Featured Application
This study provides a sustainable strategy for the generation of volatile fatty acids from diverse waste streams through targeted acidogenic fermentation, offering a cost-effective and circular alternative for the production of bioplastic precursors such as polyhydroxyalkanoates.
Abstract
The sustainable production of bioplastics is increasingly important for reducing reliance on fossil fuels and addressing environmental challenges. The acidogenic fermentation of waste streams offers a promising pathway for generating key bioplastic precursors, such as volatile fatty acids, which can be used to produce polymers like polyhydroxyalkanoates. This review explores the potential of various waste streams, including agricultural residues, industrial by-products, and food waste, as substrates for acidogenic fermentation, aligning with circular economy principles by reducing waste and environmental impact. A key feature of this review is its focus on targeted acidogenic fermentation, which optimizes process conditions to maximize the production of specific acids based on waste characteristics. The analysis emphasizes how the chemical composition and biodegradability of waste streams influence the selection of microbial consortia and metabolic pathways, determining the yield and composition of the products generated. The review also highlights the adaptability of acidogenic fermentation to heterogeneous and variable waste streams, underlining its potential as a scalable and sustainable solution for bioplastic precursor production. By tailoring process parameters such as pH and hydraulic retention time to the specific characteristics of the substrate, targeted acidogenic fermentation can effectively transform waste into high-value intermediates. Finally, challenges related to the scalability and economic feasibility of these processes are discussed, along with opportunities for integrating acidogenic fermentation with complementary waste valorization technologies to advance the bio-based economy. The findings underscore the critical role of waste streams in enabling the sustainable and efficient generation of bioplastic precursors, contributing to a circular economy framework.
1. Introduction
The utilization of heterogeneous waste materials as precursors for the production of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) has garnered considerable attention in sustainable bioproduction. This approach holds promise as it aligns with the principles of the circular economy, providing a dual benefit of waste valorization and the generation of valuable chemical building blocks [1]. In particular, targeted acidogenic fermentation—a refined process of acidogenic fermentation in which operational parameters and microbial consortia are optimized to selectively produce specific VFAs from organic waste streams—has emerged as a powerful tool to fine-tune the production of VFAs, enabling the generation of tailored chemical intermediates for diverse industries [2]. Unlike conventional acidogenic fermentation, where a mixture of VFAs is often generated, targeted fermentation is designed to steer the metabolic pathways of microorganisms toward the production of desired VFAs, depending on the end-use application. This approach enhances process efficiency, reduces downstream processing, and ensures that the VFA profile is tailored to meet industrial needs [3].
The circular economy concept seeks to create a closed-loop system where resources are reused, recycled, or repurposed, minimizing environmental impact. Within this framework, VFAs act as critical intermediates in the production of high-value products such as bioplastics, biofuels, and other chemicals, providing a renewable alternative to fossil fuel-based processes [4,5]. As the demand for sustainable solutions grows, biologically derived VFAs, including acetic, propionic, butyric, and valeric acids, offer significant potential due to their versatility and broad industrial applications. Table 1 highlights their chemical properties and current market data, underscoring their economic relevance.

Table 1.
VFA properties and market price [6,7,8,9].
The market for VFAs is projected to experience significant growth between 2024 and 2032. This growth is driven by several key factors, including increasing demand for sustainable solutions, the adoption of circular economy practices, and the expansion of industrial applications such as biogas production, bioplastics, and food additives. Particularly, the increasing interest in bioplastics is positioning VFAs at the center of discussions around green alternatives to petrochemical-based plastics. Estimates suggest that the global VFA market, valued at approximately USD 29.5 billion in 2023, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.4%, reaching approximately USD 46.9 billion by 2032 [10]. The primary drivers behind this growth include rising demand in the energy sector, particularly for biogas production from organic waste, advancements in fermentation technology to improve VFA production efficiency, and the increasing use of VFAs in emerging industries like pharmaceuticals, where their therapeutic properties are being explored [11]. This anticipated growth underscores the critical role that targeted fermentation can play in addressing the rising demand for tailored VFA production to meet the specific requirements of bioplastics and other emerging bio-based industries.
The use of diverse waste materials, from agricultural residues to industrial by-products, as substrates for targeted acidogenic fermentation is a cornerstone in the development of more sustainable industrial processes. This strategy not only addresses the pressing need for effective waste management but also helps shift away from the consumption of edible raw materials, which is crucial in tackling global food security challenges [12]. Moreover, targeting specific VFAs in the fermentation process provides greater control over downstream applications, demonstrating their versatility as chemical intermediates in sectors ranging from food and pharmaceuticals to emerging bio-based industries such as bioplastics. VFAs produced through targeted fermentation offer a more refined approach for creating bioplastics with desirable properties, reducing the dependency on complex downstream purification processes [13]. Current research focuses on optimizing acidogenic fermentation to ensure scalable and efficient VFA production. This involves multiple strategies aimed at improving both the biological and operational aspects of the fermentation process. Specifically, tailoring microbial consortia and operational conditions to produce desired VFAs offers the potential to streamline the bioproduction of these compounds [14]. Advances in microbial consortia engineering and process optimization aim to overcome challenges posed by the variability in waste composition, making the bioproduction of VFAs a more reliable and sustainable solution for the future [15].
Despite the promising potential, the implementation of targeted waste-derived VFA bioproduction is not without its challenges. The heterogeneous nature of waste streams, along with the potential presence of impurities, introduces variability in organic composition, which complicates the optimization of fermentation processes [16]. For instance, lignocellulosic biomass, a common waste source, requires effective pretreatment methods to break down its complex structure and make it more amenable to fermentation [17]. These pretreatments add complexity to the bioproduction process, as they must be tailored to specific waste types to maximize VFA production efficiency. In addition to pretreatment challenges, the microbial consortia involved in acidogenic fermentation play a crucial role in determining the yield and specificity of VFAs. Many research groups are investigating ways to enhance the efficiency and reliability of this process by manipulating microbial communities to favor the production of targeted VFAs, where specific types of VFAs, such as acetic or butyric acid, are preferentially produced depending on the end-use application [12]. Operational parameters, such as pH, temperature, and substrate concentration, also significantly influence the outcomes of fermentation, and optimizing these conditions remains a key area of ongoing research [12]. Moreover, the development of robust metabolic models for the predictive control of the fermentation process is becoming increasingly important, as it offers a way to improve consistency and scalability in VFA production [18]. These models allow for real-time adjustments, optimizing yield and reducing waste during the fermentation process, and are essential for scaling up production to industrial levels.
The aim of this review is to explore the potential of waste streams for generating bioplastic precursors via targeted acidogenic fermentation. It will provide an overview of the current state of research on VFA production from waste, discuss the challenges and opportunities associated with this approach, and highlight future directions for improving the efficiency and sustainability of the process. Unlike previous reviews that offer a general perspective on acidogenic fermentation, this work specifically focuses on targeted strategies that enable the selective production of specific VFA suited for bioplastic synthesis. It integrates recent advances in microbial community engineering, operational parameter optimization, and energy-based metabolic modeling to better understand and guide VFA profiles. By addressing these topics, the review also establishes direct links between the type of VFA produced and the mechanical and thermal properties of the resulting bioplastics, offering a novel techno-economic perspective on feedstock selection and process design. In doing so, this review aims to contribute to the growing body of knowledge on sustainable bioproduction and the circular economy, with a particular focus on the role of VFA as a key intermediate in the generation of bioplastics and other high-value products.
2. Mechanisms of Acidogenic Fermentation
2.1. Biological Processes Involved in Acidogenic Fermentation
Acidogenic fermentation is a crucial phase within the broader anaerobic digestion process. During this stage, soluble organic compounds derived from the hydrolysis of complex organic materials, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, are fermented by specific microorganisms into VFA, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. The acidogenic phase is primarily responsible for the production of short-chain fatty acids, including acetic, butyric, propionic, and valeric acids, which serve as key intermediates in various biotechnological processes such as bioplastic production. This fermentation step is carried out by a wide range of facultative and obligate anaerobic bacteria. The process typically begins with the breakdown of soluble organic substrates, as carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, into simpler molecules such as monosaccharides, amino acids, and long-chain fatty acids, which are then subjected to fermentation following different metabolic pathways (Figure 1). The microbial activity during this phase is highly dependent on the availability of substrates, the composition of the microbial community, and environmental factors like pH and temperature [19].
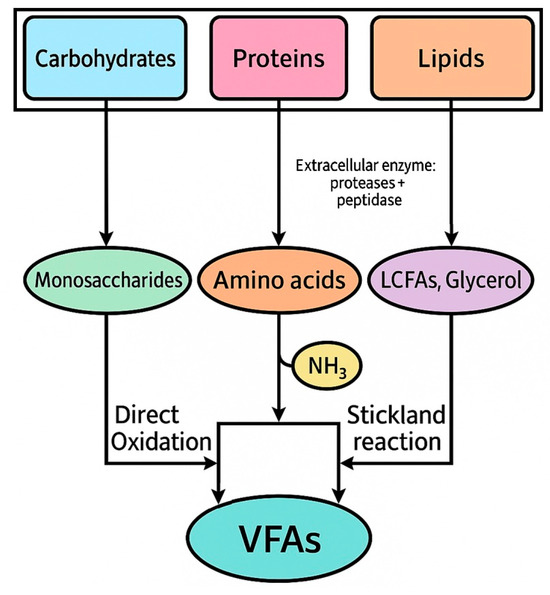
Figure 1.
VFA production from organic macromolecules (adapted from Duong and Nga [11]).
One of the key microbial genera involved in acidogenic fermentation is Clostridium, a strict anaerobe that plays a significant role in the fermentation of carbohydrates [20]. Clostridium species are known for their ability to produce VFAs, particularly butyric acid, through the fermentation of sugars [21]. This process typically involves the conversion of glucose into pyruvate via the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway, followed by the reduction in pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, which serves as a precursor for various VFAs. Acetyl-CoA can be further converted into acetic acid, while butyric acid is produced through a series of enzymatic reactions involving butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase [22]. Protein-rich substrates undergo a different set of reactions, facilitated by specific proteolytic microorganisms. Amino acids, derived from the hydrolysis of proteins, are fermented through pathways such as oxidative deamination or Stickland reactions [23]. In oxidative deamination, amino acids are converted into their corresponding keto acids, which are further fermented into VFAs, such as acetic and propionic acids. Stickland reactions, on the other hand, involve coupled oxidation and reduction in amino acids, producing VFAs, ammonia, and carbon dioxide as by-products. These reactions are carried out by species such as Selenomonas and Bacteroides, which are important for maintaining the balance of VFAs in the fermentation environment [24]. The fermentation of lipids is another critical pathway in acidogenesis. Lipids, which are hydrolyzed into glycerol and long-chain fatty acids, are broken down by lipolytic bacteria. Glycerol is fermented into pyruvate, which is subsequently converted into acetic acid, while long-chain fatty acids are subjected to β-oxidation. This process generates acetyl-CoA, which can be funneled into the VFA production pathways, yielding acetic acid and hydrogen as primary products. The fermentation of lipids is particularly important in industrial applications where lipid-rich waste streams are used as feedstock, as they can contribute significantly to the overall VFA yield [25].
A key feature of acidogenic fermentation is its dependency on the microbial consortia present in the reactor. These microbial communities are highly adaptable and can switch between different metabolic pathways depending on the substrates available and the environmental conditions. For instance, when methanogens are inhibited by maintaining a low pH (below 6), acidogenic bacteria dominate the fermentation process, ensuring that VFA are produced rather than being consumed and converted into methane [26]. This inhibition of methanogenesis is crucial for optimizing the production of VFAs, particularly in systems where VFAs are desired as end products, such as in bioplastic precursor production. Another important aspect of acidogenic fermentation is the balance between the different VFAs produced. The metabolic pathways involved are interconnected, and the ratio of acetic, butyric, propionic, and valeric acids produced can vary depending on factors such as substrate composition and reactor conditions. For example, carbohydrate-rich substrates tend to favor the production of acetic and butyric acids [27], while protein-rich substrates lead to higher levels of propionic and valeric acids [28]. Understanding and controlling these metabolic pathways is essential for optimizing the fermentation process to produce specific VFA, depending on the desired industrial application.
2.2. Key Microbial Communities Involved in VFA Production
Apart from the species mentioned in the previous section, such as Clostridium, Selenomonas, and Bacteroides, there are numerous other microorganisms that play essential roles in acidogenic fermentation. The specific VFA produced largely depends on the microbial species present, as each group of microorganisms favors the production of a particular type of acid [29]. These communities interact and adapt to substrate availability and environmental conditions, ensuring that the dominant microorganisms guide the process toward the generation of acetic, butyric, propionic acids, or other VFAs [30]. Some examples of key communities in specific VFA production are gathered in Table 2.

Table 2.
Microorganisms associated with specific VFA production.
Acetic acid is one of the most commonly produced VFA during acidogenic fermentation, driven by various bacteria, especially in carbohydrate-rich environments. Acetobacter aceti plays a central role in industrial acetic acid production due to its ability to metabolize a wide range of sugars, including glucose, ribose, and xylose [31]. This versatility makes it ideal for continuous fermentation processes, often applied in large-scale production using organic waste substrates such as date extract [32]. Furthermore, the use of Acetobacter in processes utilizing cheese whey as a substrate has led to particularly high yields of acetic acid. Under optimized conditions, A. aceti has been used to achieve efficient results, producing 84.1 g/L of acetic acid with a yield of 97.4% and a productivity of 7.2 g/(L·h) [33]. In addition, Moorella thermoacetica and Aurantiochytrium limacinum are highly effective at fermenting lignocellulosic sugars derived from agricultural residues, such as switchgrass, forest residues, wheat straw and sugarcane straw, making it crucial in waste valorization strategies aimed at producing acetic acid from renewable sources. When adapted to these waste-derived hydrolysates, these microbial strains can achieve up to 80% of theoretical yields for bio-acetic acid production, demonstrating the efficiency of using agricultural residues as feedstock. This strategy not only enhances acetic acid yields but also leads to a 75% reduction in media costs compared to traditional organic fermentation mediums, further highlighting the economic and environmental benefits of using waste materials in fermentation processes [34]. Another important microorganism, Clostridium lentocellum, is capable of converting cellulose-based materials like paddy straw and cotton straw into significant amounts of acetic acid, demonstrating its potential in cellulose-rich. In fact, this species can efficiently ferment various crystalline cellulosic materials, achieving a maximum acetic acid yield of 0.67 g acetic acid per gram of substrate [35]. Mixed cultures, like those involving Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Acetobacter pasteurianus, are also important for maximizing acetic acid yields. In such systems, Saccharomyces converts glucose into ethanol, which is then oxidized to acetic acid by Acetobacter. This co-culture has been shown to produce high concentrations of acetic acid, up to 89.3 g/L in fed-batch fermentation processes, demonstrating the benefits of microbial synergy in industrial setups [36].
