Facilitation of the Kinetics of Alkaline Water Electrolysis on Polycrystalline Nickel Electrode by Introduction of Acetone to 0.1 M NaOH Working Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
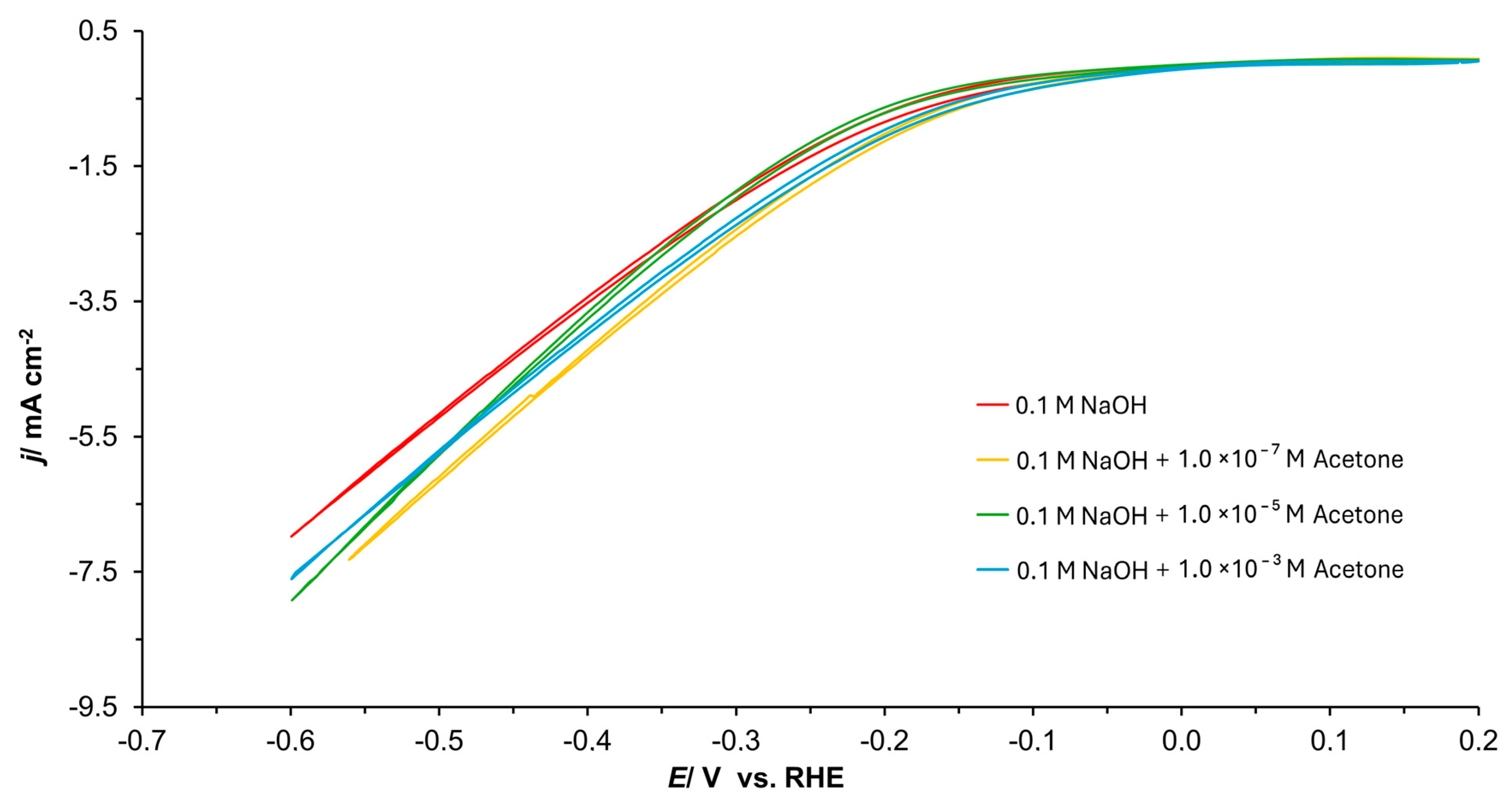
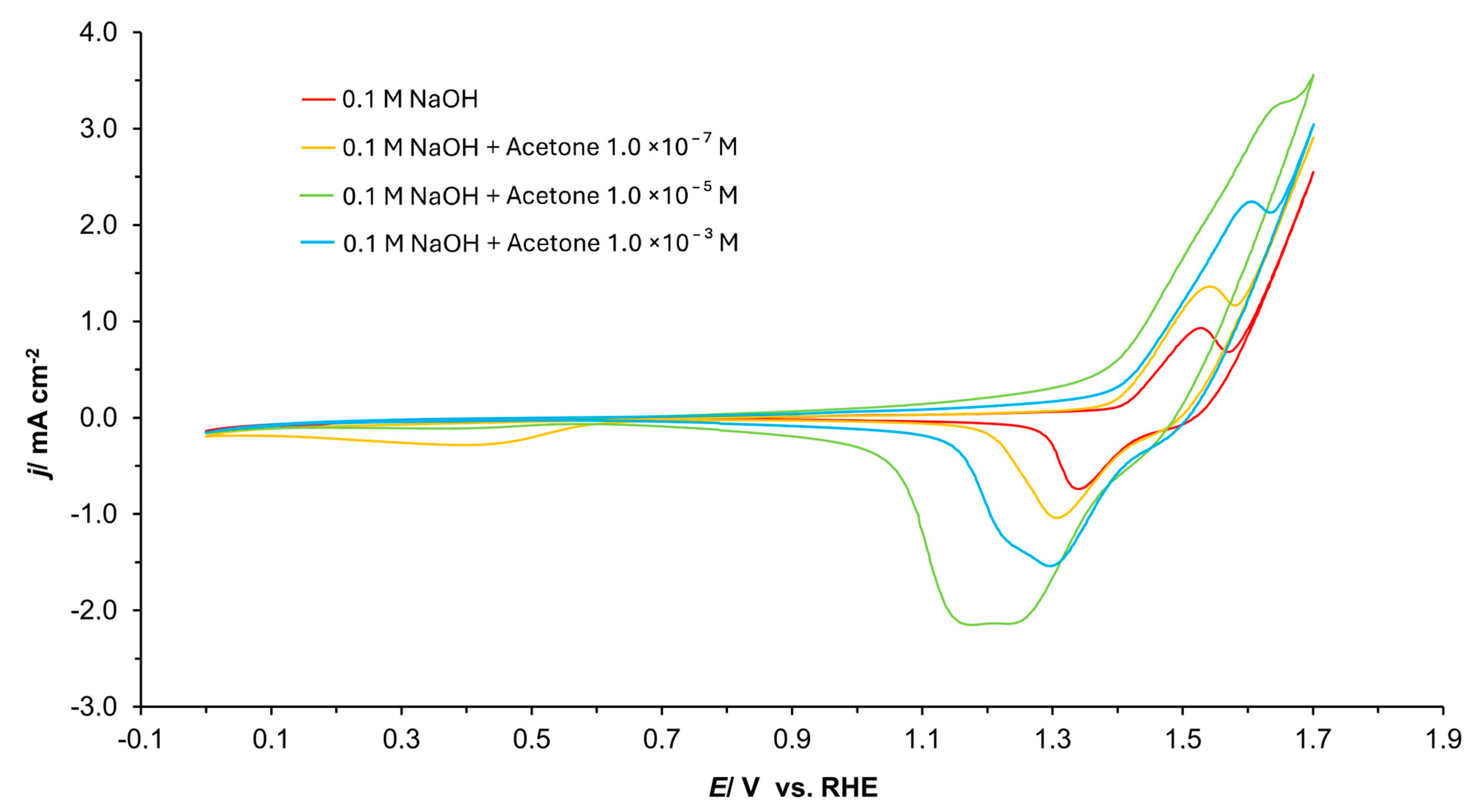
3.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
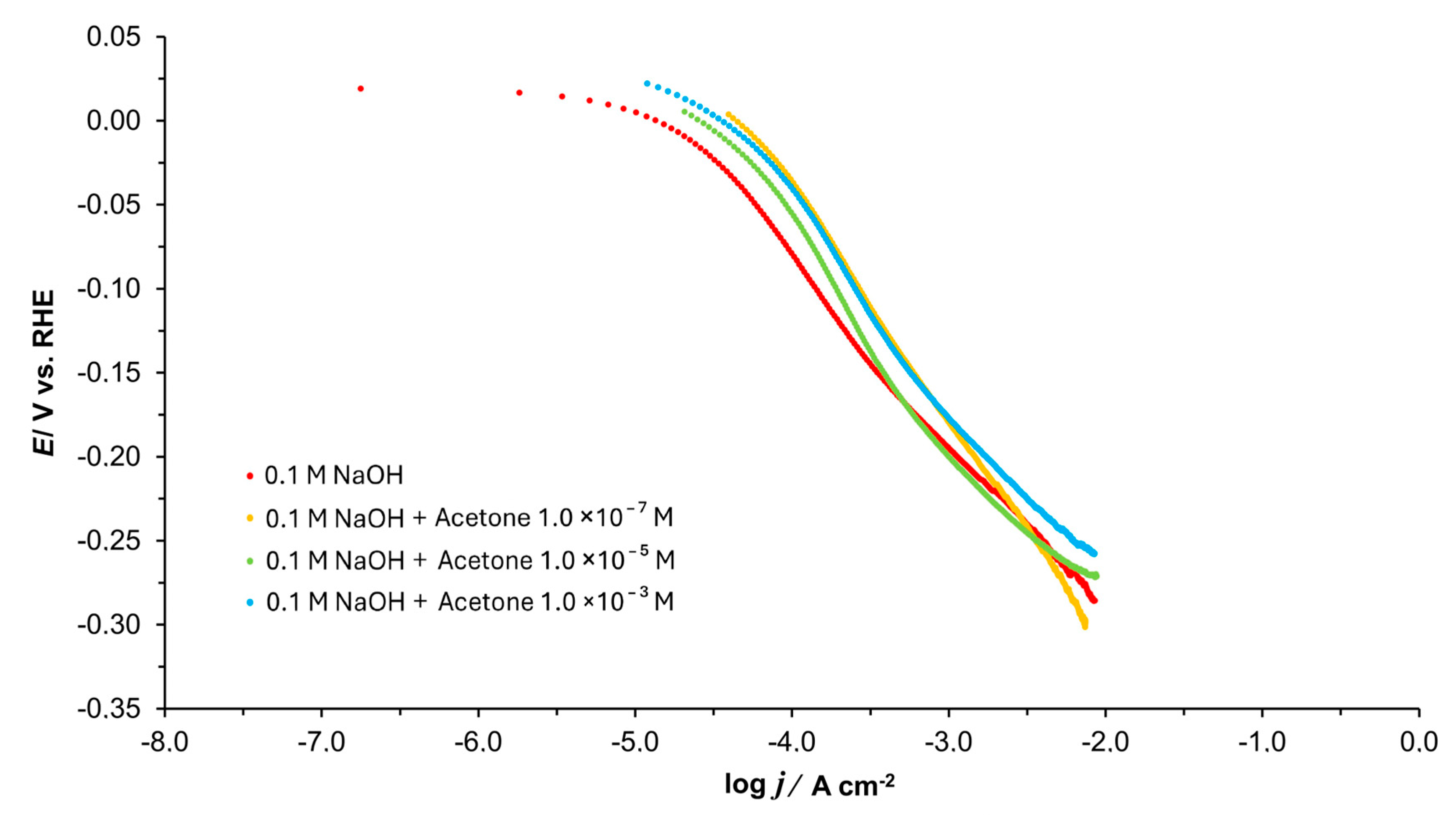
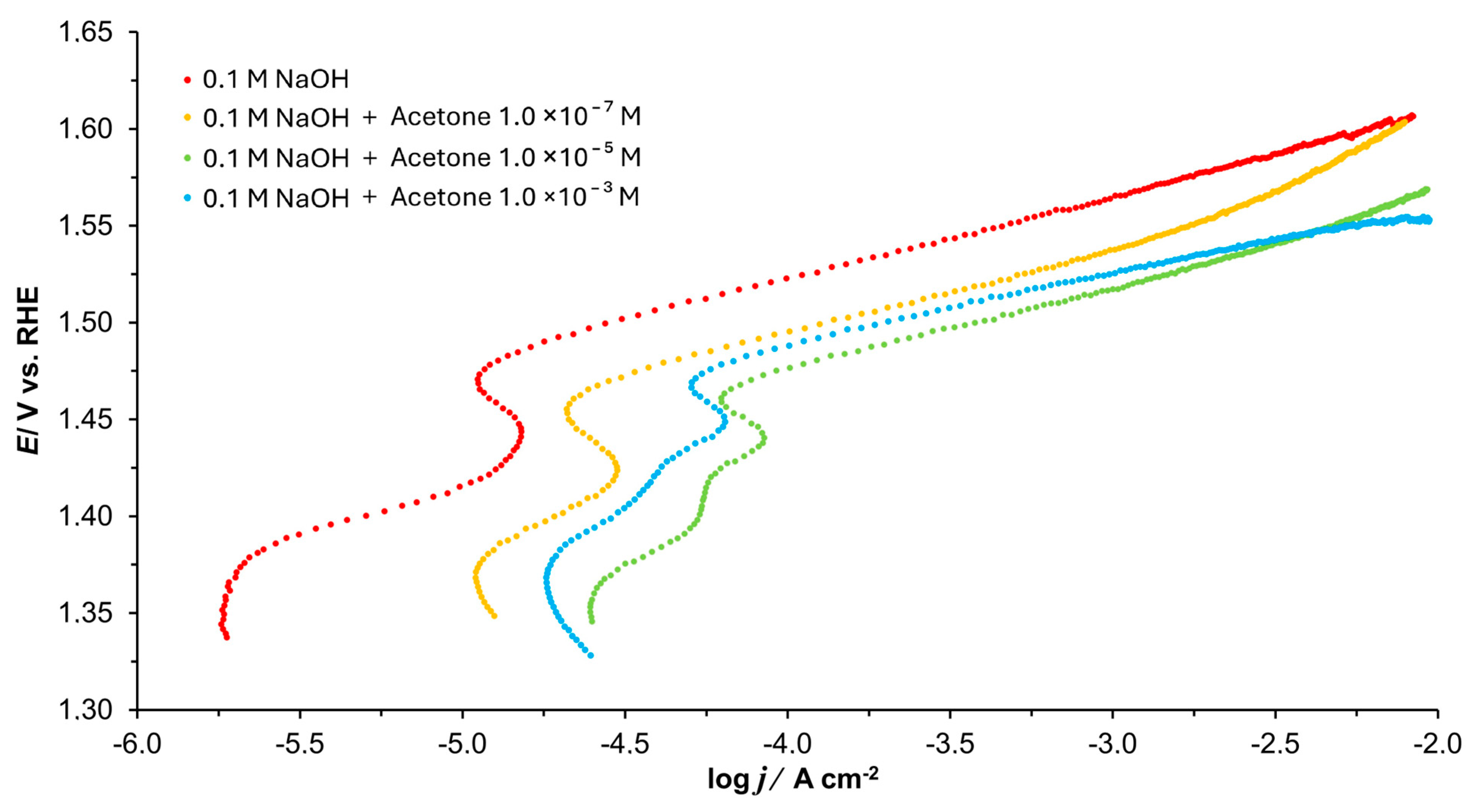
3.2. Tafel Polarization Plots
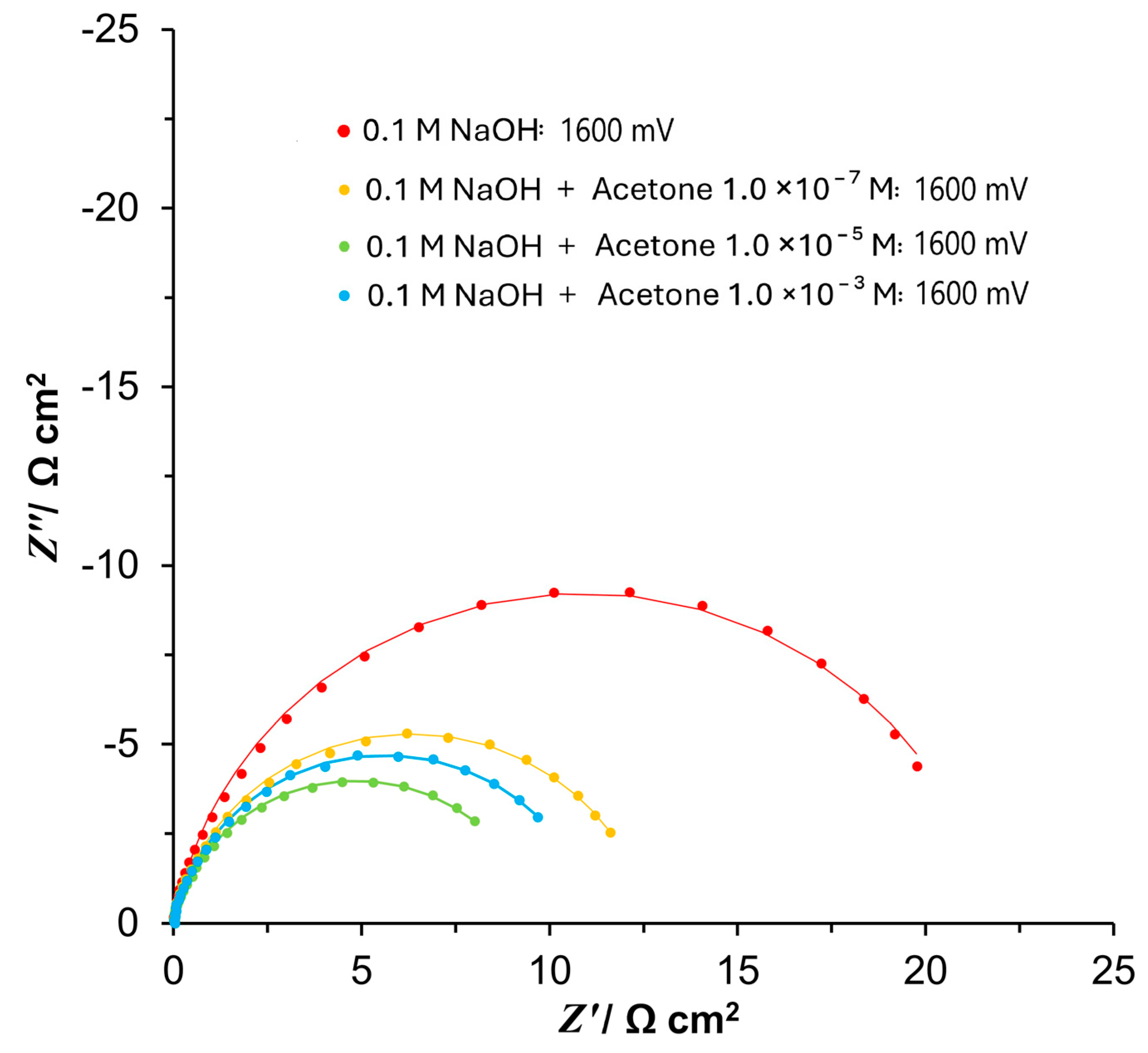
3.3. Ac. Impedance Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, S.P. High-Entropy Materials for Water Electrolysis. Energy Technol. 2022, 10, 2200573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Shi, R.; Jiao, K.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, J.; et al. Hydrogen Society: From Present to Future. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 4926–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.M.F.; Sequeira, C.A.C.; Figueiredo, J.L. Hydrogen Production by Alkaline Water Electrolysis. Quim. Nova 2013, 36, 1176–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Murawski, J.; Shinde, D.V.; Stephens, I.E.L.; Hinds, G.; Smith, G. Impact of Impurities on Water Electrolysis: A Review. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 1565–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwe, S.; Mei, B.; Masa, J.; Schuhmann, W.; Ventosa, E. Overcoming Cathode Poisoning from Electrolyte Impurities in Alkaline Electrolysis by Means of Self-Healing Electrocatalyst Films. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.; Ahn, Y.H. Alkaline Electrolysis of Wastewater and Low-Quality Water. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, R.; Ferre-Vilaplana, A.; Herrero, E.; Feliu, J.M. Ethanol Electro-oxidation Reaction Selectivity on Platinum in Aqueous Media. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 4960–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigier, F.; Coutanceau, C.; Hahn, F.; Belgsir, E.M.; Lamy, C. On the Mechanism of Ethanol Electro-oxidation on Pt and PtSn Catalysts: Electrochemical and in situ IR Reflectance Spectroscopy Studies. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 563, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondue, C.J.; Calle-Vallejo, F.; Figueiredo, M.C.; Koper, M.T.M. Structural Principles to Steer the Selectivity of the Electrocatalytic Reduction of Aliphatic Ketones on Platinum. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekazni, D.S.; Arán-Ais, R.M.; Feliu, J.M.; Herrero, E. Understanding the Electrochemical Hydrogenation of Acetone on Pt Single Crystal Electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 922, 116697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondue, C.J.; Koper, M.T.M. Electrochemical Reduction of the Carbonyl Functional Group: The Importance of Adsorption Geometry, Molecular Structure, and Electrode Surface Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 12071–12078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierozynski, B. Electrochemical Behaviour of Urea at Pt(111) Single-Crystal Surface in 0.1 M NaOH. Electrocatalysis 2013, 4, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, S.; Kahl, H.; Winkelmann, J. Surface Tension of the Ternary System Water + Acetone + Toluene. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, K.S.; McAllister, R.A. Surface Tension of Acetone-water Solutions Up to Their Normal Boiling Points. AIChE J. 1957, 3, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Ouyang, S. Effect of Hydrogen Bonding on the Surface Tension Properties of Binary Mixture (Acetone-Water) by Raman Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamicka, A.; Mikołajczyk, T.; Kuczyński, M.; Pierożyński, B. The Influence of Acetone on the Kinetics of Water Electrolysis Examined at Polycrystalline Pt Electrode in Alkaline Solution. Catalysts 2024, 14, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R. Impedance Spectroscopy, Emphasizing Solid Materials and Systems; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 1–368. ISBN 0-471-83122-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, E.B.; Tahmasebi, S.; Jerkiewicz, G. On the Catalytic Activity and Corrosion Behavior of Polycrystalline Nickel in Alkaline Media in the Presence of Neutral and Reactive Gases. Electrocatalysis 2021, 12, 