Effects of Exercise on Aerobic Capacity and Quality of Life in People with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
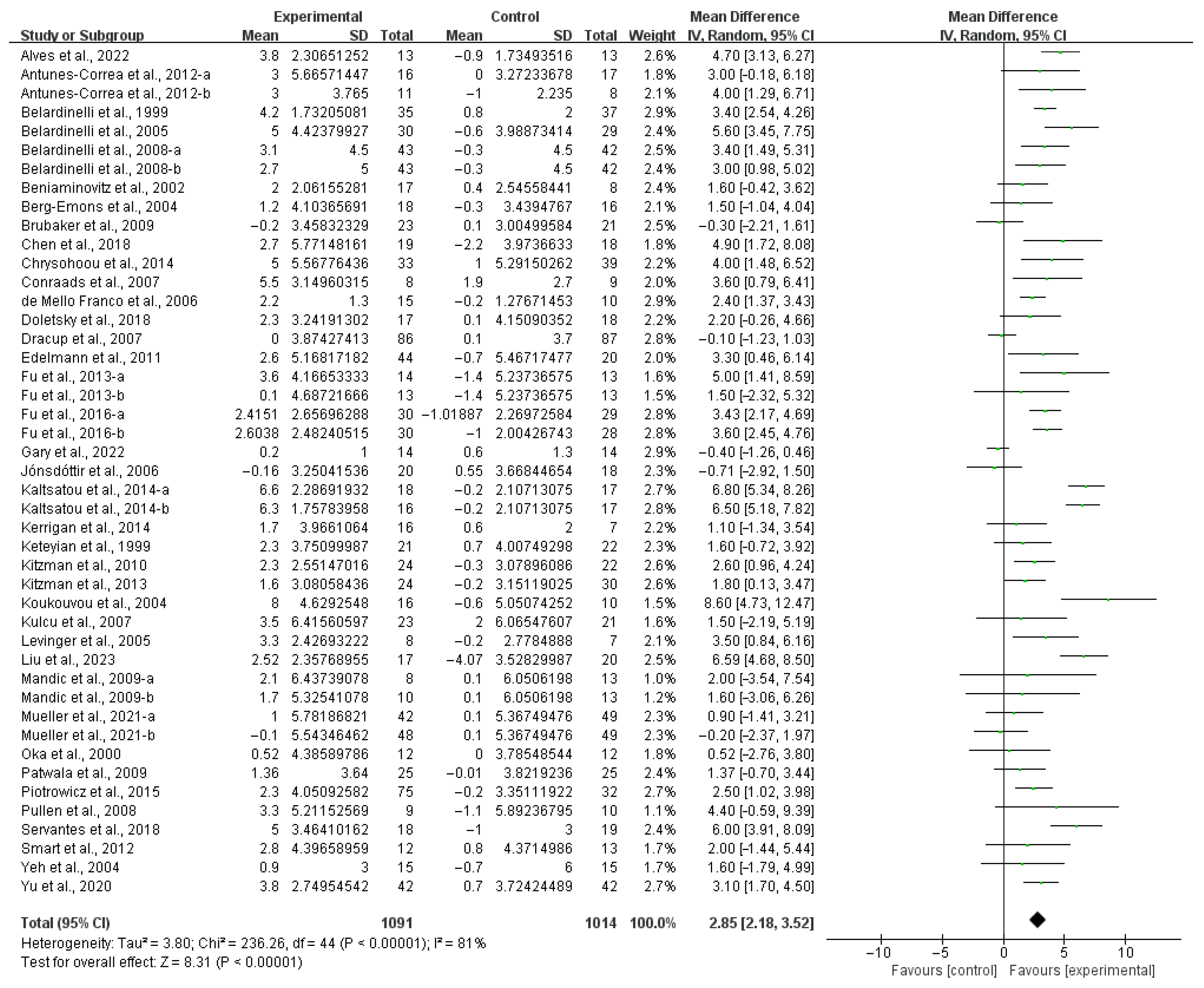
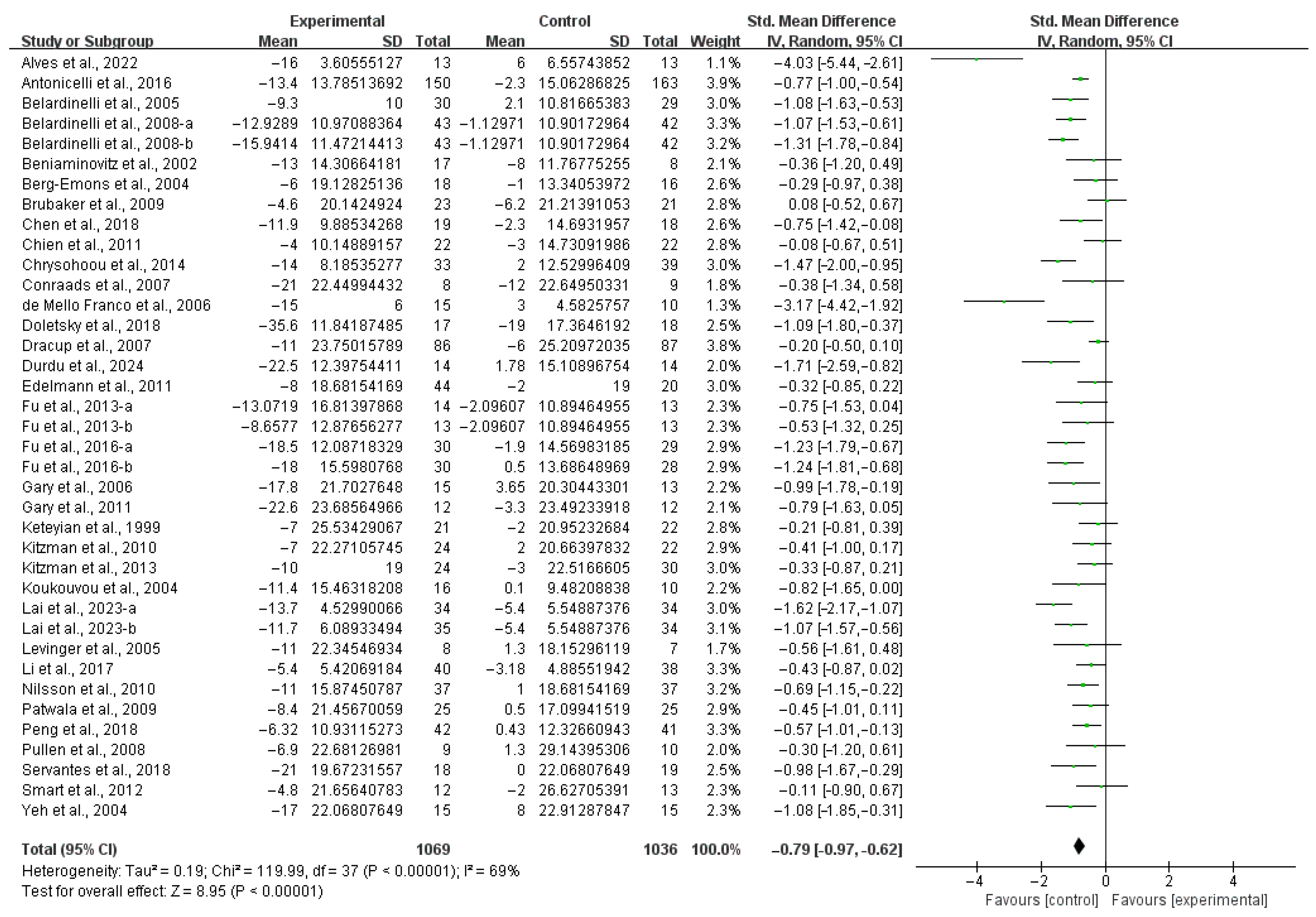
3.3. Meta-Analysis
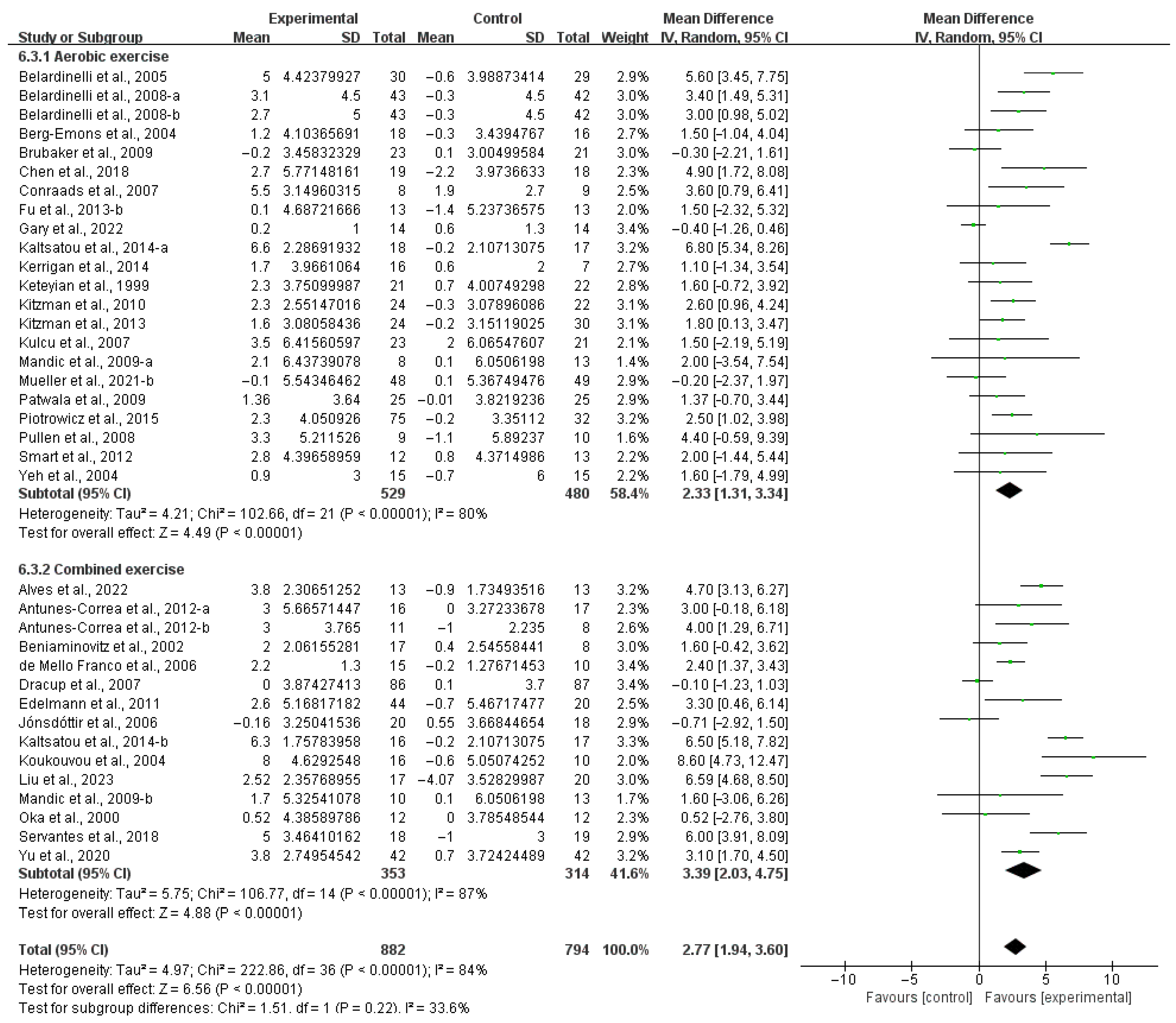
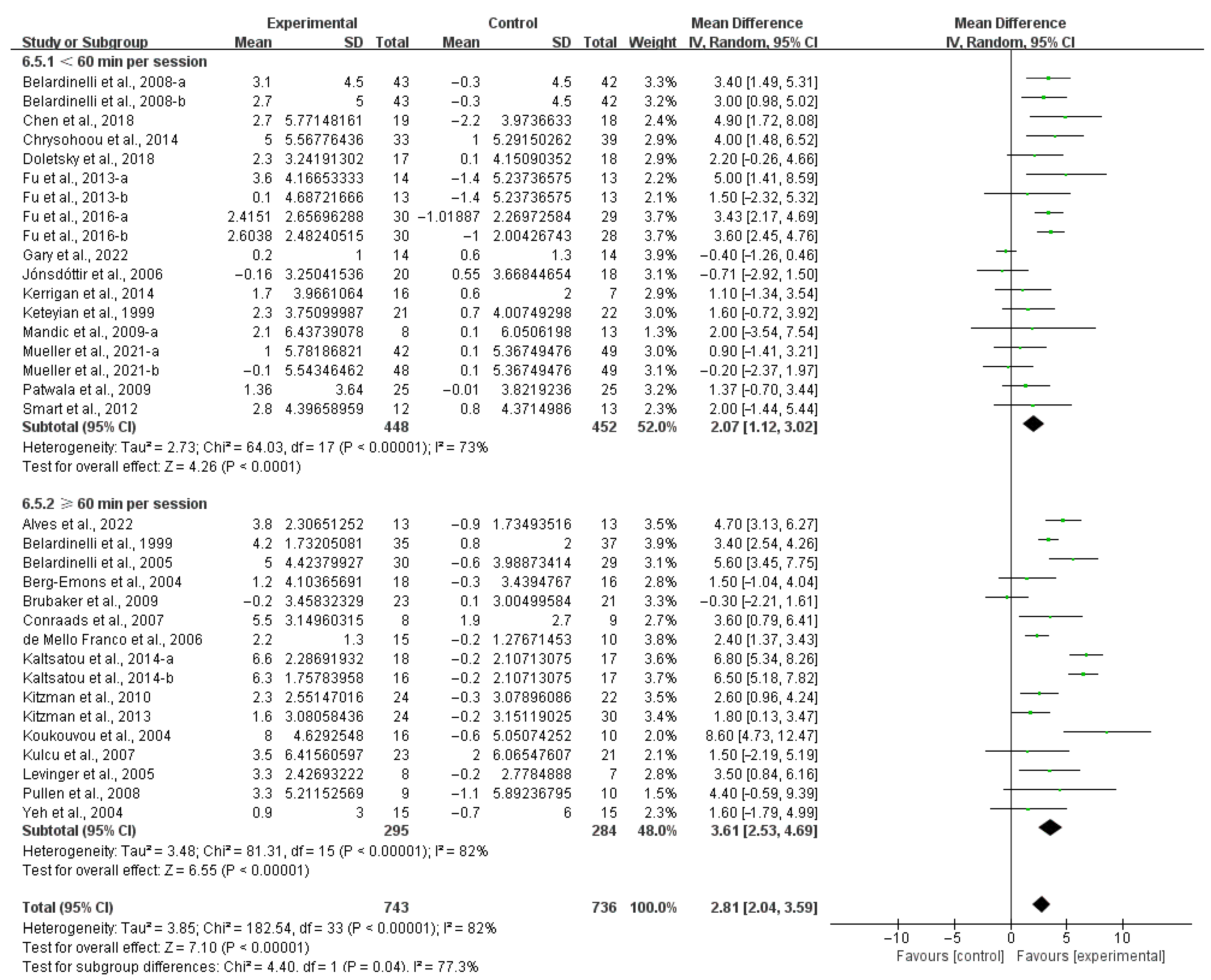
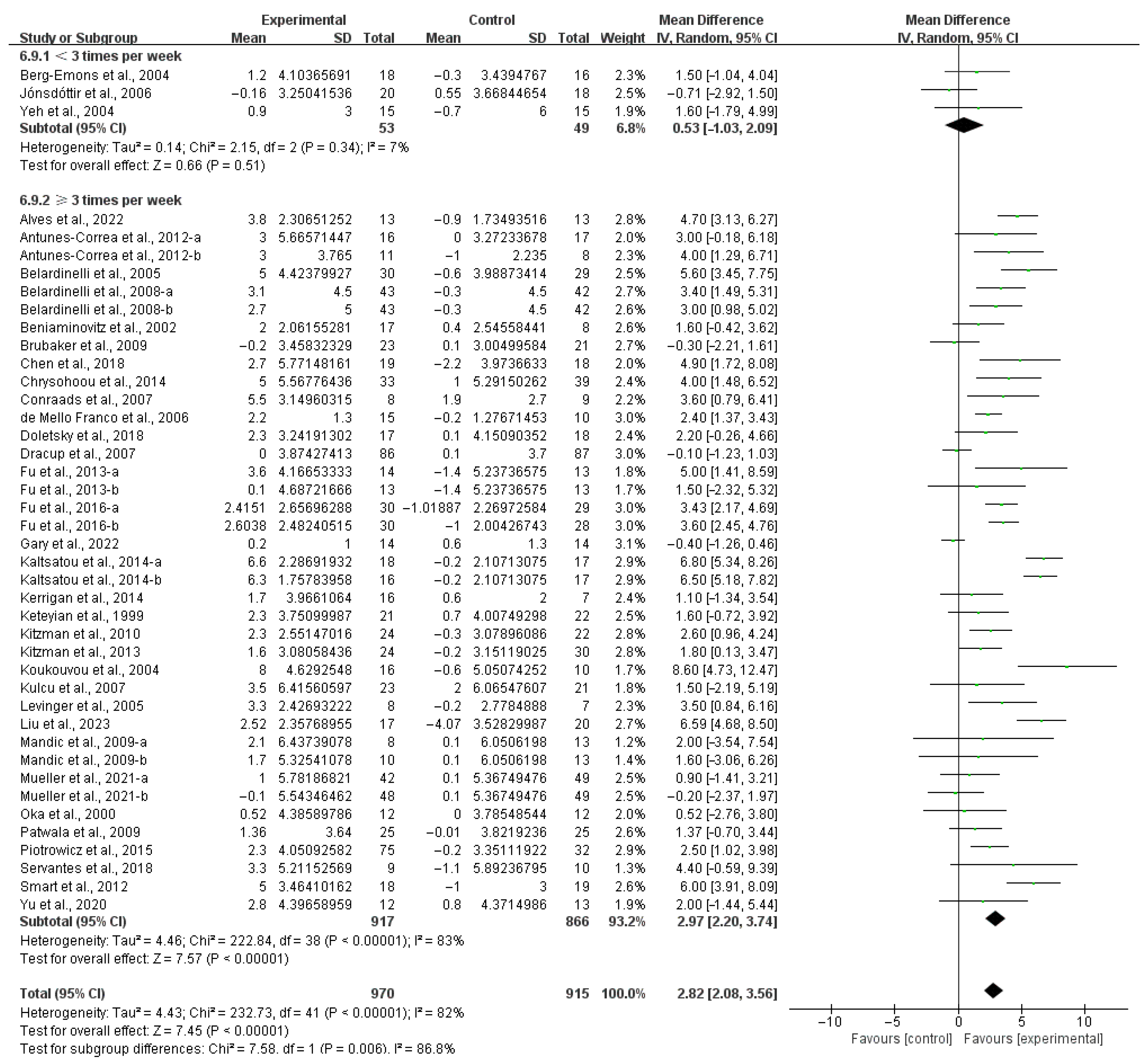
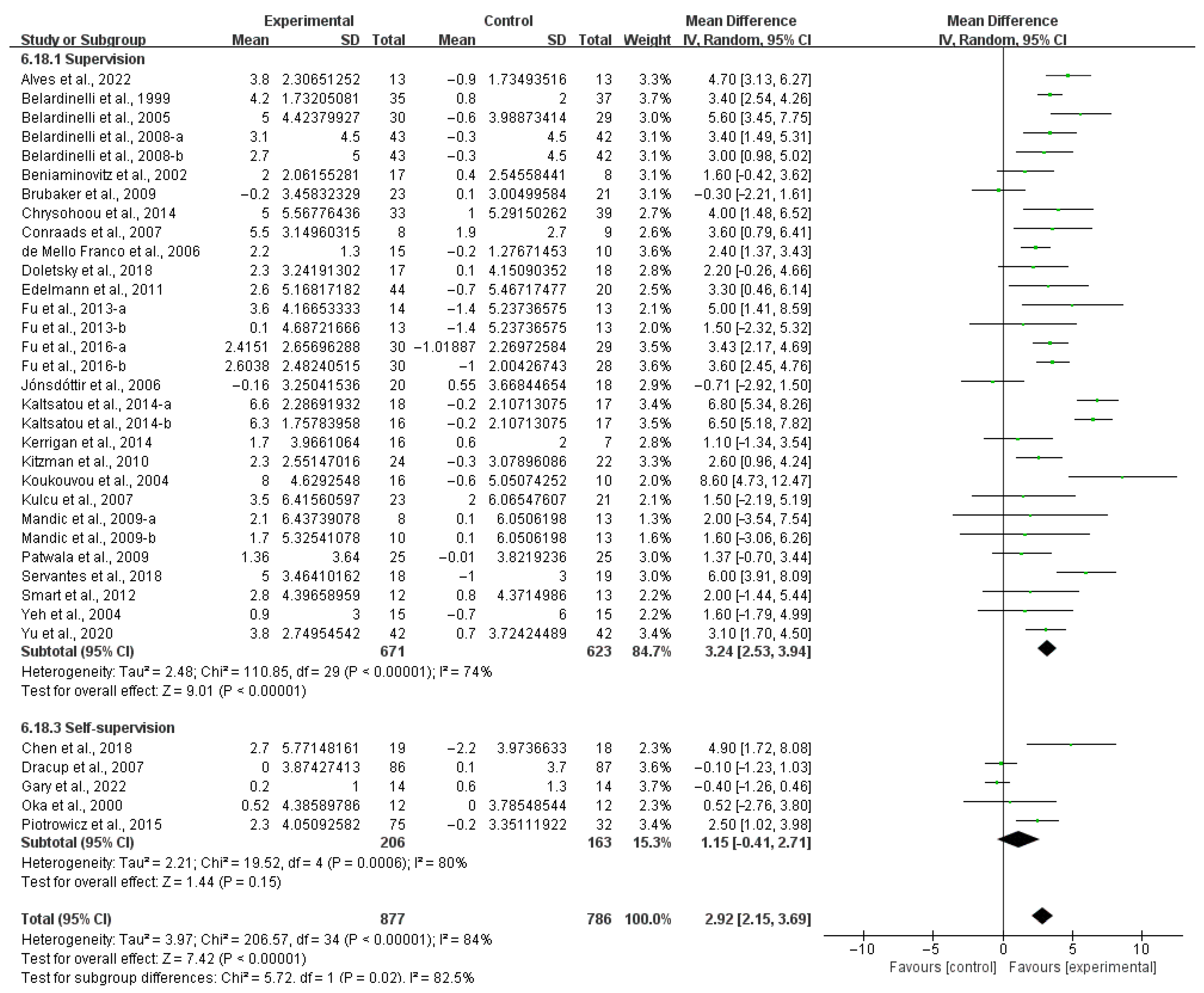
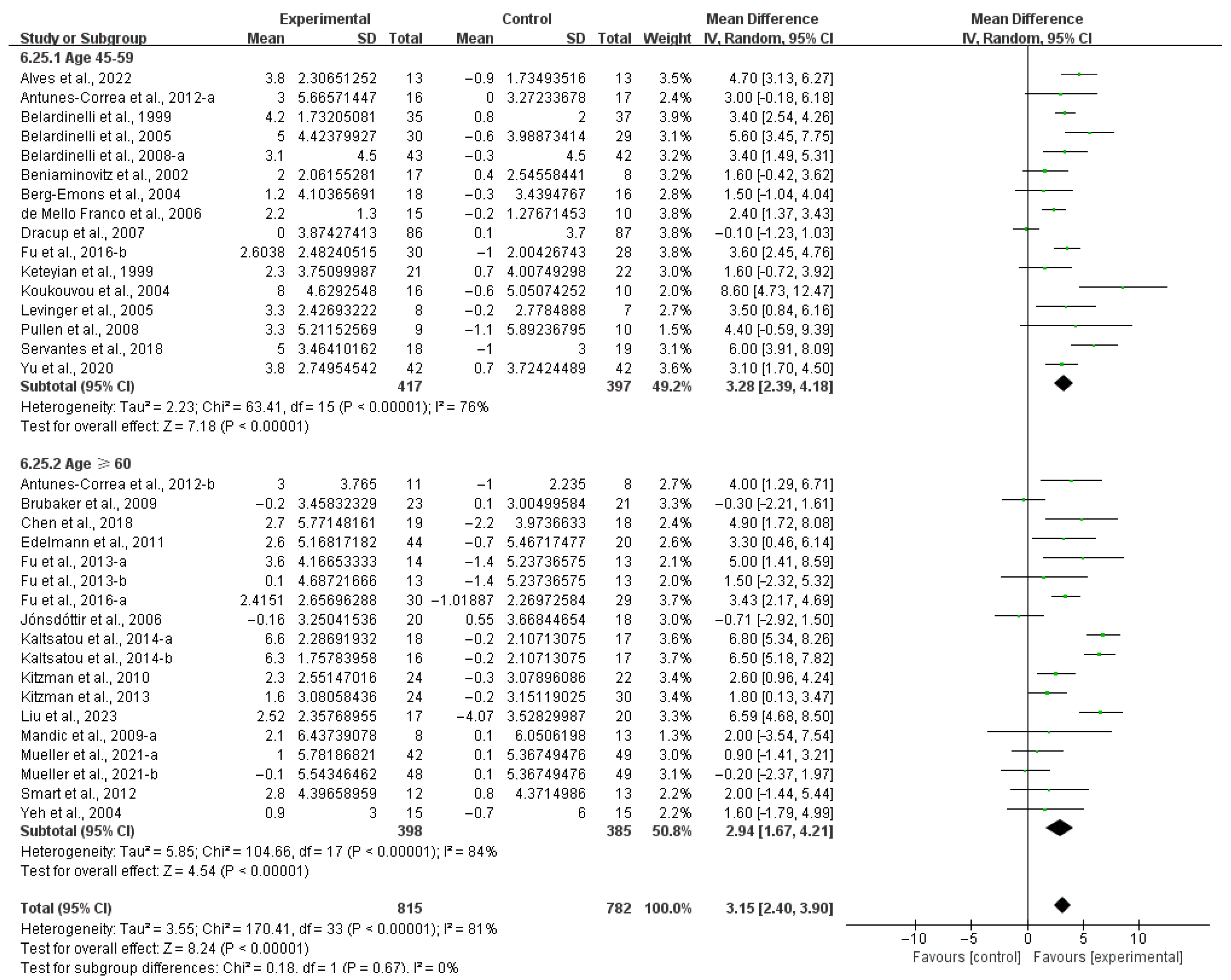
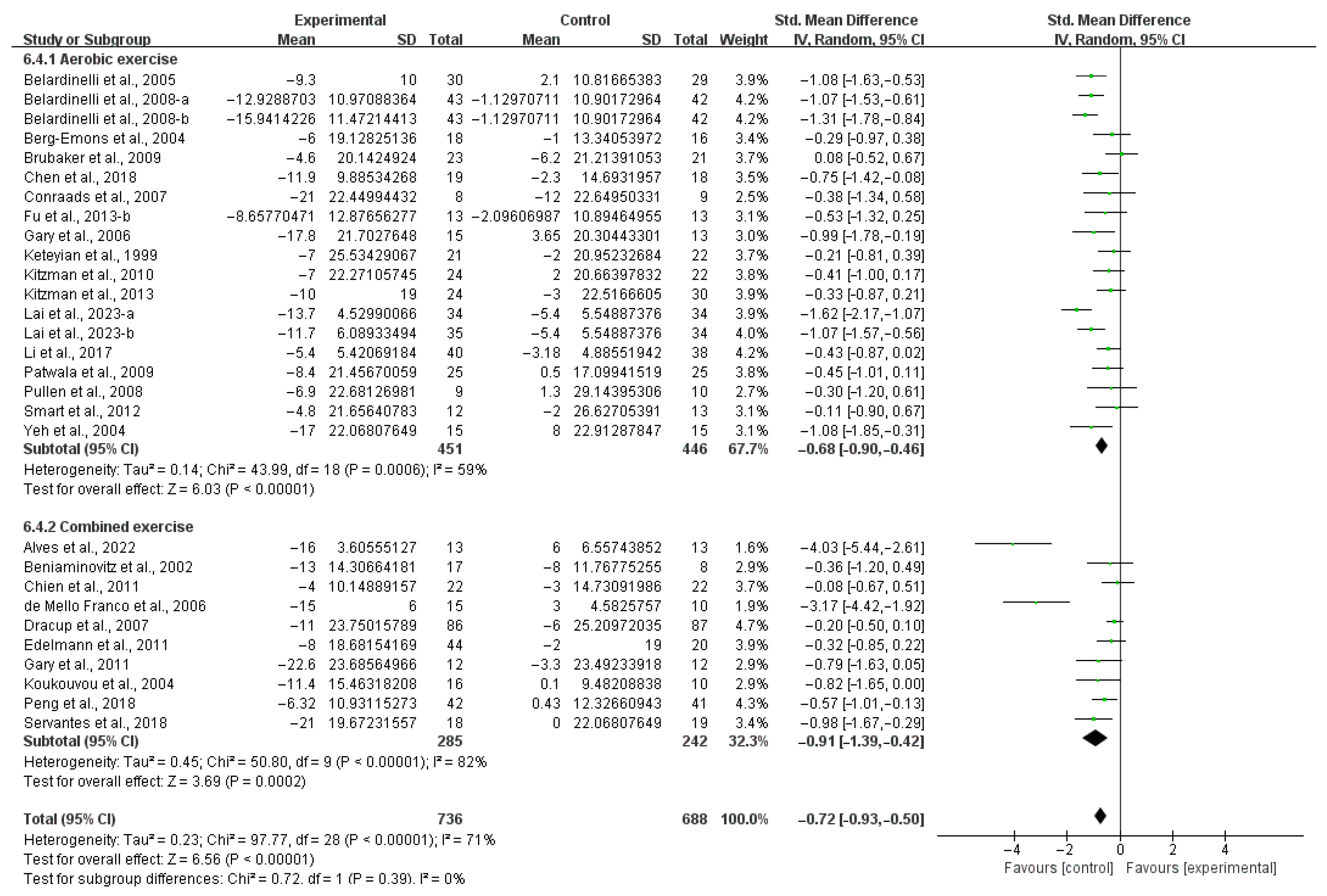
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
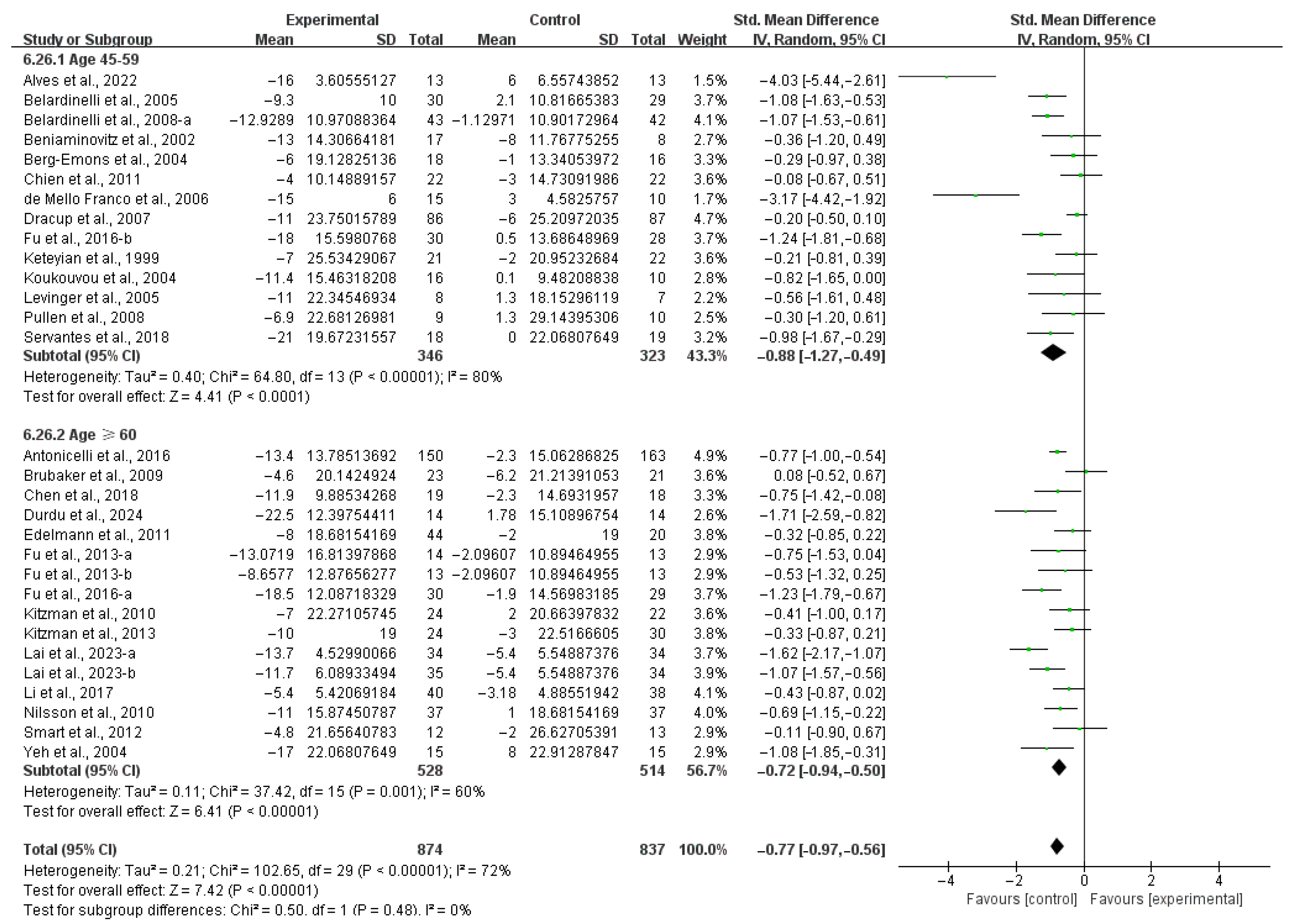
3.4.1. Aerobic Capacity
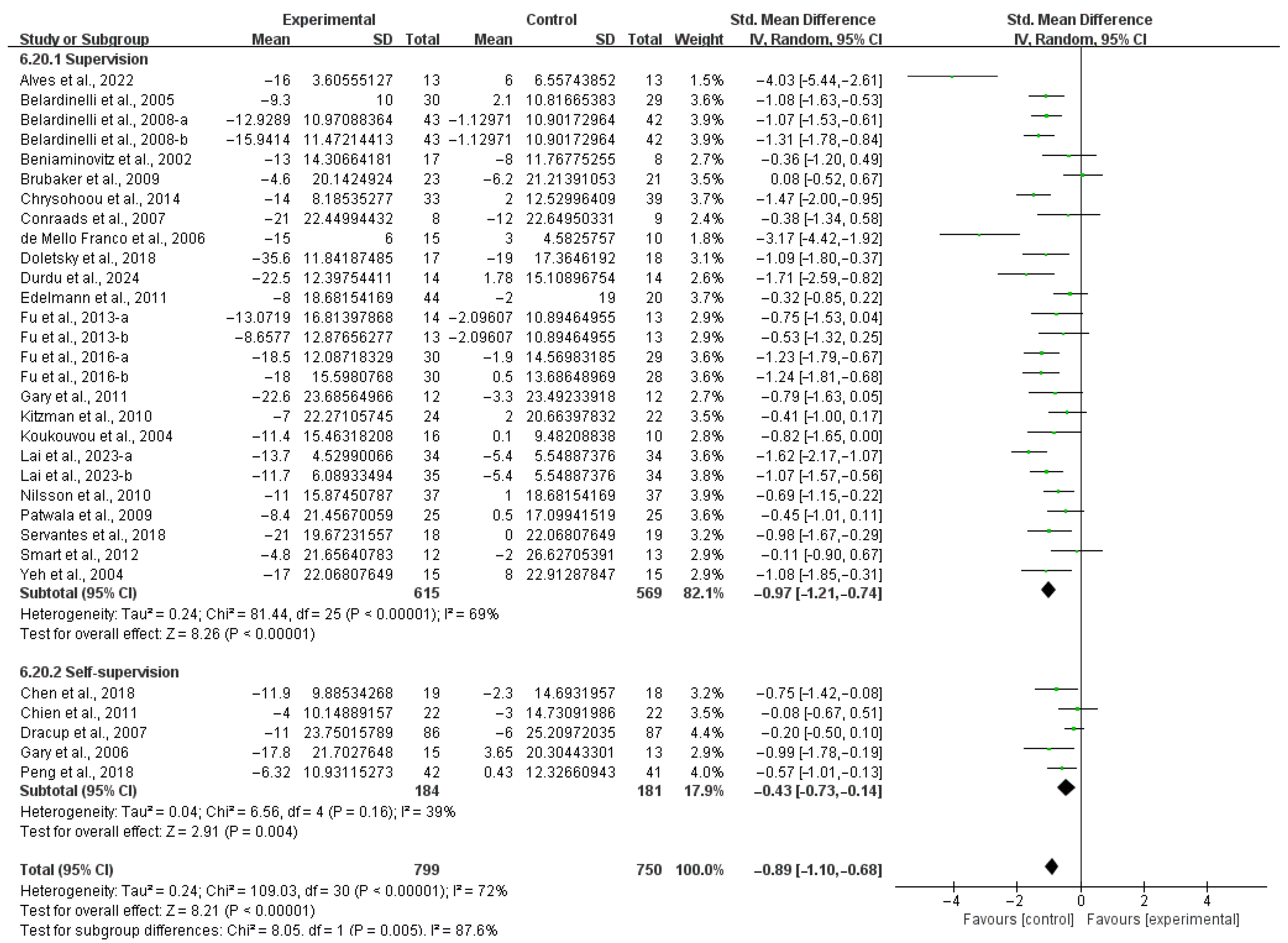
3.4.2. QOL
3.5. Risk of Bias
3.6. Publication Bias
3.7. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Effects of Exercise on Aerobic Capacity in HF Patients
4.3. Effects of Various Exercise Moderators on Aerobic Exercise Capacity in Patients with HF
4.4. Effects of Exercise on QOL in HF Patients
4.5. Effects of Various Exercise Moderators on QOL in HF Patients
4.6. Strength and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HF | Heart failure |
| HFpEF | Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction |
| HFrEF | Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction |
| QOL | Quality of life |
| VO2peak | Peak oxygen uptake |
| ESC | European Society of Cardiology |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| RCTs | Randomized controlled trials |
| VO2max | Maximal oxygen uptake |
| MLHFQ | Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| PEDro | Physiotherapy Evidence Database |
| RoB-2 | Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 |
| SE | Standard error |
| WMD | Weighted mean difference |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| CHF | Chronic heart failure |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| 6MWD | 6-minute walking distance |
| ACSM | American College of Sports Medicine |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| SF-36 | Medical Outcomes Study 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey |
References
- Metra, M.; Teerlink, J.R. Heart failure. Lancet 2017, 390, 1981–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaeian, B.; Fonarow, G.C. Epidemiology and aetiology of heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Redfield, M.M. Diastolic and systolic heart failure are distinct phenotypes within the heart failure spectrum. Circulation 2011, 123, 2006–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, R.S.; Tu, J.V.; Lee, D.S.; Austin, P.C.; Fang, J.; Haouzi, A.; Gong, Y.; Liu, P.P. Outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in a population-based study. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzman, D.W.; Little, W.C.; Brubaker, P.H.; Anderson, R.T.; Hundley, W.G.; Marburger, C.T.; Brosnihan, B.; Morgan, T.M.; Stewart, K.P. Pathophysiological characterization of isolated diastolic heart failure in comparison to systolic heart failure. JAMA 2002, 288, 2144–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonarow, G.C.; Stough, W.G.; Abraham, W.T.; Albert, N.M.; Gheorghiade, M.; Greenberg, B.H.; O’Connor, C.M.; Sun, J.L.; Yancy, C.W.; Young, J.B. Characteristics, treatments, and outcomes of patients with preserved systolic function hospitalized for heart failure: A report from the OPTIMIZE-HF Registry. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.P.; Ibrahim, N.E.; Januzzi, J.L. Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlay, S.M.; Roger, V.L.; Redfield, M.M. Epidemiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackevicius, C.A.; de Leon, N.K.; Lu, L.; Chang, D.S.; Warner, A.L.; Mody, F.V. Impact of a Multidisciplinary Heart Failure Post-hospitalization Program on Heart Failure Readmission Rates. Ann. Pharmacother. 2015, 49, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosterd, A.; Cost, B.; Hoes, A.; de Bruijne, M.; Deckers, J.; Hofman, A.; Grobbee, D. The prognosis of heart failure in the general population: The Rotterdam Study. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, S.; Parissis, J.T.; Kremastinos, D.T. New aspects for the role of physical training in the management of patients with chronic heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2003, 90, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, C.M.; Whellan, D.J.; Lee, K.L.; Keteyian, S.J.; Cooper, L.S.; Ellis, S.J.; Leifer, E.S.; Kraus, W.E.; Kitzman, D.W.; Blumenthal, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of exercise training in patients with chronic heart failure: HF-ACTION randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009, 301, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, E.; Biswas, R.K.; Koemel, N.A.; Sabag, A.; Pulsford, R.; Atkin, A.J.; Stathi, A.; Cheng, S.; Thøgersen-Ntoumani, C.; Blodgett, J.M.; et al. Dose Response of Incidental Physical Activity Against Cardiovascular Events and Mortality. Circulation 2025, 151, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, D.L.; Silva, M.G.; Silva, L.N.; Fortes, J.V.; Costa, E.T.; Assunção, R.P.; Lima, C.M.; Nina, V.J.d.S.; Bernardo-Filho, M.; Caputo, D.S. Effects of Aerobic Exercise Applied Early After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting on Pulmonary Function, Respiratory Muscle Strength, and Functional Capacity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Phys. Act Health 2016, 13, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.; Balady, G.J. The role of exercise training in heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, J.J.; Adamopoulos, S.; Anker, S.D.; Auricchio, A.; Böhm, M.; Dickstein, K.; Falk, V.; Filippatos, G.; Fonseca, C.; Gomez-Sanchez, M.