Featured Application
This study evaluated demountable, clamp-based beam-to-column connections for modular steel structures through experimental tests and numerical modeling, confirming increased stiffness and load capacity without plastic deformation.
Abstract
The increasing demand for modular and reusable steel structures has driven the development of demountable connections that preserve the integrity of structural components. This study investigated the structural performance of beam-to-column connections using clamp-based fastening systems, operating strictly within the elastic regime and targeting applications in temporary systems and industrial platforms. Two triangular steel frame configurations (180 mm and 260 mm), differing in clamp capacity and hole arrangement, were experimentally tested and numerically modeled to assess their influence on load-bearing capacity, displacements, and stress distribution. Experimental tests were conducted with controlled bolt pretension and progressive vertical loading, continuously monitoring displacements and applied forces. The finite element model (FEM), validated with high correlation (>97%) to the experimental data, confirmed that all configurations remained within the elastic domain. Results showed that increasing the number of clamps significantly enhanced both stiffness and load capacity, with gains of up to 27.3% depending on the configuration, while reductions exhibited a nonlinear performance loss. Stress concentrations were observed in clamp contact regions without plasticization. Overall, clamp-based connections demonstrated efficient structural performance and alignment with design-for-deconstruction and circular economy principles, proving to be technically feasible for systems requiring reusability and adaptability.
1. Introduction
The increasing demand for adaptable and reusable steel structures has fostered the development of connection systems that enable disassembly and structural reconfiguration without impairing material integrity. Clamp-based fastening systems have emerged as a viable solution to this challenge by offering non-invasive mechanical fixation that preserves steel components’ original geometry and strength [1,2,3,4]. These systems avoid the drawbacks of traditional welding or bolting methods, such as permanent material alteration, localized damage, or alignment limitations in successive installations [5,6].
Although clamp-based connections have demonstrated advantages in reusability and ease of assembly [7,8,9], most existing studies emphasize failure mechanisms and ultimate load-bearing capacity [10,11]. However, their performance under service-level conditions—particularly within the elastic range—remains underexplored. This behavioral domain is critical for systems intended for repeated use, where structural components must retain integrity across multiple assembly and disassembly cycles. In temporary installations, modular frames, and industrial maintenance platforms, ensuring durability, stability, and mechanical efficiency requires a clear understanding of elastic behavior [1,4,12,13,14].
In addition, recent work on alternative steel connection systems, such as semi-rigid and rigid beam-column, has highlighted the importance of preserving connection performance under varying demands [15,16]. These studies reinforce the continued interest in unconventional joints that ensure mechanical continuity and structural reliability without inducing permanent damage. Other recent investigations on innovative steel joint solutions further underscore the ongoing interest in alternative connection strategies for structural applications [14].
The finite element model has been widely employed to simulate the behavior of steel joints [17], enabling accurate prediction of stress distribution, stiffness response, and force paths, particularly in systems with contact interfaces and frictional behavior [18,19,20]. Combined with experimental validation, it provides a robust framework to evaluate the effectiveness of clamp configurations in maintaining structural performance without plastic damage [21,22]. However, prior studies have often used finite element models to study global structural responses or nonlinear behavior without detailed validation of local displacement measurements in realistic clamp-based configurations. This disconnects numerical modeling from the elastic performance observed under service-level conditions.
Recent studies have advanced the understanding of clamp-based systems in reversible and modular applications. For instance, Cavalheiro et al. [14] demonstrated that clamp-based joints maintain uniform stress distribution across the clamping surface when subjected to monotonic loads, preserving elastic behavior and enabling reuse. Cabaleiro et al. [8] compared the stiffness of clamp and bolted joints using shaking table tests, highlighting that clamped joints provide sufficient rigidity for structural systems while simplifying reconfiguration.
The structural systems investigated in this study consist of modular steel assemblies composed of linear elements—specifically, IPE profiles and triangular braces—connected via clamp-based joints. These configurations differ from conventional modular approaches used in building enclosures or residential units by prioritizing adaptability and reusability in industrial settings. Their design supports frequent reconfiguration and mechanical efficiency, particularly in maintenance platforms, modular shelving, and temporary support structures, where rapid assembly and disassembly are critical.
While such configurations have shown promise for modular industrial applications, there remains a gap in the literature regarding the systematic evaluation of the number of clamps and the geometry of the structure on the elastic behavior of complete structural assemblies, especially in models of column–top connections. Previous works have not fully explored how different clamp configurations affect the load capacity, angular rotation, or local deformation under service-level conditions. Furthermore, few studies validate their finite element models with accurate displacement tracking under realistic structural conditions.
This study investigates the mechanical behavior of clamp-based beam-to-column connections under service-level conditions, with an exclusive focus on the elastic range. Combining experimental testing and finite element modeling, two triangular steel frames—180 mm and 260 mm—are assessed under different clamp configurations to quantify their impact on load-bearing capacity, angular rotation, and strain distribution. This methodology enables analysis of how clamp numbers and frame geometry influence elastic stiffness and deformation control in demountable steel assemblies. The study contributes to filling the existing gap by integrating physical testing and validated numerical modeling to support modular and reusable structural systems design, aligning with Design for Deconstruction (DfD) principles [23,24] and circular economy strategies [2,25,26]. Unlike previous studies focused on residential or low-load applications [27], this work targets reusable systems operating under moderate-to-high service demands, such as those found in industrial maintenance platforms, modular shelving, and temporary support structures.
2. Design and Operational Principles of Clamp-Based Connections for Structural Systems
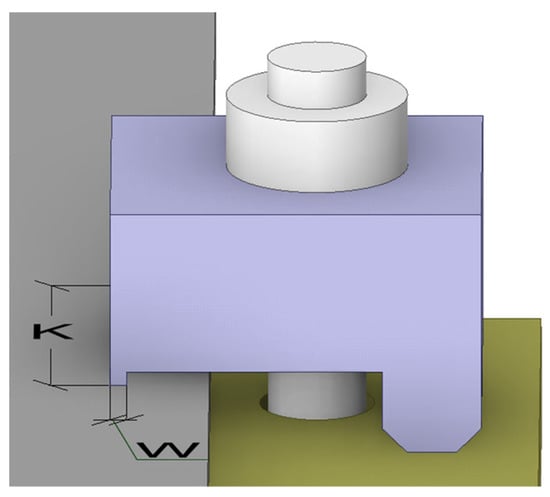
Clamp-based connections rely on a mechanical leverage principle to securely fasten structural components without invasive techniques such as welding or drilling. The operational mechanism begins with applying a preload force () to the clamp’s bolt. This preload generates tension in the bolt, which is redistributed through the lever system to produce the clamping force () that secures the connection (Figure 1). The clamping force is calculated using Equation (1):
where the following are defined:
- is the preload force applied to the bolt (N);
- is the arm lever length on the bolt side (mm);
- is the arm lever length on the clamping side (mm).
This equation describes how the preload force is redistributed through the clamp’s geometry, with the proportions of the lever arms ( and ) determining the final clamping force. The redistribution depends on the relative lengths of the lever arms, ensuring that the force is effectively applied to the contact surface without exceeding design tolerances. This formulation has been adopted in prior studies on clamp-based systems [3,14,28] and aligns with modeling approaches presented in [29].
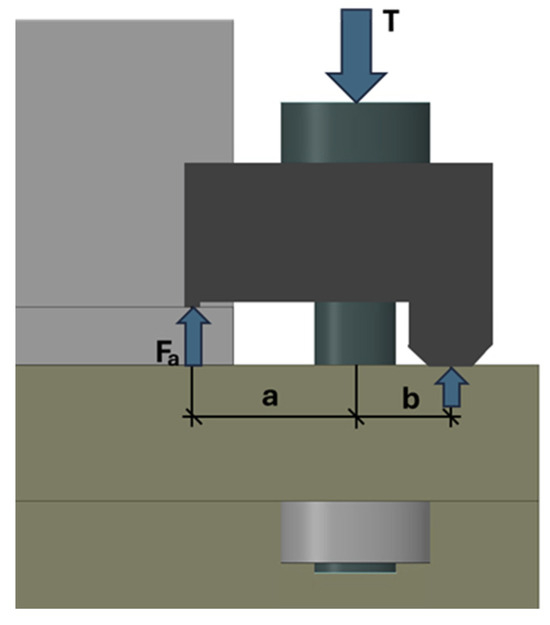
Figure 1.
Side view illustrating the clamp’s lever mechanism, where the applied force generates clamping pressure.
The preload force must be calculated to ensure the connection is reliable and avoids slippage. The required preload is determined by Equation (2).
where the following is defined:
- is the ultimate tensile strength of the bolt material (MPa);
- is the effective cross-sectional area of the bolt (mm2).
The calculated preload force (Equation (2)) also aligns with the principles of AISC 360-22 [30,31], ensuring sufficient clamping pressure for connection stability. While AISC 360-22 permits inelastic deformation under extreme conditions, this study emphasizes maintaining the integrity of components intended for reuse and operates strictly within the elastic range. The expression is consistent with the pre-tensioning method established in Eurocode 3 [29]. To account for tightening variability and installation tolerances, a factor of 1.1 was applied, as recommended by [32] and further supported by experimental studies [1,2,4,14].
Once the clamping force () is applied, the resulting pressure on the contact surface is distributed as in Equation (3):
where the following are defined:
This uniform distribution of pressure across the clamp contact surface reduces localized stress and minimizes the risk of material deformation or damage to coatings. The lever mechanism and precise clamp geometry ensure that the applied force is efficiently transmitted to the structural element. The mechanism redistributes preload during tightening to maintain stability and resistance against dynamic forces. This stress relationship reflects standard contact mechanics and is also compatible with bearing stress approaches discussed in [29] and recent applications in clamp-based structural analyses [1,2,3,14].
The equations governing clamp-based connections demonstrate their ability to redistribute forces efficiently and safely. These mechanisms make them reliable for applications that require adaptability, non-invasiveness, and structural integrity, unlike traditional methods such as welding or drilling. These systems achieve robust and efficient performance in a variety of structural applications.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Specimen Description and Configurations
This study investigates the behavior of a 90° beam-to-column connection using a clamp-based fastening system (Figure 3a). The connection at the top of the column is made using a 20 mm-thick L-shaped fixing plate (Figure 3b), while triangular frames are used at the bottom of the beam, where it interfaces with the column. These frames are critical for enhancing the assembly’s stability and load capacity.
