Study on the Combustion Behavior and Kinetic Characteristics of Semi-Coke from Oil Shale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Experimental Samples
2.2. Preparation of Semi-Coke
2.3. Characterization of Combustion Residues
2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.5. Kinetic Model Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Combustion Characteristics of Oil Shale Semi-Coke
3.1.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) Results
3.1.2. Extraction of Combustion Characteristic Parameters
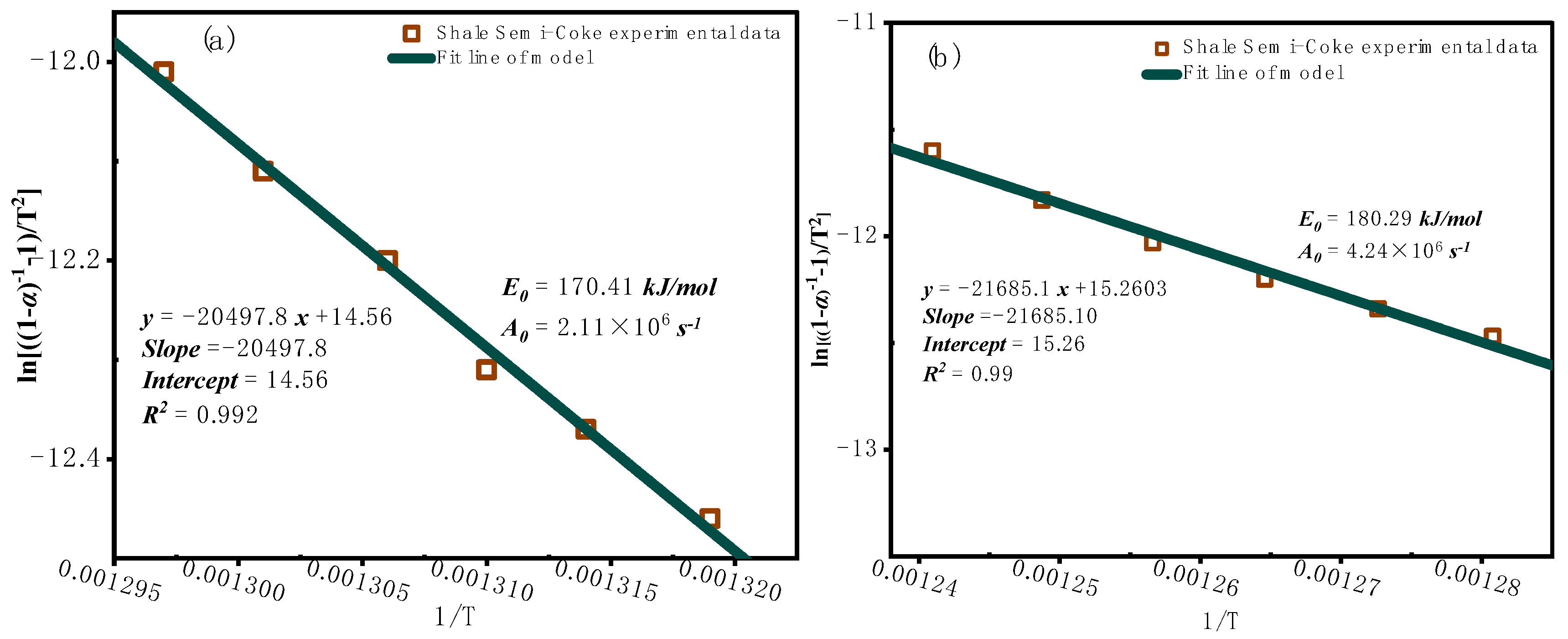
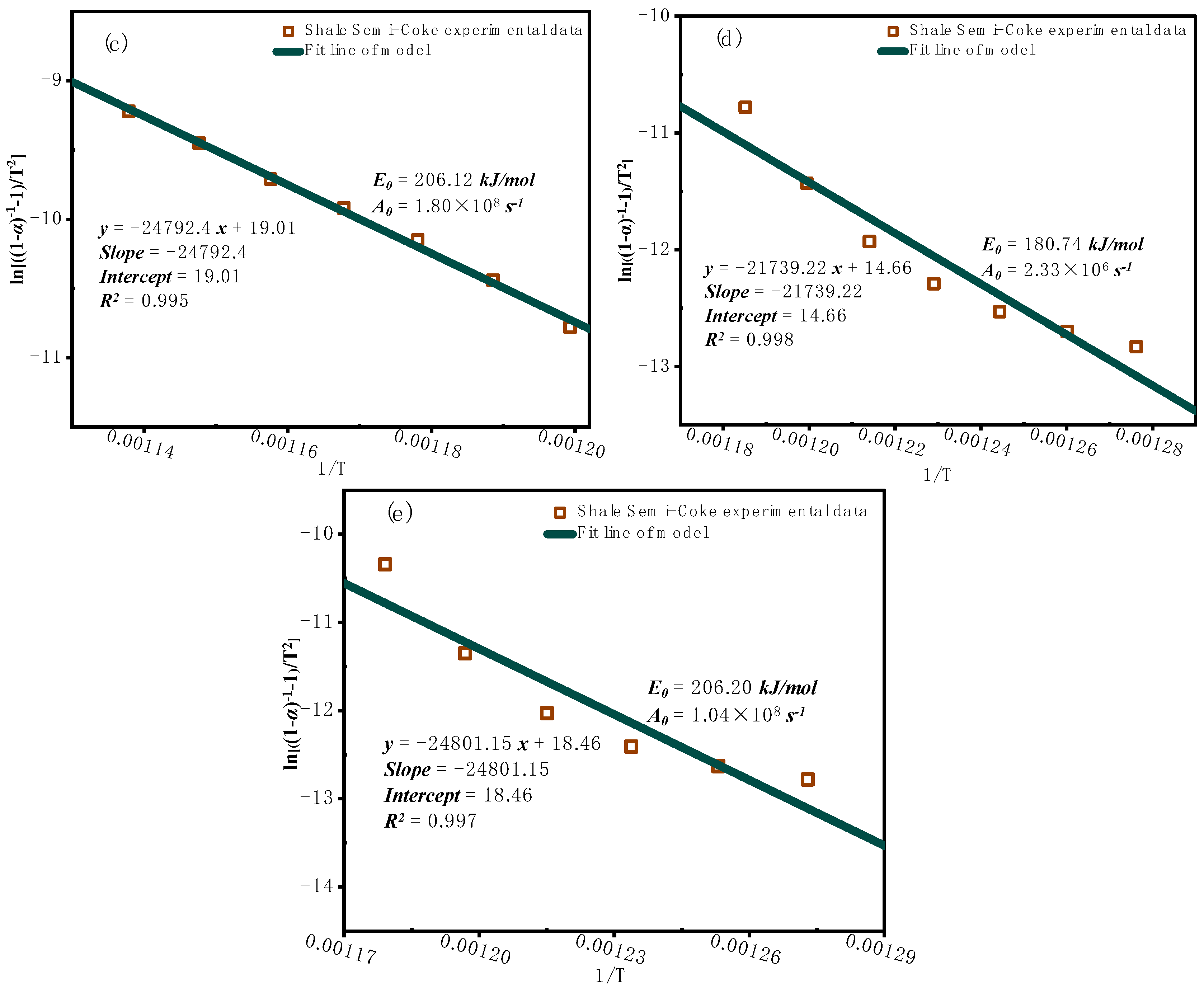
3.2. Kinetic Analysis
3.2.1. Model-Free Kinetic Analysis
3.2.2. Model-Based Kinetic Function Analysis
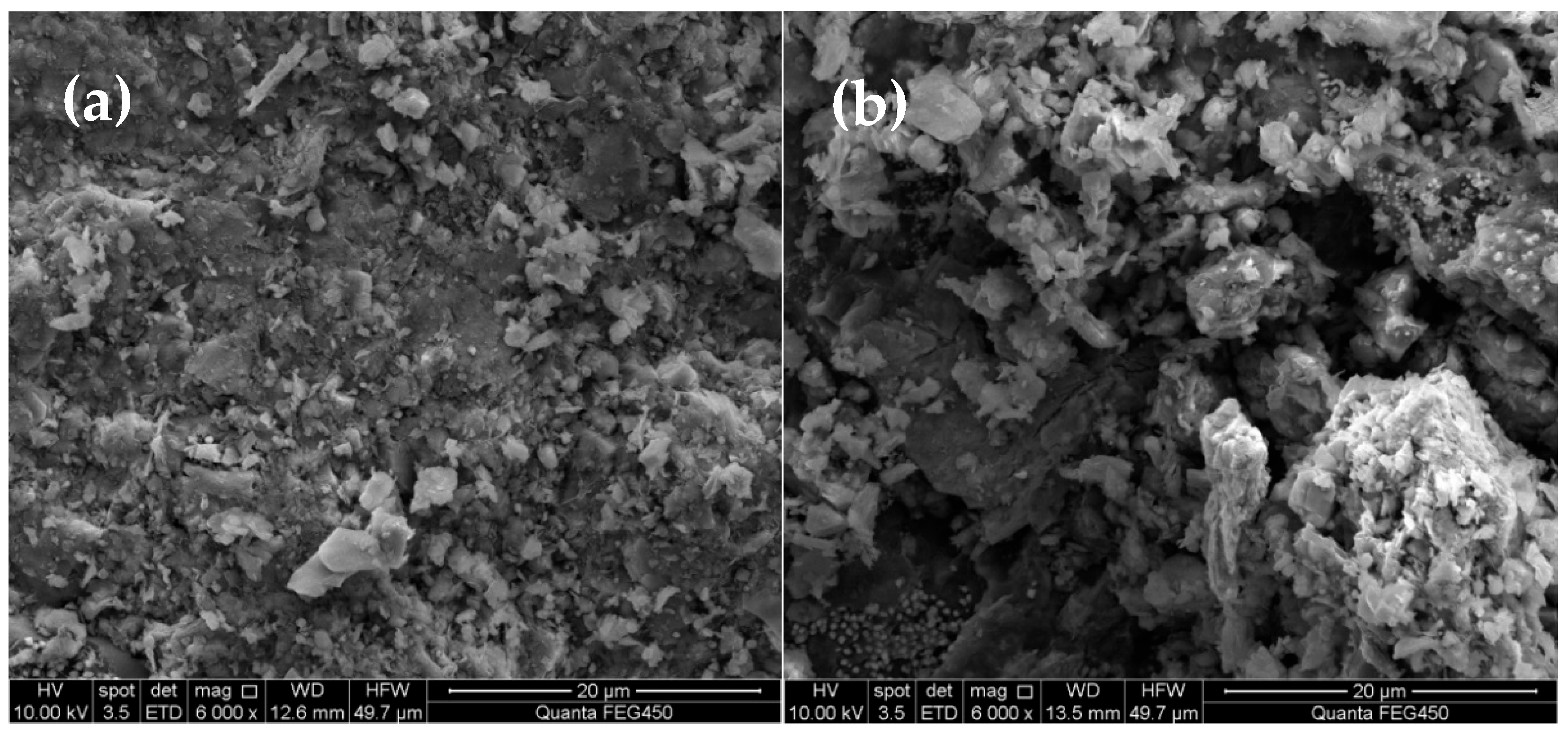
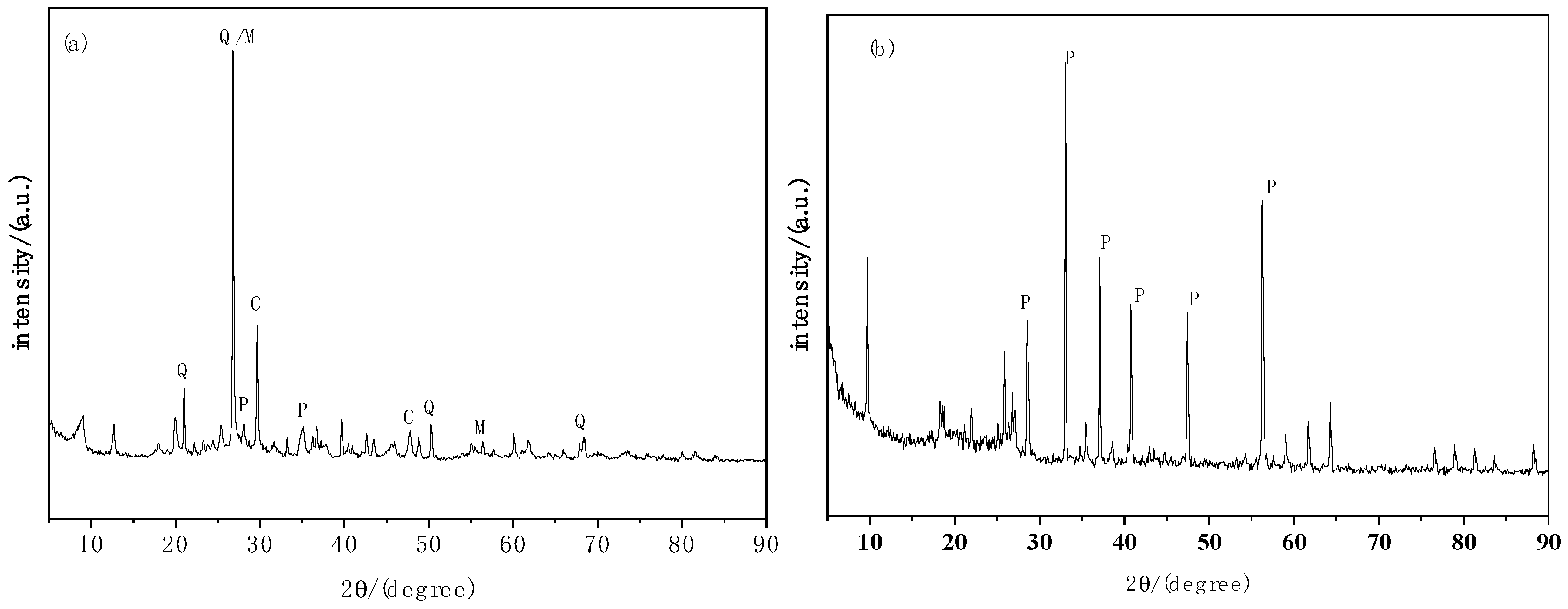
3.3. Characterization of Combustion Residues Analysis
3.3.1. SEM Characterization
3.3.2. XRD Characterization
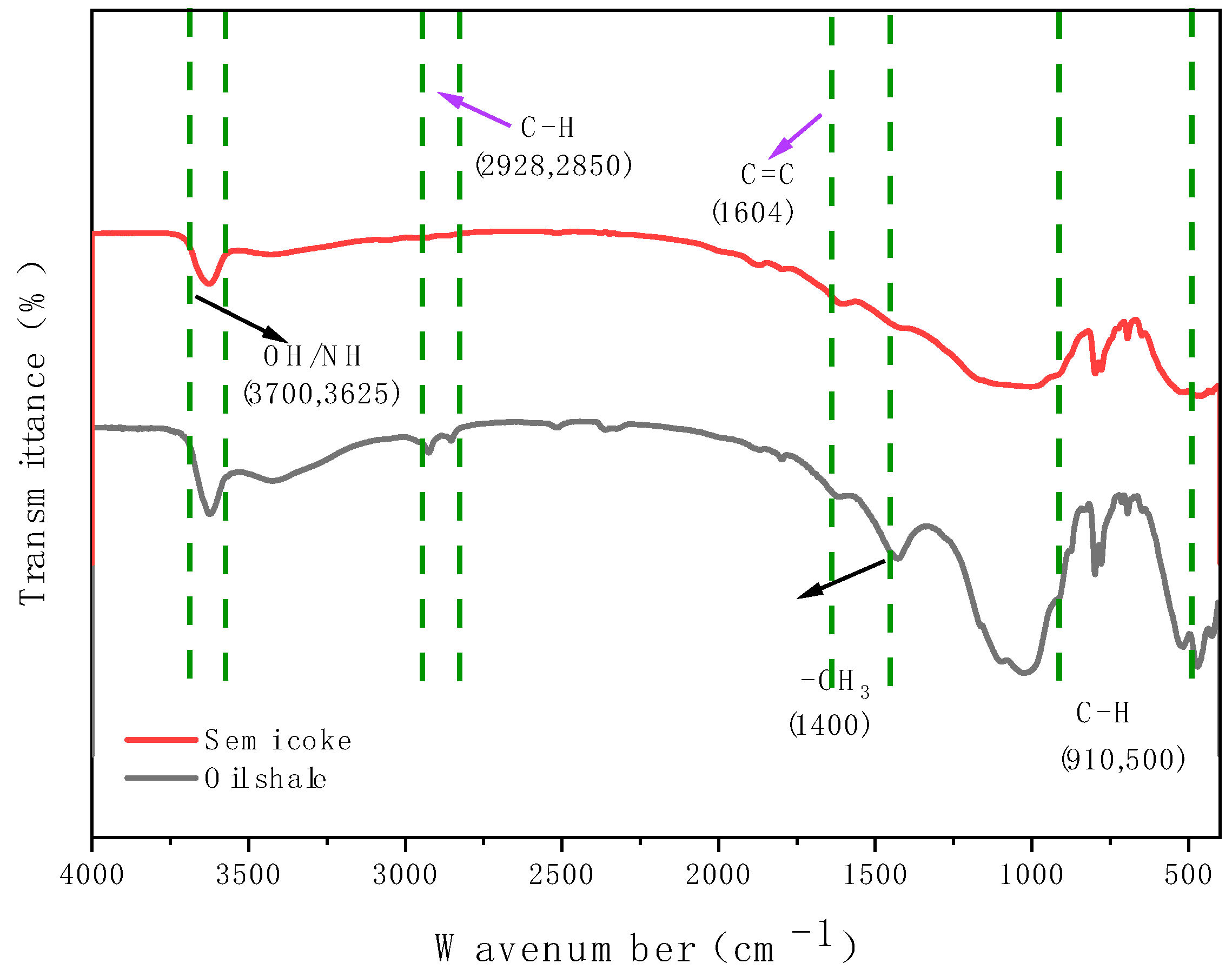
3.3.3. Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, B.Z.; Wang, Q.; Shen, P.Y.; Qin, H.; Li, S.H. Kinetic analysis of co-combustion of oil shale semi-coke with bituminous coal. Oil Shale 2012, 29, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, B.; Bai, J.; Guan, X. Interactions between oil shale and its semi-coke during co-combustion. Fuel 2009, 88, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chi, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B. Study on co-combustion kinetics of oil shale sludge and semicoke. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, B.; Wu, X.; Bai, J.; Sun, J. Influence of retorting temperature on combustion characteristics and kinetic parameters of oil shale semicoke. Oil Shale 2006, 23, 328–339. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Shi, C.; Yao, K. Thermal behavior research for co-combustion of furfural residue and oil shale semi-coke. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 120, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, C.A.; Wang, C.; Du, Y.; Che, D. Experimental investigation on co-combustion characteristics of semi-coke and coal: Insight into synergy and blending method. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 175, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N.; Li, D.; Lü, W.; Dai, F. Kinetic study on the pyrolysis behavior of Jimsar oil shale. Oil Shale 2019, 36, 462–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Xu, X.; Cui, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q. A TG-FTIR investigation and kinetic analysis of oil shale kerogen pyrolysis using the distributed activation energy model. Oil Shale 2016, 33, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Jiang, X.; Cui, Z. Thermal analysis studies on combustion mechanism of oil shale. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 84, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Kulaots, I.; Jiang, X.; Suuberg, E.M. Review of oil shale semicoke and its combustion utilization. Fuel 2014, 126, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; Jia, C.; Bai, J. Thermogravimetric Analysis of the Combustion Characteristics of Oil Shale Semi-Coke/Biomass Blends. Oil Shale 2011, 28, 284–295. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Miao, M.; Deng, B.; Cai, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H. Combustion kinetics study of oil shale semi-coke. CIESC J. 2019, 70, 3033. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.Y.; Zou, C.; Zhao, J.X.; Liang, D.; Xi, J.L.; Ma, C. Comparison of semi-coke with traditional pulverized coal injection and iron ore sintering fuels based on chemical structure and combustion behavior. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 19143-2017; National Technical Committee 355 on Petroleum and Natural Gas of Standardization Administration of China (SAC/TC 355). Analytical Methods for Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen in Rock Organic Matter. China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- DZ/T 0346-2020; National Technical Committee 93 on Natural Resources and Territorial Spatial Planning of Standardization Administration of China (SAC/TC 93). Specifications for Mineral Geological Exploration of Oil Shale, Stone-Like Coal, and Peat. Geology Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Guo, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, D.; Pan, J.; Yang, C.; Li, S. Clean Preparation of Formed Coke from Semi-coke by the Carbonated Consolidation Process. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 27398–27409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y. Thermogravimetric analysis of Huadian oil shale combustion at different oxygen concentrations. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 4450–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 38, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, A.W.; Redfern, J.P. Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature 1964, 201, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente, M.C.; Galan, M.A. Kinetics of the thermal decomposition of oil shale from Puertollano (Spain). Fuel 2001, 80, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yue, C. Study of pyrolysis kinetics of oil shale. Fuel 2003, 82, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, M.A.B.; Massard, H.; Martins, M.F. Formulating and optimizing a combustion pathways for oil shale and its semi-coke. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 3224–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, Q. Investigation on the co-combustion of low calorific oil shale and its semi-coke by using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 136, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Characteristics of co-combustion and kinetic study on hydrochar with oil shale: A thermogravimetric analysis. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, M.V.; Bal, B.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Nurgaliev, D.K. Thermal characteristics and model-free kinetics of oil shale samples. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 8933–8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, M. Thermal and kinetic characteristics of pyrolysis and combustion of three oil shales. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 97, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P.; Liang, W.X.; Qin, H.; Wang, Q. Thermal behavior of co-combustion of oil shale semi-coke with torrefied cornstalk. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 109, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Elemental Analysis (wt%) | Proximate Analytics (wt%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 13.44 | Moisture content | 3.8 |
| H | 0.46 | Volatile matter | 28.4 |
| N | 0.38 | Ash content | 64.2 |
| S | 0.58 | Fixed carbon | 3.6 |
| Elemental Composition and Content | ||
|---|---|---|
| Elemental Analysis (wt%) | C | 2.23 |
| H | 0.16 | |
| N | 0.14 | |
| S | 0.08 | |
| Heating Value Analysis (MJ/kg) | Dry distillation temperature at 500 °C | |
| HHV | 8.0 | |
| Function | Mechanism | Differential Form f(α) | Integral Form G(α) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction Order Models | |||
| First-order | F1 | (1 − α) | −ln(1 − α) |
| Second-order | Chemical reaction (F2) | (1 − α)2 | (1 − α)−1 − 1 |
| Diffusion Models | |||
| Jander equation | 2D, n = 0.5 | 4(1 − α)1/2[1 − (1 − α)1/2]1/2 | [1 − (1 − α)1/2]1/2 |
| Jander equation | 3D, n = 0.5 | 6(1 − α)2/3[1 − (1 − α)1/3]1/2 | [1 − (1 − α)1/3]1/2 |
| G-B equation | 3D, D4 (column symmetry) | 3/2[(1 − α)−1/3 − 1] − 1 | 1 − 2/3α − (1 − α)2/3 |
| Geometrical Contraction Models | |||
| Contracting area | R2, n = 2 | (1 − α)1/2 | 2[1 − (1 − α)1/2] |
| Contracting volume | R3, n = 3 | (1 − α)2/3 | 3[1 − (1 − α)1/3] |
| Nucleation Models | |||
| Avrami−Erofeev | Random nucleation and nuclei growth A2, 2D, n = 2 | 1/2(1 − α)[−ln(1 − α)]−1 | [−ln(1 − α)]2 |
| Avrami−Erofeev | Random nucleation and nuclei growth A3, 3D, n = 3 | 1/3(1 − α)[−ln(1 − α)]−2 | [−ln(1 − α)]3 |
| Mample power | n = 1/4 | 4α3/4 | α1/4 |
| Mample power | n = 1/3 | 3α2/3 | α1/3 |
| Mample power | n = 1/2 | 2α1/2 | α1/2 |
| Mample power | n = 2 | 1/2α−1 | α2 |
| Heating Rate/°C/min | Ti/°C | Tp/°C | Tf/°C | Δm/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 427.94 | 490.83 | 546.53 | 4.29 |