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Peçanha, T.; Bartels, R.; Brito, L.C.; Paula-Ribeiro, M.; Oliveira, R.S.; Goldberger, J.J. Methods of assessment of the post-exercise cardiac autonomic recovery: A methodological review. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 227, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peçanha, T.; Silva-Júnior, N.D.; Forjaz, C.L.d.M. Heart rate recovery: Autonomic determinants, methods of assessment and association with mortality and cardiovascular diseases. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2014, 34, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallauria, F.; Vitale, G.; Pacileo, M.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Oliviero, A.; Passaro, F.; Calce, R.; Parlato, A.; Testa, C.; D’ambrosio, G.; et al. Sacubitril/Valsartan Improves Autonomic Function and Cardiopulmonary Parameters in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallauria, F.; Lucci, R.; Pietrosante, M.; Gargiulo, G.; De Lorenzo, A.; D’Agostino, M.; Gerundo, G.; Abete, P.; Rengo, F.; Vigorito, C. Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation improves heart rate recovery in elderly patients after acute myocardial infarction. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbs, S.; Höllriegel, R.; Linke, A.; Beck, E.B.; Adams, V.; Gielen, S.; Möbius-Winkler, S.; Sandri, M.; Kränkel, N.; Hambrecht, R.; et al. Exercise training in patients with advanced chronic heart failure (NYHA IIIb) promotes restoration of peripheral vasomotor function, induction of endogenous regeneration, and improvement of left ventricular function. Circ. Heart Fail. 2010, 3, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Higginbotham, M.B.; Cobb, F.R. Exercise training in patients with severe left ventricular dysfunction. Hemodynamic and metabolic effects. Circulation 1988, 78, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, E.J.; Moxham, T.; Rees, K.; Singh, S.; Coats, A.J.; Ebrahim, S.; Lough, F.; Taylor, R.S. Exercise training for systolic heart failure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2010, 12, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, A.J. Optimizing exercise training for subgroups of patients with chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 1998, 19, O29–O34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.R.; Groves, J.; Rayos, G. Circulatory status and response to cardiac rehabilitation in patients with heart failure. Circulation 1996, 94, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, S.; Kans, G.; Krichten, C.; Rosen, M. Exercise improves exercise duration more than peak VO2 in elderly patients with congestive heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason-Wehrens, B.; Nebel, R.; Jensen, K.; Hackbusch, M.; Grilli, M.; Gielen, S.; Schwaab, B.; Rauch, B. Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation in patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction: The Cardiac Rehabilitation Outcome Study in Heart Failure (CROS-HF): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 929–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.S.; Walker, S.; Smart, N.A.; Piepoli, M.F.; Warren, F.C.; Ciani, O.; O’Connor, C.; Whellan, D.; Keteyian, S.J.; Coats, A.; et al. Impact of exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation in patients with heart failure (ExTraMATCH II) on mortality and hospitalisation: An individual patient data meta-analysis of randomised trials. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykowsky, M.J.; Timmons, M.P.; Kruger, C.; McNeely, M.; Taylor, D.A.; Clark, A.M. Meta-analysis of aerobic interval training on exercise capacity and systolic function in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fractions. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Hou, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, L. The effect of exercise on balance function in stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 4751–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Xi, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Tao, X.; Lv, Y.; Hou, X.; Yu, L. Effects of exercise in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1387658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Tao, X.; Lei, B.; Hou, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, L. Effects of exercise on post-stroke cognitive function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2024, 31, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Sun, T.; Yu, L. Effects of Acute Ingestion of Caffeine Capsules on Muscle Strength and Muscle Endurance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. Effects of Exercise on Cancer-Related Fatigue in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Life 2024, 14, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.