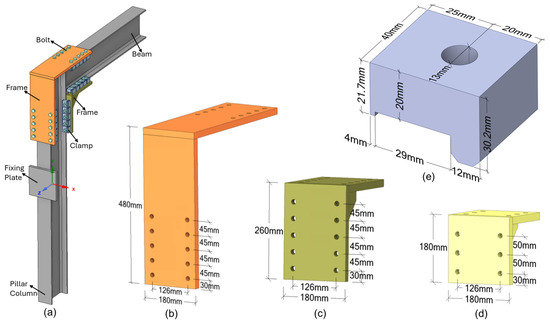
Figure 3.
Geometry and configuration of the beam-to-column connection: (a) an isometric view of the assembly shows the frames and clamp system; (b) detail of the L-shaped upper frame with its main dimensions (20 mm thickness); (c) detail of the triangular lower structure measuring 260 mm (20 mm thick); (d) detail the triangular lower structure measuring 180 mm (20 mm thick); (e) detail of clamp with its main dimensions.
Figure 3 provides a complete schematic of the beam-to-column connection, identifying the system’s primary components: the beam, column, L-shaped fixing plate, two symmetrical triangular frames, and clamps (Figure 3a). Figure 3b details the dimensions of the L-shaped plate, while Figure 3c,d presents the two triangular frame sizes, 260 mm and 180 mm, respectively. Figure 3e represents the dimensions of the clamp. This visualization supports understanding the structural arrangement and the interaction among the connection components. The fixing plates and triangular frames were assembled using standard workshop welding for S275 steel, ensuring sufficient rigidity for elastic service behavior.
Two main parameters were varied in the study: the size of the triangular frame and the number of clamps used in each configuration. The larger frame, measuring 260 mm (Figure 3c), contains five holes per side, allowing up to five clamps, whereas the smaller 180 mm frame (Figure 3d) accommodates three clamps per side, with two rows of three holes. In both frames, the outermost holes are positioned 30 mm from the edges to facilitate installation and ensure consistent bolt tightening.
The selected frame sizes reflect practical applicability in industrial maintenance, support and temporary structures, modular shelving systems, and reconfigurable industrial assemblies [33]. This choice ensured that the tested geometries represented real-world conditions while preserving experimental feasibility. The clamp arrangements were defined to capture varying levels of structural restraint, balancing mechanical efficiency with reusability and modular adaptation.
Figure 4 complements this view with side elevations of the assembled system. Figure 4a illustrates the beam-to-column connection using the 260 mm frame, while Figure 4b shows the configuration with the 180 mm frame. The column has a total height of 1600 mm, and the beam spans 1000 mm horizontally. Both components are based on the IPE200 steel profile, with a flange width of 200 mm and a web thickness of 8.5 mm.
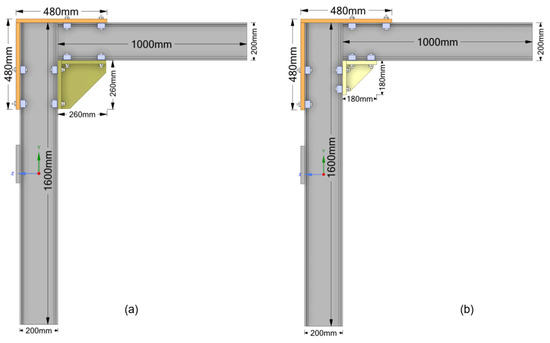
Figure 4.
Side views of the beam-to-column assembly: (a) framework with the 260 mm triangular frame; (b) framework with the 180 mm triangular frame, including key dimensions.
The IPE200 S275 profile was selected due to its standardized geometry and mechanical properties, ensuring consistent stiffness and load transfer in both beam and column. This uniformity allows the structural response to be governed primarily by the connection behavior rather than by variability in member sections, enhancing the accuracy of experimental and numerical comparisons. Furthermore, using the same profile for both elements facilitates component reusability and interchangeability, which is essential for modular structural systems and aligns with design-for-deconstruction principles.
The number of clamps was systematically varied for each frame size to assess the structural performance of the connections. For the 260 mm frame, configurations with four, three, and two clamps were tested (Figure 5). Due to geometric constraints, only three and two clamp configurations were feasible for the 180 mm frame (Figure 6). The clamps were symmetrically distributed in all setups to ensure balanced load transfer and consistent structural behavior. In the case of the 180 mm frame, the term “four-clamp configuration” used in subsequent sections refers to the total number of clamps in the connection, including both the L-shaped upper plate and the triangular frame itself. Specifically, four clamps were applied to the upper plate and three to the frame. This distinction is crucial to avoid misinterpretation and is consistent with the schematic presented in Figure 6a.
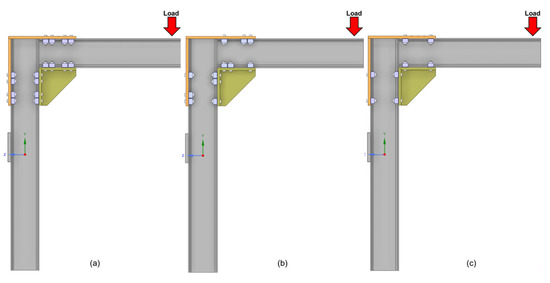
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the clamp configurations tested for the 260 mm triangular frame: (a) configuration with four symmetrically distributed clamps; (b) configuration with three clamps; (c) configuration with two clamps. The red arrow indicates the location where the vertical load was applied.
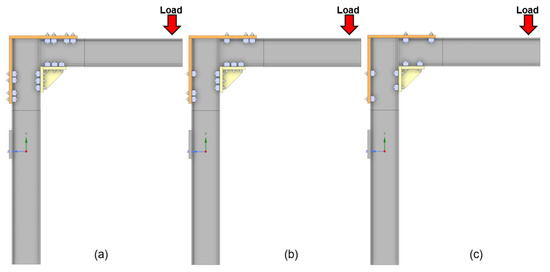
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the clamp configurations tested for the 180 mm triangular frame: (a) configuration with four clamps on the top and three on the 180 mm triangular frame; (b) configuration with three clamps on both the top and the frame; (c) configuration with two clamps on both the top and the frame.
This systematic variation in frame geometry and clamp distribution enabled a comprehensive analysis of their effects on load-bearing capacity and stress distribution.
Figure 5 illustrates the clamp configurations tested for the 260 mm triangular frame: four clamps (Figure 5a), three clamps (Figure 5b), and two clamps (Figure 5c). Similarly, Figure 6 depicts the clamp arrangements for the 180 mm frame, maintaining the same testing logic and layout across both frame types.
Clamp placement was strategically designed based on the expected load path and structural response. Under vertical loading, the connection undergoes a combination of tensile and compressive forces. As shown in Figure 7b, the rear upper clamps are primarily subjected to compression, while the front upper clamps experience traction. Conversely, the rear clamps on the lower side are under traction, and the front ones are under compression. This pattern reflects the anticipated rotational behavior of the assembly and supports structural efficiency.
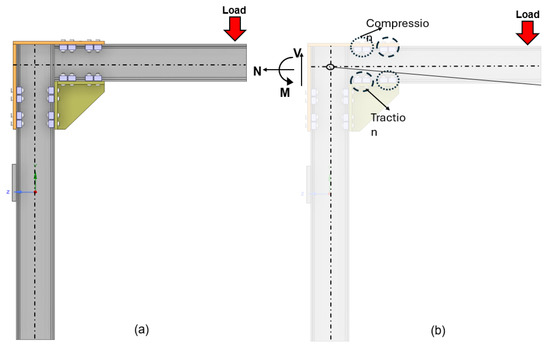
Figure 7.
Connection behavior under vertical load: (a) load application at the beam’s end; (b) rotational response showing traction and compression zones in the clamps.
Maintaining symmetric and standardized clamp distributions across all configurations ensured assembly consistency and reliable comparisons. This methodological consistency allowed for a precise evaluation of how frame size and clamp quantity influence the connection’s mechanical response, including stress distribution, load-bearing capacity, and overall structural integrity.
The fasteners used in the tests consisted of high-strength bolts in compliance with M12x70-class 8.8-zinc-coated [34,35], nuts HR-M12-class 8.8-zinc-coated [36], and washers M12-Class 300 HV-zinc-coated [37]. All fasteners were sourced from the same manufacturer to ensure uniform performance [37].
Application of Pre-Tension and Stepwise Loading
A uniform pre-tension of 42.916 N was applied to all configurations to ensure proper bolt fastening, replicating real mounting conditions. The procedure followed the continuous torque method [32]. The torque application was carried out using a manual torque wrench with ±4% precision [38] in two steps:
- First, an initial tightening was performed, applying 75% of the reference torque, resulting in 69.5 Nm;
- Second, a final tightening was applied at 110% of the reference torque, corresponding to a final torque of 102.0 Nm.
The adopted reference torque was 92.7 Nm. This procedure compensates for friction coefficient variations and ensures a final pre-load of approximately 43 kN. The applied torque was calculated according to Equation (4) [32]:
where the following are defined:
- = reference tightening torque (Nm);
- = nominal bolt diameter (m);
- = nominal minimum pre-load force (N);
- = torque coefficient.
According to EN 1090-2 [38], the torque coefficient is determined based on the friction class, following the EN 14399 series [36,37,39]. For friction class K2, applicable to hot-dip galvanized bolts, typically ranges between 0.16 and 0.22. This study adopted a value of 0.2 [5,32], as it falls within the recommended range for this type of application.
3.2. Experimental Program
3.2.1. Initial Assumptions
The experimental tests were conducted at the Structural Testing Laboratory of the Faculty of Industrial Engineering of the University of Vigo. The test program consisted of two experimental test campaigns on specimens, considering the 260 mm square and the 180 mm square, as shown in Figure 8. The first experimental test was conducted on the steel structure with the larger square (Figure 8c). In comparison, the second test was performed on the structure with the smaller square (Figure 8b).
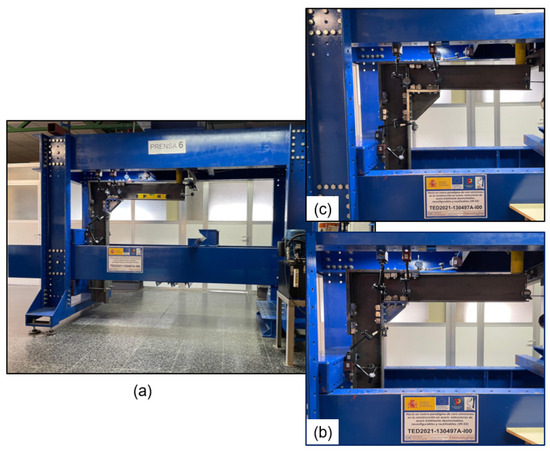
Figure 8.
