First-Arrival Constrained Physics-Informed Recurrent Neural Networks for Initial Model-Insensitive Full Waveform Inversion in Vertical Seismic Profiling
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Propose an initial velocity model-insensitive FWI method that effectively addresses the local minima caused by different initial velocity models.
- (2)
- Develop a PIRNN architecture with first-arrival time constraints by embedding the physical processes of seismic wave propagation into the recurrent neural network; through leveraging the spatiotemporal gradient information from forward propagation, this method enables back propagation under first-arrival constraints, thereby producing FWI solutions.
- (3)
- Introduce a knowledge-constrained neural network framework for FWI to avoid the instability issues of data-driven methods caused by the training data quality.
2. Problem Analysis and Theory
2.1. Math Model of FWI
2.2. Causes of Nonlinearity in FWI
2.3. Mitigating Nonlinearity Using First-Arrival Constraints
2.4. Principles of PIRNN Method
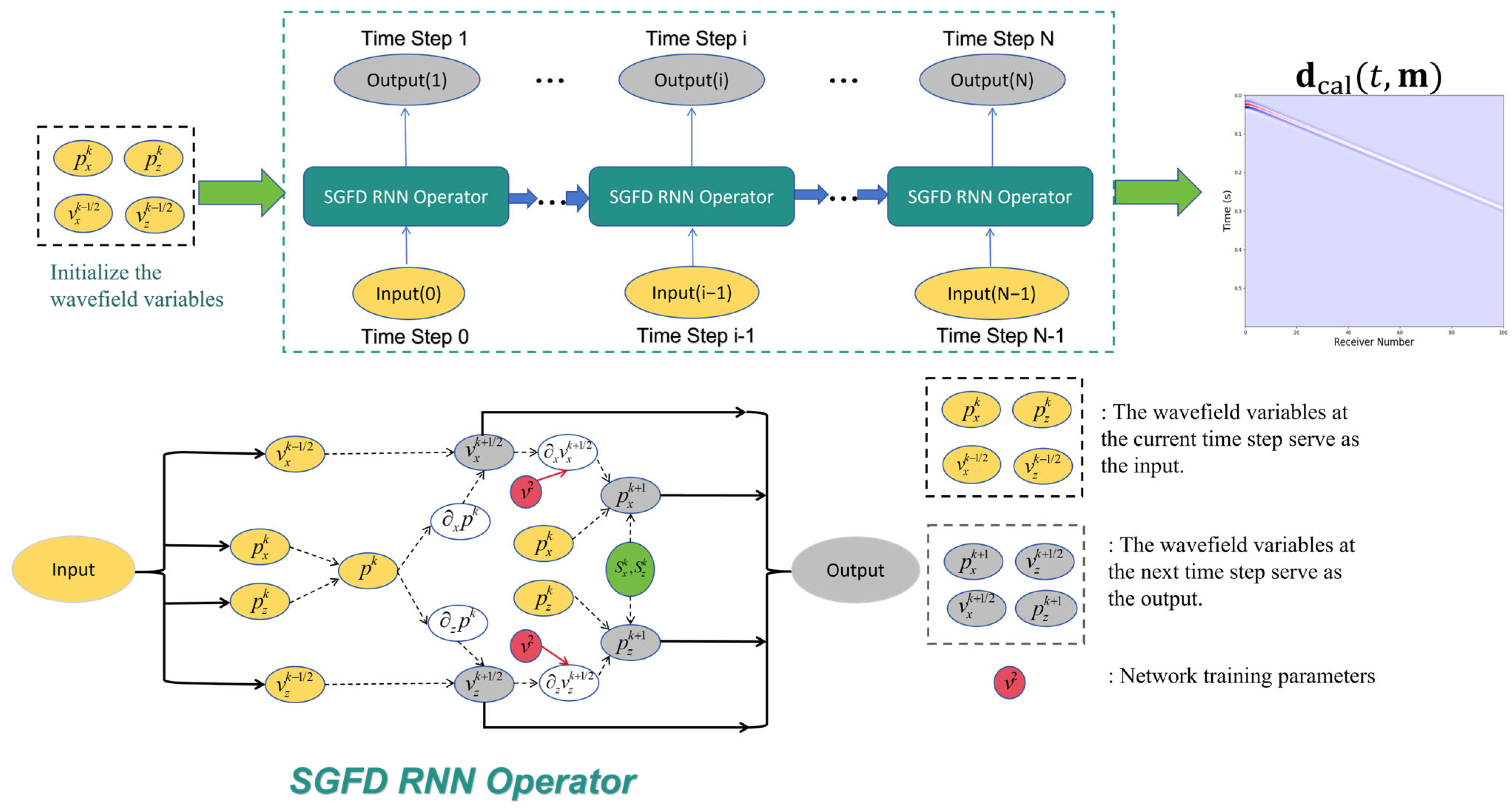
2.4.1. PIRNN Forward Modeling
2.4.2. PIRNN Full Waveform Inversion
3. Methodology
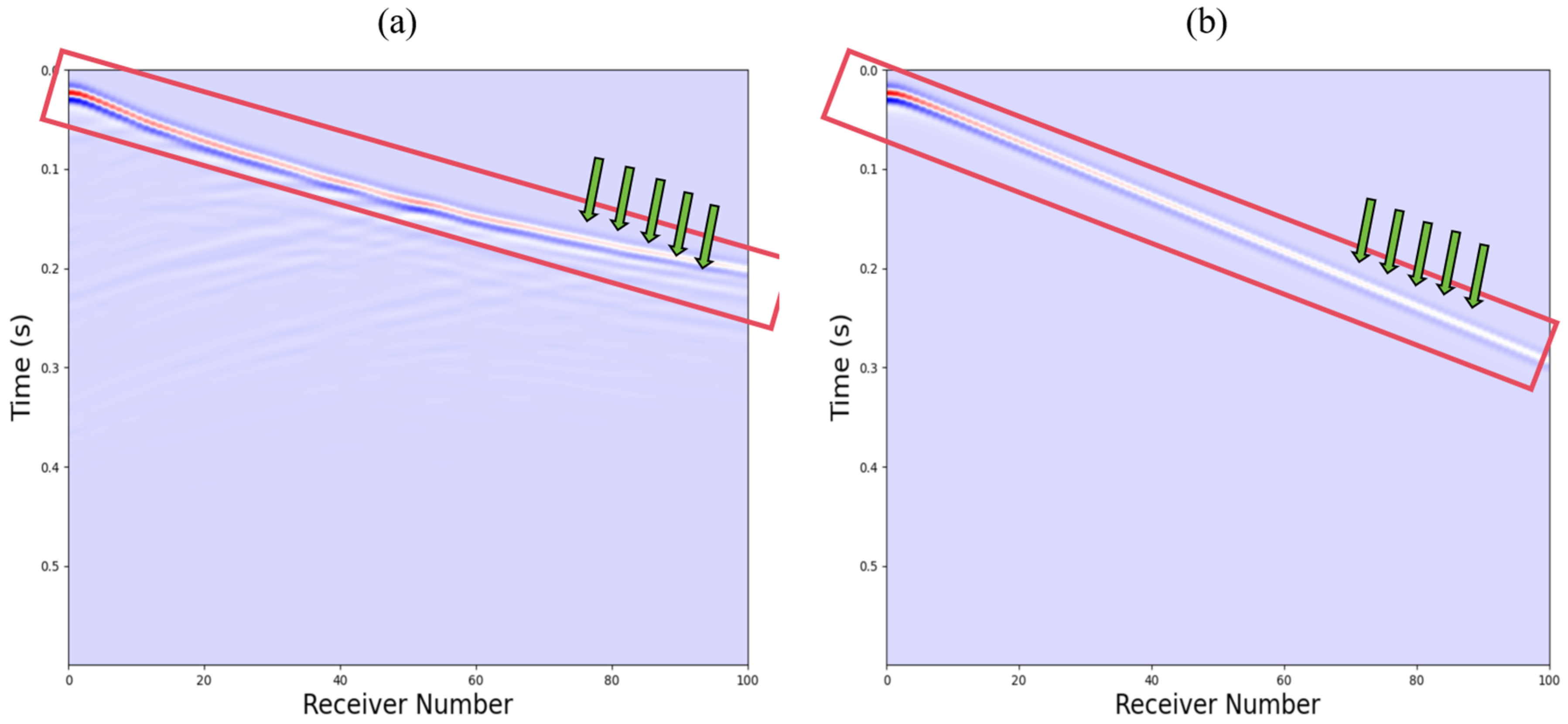
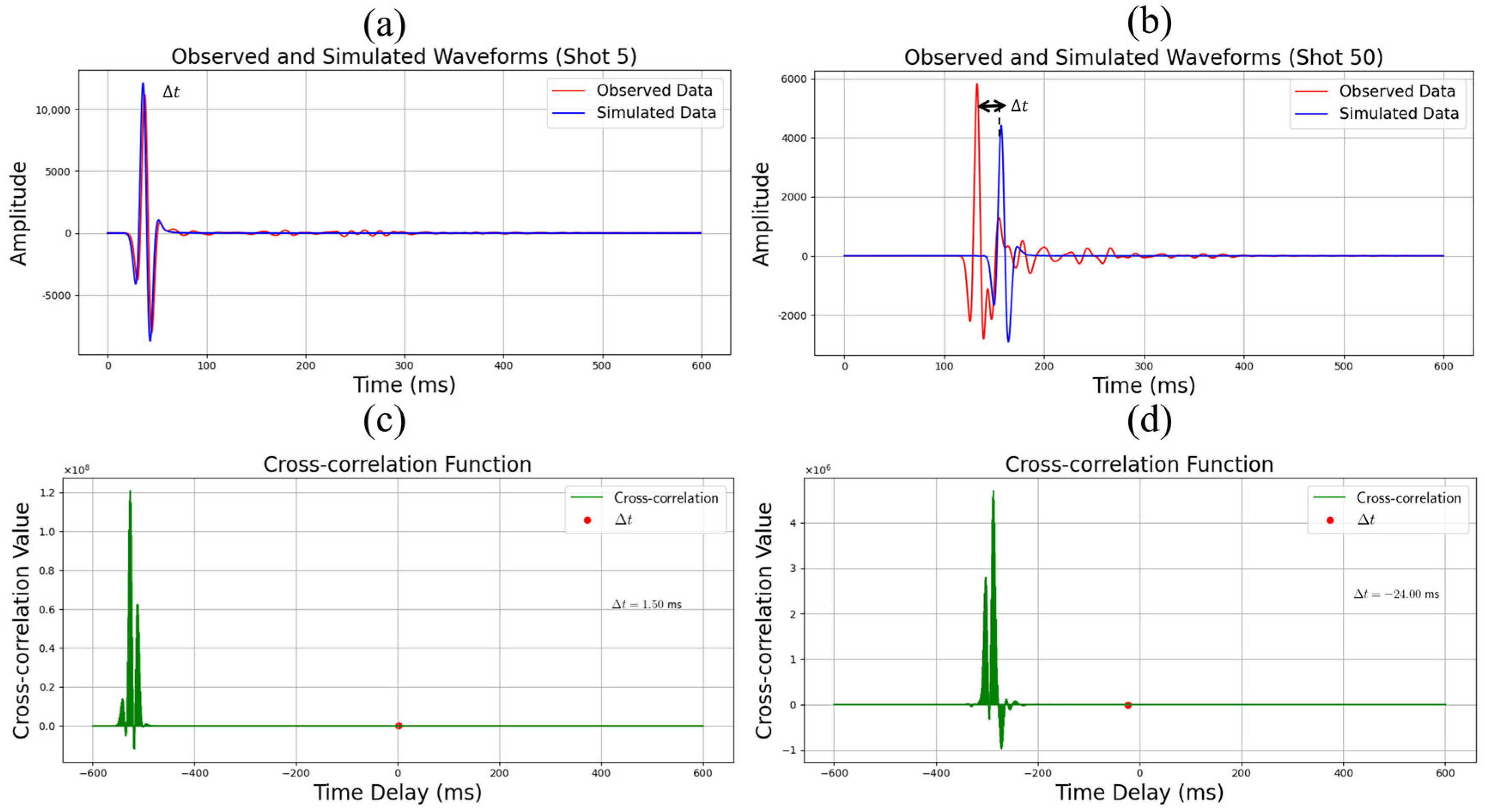
3.1. Extraction Method of First-Arrival Information