| 10 | 453.42 | 510.80 | 564.52 | 5.18 |
| 15 | 461.19 | 533.64 | 584.39 | 5.54 |
| 20 | 465.38 | 543.61 | 589.62 | 5.82 |
| 25 | 475.56 | 549.78 | 599.80 | 6.22 |
| α | Eα, kJ/mol | A (1/s) | Eα,avg, kJ/mol | Aavg | Ravg2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OFW | 0.1 | 145.58 | 6.27 × 106 | 180.80 | 1.04 × 109 | 0.998 |
| 0.2 | 194.41 | 8.95 × 109 | ||||
| 0.3 | 161.96 | 3.72 × 107 | ||||
| 0.4 | 132.61 | 2.07 × 105 | ||||
| 0.5 | 183.26 | 2.57 × 107 | ||||
| 0.6 | 205.11 | 1.57 × 108 | ||||
| 0.7 | 201.73 | 7.67 × 107 | ||||
| 0.8 | 200.39 | 6.01 × 107 | ||||
| 0.9 | 202.20 | 7.93 × 107 | ||||
| KAS | 0.1 | 145.26 | 5.1 × 106 | 180.81 | 1.07 × 109 | 0.997 |
| 0.2 | 194.31 | 9.27 × 109 | ||||
| 0.3 | 161.82 | 3.35 × 107 | ||||
| 0.4 | 132.53 | 1.41 × 105 | ||||
| 0.5 | 183.02 | 2.23 × 107 | ||||
| 0.6 | 204.93 | 1.46 × 108 | ||||
| 0.7 | 201.54 | 6.93 × 107 | ||||
| 0.8 | 200.19 | 5.36 × 107 | ||||
| 0.9 | 201.99 | 7.06 × 107 |
| F2-F2-F2 | F2-F2 | ||||
| stage I | Stage II | Stage II | stage I | Stage II | |
| Eα/KJ·mol−1 | 180.130 | 249.799 | 263.730 | 170.646 | 277.451 |
| A/S−1 | 3.93 × 109 | 4.58 × 1010 | 1.35 × 1011 | 8.04 × 108 | 4.73 × 1011 |
| Contribution | 0.395 | 0.278 | 0.355 | 0.431 | 0.596 |
| Eα,avg/KJ·mol−1 | 231.22 | 224.05 | |||
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.97 | |||
| f(α) | (1 − α)2 | (1 − α)2 | (1 − α)2 | (1 − α)2 | (1 − α)2 |
| F2-D4-F2 | F2-D4 | ||||
| stage I | Stage II | Stage II | stage I | Stage II | |
| Eα/KJ·mol−1 | 94.340 | 50.227 | 265.536 | 61.982 | 21.187 |
| A/S−1 | 3.08 × 103 | 2.19 | 5.83 × 1010 | 6.12 | 2.26 × 10−2 |
