Centralized Shared Energy Storage Optimization Framework for AC/DC Distribution Systems with Dual-Time-Scale Coordination
Abstract
1. Introduction
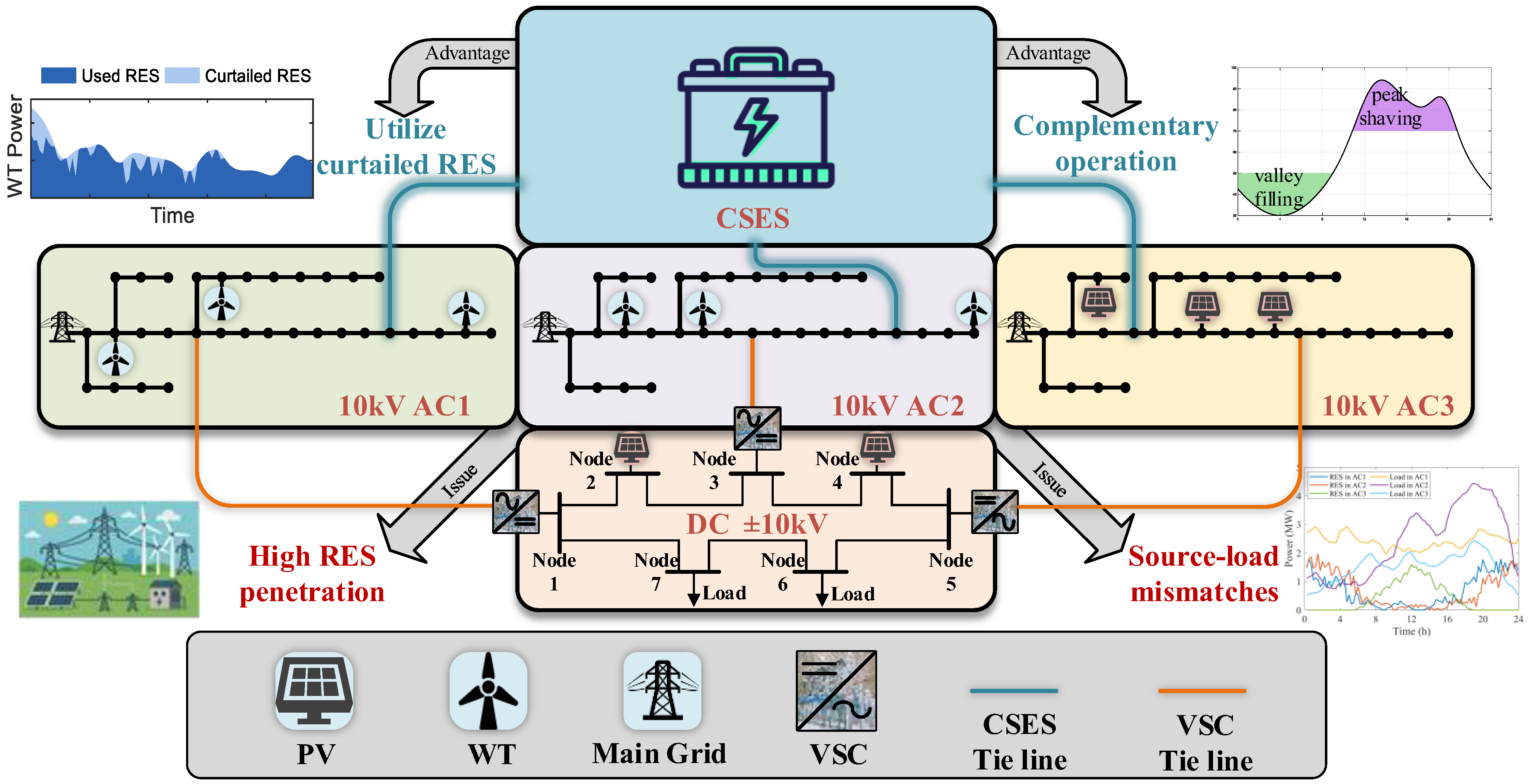
- A novel CSES optimization framework is established, where a large-scale CSES directly connects to multiple AC subnetworks. By leveraging temporal and spatial differences in RES and load profiles across subnetworks, complementary operation is achieved, thereby effectively enhancing the utilization of RES.
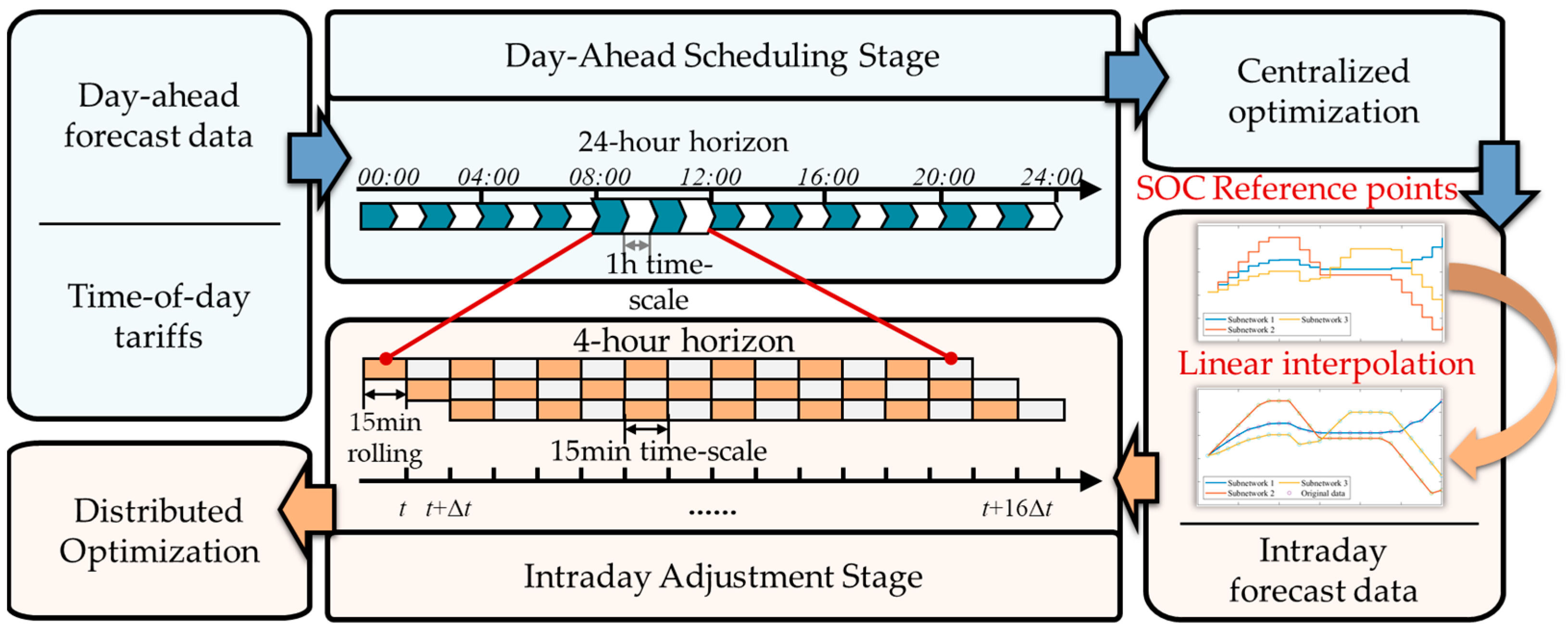
- A dual-time-scale coordination optimal scheduling with ADMM is proposed, combining day-ahead scheduling with intraday adjustments. Day-ahead SOC trajectory is converted to an intraday SOC trajectory through linear interpolation, maintaining SOC constraint compliance. This approach effectively manages CSES while addressing source–load imbalance between subnetworks.
