Statistical Analysis of Soil Parameters Affecting the Bearing Capacity and Settlement Behaviour of Gravel Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Bearing Capacity Analysis Results
3.2. Consolidation Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sigdel, L.D.; Al-Qarawi, A.; Leo, C.J.; Liyanapathirana, S.; Hu, P. Geotechnical design practices and soil–structure interaction effects of an integral bridge system: A review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B.; Peacock, W.H. Test procedures for measuring soil liquefaction characteristics. J. Soil. Mech. Found. Div. 1971, 97, 1099–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, B. Laboratory Work in Soil Mechanics (No. Monograph). 1983. Available online: https://trid.trb.org/View/205995 (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B.; Mesri, G. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kaliakin, V. Soil Mechanics: Calculations, Principles, and Methods; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Scarfone, R.; Morigi, M.; Conti, R. Assessment of dynamic soil-structure interaction effects for tall buildings: A 3D numerical approach. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 128, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiakojouri, F.; De Biagi, V.; Chiaia, B.; Sheidaii, M.R. Progressive collapse of framed building structures: Current knowledge and future prospects. Eng. Struct. 2020, 206, 110061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avğın, S.; Köse, M.M.; Özbek, A. Damage assessment of structural and geotechnical damages in Kahramanmaraş during the February 6, 2023 earthquakes. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2024, 57, 101811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.A.; Prado Soares, F.V.; Sanchez, M. Settlement of footings on compacted and natural collapsible soils upon loading and soaking. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Leshchinsky, B.; Cui, K.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Y. Influence of failure mechanism on seismic bearing capacity factors for shallow foundations near slopes. Géotechnique 2021, 71, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Acharyya, R.; Alammyan, A. Bearing capacity and failure mechanism of shallow footings on unreinforced slopes: A state-of-the-art review. J. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 15, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, I.A.; Fattah, M.Y.; Mekkiyah, H. Relationship between the matric suction and the shear strength in unsaturated soil. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A.; Dai, G.L.; Du, Y.J. Effect of the uncertainty in soil-water characteristic curve on the estimated shear strength of unsaturated soil. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2020, 21, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briaud, J.L. Geotechnical Engineering: Unsaturated and Saturated Soils; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Nie, R.; Yue, Z.; Leng, W.; Guo, Y. Dynamic behaviors of fine-grained subgrade soil under single-stage and multi-stage intermittent cyclic loading: Permanent deformation and its prediction model. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 142, 106548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fu, H.; Ma, S.; Liu, Y. Deformation response induced by surcharge loading above shallow shield tunnels in soft soil. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M. Practice in Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering. In Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering Practice in Industrial Projects; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Alowaisy, A.; Yasufuku, N.; Ishikura, R.; Hatakeyama, M.; Kyono, S. Continuous pressurization method for a rapid determination of the soil water characteristics curve for remolded and undisturbed cohesionless soils. Soils Found. 2020, 60, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mısır, G. Granüler Stabilize Dolgu İle İyileştirilen Yumuşak Kil Zeminlere Oturan Temellerin Analizi. Master’s Thesis, Çukurova Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Adana, Türkiye, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhof, G.G. Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Footings on Sand Layer Overlying Clay. Can. Geotech. J. 1974, 11, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çinicioğlu, F. Zeminlerde Statik ve Dinamik Yükler Altında Taşıma Gücü Anlayışı ve Hesabı. 2005. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/340506023/ZEM%C4%B0NLERDE-STAT%C4%B0K-VE-D%C4%B0NAM%C4%B0K-YUKLER-ALTINDA-TA%C5%9EIMA-GUCU-HESABI-F-C%C4%B0N%C4%B0C%C4%B0O%C4%9ELU-pdf (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Alkaya, D.; Çobanoğlu, İ. Toprakarme (donatılı zemin) yapılar. Denizli İMO Bülten-İnceleme Araştırma 2007, 54, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Uzundurukan, S. İnce daneli zeminlerin bazı geoteknik özelliklerinin SPT ve DPT verilerine bağlı ampirik ifadeler ile tespitine yönelik bir çalışma. Master’s Thesis, Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, İnşaat Mühendisliği Ana Bilim Dalı, Isparta, Türkiye, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Peck, R.B.; Hanson, W.E.; Thornburn, T.H. Foundation Engineering, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Coduto, D.P. Foundation Design: Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kulhawy, F.H.; Mayne, P.W. Manual on Estimating Soil Properties for Foundation Design; EL-6800; Project 1493-6; Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI): Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- TS 1900; İnşaat Mühendisliğinde Zemin Laboratuvar Deneyleri-Bölüm 2-Mekanik Özelliklerin Tayini. Türk Standartları Enstitüsü: Ankara, Turkey, 2006.