3.2. FWI Objective Function with First-Arrival Constraints
3.3. Network Structure
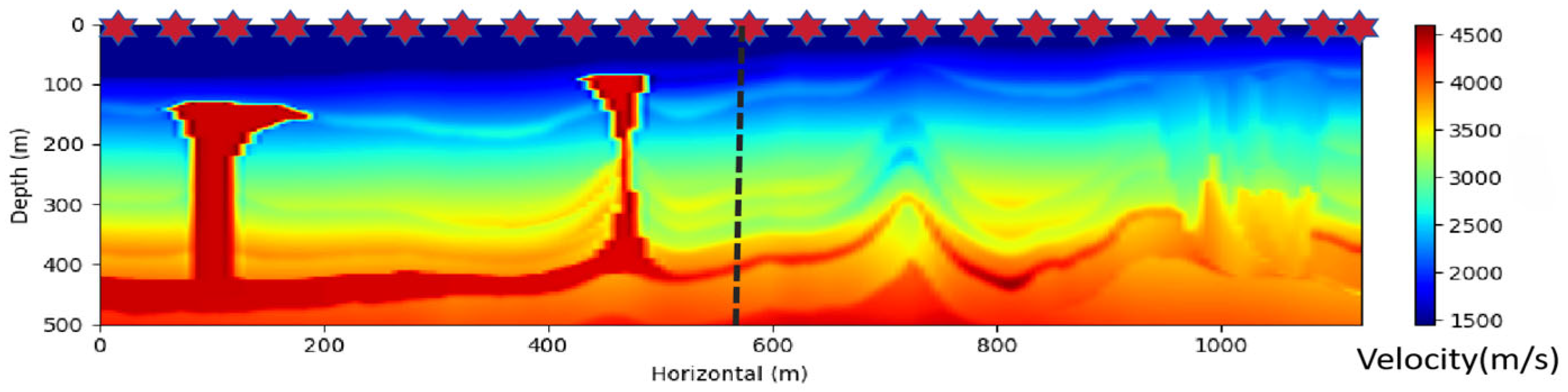
4. Numerical Application
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1. Coefficient of Determination ( Score)
4.1.2. Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM)
4.1.3. Normalized Cross-Correlation (NCC)
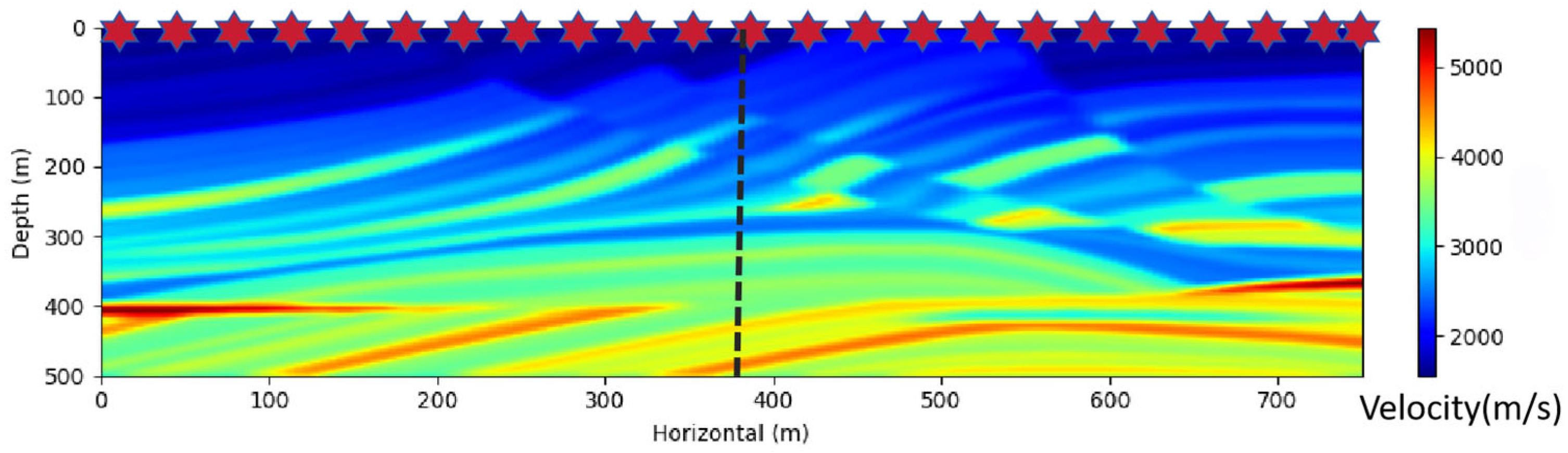
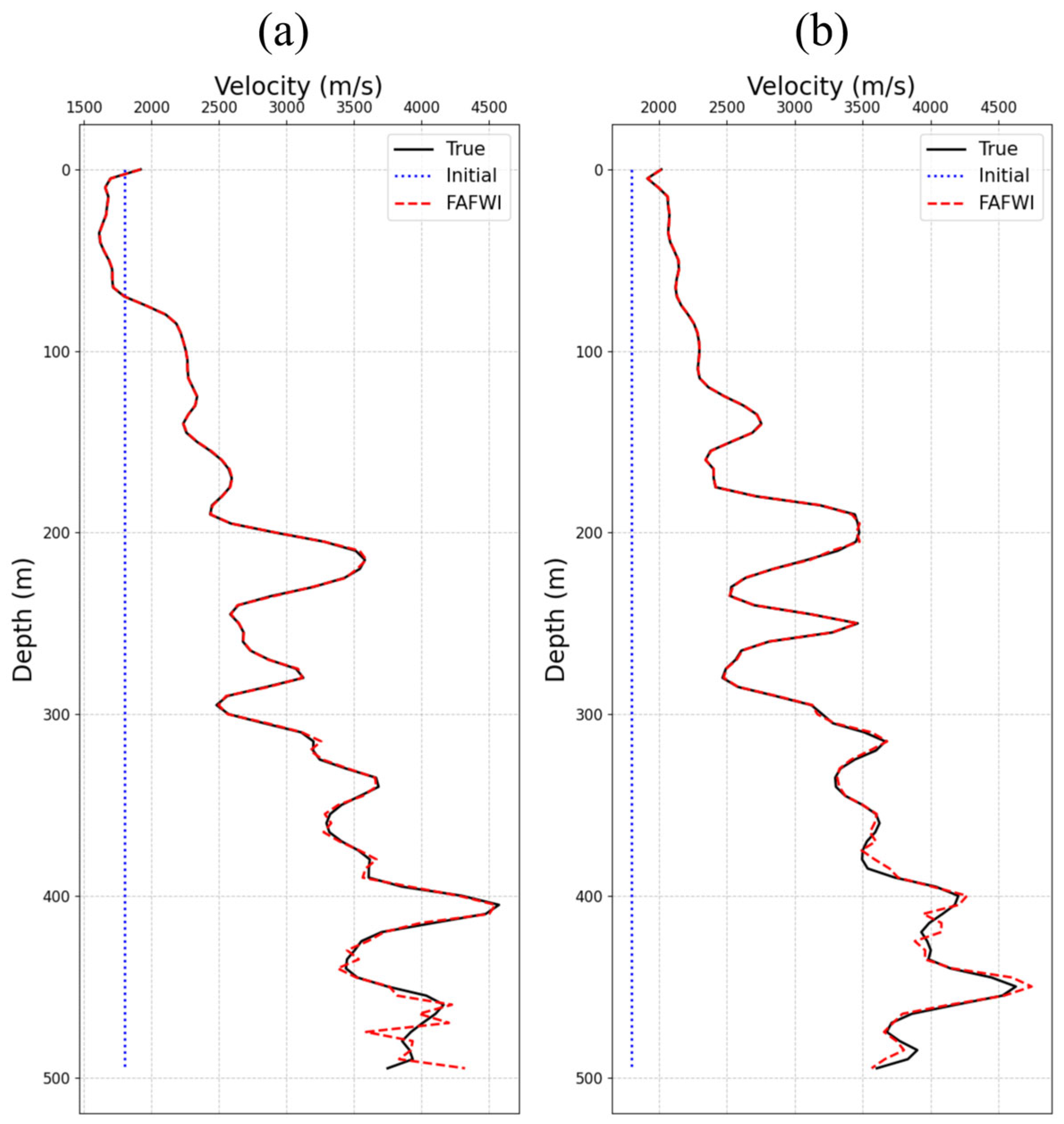
4.2. Initial Model Dependency
4.3. Robustness Analysis
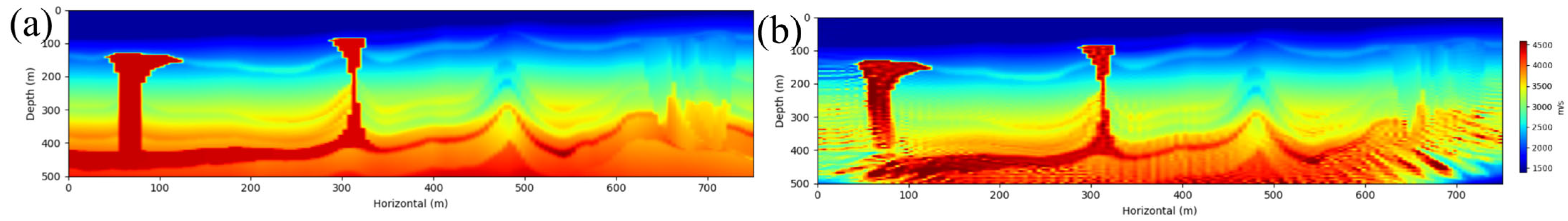
4.3.1. Method Applicability
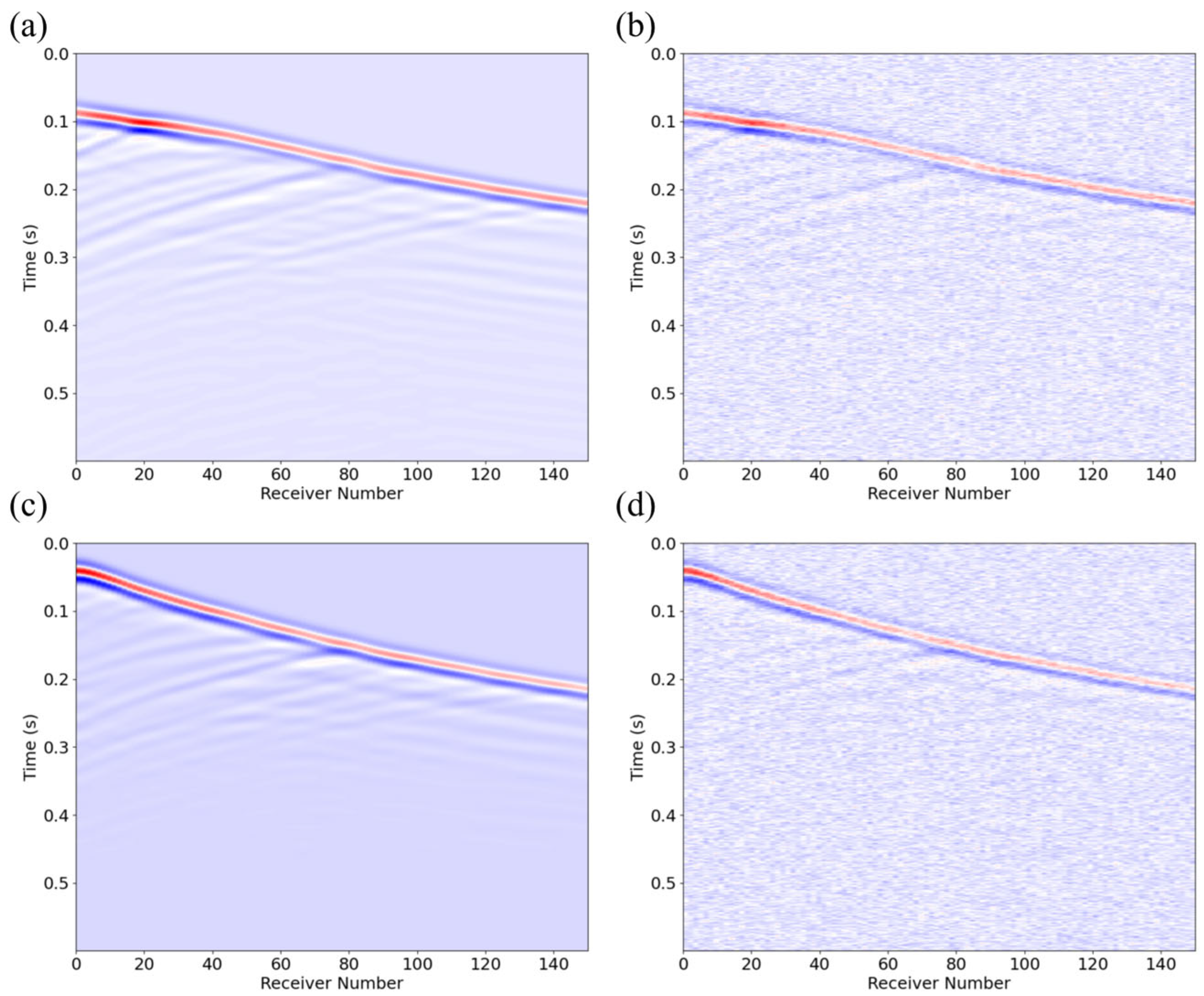
4.3.2. Noise Analysis
4.3.3. Initial Model Sensitivity Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Initial Model Dependency
5.2. Robustness Analysis
5.2.1. Method Applicability
5.2.2. Noise Analysis
5.2.3. Initial Model Sensitivity Analysis
6. Discussion
6.1. Analysis
6.2. First-Arrival Time Picking Methods
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarantola, A. Inversion of seismic reflection data in the acoustic approximation. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantola, A. Linearized inversion of seismic reflection data. Geophys. Prospect. 