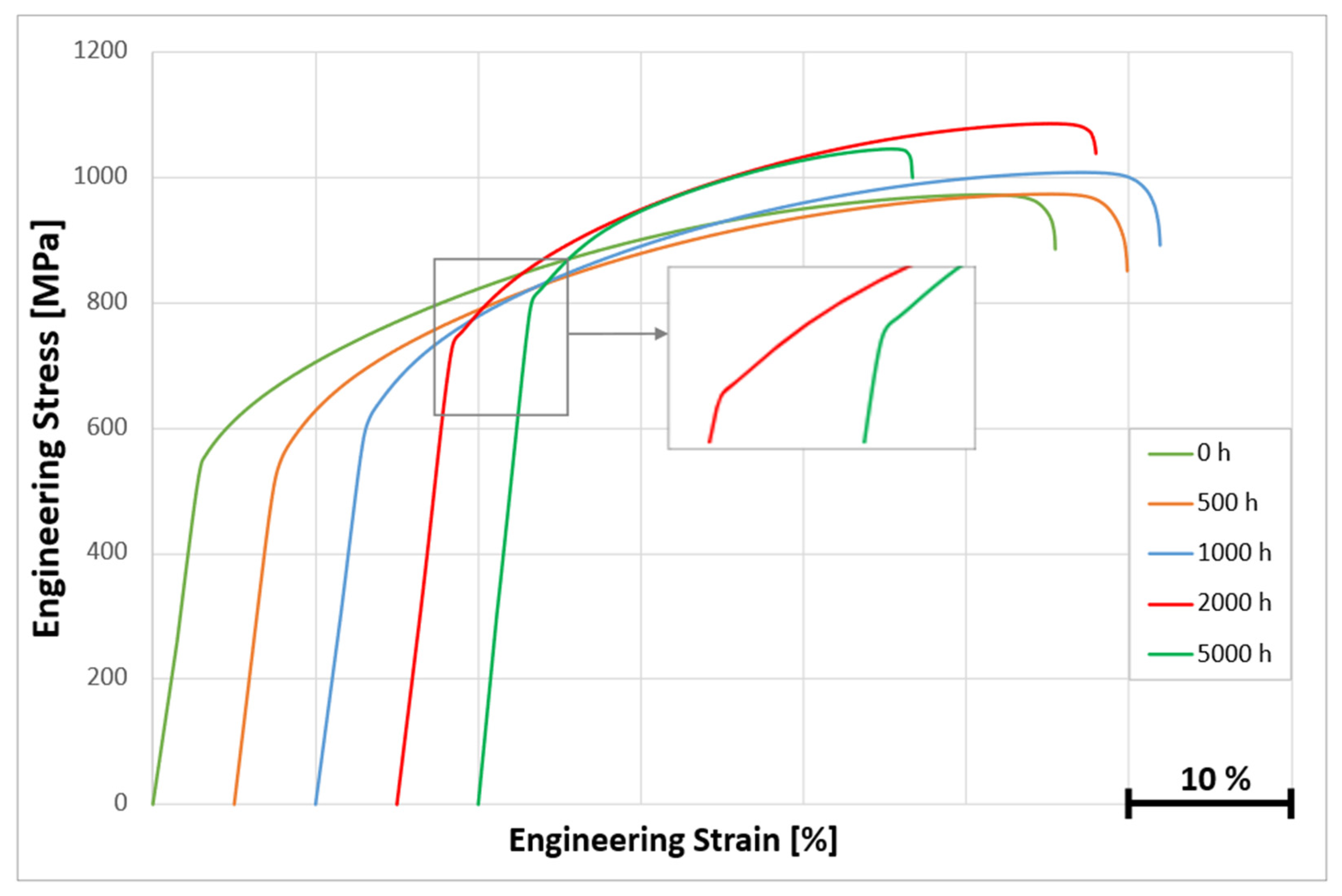
3.3.3. Microstructure and Stress–Strain Curves of KhN62M-VI Alloy After Long-Term Aging at 600 °C
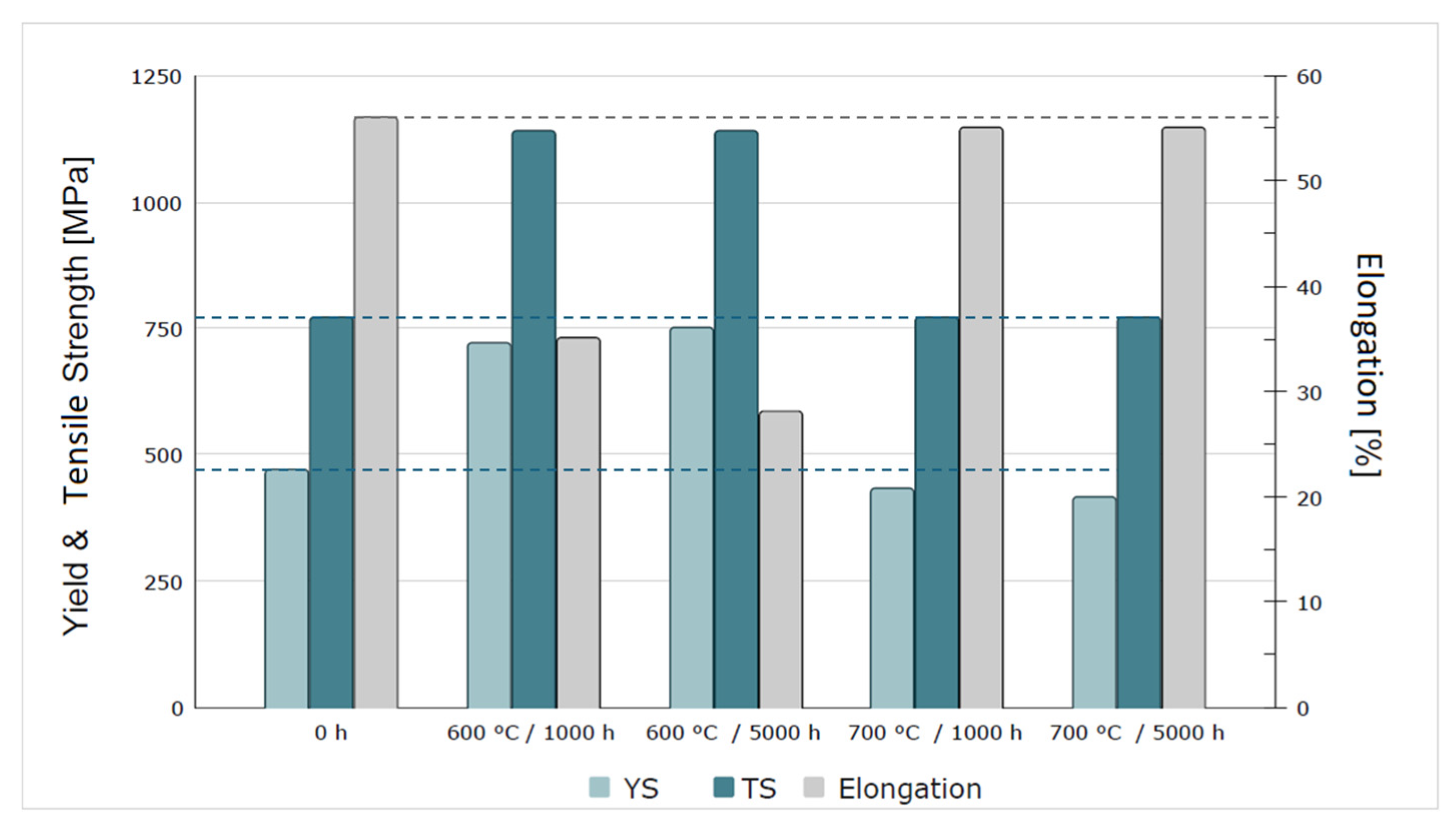
3.3.4. Microstructure and Stress–Strain Curves of KhN62M-VI Alloy After Long-Term Aging at 700 °C
3.3.5. Effect of Long-Term Aging on VDM® Alloy 59 and VDM® Alloy C-4 Properties
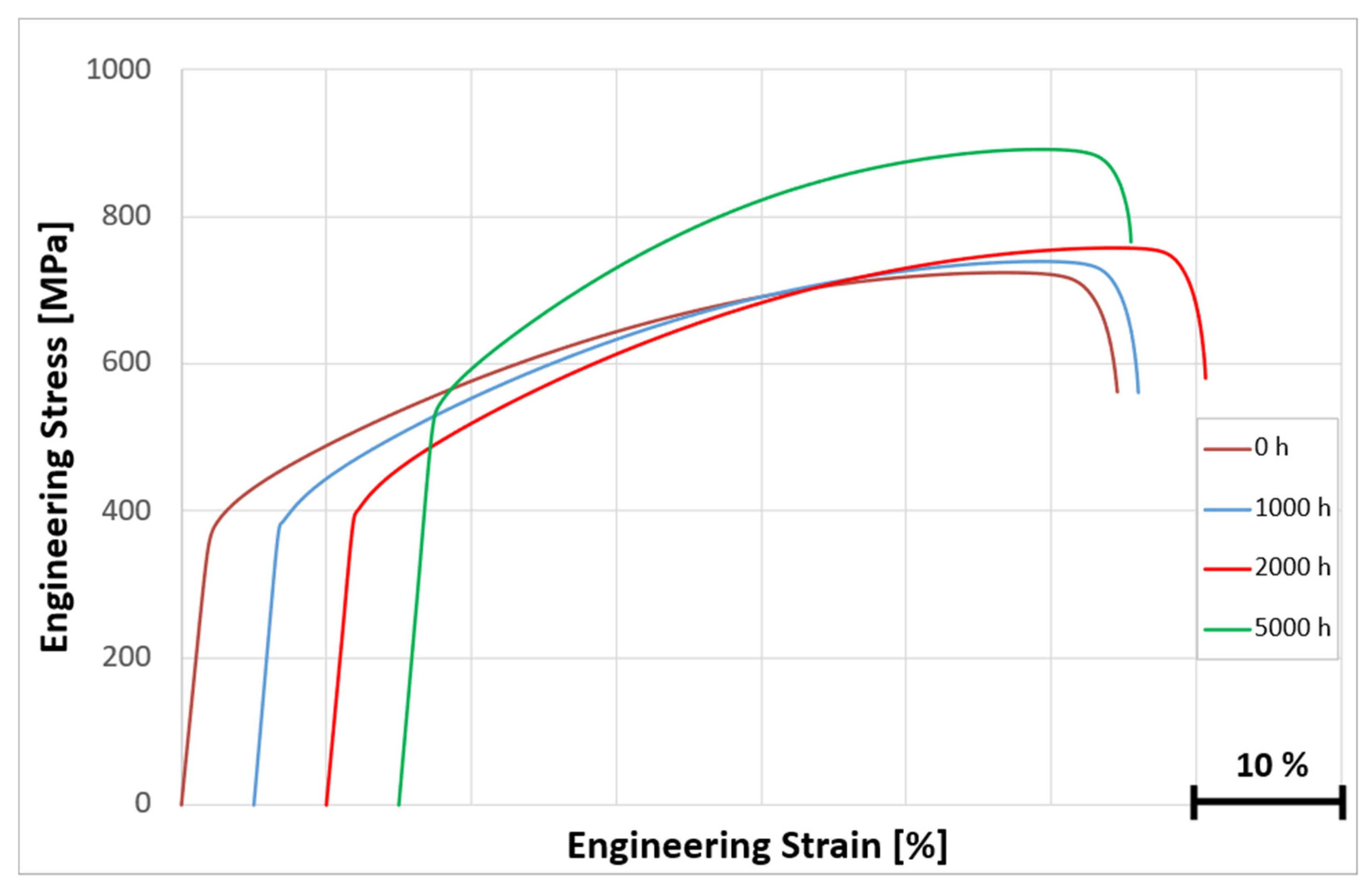
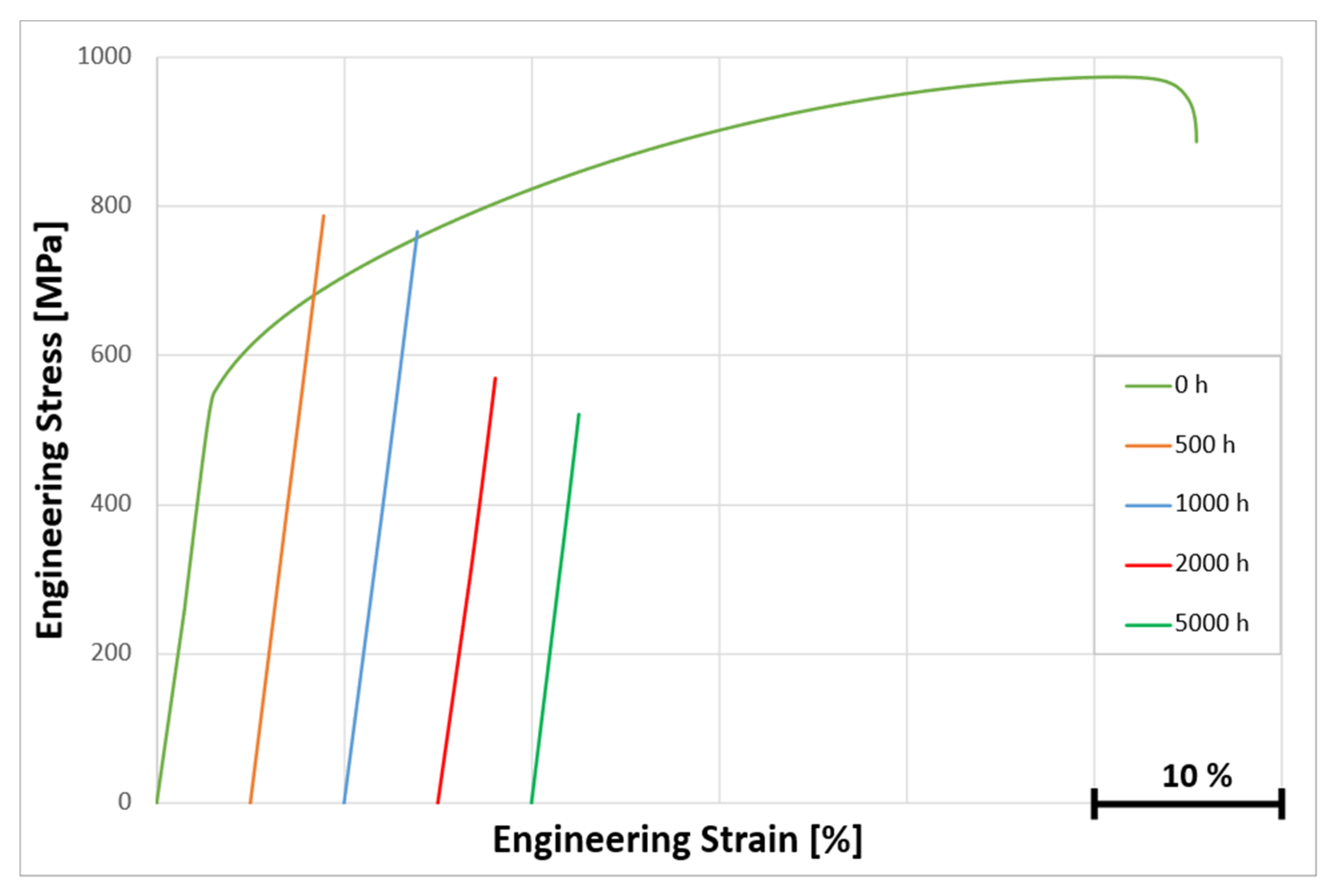
3.3.6. Microstructure and Stress–Strain Curves of Hastelloy® B-3® After Long-Term Aging at 500 °C
3.3.7. Microstructure and Stress–Strain Curves of Hastelloy® B-3® After Long-Term Aging at 650 °C
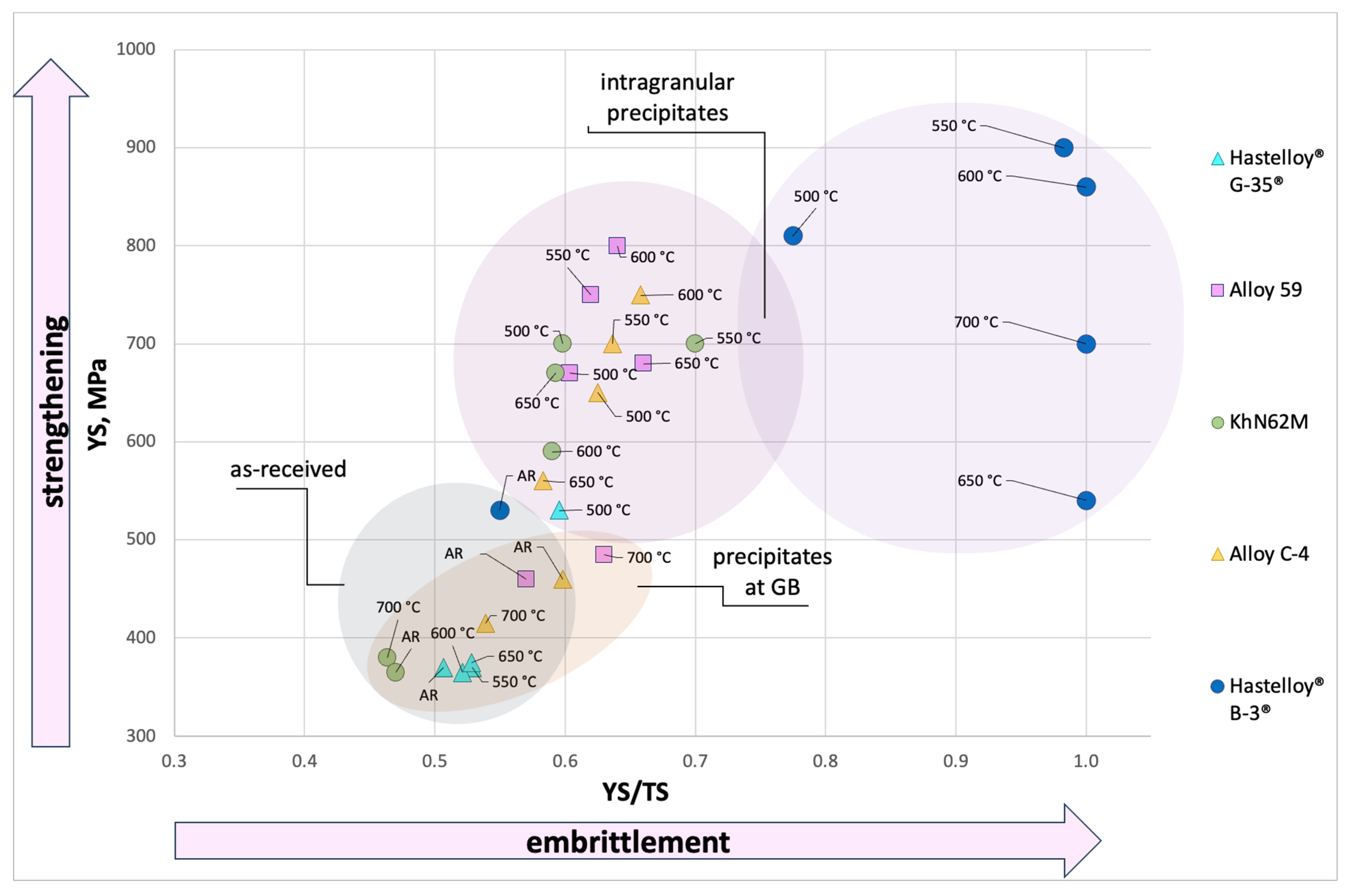
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serp, J.; Allibert, M.; Beneš, O.; Delpech, S.; Feynberg, O.; Ghetta, V.; Heuer, D.; Holcomb, D.; Ignatiev, V.; Kloosterman, J.L.; et al. The molten salt reactor (MSR) in generation IV: Overview and perspectives. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2014, 77, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettis, E.S.; Schroeder, R.W.; Cristy, G.A.; Savage, H.W.; Affel, R.G.; Hemphill, L.F. The aircraft reactor experiment–design and construction. Nucl. Sci. Eng. 1957, 2, 804–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuček, K.; Tsige-Tamirat, H.; Ammirabile, L.; Lázaro, A.; Grah, A.; Carlsson, J.; Döderlein, C.; Oettingen, M.; Fütterer, M.A.; D’Agata, E.; et al. Generation IV reactor safety and materials research by the Institute for Energy and Transport at the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2013, 265, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Status of Molten Salt Reactor Technology; Technical Reports Series No. 489; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/STI-DOC-010-489_web.