Optimization Design of Multi-Blade Centrifugal Fan Based on Variable Weight PSO-BP Prediction Model and Multi-Objective Beluga Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Establishment of Prediction Model
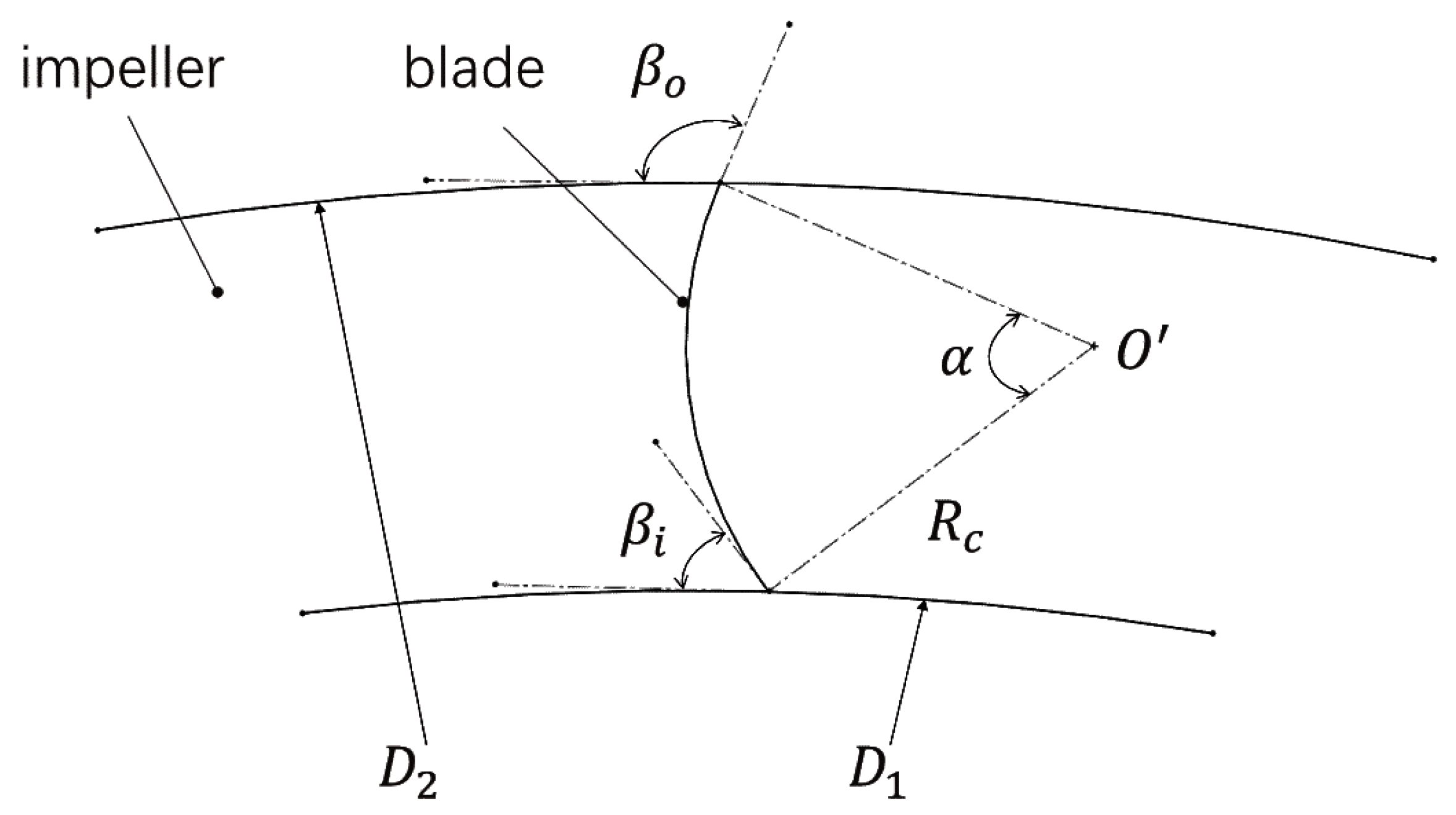
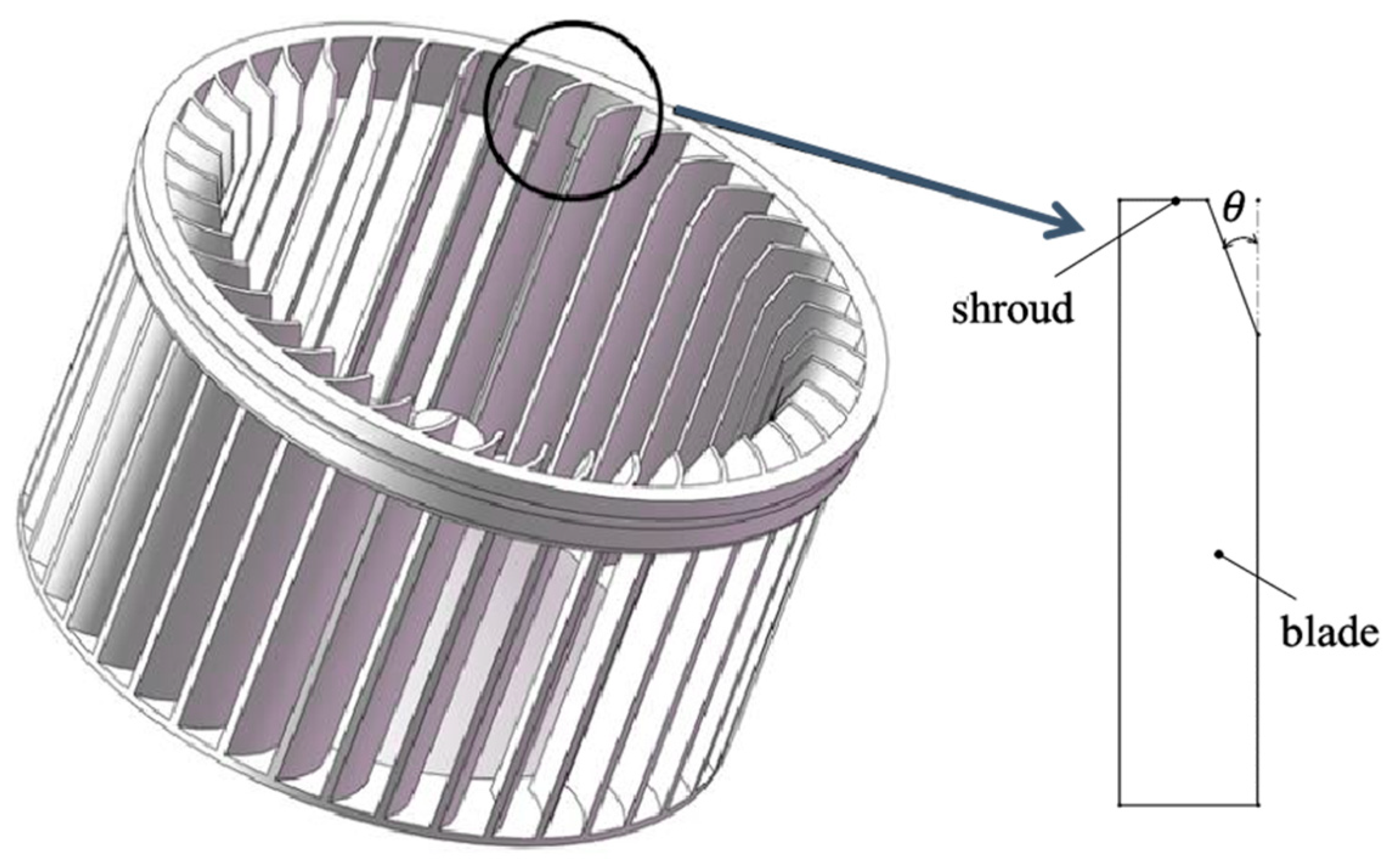
2.1. Design Variables and Optimization Objectives
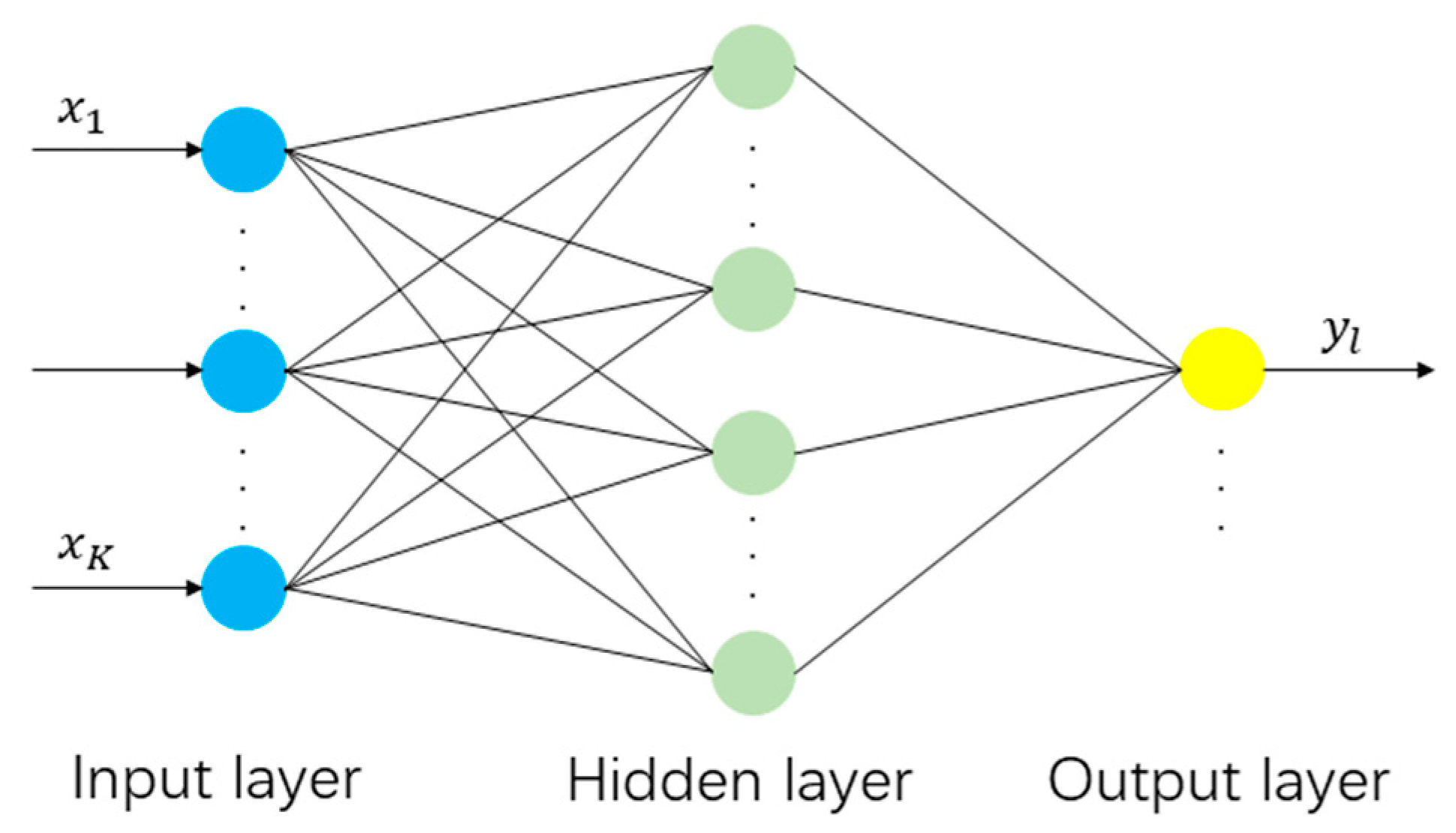
2.2. Variable-Weight PSO-Optimized BP Neural Network (wPSO-BP) Prediction Model
3. Establishment of Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithm
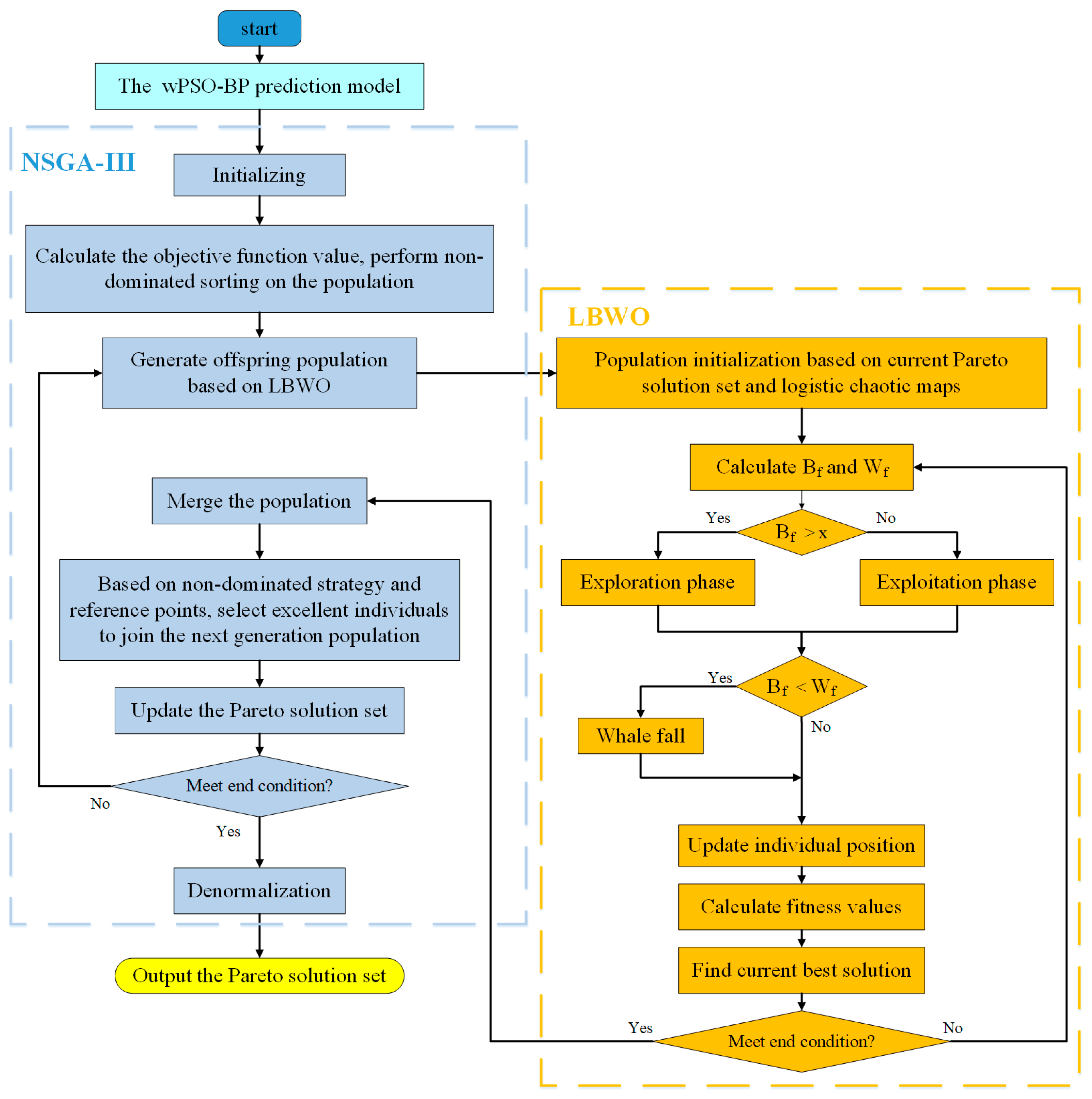
3.1. BWO Based on Logistic Chaotic Map Initialization (LBWO)
3.2. Multi-Objective Beluga Optimization Algorithm (NSGA-III-LBWO)
4. Optimization and Analysis of Multi-Blade Centrifugal Fan
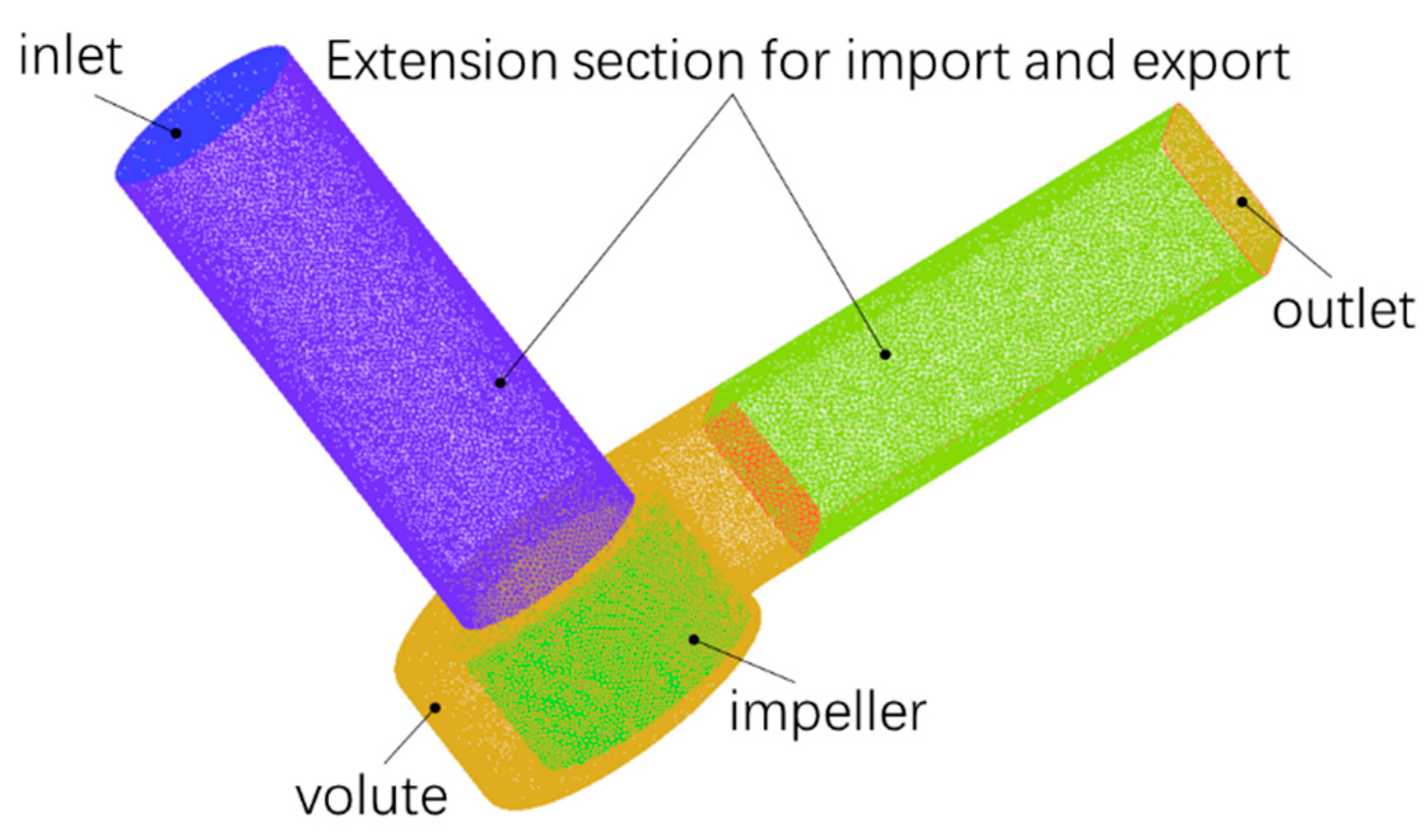
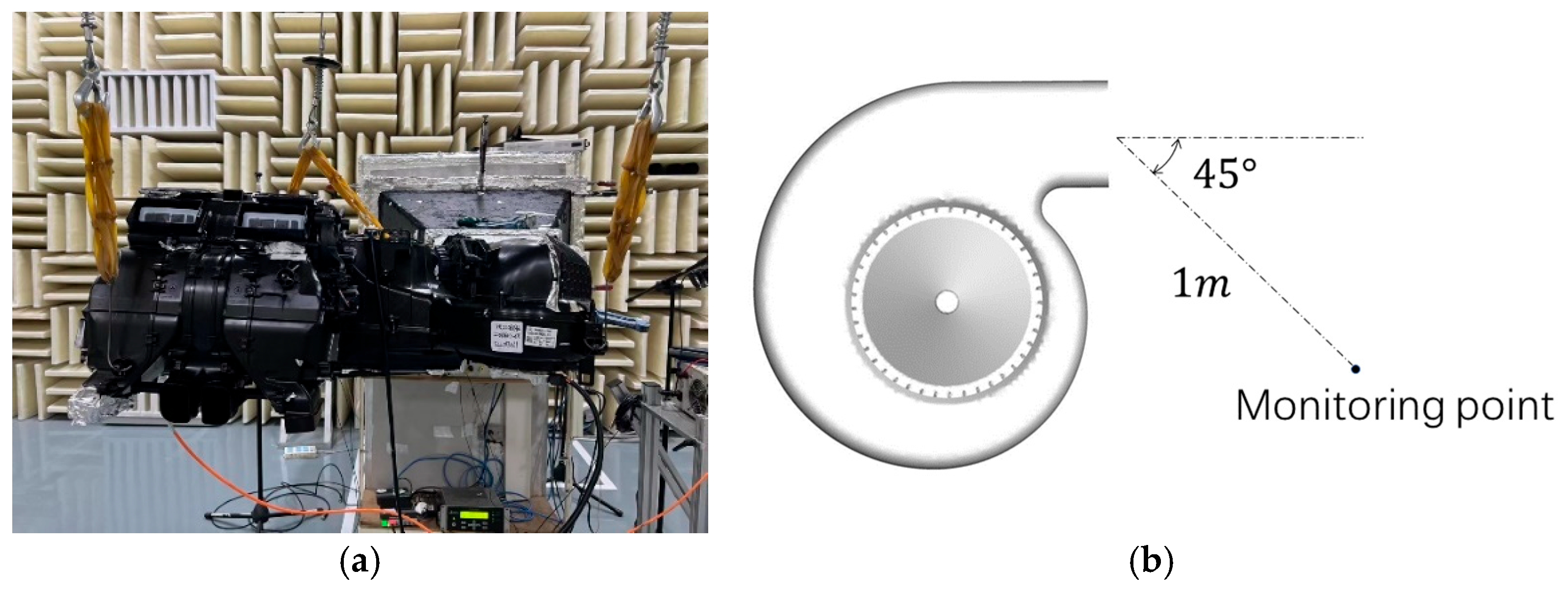
4.1. Reliability Verification of the Numerical Simulation
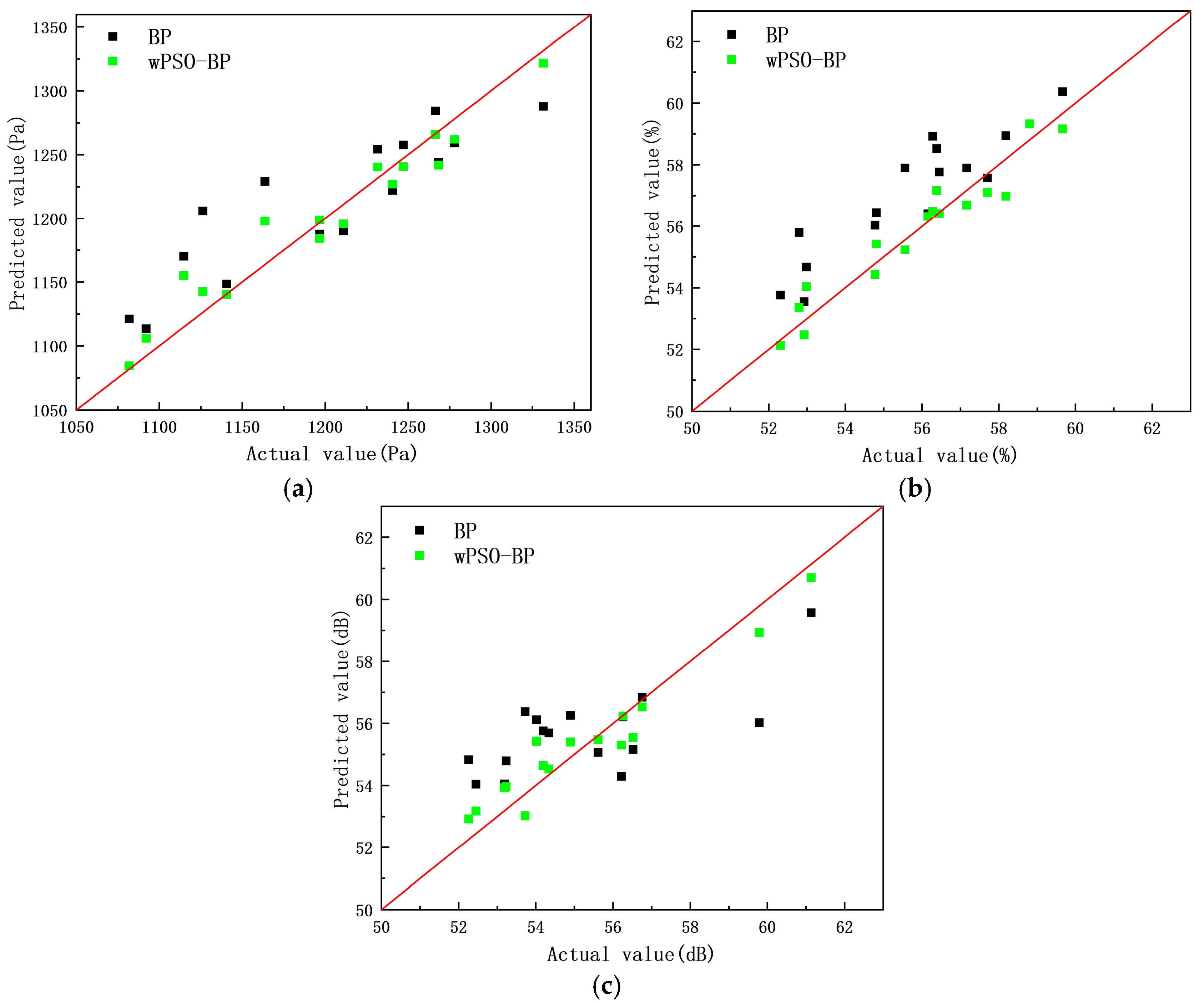
4.2. Prediction Model Results and Analysis
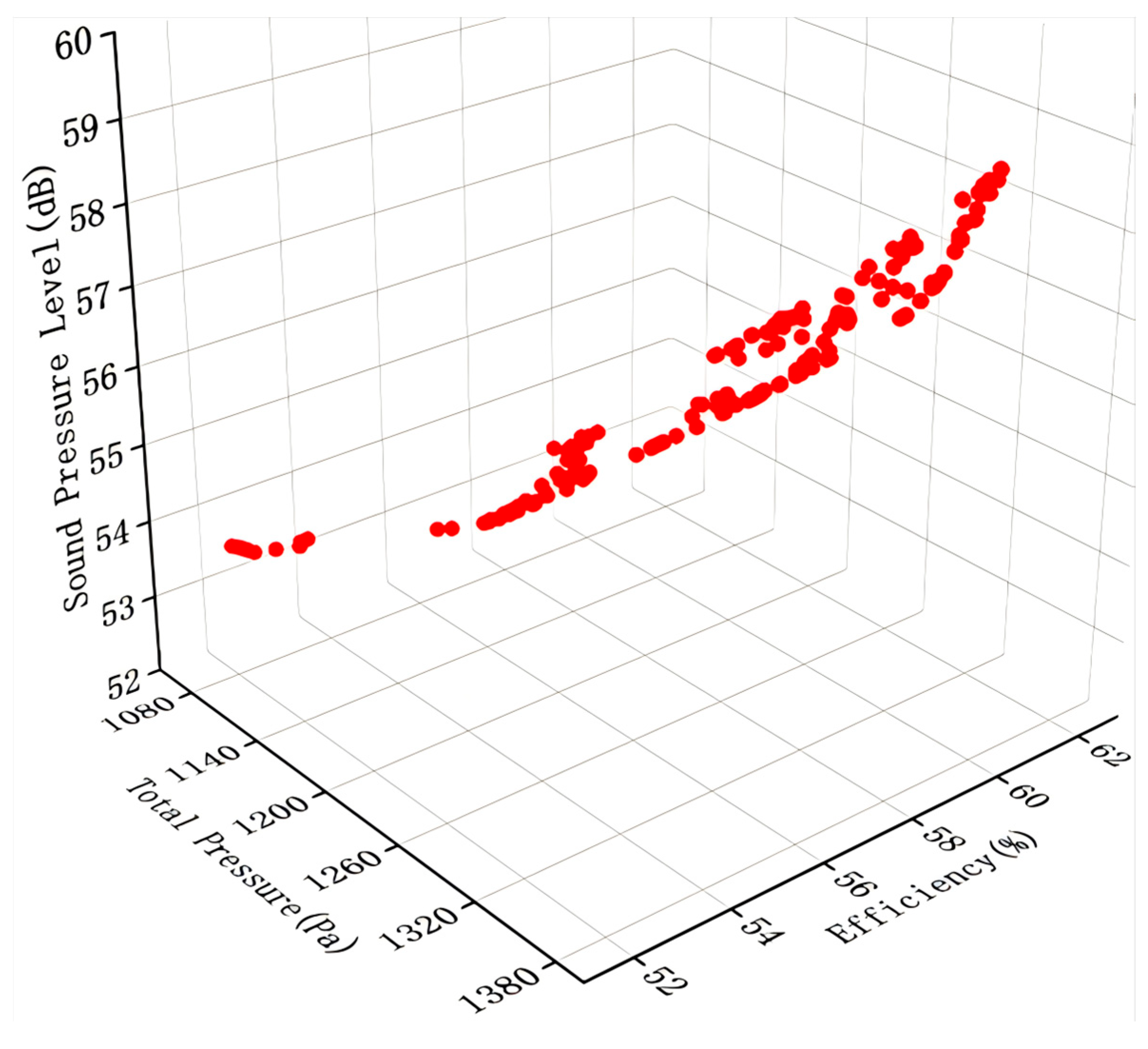
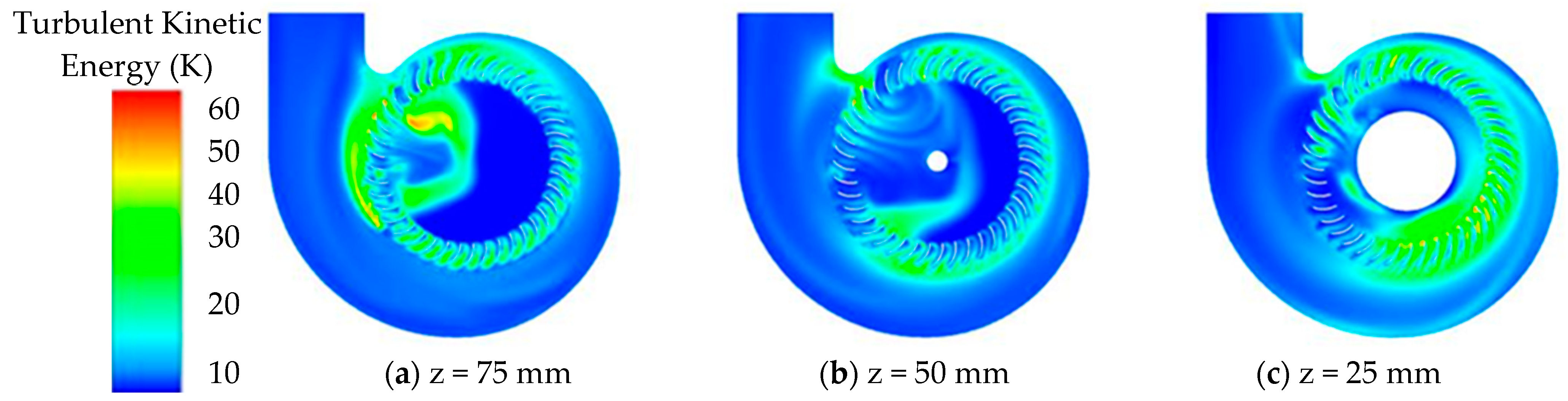
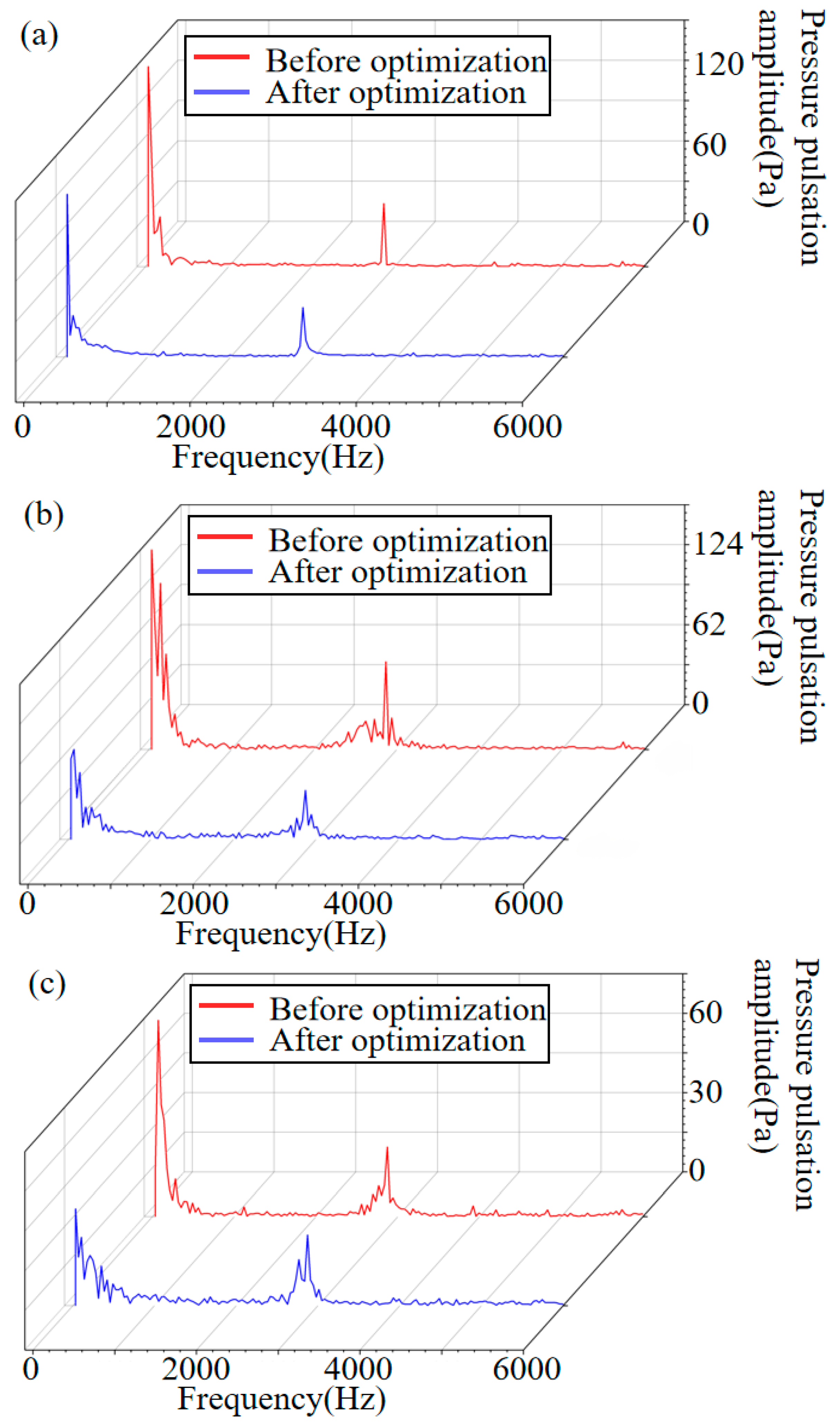
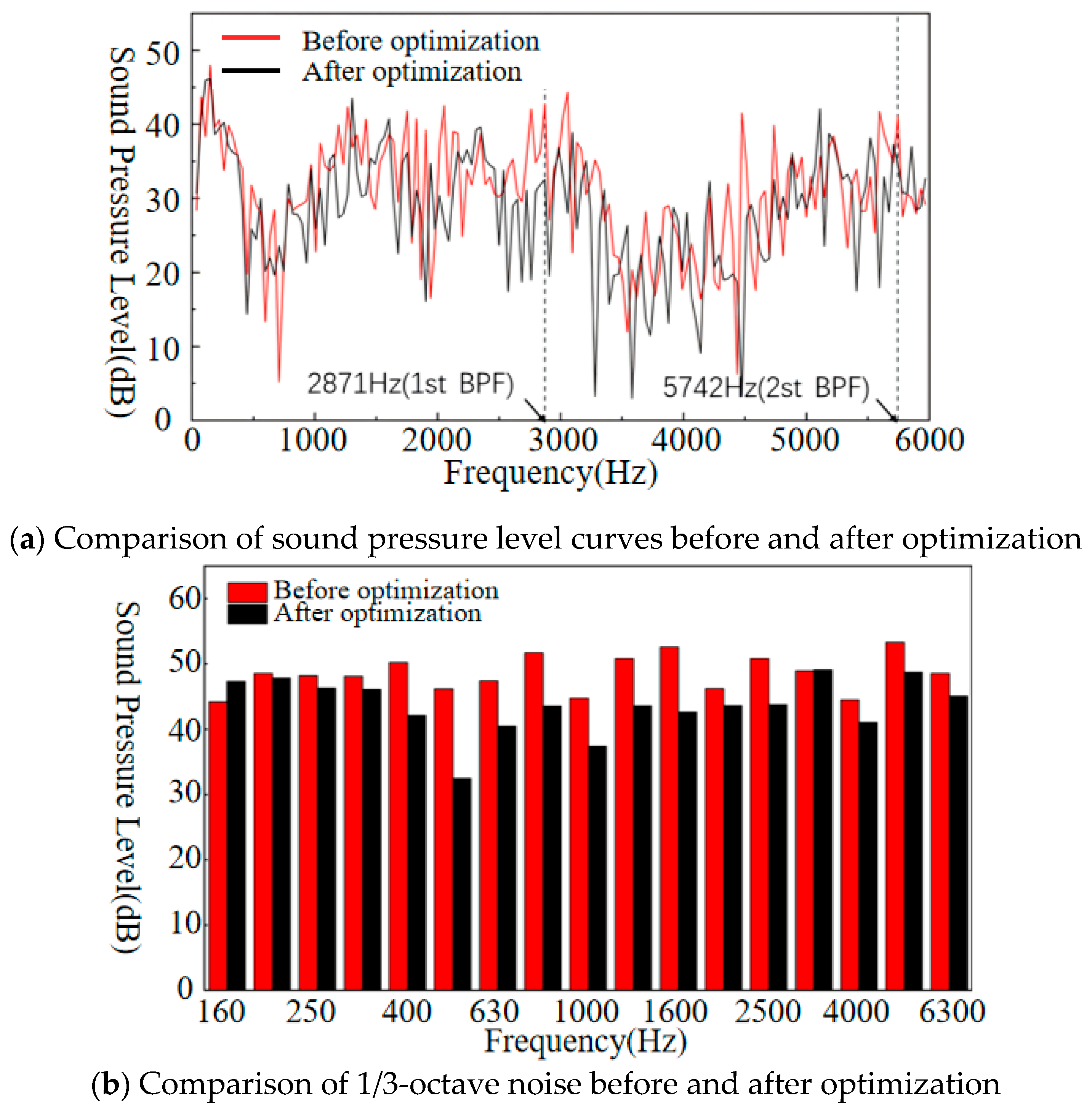
4.3. Optimization Results and Analysis
- Parameter initialization: 200 sets of initial samples are generated using the Latin hypercubic sampling technique and input into the wPSO-BP model for the prediction of full pressure (), efficiency (), and noise ();
- Pareto front search: the reference point stratification mechanism of NSGA-III is used to screen the non-dominated solutions, and the Logistic chaos mapping of LBWO is combined to enhance the global search capability.
5. Conclusions
- (a)