Laboratory tests: (a) system assembly; (b,c) detail of the positioning of the digital indicators.
After each test, all bolts were replaced, and every new configuration was analyzed, ensuring uniform experimental conditions. Additionally, post-test inspections were conducted to verify whether any pre-tension loss had occurred in the bolted connections.
After the pre-tensioning process, a stepwise vertical load was applied to the beam, progressively increasing up to a maximum of 85% of the elastic bending moment resistance, depending on the tested configuration.
The IPE200 S275 profile used in this study has an elastic bending moment resistance of 53.440 kNm. The maximum applied load varied according to the tested configuration, limited to 85% of this value in the most critical condition. This ensured that the connection remained strictly within the elastic range, preventing plastic deformation and allowing the components to be reused.
The load was applied using a hydraulic press, ensuring a controlled and gradual application. This approach enabled a precise investigation of stress distribution and deformation without compromising the structural integrity of the connection.
After reaching the maximum load, the load was gradually removed, ensuring the measuring devices returned to zero. This procedure confirmed that the structural elements remained within the elastic range throughout the test, verifying the absence of permanent deformations and the feasibility of reusing the tested components.
3.2.2. Specimens Specification
The tested prototypes consisted of a column–beam assembly forming a 90° connection, based on the components and configurations described in Section 3.1.
The portal frame was secured to the hydraulic press via S275 steel plates welded to the rear end of the column. These plates had dimensions of 200 mm × 200 mm, a thickness of 20 mm, and four holes of 20 mm diameter at each end, spaced 150 mm in one direction and 130 mm in the other. The number of clamps used during prototype assembly corresponded to the specific configuration being tested (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
Prior to testing, the linearity and alignment of all assembled components were carefully verified to ensure material reusability and prevent initial deformation effects (Figure 4 and Figure 5). The inspection of profile dimensions, linearity, and alignment was conducted in accordance with the requirements of [32,40] standards.
3.2.3. Structural Monitoring
Throughout the testing process, structural responses were continuously monitored. Detailed displacement measurements were performed to evaluate the connection’s displacement behavior under load.
High-precision digital dial indicators (±0.01 mm) were used to monitor structural displacements. The displacement at the beam’s end was recorded using dial indicators positioned on both sides, ensuring that no torsional effects occurred, which could otherwise compromise the correlation between experimental results and the numerical model. The indicators M1, M3, and M4 shown in Figure 9 also have symmetrical counterparts on the rear side of the frame, further ensuring that no torsional distortion influenced the measurements.
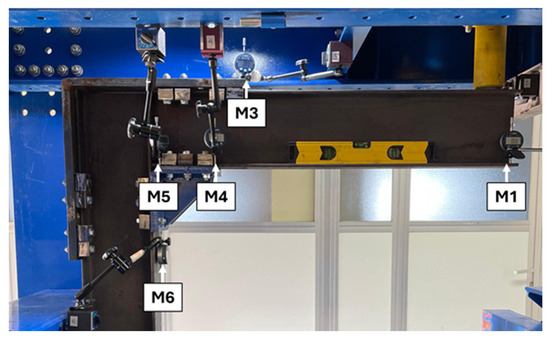
Figure 9.
Test setup and monitoring points.
Additionally, displacements in the frames, both at the beam and the column, were recorded to validate the accuracy of the numerical model. Figure 9 illustrates the monitoring layout and measurement points.
The hydraulic press used in the experiments was equipped with a digital force gauge, allowing the application of loads according to the conditions predicted by the FEM model. This ensured precise control over the applied loads throughout the testing process.
3.3. Numerical Modeling
The configurations of the experimentally tested structures were subjected to numerical modeling in ANSYS® (version 2024), ensuring the replication of specimen geometries with consistent material properties and characteristics. The three-dimensional models were developed in SolidWorks®, allowing the creation of a geometry that accurately represents the real structure.
The models were exported in. STEP format and subsequently imported into ANSYS®, where the simulations were performed using the Static Structural module. This process enabled a detailed analysis of structural behavior, providing insights into displacements, stresses, and forces under different geometric configurations.
To enhance the accuracy of the deformed structural representation, an incremental solution (based on time steps) was adopted, enabling the computation of intermediate results throughout the loading process. This approach accounted for material and geometric nonlinearities, which are crucial for realistically capturing the structural response under load.
3.3.1. Material Properties
The Bilinear Isotropic Hardening (BISO) [27,41] model was adopted in conjunction with the von Mises yield criterion [42], as implemented in ANSYS® software, to represent the mechanical behavior of the structural components. The BISO model is widely used in numerical simulations of metallic structures due to its simplicity and computational efficiency [41,43,44]. Although the present analysis is restricted to the elastic regime, defining a plastic model is essential to prevent unrealistic material behavior extrapolations and enable the software to recognize the onset of nonlinearity correctly.
The geometry was subdivided into regular volumes to generate a structured mesh, ensuring continuity between the contact surfaces. The materials implemented followed item 3.1 mentioned, and the steel implemented corresponded to S275. The material properties are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Material properties for bolted joints.
Standards such as Eurocode 3 [45] and Specification for Structural Steel Buildings (AISC) [46] recognize that the stiffness of structural elements does not remain constant throughout the applied load [47]. To capture the transition from the elastic to the plastic regime, it is necessary to reduce the initial elasticity modulus (E) using the tangent modulus (ET), which represents the decreased stiffness of the material after yielding [48].
According to AISC [46] for structural elements loaded in the inelastic regime, the tangent modulus (ET) is lower than the initial elasticity modulus (E) and decreases as plasticity develops [46]. The standard introduces the concept of the inelastic stiffness reduction factor (αa), defined as the ratio between ET and E, allowing adjustments in structural modeling to account for second-order effects [49].
Studies indicate that, for simulations using the BISO model, the tangent modulus typically varies between ET = 0.005·E and ET = 0.02·E, depending on the steel’s specific properties and the adopted hardening criterion [49]. This approach is widely applied in stability and progressive collapse analysis of steel structures [49].
In this study, S275 steel was used, with an adopted elasticity modulus of 210 GPa. To represent the elastoplastic behavior, a 0.007 factor was applied, resulting in a tangent modulus of ET = 0.007·E, equivalent to 1.45 × 10⁹ N/m2 (1.45 GPa) [41,47]. It ensures numerical stability and consistency with the physical properties of structural steel, as demonstrated in recent studies on structural resistance and progressive collapse analysis [48].
SOLID186 is a higher-order 3D 20-node element with quadratic displacement behavior, well-suited for modeling irregular geometries and complex nonlinear analyses. It supports large deformation effects, plasticity, creep, and stress stiffening, making it particularly effective for simulating structural components undergoing significant loading and contact interactions. The element formulation reduces integration without additional displacement shapes, enhancing numerical stability and computational efficiency. Given these capabilities, SOLID186 was employed in this study to ensure an accurate representation of the structural response, particularly in regions with stress concentrations and contact interactions [27].
3.3.2. Contact Interactions and Friction Coefficient
The modeling of contact interactions was carried out to ensure the correct transmission of forces between structural components and to maintain numerical stability in finite element simulations. Contact interactions were defined between pairs of surfaces subject to separation and sliding during loading, considering realistic boundary conditions [27,50,51,52].
The specified contact interactions include between the column flange and the beam head, between the bottom surface of the L-shaped plate and the flanges of the beam and column head, between the nut surface and frame, between the nut surface and the clamp surface; between the top surface of the beam and the L-shaped plate; between the bottom surface of the beam and the frame; and between the clamps and the flanges of the column and beam, as well as between the clamps and the gusset plates, ensuring that no unrealistic penetration occurs between rigid components. The contact between the bolt shank and the hole wall was modeled as frictionless, assuming free sliding [53,54].
This simplification is justified because load transfer occurs predominantly through friction between surfaces compressed by bolt pretension. Additionally, the clamp is not in direct contact with the bolt shank, as the clamping force is applied only to the bolt head and nut, considering the washers. Consequently, lateral constraints had a limited influence on the structural response [11,27,54].
CONTA174 and TARGE170 elements were used to model these interactions, representing surface-to-surface contact and ensuring compatibility between deformable bodies and rigid surfaces. The Augmented Lagrange method was employed as the contact algorithm, providing more excellent numerical stability and allowing iterative updates of contact stiffness at each iteration. This approach ensures the progressive redistribution of forces in the joint region, preventing convergence issues and instabilities in the numerical model [27,50].
The friction coefficient (μ) between steel surfaces was set to 0.20, as recommended for steel surfaces under similar conditions. This value was chosen to reflect the surface contact properties and optimize the accuracy of the simulation, ensuring consistency with experimental studies [5,11,53,54].
3.3.3. Bolt Pretension
The bolts were modeled following the nominal characteristics described in Section 3.2.2, ensuring consistency with the actual physical properties. The bolt head and nut were simplified as hexagonal shapes, omitting the thread representation on the shank, as shown in Figure 10. This simplification does not compromise the accuracy of the load transfer mechanism, as the primary function of the bolt in this application is to act as a clamping device that maintains the integrity of the connection [27].
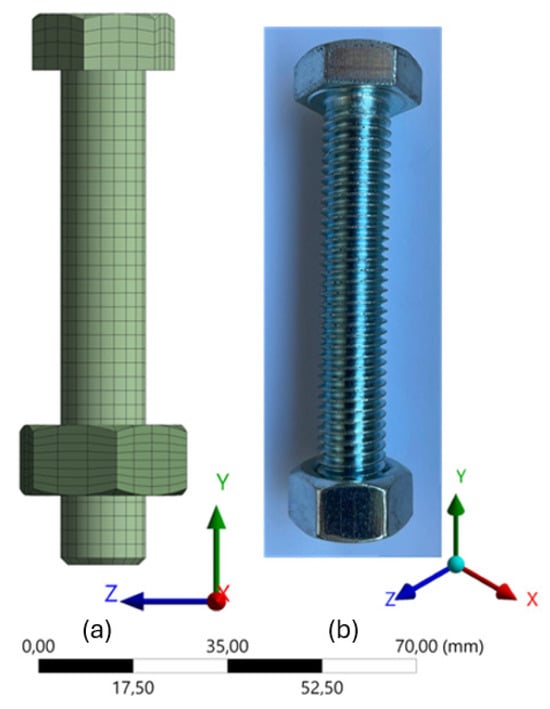
Figure 10.