- TS 1500:2000; İnşaat mühendisliğinde zeminlerin sınıflandırılması. Türk Standartları Enstitüsü: Ankara, Turkey, 2000.
- Kovačević, M.S.; Jurić-Kaćunić, D.; Librić, L.; Ivoš, G. Engineering soil classification according to EN ISO 14688-2:2018. Gradevinar 2018, 70, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.M.; Sobhan, K. Principles of Geotechnical Engineering; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Boumpoulis, V.; Depountis, N.; Pelekis, P.; Sabatakakis, N. SPT and CPT application for liquefaction evaluation in Greece. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Yamin, M.; Attom, M.; Al Hai, N. Correlations between SPT, CPT, and Vs for reclaimed lands near Dubai. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2022, 40, 4109–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragaszy, R.J.; Su, J.; Siddiqi, F.H.; Ho, C.L. Modeling strength of sandy gravel. J. Geotech. Eng. 1992, 118, 920–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.D.; Rollins, K.M. Pressuremeter testing in arid collapsible soils. Geotech. Test. J. 1997, 20, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, P.K.; Campanella, R.G.; Wightman, A. Spt-Cpt Correlations. J. Geotech. Eng. 1983, 109, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.D.; Bicalho, K.V. Proposals of SPT-CPT and DPL-CPT correlations for sandy soils in Brazil. J. Rock. Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez, J.I.; Martin, G.R.; Youd, T.L. Comparison of SPT-CPT liquefaction evaluations and CPT interpretations. Geotech. Spec. Publ. 2000, 285, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Burmister, D.M. Identification and Classification of Soil: An Apprasial and Statement of Principles; ASTM STP 113; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelpia, PA, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Burmister, D. Physical, stress-strain, and strength responses of granular soils. In Field Testing of Soils; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, B.B.A. The Consolidation and Strength Behavior of Mechanically Compressed Fine-Grained Sediments. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, S.L. Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 653. [Google Scholar]
- Önalp, A. Geoteknik Bilgisi 1, Zeminler ve Mekaniği; No. 27; Sakarya Üniversitesi Yayin: Adapazarı, Turkey, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cetin, B.; Akgün, H.; Kelam, A.A. Geotechnical properties of gravelly soils in Çankırı, Turkey. Eng. Geol. 2008, 96, 86–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kesimal, A.; Yılmaz, E.; Alp, I. Bearing capacity of gravel soils in the Mediterranean region of Turkey. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 3635–3642. [Google Scholar]
- Dündar, C. Deformation behavior of gravelly soils in the Black Sea region of Turkey. Geomech. Eng. 2016, 11, 621–630. [Google Scholar]
- Karabulut, H.; Schmittbuhl, J.; Lengline, O.; Bouchen, M. Seismicity distribution and locking depth along the Main Marmara Fault, Turkey. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2016, 17, 954–965. [Google Scholar]