-C.; Yang, N.-I.; Wang, C.-H.; Cherng, W.-J.; Chou, S.-L.; Pan, T.-L.; Wang, J.-S. Aerobic Interval Training Elicits Different Hemodynamic Adaptations Between Heart Failure Patients with Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.-C.; Wang, C.-H.; Lin, P.-S.; Hsu, C.-C.; Cherng, W.-J.; Huang, S.-C.; Liu, M.-H.; Chiang, C.-L.; Wang, J.-S. Aerobic interval training improves oxygen uptake efficiency by enhancing cerebral and muscular hemodynamics in patients with heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, D.J.; Williams, C.T.; Ehrman, J.K.; Saval, M.A.; Bronsteen, K.; Schairer, J.R.; Swaffer, M.; Brawner, C.A.; Lanfear, D.E.; Selektor, Y.; et al. Cardiac rehabilitation improves functional capacity and patient-reported health status in patients with continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices: The Rehab-VAD randomized controlled trial. JACC Heart Fail. 2014, 2, 653–659. [Google Scholar]
- Gary, R.A.; Cress, M.E.; Higgins, M.K.; Smith, A.L.; Dunbar, S.B. Combined aerobic and resistance exercise program improves task performance in patients with heart failure. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg-Emons, R.v.D.; Balk, A.; Bussmann, H.; Stam, H. Does aerobic training lead to a more active lifestyle and improved quality of life in patients with chronic heart failure? Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2004, 6, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulcu, D.G.; Kurtais, Y.; Tur, B.S.; Gülec, S.; Seckin, B. The effect of cardiac rehabilitation on quality of life, anxiety and depression in patients with congestive heart failure. A randomized controlled trial, short-term results. Eura. Medicophys. 2007, 43, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Durdu, H.; Demir, R.; Zeren, M.; Aydin, E.; Gunaydin, Z.Y.; Yigit, Z. The Effect of Computerized Wobble Board and Core Stabilization Exercises on Balance Performance and Exercise Capacity in Patients with Heart Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 105, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitzman, D.W.; Brubaker, P.H.; Herrington, D.M.; Morgan, T.M.; Stewart, K.P.; Hundley, W.G.; Abdelhamed, A.; Haykowsky, M.J. Effect of endurance exercise training on endothelial function and arterial stiffness in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: A randomized, controlled, single-blind trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conraads, V.M.; Vanderheyden, M.; Paelinck, B.; Verstreken, S.; Blankoff, I.; Miljoen, H.; De Sutter, J.; Beckers, P. The effect of endurance training on exercise capacity following cardiac resynchronization therapy in chronic heart failure patients: A pilot trial. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2007, 14, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Winzer, E.B.; Duvinage, A.; Gevaert, A.B.; Edelmann, F.; Haller, B.; Pieske-Kraigher, E.; Beckers, P.; Bobenko, A.; Hommel, J.; et al. Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training, Moderate Continuous Training, or Guideline-Based Physical Activity Advice on Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jónsdóttir, S.; Andersen, K.K.; Sigurðsson, A.F.; Sigurðsson, S.B. The effect of physical training in chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2006, 8, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dracup, K.; Evangelista, L.S.; Hamilton, M.A.; Erickson, V.; Hage, A.; Moriguchi, J.; Canary, C.; MacLellan, W.R.; Fonarow, G.C. Effects of a home-based exercise program on clinical outcomes in heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2007, 154, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic, S.; Tymchak, W.; Kim, D.; Daub, B.; Quinney, H.A.; Taylor, D.; Al-Kurtass, S.; Haykowsky, M.J. Effects of aerobic or aerobic and resistance training on cardiorespiratory and skeletal muscle function in heart failure: A randomized controlled pilot trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2009, 23, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, M.; Fang, J.; Lin, Z. The effects of cardiac exercise rehabilitation training on the cardiopulmonary function and quality of life in patients with chronic stable heart failure. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 13, 5983–5990. [Google Scholar]