M12 class 8.8 bolt, with simplified hexagonal geometry and no threading on the shank: (a) numerical model; (b) physical representation.
To accurately simulate the preloaded condition of the bolted joints, bolt pretension was applied using the PRETS179 element, which introduces a controlled axial force in the middle section of the bolt shank. This method ensures that the bolts remain in tension, providing a realistic representation of the clamping force and frictional resistance between the contact surfaces [21,27]. The preloaded force was defined according to design specifications and verified based on recommendations from numerical and experimental studies, ensuring a reliable representation of the bolted connection under operational conditions [55].
3.3.4. Mesh Generation
A mesh refinement strategy was adopted to balance computational efficiency and result accuracy, prioritizing denser elements in critical regions while using coarser elements in areas with lower structural influence. The mesh density for each model part was determined separately based on a mesh sensitivity analysis. This study was conducted by progressively reducing the element size until the differences between the finite element (FE) model results and experimental data were minimized. This approach ensured that the mesh was not excessively refined, which would significantly increase computational time, nor too coarse, which could compromise result accuracy [56,57].
Figure 11 illustrates that different mesh densities were applied according to structural importance. A finer mesh was employed in the connection region, where stress concentration and deformation behavior were of greater interest. The mesh density varied between fine (2 × 2 mm2), medium (5 × 5 mm2), and coarse (10 × 10 mm2 to 20 × 20 mm2), ensuring appropriate resolution in areas where precision was essential. Conversely, coarser elements were applied to regions farther from the connection, optimizing computational cost without compromising result accuracy [50,58]. All the elements used in the modeling were second-order, allowing for greater displacement interpolation accuracy and improved solution convergence.
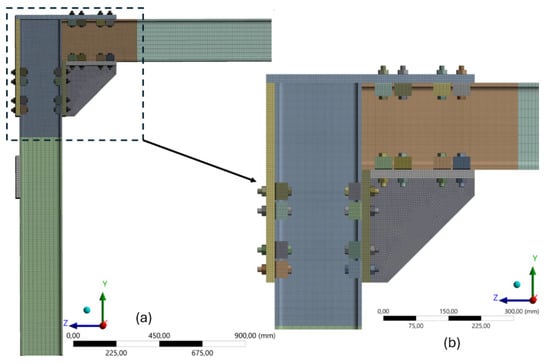
Figure 11.
Mesh representation applied to the structural model: (a) overview of the structural assembly, highlighting the variation in mesh density between critical and less relevant areas; (b) enlarged detail of the connection region, showing the refined mesh.
The mesh was generated using the multizone method, improving discretization quality by reducing element geometric distortion. This method combines mapping techniques with automatic geometry subdivision, ensuring an efficient mesh for complex structural analyses [21,27]. The multizone technique is particularly advantageous for models involving multiple contact interfaces, as it allows the generation of structured hexahedral dominant meshes while preserving geometric fidelity and minimizing numerical artifacts across surfaces under contact conditions [30]. Additionally, the Inflation method was explicitly applied to nuts and bolts, particularly at the bolt head, as the hexagonal model was adopted to represent the actual fastening geometry. This approach enabled mesh refinement in contact regions, ensuring a smooth transition and accurately capturing stress gradients on these surfaces [27,54].
The bolts used in the model corresponded to M12 class 8.8, following normative specifications. The bolt head and nut were modeled in their original hexagonal shape, without the inclusion of threading on the bolt shank, as illustrated in Figure 12. This simplification was adopted to optimize processing time without compromising the structural behavior representation of the bolted connections [58].
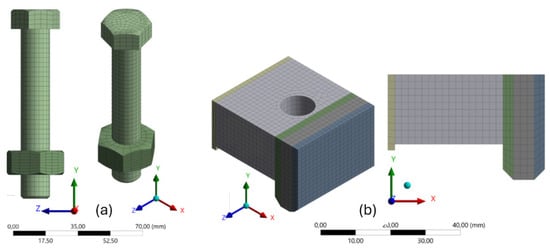
Figure 12.
Mesh representation of the structural components: (a) M12 bolt with hexagonal head and nut modeled without threading on the shank; (b) clamp with refined mesh in the contact areas, ensuring high precision in critical regions of the structural analysis.
Although finer mesh elements increase processing time, the estimated time for executing each analyzed model ranged between 4 and 6 h, depending on the complexity of the model being calculated. The finite element models (FEM) were implemented on a high-performance server, utilizing 62 processing cores, ensuring computational efficiency and greater capacity for detailed simulations [56]. The server configuration consisted of 2 AMD EPYC 7513 Processors at 2.6 GHz, a Dual MZ92-FS0 Board, 32 memory banks, 512 GB of DDR4/3200 MHz ECC Reg. memory, 1 × 2 TB SSD, 1 × 16 TB Seagate Hard Drive (ST16000NM), and a 2U Rack R282-Z93 with a redundant power supply.
This meshing strategy ensured that the numerical model achieved a high level of accuracy while maintaining computational feasibility, allowing for reliable structural simulations within a reasonable processing time [21,57].
3.4. Validation Procedure
The numerical models were validated by comparing the simulated and experimental load–displacement curves and final load-bearing capacities. The finite element model (FEM) was developed to reproduce the material properties, boundary conditions, and loading parameters observed in the physical tests, allowing consistent assessment across all configurations.
This section presents the adopted procedure for evaluating the agreement between experimental and numerical responses, particularly focusing on the displacement trends and global structural behavior under elastic loading. The comparative results, including the respective curves and observations, are analyzed in Section 4, where each configuration is discussed in detail based on its performance.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Results and Comparison
4.1.1. Comparison Between FEM and Experimental Data for the 260 mm Frame
Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15 illustrate the relationship between simulated and experimental displacements as a function of the applied force for the respective models. The Finite Element Model Curve (FEMC) and the Experimental Curve (EXPC) are presented to compare numerical and test data. The curves represent vertical displacements recorded by various gauges (C1 to C8). The FEMC curves (dashed lines) and EXPC curves (solid lines) are nearly superimposed, indicating a strong correlation between the simulation and experimental results.
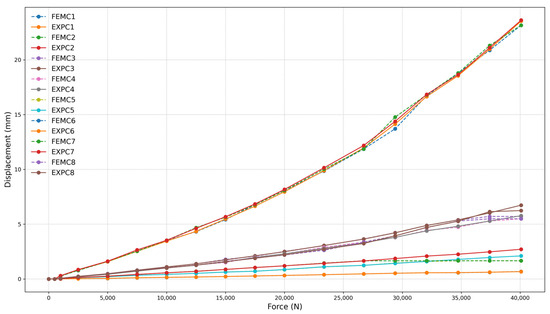
Figure 13.
Force (N) vs. displacement (mm) for frame 260 mm with four-clamp configuration.
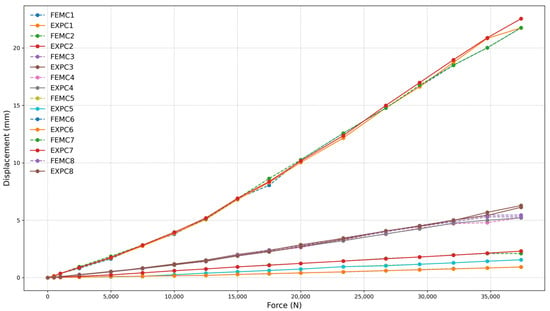
Figure 14.
Force (N) vs. displacement (mm) for frame 260 mm with three-clamp configuration.
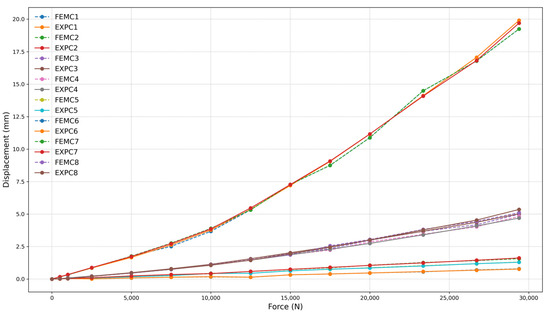
Figure 15.
Force (N) vs. displacement (mm) for frame 260 mm with two-clamp configuration.
The numerical and experimental results exhibit a high correlation, exceeding 97% for all models with a 260 mm frame, demonstrating strong agreement between FEM and experimental data. The high correlation was confirmed through statistical analysis. The coefficient of determination (R2) values ranged from 0.9989 to 0.9995, and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) values varied between 0.2507 mm and 0.3823 mm across the different test configurations. These results validate the strong agreement observed between finite element simulations and experimental measurements under service-level loading conditions. This correlation is evident in the near superimposition of FEMC (dashed lines) and EXPC (solid lines) curves, as shown in Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15. Minor deviations observed at higher force levels are within the expected range for this type of structural analysis and do not affect the overall correlation between FEM and experimental data. These variations can be attributed to inherent material properties and assembly tolerances, which are consistent with typical manufacturing and testing conditions.
Pre-tension forces were controlled using a torque-based method to ensure uniform initial conditions, and post-test verification confirmed no loss of pre-tensioning, ensuring stable clamping force throughout loading. These factors reinforce the FEM model’s reliability in accurately capturing load distribution and structural stiffness within the tested range.
Beyond the strong correlation between FEM and experimental results, the findings also highlight the practical advantages of clamp-based connections. These systems streamline assembly, reduce labor time, and minimize installation errors by eliminating the need for permanent modifications. The use of standardized profiles for columns and beams further simplifies structural reconfiguration, making them particularly suitable for industrial environments requiring frequent adjustments. Additionally, this standardization allows for a clearer understanding of connection behavior, facilitating more accurate analysis and predictive modeling. Unlike bolted or welded joints, clamp-based connections preserve component integrity, extending service life and enhancing long-term sustainability. These characteristics reinforce the versatility and efficiency of the system while aligning with circular economy principles [59,60].
Influence of Clamps and Load Capacity
The relationship between the number of clamps and the set’s load capacity was analyzed based on the three configurations tested, corresponding to the size of the frame applied to the set. The maximum applied loads for each configuration were 40.08 kN for four clamps (Figure 13), 37.41 kN for three clamps (Figure 14), and 29.39 kN for two clamps (Figure 15), respectively. The reduction in load capacity due to the decrease in the number of clamps follows a nonlinear trend.