- Ylmaz, Ö.; Özyalvaç, M.; Duman, F.; Çataklı, M.; Polat, Z. Offshore high-resolution seismic survey for a subsea tunnel across the Bosphorus Waterway, Istanbul, Turkey. Lead. Edge 2018, 37, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettis, W.; Barka, A. Geologic characterization of fault rupture hazard, Gumusova—Gerede Motorway. In Report Prepared for the Astaldi-Bayindir Joint Venture Turkey; Astaldi: Bolu, Turkey, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Şengör, A.M.C.; ve Yılmaz, Y. Tethyan evolution of Turkey: A plate tectonic approach. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 181–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, Y.; Tüysüz, O.; Yiğitbaş, E.; Genç, C.; Şengör, C. Geology and tectonic evolution of the pontides. AAPG Mem. 1997, 68, 183–226. [Google Scholar]
- Özmen, B. Düzce-Bolu Bölgesi’nin Jeolojisi, Diri Fayları ve Hasar Yapan Depremleri s:1-14, 12 Kasım 1999 Düzce Depremi Raporu; Özmen, B., Bağcı, G., Eds.; Bayındırlık ve İskan Bakanlığı Afet İşleri Genel Müdürlüğü, Deprem Araştırma Dairesi: Ankara, Turkey, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Erdik, M. Report on 1999 Kocaeli And Düzce (Turkey) Earthquakes. Structural Control for Civil and Infrastructure Engineering: 2001. pp. 149–186. Available online: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/abs/10.1142/9789812811707_0018?srsltid=AfmBOoqvCLTUCzQ77HbV2HToePiUDf4dFcc7l1ZTj95GlxGmdXmxhGKj (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Bozkurt, E.; Mittwede, S.K. Introduction to the geology of Turkey—A synthesis. Int. Geol. Rev. 2001, 43, 578–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengör, A.M.C.; Tüysüz, O.; Imren, C.; Sakınç, M.; Eyidoğan, H.; Görür, N.; Rangin, C. The North Anatolian fault: A new look. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2005, 33, 37–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, M.; Utkan, M. A New Approach to Standart Penetration Test Correlation For Kocaeli/Turkey. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Civil, Environmental and Medical Engineering (ICEME), New York, NY, USA, 4 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Karadeniz, E.; Sunbul, F. Land Use and Land Cover Change in Duzce Region Following the Major Earthquake: Implications for ANN and Markov Chain Analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MTA Genel Müdürlüğü ve Ankara Üniversitesi. 17 Ağustos 1999 Depremi Sonrası Düzce (Bolu) İlçesi Alternatif Yerleşim Alanlarının Jeolojik İncelenmesi, TÜBİTAK Yer Deniz Atmosfer Bilimleri ve Çevre Araştırma Grubu Raporu, 59s. 1999. Available online: https://eticaret.mta.gov.tr/index.php?route=product/product&product_id=10272 (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Emre, Ö. vd. (MTA), Varol, B. vd. (A.Ü.), 1999. 17 Ağustos 1999 Depremi Sonrası Düzce (Bolu) İlçesi Alternatif Yerleşim Alanlarının Jeolojik İncelemesi. TÜBİTAK (MTA Genel Müdürlüğü ve A.Ü. Ortak Araştırma Projesi). Available online: https://www.jmo.org.tr/resimler/ekler/c81efed973425e1_ek.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Available online: https://www.harita.gen.tr/81-duzce-haritasi/ (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- SPSS Statistics Version 22; IBM: Armonk, NY, USA, 2020.
