Artificial Intelligence-Based Models for Automated Bone Age Assessment from Posteroanterior Wrist X-Rays: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Selection of Studies
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment (Newcastle–Ottawa Scale)
2.5. Risk of Bias Assessment (ROBINS-E)
3. Results
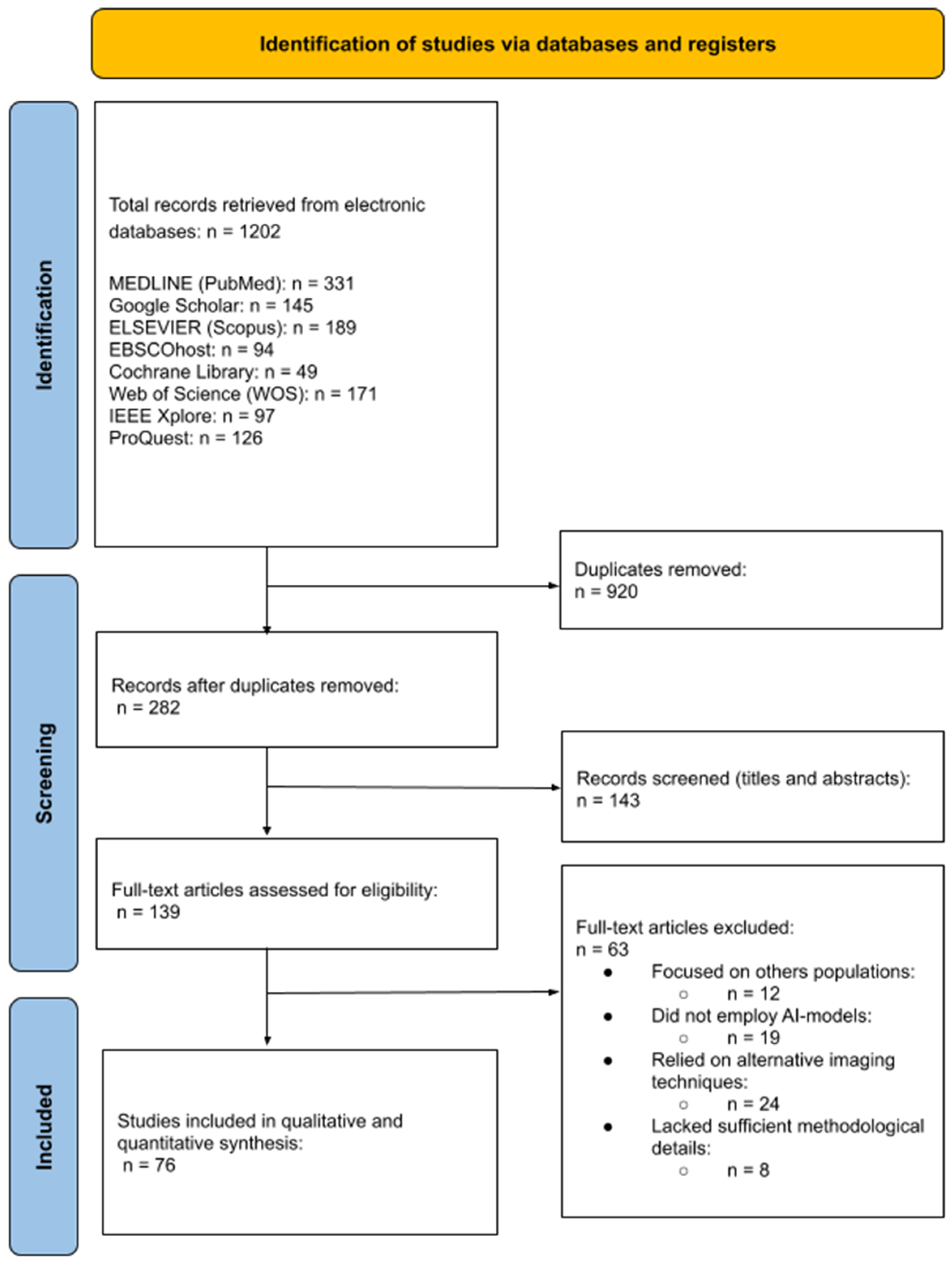
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Methodological Quality Assessment (Newcastle–Ottawa Scale)
3.4. Risk of Bias Assessment (ROBINS-E)
3.5. Main Results
3.5.1. AI-Assisted Softwares for BA Assessment Through Postero-Anterior Hand and Wrist Radiograph
3.5.2. Deep Learning Architectures for BA Assessment Through Postero-Anterior Hand and Wrist Radiograph
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
- Transfer Learning
3.5.3. Model Integration Techniques for BA Assessment Through Postero-Anterior Hand and Wrist Radiograph
- Ensemble Learning
- Hybrid models
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Recommendations for Clinical Practice
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Satoh, M. Bone Age: Assessment Methods and Clinical Applications. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2015, 24, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor Mughal, A.; Hassan, N.; Ahmed, A. Bone Age Assessment Methods: A Critical Review. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallo, F.; Mohn, A.; Chiarelli, F.; Giannini, C. Evaluation of Bone Age in Children: A Mini-Review. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 580314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sanctis, V.; Di Maio, S.; Soliman, A.T.; Raiola, G.; Elalaily, R.; Millimaggi, G. Hand X-Ray in Pediatric Endocrinology: Skeletal Age Assessment and Beyond. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 18, S63–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishori, R. The Use of Age Assessment in the Context of Child Migration: Imprecise, Inaccurate, Inconclusive and Endangers Children’s Rights. Children 2019, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzmann, C.; Golakov, M.; Malekzada, F.; Lonnroth, K.; Kranzer, K. Radiological Screening of Refugees in Germany. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1602487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossois, M.; Cyteval, C.; Baccino, E.; Peyron, P.A. Forensic Age Assessments of Alleged Unaccompanied Minors at the Medicolegal Institute of Montpellier: A 4-Year Retrospective Study. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2022, 136, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greulich, W.W.; Pyle, S.I. Radiographic Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Hand and Wrist, 2nd ed.; Stanford University Press: Stanford, CA, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Gilsanz, V.; Ratib, O. Hand Bone Age: A Digital Atlas of Skeletal Maturity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, J.M.; Realy, J.; Goldstein, H. Assessment of Skeletal Maturity and Prediction of Adult Height (TW3 Method); Harcourt Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 1–200. [Google Scholar]
- Martín Pérez, S.E.; Martín Pérez, I.M.; Molina Suárez, R.; Vega González, J.M.; García Hernández, A.M. The Validation of the Tanner–Whitehouse 3 Method for Radiological Bone Assessments in a Pediatric Population from the Canary Islands. Osteology 2025, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop-Piotrkowska, M.; Marszałek-Dziuba, K.; Moszczyńska, E.; Szalecki, M.; Jurkiewicz, E. Traditional and new methods of bone age assessment—An overview. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2021, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Pérez, I.M.; Martín Pérez, S.E.; Vega González, J.M.; Molina Suárez, R.; García Hernández, A.M.; Rodríguez Hernández, F.; Herrera Pérez, M. The Validation of the Greulich and Pyle Atlas for Radiological Bone Age Assessments in a Pediatric Population from the Canary Islands. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Pérez, S.E.; Martín Pérez, I.M.; Vega González, J.M.; Molina Suárez, R.; León Hernández, C.; Rodríguez Hernández, F.; Herrera Pérez, M. Precision and Accuracy of Radiological Bone Age Assessment in Children among Different Ethnic Groups: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, D.J.; Nelson, A.C. HANDX: A Model-Based System for Automatic Segmentation of Bones from Digital Hand Radiographs. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1989, 8, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietka, E.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Kuo, M.L.; Huang, H.K. Computer-Assisted Phalangeal Analysis in Skeletal Age Assessment. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1991, 10, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.M.; Oshman, D.; Lindgren, G.; Grunbaum, J.A.; Elsouki, R.; Labarthe, D. Reliability and Validity of Computer-Assisted Estimates of Tanner-Whitehouse Skeletal Maturity (CASAS): Comparison with the Manual Method. Horm. Res. 1994, 42, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maratova, K.; Zemkova, D.; Sedlak, P.; Pavlikova, M.; Amaratunga, S.A.; Krasnicanova, H.; Soucek, O.; Sumnik, Z. A Comprehensive Validation Study of the Latest Version of BoneXpert on a Large Cohort of Caucasian Children and Adolescents. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1130580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-T.; Chan, Y.-K.; Yuh, Y.-S.; Yu, S.-S. Applying Convolutional Neural Network in Automatic Assessment of Bone Age Using Multi-Stage and Cross-Category Strategy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.5 (Updated August 2024); Cochrane: London, UK, 2024; Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Pereson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses; Ottawa Health Research Institute: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2011; Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Morgan, R.L.; Rooney, A.A.; Taylor, K.W.; Thayer, K.A.; Silva, R.A.; Lemeris, C.; Akl, E.A.; Bateson, T.F.; Berkman, N.D.; et al. A Tool to Assess Risk of Bias in Non-Randomized Follow-Up Studies of Exposure Effects (ROBINS-E). Environ. Int. 2024, 182, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.D.; Lee, J.J.; Shin, J. Incorporated Region Detection and Classification Using Deep Convolutional Networks for Bone Age Assessment. Artif. Intell. Med. 2019, 97, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.Y.; Chokuwa, S.; Xie, X.H.; Wu, F.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, C. Skeletal bone age assessments for young children based on regression convolutional neural networks. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 6454–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.J. A multi-scale data fusion framework for bone age assessment with convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 108, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booz, C.; Yel, I.; Wichmann, J.L.; Boettger, S.; Al Kamali, A.; Albrecht, M.H.; Martin, S.S.; Lenga, L.; Huizinga, N.A.; D’Angelo, T.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Bone Age Assessment: Accuracy and Efficiency of a Novel Fully Automated Algorithm Compared to the Greulich–Pyle Method. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2020, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.-Y.; Lee, B.-D.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, H.-R.; Oh, D.H.; Lee, B.I.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, M.S.; Heo, M.-S. Evaluation of the Clinical Efficacy of a TW3-Based Fully Automated Bone Age Assessment System Using Deep Neural Networks. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2020, 50, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Gu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Pan, H.; Shi, L.; Jin, Z. Artificial Intelligence System Can Achieve Comparable Results to Experts for Bone Age Assessment of Chinese Children with Abnormal Growth and Development. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Tsai, T.-H.; Hsu, J.-S.; Chao, M.-F.; Wang, Y.-T.; Jaw, T.-S. Automatic Assessment of Bone Age in Taiwanese Children: A Comparison of the Greulich and Pyle Method and the Tanner and Whitehouse 3 Method. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 64, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koitka, S.; Kim, M.S.; Qu, M.; Fischer, A.; Friedrich, C.M.; Nensa, F. Mimicking the Radiologists’ Workflow: Estimating Pediatric Hand Bone Age with Stacked Deep Neural Networks. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 64, 101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, T.; Xu, X. Bone Age Assessment Based on Deep Convolution Neural Network Incorporated with Segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 15, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, I.; Baird, G.L.; Mutasa, S.; Merck, D.; Ruzal-Shapiro, C.; Swenson, D.W.; Ayyala, R.S. Rethinking Greulich and Pyle: A Deep Learning Approach to Pediatric Bone Age Assessment Using Pediatric Trauma Hand Radiographs. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e190198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-L.; Wang, E.-G.; Lin, Q.; Dong, G.-P.; Wu, W.; Huang, K.; Lai, C.; Yu, G.; Zhou, H.-C.; Ma, X.-H.; et al. Diagnostic Performance of Convolutional Neural Network-Based Tanner-Whitehouse 3 Bone Age Assessment System. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J. Probing an AI Regression Model for Hand Bone Age Determination Using Gradient-Based Saliency Mapping. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, C.; Gedik, M.A.; Kaya, Y. Age Estimation from Left-Hand Radiographs with Deep Learning Methods. Trait. Signal 2021, 38, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.S.; Yadhu, C.R.; Karthik, U. Chronological Age Assessment Based on Wrist Radiograph Processing: Some Novel Approaches. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 8651–8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poojary, N.B.; Pokhare, P.G.; Poojary, P.P.; Khanapuri, J. A Novel Approach for Bone Age Assessment Using Deep Learning. Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2021, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narin, N.G.; Yeniçeri, İ.Ö.; Yüksel, G. Estimation of Bone Age from Radiological Images with Machine Learning. Med. J. Mugla Sitki Kocman Univ. 2021, 8, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Xu, R.; Zhao, X. Classification of Hand–Wrist Maturity Level Based on Similarity Matching. IET Image Process. 2021, 15, 2866–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, F.A.; Dursun, A.; Ozturk, K.; Ayyildiz, V.A. Determination of Bone Age Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Ann. Med. Res. 2021, 28, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, C.; Ayeesha, B.; Sotakanal, A.; Desai, S.D.; Ganguly, A.D.; Shetty, V. Deep Learning Framework for Automatic Bone Age Assessment. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2021, 2021, 3093–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.D.; Lee, M.S. Automated Bone Age Assessment Using Artificial Intelligence: The Future of Bone Age Assessment. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Kim, T.; Kim, Y.J.; Song, I.S.; Ahn, B.; Choo, J.; Lee, D.Y. Prediction of Hand-Wrist Maturation Stages Based on Cervical Vertebrae Images Using Artificial Intelligence. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2021, 24 (Suppl. S2), 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Yoon, H.M.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, P.H.; Bak, B.; Bae, B.U.; Sung, J.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, A.Y.; Cho, Y.A.; et al. Re-Assessment of Applicability of Greulich and Pyle-Based Bone Age to Korean Children Using Manual and Deep Learning-Based Automated Method. Yonsei Med. J. 2022, 63, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, B.; Li, S.; Zhu, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, D. A Deep Learning-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis Method of X-Ray Images for Bone Age Assessment. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, Q.; Wang, C.; Weng, J.; Chen, M.; Kong, D. A Global-Local Feature Fusion Convolutional Neural Network for Bone Age Assessment of Hand X-ray Images. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, H.; Li, Z. Automated Bone Age Assessment: A New Three-Stage Assessment Method from Coarse to Fine. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.-K.; Han, Y.; Oh, J.; Lim, J.; Ryu, J.; Yoon, M.S.; Lee, J.; Ryu, S. Automatic Segmentation for Favourable Delineation of Ten Wrist Bones on Wrist Radiographs Using Convolutional Neural Network. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, K.; Yan, D.; Liu, H.; Bai, J.; Liu, F.; Cheng, X.; Wu, T. SMANet: Multi-Region Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Network Model for Skeletal Maturity Assessment. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 3556–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.F.; Liao, K.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Tsai, F.J. A Study to Evaluate Accuracy and Validity of the EFAI Computer-Aided Bone Age Diagnosis System Compared with Qualified Physicians. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 829372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerari, A.; Djedidi, O.; Kahloul, L.; Carlo, R.; Remadna, I. Paediatric Bone Age Assessment from Hand X-ray Using Deep Learning Approach. In Advances in Computing Systems and Applications; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Senouci, M.R., Boulahia, S.Y., Benatia, M.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.J.; Bowden, S.A.; Ruess, L.; Adler, B.H.; Hu, H.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Krishnamurthy, R. Validation of Automated Bone Age Analysis from Hand Radiographs in a North American Pediatric Population. Pediatr. Radiol. 2022, 52, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Ma, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. Effect of AI-Assisted Software on Inter- and Intra-Observer Variability for the X-ray Bone Age Assessment of Preschool Children. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mame, A.B.; Tapamo, J.-R. Hand Bone Age Estimation Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Advanced Data Mining and Applications, Proceedings of the 17th International Conference, ADMA 2021, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2–4 February 2022; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 13022, pp. 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, B.; Gong, P.; Zhang, T.; Mo, Y.; Tang, J.; Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Yuan, X.; Bai, F.; et al. Artificial Intelligence–Assisted Bone Age Assessment to Improve the Accuracy and Consistency of Physicians with Different Levels of Experience. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 818061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshtian, E.; Putman, K.; Santomartino, S.M.; Parekh, V.S.; Yi, P.H. Generalizability and Bias in a Deep Learning Pediatric Bone Age Prediction Model Using Hand Radiographs. Radiology 2023, 306, e220505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, M.; Eshmawi, A.A.; Alnowaiser, K.; Mohamed, A.; Alrashidi, H.; Ashraf, I. Skeletal Age Evaluation Using Hand X-rays to Determine Growth Problems. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, R.G.V.; Shaik, M.F.; Sastry, L.V.; Sahithi, C.G.; Jagadeesh, J.; Raja, I.R. Evaluation of Bone Age by Deep Learning Based on Hand X-Rays. In Expert Clouds and Applications; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Jacob, I.J., Ed.; Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2023; Volume 673, pp. 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandavardhan, R.; Somanathan, R.; Suresh, V.; Savaridassan, P. Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Approaches for Bone Age Assessment: A Comprehensive Study on Three Distinct Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, H.; Umer, M.; Saidani, O.; Almuqren, L.; Distasi, R. Improving Prediction of Skeletal Growth Problems for Age Evaluation Using Hand X-rays. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 80027–80049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Pei, X.; Li, X.; Tong, H.; Li, X.; Huang, S. End-to-End Multi-Domain Neural Networks with Explicit Dropout for Automated Bone Age Assessment. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 3736–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Hu, M.; Ren, F. A Multi-Scale Framework Based on Jigsaw Patches and Focused Label Smoothing for Bone Age Assessment. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, D.; Chen, Y. Multi-Branch Attention Learning for Bone Age Assessment with Ambiguous Label. Sensors 2023, 23, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, K.; Li, S.; Yang, M.; Wang, S.; Song, C. Multi-Characteristic Reinforcement of Horizontally Integrated TENet Based on Wrist Bone Development Criteria for Pediatric Bone Age Assessment. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 22743–22752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarquis Serpa, A.; Elias Neto, A.; Kitamura, F.C.; Monteiro, S.S.; Ragazzini, R.; Duarte, G.A.R.; Caricati, L.A.; Abdala, N. Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Bone Age Estimation Among Patients in the City of São Paulo, Brazil. Radiol. Bras. 2023, 56, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.H.; Yoon, H.M.; Kim, J.R.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Hwang, J.; Lee, J.; Sung, J.; Jung, K.