Propionic acid is primarily produced through the fermentation of various substrates by species of the Propionibacterium genus, including P. acidipropionici, P. freudenreichii, P. shermanii, and P. thoenii, which effectively convert hexoses and pentoses into propionate [37]. P. acidipropionici plays a key role in producing propionic acid from renewable substrates. For instance, with Agave bagasse pretreated through steam explosion and enzymatic hydrolysis, it achieved a propionic acid yield of 0.44 g/g total carbohydrates and productivity of 0.069 g/L·h. This process, enhanced by pH control, demonstrated efficiency without requiring detoxification steps [38]. In high cell density fermentation, P. acidipropionici utilized glucose and glycerol/glucose mixtures effectively. With 40 g/L glucose over multiple batches, propionic acid yield averaged 18.76 g/L with a conversion rate of 0.59 g/g glucose. Using a glycerol/glucose mix (60 g/L:30 g/L), it reached 35.36 g/L propionic acid per batch, achieving 0.51 g/g carbon source [39]. These methods, especially with cell recycling and biotin supplementation, enhance propionic acid productivity and cell growth, making P. acidipropionici a promising option for sustainable biorefining. Propionibacterium freudenreichii also plays a crucial role in the sustainable production of propionic acid through various renewable substrates. This bacterium has demonstrated adaptability to a range of by-products and biomass sources, enabling efficient propionic acid production with promising yields. For instance, in the production of propionic acid from whey permeate and corn steep water, P. freudenreichii achieved a concentration of 13.10 g/L with a yield of 0.335 g/g after 72 h in batch fermentation, while a fed-batch approach allowed for pH control and the further optimization of the process. Additionally, the study employed ion exchange cryogels for purification, achieving selectivity by using taurine-functionalized cryogels, with optimal adsorption at pH 4 for propionic acid, demonstrating the potential of these residual streams as cost-effective carbon sources for propionic acid production [40]. In another study, sweet sorghum bagasse hydrolysate served as a renewable substrate, yielding 0.51 g/g propionic acid, surpassing the yield obtained from glucose (0.44 g/g). This enhancement is attributed to the added nutrients and pH-buffering properties of the sweet sorghum bagasse hydrolysate. Co-fermentation with glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, further increased yield to 0.59 g/g, with higher propionic acid concentrations achieved in bioreactor setups, demonstrating P. freudenreichii’s high tolerance to product inhibition and suitability for high cell density fermentation [41]. Additionally, apple pomace extract and potato wastewater were effectively used as substrate components, resulting in a propionic acid yield of 0.42 g/g and a concentration of 12.71 g/L. These waste-derived media showed nearly equivalent production levels to traditional laboratory media, underscoring the potential for cost reduction in fermentation. Furthermore, this medium promoted additional metabolite production, such as trehalose, highlighting P. freudenreichii’s capacity to contribute to a more sustainable propionic acid production process [42]. Finally, for protein-rich substrates, Peptostreptococcus plays a crucial role. These bacteria thrive in nitrogen-rich environments and break down amino acids into VFA such as acetic and propionic acids, contributing to the acidogenic process. Their activity is particularly important in systems where protein degradation is a key part of the substrate composition, ensuring that nitrogenous compounds are efficiently converted into useful VFAs [43]. The adaptability of Peptostreptococcus and other proteolytic bacteria makes them essential in optimizing the conversion of complex substrates into VFAs, especially in heterogeneous waste streams where protein content may vary significantly.
In the case of butyric acid, production is mainly driven by Clostridium species, particularly C. butyricum and C. tyrobutyricum, which efficiently utilize sugars like glucose and xylose to produce high levels of butyric acid [44]. For example, C. tyrobutyricum can generate butyric acid yields of up to 86.9 g/L when fermentation conditions, such as pH, are carefully controlled [45]. This strain is particularly effective in systems that use immobilized cells, such as fibrous-bed bioreactors, which enhance productivity in industrial applications by maintaining cell stability and maximizing butyric acid output. Additionally, the ability of C. tyrobutyricum to thrive on a variety of substrates, including cane molasses and wheat straw hydrolysate, makes it versatile for different industrial waste streams [46]. Furthermore, C. tyrobutyricum can utilize both glucose and xylose for butyric acid production, with yields influenced by sugar concentration and ratio. Higher glucose levels (up to 75 g/L) resulted in greater butyric acid yields, reaching 27.0 g/L, while at lower concentrations (5–15 g/L), xylose was more efficient. In mixed sugar media, C. tyrobutyricum preferentially consumed glucose before xylose, and higher xylose-to-glucose ratios (4:1 or 3:2) improved butyric acid production when total sugar was maintained at 30 g/L [47]. In addition, mixed cultures involving Bacillus and C. tyrobutyricum have been used to produce butyric acid from sucrose, reaching concentrations of over 20 g/L. Notably, C. tyrobutyricum is a hyper-butyrate-producing bacterium that can re-assimilate acetate into butyrate via butyryl-CoA/acetate CoA transferase instead of the typical PTB-BK pathway (Phosphotransbutyrylase- Butyrate kinase) found in other clostridia and microbial species. This unique metabolic route allows C. tyrobutyricum to achieve high yields of butyrate and, through metabolic engineering, also high titers of n-butanol, enhancing its potential for industrial applications in producing C4 chemicals from various substrates, including sucrose [48]. Other strains like C. acetobutylicum have also been engineered for butyric acid production, achieving up to 2889 mgCOD/L by modifying key metabolic pathways and using bioaugmentation techniques. For example, the bioaugmentation of C. butyricum in a mixed culture system increased butyric acid production significantly, from 260 to 3000 mgCOD/L under alkali pH and with dairy industry wastewater as the substrate. This approach also boosted total VFA production from 1500 to 5000 mgCOD/L. The study demonstrated that bioaugmented mixed cultures outperformed pure cultures in butyric acid yield, with efficient production achieved in the first 6 h compared to 14 h in control reactors, highlighting the potential of combined monoculture and mixed culture systems for next-generation biorefineries [49]. Megasphaera has also shown significant potential in butyric acid synthesis through chain elongation under microbial electrosynthesis (MES) conditions. In a study utilizing fed-batch MES cells, Megasphaera played a key role in achieving a selective butyric acid production yield of 78% (carbon basis). When a second MES cell was inoculated with the enriched catholyte containing Megasphaera, the butyric acid production rate was maintained, while the lag phase decreased by 82%. This highlights Megasphaera’s ability to optimize carbon utilization and chain elongation processes, enhancing butyric acid output under efficient energy conditions and underscoring its potential for advanced bioaugmentation strategies in biorefinery applications [50]. This genus is often found in mixed communities where it helps balance the VFA profile by converting organic acids into butyrate and valerate. The interaction between different microbial species in these communities enhances the overall efficiency of the fermentation process, particularly when dealing with complex substrates like lignocellulose or protein-rich wastes.
In the sustainable bioproduction of isobutyric acid, specific microorganisms have demonstrated potential as alternatives to conventional chemical synthesis. Among them, Escherichia coli has been engineered to convert glucose to isobutyric acid using the Ehrlich pathway. In this process, glucose undergoes metabolic transformations into isobutyraldehyde through enzymes such as acetolactate synthase, keto-acid reductoisomerase, dihydroxyacid dehydratase, and keto acid decarboxylase [51]. Using this pathway, engineered E. coli strains have achieved isobutyric acid concentrations up to 12 g/L [52]. Another promising candidate is Pseudomonas sp., which has been engineered to channel isobutyric acid production via isobutyryl-CoA through its valine degradation pathway. By overexpressing the 2-ketoacid decarboxylase enzyme from Lactococcus lactis and performing specific gene deletions, this strain can produce up to 2.3 g/L of isobutyric acid, achieving better selectivity by reducing unwanted byproducts like isobutanol. Unlike other microbes, Pseudomonas sp. offers simpler downstream processing due to its reduced byproduct formation when glucose is used as the primary substrate [52]. In addition to Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas sp., other microorganisms play supporting roles in isobutyric acid production [53,54]. For instance, under anaerobic or microaerobic conditions, various bacteria such as Bacillus, Corynebacterium, and Streptomyces are capable of producing mixed acids, including isobutyric acid, from pyruvate to maintain redox balance [55]. While these microorganisms are not all specifically engineered for maximizing isobutyric acid production, their metabolic capabilities to process pyruvate and maintain redox balance make them potential candidates for industrial applications, particularly in mixed culture systems.
Valeric acid production through acidogenic fermentation involves several key microorganisms, each contributing to the breakdown of organic substrates and aiding in the synthesis of valeric acid. Among the prominent bacteria involved are those from the genera Clostridium, Propionibacterium, and Megasphaera. Clostridium species are known for their robust fermentative pathways, which efficiently convert carbohydrates into a mix of volatile fatty acids, including valeric acid [49]. Propionibacterium freudenreichii, which naturally produces isovaleric acid in environments such as Swiss cheese fermentation, has shown potential for engineered pathways that extend to valeric acid production [56]. Additionally, Megasphaera species are recognized for their role in chain elongation processes, transforming shorter-chain volatile fatty acids into longer chains like valeric acid [57].
Isovaleric acid production through microbial fermentation has gained attention due to its applications in the fragrance and pharmaceutical industries. Propionibacterium freudenreichii, for example, contributes to isovaleric acid formation as part of its metabolic processes, often seen in dairy fermentation [58]. Additionally, Escherichia coli has been engineered to enhance isovaleric acid output by manipulating the branched-chain amino acid pathway, where intermediates like ketovaline are converted into isovaleric acid through specific enzymatic steps. This engineered pathway provides an effective biotechnological route for isovaleric acid synthesis, offering an alternative to traditional chemical processes [59].
Caproic acid, a medium-chain fatty acid, is also produced by microbial fermentation and has various applications, from artificial flavor production to potential use as a biofuel precursor. This acid can be synthesized via reverse β-oxidation pathways using bacteria such as Clostridium kluyveri, which elongates shorter-chain fatty acids under anaerobic conditions [5]. Through the fermentation of substrates like lactic acid derived from lignocellulosic biomass, these microbes can efficiently generate caproic acid, supporting sustainable production methods for use in food, pharmaceuticals, and biofuels.
The adaptability and diversity of these microbial communities are key to the efficiency and stability of acidogenic fermentation. Mixed microbial consortia, rather than monocultures, are typically favored in industrial applications due to their robustness against fluctuating substrate compositions and environmental changes [60]. The dynamic interactions among these microbes ensure consistent VFA production even when the conditions vary, making the process resilient and adaptable to different waste streams. This adaptability is particularly important in the treatment of heterogeneous waste materials, where the composition of the feedstock may shift depending on the source, and maintaining a stable microbial community is crucial for optimizing the production of bioplastic precursors and other valuable chemicals [61].
2.3. Biotechnological Production of Volatile Fatty Acids
Although some VFAs such as propionic and butyric acids are currently produced at industrial scale via pure culture fermentation using refined substrates, no consolidated industrial process yet exists for their production from organic waste through mixed culture acidogenic fermentation. Most developments in this area remain at the pilot or demonstration stage. Industrial production typically relies on species such as Propionibacterium acidipropionici or C. butyricum, operated under sterile conditions with defined substrates like glucose, lactose, or glycerol. These systems offer high selectivity and productivity but depend on food-grade feedstocks and tight process control (e.g., pH 6.5, long fermentation times, anaerobiosis), which limits their sustainability and scalability [62].
The biotechnological production of VFAs from organic waste streams involves a series of interconnected stages that include the preparation of the microbial inoculum, the formulation of the fermentation medium, the selection of operational parameters, and the configuration of suitable bioreactors. These steps are critical for directing microbial metabolism towards acidogenesis while suppressing competing processes such as methanogenesis. Inoculum preparation typically relies on anaerobic mixed microbial cultures due to their resilience and broad metabolic capabilities. Common sources include sewage sludge, digestate from anaerobic reactors, or animal manure. To inhibit methanogenic activity and favor acid accumulation, the inoculum is often subjected to pretreatments such as heat shock (e.g., 85 °C for 1 h), acidification (pH below 4.0 for 24 h), or chemical inhibition using agents like 2-bromoethanesulfonate [63]. These treatments selectively suppress methanogens while preserving fermentative bacteria. Following pretreatment, the inoculum is sometimes acclimated to the substrate over several batch cycles to enhance performance [64]. The fermentation medium is usually composed of selected organic substrate (e.g., food waste, lignocellulosic hydrolysates, glycerol, or agro-industrial by-products) and is sometimes supplemented with macro- and micronutrients. Fermentation is generally conducted under anaerobic conditions in mesophilic (30–37 °C) or thermophilic (50–55 °C) temperature ranges, depending on the desired acid profile and the microbial community involved. Acidogenesis is favored at mildly acidic pH values (typically 5.0–6.5), which suppress methanogenic pathways and encourage the accumulation of VFA [65]. Figure 2 schematically illustrates the main stages of VFA production from organic waste while Figure 3 shows a pilot-scale facility for VFA production from waste streams, where the excess fermentation stream is valorized through methane generation.
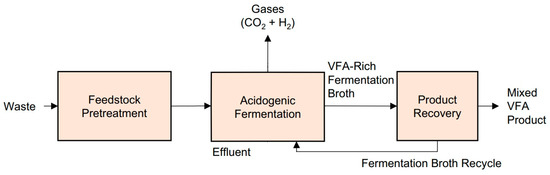
Figure 2.
Biotechnological production of VFAs from organic waste.

Figure 3.
VFA production pilot plant on Valladolid, Spain.