- Das, M.B. Principle of Geotechnical Engineering, 7th ed.; Cengage Learning: Stamford, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, M.; Shanableh, A.; Hamad, K.; Tahmaz, A.; Arab, M.G.; Al-Sadoon, Z. Nomographs for predicting allowable bearing capacity and elastic settlement of shallow foundation on granular soil. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, R.; Momeni, E.; Hajihassani, M. Prediction of spread foundations’ settlement in cohesionless soils using a hybrid particle swarm optimization-based ANN approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Civil, Structural and Mechanical Engineering—CSM 2014, London, UK, 1–2 June 2014; pp. 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, D.; Sadeghian, M. Prediction of ultimate bearing capacity of shallow foundation on granular soils using Imperialist Competitive Algorithm based ANN. Soil Struct. Interact. J. 2019, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Nazir, R.; Momeni, E.; Marsono, K.; Maizir, H. An artificial neural network approach for prediction of bearing capacity of spread foundations. Sand J. Teknol. (Sci. Eng.) 2015, 72, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Örnek, M.; Laman, M.; Demir, A.; Yildiz, A. Prediction of bearing capacity of circular footings on soft clay stabilized with granular soil. Soils Found. 2012, 52, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmini, D.; Ilamparuthi, K.; Sudheer, K.P. Ultimate bearing capacity prediction of shallow foundations on cohesionless soils using neurofuzzy models. Comput. Geotech. 2008, 35, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul, T.; Krishna, V.R.; Singh, P.N. Evaluation of soil bearing capacity and settlements of soil for various hard rock depths for a 128 m high commercial building with raft foundation Temura Rahul. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 2604–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IS Code 640; Indian Standard Code of Practice for Determination of Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundations. 