146–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, F.; Faid, A.Y.; Sunde, S.; Pollet, B.G. Sonoactivated polycrystalline Ni electrodes for alkaline oxygen evolution reaction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 86, 106013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slis, A.; Mikolajczyk, T.; Pierozynski, B. Influence of Electrooxidation of Ni Wire Electrodes on the Kinetics of Oxygen Evolution Reaction Studied in 0.1 mol dm−3 NaOH. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, R.; Wu, H.; Wang, G.; Cao, D. Poisoning of acetone to Pt and Au electrodes for electrooxidation of 2-propanol in alkaline medium. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 76, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Kumper, J.; Kumari, S.; Heiming, N.; Murtz, S.D.; Steinmann, S.N.; Palkovitz, S.; Palkovitz, R.; Sautet, P. Probing the Electric Double-Layer Capacitance to Understand the Reaction Environment in Conditions of Electrochemical Amination of Acetone. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 4087–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, M.F.; Mridha, M.S. Electrochemical Studies of the Nickel Electrode for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1996, 21, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, F. Investigation of oxygen evolution reaction kinetic process and kinetic parameters on iridium electrode by electrochemistry impedance spectroscopy analysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 871, 114281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierozynski, B.; Mikolajczyk, T.; Kowalski, I.M. Hydrogen evolution at catalytically-modified nickel foam in alkaline solution. J. Power Sources 2014, 271, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierozynski, B.; Smoczynski, L. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Nickel-Coated Carbon Fiber Materials in Various Electrolytic Media. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, C427–C436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierozynski, B.; Kowalski, I.M. Electrochemical reactivity of formamidoxime on Pt(111) and (100) single-crystal surfaces in 0.1 M NaOH solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 662, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
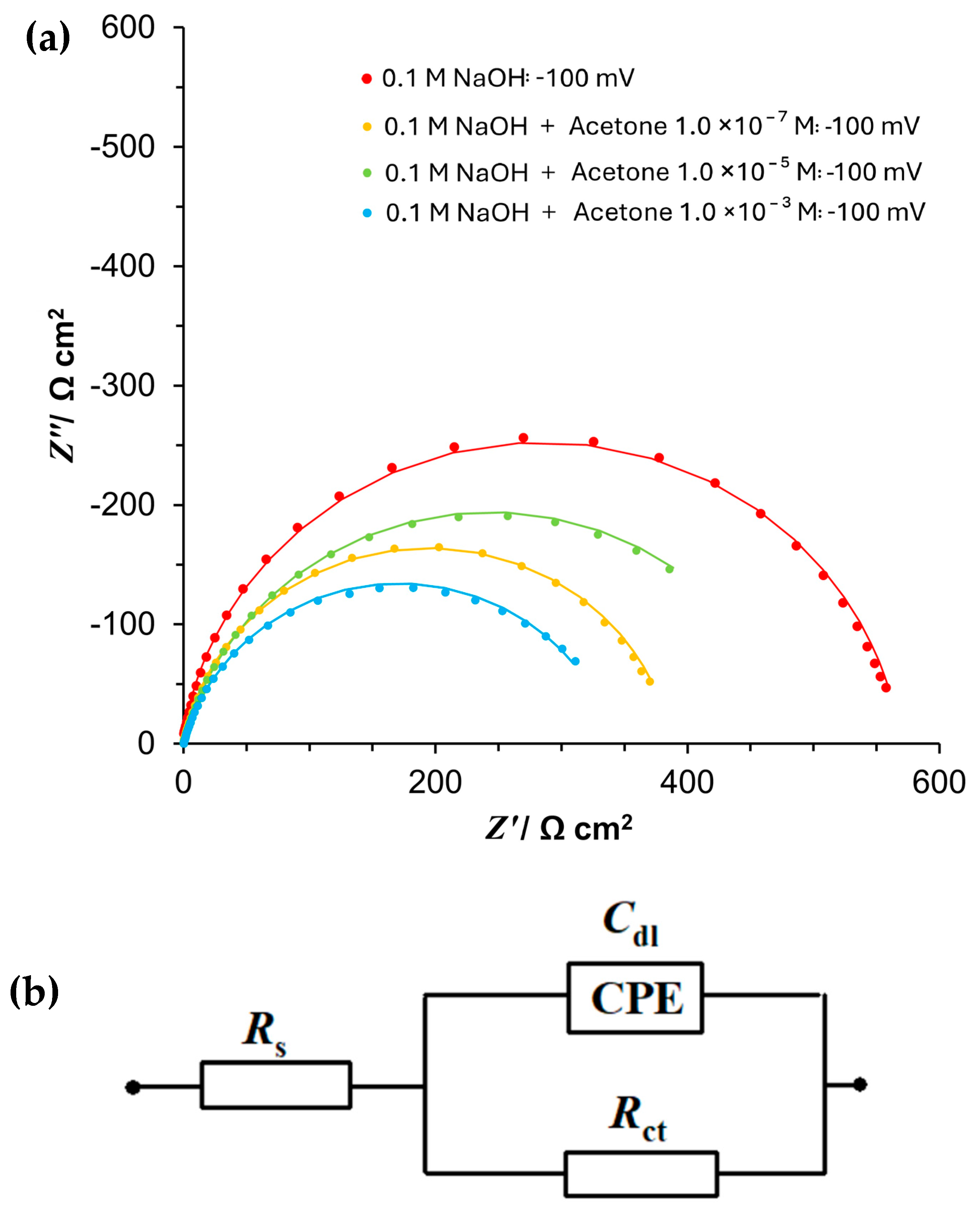
| 0.1 M NaOH | ||
|---|---|---|
| E/mV | Rct/Ω cm2 | Cdl/μF cm−2 |
| −50 | 1076.2 ± 3.7 | 217.5 ± 1.3 |
| −100 | 567.3 ± 1.4 | 179.3 ± 1.2 |
| −150 | 227.8 ± 0.9 | 159.1 ± 1.9 |
| −200 | 80.7 ± 0.3 | 132.2 ± 2.5 |
| −250 | 36.5 ± 0.1 | 120.2 ± 2.5 |
| −300 | 22.6 ± 0.1 | 113.8 ± 3.0 |
| −350 | 15.3 ± 0.1 | 108.2 ± 2.7 |
| −400 | 11.5 ± 0.0 | 89.3 ± 2.6 |
| −450 | 9.3 ± 0.0 | 89.9 ± 3.3 |
| −500 | 7.7 ± 0.0 | 85.1 ± 0.0 |
| 0.1 M NaOH + 1.0 × 10−7 M acetone | ||
| −50 | 502.0 ± 1.5 | 321.5 ± 1.0 |
| −100 | 349.0 ± 1.4 | 277.8 ± 2.2 |
| −150 | 162.1 ± 0.5 | 250.2 ± 2.3 |
| −200 | 76.2 ± 0.2 | 213.0 ± 2.7 |
| −250 | 31.3 ± 0.1 | 182.0 ± 3.6 |