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Zhou, W. Corrosion in the molten fluoride and chloride salts and materials development for nuclear applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 97, 448–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignat’ev, V.V.; Surenkov, A.I.; Gnidoi, I.P.; Fedulov, V.I.; Uglov, V.S.; Panov, A.V.; Sagaradze, V.V.; Subbotin, V.G.; Toropov, A.D.; Afonichkin, V.K.; et al. Investigation of the corrosion resistance of nickel-based alloy in fluoride melts. At. Energy 2006, 101, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, L.C.; Ambrosek, J.W.; Sridharan, K.; Anderson, M.H.; Allen, T.R. Materials corrosion in molten LiF–NaF–KF salt. J. Fluor. Chem. 2009, 130, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Pavlík, V.; Boča, M. High-temperature corrosion behavior of superalloys in molten salts—A review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 42, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M. Long-term ageing characteristics of some commercial nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1981, 16, 2883–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozlan, E.; Bamberger, M.; Dirnfeld, S.F.; Prinz, B.; Klodt, J. Topologically close-packed precipitations and phase diagrams of Ni-Mo-Cr and Ni-Mo-Fe and of Ni-Mo-Fe with constant additions of chromium. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1991, 141, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchi, P.E.A.; Kaufman, L.; Liu, Z.-K. Modeling of Ni–Cr–Mo based alloys: Part I—Phase stability. Calphad 2006, 30, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, A.V.; Karpov, V.V.; Zhilyakov, A.Y.; Gibadullina, A.F.; Polovov, I.B.; Volkovich, V.A.; Belikov, S.V.; Shak, A.V.; Rebrin, O.I. Corrosion-resistant and high-temperature nickel-based alloys in chloroaluminate melts. ECS Trans. 2014, 64, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polovov, I.B.; Abramov, A.V.; Karpov, V.V.; Gibadullina, A.F.; Zhilyakov, A.Y.; Dedov, K.V.; Belikov, S.V.; Shak, A.V.; Volkovich, V.A.; Rebrin, O.I. Corrosion of nickel-based superalloys in molten chloroaluminates. ECS Trans. 