Reducing the number of clamps from four to three resulted in a 6.67% decrease in load capacity, while reducing the number of clamps from three to two led to a 21.43% decrease. Removing half of the clamps resulted in a cumulative 26.67% decrease in the system’s load capacity. This behavior suggests that the load capacity mechanism is directly influenced by the number of clamps, indicating an internal redistribution of stresses as the clamping becomes less efficient.
The findings indicate that reducing the number of clamps initially has a moderate impact on load capacity, but larger reductions lead to a much greater loss. The transition from four to three clamps resulted in a moderate reduction in load capacity, whereas the reduction from three to two clamps significantly affected the system’s structural performance. Optimizing the number and placement of clamps is essential to ensure structural integrity under different loading conditions.
The nonlinear loss of load capacity observed with a reduced number of clamps is primarily due to the concentration of stresses in fewer contact regions, which diminishes the connection’s ability to redistribute internal forces effectively. This leads to lower global stiffness and increased localized deformations, as demonstrated by both experimental and FEM results. Such behavior is consistent with the principles outlined in Eurocode 3 [29] and confirmed in recent studies by Cavalheiro et al. [4,14] and Cabaleiro et al. [2], which demonstrate that reducing the number of fastening points in steel joints increases stress concentration and compromises structural performance. Therefore, the connection’s ability to maintain elastic behavior and resist service loads depends heavily on optimizing the number and distribution of clamps.
Stress Distributions and the Influence of the Number of Clamps
The stress distribution (Von Mises) for the different arrangements shows that the regions of highest stress occur near the connections (clamps) in the beam and along the column’s web, corresponding to the compression of the frame. The configuration with four clamps (Figure 16) exhibits higher stress concentrations in the column’s web and at specific points on the beam, particularly in compression zones (Figure 7b), which are visually represented by red-colored regions. This stress distribution aligns with the greater load capacity of this configuration, as the force-displacement graphs (Figure 13) indicate that the four-clamp setup demonstrated the highest mechanical resistance.
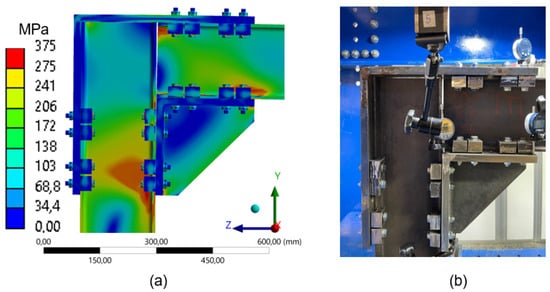
Figure 16.
Comparison between numerical simulation and experimental test (4 clamps) frame 260 mm: (a) stress distribution through Finite Element Analysis (FEA); (b) experimental setup with instrumentation for displacement measurement.
As the number of clamps is reduced to three (Figure 17) and two (Figure 18), stress concentration becomes more localized while still following the expected pattern of compressed zones (Figure 7b). This effect is particularly evident in the upper region of the beam, near the clamps fixed to the L-shaped plate (compressed zone), and in the lower part of the beam, specifically in the web and flange, close to the compressed clamps. This redistribution implies an increase in the overall flexibility of the structure and a shift in load distribution to more confined areas.
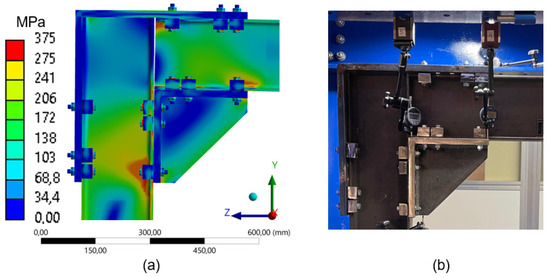
Figure 17.
Comparison between numerical simulation and experimental test (3 clamps) frame 260 mm: (a) stress distribution through Finite Element Analysis (FEA); (b) experimental setup with instrumentation for displacement measurement.
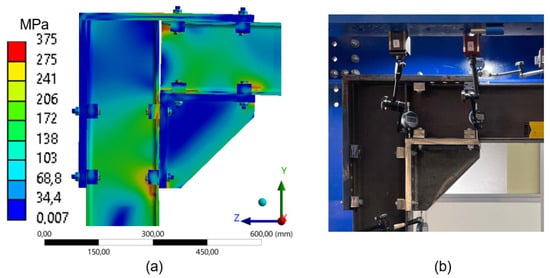
Figure 18.
Comparison between numerical simulation and experimental test (2 clamps) frame 260 mm: (a) stress distribution through Finite Element Analysis (FEA); (b) experimental setup with instrumentation for displacement measurement.
As previously noted, the stresses are more uniformly distributed in the configuration with two clamps, resulting in only a few critical points. This leads to increased displacements for the same applied load, as demonstrated in the experiment (Figure 19), which underscores the decrease in stiffness. In contrast to the transition from four to three clamps, where the variation in stiffness was relatively minor (approximately 6%), the removal of the third clamp significantly affected stress dissipation, making the system more susceptible to deformations by approximately 21%.
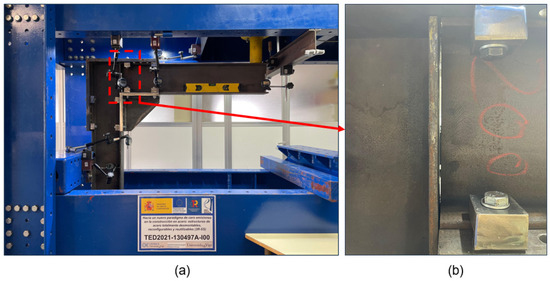
Figure 19.
Experimental setup for the test of the 2-clamp model (260 mm): (a) overview of the test; (b) detail of the displacement.
Analysis of Plastic Strain Distribution
The evaluation of the plastic equivalent strain confirms that, regardless of the number of clamps, the structure remained within the elastic regime, exhibiting no significant plasticization. For the four-clamp model (Figure 20), a slight localized plasticization is observed near the compressed zones, indicating that this region absorbs a considerable portion of the applied loads, consistent with the illustrated images (Section Stress Distributions and the Influence of the Number of Clamps). However, the structure remains within the elastic regime.
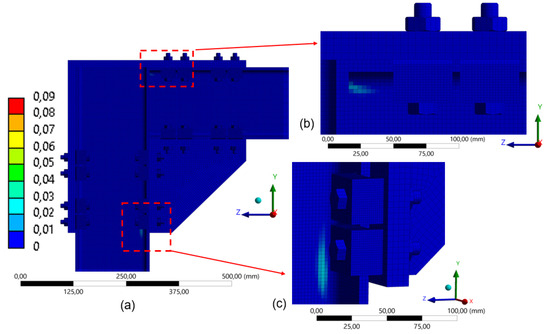
Figure 20.
Distribution of equivalent plastic strain in the model with 4 clamps (260 mm): (a) global distribution of plastic strain in FEA; (b) detail of the upper connection region; (c) detail of the lower connection region.
Plasticization is minimal for the three-clamp configuration (Figure 21), suggesting that the structure accommodates stresses through load redistribution. Finally, in the two-clamp configuration (Figure 22), the lowest level of plastic activation is observed among all configurations, indicating a more flexible structural behavior. The absence of significant plasticization in the simulations reinforces that the applied loads in the experimental analyses remained within the structure’s elastic range, validating the adopted approach and confirming that the tests did not compromise the material’s integrity.
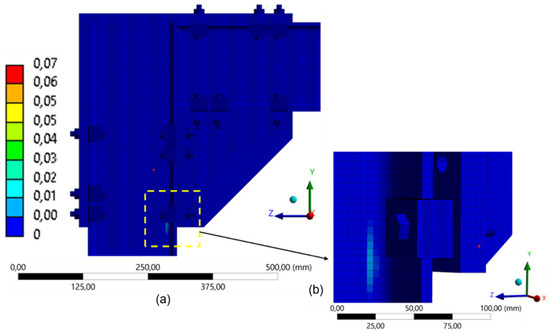
Figure 21.
Distribution of equivalent plastic strain in the model with 3 clamps (260 mm): (a) global distribution of plastic strain in FEA; (b) detail of the lower connection region.
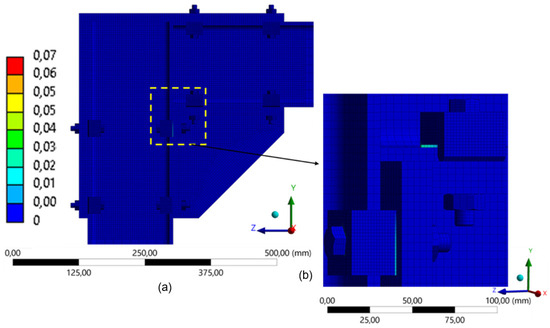
Figure 22.
Distribution of equivalent plastic strain in the model with 2 clamps (260 mm): (a) global distribution of plastic strain in FEA; (b) detail of the lower connection region.
Frame Analysis Under the Same Applied Load
To complement the structural performance assessment, three distinct frame configurations were compared, all subjected to the same vertical load of 29,392 N. The same Von Mises stress scale (0–375 MPa) was adopted across the numerical models, enabling a direct comparison of structural efficiency and stress redistribution among the configurations.
The four-clamp configuration (Figure 23a) exhibited the most efficient performance, with stresses predominantly ranging from 34.4 MPa to 138 MPa, mainly concentrated near the upper clamps and at the contact interface with the L-shaped plate. Blue and green tones dominate the stress map, indicating efficient force redistribution and low concentrations of critical stress zones.
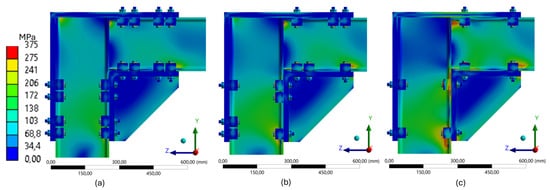
Figure 23.
Von Mises stress fields for the 260 mm frame under a constant load of 29,392 N, shown for configurations with (a) 4, (b) 3, and (c) 2 clamps.
In the three-clamp configuration (Figure 23b), localized stress is increased, with some regions reaching values between 172 MPa and 241 MPa, particularly at the beam interface. The removal of one clamp reduces stiffness, concentrating stresses in more confined areas and increasing the risk of local deformations.
The two-clamp configuration (Figure 23c) presents the most critical structural condition. Orange and red regions indicate stress levels close to the upper limit of the adopted scale. These concentrations occur primarily in the lower region of the beam and around the upper clamps, reflecting a reduced capacity for stress redistribution.