2. Optimal Scheduling Models for AC/DC Distribution Systems
2.1. Objective Function
2.1.1. AC Subnetwork Operational Cost
2.1.2. DC Ring Network Operational Benefit
2.1.3. Conventional Individual ESS Operational Cost
2.1.4. Integrated Objective Function
2.2. AC Subnetwork Constraints
2.2.1. AC Power Flow Constraints
2.2.2. Conventional Individual ESS Constraints
2.2.3. Power Balance Constraints
2.2.4. Transmission Power Constraints
2.2.5. RES Output Constraints
2.2.6. Operational Safety Constraints
2.3. DC Ring Network Constraints
2.4. VSC Constraints
3. CSES Optimization Framework with Dual-Time-Scale Coordination
3.1. System Description
3.2. Operational Models for CSES
3.2.1. Operational Constraints
- A.
- Coordination Constraints:
- B.
- SOC Constraints:
- C.
- Power Constraints:
3.2.2. Operating Costs for CSES
3.3. Dual-Time-Scale Coordination
3.3.1. SOC Linear Interpolation
 represents the floor function (rounding down); and
represents the floor function (rounding down); and  represents the ceiling function (rounding up).
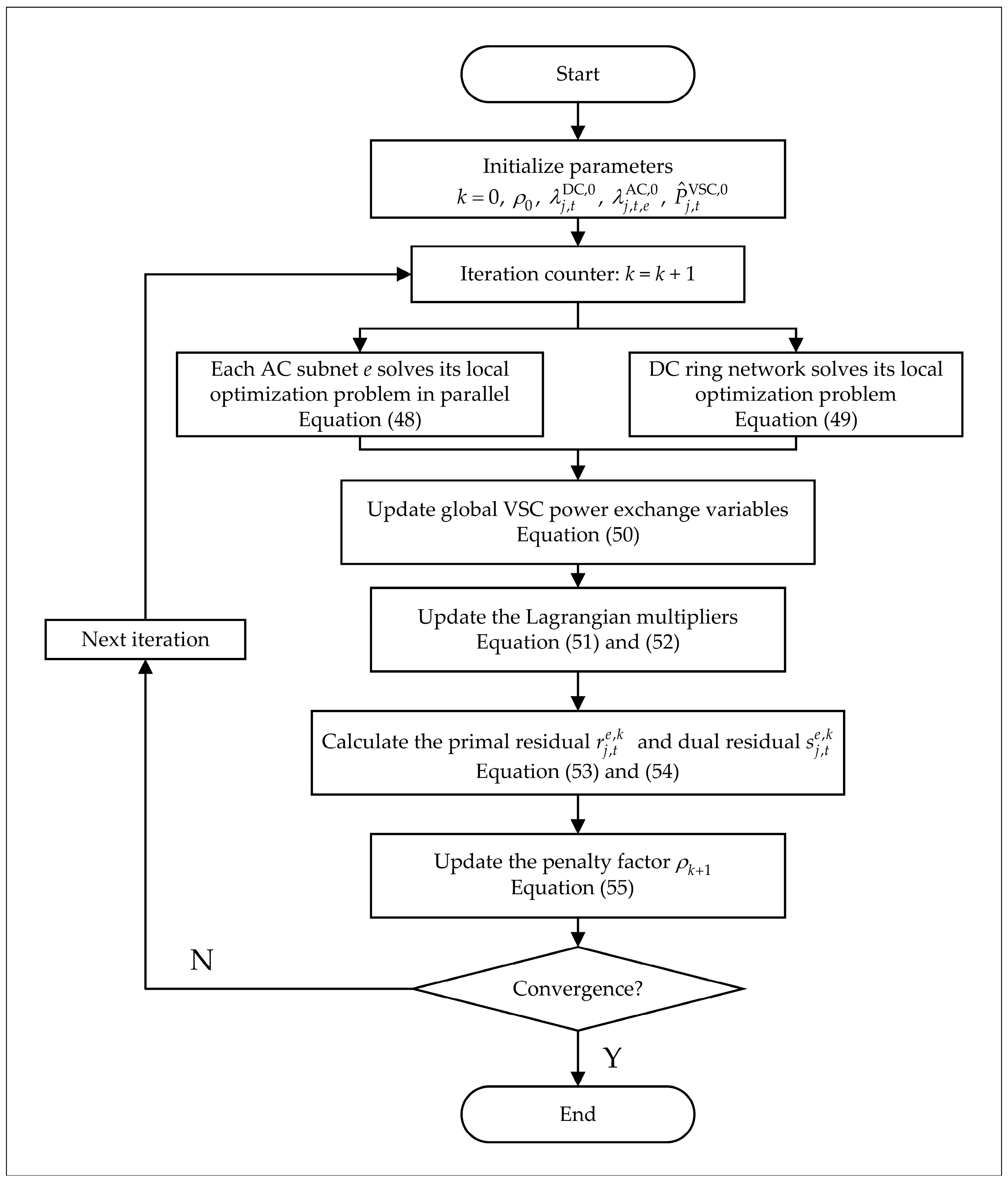
represents the ceiling function (rounding up).3.3.2. ADMM-Based Distributed Algorithm
- Initialize parameters k = 0, ;
- Each subnetwork solves its local optimization problem, as shown in Equations (48) and (49):
- The DC ring network coordinator updates the global VSC power exchange variables:
- The Lagrangian multipliers are updated:
- The primal residual and dual residual are calculated:
- An adaptive penalty parameter update strategy is adopted to accelerate convergence, with the penalty factor updated via Equation (55):
- 7.