2017, 77, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polovov, I.B.; Abramov, A.V.; Gibadullina, A.F.; Alimgulov, R.R.; Karpov, V.V.; Zhilyakov, A.Y.; Khotinov, V.A.; Belikov, S.V. The effect of microstructure on the corrosion resistance of VDM® alloy C-4 in molten salts. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 810, 151758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Copeland-Johnson, T.M.; Tucker, J.D.; Cao, G. Accelerated corrosion of Ni-based alloys in molten chloride salts, due to Ni2Cr phase formation. Materialia 2023, 31, 101875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ding, Q.; Liu, D.; Yao, X.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Bei, H. The grain boundary brittleness at intermediate temperature in a precipitation strengthened Ni-based polycrystalline alloy. Acta Mater. 2025, 285, 120681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pane, S.; Xing, Y.; Yue, X.; Chang, W. Room- and elevated-temperature mechanical property of selective laser melting-fabricated Hastelloy X with different heat treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 886, 145697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y.; Luan, J.; Jiao, Z.B.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. Evolution and Strengthening of Nanoprecipitates in a High Strength Maraging Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 915, 147198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Um, H.; Yi, H.; Kang, N. Mo addition of high-strength seismic rebars subjected to Tempcore processes for tensile strength enhancement. Mater. Des. 2022, 219, 110766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A. Performance of corrosion-resistant alloys in concentrated acids. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2017, 30, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapper, H.S.; Zadorozne, N.S.; Rebak, R.B. Localized corrosion characteristics of nickel alloys: A review. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2017, 30, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, C.A.C.; Cardoso, D.S.P.; Amaral, L.; Šljukić, B.; Santos, D.M.F. On the performance of commercially available corrosion-resistant nickel alloys: A review. Corrosion Rev. 2016, 34, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M. Long-range ordering behavior and mechanical properties of Ni–Mo-based alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.R.; Spuriell, J.E.; Stansbury, E.E. Physical metallurgy of Ni–Mo alloys. Int. Met. Rev. 1984, 29, 210–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M. Mechanism of order-induced embrittlement in Ni–Ni4Mo alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 3955–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Dey, G.K.; Vasudevan, V.K.; Banerjee, S. Effect of chromium addition on the ordering behaviour of Ni–Mo alloy: Experimental results vs. electronic structure calculations. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 3301–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M. Effect of Cr on the ordering behavior and ductility of an Ni–Ni4Mo alloy. Metall. Trans. A 1992, 23, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M. On the precipitation of intermetallic compounds in selected solid-solution-strengthened Ni-base alloys and their effects on mechanical properties. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2017, 6, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseev, M.A.; Belikov, S.; Dedov, V.K.; Kritskii, A.A.; Mityukov, R.A.; Pantyukhin, A.P.; Polovov, I.B.; Skiba, K.V.; Kharin, P.A.; Chineikin, S.V.; et al. Corrosion-resistant alloy. RU Patent 2672647, 16 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, D.C.; Herda, W.R. The “C” family of Ni-Cr-Mo alloys’ partnership with the chemical process industry: The last 70 years. Mater. Corros. 