-H.; Bae, B.; et al. Bone Age Assessment Using Artificial Intelligence in Korean Pediatric Population: A Comparison of Deep-Learning Models Trained With Healthy Chronological and Greulich-Pyle Ages as Labels. Korean J. Radiol. 2023, 24, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Gao, L.; Ji, M.; Ge, J.; Huang, L.; Qiao, H.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Sun, Y.; et al. The Uncovered Biases and Errors in Clinical Determination of Bone Age by Using Deep Learning Models. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 3544–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Heo, J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.; Jung, M.K.; Choi, H.S.; Choi, Y.; Oh, J.S.; Lee, H.I.; Lee, M.; et al. Bone Age Estimation and Prediction of Final Adult Height Using Deep Learning. Yonsei Med. J. 2023, 64, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Cong, C.; Pagnucco, M.; Song, Y. Multi-Scale Multi-Reception Attention Network for Bone Age Assessment in X-ray Images. Neural Netw. 2023, 158, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Hui, Q.; Zhu, S.; Du, W.; Qiu, C.; Ouyang, X.; Kong, D. Automated Skeletal Bone Age Assessment with Two-Stage Convolutional Transformer Network Based on X-ray Images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim Huang, S.; Su, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Su, Q.; Su, H.; Shang, Y.; Jiao, Y. Combined assisted bone age assessment and adult height prediction methods in Chinese girls with early puberty: Analysis of three artificial intelligence systems. Pediatr. Radiol. 2023, 53, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Wu, W.; Zhou, X.; Huang, K.; Wang, Z.; Song, C.; Chen, Q.; Su, Z.; Zheng, R.; et al. Validation of an Established TW3 Artificial Intelligence Bone Age Assessment System: A Prospective, Multicenter, Confirmatory Study. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Park, D.; Chang, M.C. Assessment of Bone Age Based on Hand Radiographs Using Regression-Based Multi-Modal Deep Learning. Life 2024, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamd, Z.Y.; Alorainy, A.I.; Alharbi, M.A.; Hamdoun, A.; Alkhedeiri, A.; Alhegail, S.; Absar, N.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, A.F.I. Deep Learning-Based Automated Bone Age Estimation for Saudi Patients on Hand Radiograph Images: A Retrospective Study. BMC Med. Imaging 2024, 24, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, J.; Rosolowski, M.; Pfäffle, R.; Beeskow, A.B.; Gräfe, D. A Critical Comparative Study of the Performance of Three AI-Assisted Programs for Bone Age Determination. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 35, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özmen, E.; Özen Atalay, H.; Uzer, E.; Veznikli, M. A Comparison of Two Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods for Assessing Bone Age in Turkish Children: BoneXpert and VUNO Med-Bone Age. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jing, L.; Fu, X. Data Enhancement and Deep Learning for Bone Age Assessment Using the Standards of Skeletal Maturity of Hand and Wrist for Chinese. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Guadalajara, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Zhou, D. Doctor Simulator: Delta-Age-Sex-AdaIn Enhancing Bone Age Assessment through AdaIn Style Transfer. Pediatr. Radiol. 2024, 54, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Wang, H.; Wangjiu, C.; Awang, T.; Yang, M.; Qiongda, P.; Yang, X.; Pan, H.; Wang, F. An Artificial Intelligence-Based Bone Age Assessment Model for Han and Tibetan Children. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1329145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, R.; Cheng, X.; Su, Z.; Wang, X.; Du, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, G.; Zhong, Y.; et al. Validation of an AI-Powered Automated X-ray Bone Age Analyzer in Chinese Children and Adolescents: A Comparison with the Tanner–Whitehouse 3 Method. Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 3664–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfe, D.; Beeskow, A.B.; Pfäffle, R.; Rosolowski, M.; Chung, T.S.; DiFranco, M.D. Automated Bone Age Assessment in a German Pediatric Cohort: Agreement between an Artificial Intelligence Software and the Manual Greulich and Pyle Method. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 4407–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaimo, D.; Terranova, M.C.; Palizzolo, E.; De Angelis, M.; Avella, V.; Paviglianiti, G.; Lo Re, G.; Matranga, D.; Salerno, S. Performance of Two Different Artificial Intelligence (AI) Methods for Assessing Carpal Bone Age Compared to the Standard Greulich and Pyle Method. Radiol. Med. 2024, 129, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-C.; Kang, C.H.; Ahn, K.-S.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, J.J.; Cho, K.R.; Oh, S. A Comparison of Automatic Bone Age Assessments between the Left and Right Hands: A Tool for Filtering Measurement Errors. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Song, T.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, Q. ARAA-Net: Adaptive Region-Aware Attention Network for Epiphysis and Articular Surface Segmentation from Hand Radiographs. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 2514814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, S.; Xu, K.; She, J.; Fan, J.; He, M.; Shaoyi, L.S.; Gao, Z.; Liu, X.; Yao, K. A Pediatric Bone Age Assessment Method for Hand Bone X-ray Images Based on Dual-Path Network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 9737–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P. Bone Age Estimation with HS-Optimized ResNet and YOLO for Child Growth Disorder. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 259, 125160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.J.; Song, Y.; Kim, N.; Do, Y.; Kwak, N.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, B.-D. TW3-Based Fully Automated Bone Age Assessment System Using Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 33346–33358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, W.W.; Hong, S.J.; Nam, H.K.; Kang, W.Y.; Yang, Z.P.; Noh, E.J. External Validation of Deep Learning-Based Bone-Age Software: A Preliminary Study with Real World Data. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, I.; Thodberg, H.H.; Halabi, S.S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Larson, D.B. Improving Automated Pediatric Bone Age Estimation Using Ensembles of Models from the 2017 RSNA Machine Learning Challenge. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2019, 1, e190053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibisono, A.; Saputri, M.S.; Mursanto, P.; Rachmad, J.; Alberto; Yudasubrata, A.T.W.; Rizki, F.; Anderson, E. Deep Learning and Classic Machine Learning Approach for Automatic Bone Age Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th Asia-Pacific Conference on Intelligent Robot Systems, Tokushima, Japan, 19–22 August 2019; pp. 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.E.; Rayan, J.C.; Annapragada, A.V.; Mahmood, N.F.; Scheslinger, A.E.; Zhang, W.; Kan, J.H. Bone Age Determination Using Only the Index Finger: A Novel Approach Using a Convolutional Neural Network Compared with Human Radiologists. Pediatr. Radiol. 2020, 50, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Hermann, A.-L.; Ventre, J.; Ducarouge, A.; Pourchot, A.; Marty, V.; Regnard, N.-E.; Guermazi, A. High Performance for Bone Age Estimation with an Artificial Intelligence Solution. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2023, 104, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifley, M.A.; Mohamed, N.A.; Abdani, S.R.; Kamari, N.A.M.; Moubark, A.M.; Ibrahim, A.A. Intelligent Bone Age Assessment: An Automated System to Detect a Bone Growth Problem Using Convolutional Neural Networks with Attention Mechanism. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, G.; Patel, B. Charting the Growth through Intelligence: A SWOC Analysis on AI-Assisted Radiologic Bone Age Estimation. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2025, 139, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajmir, S.H.; Lee, H.; Shailam, R.; Gale, H.I.; Nguyen, J.C.; Westra, S.J.; Lim, R.; Yune, S.; Gee, M.S.; Do, S. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Interpretation of Bone Age Radiographs Improves Accuracy and Decreases Variability. Skelet. Radiol. 2019, 48, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasani, A.A.; Sajedi, H. Hand Bone Age Estimation Using Divide and Conquer Strategy and Lightweight Convolutional Neural Networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 120, 105935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonca, M.; Sert, M.F.; Gunacar, D.N.; Kose, T.E.; Beser, B. Determination of Growth and Developmental Stages in Hand-Wrist Radiographs: Can Fractal Analysis in Combination with Artificial Intelligence Be Used? J. Orofac. Orthop. 