- The convergence criterion is checked:
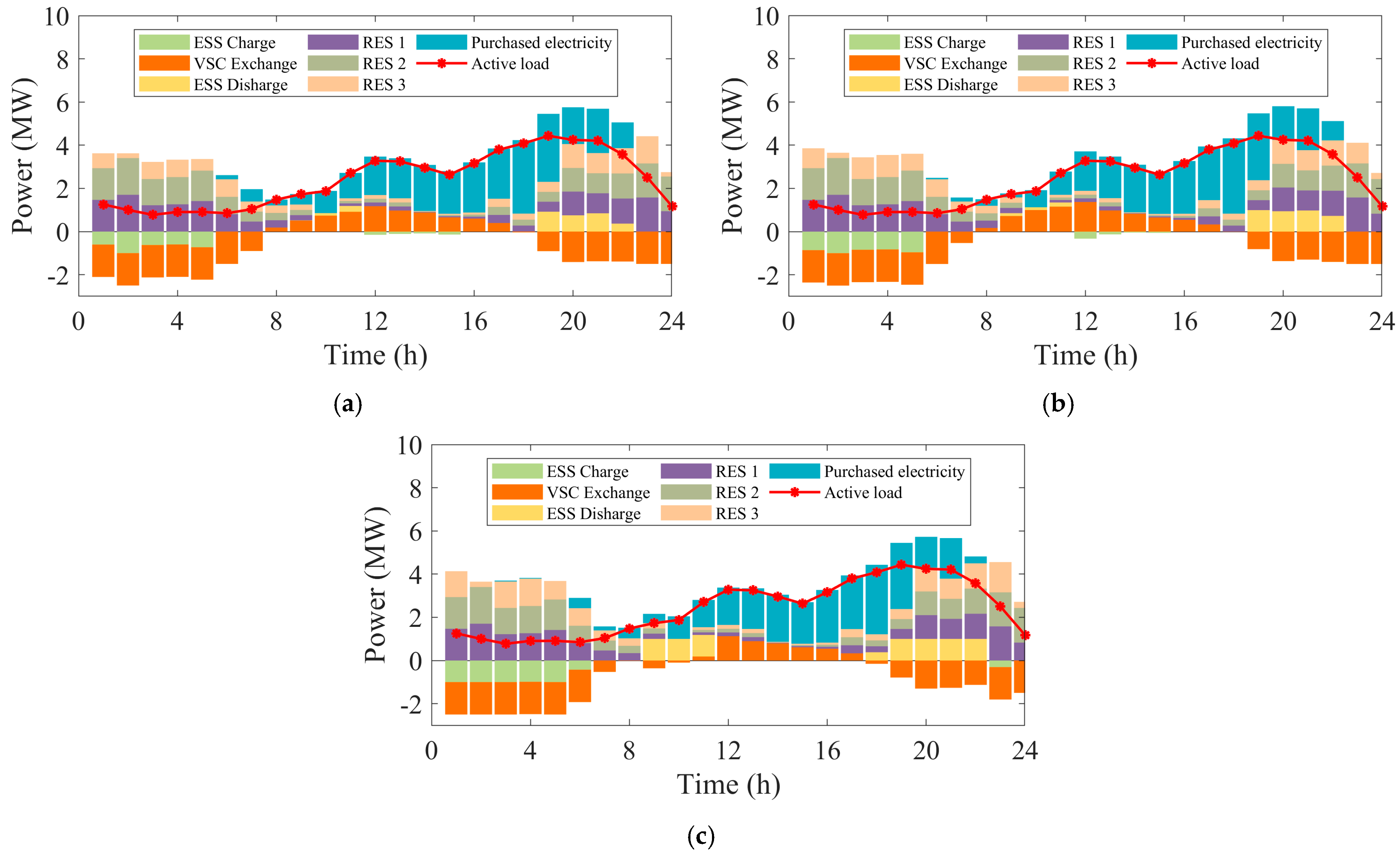
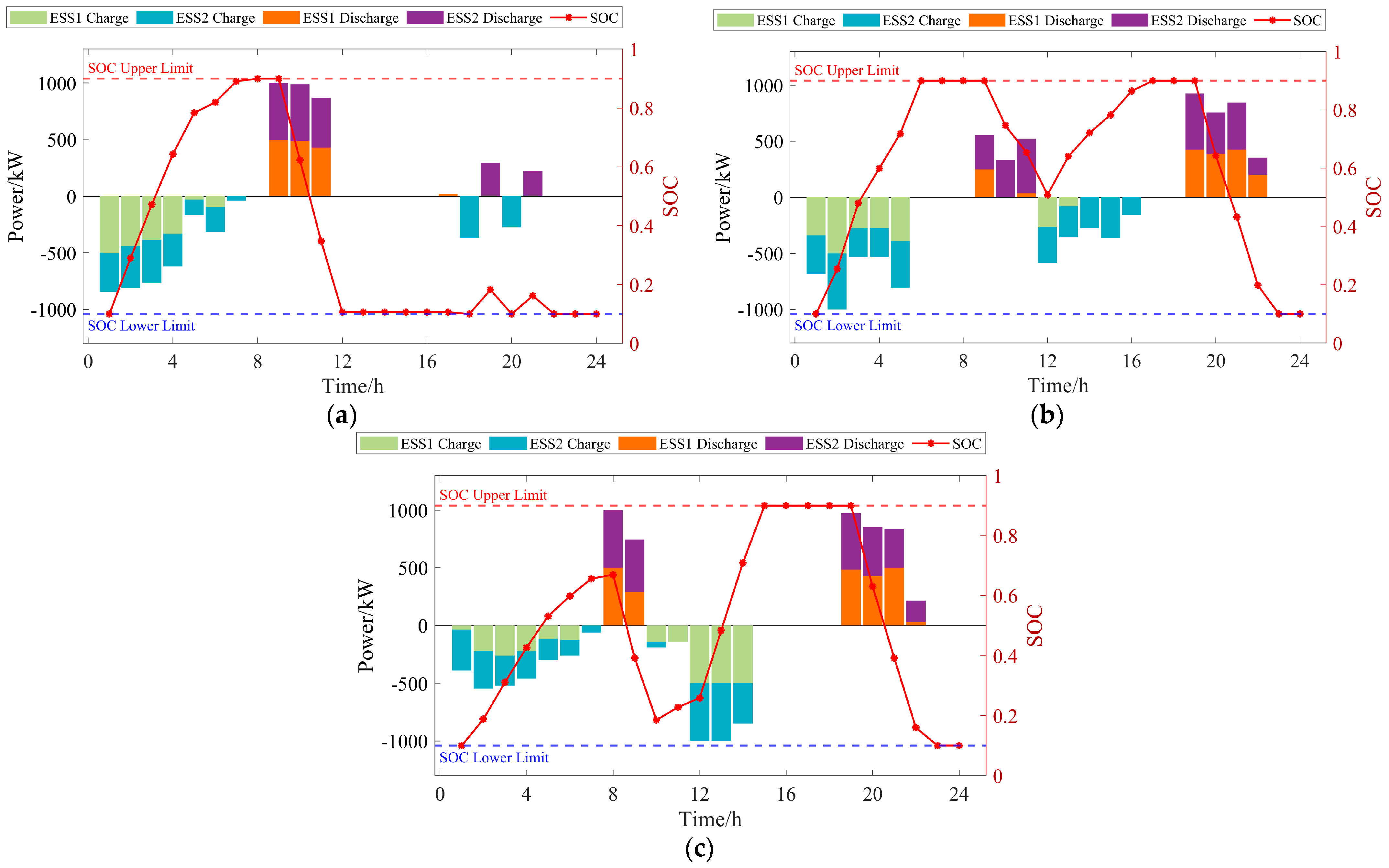
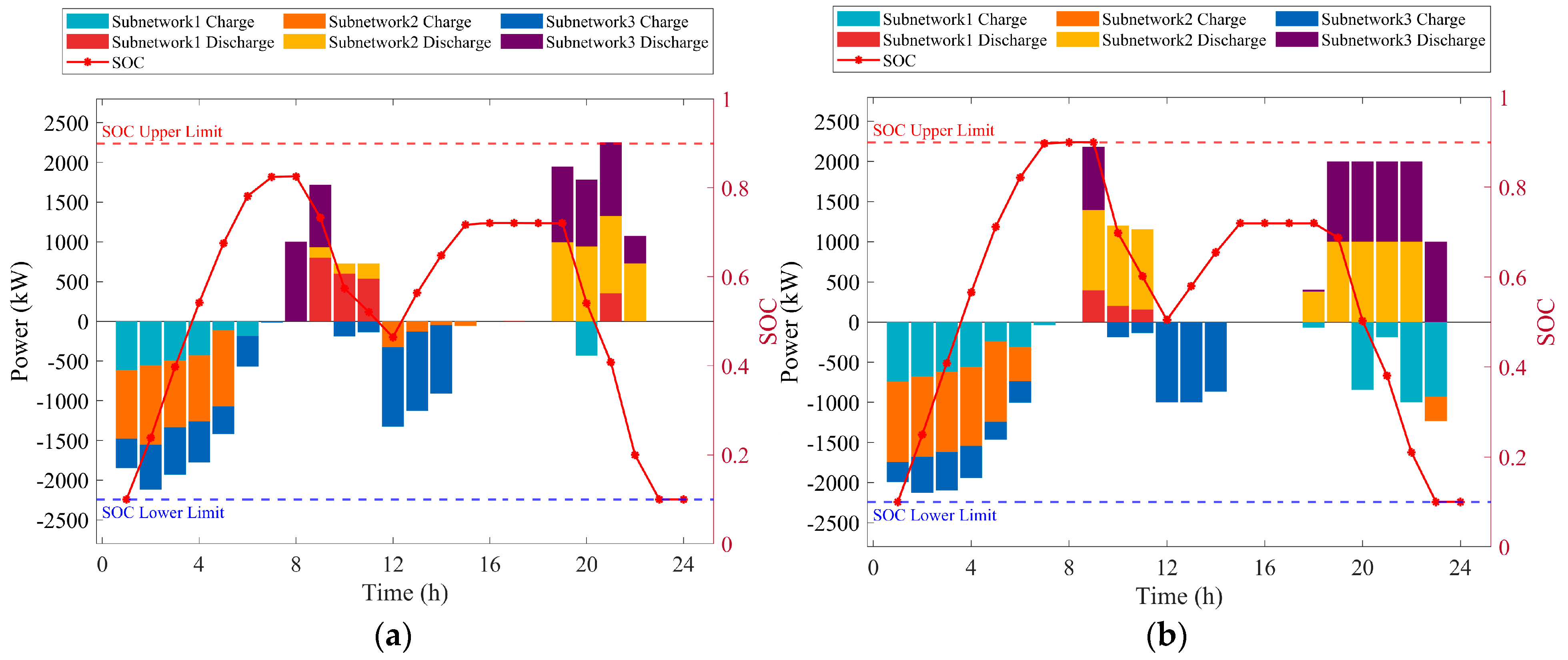
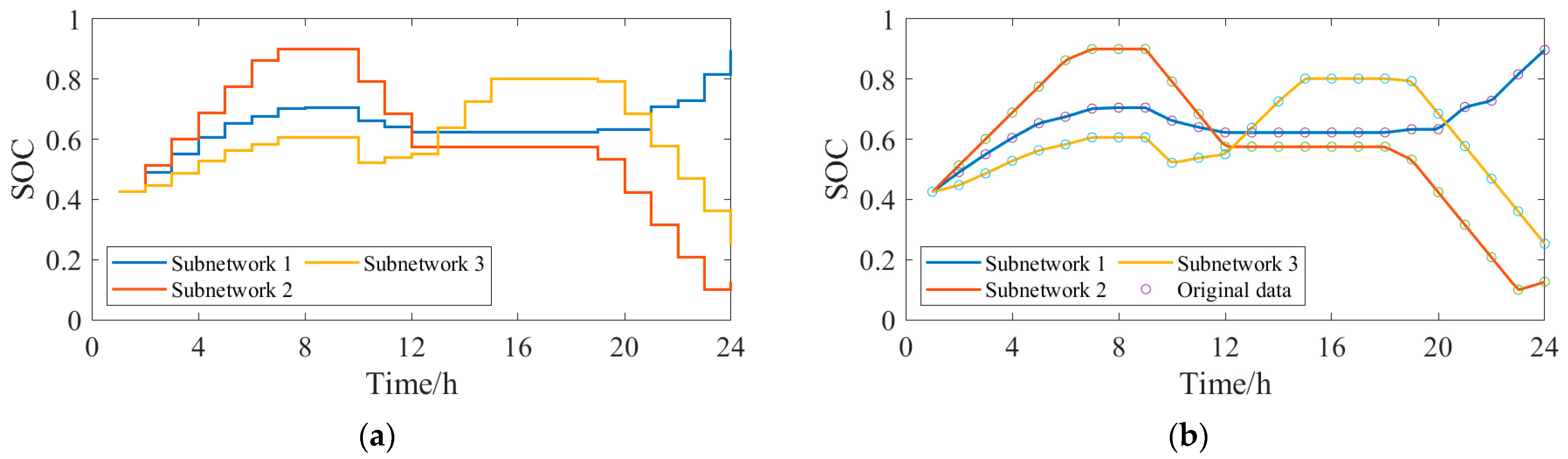
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Case Study