1997, 48, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, F.G.; Kirchner, R.W.; Silence, W.L.U.S. Nickel-Base Alloys. Patent 4,080,201, 21 March 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner, R.W.; Hodge, F.G. New Ni-Cr-Mo alloy demonstrates high-temperature structural stability with resultant increases in corrosion-resistance and mechanical properties. Mater. Corros. 1973, 24, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, F.G.; Kirchner, R.W. An improved Ni-Cr-Mo alloy for corrosion service. Corrosion 1974, 32, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubner, U.; Köhler, M. Das Zeit-Temperatur-Ausscheidungs- und das Zeit-Temperatur-Sensibilisierungs-Verhalten von hochkorrosionsbeständigen Nickel-Chrom-Molybdän-Legierungen. Mater. Corros. 1992, 43, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchheiner, R.; Köhler, M.; Heubner, U. Nicrofer 5923 hMo, ein neuer hochkorrosionsbeständiger werkstoff für die chemische industrie, die umwelttechnik und verwandte anwendungen. Mater. Corros. 1992, 43, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltschev, M.; Baessler, R. Use of alloy 59 for the transport of highly corrosive dangerous goods. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 278, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, M.; Kloewer, J.; Agarwal, D.C. Why should one consider alloy 59 (UNS N06059) filler metal in marine applications? Presented at CORROSION 2001, Houston, TX, USA, 11 March 2001; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, H.; Wahl, V.; Ibas, O.; Stenner, F. New results on long-term aging tests for rad-waste container alloy selection. In Proceedings of the Long-Term Prediction and Modeling of Corrosion (EUROCORR 2004), Nice, France, 12–16 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pyrin, D.V.; Popkova, D.S.; Zhilyakov, A.Y.; Belikov, S.V. Identification of the second phases formed in VDM® alloy C-4. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1029, 012055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashu, S.; Trabadelo, V. A critical review on development, performance and selection of stainless steels and nickel alloys for the wet phosphoric acid process. Mater. Des. 2023, 227, 111739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlle, P.; Chagraoui, M. Interest of alloy G-35® heat exchangers in phos-acid concentration loops. Procedia Eng. 2012, 46, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belikov, S.V.; Zhilyakov, A.Y.; Popov, A.A.; Karabanalov, M.S.; Polovov, I.B. Special features of formation of excess phases during aging of corrosion-resistant high-alloy austenitic alloys based on Fe and Ni. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2015, 56, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Singh, J.; Wanderka, N.; Chakravartty, J.K. Delineating the roles of Cr and Mo during ordering transformations in stoichiometric Ni2(Cr1−x,Mox) alloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 96, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilyakov, A.Y.; Belikov, S.V.; Gibadullina, A.F.; Polovov, I.B.; Ilikbaev, I.V. Relation between short-range and long-range ordering and physical properties of corrosion-resistant alloys of the Ni–Cr–Mo system. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2020, 61, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M.; Aboelfotoh, M.O. High strength and high ductility in a nanoscale superlattice of Ni2(Cr,Mo) deformable by twinning. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metals. GOST 1497-2023; Tensile test methods. GOST: Moscow, Russia, 2024.