- A prediction model between design variables and optimization objectives called wPSO-BP is proposed and compared with the BP prediction model. The result indicates that wPSO-BP has a better effect.
- (b)
- A Logistic chaotic map is used for population initialization in beluga whale optimization (LBWO), and a multi-objective optimization algorithm is proposed based on NSGA-III and LBWO (NSGA-III-LBWO).
- (c)
- Based on the wPSO-BP prediction model and NSGA-III-LBWO, the prototype fan is optimized, and the result shows that the aerodynamic and noise performance of the fan improved, which provides a certain reference value for the optimization of multi-blade centrifugal fans.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamada, M.; Shimoyama, K.; Sato, F.; Washiashi, J.; Konishi, Y. Multi-objective design optimization of a high efficiency and low noise blower unit of a car air-conditioner. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2019, 233, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Lun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W. Effect of Volute-Tongue Clearance on the Aerodynamic Performance and Noise of Multi-Wing Centrifugal Fan for Air Conditioning. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2023, 16, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, W.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y. Reduction of aerodynamic noise of single-inlet centrifugal fan with inclined volute tongue. Meas. Control 2020, 53, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ming, P.; Lu, H. The aerodynamic and noise characteristics of centrifugal fan with partially tilted tongue. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 127113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, Y.; Lin, L.; He, H.; Ye, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wei, Y. Effects of vortex structure on performance characteristics of a multiblade fan with inclined tongue. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2019, 233, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, M. Effects of bionic volute tongue on aerodynamic performance and noise characteristics of centrifugal fan used in the air-conditioner. J. Bionic Eng. 2020, 17, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ju, Y.; Zhang, C. A quantitative evaluation method for impeller-volute tongue interaction and application to squirrel cage fan with bionic volute tongue. J. Fluids Eng. 2019, 141, 081104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dou, H.S.; Wei, Y.K.; Chen, X.P.; Chen, Y.N.; Cao, W.B. Effect of attack angle on flow characteristic of centrifugal fan. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 129, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Chang, T.; Lin, F. The influence of the blade outlet angle on the flow field and pressure pulsation in a centrifugal fan. Process 2020, 8, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Ryu, S.Y.; Cheong, C.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, K. Blade shape optimization of centrifugal fan for improving performance and reducing aerodynamic noise of clothes dryer. J. Acoust. Soc. Korea 2019, 38, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, F.; Zhang, X.; Chu, W. Numerical Investigation of Effect of Blade Surface Slot on the Performance and Flow Field of a Low Speed Centrifugal Fan. In Proceedings of the Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, London, UK, 22–26 June 2020; Volume 84102, p. V02ET39A011. [Google Scholar]