Even under a constant load, the structural response varies significantly depending on the geometry and number of fastening points. There is a progressive reduction in structural efficiency from the most rigid configuration (four clamps) to the least rigid (two clamps). This reinforces the importance of optimizing the number and layout of clamps according to the desired stiffness and applied load, aiming to enhance the efficiency and safety of reusable systems operating within the elastic range.
4.1.2. Comparison Between FEM and Experimental Data for the 180 mm Frame
Figure 24, Figure 25 and Figure 26 present the relationship between simulated (FEMC) and experimental (EXPC) displacements as a function of the applied force for the 180 mm frame. Similar to the larger frame, the FEMC curves (dashed lines) and EXPC curves (solid lines) exhibit a high correlation, exceeding 97% for all tested configurations. The strong agreement between numerical and experimental results reinforces the reliability of the computational model in predicting mechanical behavior. This high correlation was quantitatively confirmed through statistical analysis. The coefficient of determination (R2) values ranged from 0.9986 to 0.9996, and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) values varied between 0.1561 mm and 0.3322 mm across the different test configurations. These results validate the strong alignment observed between finite element simulations and experimental measurements under service-level loading conditions.
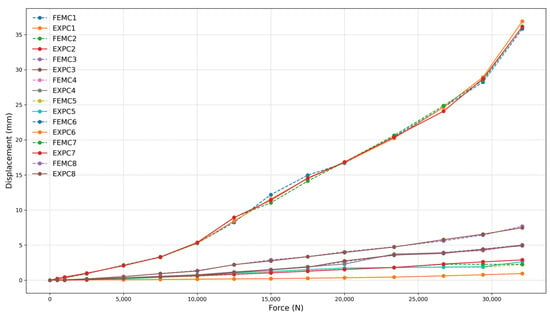
Figure 24.
Force (N) vs. displacement (mm) for frame 180 mm with four-clamp configuration.
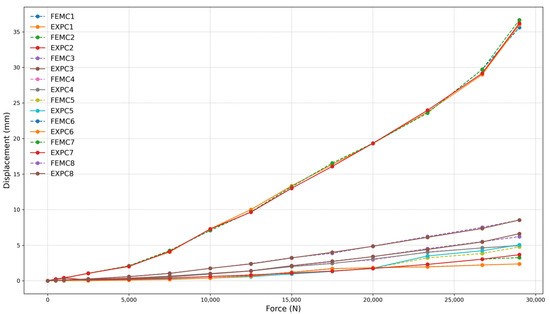
Figure 25.
Force (N) vs. displacement (mm) for frame 180 mm with three-clamp configuration.
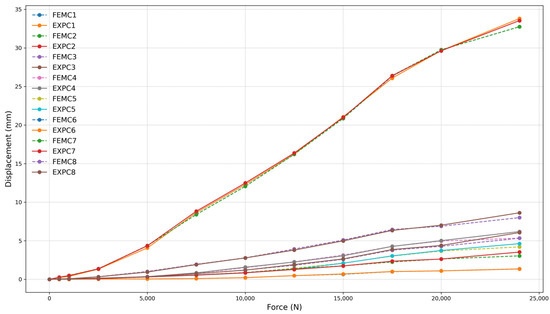
Figure 26.
Force (N) vs. displacement (mm) for frame 180 mm with two-clamp configuration.
As observed in the 260 mm frame, minor deviations occur at higher force levels, particularly beyond 80% of the total load capacity. These variations remain within an expected range and are more noticeable in configurations with fewer clamps, such as the two-clamp setup. The increase in displacement in these cases suggests a reduction in overall system stiffness, which is expected as the number of clamping points decreases.
Despite these small deviations, the overall behavior of the 180 mm frame closely follows the trend observed in the larger frame. This consistency further validates the FEM model’s accuracy across different frame sizes and configurations, demonstrating its robustness in capturing the structural response under varying loading conditions.
Influence of Clamps and Load Capacity
The analysis of the load-bearing capacity of the second set, with a 180 mm frame, also indicated a nonlinear relationship between the number of clamps and structural performance. The maximum applied loads recorded were 32.06 kN for four clamps (Figure 24), 29.39 kN for three clamps (Figure 25), and 24.00 kN for two clamps (Figure 26). Reducing the number of clamps from four to three resulted in an 8.33% decrease in load capacity, while the transition from three to two led to an 18.35% reduction. Overall, the removal of half of the clamps resulted in a cumulative 25.15% decrease in system load capacity.
These findings exhibit a similar trend to the previously tested configuration with a 260 mm frame, suggesting that initial reductions in the number of clamps cause moderate proportional decreases, whereas further reductions lead to more pronounced losses in load-bearing capacity. The decrease in the number of clamps directly affects load capacity and induces an internal stress redistribution due to the modified fastening system, influencing overall structural behavior. Therefore, an exact delineation of both the quantity and strategic placement of clamps is essential for achieving optimal structural efficiency under loading scenarios.
Stress Distributions and the Influence of the Number of Clamps
The Von Mises stress distribution for the different configurations using the 180 mm frame shows that the regions of the highest concentration occur near the connections (clamps) on the beam and along the web of the column, corresponding to the compressed zones of the structure. The configuration with four clamps (Figure 27) presents higher stress concentrations at specific points on the beam, particularly in the compressed regions (Figure 7b), located in the web and flange of the beam, as well as in the column, also in the web and flange. Red-colored regions visually represent these critical areas. This stress distribution is consistent with the higher load-bearing capacity observed for this configuration, as indicated by the force-displacement graphs (Figure 24), which show that the four-clamp setup also achieved the most significant mechanical resistance in this set.
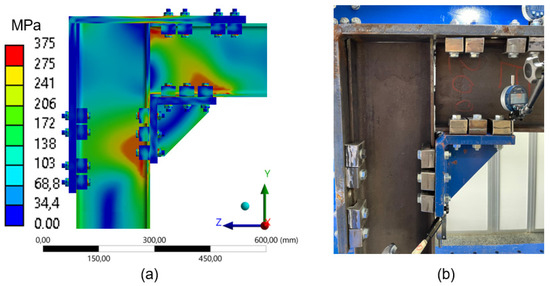
Figure 27.
Comparison between numerical simulation and experimental test (4 clamps) frame 180mm: (a) stress distribution through Finite Element Analysis (FEA); (b) experimental setup with instrumentation for displacement measurement.
As the number of clamps is reduced to three (Figure 28), the stress concentration becomes more localized, although it still follows the expected pattern within the compressed zones (Figure 7b). This effect is particularly evident in the upper region of the beam, near the clamps attached to the L-shaped plate (compressed zone), and in the lower part of the beam, especially in the web and flange, close to the clamps under compression. This redistribution implies an increase in the overall flexibility of the structure and a concentration of loads in more confined areas.
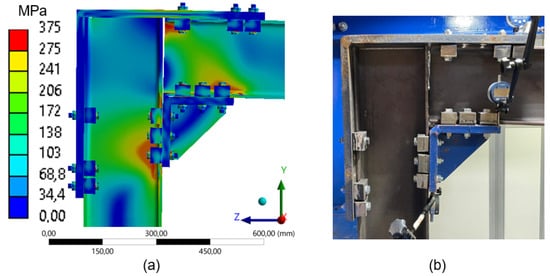
Figure 28.
Comparison between numerical simulation and experimental test (3 clamps) frame 180mm: (a) stress distribution through Finite Element Analysis (FEA); (b) experimental setup with instrumentation for displacement measurement.
When further reducing the number of clamps to a two-clamp configuration (Figure 29), the structural behavior remains consistent with previous cases but shows a seemingly more efficient stress distribution. However, this efficiency is associated with a reduction in the set’s ability to support loading within the elastic range considered in this study.
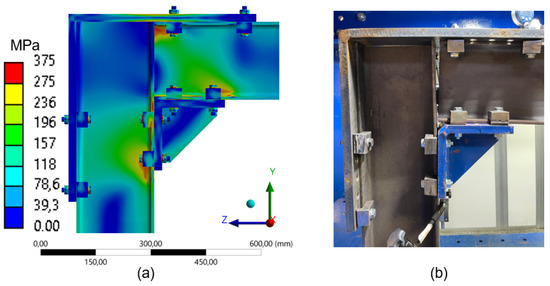
Figure 29.
Comparison between numerical simulation and experimental test (2 clamps) frame 180mm: (a) stress distribution through Finite Element Analysis (FEA); (b) experimental setup with instrumentation for displacement measurement.
Comparing the analyzed configurations, it is observed that in the two-clamp arrangement, stress is distributed more homogeneously, predominantly in regions represented by green and blue colorations, resulting in fewer critical points. Even so, this arrangement leads to more significant displacements under the same applied load, as experimentally verified (Figure 26), highlighting a decrease in stiffness. In contrast to the transition from four to three clamps, where the variation in stiffness was moderate (approximately 9%), the removal of the third clamp more significantly affected stress dissipation, making the system approximately 19% more susceptible to deformation.
Analysis of Plastic Strain Distribution
The analysis of equivalent plastic strain shows that, for all evaluated configurations, the structure operated within the elastic range defined in this study, with no significant plasticization observed. In the model with four clamps (Figure 30), slight localized plastic strains appear in the compressed regions, indicating a concentration of applied loads in these areas, behavior consistent with the patterns illustrated in Section Stress Distributions and the Influence of the Number of Clamps. Nevertheless, the system remained within the elastic domain.
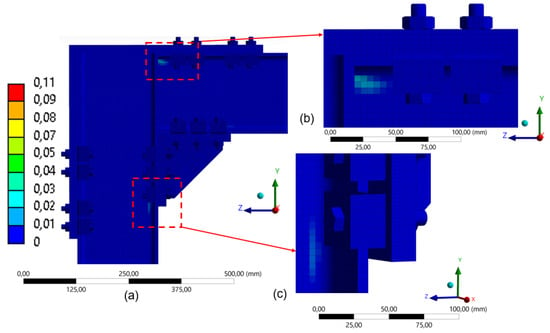
Figure 30.
Distribution of equivalent plastic strain in the model with 4 clamps (180 mm): (a) global distribution of plastic strain in FEA; (b) detail of the upper connection region; (c) detail of the lower connection region.
Moreover, the connection behavior exhibited similar patterns across the different frame sizes tested. The four-clamp configuration displayed a response comparable to the three-clamp arrangement, concentrating stress absorption in the compression zones.
