Context-Aware Systems Architecture in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Industry 4.0
2.2. Context Awareness
2.3. Systems Architecture for Industry 4.0
2.3.1. The 5C Framework
2.3.2. RAMI 4.0 Architecture
2.3.3. IIRA Architecture
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Questions
- RQ1—What requirements are supported by the context-aware systems architectures for I4.0?
- RQ2—What are the context modelling and inference techniques presented?
- RQ3—What software architecture models and standards are used?
3.2. Research Strategy
3.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
3.4. Review Procedures
- We identified records by using the Google Scholar search tool. Search filters were applied, including a specific date range, a preference for the English language, and all types of articles, including review articles. At this stage, a NodeJS script automated the extraction of 2751 records (see Supplementary Materials for the dataset).Expression:(architecture) (“industry 4.0” OR “industrie 4.0”) “context aware”
- Records for which full access to the content was not possible, did not provide an abstract, or were not classified as journals or conference articles were automatically excluded. After this step, 649 records were ignored.
- The titles of each record were automatically analysed, and we excluded 378 records that included the words “review(s)”, “survey”, and “systematic”. At the end of this step, 1724 records remained.
- Records that explicitly included terms associated with other application domains and unrelated to the manufacturing sector were excluded from the review. Considering that this systematic review focused on the I4.0 paradigm, we eliminated records that did not include the concepts associated with and identified by Hermann et al. [29] and the term “context” in the title or abstract. After this process, 1463 records were eliminated, leaving 261 that were subjected to manual evaluation.
- At this stage, we first manually read the abstracts of each article identified, and then we read the articles that required a more in-depth analysis for decision-making. We excluded articles classified as literature reviews (30), articles focused on areas of study that did not contribute to the design of the architecture and the respective discussion of the context-aware concept (119), articles related to other domains of applicability (63), articles with the absence or duplication of software architectures (12), and articles with no discussion of the concept of context (8), and articles (4) were also excluded due to the impossibility of obtaining relevant information for the state-of-the-art review. In the end, 25 articles remained.
4. Results
5. Analysis and Discussion
5.1. Requirements of the Architectures Researched
5.1.1. Interoperability
5.1.2. Automation
5.1.3. Decision-Making
5.2. Context Modelling and Inference Techniques
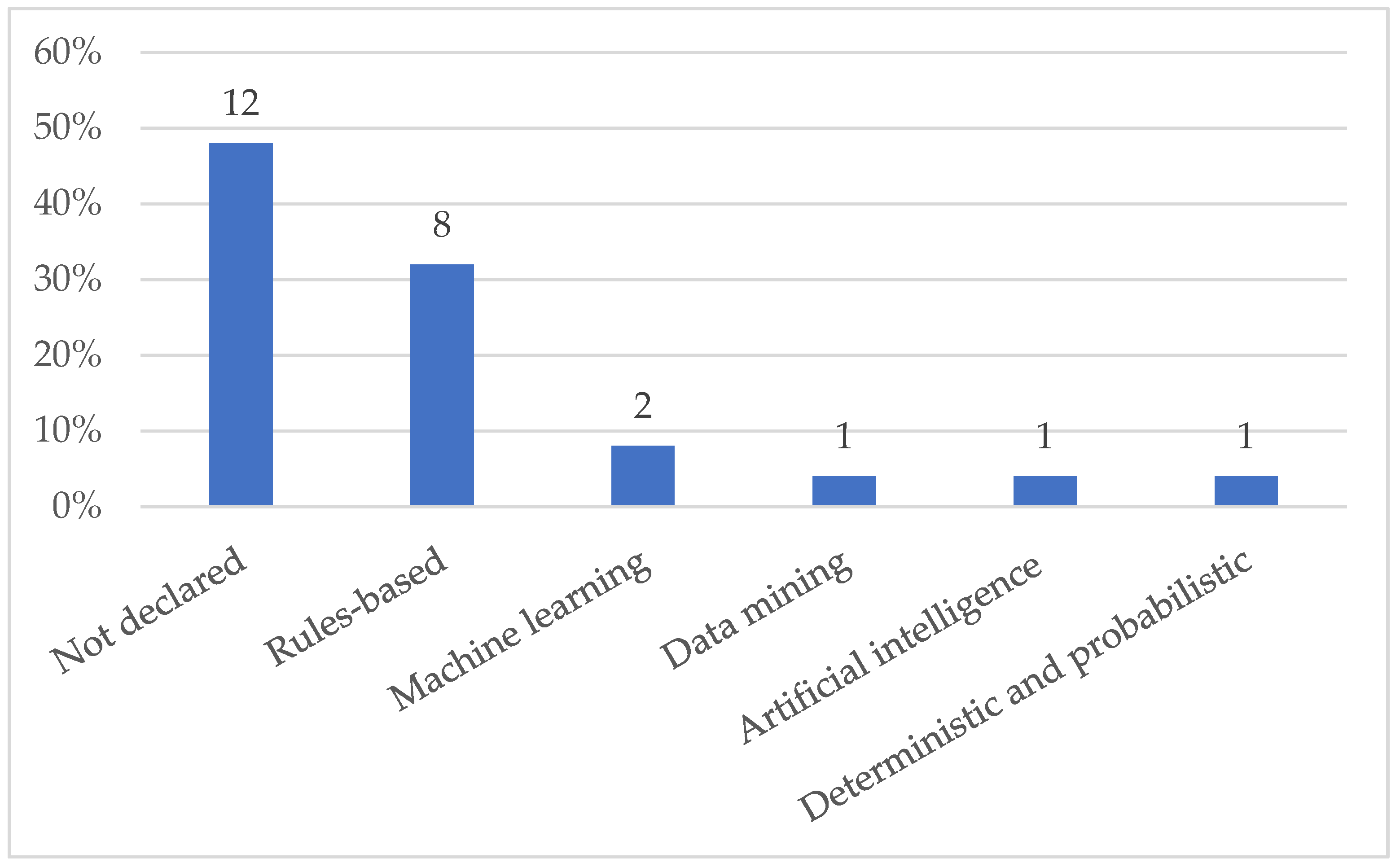
5.2.1. Modelling Techniques
5.2.2. Context Inference
5.3. Architecture Technologies, Norms, Models, and Standards
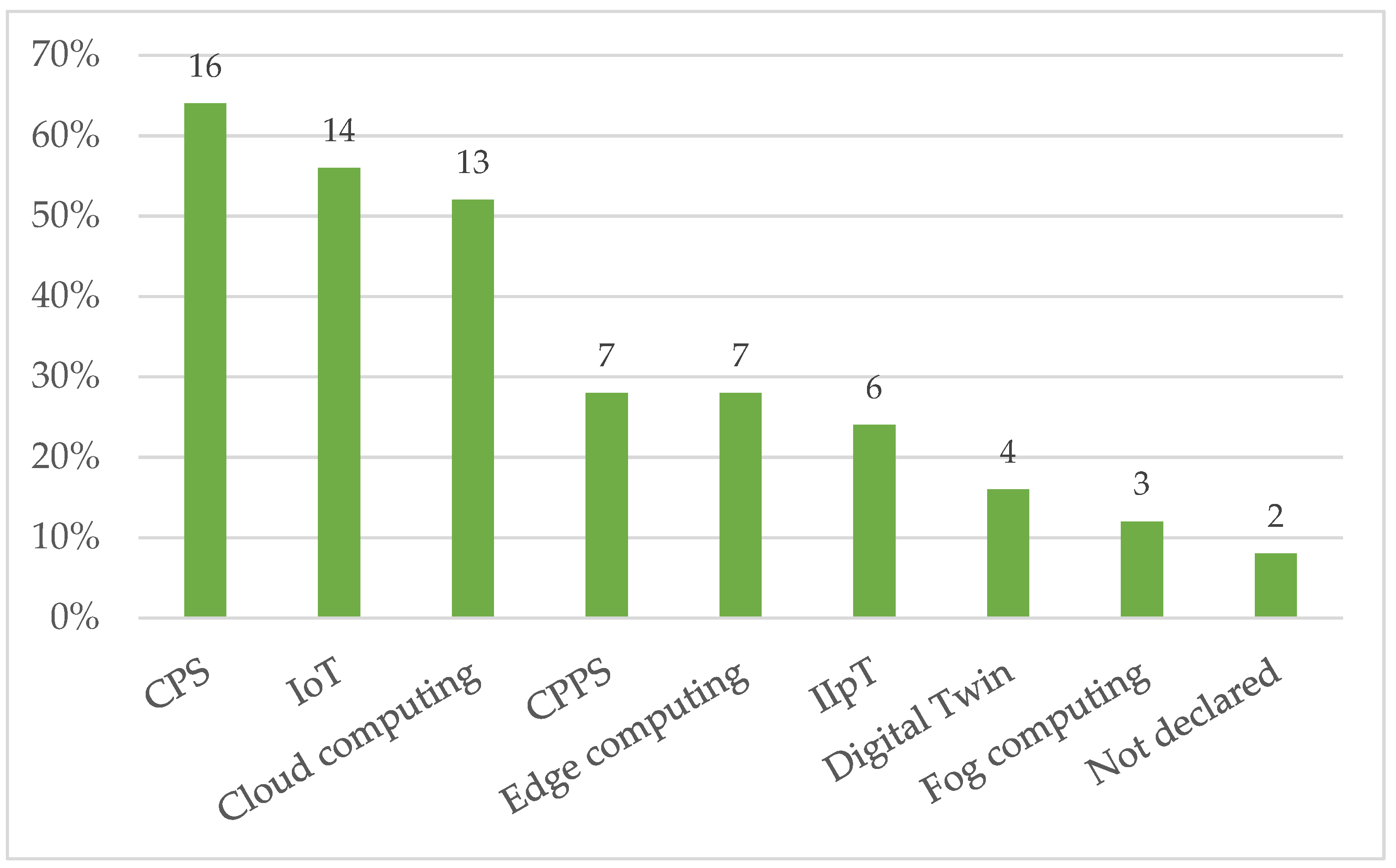
5.3.1. Technologies
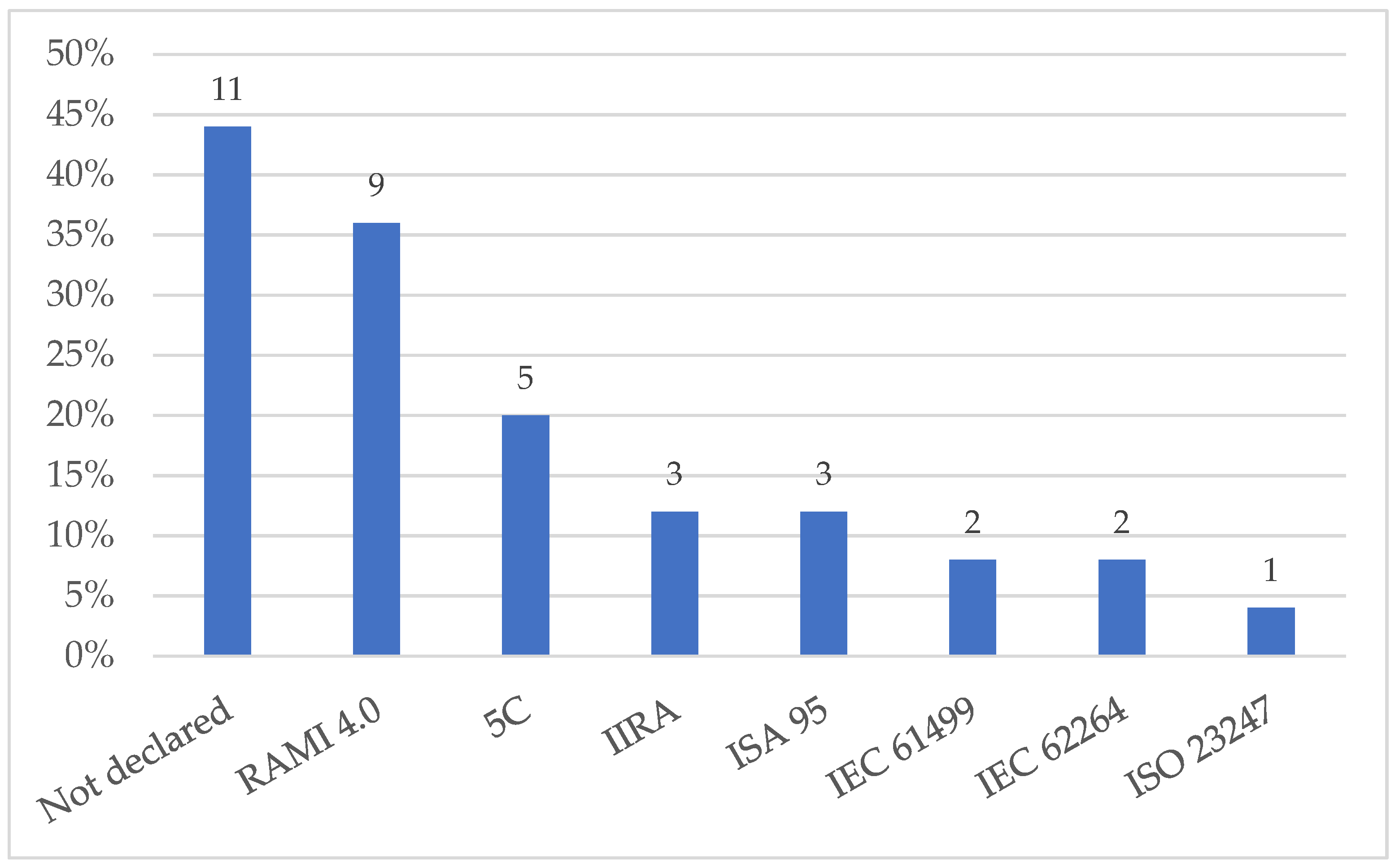
5.3.2. Standards and Reference Models
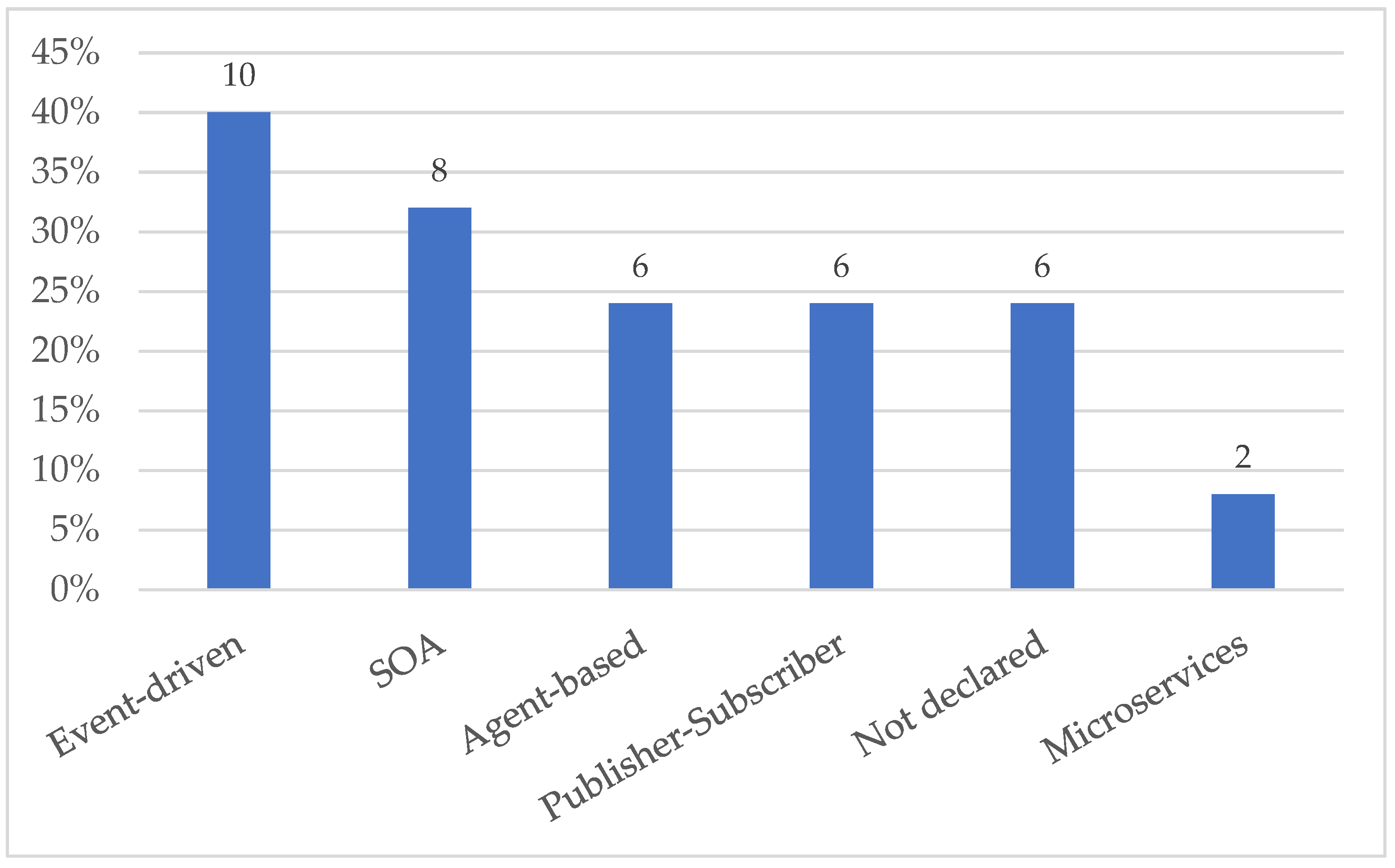
5.3.3. Architecture Standards
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weiser, M. The Computer for the 21st Century. Sci. Am. 1991, 265, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steventon, A.; Wright, S. Intelligent Spaces: The Application of Pervasive ICT; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Calvaresi, D.; Cesarini, D.; Sernani, P.; Marinoni, M.; Dragoni, A.F.; Sturm, A. Exploring the ambient assisted living domain: A systematic review. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2017, 8, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohr, A.; Modre-Opsrian, R.; Drobics, M.; Hayn, D.; Schreier, G. The Internet of Things for Ambient Assisted Living. In Proceedings of the 2010 Seventh International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 April 2010; pp. 804–809. [Google Scholar]