Various bioreactor configurations have been employed for VFA production. For continuous production, systems such as continuous stirred tank reactors (CSTRs; such as those shown in Figure 3), sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactors (UASBs), and anaerobic membrane bioreactors (AnMBRs) are employed. These configurations enable better control over solid and hydraulic retention times (HRTs) and improve process stability. However, industrial implementations increasingly favor membrane-based systems, which allow the decoupling of biomass retention and HRT, thereby increasing volumetric productivity [13].
2.4. Technical and Operational Challenges
Converting organic waste and wastewater into valuable VFAs presents a promising avenue for resource recovery. However, this process faces significant challenges, such as slow substrate hydrolysis, low yields, unstable acid compositions, and the complexity and expense of purification and post-processing methods [11]. To overcome these obstacles, optimizing operational strategies is essential. This includes enhancing substrate hydrolysis, managing factors that influence fermentation processes, improving VFA yields and profiles, and mitigating process inhibition. As a direct consequence, the selective production of VFAs from diverse feedstocks is an emerging research focus. It seeks to address the challenges posed by the complex composition of organic-rich waste streams, the dynamic nature of mixed microbial communities, the unpredictability of product types and concentrations, and the demand for efficient extraction and purification techniques [66].
Among the key parameters that govern acidogenic fermentation performance are pH, temperature, HRT, and organic loading rate (OLR). These variables shape the activity of microbial communities and determine both the rate and spectrum of VFA production. pH plays a central role in directing metabolic pathways. Acidogenic bacteria typically perform best under mildly acidic conditions (pH 5.0–6.5), which inhibit methanogenesis and favor VFA accumulation [65]. More acidic environments can hinder microbial activity due to proton accumulation, while near-neutral or alkaline pH may promote competing pathways such as methanogenesis or solventogenesis [67]. Temperature affects microbial kinetics and community structure. Mesophilic conditions (30–37 °C) are the most widely used due to their operational stability and balance between activity and robustness [21]. Thermophilic regimes (50–55 °C) may improve the hydrolysis and solubilization of complex substrates but often reduce microbial diversity and increase sensitivity to process fluctuations [68]. HRTs determine the contact time between biomass and substrate. Short HRTs (2–5 d) are frequently applied to wash out slow-growing methanogens and favor acidogenic pathways, although excessively short HRTs can limit substrate conversion and result in acidification inefficiencies [69]. The OLR defines the daily input of organic matter and strongly influences microbial stress and product accumulation. Moderate OLRs (2–6 g VS/L·d) are commonly used in acidogenic systems to balance productivity and microbial inhibition [70]. High OLRs may cause rapid pH drops and VFA accumulation, leading to process inhibition if not adequately buffered. Together, these parameters must be carefully balanced to maintain stable and efficient acidogenic conditions. In this section, we focus on the general operational challenges associated with real organic waste streams. Specific strategies for directing VFA composition by tuning these parameters are addressed in Section 5.
One of the major challenges in VFA production is the rate-limiting step in the hydrolysis of biopolymers. This phase, catalyzed by enzymes secreted by anaerobic acidogenic bacteria, plays a crucial role in determining process efficiency. The hydrolysis rate depends on substrate characteristics, particularly the available surface area for enzymatic activity [71]. Enzymatic interactions follow the induced-fit model, where substrate binding induces changes in the enzyme’s active site, enabling catalysis. Bacteria either secrete exoenzymes into the bulk liquid for subsequent adsorption onto the substrate or colonize the substrate surface, maximizing enzymatic activity through localized interactions [72]. For particulate substrates, hydrolysis is often described using first-order kinetics, with the rate influenced by substrate concentration and surface availability. In dissolved polymer substrates, however, the hydrolysis rate is governed by the concentration of active enzymes, which is affected by sludge concentrations and microbial dynamics [73]. This distinction underscores the importance of adapting operational strategies to the specific substrate type. However, hydrolysis is not always the limiting step. Duong et al. [69] found that acidification could become the primary constraint during protein degradation. In their study with gelatin, acidification rates were slower than hydrolysis rates under both methanogenic and non-methanogenic conditions. This led to amino acid accumulation—up to 40% of the substrate COD in batch experiments and 13% in continuous systems with retention times shorter than 8 d. These findings highlight the importance of addressing both hydrolysis and acidification to optimize VFA production. To overcome these challenges, process optimization must focus on enhancing enzymatic activity, managing microbial community dynamics, and tailoring operational parameters to substrate characteristics. By addressing rate-limiting steps and refining process conditions, the production of VFA from diverse organic feedstocks can achieve greater efficiency and scalability.
Substrate characteristics also influence the accessibility and degradation efficiency of biopolymers. For cellulose, properties like polymerization degree and crystallinity impact its susceptibility to cellulases [74]. Proteins are affected by structural traits and amino acid end groups, with highly soluble proteins hydrolyzing more rapidly than fibrous ones [75]. Lipids, due to their hydrophobicity, are less accessible to enzymes and often require emulsification to improve degradation [76]. Additionally, the presence of proteins and lipids in anaerobic reactors can cause operational issues, such as sludge flotation, biomass washout, and reduced mass transfer, further hindering system performance [77]. Strategies like physical or chemical pretreatment, lipid recovery, or the use of extracellular enzymes and Fenton oxidation have been proposed to mitigate these effects and enhance degradation [78]. Interactions among biopolymers further complicate the fermentation process. Research shows that carbohydrates are often prioritized for acidification over proteins and lipids [79]. Duong et al. [73] found that while carbohydrates do not directly inhibit the hydrolysis of dissolved proteins, their rapid degradation under non-methanogenic conditions can suppress protein breakdown due to the accumulation of VFA, particularly acetate. The relationship between substrate types and fermentation products also varies. Carbohydrates are generally associated with higher acetate production, proteins with increased levels of propionate and isovalerate, and lipids with the formation of medium- and long-chain fatty acids like caproic acid [11]. These complexities highlight the need for tailored strategies to optimize substrate degradation and manage interactions in mixed culture systems.
The carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio, or its equivalent in chemical oxygen demand to total nitrogen (COD/TN), is a key parameter influencing acidification processes in VFA production. This ratio governs microbial activity, substrate degradation, and the resulting VFA composition. Optimal C/N ratios, typically between 15 and 70, enable efficient acidification by balancing carbon and nitrogen availability. Deviations from this range can disrupt the process: high C/N ratios lead to nitrogen deficiency, slowing microbial metabolism and reducing acid yields, while low ratios result in ammonia accumulation, which is toxic to microbes [67]. For instance, increasing the C/N ratio in biowaste fermentation liquid by recovering ammoniacal nitrogen through a gas-permeable membrane contactor demonstrated its potential for improved VFA production. This process maintained high and stable VFA concentrations (37–39 g CODVFA/L), where VFA represented 73–81% of the soluble COD, predominantly acetic, propionic, and butyric acids. The enhanced C/N ratio supported optimal microbial activity, highlighting the effectiveness of this approach in maximizing VFA yields from biowaste [70]. Similarly, Tennison-Omovoh et al. [68] demonstrated the impact of varying C/N ratios on VFA production during the acidogenic fermentation of sucrose. Their study revealed that lower C/N ratios, such as 5, resulted in the highest VFA concentrations (26.08 g L−1), underscoring the importance of nitrogen availability for efficient acidogenesis. As the C/N ratio increased to 100, VFA production decreased significantly, accompanied by reductions in volatile solid degradation and carbohydrate utilization rates. Acetic acid remained the dominant VFA across all conditions, with its proportion rising at higher C/N ratios, while butyric acid production declined. These results reinforce the pivotal role of C/N ratio optimization in enhancing VFA yields and tailoring acid profiles, aligning with findings that nitrogen balance is critical for sustaining microbial activity and process efficiency. Co-digestion studies, such as those by Owusu-Agyeman et al. [80], demonstrated that mixing sewage sludge (COD/TN of 72) with organic waste (COD/TN of 57) increased valeric acid concentrations in the VFA spectrum from 11% to 22%, due to higher nitrogen content in the organic waste. This observation aligns with Duong et al. [73], who found that co-fermenting carbohydrates and proteins altered acidification pathways, favoring the production of protein-derived VFA. Substrate concentration is another influential factor in acidification. While higher substrate concentrations generally yield more VFA, excessive acid accumulation can inhibit microbial activity unless separated efficiently [70]. Wang et al. [21] observed that substrate concentration significantly influences VFA production, identifying a concentration of 200 g/L as optimal for both total VFA and n-butyrate production using food waste saccharified residue. At this concentration, the highest VFA yield was 280.87 mg COD/g VS, with n-butyrate comprising over 90% of the VFA composition. The efficiency of acidogenesis reached 82.39% (VFA/solubleCOD). Chain elongation, primarily driven by Clostridium Sensu Stricto 12, contributed 43.93% to n-butyrate formation, while 38.47% of the organic matter was further utilized. This demonstrates the critical role substrate concentration plays not only in determining VFA yields but also in influencing the metabolic pathways and microbial dynamics involved in the acidogenic process. When considered alongside other parameters, such as the C/N ratio and substrate composition, substrate concentration further underscores the need for tailored operational strategies to maximize VFA production. The interplay of these factors highlights the complexity of acidogenic fermentation and the importance of precise control over conditions to achieve optimal results. By addressing these interconnected variables, it is possible to refine acidification processes and enhance the efficiency of VFA production systems.
The microbial also community plays a critical role in determining the efficiency and composition of VFAs during acidogenic fermentation. Anaerobic mixed cultures, commonly used in these processes, offer several advantages, such as robustness, stability, and the ability to adapt quickly to diverse substrates without requiring feedstock sterilization [66]. However, the diversity of these microbial consortia often results in complex syntrophic interactions and unpredictable metabolic networks, making it challenging to control the production of specific acids in downstream processes. Bacillota, Bacteroidota, and Pseudomonadota are frequently reported as key phyla associated with VFA production [81]. Atasoy et al. [66] found that higher VFA yields were associated with an increased relative abundance of Clostridium, a genus within the Firmicutes phylum known for its role in butyric acid production. Their study also highlighted the influence of sludge structure, showing that granular sludge systems were more efficient for VFA production compared to slurry systems. Specifically, reactors seeded with granular sludge exhibited up to three times the relative abundance of Clostridium, leading to enhanced VFA production efficiency. Conversely, a higher presence of Chloroflexi was linked to reduced VFA yields, indicating its less effective role in acidogenic fermentation processes. High sludge concentration systems have been shown to enhance hydrolysis and VFA productivity by providing a stable microbial environment. Additionally, the long-term operation of these systems can lead to changes in the dominant microbial species, which in turn affect the VFA spectrum. For instance, Owusu-Agyeman et al. [80] observed a shift in their semi-continuous fermenter, where acetic acid was initially dominant, but caproic acid became the primary VFA, accounting for 55% of the total VFAs by day 23 and remaining stable throughout 115 days of operation. This transition was attributed to the adaptation of the microbial community to the substrate mix of primary sewage sludge and organic waste (50/50 COD ratio in the feed).
A critical insight from this analysis is that overcoming the challenges associated with VFA production requires a comprehensive approach that transcends the optimization of individual parameters such as substrate concentration, C/N ratio, or microbial community composition. The complexity lies in the multifaceted interactions among these factors within dynamic systems, where each operational adjustment impacts microbial activity, substrate degradation pathways, and VFA composition in a cascading manner. Future research should prioritize the development of integrated strategies that address these complexities holistically. For instance, the co-digestion of substrates with complementary characteristics could mitigate nutrient imbalances and enhance microbial efficiency. Additionally, the application of advanced predictive models to simulate microbial interactions and metabolic outputs under varying operational conditions would facilitate the more precise control of the fermentation process.
3. VFA as Bioplastic Precursors
The economic feasibility of bioplastics production remains a significant barrier to its widespread adoption, with costs being 5 to 10 times higher than those of conventional plastics [19,82]. A substantial portion of these costs—up to 50%—is attributed to the carbon source used in production [83]. This makes VFAs, derived from organic waste streams, a highly attractive alternative. VFAs are critical intermediates in the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), a class of biodegradable polyesters synthesized by bacteria. As direct metabolic precursors, VFAs provide the carbon building blocks for PHAs, making them a key component in sustainable bioplastic production. Their compatibility with both pure and mixed microbial cultures (MMCs) enhances the feasibility of integrating VFA production into bioplastic manufacturing processes [84,85]. In particular, MMCs provide a cost-effective alternative by eliminating the sterilization requirements associated with pure cultures, thereby significantly reducing production expenses [86]. This approach takes advantage of the metabolic flexibility of various bacterial genera, such as Bacillus megaterium, Alcaligenes eutrophus, and Pseudomonas oleovorans, which can efficiently utilize VFAs as carbon sources for PHA synthesis, further emphasizing their adaptability and industrial potential [87].
The composition of VFAs is a decisive factor in determining the monomeric structure and resulting properties of PHAs. Even-chain VFAs, such as acetic and butyric acids, predominantly promote the production of 3-hydroxybutyrate, which is associated with high crystallinity and thermal stability, making them suitable for rigid applications like packaging materials and agricultural films. Conversely, odd-chain VFAs, including propionic and valeric acids, facilitate the synthesis of 3-hydroxyvalerate, which enhances flexibility and elasticity, key for medical applications such as drug delivery systems, tissue engineering scaffolds, and surgical sutures [88,89]. By tailoring the ratio of even-chain VFAs to odd-chain VFAs during acidogenic fermentation, PHA can be customized to meet specific performance requirements across diverse applications. The synthesis of PHAs relies heavily on achieving optimal concentrations of 3-hydroxybutyrate and 3-hydroxyvalerate, as these monomers are pivotal for efficient polymer formation [28]. Strategies to refine the fatty acid composition for enhanced production include the use of nano zero-valent iron, which has shown promise in promoting 3-hydroxybutyrate synthesis [90,91], and the addition of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate to facilitate 3-hydroxyvalerate production [92]. The further diversification of PHA properties can be achieved by introducing additional monomers, such as 3-hydroxyhexanoate and 4-hydroxybutyrate. These components enable the development of high-performance bioplastics for demanding applications, including automotive parts and electronic casings, where enhanced mechanical and thermal properties are essential [93]. This ability to fine-tune PHA characteristics underscores the importance of precise control over VFA composition during fermentation, aligning with the needs of various industries.