| Contribution | 0.431 | 0.157 | 0.443 | 0.542 | 0.410 |
| Eα,avg/KJ·mol−1 | 136.70 | 41.58 | |||
| R2 | 0.94 | 0.82 | |||
| f(α) | (1 − α)2 | 3/2[(1 − α)−1/3 − 1]−1 | (1 − α)2 | (1 − α)2 | 3/2[(1 − α)−1/3 − 1] − 1 |
| F2-R3-F2 | A2-F2 | ||||
| stage I | Stage II | Stage III | stage I | Stage II | |
| Eα/KJ·mol−1 | 131.344 | 102.546 | 203.089 | 114.196 | 221.454 |
| A/S−1 | 2.21 × 106 | 9.08 × 103 | 2.95 × 107 | 1.17 × 105 | 7.11 × 108 |
| Contribution | 0.248 | 0.187 | 0.583 | 0.386 | 0.649 |
| Eα,avg/KJ·mol−1 | 145.66 | 167.83 | |||
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.95 | |||
| f(α) | (1 − α)2 | (1 − α)2/3 | (1 − α)2 | 1/2(1 − α)[−ln(1 − α)]−1 | (1 − α)2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Xue, P.; Wu, M.; Yun, J. Study on the Combustion Behavior and Kinetic Characteristics of Semi-Coke from Oil Shale. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115797
Zhao F, Zhang L, Liu S, Wang T, Xue P, Wu M, Yun J. Study on the Combustion Behavior and Kinetic Characteristics of Semi-Coke from Oil Shale. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115797
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Fajun, Lei Zhang, Sen Liu, Tianyu Wang, Peiyong Xue, Mingxuan Wu, and Jiankang Yun. 2025. "Study on the Combustion Behavior and Kinetic Characteristics of Semi-Coke from Oil Shale" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115797
APA StyleZhao, F., Zhang, L., Liu, S., Wang, T., Xue, P., Wu, M., & Yun, J. (2025). Study on the Combustion Behavior and Kinetic Characteristics of Semi-Coke from Oil Shale. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115797