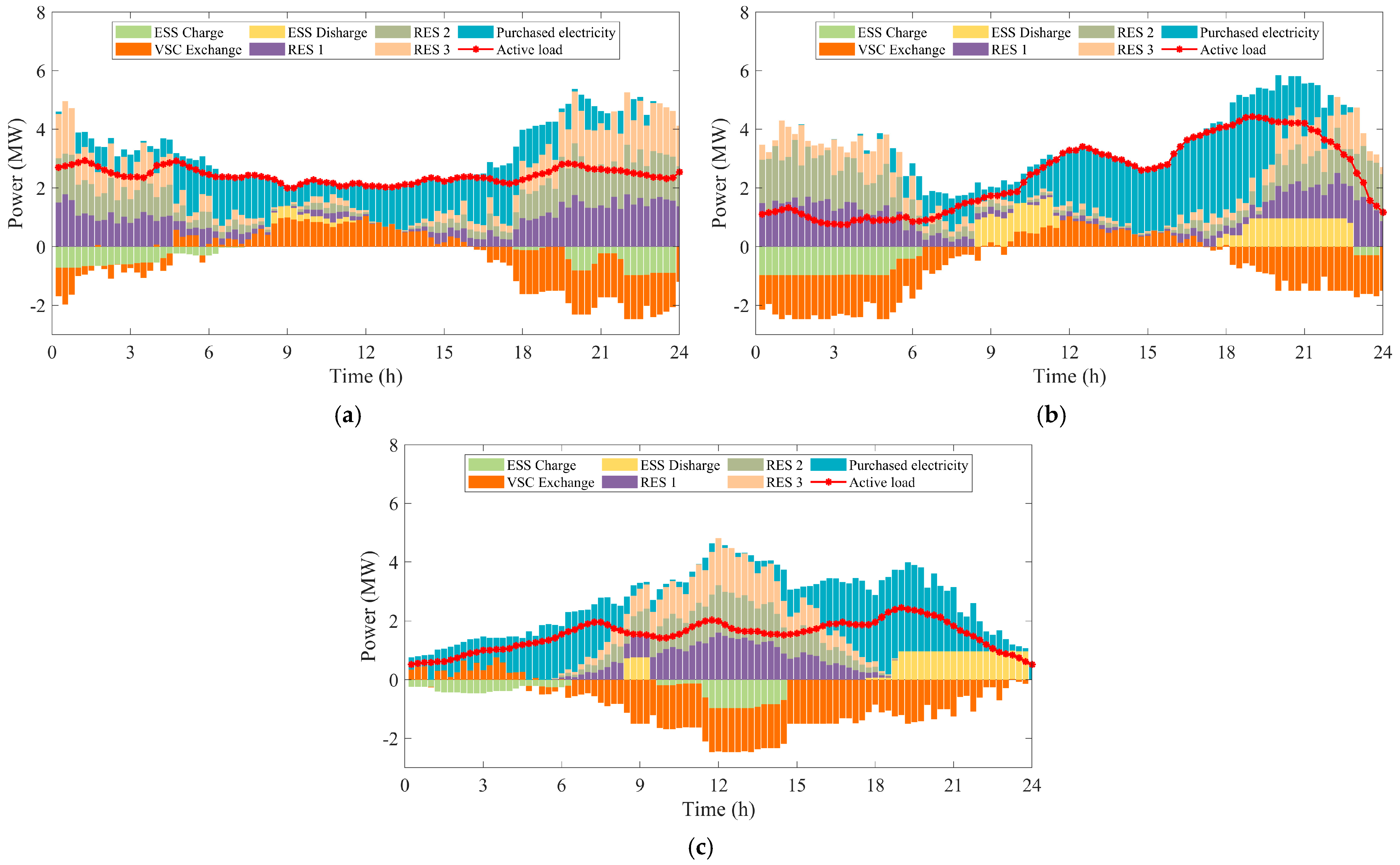
4.2. Analysis of Day-Ahead Optimization
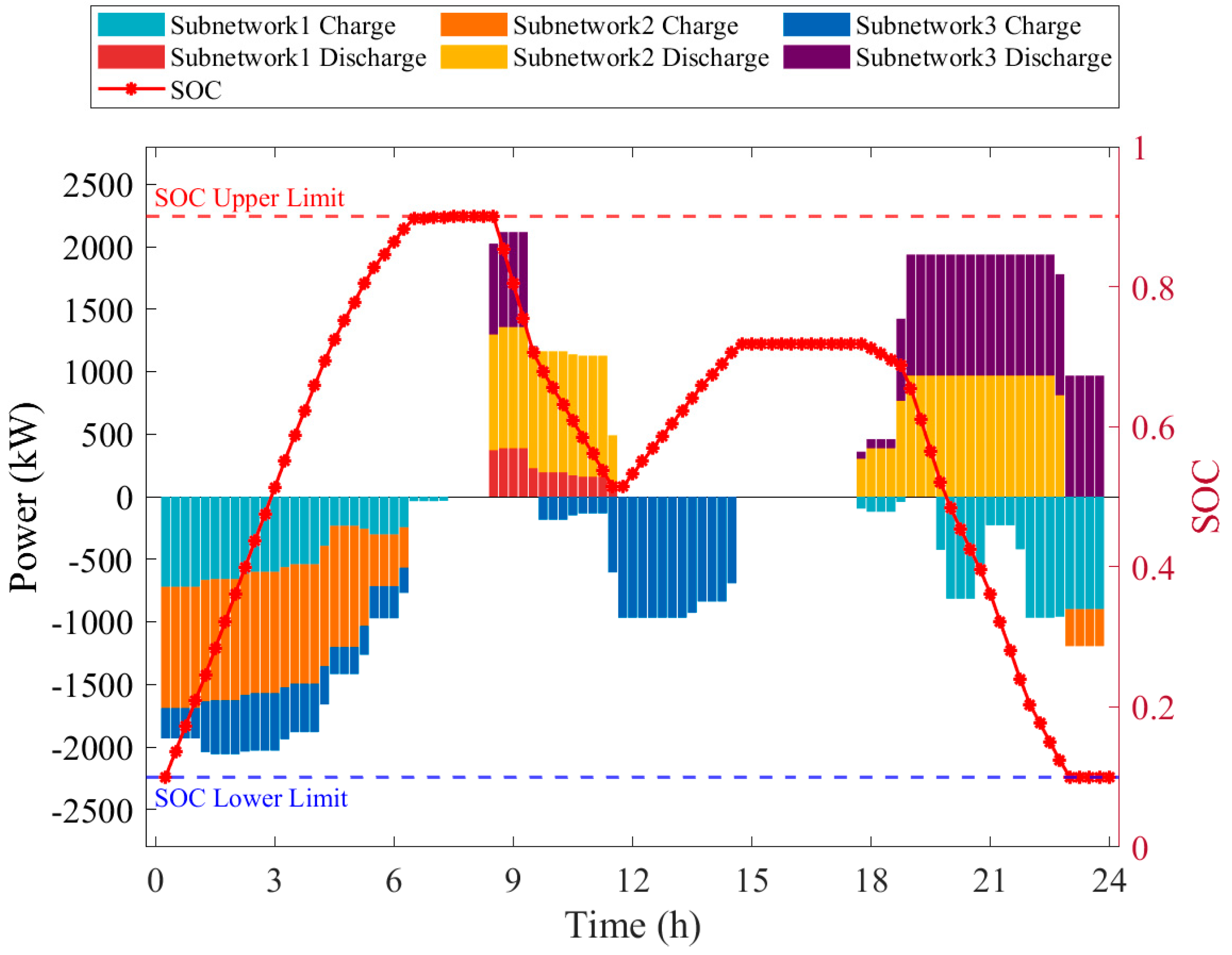
4.3. Analysis of Intraday Optimization
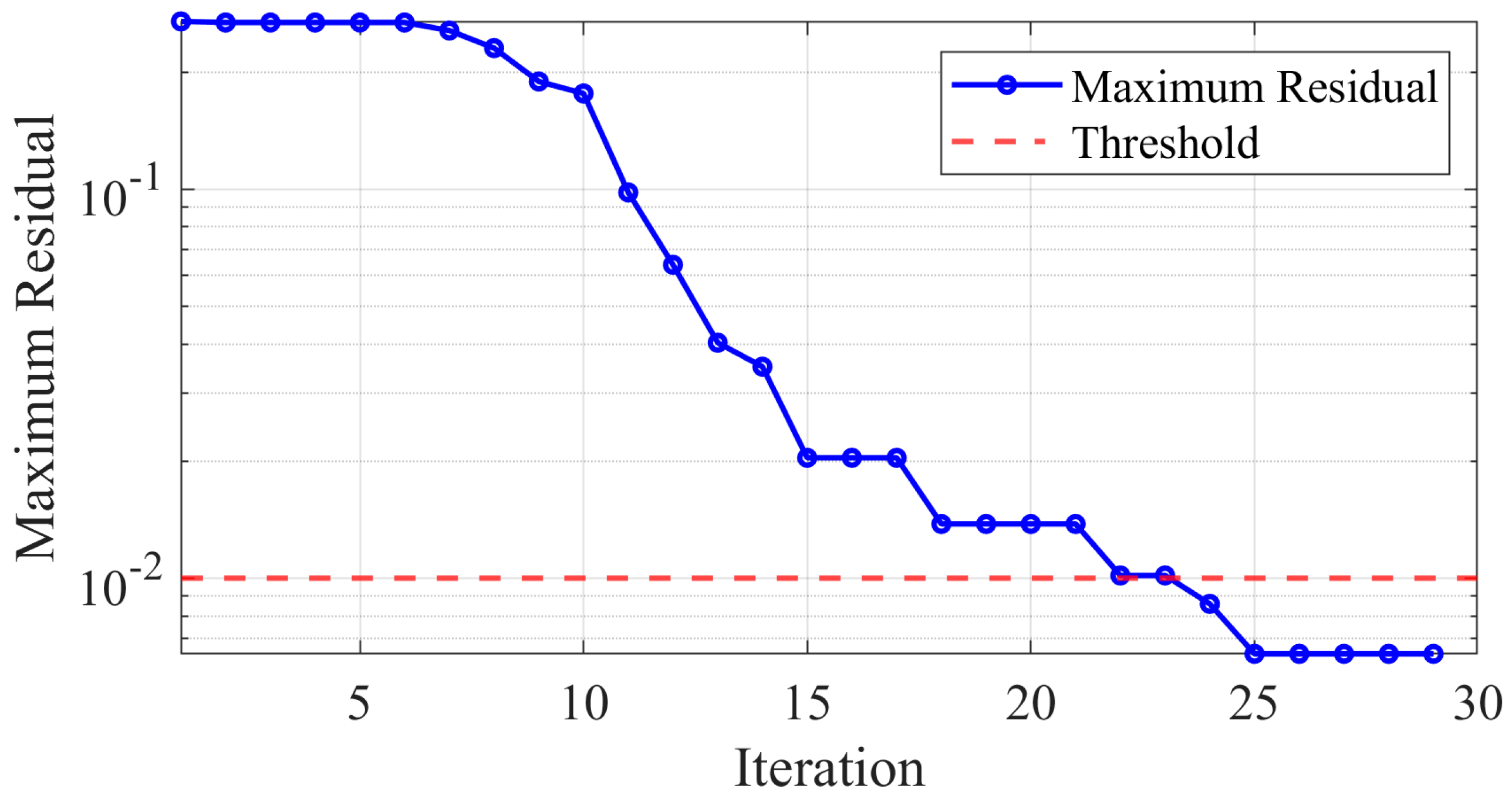
4.4. Analysis of ADMM Effectiveness
5. Conclusions
- The proposed CSES framework effectively leverages temporal–spatial complementarity across subnetworks, achieving significant improvements in RES utilization with rates of 99.31%, 88.10%, and 99.91% for AC1, AC2, and AC3 subnetworks, respectively, compared to 96.15%, 71.51%, and 92.47% under independent ESS operation.
- The dual-time-scale coordination of CSES successfully reduces total operational costs by 16.51% compared to independent ESS operation and 3.31% compared to capacity-leasing CSES allocation while ensuring system-wide optimization.