- Ch, S.V.; Anantharaman, K.; Rajasekaran, G. Effect of blade number on the performance of centrifugal fan. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 72, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Prezelj, J.; Novaković, T. Centrifugal fan with inclined blades for vacuum cleaner motor. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 140, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Heo, S.; Cheong, C.; Kim, T.H.; Jung, J. Performance/noise optimization of centrifugal fan using response surface method. Trans. Korean Soc. Mech. Eng. A 2017, 41, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Chu, W.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Y. Vibroacoustic optimization study for the volute casing of a centrifugal fan. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamberger, K.; Carolus, T.; Belz, J.; Nelles, O. Development, validation, and application of an optimization scheme for impellers of centrifugal fans using computational fluid dynamics-trained metamodels. J. Turbomach. 2020, 142, 111005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Aerodynamic Optimization of a Centrifugal Fan Using Response Surface Methodology. Open J. Fluid Dyn. 2019, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, L.; Ming, W.; Zhang, H. Aerodynamics optimization of multi-blade centrifugal fan based on extreme learning machine surrogate model and particle swarm optimization algorithm. Metals 2023, 13, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avşar, G.; Ezertaş, A.A.; Başkan Perçin, Ö. Aerodynamic Design and Performance Optimization of a Centrifugal Fan Impeller. In Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: Boston, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 87110, p. V13DT34A008. [Google Scholar]
- Salaria, U.A.; Menhas, M.I.; Manzoor, S. Quasi Oppositional Population Based Global Particle Swarm Optimizer With Inertial Weights (QPGPSO-W) for Solving Economic Load Dispatch Problem. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 134081–134095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Li, G.; Meng, Z. Beluga whale optimization: A novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 251, 109215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, M.; Duhan, M. Levy flights in metaheuristics optimization algorithms–a review. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 32, 802–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, N.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Li, C. Chaos-enhanced synchronized bat optimizer. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 77, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y. 2D logistic-modulated-sine-coupling-logistic chaotic map for image encryption. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 14081–14098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, K. Nonlinear Multiobjective Optimization; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Jain, H. An Evolutionary Many-Objective Optimization Algorithm Using Reference-Point-Based Nondominated Sorting Approach, Part I: Solving Problems With Box Constraints. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2014, 18, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Liao, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y. Co-Evolutionary NSGA-III with deep reinforcement learning for multi-objective distributed flexible job shop scheduling. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 203, 110990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palakonda, V.; Mallipeddi, R. Pareto dominance-based algorithms with ranking methods for many-objective optimization. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 11043–11053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Nakayama, M.K. Quantile estimation with Latin hypercube sampling. Oper. Res. 2017, 65, 1678–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordanis, I.; Koukouvinos, C.; Silou, I. On the efficacy of conditioned and progressive Latin hypercube sampling in supervised machine learning. Appl. Numer. Math. 2025, 208, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





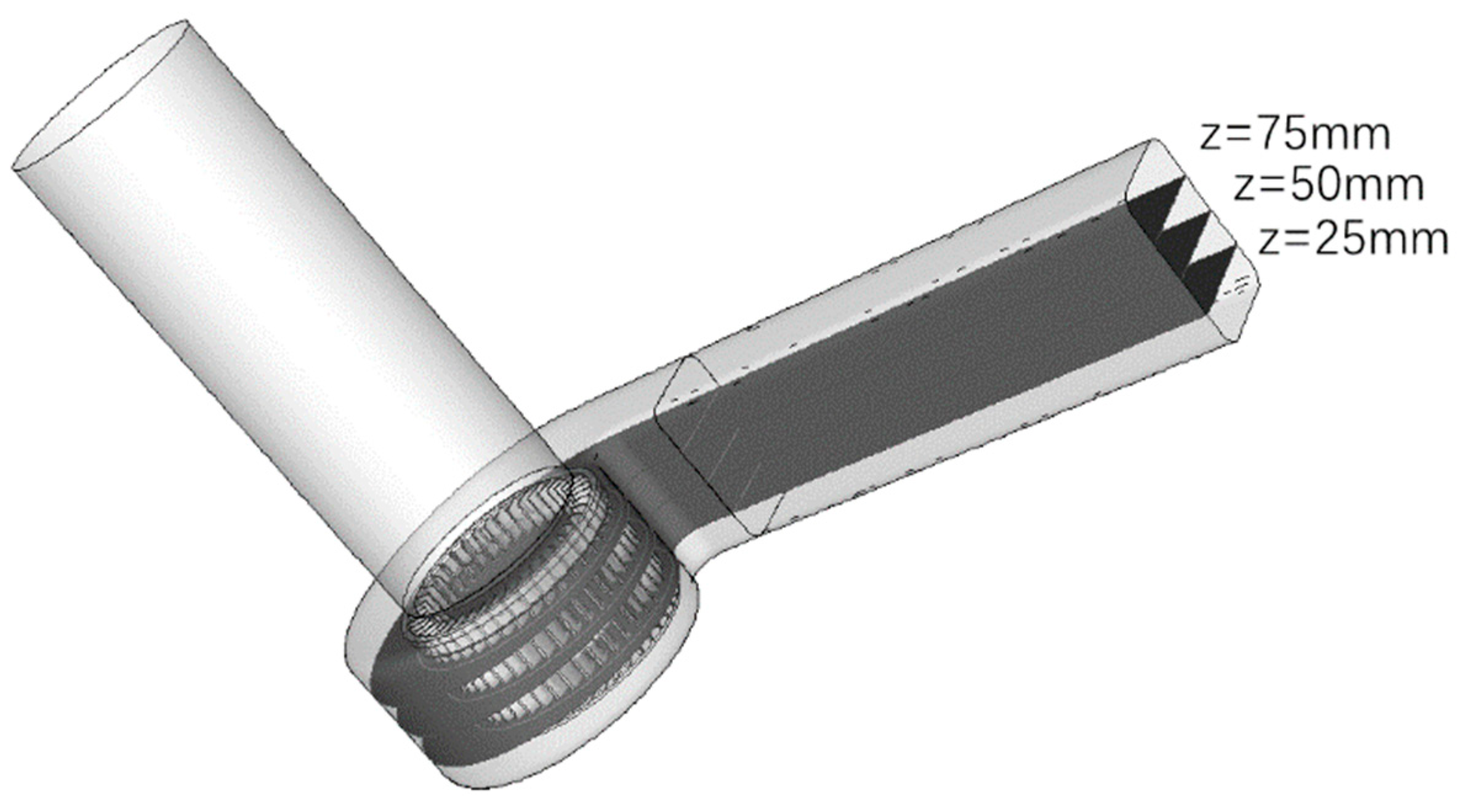
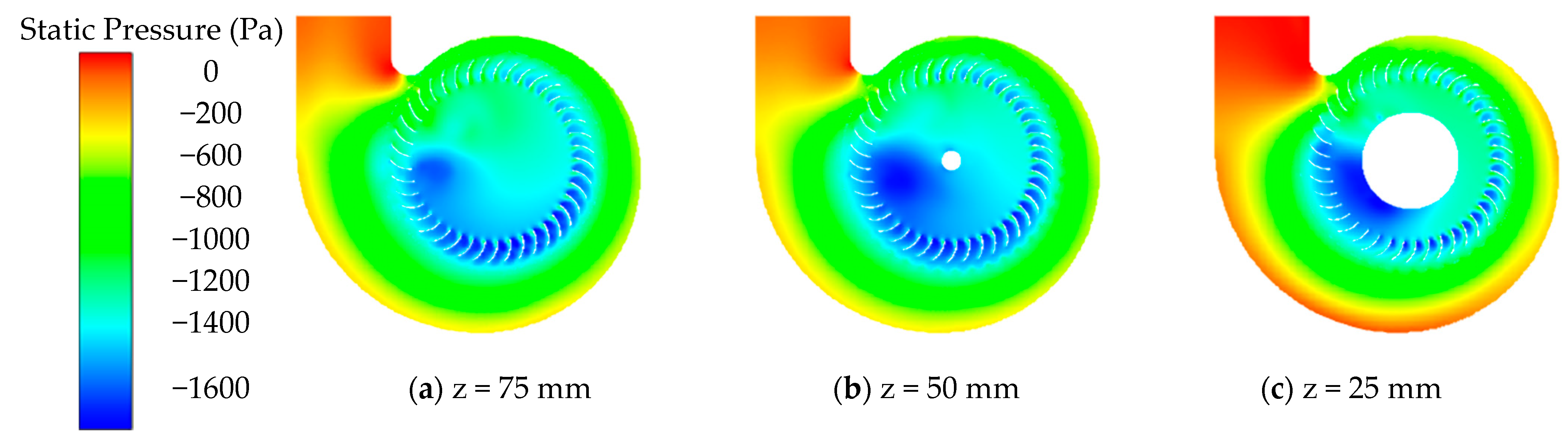
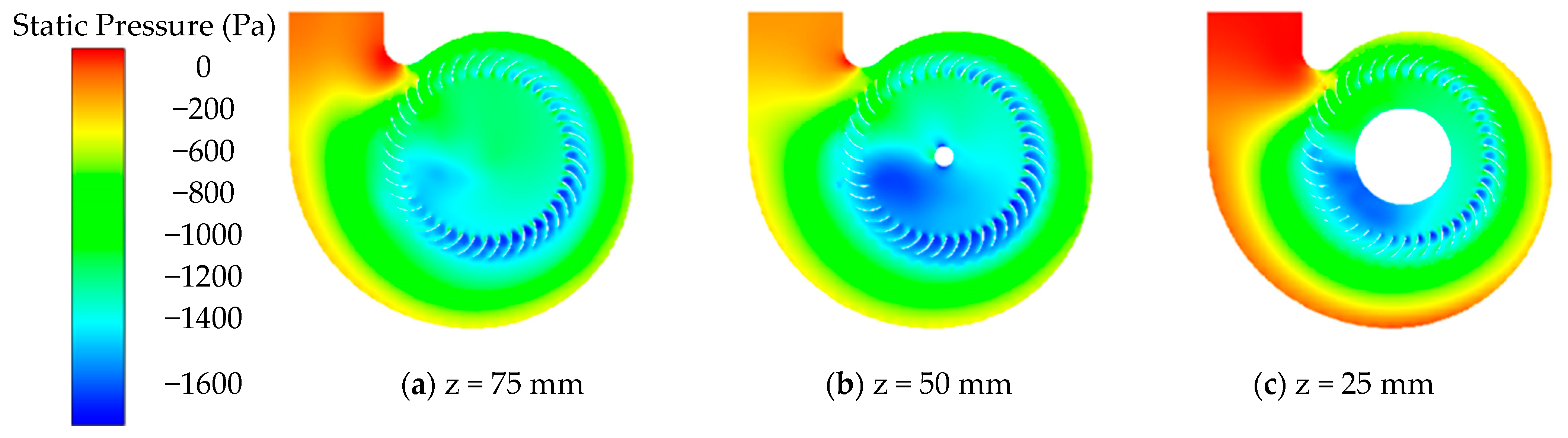
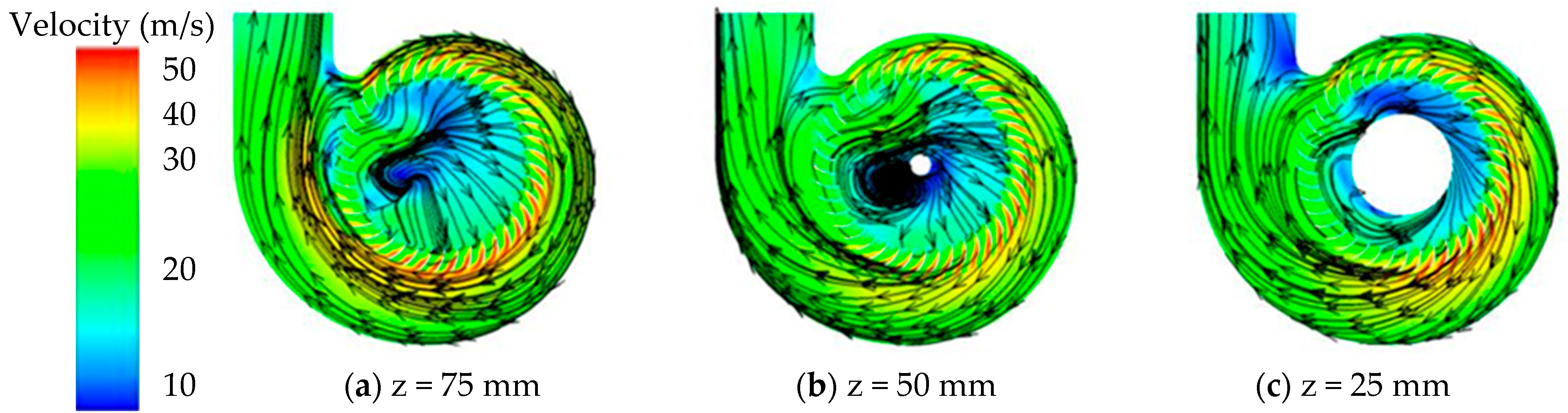


| Category | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Parameters | Blade inlet angle | 90° |
| Blade outlet angle | 139° | |
| Volute tongue radius | 13 mm | |
| Number of blades | 41 | |
| Operational Parameters | Impeller speed | 4202 r/min |
| Rated flow rate | 500 m3/h |
| Parameter | Symbol | Boundary Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Blade Inlet Angle | 80°~115° | |
| Blade Outlet Angle | 129°~149° | |
| Volute Tongue Radius | 16 mm~25 mm | |