Plastic strain was minimal in the three-clamp configuration (Figure 31), suggesting that the structure effectively redistributed internal forces. Finally, in the two-clamp configuration (Figure 30), the lowest level of plastic activation was observed among all setups, indicating a more flexible structural response (Figure 32). This corroborates the behavior observed in the 260 mm frame for the corresponding arrangement.
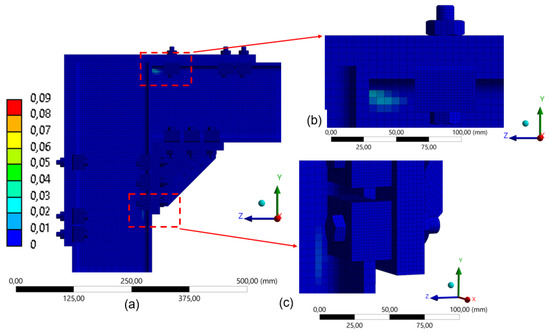
Figure 31.
Distribution of equivalent plastic strain in the model with 3 clamps (180 mm): (a) global distribution of plastic strain in FEA; (b) detail of the upper connection region; (c) detail of the lower connection region.
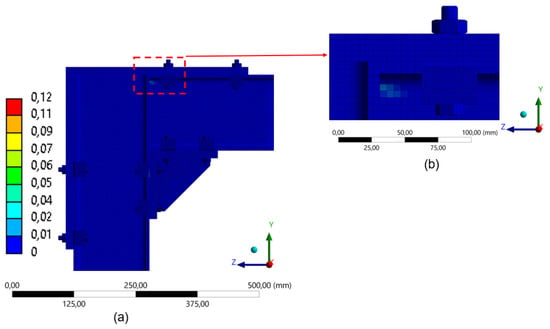
Figure 32.
Distribution of equivalent plastic strain in the model with 2 clamps (180 mm): (a) global distribution of plastic strain in FEA; (b) detail of the upper connection region.
The absence of significant plasticization in the numerical models confirms that the applied loads in the experimental procedures remained within the elastic limit, validating the adopted methodology and ensuring the preservation of material integrity.
Analysis of the 180 mm Frame Under the Same Applied Load
To further evaluate the structural behavior of the 180 mm frame, three different configurations were analyzed, each subjected to the same vertical load of 20,000 N. The application of a constant load enabled a direct comparison between models based on the results of finite element numerical simulations. A uniform Von Mises stress scale (0–375 MPa) was adopted across all models, allowing for a consistent visual comparison of the results.
The configuration with four clamps (Figure 33a) exhibited the most uniform structural behavior. Blue and light green regions predominated, indicating moderate stress levels distributed evenly across the structure, with only small, localized areas near the upper clamps reaching higher levels (172–241 MPa). The absence of continuous critical zones suggests good stiffness and effective stress redistribution, with low concentrations and preserved structural integrity within the elastic range.
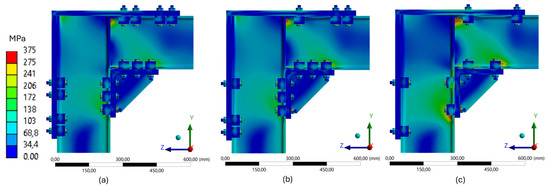
Figure 33.
Von Mises stress fields for the 180 mm frame under a constant load of 20,000 N, shown for configurations with (a) 4, (b) 3, and (c) 2 clamps.
The configuration with three clamps (Figure 33b) showed a comparable stress pattern, with most of the structure maintaining moderate stress levels. However, localized critical zones emerged in the lower and upper regions of the beam, highlighted by yellow and reddish tones (>241 MPa). This shift in the stress pattern indicates a slight loss in the uniformity of stress distribution, which may influence the structural response under varying load intensities.
The configuration with two clamps (Figure 33c) presented the most critical scenario. Large areas along the web of the beam, as well as regions around the upper and lower clamps, displayed yellow-orange and red tones, indicating elevated stress levels. The distribution became visibly less uniform, with stress concentrations in specific regions under tension and compression. This behavior reflects a reduced capacity for stress redistribution and a greater tendency toward localized deformations, although the structure remained within the elastic regime.
The comparison between the three configurations reveals a gradual reduction in the ability to control internal stress as the number of clamps decreases. The configuration with four fixation points demonstrated greater uniformity in stress distribution, minimizing critical regions. In contrast, configurations with fewer clamps showed reduced structural stiffness, higher stress concentrations, and less efficient redistribution of internal forces. These results highlight the importance of properly dimensioning both the number and placement of fixation elements, particularly in compact structural systems designed for modularity, disassembly, and reuse.
4.2. Comparative Structural Assessment and Design Implications of Clamp-Based Connections
The graph presented (Figure 34) illustrates the relationship between the number of clamps and the mechanical efficiency of the connection, based on normalized performance indicators—displacement per unit load and angular rotation per unit load (Ø/N)—for both 180 mm and 260 mm frame geometries.
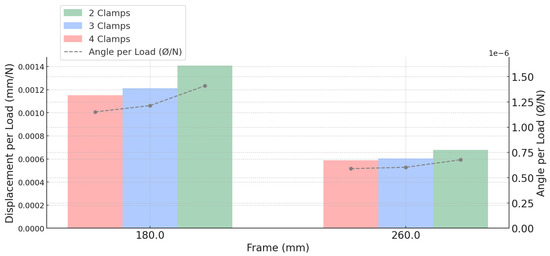
Figure 34.
Normalized displacement and rotation per load for 180 mm and 260 mm frames with 2, 3, and 4 clamps.
The clamp setup with four fastening points exhibited the lowest displacement and angular rotation per applied force for both frame configurations, confirming the greatest structural stiffness. A moderate increase in both parameters was observed when the system was reduced to three clamps, followed by a more substantial rise when it was reduced to only two clamps. This progression reflects the direct impact of clamp quantity on stiffness, especially between the three- and two-clamp setups, where the loss in rigidity becomes notably nonlinear.
In the 260 mm frame, lower displacement and rotational values were recorded across all clamp configurations compared to the 180 mm frame, reinforcing its superior stiffness and load-distribution capability. These findings demonstrate that the 260 mm geometry is better suited for high-demand applications requiring minimal deformation, while the 180 mm configuration remains advantageous in lightweight or space-restricted contexts, provided a sufficient number of clamps is used.
The consistent reduction in both displacement and angular rotation across configurations aligns with experimental and numerical analyses, all of which confirmed that the system remained entirely within the elastic regime, with no evidence of plastic deformation.
This behavior reflects the Design for Deconstruction (DfD) principles, showcasing the versatility of clamp-based connections for applications requiring repeated assembly, disassembly, or structural reconfiguration. By adjusting the number of clamps, designers can modulate connection stiffness and performance without compromising the integrity of the elements [1,4,61].
5. Conclusions
This study examined the elastic performance of clamp-based beam-to-column connections through experimental testing and finite element modeling (FEM), with a focus on reusability and sustainable structural design. Two frame geometries (180 mm and 260 mm) and various clamp configurations were evaluated under elastic conditions. The main conclusions are as follows:
- Elastic Response: All configurations remained within the elastic range throughout both experimental and numerical analyses, confirming their applicability in dismountable structural systems;
- Clamp Quantity and Performance: Increasing the number of clamps enhanced stiffness and load capacity, with up to 27.3% gain when moving from two to three clamps, particularly in the 260 mm frame;
- Numerical Validation: FEM simulations showed over 97% correlation with experimental results, supporting their use for future design and parametric studies;
- Frame Geometry Comparison: The 260 mm frame provided superior stiffness and capacity, while the 180 mm frame offered advantages in weight, assembly, and space efficiency;
- Stress and Deformation: Higher stress concentrations were observed in configurations with fewer clamps, yet all systems remained within the elastic range, ensuring safety and performance;
- Sustainability Aspects: The removable clamp design aligns with Design for Deconstruction (DfD), promoting ease of reuse, reduced waste, and extended structural lifecycle;
- Design Guidance: For practical use, clamp-based systems should consider clamp number, preload level, and frame geometry based on loading demands and spatial constraints.
Overall, clamp-based connections present a reliable, reusable, and sustainable alternative to conventional joints, offering structural efficiency and adaptability for modern modular and temporary applications.
6. Future Work
This study experimentally and numerically validated the elastic behavior of clamp-based beam-to-column connections, confirming their structural adequacy for modular and reusable steel systems. The configurations tested demonstrated consistent performance under service-level loads, and the substantial agreement between experimental measurements and finite element simulations reinforces the reliability of the adopted modeling strategy.
Future investigations will broaden the understanding of clamp-based systems by incorporating complementary measurement techniques, such as stress and deformation tracking, and exploring their response under dynamic or repeated loading conditions. These developments will support the continued evolution of this connection strategy toward more complex structural scenarios, while maintaining alignment with principles of modular construction, deconstruction, and circular economy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.N.C., M.C., B.C. and Y.C.; methodology, F.N.C., M.C. and B.C.; software, F.N.C.; validation, F.N.C., M.C. and B.C.; formal analysis, F.N.C., M.C., B.C. and Y.C.; investigation, F.N.C. and M.C.; resources, M.C. and B.C.; data curation, F.N.C. and Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, F.N.C.; writing—review and editing, F.N.C., M.C., B.C. and Y.C.; visualization, F.N.C., M.C., B.C. and Y.C.; supervision, M.C. and B.C.; project administration, M.C. and B.C.; funding acquisition, M.C. and B.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by TED2021–130497A-I00, MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033, and by the European Union ‘NextGenerationEU’/PRTR. La publicación es parte del proyecto TED2021–130497A-I00, financiado por MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 y por la Unión Europea “NextGenerationEU”/PRTR.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cabaleiro, M.; Conde, B.; González-Gaya, C.; Barros, B. A Novel Fully Removable Walkway System with Non-Invasive Anchors for Structural Health Inspection and Maintenance of Historic Steel Structures. Structures 2023, 53, 1435–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, M.; Conde, B.; Riveiro, B.; Caamaño, J.C. Analysis of Steel Connections with Girder Clamps According to the Bolts Preload. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 168, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, M.; Riveiro, B.; Conde, B.; Caamaño, J.C. Analytical T-Stub Model for the Analysis of Clamps in Structural Metal Joints. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 130, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheiro, F.N.; Cabaleiro, M.; Conde, B.; Barros, B. Integration of Finite Element Simulations and Experimental Validation in the Analysis of Demountable Clamp Joints for Steel Structures. In Proceedings of the World Congress on New Technologies, Barcelona, Spain, 25–27 August 2024; Avestia Publishing: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- EN 1993-1-8; Eurocode 3—Design of Steel Structures—Part 1-8 Joints. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2024.