Predicting the composition of VFAs produced during acidogenic fermentation is challenging due to the interplay of numerous factors, including substrate type, pH, temperature, OLR, HTR, and the composition of the microbial community [1]. For instance, carbohydrates typically favor the production of butyric acid, while protein substrates are more likely to yield acetic and propionic acids. However, these relationships are highly variable and depend on specific experimental conditions, making precise predictions difficult [94]. This complexity is further compounded by interactions between substrates in mixed waste streams, which can lead to unpredictable VFA profiles [16]. To address these challenges, mathematical modeling has emerged as a valuable tool for predicting VFA composition. Among the available approaches, energy-based metabolic models are currently the most effective for capturing the intricate dynamics of these processes. These models operate on the assumption that microorganisms prioritize metabolic pathways yielding the highest net ATP gain, thereby determining which VFAs dominate under specific conditions. This makes energy-based models particularly valuable for predicting outcomes across varying operational parameters, including pH and substrate type [95]. Earlier models were based on fixed stoichiometry, which assumed constant reaction pathways without accounting for changes in operational conditions [96]. Variable stoichiometry models were later introduced, offering greater flexibility by incorporating operational factors such as pH and substrate composition. However, these models still lacked the precision needed for complex anaerobic processes, as they were more aligned with kinetics-driven aerobic systems like those described by ASM-family models [97]. In contrast, energy-based metabolic models consider thermodynamic constraints, which are critical in anaerobic environments where energy supply is low, and metabolic conversions are limited by equilibrium conditions. Energy-based metabolic models have also been applied to protein substrates [95].
One notable example is the model developed by González-Cabaleiro et al. [98], which was among the first to predict VFA profiles from glucose under varying pH conditions. This model demonstrated that butyric acid dominates at low pH, while acetic acid and ethanol prevail at higher pH levels. However, initial predictions did not fully align with experimental observations, where acetic acid often co-dominates with butyric acid at a low pH. Subsequent refinements by Regueira et al. [99] included electron bifurcation in butyrate synthesis pathways and homoacetogenesis processes, successfully improving predictions of acetic and butyric acid yields at low pH. Later, Regueira et al. [100] developed a framework to predict VFA derived from protein fermentation, accounting for amino acid interactions and NADH competition. This model highlighted how external pH influences metabolic pathways, enabling accurate predictions of VFA composition for defined amino acid profiles. Furthermore, this approach has been extended to co-fermentation systems, where mixtures of carbohydrates and proteins, such as glucose and gelatin, were modeled. These studies revealed that glucose supplementation alters the NADH balance, favoring pathways that maximize ATP yields. However, the model’s effectiveness depends heavily on detailed substrate characterization, particularly the amino acid profile of proteins used as feedstock [101]. Building on these advancements, Regueira et al. [102] proposed a novel workflow that integrates mathematical modeling with experimental validation to further refine the bioprocess design. This approach was applied to a defined co-culture of Pediococcus pentosaceus and Megasphaera cerevisiae to optimize the production of both odd- and even-carbon VFAs from food waste. An unstructured kinetic model was developed and calibrated to predict metabolic pathways, enabling the design of experiments aimed at increasing the selectivity for specific VFAs. Experimental validation demonstrated the model’s capacity to enhance process outcomes. For even-carbon VFAs, the caproate yield increased by 38%, while experiments targeting odd-carbon VFAs resulted in a significant shift in product distribution. Butyrate and caproate yields decreased by 62% and 94%, respectively, whereas propionate emerged as a dominant product, and valerate yield increased from 0.007 to 0.085 g of valerate per gram of consumed sugar. This workflow effectively utilized in silico modeling to identify optimal operational conditions, reducing the need for extensive trial-and-error experimentation.
Despite their potential, current energy-based models face limitations, particularly the exclusion of hydrolysis—a crucial step in breaking down complex substrates into simpler forms suitable for microbial uptake. Additionally, these models require extensive experimental validation and may not fully capture the dynamic interactions within diverse microbial communities. Nonetheless, their ability to mechanistically explain fermentation processes and predict VFA distributions under different environmental conditions makes them indispensable for optimizing acidogenic fermentation. Future efforts should aim to integrate hydrolysis dynamics into these models and extend their application to heterogeneous waste streams, improving their utility in real-world systems.
4. Waste Streams as a Resource for VFA Production
Currently, the commercial production of VFA primarily relies on petrochemical-derived substrates or refined carbohydrate sources such as glucose, sucrose, and molasses. Acetic acid, for example, is commonly produced via methanol carbonylation or fermentation of glucose, while propionic and butyric acids are typically obtained through the fermentation of starch, sugar beet molasses, or whey permeate. However, these raw materials compete with food and feed applications, making the transition to organic waste streams an environmentally and economically attractive alternative. Selecting an appropriate feedstock is crucial for VFA production from biomass, primarily due to variations in composition and availability. Biomass sources differ significantly in their carbohydrate, lignin, and other constituent levels, directly influencing their suitability for fermentation processes. Since VFAs are predominantly produced through carbohydrate fermentation, feedstocks with higher carbohydrate content are generally more favorable. For instance, simpler substrates like starch and fruit wastes have been shown to produce approximately 50 mmol/L of VFAs, whereas more complex substrates such as grass yield around 25 mmol/L, highlighting the impact of substrate complexity on VFA production efficiency [103]. Beyond composition, the availability of biomass feedstocks is vital for sustainable and large-scale VFA production. Factors such as geographic location, climate, and agricultural practices significantly affect the accessibility and consistency of biomass supply [104]. For industrial applications, selecting feedstocks that are not only rich in fermentable carbohydrates but also readily available in substantial quantities is essential to ensure economic viability and continuous operation. To provide a general overview of the factors influencing the conversion of residual biomass into VFAs, Figure 4 summarizes the main feedstock sources and the operational parameters that affect VFA production efficiency.
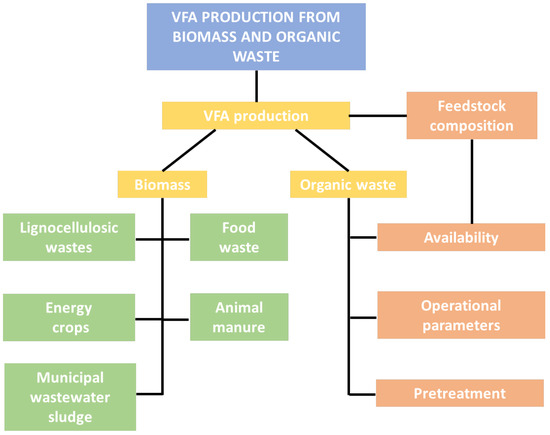
Figure 4.
Main sources of residual biomass and key factors influencing the production of VFAs through acidogenic fermentation.
Various biomass types have been extensively studied for their potential in VFA production, considering factors such as composition, availability, and environmental impact. Some recent works are shown in Table 3. However, in most of the studies included in this table, fermentation was performed using uncharacterized mixed cultures, typically anaerobic sludge from operating digesters. Therefore, specific microorganisms used as inoculum are not reported. Lignocellulosic wastes, such as agricultural residues like corn stover, wheat straw, rice husks, and sugarcane bagasse, as well as forest residues including wood chips and sawdust, present a valuable resource for VFA production due to their abundance and potential for waste valorization. With an estimated global production of over 4 billion tons annually, these residues offer a substantial feedstock for bioconversion processes [105]. To optimize VFA yields from lignocellulosic biomass, it is crucial to carefully regulate key operational parameters. Sun et al. [105] emphasized the importance of maintaining particle size within an acceptable range and operating under mesophilic conditions (35–40 °C). Additionally, a carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio between 20 and 40, an OLR below 12 g of volatile solids (VSs)/(L·d), and a HRT of 8–12 days have been recommended as optimal conditions to maximize VFA production. These parameters ensure efficient fermentation by creating an environment conducive to microbial activity while preventing process inhibition. Among these types of biomass, rice straw has shown remarkable potential for VFA production through altered anaerobic digestion processes. More et al. [106] reported a VFA yield of 0.63 g/g COD, with a productivity of 6.4 gCOD/L·d. These results were achieved under specific conditions, including an organic OLR of 12 gCOD/L·d and HRT of 1 day. Dedicated energy crops, such as switchgrass (Panicum virgatum), miscanthus (Miscanthus × giganteus), and giant reed (Arundo donax), are cultivated specifically for biomass production. These crops are characterized by high biomass yields and can be grown on marginal lands, reducing competition with food crops and enhancing land-use efficiency. Switchgrass has been investigated for its ethanol production potential, which indirectly relates to VFA production as intermediates in the fermentation process. Switchgrass can theoretically yield between 4800 and 7900 L of ethanol per hectare annually, depending on cultivation conditions [107]. This corresponds to a theoretical VFA production in a similar range, estimated to be between 4900 and 8000 kg per hectare annually, depending on the initial ethanol yield and the efficiency of the conversion process. Recent studies have explored the potential of switchgrass for VFA production through anaerobic digestion demonstrating that pretreated switchgrass can yield significant concentrations of VFAs, with acetic acid being the predominant component [108].
Various organic waste streams, including food waste, animal manure, and industrial byproducts like glycerol from biodiesel production, serve as viable feedstocks for VFA production. Food waste, for instance, contains high concentrations of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates, making it a promising substrate for VFA production [109]. Studies have demonstrated that the acidogenic fermentation of food waste can yield significant VFA concentrations. Kumar et al. [110] demonstrated that untreated food waste effectively supports targeted butyric acid production under psychrophilic fermentation conditions (17 °C), achieving concentrations of 0.5 g/L after 7 days. In contrast, thermal–alkaline pretreatment reduced butyric acid yields, emphasizing the importance of intrinsic food waste microflora. These findings highlight psychrophilic fermentation as a potential strategy for VFA production from food waste. Castro-Fernández et al. [14] investigated the scale-up of VFA production from food waste via anaerobic digestion and compared it with biomethane generation. At lab scale (5 L), optimal conditions of pH 7 and an OLR of 10 g COD/L/d achieved a VFA yield of 36.6% COD-VFA/g COD substrate and a production rate of 3.9 g COD-VFA/L/d. These results were successfully replicated in a semi-industrial pilot plant (1.5 m3), maintaining similar performance metrics. Acetic acid was the predominant VFA (50% mass basis), followed by propionic and butyric acids (20% each). The economic analysis revealed that VFA production yields significantly higher revenues (22.9 EUR/t food waste) compared to biomethane production (11.7 EUR/t food waste), highlighting the economic advantage of VFA recovery from food waste.
Animal manure is a typical co-substrate in VFA production processes. Ma and Huang [111] explored the anaerobic co-fermentation of sludge and chicken manure, highlighting the impact of pH on VFA production and microbial dynamics. Alkaline conditions increased VFA concentrations by 1.4 times, with acetic and propionic acids dominating. pH influenced NH4+-N and PO43−-P levels, metabolic pathways, and microbial communities, with Firmicutes prevailing and Bacteroidota and Proteobacteria abundant at pH 9. A strategy to achieve high concentrations of free VFAs involves regulating pH during the anaerobic digestion of nitrogen-rich animal manure. In a 150-day study of high-solid chicken manure digestion, the process initially stabilized at pH 6.0 with total ammonia nitrogen at 7.0 g/L, yielding a low free VFA concentration of 3.1 g/L. On day 70, hydrogen chloride was added to lower the pH to 5.5, eventually dropping further to 4.3, with ammonia decreasing to 2.3 g/L. This adjustment significantly increased free VFA concentration to 12.6 g/L, demonstrating that targeted pH regulation can enhance free VFA production in nitrogen-rich substrates [112]. Municipal wastewater sludge is another valuable substrate for VFA production due to its high organic content. Fu et al. [113] demonstrated that pretreatment methods, such as thermal hydrolysis at 150 °C or alkali addition to adjust pH to 10, significantly increased solubilized organic matter by up to 40%, enhancing VFA yields. Optimal operational conditions included a HRT of 10 days and mesophilic temperatures (35 °C), which resulted in VFA concentrations of approximately 8.5 g/L. Additionally, co-digestion with food waste was shown to balance carbon-to-nitrogen ratios, further improving process efficiency and VFA production.
The examples discussed underline how the choice of feedstock significantly shapes the efficiency and feasibility of VFA production. From carbohydrate-rich agricultural residues to complex organic streams like sludge and food waste, the diversity of substrates demands tailored approaches to optimize yields. Strategies such as co-digestion and specific pretreatments play a key role in enhancing substrate performance, demonstrating the potential for sustainable and scalable VFA production across a variety of waste streams.

Table 3.
Waste streams for VFA generation.
Table 3.