- The ADMM-based distributed algorithm achieves solution accuracy within 0.1% deviation of centralized optimization results while protecting privacy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Parameters | |
| T | Total number of time slots in a scheduling day |
| Time interval | |
| Time-of-day tariffs at time t | |
| Cost coefficient for network losses | |
| Interaction tariff at time t | |
| Operational cost coefficient of ESS | |
| , | Resistance and reactance of AC branch ij |
| Resistance of DC branch ij | |
| , | VSC resistance and reactance at node j |
| DC voltage utilization rate | |
| VSC capacity at node j | |
| , | Active and reactive load at node j at time t |
| , | Lower and upper limits of active power purchased |
| , | Lower and upper limits of reactive power purchased |
| , | Lower and upper limits of active power on branch ij |
| , | Lower and upper limits of reactive power on branch ij |
| , | Lower and upper limits of voltage magnitude at node j |
| , | Lower and upper limits of current on branch ij |
| , | Maximum charging and discharging power of the entire CSES |
| , | Maximum charging and discharging power limit for subnetwork e at time t |
| , | Maximum charging and discharging power limit for the ESS at node j |
| , | Minimum and maximum CSES SOC |
| , | Minimum and maximum ESS SOC |
| , | Charging and discharging efficiency |
| Kth penalty parameter | |
| Convergence threshold |
References
- Lu, W.; Xiao, Q.; Jia, H.; Jin, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Shen, C.; Teodorescu, R.; Guerrero, J.M. A Projected Gradient Descent-Based Distributed Optimal Control Method of Medium-Voltage DC Distribution System Considering Line Loss. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2025, 40, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Yu, H.; Jin, Y.; Jia, H.; Mu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Teodorescu, R.; Blaabjerg, F. A Novel Fault-Tolerant Operation Approach for Cascaded H-Bridge Converter-Based Battery Energy Storage Systems to Avoid Overcharge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, J.; Arévalo, P.; Montaleza, C.; Jurado, F. Sustainable Electrification—Advances and Challenges in Electrical-Distribution Networks: A Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, E.; Zhang, N. Optimal Planning of Multi-Microgrid System with Shared Energy Storage Based on Capacity Leasing and Energy Sharing. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zheng, W.; Yu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, M. Optimizing Grid-Connected Multi-Microgrid Systems with Shared Energy Storage for Enhanced Local Energy Consumption. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 13663–13677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Z.; He, X.; Min, H.; Zhou, S.; Liu, K.; Qin, L. A Fully Decentralized Optimal Dispatch Scheme for an AC–DC Hybrid Distribution Network Formed by Flexible Interconnected Distribution Station Areas. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. An Improved ADMM-Based Distributed Optimal Operation Model of AC/DC Hybrid Distribution Network Considering Wind Power Uncertainties. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Lu, W.; Liu, H.; Jia, H.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Hui, H. ADMM Based Multi-Objective Distributed Optimization of AC/DC Distribution System. In Proceedings of the 2024 9th Asia Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering (ACPEE), Shanghai, China, 11–13 April 2024; pp. 398–403. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, H.; Mu, Y.; Wu, Q.-W.; Wei, W. Peer-to-Peer Multi-Energy Trading Among Heterogeneous Building Prosumers via Asynchronous Distributed Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2025, 16, 1590–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Bi, T. Robust Two-Stage Dispatch of Multi-Area Integrated Electric-Gas Systems: A Decentralized Approach. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 11, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Li, Q.; Luo, S.; Chen, W.; Breaz, E.; Gao, F. Peer-to-Peer Electricity-Hydrogen Trading Among Integrated Energy Systems Considering Hydrogen Delivery and Transportation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 3895–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Rong, F. Hierarchical Active Power Control of DFIG-Based Wind Farm with Distributed Energy Storage Systems Based on ADMM. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; Tian, Z.; Shen, J.; He, D.; Dong, Z. Admm-Based Health-Conscious Energy Management Strategy with Fuel Cell and Battery Degradation Synergy Real-Time Control for Fuel Cell Vehicle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 333, 119812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-W.; Chu, C.-C. Optimal Distributed ADMM-Based Control for Frequency Synchronization in Isolated AC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 2458–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wu, Q.; Liao, W.; Wu, G.; Li, X.; Wei, J. Adaptive Droop-Based Hierarchical Optimal Voltage Control Scheme for VSC-HVdc Connected Offshore Wind Farm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 8165–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, Q.; Huang, S.; Li, C.; Zhou, B. ADMM-Based Distributed Active and Reactive Power Control for Regional AC Power Grid with Wind Farms. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2022, 10, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.M.; Uddin, M.; Sarkar, M.R.; Meraj, S.T.; Shafiullah, G.M.; Muyeen, S.M.; Islam, M.A.; Jamal, T. Applications of Energy Storage Systems in Power Grids with and without Renewable Energy Integration—A Comprehensive Review. J. Energy Storage 2023, 68, 107811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.A.; Ramachandaramurthy, V.K.; Taylor, P.; Ekanayake, J.B.; Walker, S.L.; Padmanaban, S. Review on the Optimal Placement, Sizing and Control of an Energy Storage System in the Distribution Network. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Oni, A.O.; Gemechu, E.; Kumar, A. Assessment of Energy Storage Technologies: A Review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 223, 113295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Esmaeilbeigi, R.; Charkhgard, H. The Utilization of Shared Energy Storage in Energy Systems: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 3163–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cao, X.; Zhang, S. Shared Energy Storage System for Prosumers in a Community: Investment Decision, Economic Operation, and Benefits Allocation under a Cost-Effective Way. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Li, Z.; Tan, Q.; Li, Y.; Wan, M. Multi-Time-Scale Resource Allocation Based on Long-Term Contracts and Real-Time Rental Business Models for Shared Energy Storage Systems. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Cai, Z.; Jiao, X.; Long, D. Multi-Timescale Optimization Scheduling of Integrated Energy Systems Oriented towards Generalized Energy Storage Services. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Dong, H. A Novel Energy Sharing Mechanism for Smart Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 5475–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, Y.-W.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, J.-W. A New and Fair Peer-to-Peer Energy Sharing Framework for Energy Buildings. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 3817–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Jiang, X.; Lin, Z.; Li, L.; Pei, Y.; Tao, Y. A Contract-Based, Decentralized and Privacy-Preserving Computation Scheme of Evaluation Indices of Shared Energy Storage Market for Renewable Energy Accommodation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 2546–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Qiu, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Yang, L. Cooperative-Game-Based Day-Ahead Scheduling of Local Integrated Energy Systems with Shared Energy Storage. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 1994–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Chen, Y. Distributed Coordination of Charging Stations with Shared Energy Storage in a Distribution Network. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 4666–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.; Gu, W.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.G. Optimal Operation of Micro-Energy Grids Considering Shared Energy Storage Systems and Balanced Profit Allocations. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 9, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Wang, K.; Fu, Y.; Li, G.; Han, B.; Huang, R.; Pu, T. A Decentralized Optimal Operation of AC/DC Hybrid Distribution Grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 6095–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.A.; Salama, M.M.A. Energy Management of AC–DC Hybrid Distribution Systems Considering Network Reconfiguration. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 4583–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, B.; Xie, F.; Tang, W. An Overvoltage-Averse Model for Renewable-Rich AC/DC Distribution Networks Considering the Sensitivity of Voltage Violation Probability. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2025, 16, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Mi, Y. Energy Management for Hybrid AC/DC Distribution System with Microgrid Clusters Using Non-Cooperative Game Theory and Robust Optimization. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1510–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zeng, K.; Yang, Y.; Xie, P. Flexibility-Oriented AC/DC Hybrid Grid Optimization Using Distributionally Robust Chance-Constrained Method. Energies 2024, 17, 4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitaraf, H.; Rahman, S. Reducing Curtailed Wind Energy Through Energy Storage and Demand Response. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Teh, J. Two-Stage Optimal Dispatching of AC/DC Hybrid Active Distribution Systems Considering Network Flexibility. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2023, 11, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Jia, H.; Xu, T.; Wei, W.; Wang, X. Battery Storage Configuration of AC/DC Hybrid Distribution Networks. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 9, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.A.; Eltantawy, A.B.; Salama, M.M.A. A Generalized Approach to the Load Flow Analysis of AC–DC Hybrid Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.M.-U.-T.; Murari, K.; Hasan, M.S.; Kamalasadan, S. Optimal Power Flow (OPF) Analysis for AC–DC Active Distribution Networks Utilizing Second-Order Cone Programming (SOCP) Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2025, 21, 3555–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murari, K.; Padhy, N.P.; Kamalasadan, S. A Backward-Forward Sweep Based Power Flow Algorithm for Generalized AC-DC Distribution Network with Distributed Generations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 5032–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.E.; Wu, F.F. Network Reconfiguration in Distribution Systems for Loss Reduction and Load Balancing. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1989, 4, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Gu, W.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Pan, G. Robustly Multi-Microgrid Scheduling: Stakeholder-Parallelizing Distributed Optimization. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 11, 988–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| References | Application Area | Time Resolution | Scale | Key Features | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [6,7,8] | AC/DC distribution network | Minutes to hours | 33-node or larger distribution network | Decentralized dispatch | Privacy, reduced communication |
| [9,10,11] | Integrated energy systems (IES) | Minutes to hours | Buildings to large-scale systems | Decoupled energy sector | Handles temporal couplings, scalability |
| [12,13,14,15,16] | Power electronics | Milliseconds to seconds | Small subsystems to wind farms (around 30 WTs) | Reduced communication and computation burden | Real-time control, scalability |
| Type | Ownership | Sharing Mechanism | Available Capacity | System Coordination Performance | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESS | Single user or entity | N/A | Fixed | Low | Can be a component of SES |
| SES | Multiple users or third-party aggregator | Users share idle capacity | Pre-allocate | Moderate to low | Broader concept for shared storage |
| CSES | Central entity | Dynamic sharing of both capacity and energy | Flexible | High | Specific SES type: unified asset for multiple users |
| Branch | Resistance (Ω) |
|---|---|
| 1–2 | 0.3075 |
| 2–3 | 0.3600 |
| 3–4 | 0.3825 |
| 4–5 | 0.5850 |
| 5–6 | 0.9225 |
| 6–7 | 0.8475 |
| 7–1 | 0.4725 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Total number of time slots in a scheduling day | 24/96 |
| Time interval | 1 h/15 min |
| Cost coefficient for network losses | 0.4 CNY/kWh |
| Operational cost coefficient of ESS | 0.028 CNY/kWh |
| Peak efficiency | 0.9 |
| VSC resistance and reactance | 0.5 Ω/1.5 Ω |
| DC voltage utilization rate | 0.866 |
| Limits of RES power | 2 MW |
| VSC rated active and reactive power | 2 MW/1 MVar |
| Maximum charging and discharging power of the entire CSES | 3 MW |
| Maximum charging and discharging power for the subnetwork | 1 MW |
| Maximum charging and discharging power for the ESS | 0.5 MW |
| Minimum and maximum CSES SOC | 0.1/0.9 |
| Minimum and maximum ESS SOC | 0.1/0.9 |
| Charging and discharging efficiency | 0.9 |
| ADMM initial penalty parameter | 1 × 103 |
| ADMM convergence threshold | 10−2 |
| Network | DG Positions | VSC Positions |
|---|---|---|
| AC1 | 3, 17, 27 | 7 |
| AC2 | 4, 7, 18 | 9 |
| AC3 | 12, 13, 25 | 13 |
| DC | 2, 4 | 1, 3, 5 |
| Time Period | Price (CNY/kWh) |
|---|---|
| 00:00–07:00 | 0.48 |
| 07:00–08:00 | 0.9 |
| 08:00–11:00 | 1.35 |
| 11:00–18:00 | 0.9 |
| 18:00–23:00 | 1.35 |
| 23:00–24:00 | 0.48 |
| Network | Source–Load Difference (MWh) | Allocation Ratio | Allocated Capacity (MWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC1 | 6.9709 | 0.2239 | 2.6868 |
| AC2 | 13.0971 | 0.4207 | 5.0480 |
| AC3 | 11.0660 | 0.3554 | 4.2652 |
| Total | 31.1340 | 1.0000 | 12.0000 |
| Type | Electricity Purchase Cost (CNY) | Network Loss Cost (CNY) | ESS Operational Cost (CNY) | DC Network Interaction Benefit (CNY) | Total Operational Cost (CNY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 70,232.53 | 2292.63 | 770.57 | 29,128.68 | 44,167.06 |
| Case 2 | 69,866.01 | 2531.04 | 702.80 | 29,129.16 | 43,970.69 |
| Case 3 | 65,698.64 | 2663.45 | 871.75 | 29,136.22 | 40,097.62 |
| Type | AC1 | AC2 | AC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 94.55% | 85.23% | 99.07% |
| Case 2 | 94.77% | 88.61% | 98.82% |
| Case 3 | 99.57% | 91.07% | 98.82% |
| Type | Network | Electricity Purchase Cost (CNY) | Network Loss Cost (CNY) | ESS Operational Cost (CNY) | DC Network Interaction Benefit (CNY) | Total Operational Cost (CNY) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | AC1 | 21,766.04 | 992.05 | 209.54 | 29,860.16 | 60,530.71 |
| AC2 | 38,939.16 | 749.10 | 317.37 | |||
| AC3 | 25,532.86 | 1639.21 | 245.55 | |||
| Case 2 | AC1 | 19,617.78 | 962.31 | 149.13 | 29,846.15 | 52,266.82 |
| AC2 | 33,597.38 | 741.70 | 293.22 | |||
| AC3 | 25,958.94 | 556.41 | 236.10 | |||
| Case 3 | AC1 | 19,521.93 | 716.05 | 198.49 | 29,859.78 | 50,538.56 |
| AC2 | 31,061.62 | 1538.19 | 366.77 | |||
| AC3 | 25,888.00 | 797.85 | 309.43 |
| Type | AC1 | AC2 | AC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 96.15% | 71.51% | 92.47% |
| Case 2 | 97.04% | 79.74% | 99.63% |
| Case 3 | 99.31% | 88.10% | 99.91% |
| Objective | Centralized (CNY) | Distributed (CNY) | Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 79,531.35 | 79,523.65 | 0.01% | |
| 29,884.75 | 29,859.78 | 0.08% | |
| 874.68 | 874.68 | 0.00% | |
| 50,521.28 | 50,538.56 | 0.03% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Jia, H.; Lu, W.; Jin, Y. Centralized Shared Energy Storage Optimization Framework for AC/DC Distribution Systems with Dual-Time-Scale Coordination. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115941
Zhu Y, Xiao Q, Jia H, Lu W, Jin Y. Centralized Shared Energy Storage Optimization Framework for AC/DC Distribution Systems with Dual-Time-Scale Coordination. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115941
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yidi, Qian Xiao, Hongjie Jia, Wenbiao Lu, and Yu Jin. 2025. "Centralized Shared Energy Storage Optimization Framework for AC/DC Distribution Systems with Dual-Time-Scale Coordination" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115941
APA StyleZhu, Y., Xiao, Q., Jia, H., Lu, W., & Jin, Y. (2025). Centralized Shared Energy Storage Optimization Framework for AC/DC Distribution Systems with Dual-Time-Scale Coordination. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115941