| −300 | 20.2 ± 0.1 | 138.1 ± 3.7 |
| −350 | 13.9 ± 0.1 | 129.9 ± 5.1 |
| −400 | 10.0 ± 0.1 | 130.4 ± 6.4 |
| −450 | 7.8 ± 0.1 | 119.3 ± 6.6 |
| −500 | 7.4 ± 0.1 | 111.0 ± 1.3 |
| 0.1 M NaOH + 1.0 × 10−5 M acetone | ||
| −50 | 613.4 ± 3.3 | 338.9 ± 1.7 |
| −100 | 482.4 ± 0.9 | 266.8 ± 0.9 |
| −150 | 239.0 ± 0.7 | 205.6 ± 1.5 |
| −200 | 104.4 ± 0.4 | 142.2 ± 2.2 |
| −250 | 44.1 ± 0.2 | 95.8 ± 2.9 |
| −300 | 29.3 ± 0.2 | 84.8 ± 3.7 |
| −350 | 17.5 ± 0.1 | 66.8 ± 3.2 |
| −400 | 11.4 ± 0.1 | 66.3 ± 3.4 |
| −450 | 8.7 ± 0.1 | 72.9 ± 3.5 |
| −500 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 57.1 ± 0.3 |
| 0.1 M NaOH + 1.0 × 10−3 M acetone | ||
| −50 | 430.1 ± 4.2 | 371.3 ± 4.1 |
| −100 | 341.1 ± 1.2 | 318.7 ± 2.4 |
| −150 | 189.2 ± 0.3 | 213.3 ± 1.2 |
| −200 | 80.6 ± 0.4 | 138.0 ± 2.6 |
| −250 | 40.2 ± 0.3 | 119.1 ± 3.7 |
| −300 | 23.4 ± 0.2 | 94.9 ± 4.2 |
| −350 | 11.8 ± 0.1 | 84.1 ± 4.3 |
| −400 | 12.2 ± 0.1 | 58.4 ± 4.2 |
| −450 | 8.1 ± 0.1 | 53.3 ± 4.5 |
| −500 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 57.4 ± 1.0 |
| 0.1 M NaOH | ||
|---|---|---|
| E/mV | Rct/Ω cm2 | Cdl/μF cm−2 |
| 1550 | 74.1 ± 0.6 | 2406.8 ± 23.3 |
| 1600 | 21.5 ± 0.1 | 2217.8 ± 26.2 |
| 1650 | 11.2 ± 0.0 | 2182.0 ± 26.7 |
| 1700 | 7.4 ± 0.0 | 2220.5 ± 29.7 |
| 1750 | 5.5 ± 0.0 | 2274.6 ± 34.3 |
| 1800 | 4.3 ± 0.0 | 2178.1 ± 67.4 |
| 1850 | 3.6 ± 0.0 | 2215.5 ± 59.0 |
| 1900 | 3.1 ± 0.0 | 2423.7 ± 20.2 |
| 1950 | 2.6 ± 0.0 | 2167.4 ± 70.2 |