Waste streams for VFA generation.
| Substrate | Operational Setup | Yield | VFA Composition (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citrus residues | Batch fermentation: pH 6, 37.5 °C, S:I ratio 1:1, duration 14 days | 0.79 g-VFA/g-VS | Acetic: 40, Propionic: 5.3, Butyric: 18.3, Others: 36.4 | [114] |
| Potato peels | Batch fermentation: pH 7, 37 °C, duration 5 days | 0.63 g-COD/g-VS | Acetic: 45.8, Propionic: 28.5, Butyric: 24.2, Others: 1.5 | [115] |
| Brewery spent grain | Batch fermentation: pH 6.5, 30 °C, duration 10 days | 0.68 g-VFA/g-VS | Acetic: 50, Propionic: 20, Butyric: 25, Others: 5 | [116] |
| Rice straw hydrolysate | Anaerobic digestion; pH 9.0; 37 °C; 1 day HRT | 0.63 g VFA/g COD | Acetic: 45, Propionic: 30, Butyric: 25 | [106] |
| Food waste | Semi-continuous membrane bioreactor: uncontrolled pH, OLR 2 g-VS/L·d | 0.54 g-VFA/g-VS | Acetic: 20–30, Propionic: 3–10, Butyric: 14–23, Others: 35–65 | [117] |
| Food waste | Leach bed fermentation: pH 7, 22 °C, S:I ratio 25:1, duration 6 days | 0.65 g-COD/g-VS | Acetic: 27.9, Propionic: 12.9, Butyric: 33.7, Others: 25.5 | [118] |
| Food waste | Anaerobic digestion: pH 7.0; 35 °C; 20 days | 0.4–0.6 g VFA/g VS | Acetic: 50–60, Propionic: 15–25, Butyric: 10–20 | [119] |
| Food waste | Batch fermentation: initial pH 10 (alkaline condition), inoculum acclimated to food waste, 35 °C, 15 days | 21.98 g COD/L (highest VFA concentration reported) | Acetic: 38–57, Propionic: 25–30 | [120] |
| Dairy manure | Semi-continuous anaerobic membrane bioreactor: uncontrolled pH, OLR 4.7 g-VS/L·d, 114 days | 0.41 g-VFA/g-VS | Acetic: 53–89, Propionic: 4–15, Butyric: 1–12 | [121] |
| Poultry manure | Batch fermentation: uncontrolled pH, 37 °C, S:I ratio 3:1, duration 35 days | 0.53 g-VFA/g-VS | Acetic: 80–90, Propionic: 10–15 | [122] |
| Chicken manure | Batch reactor: pH 5.5, 37 °C, duration 30 days | 1.20 g-VFA/g-VS | Acetic: 60, Propionic: 15, Butyric: 20, Others: 5 | [123] |
| Waste sludge | Semi-continuous bioreactor: S:I ratio 2:1, 35 °C, duration 12 days | 0.33 g-COD/g-VS | Acetic: 25–43, Propionic: 8–33, Butyric: 11–50, Others: 14–34 | [124] |
| Waste sludge | Batch fermentation: pH 9, S:I ratio 1:1, 55 °C, duration 10 days | 0.52 g-VFA/g-VS | Acetic: 53, Propionic: 10, Butyric: 10, Others: 27 | [125] |
| Waste sludge and apple pulp | Co-fermentation under thermophilic conditions (55 °C), alkaline pH (9), batch operation | 15.50 g COD/L; 255.68 mg VFA/g COD substrate | Acetic acid: 60%, Butyric acid: 30%, Others: 10% | [126] |
| Sewage sludge and organic waste | Acidogenic fermentation: pH 5.5, ambient temperature, HRT of 5 days | VFA production of 4.5 g/L | Acetic acid: 45%, Propionic acid: 25%, Butyric acid: 20%, Others: 10% | [127] |
| Organic fraction of municipal solid waste | Anaerobic digestion: pH 6.0; 37 °C; 15 days | 0.5–0.7 g VFA/g VS | Acetic: 40–50, Propionic: 20–30, Butyric: 15–25 | [5] |
| Organic solid waste leachate | Upflow anaerobic bioreactors: uncontrolled pH, 186 days of operation | Net acidification degree (NAD) of 0.45 | Acetic acid: 50%, Propionic acid: 20%, Butyric acid: 15%, Others: 15% | [128] |
5. Targeted Acidogenic Fermentation for Bioplastics Production
Targeted acidogenic fermentation, understood as the deliberate manipulation of fermentation conditions to produce specific VFA profiles, has emerged as a critical strategy for optimizing bioplastic synthesis [116,123]. The specific VFA—such as acetic, propionic, butyric, or valeric acids—are key determinants of the mechanical, thermal, and degradation properties of bioplastics, enabling the tailoring of these materials for diverse applications. Achieving a desired VFA profile requires a holistic approach, encompassing the selection of appropriate substrates, the application of effective pretreatment methods, the optimization of operational parameters (e.g., pH, temperature, and retention time), and the management of microbial community dynamics. This section examines the latest advancements in operational strategies and process innovations aimed at enhancing the precision and efficiency of VFA production with the focus on bioplastic applications.
Targeted acidogenic fermentation enables the efficient conversion of complex organic waste into VFA with tailored profiles, significantly influencing microbial metabolic pathways. For instance, elevated acetic acid concentrations can enhance lipid accumulation in yeast, while higher caproic acid levels have been associated with inhibitory effects on microbial activity [129]. These dynamics underscore the importance of fine-tuning fermentation conditions to achieve the optimal VFA composition for specific applications. Current research emphasizes the strategic manipulation of substrate composition and operational parameters, such as pH, temperature, and retention time, to direct VFA production toward profiles that maximize their utility, particularly in the context of bioplastic synthesis [28]. As highlighted earlier, the VFA profile is strongly influenced by the composition of the feedstock, while operational parameters in the bioreactor significantly shape the microbial community and its metabolic outcomes. These parameters play a critical role in steering the fermentation process, as they determine which microbial groups thrive and which metabolic pathways dominate. For instance, a high OLR combined with a short HRT favors the proliferation of hydrolytic and acidogenic bacteria, while inhibiting slow-growing methanogens, thereby minimizing VFA degradation. Similarly, factors such as pH and temperature uniquely impact the activity and functionality of different microbial groups. To optimize VFA production, the careful adjustment of these conditions is essential. To visually summarize the overall process from biomass to application, Figure 5 illustrates the main stages and influencing factors in the conversion of organic waste into VFAs, including feedstock types, pretreatment strategies, microbial fermentation conditions, and end-use applications.
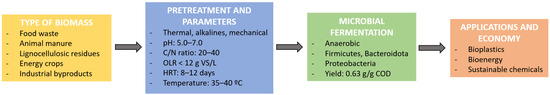
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the biomass-to-VFA pathway.
The pH of the acidogenic fermentation process is a critical factor that directly influences microbial activity, substrate degradation, and the resulting VFA profile. Maintaining an optimal pH range is essential for maximizing VFA production and steering the fermentation process toward desired outcomes. The ideal pH for acidogenesis typically lies within the acidic range of 4.5–6.0, where methanogenic activity is effectively suppressed, enabling the accumulation of VFA. In this range, acetic acid is usually the dominant product, followed by propionic and butyric acids, depending on the substrate composition [130]. Maintaining a pH below 6.0 prevents methanogens from consuming VFAs, resulting in acidification yields as high as 60–80% of the soluble COD [131,132]. However, if the pH drops below 4.5, the acidogenic pathways can be disrupted, leading to the production of undesired byproducts like ethanol or lactic acid due to shifts in microbial activity [133]. As the pH increases beyond 6.0 and approaches neutral or alkaline conditions (7.0–9.0), the microbial dynamics and metabolic pathways change significantly. Alkaline pH conditions enhance the hydrolysis of protein-rich substrates and support the production of butyric and valeric acids [15]. However, extremely high pH levels (10–12) may promote substrate hydrolysis but significantly inhibit acidogenic activity, resulting in lower VFA accumulation [130]. The specific pH also affects the VFA profile, with acetic and propionic acids dominating under acidic conditions, while butyric and valeric acids are more prevalent in alkaline environments.
The VFA profile generated under different pH conditions plays a pivotal role in determining the type of bioplastic that can be synthesized. Acetic acid, produced predominantly at acidic pH, serves as a key precursor for polyhydroxybutyrate, a bioplastic valued for its high crystallinity and biodegradability, ideal for packaging and agricultural applications [134]. Propionic acid, also favored in acidic environments, supports the production of polyhydroxyvalerate, which can be copolymerized with polyhydroxybutyrate to form poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate). This copolymer offers enhanced flexibility and toughness, expanding its potential uses [135]. In contrast, alkaline conditions promote the production of butyric acid, which is a precursor for medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates (mcl-PHA). These mcl-PHA have elastomeric properties, making them suitable for applications requiring flexibility, such as medical devices and adhesives [136]. By carefully managing the process pH, it is possible to tailor the VFA profile to synthesize bioplastics with specific mechanical, thermal, and degradation properties, aligning the fermentation process with industrial and environmental demands.
Apart from pH, HRT and OLR are pivotal operational parameters in anaerobic digestion processes, significantly influencing the production of specific VFA, which serve as precursors for bioplastics like PHA. Adjusting HRT impacts microbial growth and the quantity of organic matter introduced into the reactor. Extended HRTs facilitate the degradation of complex substrates by allowing for increased bacterial proliferation and the establishment of microbial communities capable of hydrolyzing feedstock components, thereby enhancing the availability of soluble organic matter for the acidogenic phase. However, prolonged HRTs, associated with low flow rates, may encourage the growth of slow-growing microorganisms such as methanogenic archaea, which are undesirable in this context. Therefore, shorter HRTs are often preferred to suppress methanogenic activity [28]. High OLRs, typically linked with short HRTs, can lead to process overloads that lower pH levels, thereby promoting the production of short-chain fatty acids and further inhibiting methanogenic activity. For instance, Cavinato et al. [137] observed that HRTs shorter than 6 days enhanced VFA production, while Teixeira et al. [138] reported a twofold increase in VFA production when increasing HRT from 19 to 41 days using untreated complex substrates. Additionally, short HRTs are generally associated with the production of shorter VFAs, such as acetic and propionic acids [19], whereas longer HRT with carbohydrate-rich feedstocks combined with acidic pH conditions tend to result in the accumulation of longer VFAs like butyric and caproic acids [139]. Consequently, selecting appropriate operational conditions should consider the macromolecular composition of the feedstock and the desired VFA profile for subsequent processes. Given the substantial impact of HRT and OLR on process performance and VFA profiles, alternative reactor configurations to continuous stirred tank reactors are under active investigation. Depending on feedstock characteristics, systems such as up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactors [140], sequencing batch reactors [141], and anaerobic membrane bioreactors [142] are studied, as these designs allow for the decoupling of HRT and solid retention time. This decoupling enables the maintenance of high flow rates without necessitating significantly larger tank volumes, due to the high solid retention within the system, thereby enhancing the cost-effectiveness of the process. As already discussed for pH, the selection of operational parameters, including HRT and OLR, significantly impacts the VFA profile generated during anaerobic digestion, which subsequently determines the type of bioplastic that can be produced. For instance, a study on the acidogenic fermentation of wood mill effluents operated at pH 5.5 with HRT of 1.0 and 1.5 days, corresponding to OLR of 5.6 and 2.9 g COD/L·d, respectively, found that while acidification yields were similar, higher HRTs led to increased concentrations of longer-chain VFAs [143]. These longer-chain VFAs, such as butyric and valeric acids, are crucial precursors for the production of mcl-PHAs. Therefore, by adjusting HRT and OLR, it is also possible to steer the fermentation process toward the production of specific VFAs, thereby tailoring the synthesis of desired bioplastics.
Another crucial parameter influencing VFA production during acidogenic fermentation is temperature. The optimal temperature range is determined by the microbial community, which is influenced by the composition and complexity of the feedstock. Since hydrolysis is often the limiting step in the anaerobic fermentation process, mesophilic and thermophilic conditions are commonly employed to enhance microbial enzymatic activities. Mesophilic processes operate at temperatures between 20 and 43 °C, with 35–37 °C typically considered optimal. These conditions have been found to be effective for feedstocks such as cow manure, maize silage, or the organic fraction of municipal solid waste, as both hydrolytic and acidogenic activities are enhanced. For instance, a study on the anaerobic fermentation of cow manure and maize silage reported that mesophilic conditions favored the production of acetic and butyric acids. The optimal condition was identified as an organic loading rate of 17.9 g TVS m−3 with a 4-day HRT at 37 °C, achieving an acidification yield of 183.2 g COD kg VS−1 [137]. These VFAs were essential precursors for PHAs synthesis. Thermophilic processes, conducted at 50–60 °C, are often utilized for the anaerobic fermentation of recalcitrant feedstocks, such as protein-rich substrates [144]. Although thermophilic processes involve higher energy demands, they can achieve high bioconversion efficiencies with a specific VFA profile, simplifying downstream processes [145]. Urbina et al. [85] investigated the acidogenic fermentation of cheese whey under thermophilic conditions to produce VFAs for subsequent PHA biosynthesis. The study found that thermophilic conditions favored the production of butyric acid. Other works [146,147] indicate that thermophilic conditions can lead to increased concentrations of longer-chain VFAs, such as caproic and valeric acids, which are valuable for producing mcl-PHAs. Both mesophilic and thermophilic conditions can promote the growth of methanogenic archaea, leading to the conversion of VFAs into methane and reducing fermentation efficiency. To mitigate this, high temperatures should be combined with operational parameters like short hydraulic retention times and acidic pH to suppress methanogenesis [28]. Conversely, psychrophilic processes operate at temperatures below 20 °C and can be effective for feedstocks characterized by a high content of readily biodegradable carbohydrates [148]. Low temperatures significantly limit the growth rate of methanogens, promoting VFA accumulation. Studies have shown that psychrophilic conditions favor the production of acetic and propionic acids [149], which are key precursors for synthesizing polyhydroxybutyrate and polyhydroxyvalerate, respectively. In summary, temperature control is crucial in directing the VFA profile during anaerobic fermentation, thereby determining the specific types of bioplastics that can be synthesized. Mesophilic conditions tend to favor the production of shorter-chain VFAs like acetic and butyric acids, suitable for PHB production, while thermophilic conditions can enhance the production of longer-chain VFAs, beneficial for mcl-PHA synthesis. Psychrophilic conditions, by suppressing methanogenesis, can also be tailored to produce specific VFAs for targeted bioplastic production.