1984, 32, 998–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virieux, J.; Operto, S. An overview of full-waveform inversion in exploration geophysics. Geophysics 2009, 74, WCC1–WCC26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Grobbe, N.; Slob, E.; Wapenaar, K. Source estimation for wavefield-reconstruction inversion. Geophysics 2018, 83, R345–R359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, B.; Almomin, A. Simultaneous inversion of full data bandwidth by tomographic full-waveform inversion. Geophysics 2014, 79, WA129–WA140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunks, C.; Saleck, F.M.; Zaleski, S.; Chavent, G. Multiscale seismic waveform inversion. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1457–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, T.; Herrmann, F.J. Mitigating local minima in full-waveform inversion by expanding the search space. Geophys. J. Int. 2013, 195, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, E.; Guasch, L.; van Leeuwen, T.; Aravkin, A.; Herrmann, F.J. Total-variation regularization strategies in full-waveform inversion. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2018, 11, 376–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, M.; Guasch, L. Adaptive waveform inversion: Theory. Geophysics 2016, 81, R429–R445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Engquist, B. Analysis of optimal transport and related misfit functions in full-waveform inversion. Geophysics 2018, 83, A7–A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Engquist, B.; Sun, J.; Hamfeldt, B.F. Application of optimal transport and the quadratic Wasserstein metric to full-waveform inversion. Geophysics 2018, 83, R43–R62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, B.; Dong, L.; Liu, Y. Full waveform inversion method using envelope objective function without low frequency data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 109, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-W.; Alkhalifah, T. Full waveform inversion using envelope-based global correlation norm. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 213, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. A theory-guided deep-learning formulation and optimization of seismic waveform inversion. Geophysics 2020, 85, R87–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y. Data-driven seismic waveform inversion: A study on the robustness and generalization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6900–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, Y. InversionNet: An efficient and accurate data-driven full waveform inversion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2019, 6, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 378, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasht-Behesht, M.; Gholami, A.; Kamal, M.; Siahkoohi, H.R. Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for wave propagation and full waveform inversions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2021JB023120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Niu, Z.; Innanen, K.A.; Li, J.; Trad, D.O. Physics-guided deep learning for seismic inversion with hybrid training and uncertainty analysis. Geophysics 2021, 86, R303–R317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Physics-informed robust and implicit full waveform inversion without prior and low-frequency information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5918712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Geng, Y.; Dickson, A.D.; Lin, Y. Integrating deep neural networks with full-waveform inversion: Reparameterization, regularization, and uncertainty quantification. Geophysics 2022, 87, R93–R109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, S.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Full waveform inversion based on dynamic data matching of convolutional wavefields. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1134871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J. Joint seismic traveltime and waveform inversion for near surface imaging. In Proceedings of the SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 26–31 October 2014; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2014; p. SEG-2014-1501. [Google Scholar]
- Treister, E.; Haber, E. Joint full waveform inversion and travel time tomography. In Proceedings of the 78th EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2016, Vienna, Austria, 30 May–2 June 2016; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Houten, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, K.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Lin, T.Y. First-break automatic picking with deep semisupervised learning neural network. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2018; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2018; pp. 2181–2185. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J. Seismic first break picking in a higher dimension using deep graph learning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.08408. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Ma, J. Effective First-Break Picking of Seismic Data Using Geometric Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.R.; Huddleston, P.D.; Kan, T.K. Seismic versus sonic velocities: A vertical seismic profiling study. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O. Seismic Data Analysis: Processing, Inversion and Interpretation of Seismic Data; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sheriff, R.E.; Geldart, L.P. Exploration Seismology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirgue, L.; Pratt, R.G. Efficient waveform inversion and imaging: A strategy for selecting temporal frequencies. Geophysics 2004, 69, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P. A Numerical Tour of Wave Propagation; Xi’an Jiaotong University Press: Xi’an, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Qu, L.; Gao, J.; Cai, H.; Liang, J. Elastic full-waveform inversion via physics-informed recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4510616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





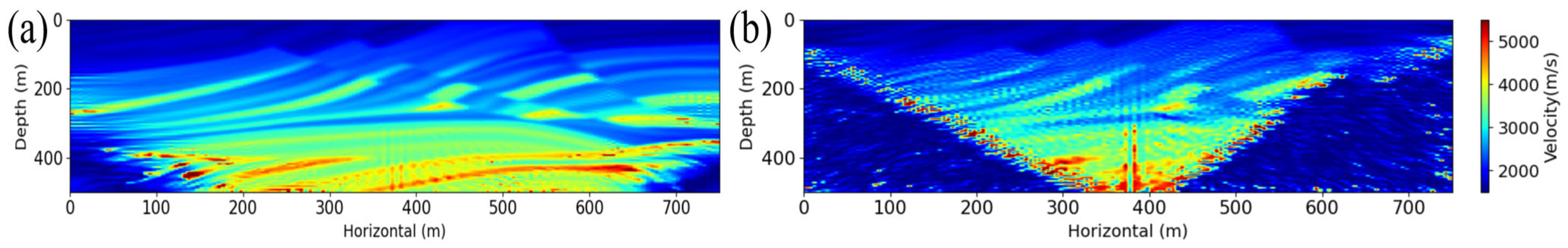

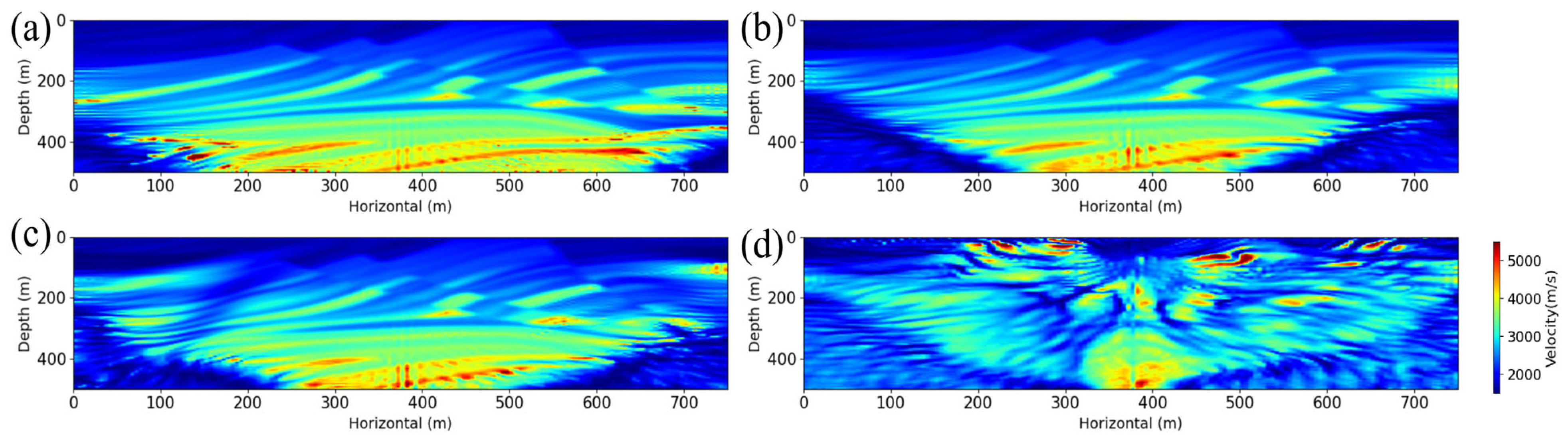
| Parameters | Marmousi |
|---|---|
| Score | 0.5471 |
| SSIM | 0.8390 |
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.7858 |
| Parameters | BP TTI |
|---|---|
| Score | 0.9118 |
| SSIM | 0.8413 |
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.9566 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Qu, L.; Gao, J.; Cai, H.; Liang, J. First-Arrival Constrained Physics-Informed Recurrent Neural Networks for Initial Model-Insensitive Full Waveform Inversion in Vertical Seismic Profiling. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5757. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105757
Lu C, Liu J, Qu L, Gao J, Cai H, Liang J. First-Arrival Constrained Physics-Informed Recurrent Neural Networks for Initial Model-Insensitive Full Waveform Inversion in Vertical Seismic Profiling. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5757. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105757
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Cai, Jijun Liu, Liyuan Qu, Jianbo Gao, Hanpeng Cai, and Jiandong Liang. 2025. "First-Arrival Constrained Physics-Informed Recurrent Neural Networks for Initial Model-Insensitive Full Waveform Inversion in Vertical Seismic Profiling" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5757. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105757
APA StyleLu, C., Liu, J., Qu, L., Gao, J., Cai, H., & Liang, J. (2025). First-Arrival Constrained Physics-Informed Recurrent Neural Networks for Initial Model-Insensitive Full Waveform Inversion in Vertical Seismic Profiling. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5757. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105757