- Koleva, P.; Tonchev, K.; Balabanov, G.; Manolova, A.; Poulkov, V. Challenges in designing and implementation of an effective Ambient Assisted Living system. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Conference on Telecommunication in Modern Satellite, Cable and Broadcasting Services (TELSIKS), Nis, Serbia, 14–17 October 2015; pp. 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, A.; Paulino, D.; Paredes, H.; Barroso, J. Using Intelligent Personal Assistants to Strengthen the Elderlies’ Social Bonds: A Preliminary Evaluation of Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, Microsoft Cortana, and Apple Siri, Proceedings of the Universal Access in Human–Computer Interaction. Human and Technological Environments: 11th International Conference, UAHCI 2017, Held as Part of HCI International 2017; Part III, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–14 July 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 593–602. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, A.; Rocha, T.; Barroso, J.; Carvalho, D. The Ambient Assisted Working (AAW) concept: Assistance according to I4.0 Technical Assistance design principle. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 29 June–1 July 2022; pp. 316–318. [Google Scholar]
- Clemons, J. The Anatomy of Smart Manufacturing. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2018/03/19/the-anatomy-of-smart-manufacturing/ (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Kotler, P.; Kartajaya, H.; Setiawan, I. Marketing 5.0: Technology for Humanity; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-119-66851-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hribernik, K.; Cabri, G.; Mandreoli, F.; Mentzas, G. Autonomous, context-aware, adaptive Digital Twins—State of the art and roadmap. Comput. Ind. 2021, 133, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubina, M.; Varmus, M.; Kubinova, I. Use of big data for competitive advantage of company. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2015, 26, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiku, M.N.O.; Ajayi-Majebi, A.J.; Adebo, P.O. Big Data in Manufacturing. In Emerging Technologies in Manufacturing; Sadiku, M.N.O., Ajayi-Majebi, A.J., Adebo, P.O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 95–107. ISBN 978-3-031-23156-8. [Google Scholar]
- El Kadiri, S.; Grabot, B.; Thoben, K.-D.; Hribernik, K.; Emmanouilidis, C.; von Cieminski, G.; Kiritsis, D. Current trends on ICT technologies for enterprise information systems. Comput. Ind. 2016, 79, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasi, H.; Fettke, P.; Kemper, H.-G.; Feld, T.; Hoffmann, M. Industry 4.0. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2014, 6, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoben, K.-D.; Wiesner, S.; Wuest, T. “Industrie 4.0” and Smart Manufacturing—A Review of Research Issues and Application Examples. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2017, 11, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wan, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, C. Implementing Smart Factory of Industrie 4.0: An Outlook. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2016, 12, 3159805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Deschamps, F.; Loures, E.d.F.R.; Ramos, L.F.P. Past, present and future of Industry 4.0—A systematic literature review and research agenda proposal. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 3609–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagermann, H.; Wahlster, W.; Helbig, J. (Eds.) Recommendations for Implementing the Strategic Initiative INDUSTRIE 4.0; Industrie 4.0 Working Group: Frankfurt, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Folgado, F.J.; Calderón, D.; González, I.; Calderón, A.J. Review of Industry 4.0 from the perspective of automation and supervision systems: Definitions, architectures and recent trends. Electronics 2024, 13, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivoto, D.G.S.; de Almeida, L.F.F.; da Rosa Righi, R.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Lugli, A.B.; Alberti, A.M. Cyber-physical systems architectures for industrial internet of things applications in Industry 4.0: A literature review. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, M.; Cadavid, M.N.; Kenley, C.R.; Deshmukh, A.V. Reference architectures for smart manufacturing: A critical review. J. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 49, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ardakani, H.D.; Yang, S.; Bagheri, B. Industrial Big Data Analytics and Cyber-physical Systems for Future Maintenance & Service Innovation. Procedia CIRP 2015, 38, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, E.; Fumagalli, L.; Macchi, M. A Review of the Roles of Digital Twin in CPS-based Production Systems. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 11, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, A.; Warshaw, L. Industry 4.0 and the Digital Twin; Deloitte University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Plattform Industrie 4.0. 2030 Vision for Industrie 4.0; Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi): Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Roblek, V.; Meško, M.; Krapež, A. A complex view of industry 4.0. SAGE Open 2016, 6, 2158244016653987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, J.; Toro, C.; Barandiaran, I.; Oyarzun, D.; Stricker, D.; de Amicis, R.; Pinto, E.B.; Eisert, P.; Döllner, J.; Vallarino, I. Visual Computing as a Key Enabling Technology for Industrie 4.0 and Industrial Internet. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2015, 35, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. Industry 4.0: A survey on technologies, applications and open research issues. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2017, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, M.; Pentek, T.; Otto, B. Design principles for industrie 4.0 scenarios. In Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Koloa, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2016; Volume 2016-March, pp. 3928–3937. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.C.; Romero, F. A review of the meanings and the implications of the Industry 4.0 concept. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 13, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, F.B.; Júnior, A.S.C. Industry 4.0: An investigation of benefits and barriers with managers of Brazilian manufacturers adopters. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2024, 71, 101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, R.F.; Reis, L.P.; Fernandes, J.M. A study on the barriers that impact the adoption of Industry 4.0 in the context of Brazilian companies. TQM J. 2024, 36, 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadir, B.A.; Broberg, O. Human well-being and system performance in the transition to industry 4.0. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2020, 76, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilit, B.; Adams, N.; Want, R. Context-aware computing applications. In Proceedings of the Mobile Computing Systems and Applications—Workshop Proceedings, Santa Cruz, CA, USA, 8–9 December 1994; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Abowd, G.D.; Dey, A.K.; Brown, P.J.; Davies, N.; Smith, M.; Steggles, P. Towards a better understanding of context and context-awareness. In Handheld and Ubiquitous Computing: First International Symposium, Proceedings of the Handheld and Ubiquitous Computing (HUC 1999), Karlsruhe, Germany, 27–29 September 1999; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; Volume 1707, pp. 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, A.; Campbell, R.H. An infrastructure for context-awareness based on first order logic. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2003, 7, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P.; Lima, C.; Pinto, T.; Nogueira, P.; Reis, A.; Filipe, V. Context-Aware Applications in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review, Proceedings of the Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Special Sessions I, 20th International Conference, Guimarães, Portugal, 12–14 July 2023; Mehmood, R., Alves, V., Praça, I., Wikarek, J., Parra-Domínguez, J., Loukanova, R., de Miguel, I., Pinto, T., Nunes, R., Ricca, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, P.; Pereira, R.; Nunes, R.; Reis, A.; Pinto, T. Context-Aware System for Information Flow Management in Factories of the Future. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, K.; Sipsas, K.; Xanthakis, E.; Makris, S.; Mourtzis, D. An industrial Internet of things based platform for context-aware information services in manufacturing. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2018, 31, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholze, S.; Barata, J. Context Awareness for Flexible Manufacturing Systems Using Cyber Physical Approaches, Proceedings of the Technological Innovation for Cyber-Physical Systems: 7th IFIP WG 5.5/SOCOLNET Advanced Doctoral Conference on Computing, Electrical and Industrial Systems, DoCEIS 2016, Costa de Caparica, Portugal, 11–13 April 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Eckert, M.; Martinez, J.F.; Rubio, G. Context Aware Middleware Architectures: Survey and Challenges. Sensors 2015, 15, 20570–20607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagar, V.; Mohammad, M.; Wan, K.; Hnaide, S.A. A Framework for Developing Context-aware Systems. EAI Endorsed Trans. Context-Aware Syst. Appl. 2014, 1, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, J.C.; Quinde, M.J.; Oguego, C.L.; Giménez Manuel, J. Context-aware systems architecture (CaSa). Cybern. Syst. 2022, 53, 319–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Lima, C.; Reis, A.; Pinto, T.; Nogueira, P.; Barroso, J. Design of Context-Aware Information Systems in Manufacturing Industries: Overview and Challenges, Proceedings of the Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Special Sessions I, 20th International Conference, Guimarães, Portugal, 12–14 July 2023; Mehmood, R., Alves, V., Praça, I., Wikarek, J., Parra-Domínguez, J., Loukanova, R., de Miguel, I., Pinto, T., Nunes, R., Ricca, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 322–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bazire, M.; Brézillon, P. Understanding context before using it. In Modeling and Using Context, Proceedings of the 5th International and Interdisciplinary Conference, CONTEXT 2005, Paris, France, 5–8 July 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, C.; Zaslavsky, A.; Christen, P.; Georgakopoulos, D. Context aware computing for the internet of things: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 414–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, P.; Grafinger, M.; Gerhard, D.; Hennig, M.; Dumss, S. The CASAD Matrix Method: Introduction of a Technique for the Documentation, Analysis, and Optimization of Context-Aware Systems. Procedia CIRP 2020, 91, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, U.; Augusto, J.C.; Clark, T. Engineering context-aware systems and applications: A survey. J. Syst. Softw. 2016, 117, 55–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkadi, F.; Dhuieb, M.A.; Aguado, J.V.; Laroche, F.; Bernard, A.; Chinesta, F. Intelligent assistant system as a context-aware decision-making support for the workers of the future. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 139, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Horizon 2020 Work Programme 2016–2017; ENRD: European Network for Rural Development: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- Apilioğulları, L. Digital transformation in project-based manufacturing: Developing the ISA-95 model for vertical integration. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 245, 108413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupek, R.; Ziebinski, A.; Huczala, L.; Erdogan, H. Agent-based manufacturing execution systems for short-series production scheduling. Comput. Ind. 2016, 82, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafortune, S. On decentralized and distributed control of partially-observed discrete event systems. In Advances in Control Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrielli, G.; Matta, A.; Alfieri, A.; Zhang, M. Design and control of manufacturing systems: A discrete event optimisation methodology. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modoni, G.E.; Trombetta, A.; Veniero, M.; Sacco, M.; Mourtzis, D. An event-driven integrative framework enabling information notification among manufacturing resources. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2019, 32, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruchten, P.; Capilla, R.; Dueñas, J.C. The Decision View’s Role in Software Architecture Practice. IEEE Softw. 2009, 26, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, O. Architectural Decisions as Reusable Design Assets. IEEE Softw. 2011, 28, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruchten, P. The 4+1 View Model of Architecture. IEEE Softw. 1995, 12, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, E.Y.; Antonino, P.O.; Schnicke, F.; Capilla, R.; Kuhn, T.; Liggesmeyer, P. Industry 4.0 reference architectures: State of the art and future trends. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 156, 107241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadravan, A.; Parsaei, H.R. A Review of Reference Architectures for Industry 4.0 and Their Impacts in Smart Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 1st World Congress on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Detroit, MI, USA, 9–11 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sony, M. Design of cyber physical system architecture for industry 4.0 through lean six sigma: Conceptual foundations and research issues. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2020, 8, 158–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavčar, J.; Horváth, I. A Review of the Principles of Designing Smart Cyber-Physical Systems for Run-Time Adaptation: Learned Lessons and Open Issues. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 49, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Goepp, V.; Siadat, A. Concept and engineering development of cyber physical production systems: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 111, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankel, M.; Rexroth, B. The Reference Architectural Model Industrie 4.0 (RAMI 4.0); Zvei: Frankfurt, Germany, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wegener, D. German Standardization Roadmap on Industry 4.0; DKE German Commission for Electrical, Electronic & Information Technologies: Offenbach, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nagorny, K.; Scholze, S.; Colombo, A.W.; Oliveira, J.B. A DIN Spec 91345 RAMI 4.0 Compliant Data Pipelining Model: An Approach to Support Data Understanding and Data Acquisition in Smart Manufacturing Environments. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 223114–223129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisching, M.A.; Pessoa, M.A.; Junqueira, F.; dos Santos Filho, D.J.; Miyagi, P.E. An architecture based on RAMI 4.0 to discover equipment to process operations required by products. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 125, 574–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, C. Introduction to the “RAMI 4.0 Toolbox”; Josef Ressel Center for User-Centric Smart Grid Privacy, Security and Control: Salzburg, Austria, 2020; Volume 43, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.-W.; Miller, B.; Durand, J.; Joshi, R.; Didier, P.; Chigani, A.; Torenbeek, R.; Duggal, D.; Martin, R.; Bleakley, G. Industrial Internet Reference Architecture; Industrial Internet Consortium: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Watson, M. Guidance on Conducting a Systematic Literature Review. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2017, 39, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazman, R.; Klein, M.; Clements, P. ATAM: Method for Architecture Evaluation; Carnegie Mellon University, Software Engineering Institute: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wieland, M.; Schwarz, H.; Breitenbücher, U.; Leymann, F. Towards situation-aware adaptive workflows: SitOPT—A general purpose situation-aware workflow management system. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communication Workshops (PerCom Workshops), St. Louis, MO, USA, 23–27 March 2015; pp. 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Flatt, H.; Koch, N.; Röcker, C.; Günter, A.; Jasperneite, J. A context-aware assistance system for maintenance applications in smart factories based on augmented reality and indoor localization. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 20th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation (ETFA), Luxembourg, 8–11 September 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, M.; Agostinho, C.; Poler, R.; Zacharewicz, G.; Jardim-Gonçalves, R. An architecture to support responsive production in manufacturing companies. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 8th International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS), Sofia, Bulgaria, 4–6 September 2016; pp. 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Negri, E.; Fumagalli, L.; Garetti, M.; Tanca, L. Requirements and languages for the semantic representation of manufacturing systems. Comput. Ind. 2016, 81, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirvu, B.-C.; Zamfirescu, C.-B.; Gorecky, D. Engineering insights from an anthropocentric cyber-physical system: A case study for an assembly station. Mechatronics 2016, 34, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siafara, L.C.; Kholerdi, H.A.; Bratukhin, A.; TaheriNejad, N.; Wendt, A.; Jantsch, A.; Treytl, A.; Sauter, T. SAMBA: A self-aware health monitoring architecture for distributed industrial systems. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017—43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 3512–3517. [Google Scholar]
- Podgórski, D.; Majchrzycka, K.; Dąbrowska, A.; Gralewicz, G.; Okrasa, M. Towards a conceptual framework of OSH risk management in smart working environments based on smart PPE, ambient intelligence and the Internet of Things technologies. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2017, 23, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Dong, Z. CASOA: An Architecture for Agent-Based Manufacturing System in the Context of Industry 4.0. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 12746–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnin, R.L.; Guilherme, I.R.; Queiroz, J.; Paulo, B.; Neto, M.F.O. A Multi-agent System Approach for Management of Industrial IoT Devices in Manufacturing Processes. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 16th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Porto, Portugal, 18–20 July 2018; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Hua, Q. Artificial Intelligence for Cloud-Assisted Smart Factory. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 55419–55430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolakis, N.; Sipsas, K.; Makris, S. A cyber-physical context-aware system for coordinating human-robot collaboration. Procedia CIRP 2018, 72, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Benfenatki, H.; Biennier, F.; Ghodous, P. Control as a Service Architecture to Support Context-aware Control Application Development. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Exposito, E.; Aguilar, J. Implementing self-* autonomic properties in self-coordinated manufacturing processes for the Industry 4.0 context. Comput. Ind. 2020, 121, 103247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolakis, N.; Marguglio, A.; Veneziano, G.; Greco, P.; Panicucci, S.; Cerquitelli, T.; Macii, E.; Andolina, S.; Alexopoulos, K. A microservice architecture for predictive analytics in manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 51, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.Y.H.; Zheng, P.; Chen, C.-H.; Huang, L. A digital twin-enhanced system for engineering product family design and optimization. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 57, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Asghar, M.R. Semantic communications between distributed cyber-physical systems towards collaborative automation for smart manufacturing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 55, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozi, A.; Bianchini, D.; Antonellis, V.D. Context-Based Resilience in Cyber-Physical Production System. Data Sci. Eng. 2021, 6, 434–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traganos, K.; Grefen, P.; Vanderfeesten, I.; Erasmus, J.; Boultadakis, G.; Bouklis, P. The HORSE framework: A reference architecture for cyber-physical systems in hybrid smart manufacturing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 61, 461–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, J.; Leitão, P.; Barbosa, J.; Oliveira, E.; Garcia, G. Agent-Based Distributed Data Analysis in Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2022, 3, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Dong, X.; Dong, Q.; He, Y.; Zeng, P. Context-aware scheduling and control architecture for cyber-physical production systems. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 62, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiger, R.; Malburg, L.; Weber, B.; Bergmann, R. Integrating process management and event processing in smart factories: A systems architecture and use cases. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 63, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlab, N.; Braun, D.; Köhler, C.; Jazdi, N.; Weyrich, M. Extending the Intelligent Digital Twin with a context modeling service: A decision support use case. Procedia CIRP 2022, 107, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedone, G.; Mezgár, I. Model similarity evidence and interoperability affinity in cloud-ready Industry 4.0 technologies. Comput. Ind. 2018, 100, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemlinger, Z.; Holder, L. The COSE Ontology: Bringing the Semantic Web to Smart Environments. In Toward Useful Services for Elderly and People with Disabilities, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Smart Homes and Health Telematics, ICOST 2011, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–22 June 2011; Abdulrazak, B., Giroux, S., Bouchard, B., Pigot, H., Mokhtari, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Haindl, P.; Buchgeher, G.; Khan, M.; Moser, B. Towards a reference software architecture for human-AI teaming in smart manufacturing. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: New Ideas and Emerging Results, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 21–29 May 2022; pp. 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Leitão, P.; Karnouskos, S.; Ribeiro, L.; Lee, J.; Strasser, T.; Colombo, A.W. Smart Agents in Industrial Cyber–Physical Systems. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 1086–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtari Talkhestani, B.; Jung, T.; Lindemann, B.; Sahlab, N.; Jazdi, N.; Schloegl, W.; Weyrich, M. An Architecture of an Intelligent Digital Twin in a Cyber-Physical Production System. Available online: https://openurl.ebsco.com/contentitem/doi:10.1515%2Fauto-2019-0039?sid=ebsco:plink:crawler&id=ebsco:doi:10.1515%2Fauto-2019-0039 (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- Muccini, H.; Moghaddam, M.T. IoT Architectural Styles. In Software Architecture, Proceeding of the 12th European Conference on Software Architecture, ECSA 2018, Madrid, Spain, 24–28 September 2018; Cuesta, C.E., Garlan, D., Pérez, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 68–85. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, R.; Lima, C.; Pinto, T.; Reis, A. Virtual Assistants in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Electronics 2023, 12, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.; Pereira, R.; Nogueira, P.; Barroso, J.; Rocha, T.; Reis, A. Wearable Devices for Communication and Problem-Solving in the Context of Industry 4.0. In HCI International 2023—Late Breaking Papers, Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, HCII 2023, Copenhagen, Denmark, 23–28 July 2023; Duffy, V.G., Krömker, H.A., Streitz, N., Konomi, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 583–592. [Google Scholar]
- Alexopoulos, K.; Makris, S.; Xanthakis, V.; Sipsas, K.; Chryssolouris, G. A concept for context-aware computing in manufacturing: The white goods case. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2016, 29, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, E.; Martín Toral, I.; Calvo, I.; Barambones, O.; Fernández-Bustamante, P. Architectures for Industrial AIoT Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| concept | context-aware |
| artefact | architecture |
| domain | Industry 4.0 |
| tool | Google Scholar |