The composition of the substrate is another factor that significantly influences the profile of VFAs produced during anaerobic fermentation. The relative proportions of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids in the feedstock determine the metabolic pathways activated by the microbial community, leading to the formation of specific VFAs [43,142]. For instance, carbohydrate-rich substrates typically result in higher production of acetic and butyric acids [150], while protein-rich substrates tend to increase the formation of propionic and valeric acids [151]. The microbial community’s composition adapts to the substrate, with certain bacterial phyla playing pivotal roles in VFA production. Notably, bacteria from the Firmicutes phylum are instrumental in hydrolyzing complex polymers and fermenting them into VFAs [152]. Within this phylum, genera such as Clostridium and Butyrivibrio are recognized for their butyric-producing capabilities [153]. Understanding the relationship between substrate composition and VFA profiles is crucial for optimizing the production of specific acids, which serve as precursors for various bioplastics, as previously indicated. Proteinaceous substrates, such as sewage sludge or microalgae, play a significant role in anaerobic fermentation due to their ability to release amino acids during degradation. These amino acids are subsequently converted into carboxylic acids through two primary metabolic pathways. The first pathway, Stickland fermentation, involves the utilization of amino acids as electron acceptors, resulting in the production of VFAs with the same carbon chain length as the originating amino acid [154]. The second pathway, amino acid reduction via the Wood–Ljungdahl pathway, relies on hydrogen-utilizing bacteria for successful conversion [155]. Studies have demonstrated that protein-rich substrates predominantly lead to the formation of acetic and propionic acids as the major VFA. For example, Magdalena et al. [156] reported that microalgae biomass subjected to acidogenesis produced VFA profiles dominated by acetic and propionic acids, constituting 50% of the total carboxylic acids. Similarly, Llamas et al. [43] observed the dominance of these acids in 60–65% of the VFA profile, while Iglesias-Iglesias et al. [157] noted an increase to 70–80% when sewage sludge was used as a substrate. The microbial community in protein-rich anaerobic fermentation processes is typically dominated by members of the phylum Firmicutes, accounting for 65–85% of the total community [154]. Specific genera, such as Peptostreptococcus and Sporoanaerobacter, are responsible for producing propionic and acetic acids, respectively, while Clostridium, known for its capability to perform Stickland fermentation, facilitates further VFA production under anaerobic conditions [28]. The coexistence of these microbial mechanisms highlights the intricate interplay between Stickland fermentation and the WoodLjungdahl pathway in shaping the VFA profile during anaerobic fermentation of proteinaceous substrates. In contrast, carbohydrate-rich substrates yield distinct VFA profiles, with acetic and butyric acids emerging as the predominant carboxylic acids [158]. Carbohydrate degradation produces a variety of sugars, such as fructose, glucose, and galactose, which are metabolized into VFAs. Butyrate-type fermentation and acetogenic pathways dominate this process under mild operational conditions. Studies show variability based on substrate composition; for example, Zhang et al. [159] found that anaerobic fermentation of potato peels resulted in 40% acetic acid dominance, while Greses et al. [132] reported butyric acid concentrations of 41.1–43.5% from cucumber and tomato residues. Increased carbohydrate content in substrates has been correlated with higher butyric acid yields. The microbial community involved in carbohydrate degradation includes bacteria from the orders Lactobacillales and Clostridiales. Lactobacillales encompass metabolically diverse organisms capable of producing lactic acid, which can be further converted into VFA. Key species such as C. tyrobutyricum and Acetobacterium woodii drive butyrate and acetate production, respectively [159], while Ruminococcus plays a critical role in converting carbohydrates into acetic and butyric acids [133]. It is worth noting that the bioconversion efficiency of organic matter into VFAs depends on the substrate’s composition and biodegradability. Typically, 10–50% of the COD in feedstocks is converted into VFAs [160]. However, substrates containing recalcitrant compounds, such as lignin in lignocellulosic biomass, require pretreatment to improve microbial access. Common pretreatment methods, including enzymatic hydrolysis, steam explosion, and chemical catalysis, enhance substrate bioavailability but add complexity and cost to the process [161]. Optimizing substrate composition and operational conditions not only improves bioconversion efficiency but also enables anaerobic fermentation processes to be tailored for the production of specific VFAs, which serve as key precursors for bioplastics. This highlights the critical role of advanced microbial and substrate engineering in boosting the economic feasibility of bioplastic production, bridging the gap between sustainable waste valorization and industrial-scale application.
While the strategies discussed above focus on manipulating operational conditions to influence microbial activity and VFA profiles, recent developments in synthetic and systems biology have opened up new avenues for controlling fermentation outcomes at the genetic level. In addition to the manipulation of environmental and operational parameters, advances in genetic and metabolic engineering have emerged as complementary strategies to improve the selectivity and efficiency of VFA production [5]. These approaches aim to reprogram microbial metabolism by redirecting carbon fluxes toward the synthesis of specific carboxylic acids. Gene knockouts are frequently used to suppress competing pathways, such as those involved in ethanol or lactate production [162], while the overexpression of key enzymes—such as acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, phosphotransbutyrylase, butyrate kinase, or propionyl-CoA transferase—enhances the conversion of central intermediates toward target VFAs [163]. In parallel, CRISPR-based genome editing and synthetic regulatory circuits have enabled the dynamic control of gene expression in response to environmental cues, allowing for more precise metabolic steering [164]. These strategies have been successfully applied in model microorganisms, including Escherichia coli, C. acetobutylicum, and Propionibacterium acidipropionici, particularly in systems utilizing defined substrates like glucose, glycerol, or lactate under sterile conditions [165]. However, the application of these tools to VFA production from organic waste remains limited. The majority of waste valorization systems rely on undefined mixed microbial cultures, where genetic manipulation is not feasible due to the lack of genetic tractability and the complexity of community interactions. Furthermore, the non-sterile, variable nature of waste feedstocks makes it difficult to maintain the stability and dominance of engineered strains in open systems. As a result, most current research efforts still focus on tuning operational conditions to guide metabolic pathways naturally selected under selective pressures. Nevertheless, the development of engineered consortia, host strains with broad substrate utilization capabilities, and community-level synthetic biology approaches may pave the way for more controlled and efficient microbial platforms for VFA production in future applications.
6. Summary and Future Perspectives
The acidogenic fermentation of waste streams has demonstrated significant potential as a pathway for the production of VFAs, which are essential intermediates for bioplastic synthesis. This approach aligns with circular economy principles, enabling waste valorization and fostering sustainable alternatives to petrochemical-based processes. However, transitioning from laboratory-scale studies to industrial applications remains a critical challenge, requiring holistic advancements in operational strategies, policy frameworks, and market integration. Key future directions include integrating acidogenic fermentation with complementary waste valorization technologies to enhance efficiency and product specificity. For instance, combining fermentation with anaerobic digestion or bioelectrochemical systems could optimize substrate utilization while enabling the co-production of energy or other value-added products. Research into microbial engineering and metabolic modeling is pivotal for achieving targeted VFA profiles tailored to specific industrial demands, such as bioplastics with desired mechanical and thermal properties. Currently, there is a growing body of research focusing on synthesizing PHAs from various organic waste streams, including industrial, agricultural, and urban organic wastes. However, improving the synthesis efficiency and yield of PHAs is challenging due to the complexity of substrate properties. Complex substrates can introduce inhibitors that negatively affect PHA accumulation. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the impact of these complex substrate components on PHA accumulation based on different substrate types and to develop improved pretreatment methods, fermentation strategies, and synthesis processes to mitigate the negative effects of such inhibitors. Fermentation conditions such as pH, carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, OLR, and temperature are important factors influencing PHA production. Before large-scale production, optimizing these reaction conditions is essential to provide strong support for the standardization of synthesis. In terms of kinetics, establishing a comprehensive kinetic model based on chemical processes, enzyme processes, and biological processes—from pretreatment to fermentation—is necessary to provide reasonable assumptions and an accurate mathematical framework for the large-scale production of PHAs and the development of related systems. Moreover, research on the coupling process experimental platform of “substrate fermentation-strain enrichment-PHA synthesis” is needed, along with exploration of coupling process reactor design and parameter optimization, to realize the recycling of organic waste streams and the efficient, low-cost industrial synthesis of PHAs. Policy and market drivers will play a crucial role in the widespread adoption of these technologies. Increasing the awareness of environmental sustainability and the need to reduce reliance on fossil fuels are expected to accelerate regulatory support for bio-based production systems. Nonetheless, overcoming economic barriers, such as the high costs associated with pretreatment, fermentation, and downstream processing, will be essential. Advancements in low-cost feedstock utilization, particularly from heterogeneous waste streams, and scalable reactor designs are critical for improving economic feasibility. Despite these opportunities, challenges persist in scaling up acidogenic fermentation processes. The variability of waste stream compositions, along with the need for robust microbial consortia capable of adapting to fluctuating conditions, complicates process optimization. Innovations in real-time monitoring and predictive modeling can mitigate these issues by ensuring process stability and efficiency.
7. Conclusions
The establishment of industrial-scale biotechnological processes for the production of VFA from waste streams requires coordinated progress across multiple disciplines. Interdisciplinary efforts involving microbial ecology, chemical engineering, process optimization, and techno-economic analysis will be essential to advance targeted acidogenic fermentation from a promising concept to a scalable industrial reality. The integration of microbial engineering, predictive modeling, and optimized fermentation strategies can significantly improve the selectivity and efficiency of VFA production. Furthermore, aligning these advances with supportive policy frameworks and industrial practices will facilitate the deployment of sustainable, bio-based alternatives to petrochemical processes. Ultimately, the transition to a circular and bio-based economy will depend not only on technical innovation but also on the ability to integrate these solutions into real-world waste management systems and value chains. This review contributes to that transition by identifying the key parameters, challenges, and opportunities for transforming organic waste into high-value precursors for bioplastics.
Author Contributions
D.H. had the idea for the article. All authors contributed to the literature search. The first draft of the manuscript was written by D.H. and all authors commented and critically revised the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge support of the European Union under the Circular Bio-based Joint Undertaking (CBE JU) project, number HORIZON-JU-CBE-2022-IA-04 (ELLIPSE Project, grant agreement no. 101112581).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time |
| mcl-PHA | Medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates |
| MES | Microbial electrosynthesis |
| MMC | Mixed microbial cultures |
| OLR | Organic loading rate |
| PHA | Polyhydroxyalkanoates |
| S:I | Substrate/inoculum ratio |
| VFA | Volatile fatty acids |
| VS | Volatile solids |
References
- Vázquez-Fernández, A.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.E.; Carrera, J. Review about bioproduction of volatile fatty acids from wastes and wastewaters: Influence of operating conditions and organic composition of the substrate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, C.; Foglia, A.; Eusebi, A.L.; Frison, N.; Akyol, C.; Fatone, F. Targeted bio-based volatile fatty acid production from waste streams through anaerobic fermentation: Link between process parameters and operating scale. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 9970–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palar, S. Comparison of Conventional and Electro-Selective Fermentations of Swine Manure to Produce Short and Medium Chain Volatile Fatty Acids. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2024. Available online: https://krex.k-state.edu/bitstreams/3c7fec1c-3b20-4b2a-8358-503623ca1915/download (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Moza, A.; Ram, N.R.; Srivastava, N.K.; Nikhil, G.N. Bioprocessing of low-value food waste to high value volatile fatty acids for applications in energy and materials: A review on process-flow. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Yin, D.M.; Mahboubi, A.; Sapmaz, T.; Varjani, S.; Qiao, W.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A glimpse of the world of volatile fatty acids production and application: A review. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 1249–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, W.M. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IMARC. Fatty Acid Prices, Trend, Chart, Demand, Market Analysis, News, Historical and Forecast Data Report. 2024. Available online: https://www.imarcgroup.com/fatty-acid-pricing-report (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- PR (Precedence Research). Butyric Acid Market Size, Share, and Trends 2024 to 2034. 2023. Available online: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/butyric-acid-market (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- RN (Research Nester). Valeric Acid Market Size and Share. 2023. Available online: https://www.researchnester.com/reports/valeric-acid-market/5809 (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- MarkWide Research. Volatile Fatty Acids Market—Industry Analysis, Trends, and Forecast (2024–2032). MarkWide Research. 2024. Available online: https://markwideresearch.com/volatile-fatty-acids-market/ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Duong, T.H.; Nga, T.T.V. Production of volatile fatty acids from organic-rich waste streams: Current issues, challenges, and opportunities. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2024, 10, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, N.R.; Nikhil, G.N. Assessment of microbial consortiums and their metabolic patterns during the bioconversion of food waste. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, V.K.; Poddar, B.J.; Shah, M.P.; Purohit, H.J.; Khardenavis, A.A. A comprehensive review on current status and future perspectives of microbial volatile fatty acids production as platform chemicals. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Fernandez, A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, L.; Castro-Barros, C.M.; Lema, J.M.; Taboada-Santos, A. Scale-up and economic assessment of volatile fatty acids production from food waste. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 182, 107112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Suarez, M.; Zhang, Y.; Outram, V. Current perspectives on acidogenic fermentation to produce volatile fatty acids from waste. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 20, 439–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ledesma, L.M.; Ramírez-Malule, H.; Rodríguez-Victoria, J.A. Volatile fatty acids production by acidogenic fermentation of wastewater: A bibliometric analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xin, W.; Shao, Z.; Usman, M.; Li, J.; Shang, P.; Kou, Y.; El-Din, M.G.; Chen, C. Role of pretreatment type and microbial mechanisms on enhancing volatile fatty acids production during anaerobic fermentation of refinery waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 381, 129122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Simeonov, I.; Christov, N. A volatile fatty acids adaptive observer-based hierarchical optimal controller design to maximum gas production of two-stage anaerobic digestion process. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 181, 108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheira, M.; Marreiros, B.C.; Reis, M.A.M. Acids (VFA) and bioplastic (PHA) recovery. Clean Energy Resour. Recovery 2022, 2, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harirchi, S.; Wainaina, S.; Sar, T.; Nojoumi, S.A.; Parchami, M.; Parchami, M.; Varjani, S.; Khanal, K.S.; Wong, J.; Awasthi, M.K.; et al. Microbiological insights into anaerobic digestion for biogas, hydrogen or volatile fatty acids (VFA): A review. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 6521–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, X.; Ren, J.L.; Zhang, M.M.; Wu, Q.F.; Yuan, S.; Liu, W.; Lu, D. Highly efficient utilization of sugar in molasses for butyric acid production by Clostridium tyrobutyricum. Sugar Tech 2023, 25, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ye, F.; Nan, C.; Cheng, J.; Feng, J.; Fu, H.; Wang, J. Efficient production of butyl butyrate from mannitol by engineered Clostridium tyrobutyricum. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrado, L.; McCoy, J.; Rabinovich, L.; Davoudimehr, M.; Stamatopoulou, P.; Scarborough, M. Anaerobic conversion of proteinogenic amino acids when methanogenesis is inhibited: Carboxylic acid production from single amino acids. Fermentation 2024, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijande, C.; Bevilacqua, R.; Balboa, S.; Carballa, M. Altering operational conditions during protein fermentation to volatile fatty acids modifies the associated bacterial community. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.W.S.; Rincón, F.R.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Al Saffar, Z.; Welles, L.; Rene, E.R.; Vazquez, C.L. Volatile fatty acid production from food waste: The effect of retention time and lipid content. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 367, 128298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhang, X.; Xia, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Ge, S. Effect of extreme pH conditions on methanogenesis: Methanogen metabolism and community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Han, S.; Meng, F.; Chen, K.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, E.; Jiang, J. Impacts of seasonal variation on volatile fatty acids production of food waste anaerobic fermentation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás-Pejó, E.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, C.; Greses, S.; Kennes, C.; Otero-Logilde, N.; Veiga, M.C.; Bolzonella, D.; Müller, B.; Passoth, V. Production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) as chemicals or substrates for microbes to obtain biochemicals. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasoy, M.; Cetecioglu, Z. Bioaugmentation as a strategy for tailor-made volatile fatty acid production. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Yang, Y.H. Microbial production of volatile fatty acids: Current status and future perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Camacho, J.J.; García-García, I.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; García-Martínez, T.; Mauricio, J.C. Latest trends in industrial vinegar production and the role of acetic acid bacteria: Classification, metabolism, and applications—A comprehensive review. Foods 2023, 12, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.K.; Wartu, J.R.; Orukotan, A.A. Production of vinegar from waste fruits using Acetobacter species. Ife J. Sci. 2024, 26, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, J.; Chakrabortty, S. Production of acetic acid and whey protein from cheese whey in a hybrid reactor under response surface optimized conditions. Fine Chem. Eng. 2023, 4, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.R.; Rao, P.; Prakash, G.; Lali, A.M. Organic waste streams as feedstock for the production of high volume-low value products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 11904–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammali, R.; Seenayya, G.; Reddy, G. Fermentation of cellulose to acetic acid by Clostridium lentocellum SG6: Induction of sporulation and effect of buffering agent on acetic acid production. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 37, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, M.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Qin, L.; Li, Z.; Yao, J.; Liang, X. Mixed culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Acetobacter pasteurianus for acetic acid production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 79, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaei, V.; Pilevar, Z.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Hosseini, H. Propionic acid: Method of production, current state and perspectives. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 58, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Cruz, V.; Hernández, S.; Ortíz, I. Propionic acid production by Propionibacterium acidipropionici CDBB-B-1981 from enzymatic hydrolysates of Agave bagasse pretreated by steam explosion. Eng. Rep. 2024, 6, e12858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dishisha, T.; Jain, M.; Hatti-Kaul, R. High cell density sequential batch fermentation for enhanced propionic acid production from glucose and glycerol/glucose mixture using Acidipropionibacterium acidipropionici. Microb. Cell Fact. 2024, 23, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, L.A.; de Oliveira Meira, A.C.F.; da Silva, F.L.; Veríssimo, L.A.A.; Piccoli, R.H.; Paiva, L.V.; Mondragon-Bernal, L.V.; Alves, J.G.L.F. Biosynthesis of propionic acid from whey permeate and corn steep liquor by Propionibacterium freudenreichii subsp ATCC 6207 and partial purification using ion exchange cryogels. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, E.M.; Martin, J.; Brabo-Catala, L.; Philippidis, G.P. Propionic acid production by Propionibacterium freudenreichii using sweet sorghum bagasse hydrolysate. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 9619–9629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowarek, K.; Lipińska, E.; Hać-Szymańczuk, E.; Kot, A.M.; Kieliszek, M.; Bonin, S. Use of Propionibacterium freudenreichii T82 strain for effective biosynthesis of propionic acid and trehalose in a medium with apple pomace extract and potato wastewater. Molecules 2021, 26, 3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamas, M.; Magdalena, J.A.; Greses, S.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; González-Fernández, C. Insights on the microbial communities developed during the anaerobic fermentation of raw and pretreated microalgae biomass. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Duan, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, X.; Song, Z.; Yi, J.; Wang, T. A synergistic fermentation system of probiotics with low-cost and high butyric acid production: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Clostridium tyrobutyricum. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelbert, M.; Machado, T.O.; Araújo, P.H.; Sayer, C.; de Oliveira, D.; Maziero, P.; Carciofi, B.A. Perspectives on biotechnological production of butyric acid from lignocellulosic biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 202, 114717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Yang, N.; Wu, Y.; Fang, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Fu, C.; Zhang, P. Volatile fatty acid production in anaerobic fermentation of food waste saccharified residue: Effect of substrate concentration. Waste Manag. 2023, 164, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, T.; Yuan, W.; Geng, Y. Butyric acid fermentation in xylose and glucose by Clostridium tyrobutyricum. Bioresources 2017, 12, 2930–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Feng, J.; Jiang, W.; Fu, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.T. Recent advances in n-butanol and butyrate production using engineered Clostridium tyrobutyricum. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasoy, M.; Cetecioglu, Z. Butyric acid dominant volatile fatty acids production: Bio-augmentation of mixed culture fermentation by Clostridium butyricum. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romans-Casas, M.; Feliu-Paradeda, L.; Tedesco, M.; Hamelers, H.V.; Bañeras, L.; Balaguer, M.D.; Puig, S.; Dessì, P. Selective butyric acid production from CO2 and its upgrade to butanol in microbial electrosynthesis cells. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 17, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, J. Efficient synthesis of tyrosol from L-tyrosine via heterologous Ehrlich pathway in Escherichia coli. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 47, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, K.; Zierow, J.; Buehler, K.; Schmid, A. Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas sp. strain VLB120 as platform biocatalyst for the production of isobutyric acid and other secondary metabolites. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, P.; Udaondo, Z.; Duque, E.; Ramos, J.L. Biosynthesis of fragrance 2-phenylethanol from sugars by Pseudomonas putida. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2024, 17, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschel, R.; Ankenbauer, A.; Welsch, I.; Wirth, N.T.; Massner, C.; Ahmad, N.; McColm, S.; Borges, F.; Fotheringham, I.; Takors, R.; et al. Engineering Pseudomonas putida KT2440 for the production of isobutanol. Eng. Life Sci. 2020, 20, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, G.N.; Altman, E.; Sangurdekar, D.P.; Khodursky, A.B.; Eiteman, M.A. Overflow metabolism in Escherichia coli during steady-state growth: Transcriptional regulation and effect of the redox ratio. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3653–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.N.; Ranadheera, C.S.; Fang, Z.; Ajlouni, S. Production of short chain fatty acids and vitamin B12 during the in-vitro digestion and fermentation of probiotic chocolate. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras, S.T.S.; Cavalcante, W.A.; Gehring, T.A.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Ferreira, T.J.T.; Kato, M.T.; Rojas-Ojeda, P.; Sanz-Martin, J.L.; Leitão, R.C. Anaerobic production of valeric acid from crude glycerol via chain elongation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 1847–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, B.G.; Fuchsmann, P.; Fröhlich-Wyder, M.T. Sensory Characteristics of Swiss-Type Cheese Varieties. In Sensory Profiling of Dairy Products; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 195–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Deng, J.; Woodruff, A.P.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, J.; Park, S.W.; Li, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, K. A bio-catalytic approach to aliphatic ketones. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, N.; Ayeni, A.O.; Soni, D.; Chandrashekhar, B. Microbial Consortia: A Mixed Cell Catalyst for Biotransformation of Biomass into Biofuels and Chemicals. In Whole-Cell Biocatalysis; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 269–307. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.P.; Ke, X.; Jin, L.Q.; Xue, Y.P.; Zheng, Y.G. Sustainable management and valorization of biomass wastes using synthetic microbial consortia. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 395, 130391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, G.; Becci, A.; Amato, A.; Beolchini, F. Acetic acid bioproduction: The technological innovation change. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Pan, L.; Wang, L. Effect of inoculum pretreatment and substrate/inoculum ratio on acidogenic fermentation of chemically enhanced primary treatment sludge. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyawati, A.I.; Suraraksa, B.; Chaiprasert, P. Efficacies of anaerobic microbial consortium for starchy lignocellulose hydrolysis and acidogenic fermentation of cassava pulp. BioEnergy Res. 2023, 16, 2314–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, T.; Feng, L.; Chen, Y. The mechanisms of pH regulation on promoting volatile fatty acids production from kitchen waste. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atasoy, M.; Scott, W.T.; Regueira, A.; Mauricio-Iglesias, M.; Schaap, P.J.; Smidt, H. Biobased short chain fatty acid production—Exploring microbial community dynamics and metabolic networks through kinetic and microbial modeling approaches. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 73, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyadi, T.; Bharti, A.; Basack, S.; Kumar, P.; Lucchi, E. Influential factors in anaerobic digestion of rice-derived food waste and animal manure: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 413, 131398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennison-Omovoh, C.A.; Fagbohungbe, M.O.; Bankole, P.O.; Semple, K.T. The effect of different C-N ratios on volatile fatty acid (VFA) production from acidogenic fermentation of sucrose in continuous-stirred tank reactors. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2023, 13, 9339–9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.H.; Grolle, K.; Nga, T.T.V.; Zeeman, G.; Temmink, H.; van Eekert, M. Protein hydrolysis and fermentation under methanogenic and acidifying conditions. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Picola, S.; Serra-Toro, A.; Da Silva, C.; Peces, M.; Jordán, M.; Vila, J.; Grifoll, M.; Valentino, F.; Astals, S.; Dosta, J. Acidogenic fermentation of biowaste coupled with nitrogen recovery using selective membranes to produce a VFA-rich liquid with a high C/N ratio. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baksi, S.; Sarkar, U.; Villa, R.; Basu, D.; Sengupta, D. Conversion of biomass to biofuels through sugar platform: A review of enzymatic hydrolysis highlighting the trade-off between product and substrate inhibitions. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 55, 102963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, N.R.; Nikhil, G.N. A critical review on sustainable biogas production with focus on microbial-substrate interactions: Bottlenecks and breakthroughs. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.H.; van Eekert, M.; Grolle, K.; Tran, T.V.N.; Zeeman, G.; Temmink, H. Effect of carbohydrates on protein hydrolysis in anaerobic digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelar Molina, G.; Schaller, K.; Kari, J.; Schiano-di-Cola, C.; Peters, G.H.J.; Borch, K.; Westh, P. Interrelationship of substrate crystallinity, enzyme binding strength, and cellulase activity. bioRxiv 2024. biorXiv:20.607150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, V.; Singha, S. Protein digestibility of soybean: How processing affects seed structure, protein and non-protein components. Discov. Food 2024, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Juan, M.; Kou, X.; Gao, X.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Zheng, B.; Liu, Y.; Xue, Z. Investigation on the emulsification mechanism in aqueous enzymatic extraction of edible oil from Schizochytrium sp. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2904–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworanti, O.A.; Agbede, O.O.; Agarry, S.E.; Ajani, A.O.; Ogunkunle, O.; Laseinde, O.T.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Fattah, I.M.R. Decoding anaerobic digestion: A holistic analysis of biomass waste technology, process kinetics, and operational variables. Energies 2023, 16, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Kulupa, T.; Kubiak, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Pilarski, K.; Niewiadomska, A. Anaerobic digestion of food waste—A short review. Energies 2023, 16, 5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Sierra, J.M.; Ferreira, A.L.M.; Cerqueda-Garcia, D.; Spanjers, H.; van Lier, J.B. Effect of operational parameters on the performance of an anaerobic sequencing batch reactor (AnSBR) treating protein-rich wastewater. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 17, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owusu-Agyeman, I.; Plaza, E.; Cetecioglu, Z. Production of volatile fatty acids through co-digestion of sewage sludge and external organic waste: Effect of substrate proportions and long-term operation. Waste Manag. 2020, 112, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, P.; Puchol-Royo, R.; Ortega-Legarreta, A.; Tanner, K.; Tideman, J.; de Vries, S.J.; Pascual, J.; Porcar, M.; Latorre-Pérez, A.; Abendroth, C. Multivariate comparison of taxonomic, chemical and operational data from 80 different full-scale anaerobic digester-related systems. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2024, 17, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, Z.A.; Abid, S.; Banat, I.M. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Characteristics, production, recent developments and applications. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 126, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, S.; Kuzhiumparambil, U.; Pernice, M.; Ralph, P. Techno-economic analysis of cyanobacterial PHB bioplastic production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Porras, G.; Fernández-Güelfo, L.A.; Álvarez-Gallego, C.J.; Carbú, M.; Sales, D.; Romero-García, L.I. Influence of the total concentration and the profile of volatile fatty acids on polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production by mixed microbial cultures. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, L.; Rovira-Cal, E.; Nafarrate, I.; Urkiaga, A.; Berganza, J.; Aymerich, E.; Suárez, M.J. Acidogenic fermentation of dairy by-products for the utilization of volatile fatty acids in PHBV production by Haloferax mediterranei. Sustain. Food Technol. 2025, 3, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalampokidis, A.; Klontza, E.; Vakalis, S.; Naddeo, V.; Lekkas, D.F. Is it possible to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) bioplastics of consistent composition from organic wastes? A review. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 2024, 4, 2775–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagi, V.N.; Bhat, S.G.; Paduvari, R.; Kodavooru, D.; Somashekara, D.M. Waste to value-added products: An innovative approach for sustainable production of microbial biopolymer (PHA)—Emphasis on inexpensive carbon feedstock. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2023, 12, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, T.; Qin, Z.; Mou, J.; Sun, J.; Huang, S.; Chaces, A.V.; Gao, L.; et al. Bioproduction and applications of short-chain fatty acids from secondary sludge anaerobic fermentation: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Peng, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Ni, B.-J.; et al. Towards scaling-up implementation of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production from activated sludge: Progress and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 447, 141542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bai, C.; Li, Z.; Cao, D.; Zu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Nan, J.; Wang, H.; Liang, B.; et al. Directional bioelectrochemical dechlorination of trichloroethene to valuable ethylene by introduction poly-3-hydroxybutyrate as a slow release carbon source. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisafi, F.; Valentino, F.; Micolucci, F.; Denaro, R. From organic wastes and hydrocarbons pollutants to polyhydroxyalkanoates: Bioconversion by terrestrial and marine bacteria. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, H.R.; Winterburn, J.B. Influence of emulsified plant oil composition on growth and biopolymer production of Cupriavidus necator DSM 545. Food Bioprod. Process. 