- Servantes, D.M.; Javaheri, S.; Kravchychyn, A.C.P.; Storti, L.J.; Almeida, D.R.; de Mello, M.T.; Cintra, F.D.; Tufik, S.; Bittencourt, L. Effects of Exercise Training and CPAP in Patients with Heart Failure and OSA: A Preliminary Study. Chest 2018, 154, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keteyian, S.J.; Brawner, C.A.; Schairer, J.R.; Levine, T.; Levine, A.B.; Rogers, F.J.; Goldstein, S. Effects of exercise training on chronotropic incompetence in patients with heart failure. Am. Heart J. 1999, 138 Pt 1, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, F.G.d.M.; Santos, A.C.; Rondon, M.U.P.; Trombetta, I.C.; Strunz, C.; Braga, A.M.W.; Middlekauff, H.; Negrão, C.E.; Barretto, A.C.P. Effects of home-based exercise training on neurovascular control in patients with heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2006, 8, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Yu, H.; Xu, S.L.; Li, R.; Gao, Y. Effects of Low-Intensity Exercise in Older Adults with Chronic Heart Failure During the Transitional Period From Hospital to Home in China A Randomized Controlled Trial. Res. Gerontol. Nurs. 2017, 10, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Belardinelli, R.; Lacalaprice, F.; Faccenda, E.; Purcaro, A.; Perna, G. Effects of short-term moderate exercise training on sexual function in male patients with chronic stable heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 101, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, G.Y.; Wood, M.J.; Lorell, B.H.; Stevenson, L.W.; Eisenberg, D.M.; Wayne, P.M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Davis, R. B Effects of tai chi mind-body movement therapy on functional status and exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Zhang, J. Effects of traditional Chinese eight brocade exercise with same frequency and different durations on the quality of life, 6-min walk and brain natriuretic peptide in patients with chronic heart failure. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 172, 112059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullen, P.R.; Nagamia, S.H.; Mehta, P.K.; Thompson, W.R.; Benardot, D.; Hammoud, R.; Parrott, J.M.; Sola, S.; Khan, B.V. Effects of Yoga on Inflammation and Exercise Capacity in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2008, 14, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, P.H.; Moore, J.B.; Stewart, K.P.; Wesley, D.J.; Kitzman, D.W. Endurance exercise training in older patients with heart failure: Results from a randomized, controlled, single-blind trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary, R.A.; Paul, S.; Corwin, E.; Butts, B.; Miller, A.H.; Hepburn, K.; Waldrop, D. Exercise and Cognitive Training Intervention Improves Self-Care, Quality of Life and Functional Capacity in Persons with Heart Failure. J. Appl. Gerontol. 2022, 41, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary, R. Exercise self-efficacy in older women with diastolic heart failure: Results of a walking program and education intervention. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 2006, 32, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann, F.; Gelbrich, G.; Dngen, H.D.; Fröhling, S.; Wachter, R.; Stahrenberg, R.; Binder, L.; Töpper, A.; Lashki, D.J.; Schwarz, S.; et al. Exercise training improves exercise capacity and diastolic function in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Results of the Ex-DHF (exercise training in diastolic heart failure) pilot study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1780–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes-Correa, L.M.; Kanamura, B.Y.; Melo, R.C.; Nobre, T.S.; Ueno, L.M.; Franco, F.G.; Roveda, F.; Braga, A.M.; Rondon, M.U.; Brum, P.C.; et al. Exercise training improves neurovascular control and functional capacity in heart failure patients regardless of age. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2012, 19, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, N.A.; Haluska, B.; Jeffriess, L.; Leung, D. Exercise training in heart failure with preserved systolic function: A randomized controlled trial of the effects on cardiac function and functional capacity. Congest. Heart Fail. 2012, 18, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, L.S.; Bocchi, E.A.; Chizzola, P.R.; Castro, R.E.; Salemi, V.M.C.; de Melo, M.D.T.; Andreta, C.R.L.; Guimarães, G.V. Exercise training in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and permanent atrial fibrillation: A randomized clinical trial. Heart Rhythm. 2022, 19, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitzman, D.W.; Brubaker, P.H.; Morgan, T.M.; Stewart, K.P.; Little, W.C. Exercise training in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: A randomized, controlled, single-blind trial. Circ. Heart Fail. 2010, 3, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonicelli, R.; Spazzafumo, L.; Scalvini, S.; Olivieri, F.; Matassini, M.V.; Parati, G.; Del Sindaco, D.; Gallo, R.; Lattanzio, F. Exercise: A “new drug” for elderly patients with chronic heart failure. Aging 2016, 8, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsatou, A.C.H.; Kouidi, E.I.; Anifanti, M.A.; Douka, S.I.; Deligiannis, A.P. Functional and psychosocial effects of either a traditional dancing or a formal exercising training program in patients with chronic heart failure: A comparative randomized controlled study. Clin. Rehabil. 2014, 28, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysohoou, C.; Tsitsinakis, G.; Vogiatzis, I.; Cherouveim, E.; Antoniou, C.; Tsiantilas, A.; Tsiachris, D.; Dimopoulos, D.