| 2000 | 2.4 ± 0.0 | 2412.6 ± 129.2 |
| 0.1 M NaOH + 1.0×10−7 M acetone | ||
| 1550 | 28.5 ± 0.3 | 3959.7 ± 59.4 |
| 1600 | 12.7 ± 0.1 | 3774.8 ± 39.6 |
| 1650 | 8.4 ± 0.0 | 3909.2 ± 67.4 |
| 1700 | 5.3 ± 0.0 | 4143.2 ± 76.5 |
| 1750 | 4.3 ± 0.0 | 4334.3 ± 82.3 |
| 1800 | 3.4 ± 0.0 | 4345.0 ± 169.3 |
| 1850 | 3.0 ± 0.0 | 4353.7 ± 216.6 |
| 1900 | 2.5 ± 0.0 | 4316.0 ± 125.6 |
| 1950 | 2.5 ± 0.0 | 4039.5 ± 182.5 |
| 2000 | 2.3 ± 0.0 | 4795.0 ± 242.6 |
| 0.1 M NaOH + 1.0 × 10−5 M acetone | ||
| 1550 | 19.6 ± 0.1 | 7897.5 ± 37.2 |
| 1600 | 10.0 ± 0.1 | 7855.6 ± 77.3 |
| 1650 | 6.8 ± 0.0 | 7918.5 ± 115.7 |
| 1700 | 4.8 ± 0.0 | 7442.3 ± 109.0 |
| 1750 | 3.9 ± 0.0 | 7932.6 ± 209.6 |
| 1800 | 3.3 ± 0.0 | 8871.9 ± 188.8 |
| 1850 | 2.8 ± 0.0 | 8536.7 ± 266.0 |
| 1900 | 2.4 ± 0.0 | 9459.6 ± 213.2 |
| 1950 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 9268.2 ± 840.0 |
| 2000 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 6252.8 ± 640.5 |
| 0.1 M NaOH + 1.0 × 10−3 M acetone | ||
| 1550 | 24.9 ± 0.1 | 6070.5 ± 31.3 |
| 1600 | 11.2 ± 0.0 | 5906.9 ± 53.5 |
| 1650 | 7.0 ± 0.0 | 6116.9 ± 94.7 |
| 1700 | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 5783.4 ± 250.5 |
| 1750 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 6303.2 ± 202.7 |
| 1800 | 3.7 ± 0.0 | 6324.7 ± 208.0 |
| 1850 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 4525.9 ± 552.1 |
| 1900 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 4982.4 ± 125.2 |