| Blade Tip Chamfer Angle | 10°~40° |
| Category | LBWO | NSGA-III | NSGA-III-LBWO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Logistic chaotic initialization + Levy flight search | Non-dominated sorting + Reference point mechanism | Hybrid of LBWO and NSGA-III, dynamically generates Pareto offspring |
| Advantages | 1. Strong global search 2. High population diversity | 1. High-dimensional multi-objective optimization 2. Uniform solution distribution | 1. Global–local balance 2. High-quality solutions (verified in engineering applications) |
| Limitations | Single-objective, prone to local optima | Slow convergence, weak local search | Parameter sensitivity, moderate computational cost |
| Summary | NSGA-III-LBWO integrates the global search capability of single-target LBWO and the diversity maintenance mechanism of multi-target NSGA-III, realizing the complementary advantages of both. | ||
| Design Variables | Optimization Objectives | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.72 | 141.49 | 23.65 | 13.25 | 1237.46 | 56.48 | 56.39 |
| 100.57 | 143.81 | 19.53 | 28.7 | 1268.53 | 57.4 | 56.73 |
| 102.94 | 133.66 | 17.93 | 22.98 | 1175.38 | 55.18 | 55.85 |
| 102.28 | 141.84 | 19.86 | 14.79 | 1226.4 | 55.47 | 55.63 |
| 82.98 | 132.66 | 24.39 | 33.03 | 1183.22 | 57.77 | 56.77 |
| 104.52 | 129.22 | 19.25 | 14.45 | 1074.04 | 52.91 | 53.87 |
| 93.33 | 135.77 | 19.04 | 38.95 | 1168.31 | 56.46 | 54.11 |
| 93.83 | 131.69 | 19.39 | 34.81 | 1114.82 | 52.79 | 52.26 |
| 84.12 | 135.42 | 20.68 | 16.18 | 1223.67 | 59.41 | 56.83 |
| 93.19 | 146.36 | 23.73 | 34.01 | 1314.61 | 59.05 | 57.64 |