| Criterion |
|---|
| Date range: 2013–2022 |
| Language: English |
| Databases: ACM, Springer, Elsevier, IEEE, Wiley Online Library, Taylor & Francis |
| Criterion |
|---|
| Articles without access to the full version or an abstract |
| Articles associated with other domains |
| Articles that do not explicitly incorporate the context-aware concept or do not describe an architecture |
| ID | Title | Author | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Towards situation-aware adaptive workflows: SitOPT—A general purpose situation-aware workflow management system | [73] | 2015 |
| 2 | A context-aware assistance system for maintenance applications in smart factories based on augmented reality and indoor localization | [74] | 2015 |
| 3 | An architecture to support responsive production in manufacturing companies | [75] | 2016 |
| 4 | Requirements and languages for the semantic representation of manufacturing systems | [76] | 2016 |
| 5 | Engineering insights from an anthropocentric cyber-physical system: A case study for an assembly station | [77] | 2016 |
| 6 | SAMBA: A self-aware health monitoring architecture for distributed industrial systems | [78] | 2017 |
| 7 | Towards a conceptual framework of OSH risk management in smart working environments based on smart PPE, ambient intelligence and the Internet of Things technologies | [79] | 2017 |
| 8 | CASOA: An Architecture for Agent-Based Manufacturing System in the Context of Industry 4.0 | [80] | 2018 |
| 9 | A Multi-agent System Approach for Management of Industrial IoT Devices in Manufacturing Processes | [81] | 2018 |
| 10 | Artificial Intelligence for Cloud-Assisted Smart Factory | [82] | 2018 |
| 11 | A cyber-physical context-aware system for coordinating human-robot collaboration | [83] | 2018 |
| 12 | An industrial Internet of Things-based platform for context-aware information services in manufacturing | [39] | 2018 |
| 13 | Control as a Service Architecture to Support Context-aware Control Application Development | [84] | 2019 |
| 14 | An event-driven integrative framework enabling information notification among manufacturing resources | [55] | 2019 |
| 15 | Implementing self-* autonomic properties in self-coordinated manufacturing processes for the Industry 4.0 context | [85] | 2020 |
| 16 | Intelligent assistant system as a context-aware decision-making support for the workers of the future | [49] | 2020 |
| 17 | A microservice architecture for predictive analytics in manufacturing | [86] | 2020 |
| 18 | A digital twin-enhanced system for engineering product family design and optimisation | [87] | 2020 |
| 19 | Semantic communications between distributed cyber-physical systems towards collaborative automation for intelligent manufacturing | [88] | 2020 |
| 20 | Context-Based Resilience in Cyber-Physical Production System | [89] | 2021 |
| 21 | The HORSE framework: A reference architecture for cyber-physical systems in hybrid smart manufacturing | [90] | 2021 |
| 22 | Agent-Based Distributed Data Analysis Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems | [91] | 2022 |
| 23 | Context-aware scheduling and control architecture for cyber-physical production systems | [92] | 2022 |
| 24 | Integrating process management and event processing in smart factories: A systems architecture and use cases | [93] | 2022 |
| 25 | Extending the Intelligent Digital Twin with a context modelling service: A decision support use case | [94] | 2022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, A.; Lima, C.; Pinto, T.; Reis, A.; Barroso, J. Context-Aware Systems Architecture in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115863
Santos A, Lima C, Pinto T, Reis A, Barroso J. Context-Aware Systems Architecture in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115863
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Arlindo, Claudio Lima, Tiago Pinto, Arsénio Reis, and João Barroso. 2025. "Context-Aware Systems Architecture in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115863
APA StyleSantos, A., Lima, C., Pinto, T., Reis, A., & Barroso, J. (2025). Context-Aware Systems Architecture in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115863