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; et al. High intensity, interval exercise improves quality of life of patients with chronic heart failure: A randomized controlled trial. QJM 2014, 107, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Wang, C.Y.; Lai, Y.H.; Liao, Y.C.; Wen, Y.K.; Chang, S.T.; Huang, J.L.; Wu, T.J. Home-based cardiac rehabilitation improves quality of life, aerobic capacity, and readmission rates in patients with chronic heart failure. Medicine 2018, 97, e9629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.L.; Lee, C.M.; Wu, Y.W.; Wu, Y.T. Home-based exercise improves the quality of life and physical function but not the psychological status of people with chronic heart failure: A randomised trial. J. Physiother. 2011, 57, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Su, Y.; Hu, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Dolansky, M.A.; Qu, M.; Hu, X. Home-based telehealth exercise training program in Chinese patients with heart failure: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2018, 97, e12069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowicz, E.; Zieliłski, T.; Bodalski, R.; Rywik, T.; Dobraszkiewicz-Wasilewska, B.; Sobieszczan´ska-Małek, M.; Stepnowska, M.; Przybylski, A.; Browarek, A.; Szumowski, L.; et al. Home-based telemonitored Nordic walking training is well accepted, safe, effective and has high adherence among heart failure patients, including those with cardiovascular implantable electronic devices: A randomised controlled study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2015, 22, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, R.K.; De Marco, T.; Haskell, W.L.; Botvinick, E.; Dae, M.W.; Bolen, K.; Chatterjee, K. Impact of a home-based walking and resistance training program on quality of life in patients with heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 85, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doletsky, A.; Andreev, D.; Giverts, I.; Svet, A.; Brand, A.; Kuklina, M.; Sedov, V.; Dikur, O.; Syrkin, A.; Saner, H. Interval training early after heart failure decompensation is safe and improves exercise tolerance and quality of life in selected patients. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwala, A.Y.; Woods, P.R.; Sharp, L.; Goldspink, D.F.; Tan, L.B.; Wright, D.J. Maximizing patient benefit from cardiac resynchronization therapy with the addition of structured exercise training: A randomized controlled study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 2332–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, B.B.; Westheim, A.; Risberg, M.A.; Arnesen, H.; Seljeflot, I. No effect of group-based aerobic interval training on N-terminal pro- B-type natriuretic peptide levels in patients with chronic heart failure. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2010, 44, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouvou, G.; Kouidi, E.; Iacovides, A.; Konstantinidou, E.; Kaprinis, G.; Deligiannis, A. Quality of life, psychological and physiological changes following exercise training in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Rehabil. Med. 2004, 36, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belardinelli, R.; Georgiou, D.; Cianci, G.; Purcaro, A. Randomized, controlled trial of long-term moderate exercise training in chronic heart failure: Effects on functional capacity, quality of life, and clinical outcome. Circulation 1999, 99, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinger, I.; Bronks, R.; Cody, D.V.; Linton, I.; Davie, A. Resistance training for chronic heart failure patients on beta blocker medications. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 102, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniaminovitz, A.; Lang, C.C.; LaManca, J.; Mancini, D.M. Selective low-level leg muscle training alleviates dyspnea in patients with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.P.; Zhou, J.G.; Jin, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, S.W.; Lin, M.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.N.; Guan, X.F.; Wang, L. Therapeutic Efficacy of Shexiang Baoxin Pill Combined with Exercise in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Single-Center, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2023, 29, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belardinelli, R.; Lacalaprice, F.; Ventrella, C.; Volpe, L.; Faccenda, E. Waltz dancing in patients with chronic heart failure: New form of exercise training. Circ. Heart Fail. 2008, 1, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Kurl, S.; Khan, H.; Zaccardi, F.; Rauramaa, R.; Laukkanen, J.A. Oxygen uptake at aerobic threshold is inversely associated with fatal cardiovascular and all-cause mortality events. Ann. Med. 2017, 49, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turri-Silva, N.; Vale-Lira, A.; Verboven, K.; Quaglioti Durigan, J.L.; Hansen, D.; Cipriano, G., Jr. High-intensity interval training versus progressive high-intensity circuit resistance training on endothelial function and cardiorespiratory fitness in heart failure: A preliminary randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teffaha, D.; Mourot, L.; Vernochet, P.; Ounissi, F.; Regnard, J.; Monpère, C.; Dugué, B. Relevance of water gymnastics in rehabilitation programs in patients with chronic heart failure or coronary artery disease with normal left ventricular function. J. Card. Fail. 2011, 17, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägglund, E.; Hagerman, I.; Dencker, K.; Strömberg, A. Effects of yoga versus hydrotherapy training on health-related quality of life and exercise capacity in patients with heart failure: A randomized controlled study. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2017, 16, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Wu, S.J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Hou, J.C.; Zhang, K.; Fang, X.M. Tai Chi Exercise for Patients with Chronic Heart Failure: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 96, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Okamura, M.; Akashi, Y.J.; Tanaka, S.; Shimizu, M.; Tsuchikawa, Y.; Ashikaga, K.; Kamiya, K.; Kato, Y.; Nakayama, A.; et al. Impact of Long-Term Exercise-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Circ. J. 2024, 88, 1360–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Li, Y. Safety and efficacy of exercise training in elderly heart failure patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2013, 67, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambrecht, R.; Fiehn, E.; Weigl, C.; Gielen, S.; Hamann, C.; Kaiser, R.; Yu, J.; Adams, V.; Niebauer, J.; Schuler, G. Regular physical exercise corrects endothelial dysfunction and improves exercise capacity in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 1998, 98, 2709–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Craenenbroeck, E.M.; Hoymans, V.Y.; Beckers, P.J.; Possemiers, N.M.; Wuyts, K.; Paelinck, B.P. Exercise training improves function of circulating angiogenic cells in patients with chronic heart failure. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2010, 105, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haykowsky, M.J.; Liang, Y.; Pechter., D.; Jones, L.W.; McAlister, F.A.; Clark, A.M. A meta-analysis of the effect of exercise training on left ventricular remodeling in heart failure patients: The benefit depends on the type of training performed. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 2329–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, M.; Kozarez, I.; Adams, V.; Mangner, N.; Höllriegel, R.; Erbs, S.; Linke, A.; Möbius-Winkler, S.; Thiery, J.; Kratzsch, J.; et al. Age-related effects of exercise training on diastolic function in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: The Leipzig Exercise Intervention in Chronic Heart Failure and Aging (LEICA) Diastolic Dysfunction Study. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.I.; Aukrust, P.; Aarsland, T.; Dickstein, K. Effect of aerobic exercise training on plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha in patients with heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 88, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca-Mallada, R.; Migliaro, E.R.; Piskorski, J.; Guzik, P. Exercise training slows down heart rate and improves deceleration and acceleration capacity in patients with heart failure. J. Electrocardiol. 2012, 45, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Choi, Y.; Sajgalik, P.; No, M.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.; Heo, J.W.; Cho, E.J.; Chang, E.; Kang, J.H.; et al. Exercise as a Therapeutic Strategy for Sarcopenia in Heart Failure: Insights into Underlying Mechanisms. Cells 2020, 9, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechwatal, R.M.; Duck, C.; Gruber, G. Körperliches Training als Intervall- oder kontinuierliches Training bei chronischer Herzinsuffizienz zur Verbesserung der funktionellen Leistungskapazität, Hämodynamik und Lebensqualität—Eine kontrollierte Studie. Z. Für Kardiol. 2002, 91, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, D.C.; Richardson, R.S.; Haykowsky, M.J.; Hirai, D.M.; Musch, T.I. Exercise limitations in heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2018, 124, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.D.; Carey, M.F.; Selig, S.; Hayes, A.; Krum, H.; Patterson, J.; Toia, D.; Hare, D.L. Circuit resistance training in chronic heart failure improves skeletal muscle mitochondrial ATP production rate—A randomized controlled trial. J. Card. Fail. 2007, 13, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostakou, V.; Chatzimichail, K.; Dimopoulos, S.; Karatzanos, E.; Papazachou, O.; Tasoulis, A.; Anastasiou-Nana, M.; Roussos, C.; Nanas, S. Effects of interval cycle training with or without strength training on vascular reactivity in heart failure patients. J. Card. Fail. 2011, 17, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degache, F.; Garet, M.; Calmels, P.; Costes, F.; Bathélémy, J.C.; Roche, F. Enhancement of isokinetic muscle strength with a combined training programme in chronic heart failure. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2007, 27, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, B.A.; Lanza, I.R.; Henderson, G.C.; Rao, R.R.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Nair, K.S. Combined training enhances skeletal muscle mitochondrial oxidative capacity independent of age. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamari, M.; Kourek, C.; Sanoudou, D.; Delis, D.; Dimopoulos, S.; Rovina, N.; Nanas, S.; Karatzanos, E.; Philippou, A. Does the Addition of Strength Training to a High-Intensity Interval Training Program Benefit More the Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 24, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitzman, D.W.; Brubaker, P.; Morgan, T.; Haykowsky, M.; Hundley, G.; Kraus, W.E.; Eggebeen, J.; Nicklas, B.J. Effect of Caloric Restriction or Aerobic Exercise Training on Peak Oxygen Consumption and Quality of Life in Obese Older Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama 2016, 315, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borland, M.; Rosenkvist, A.; Cider, A. A group-based exercise program did not improve physical activity in patients with chronic heart failure and comorbidity: A randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 46, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, C.; Bajpeyi, S.; Smith, S.R. Determinants of intramyocellular triglyceride turnover: Implications for insulin sensitivity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 294, E203–E213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, A.J.; Adamopoulos, S.; Meyer, T.E.; Conway, J.; Sleight, P. Effects of physical training in chronic heart failure. Lancet 1990, 335, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvera-Tindel, T.; Doering, L.V.; Woo, M.A.; Khan, S.; Dracup, K. Effects of a home walking exercise program on functional status and symptoms in heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2004, 147, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, P.; Pozehl, B.; Williams, M.A.; Yates, B. Adherence to recommended exercise guidelines in patients with heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2017, 22, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. WHO Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hambrecht, R.; Niebauer, J.; Fiehn, E.; Kälberer, B.; Offner, B.; Hauer, K.; Riede, U.; Schlierf, G.; Kübler, W.; Schuler, G. Physical training in patients with stable chronic heart failure: Effects on cardiorespiratory fitness and ultrastructural abnormalities of leg muscles. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1995, 25, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyni-Lenné, R.; Dencker, K.; Gordon, A.; Jansson, E.; Sylvén, C. Comprehensive local muscle training increases aerobic working capacity and quality of life and decreases neurohormonal activation in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2001, 3, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, R.A.; Yakobov, S.; Polidovitch, N.; Debi, R.; Sanfrancesco, V.C.; Hood, D.A.; Lakin, R.; Backx, P.H. The effects of daily dose of intense exercise on cardiac responses and atrial fibrillation. J. Physiol. 2024, 602, 569–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, K.; Herrmann-Lingen, C.; Wachter, R.; Gelbrich, G.; Düngen, H.D.; Duvinage, A.; Hoischen, N.; von Oehsen, K.; Schwarz, S.; Hasenfuss, G.; et al. Effects of exercise training on different quality of life dimensions in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: The Ex-DHF-P trial. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2015, 22, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.F.; Lamas, G.A.; O’Meara, E.; Granger, C.B.; Dunlap, M.E.; McKelvie, R.S.; Probstfield, J.L.; Young, J.B.; Michelson, E.L.; Halling, K.; et al. Characterization of health-related quality of life in heart failure patients with preserved versus low ejection fraction in CHARM. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2007, 9, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary, R.A.; Sueta, C.A.; Dougherty, M.; Rosenberg, B.; Cheek, D.; Preisser, J.; Neelon, V.; McMurray, R. Home-based exercise improves functional performance and quality of life in women with diastolic heart failure. Heart Lung 2004, 33, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yan, J.; Guo, Y.; Yan, J. Effects of Tai Chi training on exercise capacity and quality of life in patients with chronic heart failure: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2013, 15, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysohoou, C.; Angelis, A.; Tsitsinakis, G.; Spetsioti, S.; Nasis, I.; Tsiachris, D.; Rapakoulias, P.; Pitsavos, C.; Koulouris, N.G.; Vogiatzis, I.; et al. Cardiovascular effects of high-intensity interval aerobic training combined with strength exercise in patients with chronic heart failure. A randomized phase III clinical trial. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 179, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, P.J.; Denollet, J.; Possemiers, N.M.; Wuyts, F.L.; Vrints, C.J.; Conraads, V.M. Combined endurance-resistance training vs. endurance training in patients with chronic heart failure: A prospective randomized study. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, G.Y.; McCarthy, E.P.; Wayne, P.M.; Stevenson, L.W.; Wood, M.J.; Forman, D.; Davis, R.B.; Phillips, R.S. Tai chi exercise in patients with chronic heart failure: A randomized clinical trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliou, M.C.; Vergès-Patois, B.; Pavy, B.; Charles-Nelson, A.; Monpère, C.; Richard, R.; Verdier, J.C. Effects of combined exercise training and electromyostimulation treatments in chronic heart failure: A prospective multicentre study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, T.D.; Cotter, J.D.; Ainslie, P.N.; Abraham, W.C.; Mockett, B.G.; Campbell, H.A.; Jones, E.M.W.; Jenkins, E.J.; Thomas, K.N. Fasting for 20 h does not affect exercise-induced increases in circulating BDNF in humans. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 2121–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; You, Q.; Hou, X.; Zhang, S.; Du, L.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. The effect of exercise on cognitive function in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 2908–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, E.; George, K.; Shave, R.; Whyte, G.; Ball, D. Does the human heart fatigue subsequent to prolonged exercise? Sports Med. 2003, 33, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-T.; Etnier, J.L.; Wu, C.-H.; Cho, Y.M.; Hung, T.M.; Chang, Y.K. Dose-Response Relationship between Exercise Duration and Executive Function in Older Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gary, R.; Lee, S.Y. Physical function and quality of life in older women with diastolic heart failure: Effects of a progressive walking program on sleep patterns. Prog. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2007, 22, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowicz, E.; Pencina, M.J.; Opolski, G.; Zareba, W.; Banach, M.; Kowalik, I.; Orzechowski, P.; Szalewska, D.; Pluta, S.; Glówczynska, R.; et al. Effects of a 9-Week Hybrid Comprehensive Telerehabilitation Program on Long-term Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure: The Telerehabilitation in Heart Failure Patients (TELEREH-HF) Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorana, A.; O’Driscoll, G.; Cheetham, C.; Collis, J.; Goodman, C.; Rankin, S.; Taylor, R.; Green, D. Combined aerobic and resistance exercise training improves functional capacity and strength in CHF. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2000, 88, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Conraads, V.; Corrà, U.; Dickstein, K.; Francis, D.P.; Jaarsma, T.; McMurray, J.; Pieske, B.; Piotrowicz, E.; Schmid, J.P.; et al. Exercise training in heart failure: From theory to practice. A consensus document of the Heart Failure Association and the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2011, 13, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, S.; Zwerink, M.; van Brussel, M.; van der Valk, P.; Wajon, E.; van der Palen, J. Effect of outpatient exercise training programmes in patients with chronic heart failure: A systematic review. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2012, 19, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvie, R.S.; Teo, K.K.; Roberts, R.; McCartney, N.; Humen, D.; Montague, T.; Hendrican, K.; Yusuf, S. Effects of exercise training in patients with heart failure: The Exercise Rehabilitation Trial (EXERT). Am. Heart. J. 2002, 144, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, K.M.; Langlo, K.A.R.; Salvesen, Ø.; Øyvind Ellingsen, R.M.; Vesterbekkmo, E.; Zanaboni, P.; Dalen, H.; Aksetøy, I.-L. Exercise-Based Telerehabilitation for Heart Failure Patients Declining Outpatient Rehabilitation—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2024, 57, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleg, J.L. Aerobic exercise in the elderly: A key to successful aging. Discov. Med. 2012, 13, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Su, H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Lv, Y.; Feng, L.; Yu, L. Effects of Exercise on Aerobic Capacity and Quality of Life in People with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105393
Liang Y, Su H, Xu Z, Liu X, Lv Y, Feng L, Yu L. Effects of Exercise on Aerobic Capacity and Quality of Life in People with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105393
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yin, Hao Su, Ze Xu, Xiaojie Liu, Yuanyuan Lv, Lin Feng, and Laikang Yu. 2025. "Effects of Exercise on Aerobic Capacity and Quality of Life in People with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105393
APA StyleLiang, Y., Su, H., Xu, Z., Liu, X., Lv, Y., Feng, L., & Yu, L. (2025). Effects of Exercise on Aerobic Capacity and Quality of Life in People with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105393