| 1950 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 4573.2 ± 356.6 |
| 2000 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 7389.7 ± 1254.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuczyński, M.; Mikołajczyk, T.; Pierożyński, B.; Pszczółkowski, B. Facilitation of the Kinetics of Alkaline Water Electrolysis on Polycrystalline Nickel Electrode by Introduction of Acetone to 0.1 M NaOH Working Solution. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115949
Kuczyński M, Mikołajczyk T, Pierożyński B, Pszczółkowski B. Facilitation of the Kinetics of Alkaline Water Electrolysis on Polycrystalline Nickel Electrode by Introduction of Acetone to 0.1 M NaOH Working Solution. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115949
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuczyński, Mateusz, Tomasz Mikołajczyk, Bogusław Pierożyński, and Bartosz Pszczółkowski. 2025. "Facilitation of the Kinetics of Alkaline Water Electrolysis on Polycrystalline Nickel Electrode by Introduction of Acetone to 0.1 M NaOH Working Solution" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115949
APA StyleKuczyński, M., Mikołajczyk, T., Pierożyński, B., & Pszczółkowski, B. (2025). Facilitation of the Kinetics of Alkaline Water Electrolysis on Polycrystalline Nickel Electrode by Introduction of Acetone to 0.1 M NaOH Working Solution. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5949. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115949