- UNE-EN 1993-1-1; Eurocódigo 3: Proyecto de Estructuras de Acero 1-1: Reglas Generales y Reglas Para Edificios. Organización Española de Normalización (UNE): Madrid, Spain, 2013.
- Jung, D.S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Han, J.W.; Kim, C.Y. Demountable Bolted Shear Connector for Easy Deconstruction and Reconstruction of Concrete Slabs in Steel–Concrete Bridges. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, M.; Moutinho, C.; González-Gaya, C.; Caetano, E.; Rosales-Prieto, V.F. Analysis of Stiffness of Clamped Joints versus Bolted Joints in Steel Structures by Means of Accelerometers and Shaking Table Tests. Sensors 2021, 21, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, E.F.; Lian, J.Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.C.; Wang, S.B.; Cao, D. Bin Compressive Behavior of a Fully Prefabricated Liftable Connection for Modular Steel Construction. Buildings 2022, 12, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Application of Finite Element Analysis in Structural Analysis and Computer Simulation. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2024, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chu, H. Analysis of Self-Loosening Behavior of High Strength Bolts Based on Accurate Thread Modeling. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 127, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, G.; Qi, J.; Wu, H.; Ye, J.; Gao, B.; Xu, N.; Hu, B. Experimental and Numerical Study on the Performance of New Prefabricated Connections for Free-Form Grid Structures. Structures 2022, 36, 1050–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L.; Zhu, J.Z. The Finite Element Method: Its Basis and Fundamentals; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 0750663200. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalheiro, F.N.; Cabaleiro, M.; Conde, B.; Bouzas, Ó. Clamp-Based Steel Connections for Structural Reusability: Experimental and Finite Element Analysis in the Elastic Range. Structures 2025, 75, 108767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Ghafar, W.; Zhong, T.; Abid, M.; Faizan, E.; Mohamed, A.; Yosri, A.M. Seismic Performance Investigation of an Innovative Steel Shear Wall with Semi-Rigid Beam-to-Column Connections. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 1075300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Ghafar, W.; Tao, Z.; Tao, Y.; He, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Z. Experimental and Numerical Study of an Innovative Infill Web-Strips Steel Plate Shear Wall with Rigid Beam-to-Column Connections. Buildings 2022, 12, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quillupangui, I.; Somodi, B.; Kövesdi, B. Overview of FEM-Based Resistance Models for Local Buckling of Welded Steel Box Section Columns. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldakheel, F.; Hudobivnik, B.; Wriggers, P. Virtual Elements for Finite Thermo-Plasticity Problems. Comput. Mech. 2019, 64, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, M.; Pechstein, A.; Humer, A. A Mixed Finite Element Formulation for Elastoplasticity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2022, 123, 5346–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemiro-Maźniak, J.; Lacki, P. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Joints and Thin-Walled Steel Beams Fabricated through Resistance Spot Welding and Hot-Dip Galvanizing. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 202, 112105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Liu, Y.K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, A.L. Analysis of Bolted Connection for H-Section Beam and Square Steel Tube Column. Structures 2024, 60, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.Z. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Bending Behavior in Nontraditional Steel Beam-to-Beam Tip Connections. Structures 2024, 62, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Ajayi, S.O.; Bilal, M.; Alaka, H.A.; Owolabi, H.A.; Bello, S.A.; Jaiyeoba, B.E.; Kadiri, K.O. Design for Deconstruction (DfD): Critical Success Factors for Diverting End-of-Life Waste from Landfills. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabirifar, K.; Mojtahedi, M.; Wang, C.; Tam, V.W.Y. Construction and Demolition Waste Management Contributing Factors Coupled with Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle Strategies for Effective Waste Management: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torra-Bilal, I.; Mahamid, M.; Baran, E. Cyclic Behaviour of Precast Beam-to-Column Connections: An Experimental and Numerical Investigation. Structures 2022, 35, 939–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRFAN, S.; SIDDIQUI, F. A Review of Recent Advancements in Finite Element Formulation for Sandwich Plates. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO9001: 2015; Contact Technology Guide—Ansys 2024/R2. ANSYS, Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2024.
- Cabaleiro, M.; Comesaña, R.; González-Gaya, C.; Caamaño, C. Analytical Model for the Fatigue Analysis of Steel Joints by Clamps According to the Lever Length. Materials 2021, 14, 7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNE-EN 1993-1-8; Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures—Part 1-8: Design of joints. Organización Española de Normalización (UNE): Madrid, Spain, 2013.
- ANSI/AISC 360-16; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC): Chicago, IL, USA, 2016.
- ANSI/AISC 360-22; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC): Chicago, IL, USA, 2022.
- EN 1090-2:2018+A1; Execution of Steel Structures and Aluminium Structures-Part 2: Technical Requirements for Steel Structures. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2024.
- Di Lorenzo, G.; Babilio, E.; Formisano, A.; Landolfo, R. Innovative Steel 3D Trusses for Preservating Archaeological Sites: Design and Preliminary Results. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 154, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4017:2022; Fasteners Head Screws Grades A and B. Organización Española de Normalización (UNE): Madrid, Spain, 2023.
- UNE-EN ISO 898-1; Mechanical Properties of Fasteners Made of Carbon Steel and alloy Steel. Part 1: Bolts, Screws and Studs with Specified Property Classes. Organización Española de Normalización (UNE): Madrid, Spain, 2015.
- UNE-EN 14399-3; Part 3: System HR. Hexagon Bolt and Nut Assemblies. Organización Española de Normalización (UNE): Madrid, Spain, 2016.
- EN 14399-5; High-Strength Structural Bolting Assemblies for Preloading—Part: Plain Washers. Organización Española de Normalización (UNE): Madrid, Spain, 2016.
- UNE-EN ISO 6789-1; Assembly Tools for Screws and Nuts Hand Torque Tools Part 1: Requirements and Methods for Design Conformance Testing and Quality Conformance Testing: Minimum Requirements for Declaration of Conformance. Asociación Española de Normalización: Madrid, Spain, 2019.
- UNE-EN 14399-1; High Strength Structural Bolting Assemblies for Preloading Part 1: General Requirements. Organización Española de Normalización: Madrid, Spain, 2016.
- UNE-EN 10034; Structural Steels I and H Sections Tolerances on Shape and Dimensions. Organización Española de Normalización (UNE): Madrid, Spain, 1994.
- Li, D.; Huang, Z.; Uy, B.; Thai, H.T.; Hou, C. Slenderness Limits for Fabricated S960 Ultra-High-Strength Steel and Composite Columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 159, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebinia, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Ho, J.; Shen, W.; Ma, H.; Sepasgozar, S.M.E.; Marroquin, F.A.; Tsavdaridis, D.; Cai, G.; et al. Advanced Structural Analysis of Innovative Steel-Glass Structures with Respect to the Architectural Design. Buildings 2021, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, M.X. Experimental Behavior and Design Method of Rectangular Concrete-Filled Tubular Columns Using Q460 High-Strength Steel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 856–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liew, J.Y.R.; Xiong, M.X. Rectangular Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Beam-Columns Using High-Strength Steel: Experiments and Design. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 131, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE-EN 1993-1-1:2013/A1; Eurocódigo 3: Proyecto de Estructuras de Acero Parte 1-1: Reglas Generales y Reglas Para Edificios. Organización Española de Normalización (UNE): Madrid, Spain, 2014.
- ANSI/AISC 360-05; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC): Chicago, IL, USA, 2005.
- Li, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Teh, L.H. Column-Wall Failure Mode of Steel Moment Connection with Inner Diaphragm and Catenary Mechanism. Eng. Struct. 2017, 131, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shayan, S.; Rasmussen, K.J.R.; Ellingwood, B.R. System-Based Design of Planar Steel Frames, I: Reliability Framework. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 123, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.G.; Koh, C.G.; Liew, J.Y.R. Efficient Progressive Collapse Analysis for Robustness Evaluation of Buildings Experiencing Column Removal. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 122, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, D.; Kozlowski, A.; Ślęczka, L.; Wójcik-Grząba, I.; Nykiel, D.; Gubernat, S. Innovative Steel Beam-to-Column Joint under Central Column Loss Situation: Experimental Tests and Analytical Model. Eng. Struct. 2025, 326, 119513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmat, A.M.A.; Langlois, S.; Labossière, P. Strain Distribution and Failure Modes of Steel Lattice Tower Gusset Plates as a Function of Their Geometry. Structures 2024, 69, 107510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Uy, B.; Aslani, F.; Patel, V. Behaviour and Design of Demountable CFST Column-Column Connections under Tension. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 138, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Meng, K.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.M.; Cui, Y. Seismic Performance of Bolted Connection between T-Shaped Section Column and I-Section Beam with L-Stubs. Eng. Struct. 2023, 285, 116022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournaghshband, A.; Maher, R. Numerical Investigation of Cyclic Behaviour in H-Shaped Stainless-Steel Beam-Columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2025, 227, 109370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarquis, F.R.; de Lima, L.R.O. Numerical Investigation of Short-to-Intermediate Fixed-Ended Stainless Steel Bolted Starred Equal-Leg Angle Columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 215, 108557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, B.; Bai, L. Experimental and Numerical Investigation on Global-Stability of Welded BS700 High-Strength Steel Beams. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2025, 227, 109373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrubaidi, M.; Abadel, A.A. Numerical Study on Upgrading Beam-Column Connections in Steel Framed Buildings for Progressive Collapse Mitigation. Structures 2023, 48, 1576–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhi, X.; Zhang, R.; Fan, F. Experimental and Numerical Investigation on the Impact Response of Bolt-Ball Joints. Structures 2024, 64, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broniewicz, E.; Dec, K. Environmental Impact of Demolishing a Steel Structure Design for Disassembly. Energies 2022, 15, 7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavoura, F.; Veljkovic, M. Design Strategies for Reusable Structural Components in the Built Environment. In Life-Cycle of Structures and Infrastructure Systems, Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Life-Cycle Civil Engineering, IALCCE 2023, Milan, Italy, 2–6 July 2024; CRC Press/Balkema: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 799–806. [Google Scholar]
- Cabaleiro, M.; Conde, B.; González-Gaya, C.; Barros, B. Removable, Reconfigurable, and Sustainable Steel Structures: A State-of-the-Art Review of Clamp-Based Steel Connections. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).