2024, 85 (Suppl. S2), 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, J.; Hirsch, F.W.; Deffaa, O.J.; DiFranco, M.D.; Rosolowski, M.; Gräfe, D. Applicability and Robustness of an Artificial Intelligence-Based Assessment for Greulich and Pyle Bone Age in a German Cohort. Fortschr. Röntgenstr. 2024, 196, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offiah, A.C. Current and Emerging Artificial Intelligence Applications for Pediatric Musculoskeletal Radiology. Pediatr. Radiol. 2022, 52, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.G. Applying Deep Learning in Medical Images: The Case of Bone Age Estimation. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2018, 24, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Tajmir, S.; Lee, J.; Zissen, M.; Yeshiwas, B.A.; Alkasab, T.K.; Choy, G.; Do, S. Fully Automated Deep Learning System for Bone Age Assessment. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 30, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spampinato, C.; Palazzo, S.; Giordano, D.; Aldinucci, M.; Leonardi, R. Deep Learning for Automated Skeletal Bone Age Assessment in X-ray Images. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 36, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thodberg, H.H. Clinical review: An automated method for determination of bone age. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2239–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallora, A.L.; Anderberg, P.; Kvist, O.; Mendes, E.; Diaz Ruiz, S.; Sanmartin Berglund, J. Bone age assessment with various machine learning techniques: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, F. The Growth of Children. Science 1897, 5, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, F. Plasticity in Child Development. In Anthropology and Child Development: A Cross-Cultural Reader, 1st ed.; LeVine, R.A., New, R.S., Eds.; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiran, F.; Calders, T.G.K. Data preprocessing techniques for classification without discrimination. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2012, 33, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, M.; Prabakaran, B.S.; Hasan, O.; Shafique, M. UnbiasedNets: A dataset diversification framework for robustness bias alleviation in neural networks. Mach. Learn. 2024, 113, 2499–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, C.; Sellitto, G.; Ferrucci, F.; Palomba, F.; De Lucia, A. Fairness-aware Machine Learning Engineering: How Far Are We? Empir. Softw. Eng. 2024, 29, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Ju, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Z.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y. Bone Age Assessment Based on Deep Neural Networks with Annotation-Free Cascaded Critical Bone Region Extraction. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1142895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo Rodríguez, F.; Rodríguez, F. Atlas Radiológico de Referencia de la Edad Ósea en la Población Canaria; Fundación Canaria Salud y Sanidad, Cabildo de Tenerife: Tenerife, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.-T.; Tjia, V.; Noga, T.; Febri, J.; Lien, C.-Y.; Chu, W.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Hsiao, C.-H. Creating a Medical Imaging Workflow Based on FHIR, DICOMweb, and SVG. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, O.; Kushibar, K.; Osuala, R.; Linardos, A.; Garrucho, L.; Igual, L.; Radeva, P.; Prior, F.; Gkontra, P.; Lekadir, K. Data preparation for artificial intelligence in medical imaging: A comprehensive guide to open-access platforms and tools. Phys. Med. 2021, 83, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebad, S.A.; Alhashmi, A.; Amara, M.; Miled, A.B.; Saqib, M. Artificial Intelligence-Based Software as a Medical Device (AI-SaMD): A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2025, 13, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 13485:2016; Medical Devices—Quality Management Systems—Requirements for Regulatory Purposes. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- ISO 14971:2019; Medical Devices—Application of Risk Management to Medical Devices. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Bartels, R.; Dudink, J.; Haitjema, S.; Oberski, D.; van’t Veen, A. A Perspective on a Quality Management System for AI/ML-Based Clinical Decision Support in Hospital Care. Front. Digit. Health 2022, 4, 942588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogiannos, N.; Gillan, C.; Precht, H.; Sa Dos Reis, C.; Kumar, A.; O’Regan, T.; Ellis, V.; Barnes, A.; Meades, R.; Pogose, M.; et al. A multidisciplinary team and multiagency approach for AI implementation: A commentary for medical imaging and radiotherapy key stakeholders. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2024, 55, 101717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, O.; Yaya-Stupp, D.; Traynis, I.; Cole-Lewis, H.; Bennett, C.R.; Lyles, C.; Lau, C.; Irani, M.; Semturs, C.; Webster, D.R.; et al. Using Generative AI to Investigate Medical Imagery Models and Datasets. eBioMedicine 2024, 102, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | Study Design |
|---|---|
| Population (P) | Children and adolescents undergoing BA assessment using left PA-HW radiographs |
| Exposure (E) | AI-based models for BA estimation using left PA-HW radiographs |
| Comparator (C) | Conventional manual BA methods or alternative computational techniques |
| Outcomes (O) | Model accuracy, precision, predictive validity, inter-observer variability, intra-observer variability, processing time, clinical applicability |
| Criteria | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Study Design | Diagnostic accuracy, cohort, case–control, cross-sectional, validation, case series, chapters, or conference proceedings studies. | Randomized controlled trials, clinical trials, abstracts, editorials, opinion pieces |
| Publication Date | 1 January 2019, and 23 December 2024 | Before 1 January 2019, or after 23 December 2024 |
| Availability | Full-text, peer-reviewed publications | Not available as full-text, peer-reviewed publications |
| Language | English, Spanish, French, Portuguese, Arabic | Any other language |
| Computational Technique | Datasets | Performance | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-assisted Software | |||
| AI-assisted software (BoneXpert®,VUNO Med®-BoneAge, BoneView®, etc.) | RSNA, DHA, TW3 sets | MAE: 2–4 mos. | [27,30,45,53,76,77,83,89,93,99] |
| Deep Learning Architectures | |||
| Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) | RSNA, Digital Hand Atlas, Private datasets | MAE: 2.75–7.08 mos. | [24,25,26,28,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,40,41,42,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,69,70,71,72,74,75,78,79,80,84,85,86,87,88,90,91,92,94,96,97] |
| Transfer Learning (InceptionV3, VGG16, ResNet50, MobileNetV2, EfficientNetV2B0, etc.) | RSNA | MAE: 3.85–31.8 mos. | [36,38,42,44,59,87,97] |
| Custom DL Architectures (AXNet, MMANet, DADPN, etc.) | RSNA | MAE: 4–5.8 mos. | [70,86,94] |
| Multi-domain Neural Networks | RSNA, Local datasets | MAE: ~4–5.5 mos. | [62,71,72] |
| Model Integration Techniques | |||
| Ensemble Learning | RSNA | MAD: 3.79–4.55 mos. | [31,38,90,91] |
| Hybrid Models (CNN + TW3/GPA) | RSNA, DHA, TW3 sets | MAE: 5.52–7.08 mos. | [24,28,43,73,88] |
| Region Processing and Enhancement | |||
| U-Net Segmentation | RSNA | MAE: 6–7.35 mos. | [32,33,46,48,85] |
| Attention Mechanisms | RSNA, Chinese datasets | MAE: ~4–6 mos. | [32,64,71,81,94] |
| Region Localization (YOLOv3, YOLOv5) | RSNA | MAE: 4.8–6.2 mos. | [47,48,71,85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martín Pérez, I.M.; Bourhim, S.; Martín Pérez, S.E. Artificial Intelligence-Based Models for Automated Bone Age Assessment from Posteroanterior Wrist X-Rays: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115978
Martín Pérez IM, Bourhim S, Martín Pérez SE. Artificial Intelligence-Based Models for Automated Bone Age Assessment from Posteroanterior Wrist X-Rays: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115978
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartín Pérez, Isidro Miguel, Sofia Bourhim, and Sebastián Eustaquio Martín Pérez. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence-Based Models for Automated Bone Age Assessment from Posteroanterior Wrist X-Rays: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115978
APA StyleMartín Pérez, I. M., Bourhim, S., & Martín Pérez, S. E. (2025). Artificial Intelligence-Based Models for Automated Bone Age Assessment from Posteroanterior Wrist X-Rays: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5978. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115978