| Model | RMSE | MAE | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total pressure | BP | 35.82 | 29.18 | 0.74 |
| wPSO-BP | 17.74 | 13.74 | 0.93 | |
| Efficiency | BP | 2.30 | 1.71 | <0 |
| wPSO-BP | 0.58 | 0.50 | 0.92 | |
| Sound pressure level | BP | 1.81 | 1.56 | 0.43 |
| wPSO-BP | 0.70 | 0.61 | 0.91 |
| Prototype fan | 90 | 139 | 12.87 | 0 | 1275.89 | 60.07 | 57.75 |
| Optimized fan | 98.81 | 147.06 | 17.47 | 39.85 | 1310.68 | 60.74 | 56.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, W.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Zhou, M.; Huang, Q. Optimization Design of Multi-Blade Centrifugal Fan Based on Variable Weight PSO-BP Prediction Model and Multi-Objective Beluga Optimization Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115950
Jin W, Wang J, Li J, Xu R, Zhou M, Huang Q. Optimization Design of Multi-Blade Centrifugal Fan Based on Variable Weight PSO-BP Prediction Model and Multi-Objective Beluga Optimization Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115950
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Wenyang, Jiaxuan Wang, Junyu Li, Ren Xu, Ming Zhou, and Qibai Huang. 2025. "Optimization Design of Multi-Blade Centrifugal Fan Based on Variable Weight PSO-BP Prediction Model and Multi-Objective Beluga Optimization Algorithm" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115950
APA StyleJin, W., Wang, J., Li, J., Xu, R., Zhou, M., & Huang, Q. (2025). Optimization Design of Multi-Blade Centrifugal Fan Based on Variable Weight PSO-BP Prediction Model and Multi-Objective Beluga Optimization Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5950. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115950