- Abramov, A.V.; Dedov, K.V.; Gibadullina, A.F.; Zhilyakov, A.Y.; Karpov, V.V.; Volkovich, V.A.; Polovov, I.B. Corrosive resistance of nickel Hastelloy G-35 superalloy in various aggressive media. ECS Trans. 2018, 86, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhou, L. Precipitation behavior of sigma phase and its influence on mechanical properties of a Ni-Fe based alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 784, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarti, B.; Starke, E.A.; Lefevre, B.G. Order-induced strengthening in Ni4Mo. J. Mater. Sci. 1970, 5, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Alloy | Content, wt.% | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Cr | Mo | Fe | Mn | Ti | Cu | Co | Al | Si | S | C | P | |
| Hastelloy® G-35® (UNS N06035) (1) | 57.2 | 33.1 | 8.2 | 0.8 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.012 | 0.003 |
| KhN62M-VI (2) | 63.2 | 23.2 | 12.8 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.004 | ||
| VDM® Alloy 59 (UNS N06059) | 60.4 | 22.6 | 15.4 | 0.9 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | |
| VDM® Alloy C-4 (UNS N06455) | 67.05 | 16.12 | 15.62 | 0.84 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | ||
| Hastelloy®B-3® (UNS N10675) (3) | 67.1 | 1.6 | 28.5 | 1.41 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.04 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.004 |
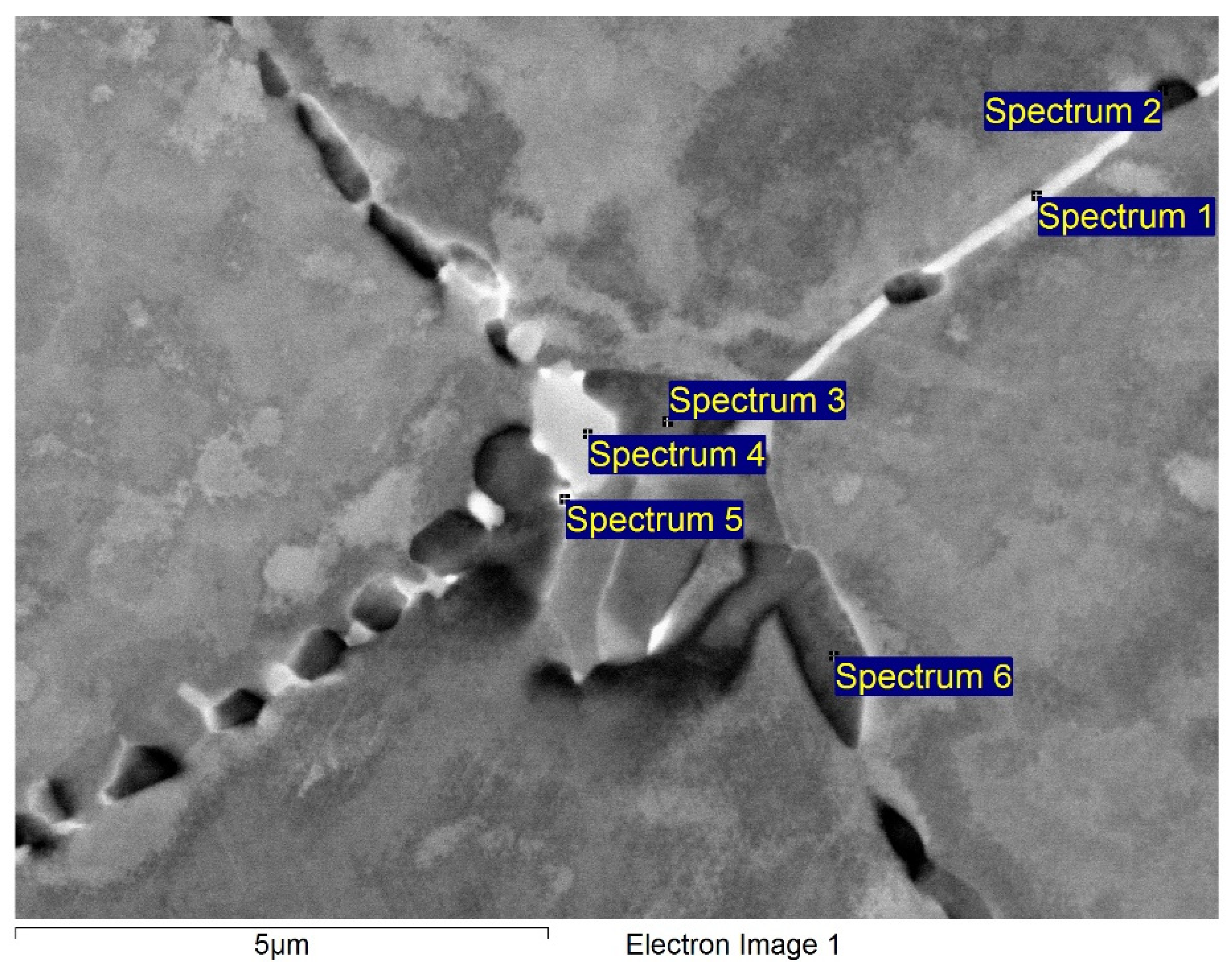
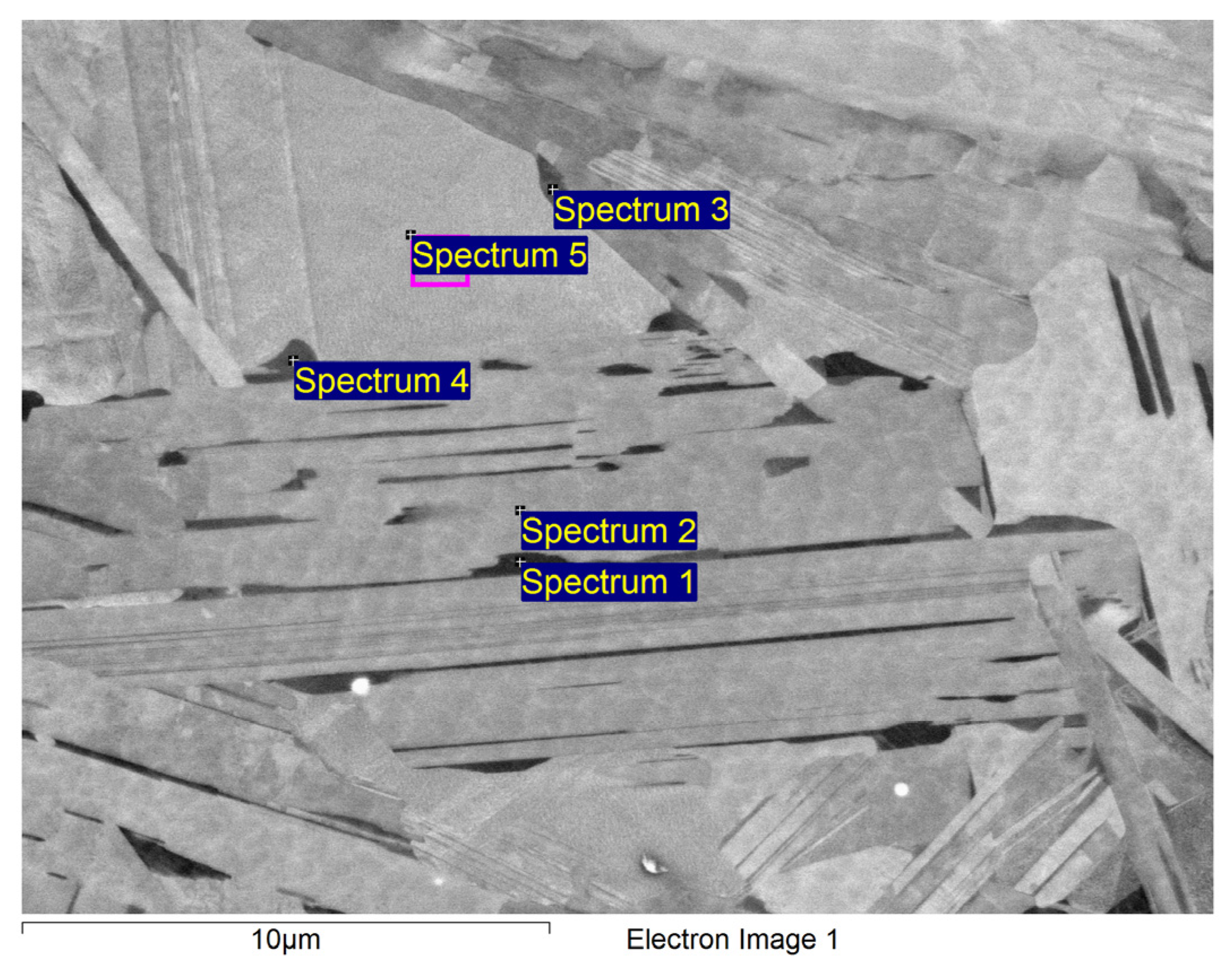
| Spectrum | Cr | Fe | Ni | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrum 1 | 49.76 | 0.66 | 37.62 | 11.96 |
| Spectrum 2 | 21.67 | 0.47 | 72.59 | 5.27 |
| Spectrum 3 | 16.73 | 0.18 | 77.42 | 5.68 |
| Spectrum 4 | 45.66 | 0.48 | 41.51 | 12.35 |
| Spectrum 5 | 50.18 | 0.55 | 34.02 | 15.24 |
| Spectrum 6 | 12.64 | 0.24 | 80.81 | 6.32 |
| Spectrum | Cr | Ni | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrum 1 | 21.78 | 37.55 | 40.67 |
| Spectrum 2 | 21.95 | 37.83 | 40.22 |
| Spectrum 3 | 70.40 | 18.75 | 10.85 |
| Spectrum 4 | 26.31 | 64.90 | 8.79 |