2022, 132, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J.; Kockler, K.; Parisi, E.; Chan, C.M.; Pratt, S.; Laycock, B. Synthesis and physical properties of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-based block copolymers: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel-Jarillo, G.; Gea, T.; Artola, A.; Fuentes, J.; Carrera, J.; Suárez-Ojeda, M.E. Towards PHA production from wastes: The bioconversion potential of different activated sludge and food industry wastes into VFA through acidogenic fermentation. Waste Biomass Valor. 2021, 12, 6861–6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueira, A.; Bevilacqua, R.; Lema, J.M.; Carballa, M.; Mauricio-Iglesias, M. A metabolic model for targeted volatile fatty acids production by cofermentation of carbohydrates and proteins. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penumathsa, B.K.V.; Premier, G.C.; Kyazze, G.; Dinsdale, R.; Guwy, A.J.; Esteves, S.; Rodríguez, J. ADM1 can be applied to continuous bio-hydrogen production using a variable stoichiometry approach. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4379–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savun-Hekimoğlu, B. On the use of mathematical models for wastewater treatment: A review and analysis of activated sludge models ASM1 and ASM3. Int. J. Environ. Geoinf. 2021, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cabaleiro, R.; Lema, J.M.; Rodríguez, J. Metabolic energy-based modelling explains product yielding in anaerobic mixed culture fermentations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueira, A.; González-Cabaleiro, R.; Ofiţeru, I.D.; Rodríguez, J.; Lema, J.M. Electron bifurcation mechanism and homoacetogenesis explain products yields in mixed culture anaerobic fermentations. Water Res. 2018, 141, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regueira, A.; Lema, J.M.; Carballa, M.; Mauricio-Iglesias, M. Metabolic modeling for predicting VFA production from protein-rich substrates by mixed-culture fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.R.; Li, W.W.; Huang, L.; Liu, H.Q.; Wang, Y.K.; Geng, Y.K.; Kwan-Sing Lam, P.; Yu, H.Q. Recovery of high-concentration volatile fatty acids from wastewater using an acidogenesis-electrodialysis integrated system. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regueira, A.; Turunen, R.; Vuoristo, K.S.; Carballa, M.; Lema, J.M.; Uusitalo, J.; Mauricio-Iglesias, M. Model-aided targeted volatile fatty acid production from food waste using a defined co-culture microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacaribu, A.A.; Darwin, D. Sustainable bioproduct production via anaerobic bioconversion by landfill soil inoculum in various carbohydrate wastes. Acta Technol. Agric. 2024, 27, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urfi, M.; Babar, Z.B.; Munir, S.; Rizwan, K.; Majeed, I. Production of volatile fatty acids from biomass, their recovery and applications in fuel and other valued products formation. In Nanomaterials in Biomass Conversion; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2024; pp. 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Loh, K.C. Review and perspectives of enhanced volatile fatty acids production from acidogenic fermentation of lignocellulosic biomass wastes. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, P.P.; Gore, S.; Dargode, P.; Sharma, M.D.; Lali, A.M. Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA) Production through altered anaerobic digestion (AD) process for efficient utilization of residual liquid stream of pretreated lignocellulosic biomass. Bioenerg. Res. 2022, 15, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.P.; Dien, B.S.; Jung, H.G.; Casler, M.D.; Masterson, S.D.; Mitchell, R.B. Quantifying actual and theoretical ethanol yields for switchgrass strains using NIRS analyses. Bioenerg. Res. 2011, 4, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, U. Bio-Valorization of Physical and Chemical Pretreated Switchgrass on Volatile Fatty Acid Production. Ann. Agric. Crop Sci. 2021, 6, 1085. [Google Scholar]
- Battista, F.; Strazzera, G.; Valentino, F.; Gottardo, M.; Villano, M.; Matos, M.; Silva, F.; Reis, M.A.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Astals, S.; et al. New insights in food waste, sewage sludge and green waste anaerobic fermentation for short-chain volatile fatty acids production: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kaur, G.; Brar, S.K. Tailored production of butyric acid from mixed culture fermentation of food waste. Food Bioprod. Process. 2025, 150, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Huang, X. Volatile fatty acid (VFA) production from sludge and chicken manure co-fermentation: Role of acid/alkali-treatment and microbial characteristics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Qiao, W.; Xue, T.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, R. Generation of high concentration free volatile fatty acids from continuous anaerobic digestion of chicken manure by suppressing the decomposition of nitrogenous components. Mol. Biotechnol. 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xi, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, M.; Xi, B. A review on polyhydroxyalkanoates production from various organic waste streams: Feedstocks, strains, and production strategy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 198, 107166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eryildiz, B.; Lukitawesa Taherzadeh, M.J. Effect of pH, substrate loading, oxygen, and methanogens inhibitors on volatile fatty acid (VFA) production from citrus waste by anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, J. Effect of pH on volatile fatty acid production from anaerobic digestion of potato peel waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Barragán, J.; Martínez-Fraile, C.; Muñoz, R.; Quijano, G.; Maya-Yescas, R.; León-Becerril, E.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; García-Depraect, O. Brewery spent grain valorization through fermentation: Targeting biohydrogen, carboxylic acids, and methane production. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 191, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainaina, S.; Parchami, M.; Mahboubi, A.; Horváth, I.S.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Food waste-derived volatile fatty acids platform using an immersed membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewa, W.A.; Hussain, A.; Chandra, R.; Lee, J.; Saha, S.; Lee, H.S. Valorization of food waste and economical treatment: Effect of inoculation methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukphun, N.; Sittijunda, S.; Reungsang, A. Volatile fatty acid production from food waste with the emphasis on membrane-based recovery. Fermentation 2021, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, K.; Atasoy, M.; Ludtke, M.; Baresel, C.; Eyice, Ö.; Cetecioglu, Z. Bioconversion of food waste to volatile fatty acids: Impact of microbial community, pH and retention time. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomnonkhaow, U.; Uwineza, C.; Mahboubi, A.; Wainaina, S.; Reungsang, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Membrane bioreactor-assisted volatile fatty acids production and in situ recovery from cow manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.M.; Mahboubi, A.; Wainaina, S.; Qiao, W.; Taherzadeh, M.J. The effect of mono- and multiple fermentation parameters on volatile fatty acids (VFA) production from chicken manure via anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 124992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Jin, J.; Wang, J.; Fang, H.; Yu, X.; He, J.; Chen, T. Targeted volatile fatty acid production based on lactate platform in mixed culture fermentation: Insights into carbon conversion and microbial metabolic traits. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 417, 131835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; She, Y.; Hong, J. Insights into microbial interaction profiles contributing to volatile fatty acids production via acidogenic fermentation of waste activated sludge assisted by calcium oxide pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Gutiérrez, M.; Garcia-Aguirre, J.; Irizar, I.; Aymerich, E. From sewage sludge and agri-food waste to VFA: Individual acid production potential and up-scaling. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdán Morillo, J.M.A. Potencial de Producción de Ácidos Grasos Volátiles en Lodos de PTAR y Residuos Agroindustriales en Condiciones Termofílicas. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina, Lima, Peru, 2020. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12996/4445 (accessed on 27 December 2024).
- AquaVall. Producción de Ácidos Grasos Volátiles a Partir de Lodos de Depuradora y Residuos Orgánicos Mediante Fermentación Acidogénica. Apuntes de Innovación AquaVall, 1. 2020. Available online: https://aquavall.es/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Apuntes-de-Innovacion-AquaVall-01-Produccion-de-acidos-grasos-TROVANT-web.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2024).
- Ortegón Velandia, M.F. Evaluación del Potencial Acidogénico para Producción de Ácidos Grasos Volátiles (AGV) a Partir de Lixiviados de los Residuos Sólidos Orgánicos, Como Plataforma de Biorefinería. Bachelor’s thesis, Universidad Santo Tomás, Manila, Phillipines, 2016. Available online: https://repository.usta.edu.co/handle/11634/2471 (accessed on 27 December 2024).
- Dong, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.; Luo, L.; Wu, G.; Awasthi, M.K.; Yan, B. Caproic acid production from anaerobic fermentation of organic waste: Pathways and microbial perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 175, 113181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ledesma, L.M.; Rodríguez-Victoria, J.A.; Ramírez-Malule, H. Effect of fermentation time, pH, and their interaction on the production of volatile fatty acids from cassava wastewater. Water 2024, 16, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalheira, M.; Duque, A.F. From food waste to volatile fatty acids towards a circular economy. In Fermentation—Processes, Benefits and Risks; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greses, S.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; Gónzalez-Fernández, C. Agroindustrial waste as a resource for volatile fatty acids production via anaerobic fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greses, S.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; González-Fernández, C. Assessing the relevance of acidic pH on primary intermediate compounds when targeting carboxylate accumulation. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022, 12, 4519–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourang, M.; Xiong, X.; Sarkhosh, S.; Chen, S. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) biosynthesis by an engineered Yarrowia lipolytica strain using co-substrate strategy. Fermentation 2023, 9, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Policastro, G.; Panico, A.; Fabbricino, M. Improving biological production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) co-polymer: A critical review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2021, 20, 479–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartiailh, C.; Blunt, W.; Sharma, P.K.; Liu, S.; Cicek, N.; Levin, D.B. The thermal and mechanical properties of medium chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates produced by Pseudomonas putida LS46 on various substrates. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 617489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavinato, C.; Da Ros, C.; Pavan, P.; Bolzonella, D. Influence of temperature and hydraulic retention on the production of volatile fatty acids during anaerobic fermentation of cow manure and maize silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.R.; Guarda, E.C.; Freitas, E.B.; Galinha, C.F.; Duque, A.F.; Reis, M.A. Valorization of raw brewers’ spent grain through the production of volatile fatty acids. New Biotechnol. 2020, 57, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greses, S.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; González-Fernández, C. Short-chain fatty acids and hydrogen production in one single anaerobic fermentation stage using carbohydrate-rich food waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-López, M.E.; Frison, N.; Bolzonella, D.; García-Morales, J.L. Enhancing anaerobic digestion with an UASB reactor of the winery wastewater for producing volatile fatty acid effluent enriched in caproic acid. Fermentation 2023, 9, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.X.; Vadivelu, V.M. Enhanced volatile fatty acid production in sequencing batch reactor: Microbial population and growth kinetics evaluation. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2124, 020040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.M.; Uwineza, C.; Sapmaz, T.; Mahboubi, A.; De Wever, H.; Qiao, W.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Volatile fatty acids (VFA) production and recovery from chicken manure using a high-solid anaerobic membrane bioreactor (AnMBR). Membranes 2022, 12, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, M.; Mato, T.; Lopez, A.; Vila, M.; Kennes, C.; Veiga, M.C. Bioplastic production using wood mill effluents as feedstock. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Hans, M.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, Y.K. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion: An advancement towards enhanced biogas production from lignocellulosic biomass. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.R.; Kim, J.Y. Feasibility assessment of thermophilic anaerobic digestion process of food waste. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakarika, M.; Regueira, A.; Rabaey, K.; Ganigué, R. Thermophilic caproic acid production from grass juice by sugar-based chain elongation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Liu, L.; Song, B.; Liu, H.; Shi, H.; Zhu, Y. Mesophilic and thermophilic fermentation of activated sludge for volatile fatty acids production: Focusing on anaerobic degradation of carbohydrate and protein. Environ. Technol. 2024, 45, 5745–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, E.; He, P.; Zhang, H.; Hao, L.; Shao, L.; Lü, F. How does temperature regulate anaerobic digestion? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Liang, B.; He, Z.; Li, M.; Zong, S.; Wang, Z.; Ge, B.; Zhang, O.; Li, X.; Wang, A. Insights into methanogenesis of mesophilic-psychrophilic varied anaerobic digestion of municipal sludge with antibiotic stress. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudi, K.; Greses, S.; González-Fernández, C. Hydraulic retention time as an operational tool for the production of short-chain carboxylates via anaerobic fermentation of carbohydrate-rich waste. Molecules 2023, 28, 6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, P.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X. Feasibility of hydrogen recovery and optimization of gas production from protein-rich food waste by bio-electrochemical system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 31241–31254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C. The impacts of cellulose on volatile fatty acid production and the microbial community in anaerobic fermentation of sludge at high and medium temperatures. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 197, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigova, J.; Šturdík, E. Advances in biotechnological production of butyric acid. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 24, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Ding, P.; Cao, Q.H.; Zhang, C.; Fu, B.; Liu, H.B.; Chen, C.J.; Liu, H. Amino acids as in-situ electron donors drive medium chain fatty acids production from sludge acidogenic fermentation liquid by electro-fermentation enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, S.; Lingam, Y.; Mohan, S.V. Understanding acidogenesis towards green hydrogen and volatile fatty acid production–critical analysis and circular economy perspective. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 141550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalena, J.A.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; Ballesteros, M.; González-Fernandez, C. Volatile fatty acids production from protease pretreated Chlorella biomass via anaerobic digestion. Biotechnol. Prog. 2018, 34, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Iglesias, R.; Campanaro, S.; Treu, L.; Kennes, C.; Veiga, M.C. Valorization of sewage sludge for volatile fatty acids production and role of microbiome on acidogenic fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonanzi, B.; Gallipoli, A.; Frugis, A.; Gianico, A.; Lazzazzara, M.; Angelini, S.; Cecchini, C.; Braguglia, C.M. Bio-based production of medium-chain carboxylic acids from food waste and sludge without chemical addition: The pivotal role of mix ratio and pretreatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J. Effect of different vegetable wastes on the performance of volatile fatty acids production by anaerobic fermentation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 142390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Charnier, C.; Kouas, M.; Latrille, E.; Torrijos, M.; Harmand, J.; Patureau, D.; Spérandio, M.; Morgenroth, E.; Béline, F.; et al. Modelling hydrolysis: Simultaneous versus sequential biodegradation of the hydrolysable fractions. Waste Manag. 2020, 101, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawad, I.; Ibrahim, H. Pretreatment of agricultural lignocellulosic biomass for fermentable sugar: Opportunities, challenges, and future trends. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 6155–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Bao, W.; Peng, Q.; Hu, W.; Yang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Xu, P.; He, Q.; et al. Metabolic engineering of Zymomonas mobilis for co-production of D-lactic acid and ethanol using waste feedstocks of molasses and corncob residue hydrolysate. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1135484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Vo, H.N.P.; Bui, X.T.; Hoang, B.N. Volatile fatty acids production from waste streams by anaerobic digestion: A critical review of the roles and application of enzymes. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 359, 127420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, E.A. Safe Chassis: Engineering Biosafety for Industrial Biotechnology. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University and Research, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2022. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/29323d322bea3d94c573927b338c571d/1?cbl=2026366&diss=y&pq-origsite=gscholar (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Ko, Y.J.; Cha, J.; Jeong, W.Y.; Lee, M.E.; Cho, B.H.; Nisha, B.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, S.E.; Han, S.O. Bio-isopropanol production in Corynebacterium glutamicum: Metabolic redesign of synthetic bypasses and two-stage fermentation with gas stripping. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).