| Spectrum | Al | Si | Cr | Mn | Fe | Ni | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrum 1 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 3.02 | 0.88 | 2.83 | 77.52 | 13.85 |
| Spectrum 2 | 0.72 | 0.13 | 2.50 | 0.72 | 1.71 | 73.24 | 20.96 |
| Spectrum 3 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 2.96 | 1.01 | 2.71 | 77.55 | 14.00 |
| Spectrum 4 | 1.32 | 0.69 | 2.88 | 1.00 | 3.07 | 77.88 | 13.16 |
| Spectrum 5 | 0.53 | 0.40 | 1.91 | 0.86 | 1.65 | 74.03 | 20.63 |
| Spectrum 6 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 3.02 | 0.88 | 2.83 | 77.52 | 13.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gibadullina, A.F.; Khotinov, V.A.; Karabanalov, M.S.; Polovov, I.B. The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Corrosion-Resistant Nickel-Based Alloys for Their Application in Nuclear Technologies. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6133. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116133
Gibadullina AF, Khotinov VA, Karabanalov MS, Polovov IB. The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Corrosion-Resistant Nickel-Based Alloys for Their Application in Nuclear Technologies. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):6133. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116133
Chicago/Turabian StyleGibadullina, Alfiya F., Vladislav A. Khotinov, Maxim S. Karabanalov, and Ilya B. Polovov. 2025. "The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Corrosion-Resistant Nickel-Based Alloys for Their Application in Nuclear Technologies" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 6133. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116133
APA StyleGibadullina, A. F., Khotinov, V. A., Karabanalov, M. S., & Polovov, I. B. (2025). The Effect of Long-Term Aging on the Mechanical Properties of Corrosion-Resistant Nickel-Based Alloys for Their Application in Nuclear Technologies. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 6133. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116133