1981. Available online: https://law.resource.org/pub/in/bis/S03/is.6403.1981.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- IS 8009 Part-II; Indian Standard Code of Practice for Calculation of Settlement of Foundations. 1980. (Reaffirmed 2006). Available online: https://archive.org/details/gov.in.is.8009.2.1980 (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Kaniraj, S.R. Design Aids in Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering; Tata McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Mayne, P.W.; Poulos, H.G. Approximate displacement influence factors for elastic shallow foundations. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1999, 125, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, O.A. Full Hand Calculation, Analysis and Design of Multi-Story Building; 2016. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/37776849/FULL_HAND_CALCULATION_ANALYSIS_AND_DESIGN_OF_MULTI_STORY_BUILDING (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Rahul, T.; Krishna, V.R.; Singh, P.N. Modelling of Foundation for a 128-metre-High Commercial Building in the Vicinity of River Krishna Subjected to Severe Wind. Indian Geotech. J. 2021, 51, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, V.; Sharma, D.K.; Kumar, K.V.P.; Jain, A.; Thakar, C. Experimental investigations and optimization of surface roughness in turning of en 36 alloy steel using response surface methodology and genetic algorithm. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 6474–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, E. Konsolidasyon Özelliklerinin Arttırılmış Veri Seti İle İstatistiksel Analizi. Master’s Thesis, İstanbul Teknik Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, İstanbul, Turkey, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kılıç, E. Konsolidasyon Özelliklerinin İstatistiksel Analizi. Master’s Thesis, İstanbul Teknik Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, İstanbul, Turkey, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.M.; Sivakugan, N. Settlement of shallow foundations on granular soil—An overview. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2007, 1, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmertmann, J.H. Static cone to compute static settlement over sand. J. Soil. Mech. Found. Div. ASCE 1970, 96, 1011–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmertmann, J.H.; Hartman, J.P.; Brown, P.R. Improved strain influence factor diagrams. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. ASCE 1978, 104, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, J.B.; Burbidge, M.C.; Wilson, E.J.; Terzaghi. Settlement of foundations on sand and gravel. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1985, 78, 1325–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakugan, N.; Johnson, K. Settlement predictions in granular soils: A probabilistic approach. Geotechnique 2004, 54, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M.A.; Maier, H.R.; Jaksa, M.B. Predicting settlement of shallow foundations using neural networks. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2002, 128, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erzin, Y.; Gul, T.O. The use of neural networks for the prediction of the settlement of one-way footings on cohesionless soils based on standard penetration test. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.M.; Vanapalli, S.K.; Saatcioglu, M. Bearing capacity and settlement behaviour of footings in an unsaturated sand. In Proceedings of the 14th Pan-American Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Toronto, ON, USA, 2–6 October 2011; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Vanapalli, S.K.; Mohamed, F.M. Bearing capacity and settlement of footings in unsaturated sands. Geomate J. 2013, 5, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


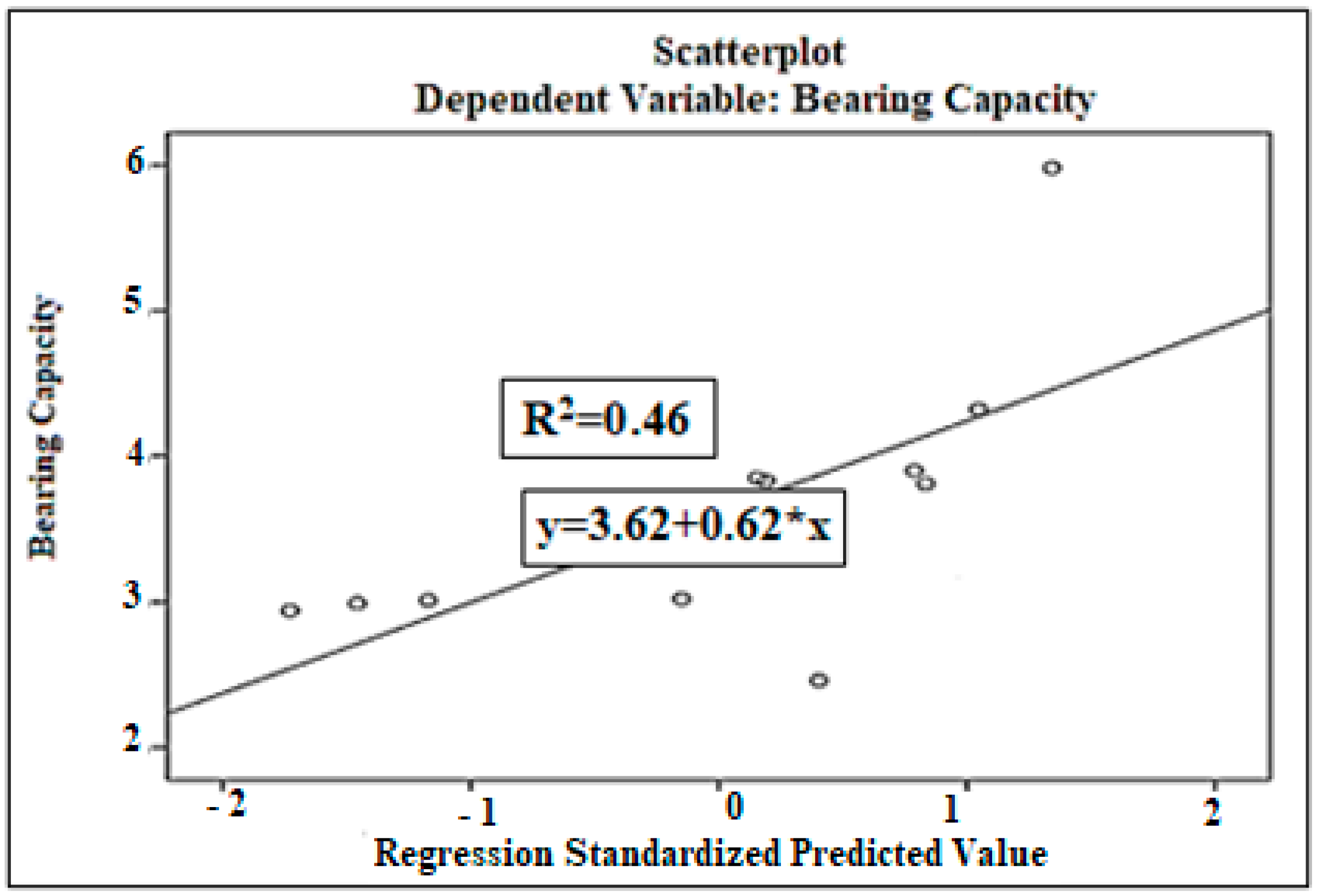
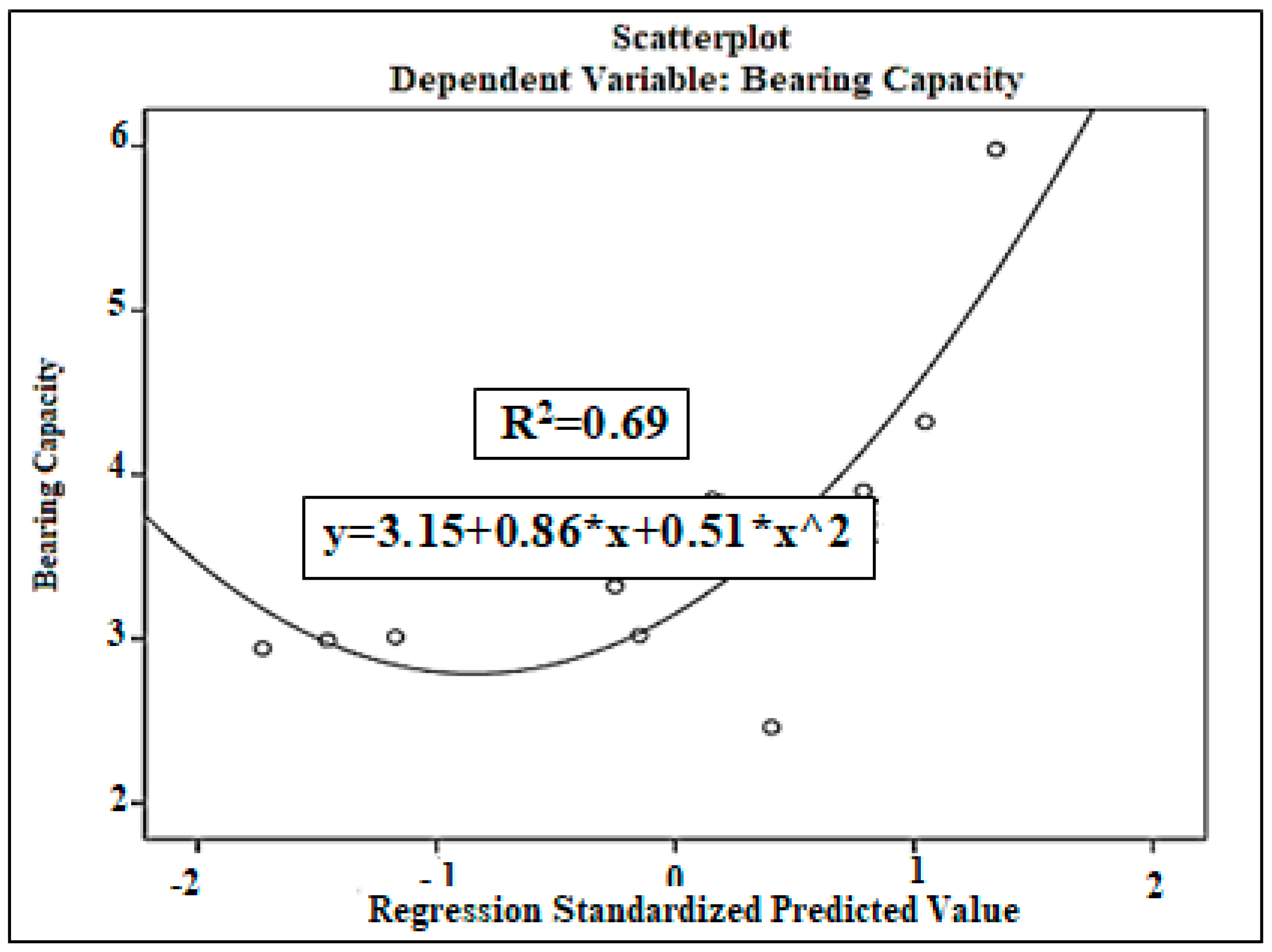
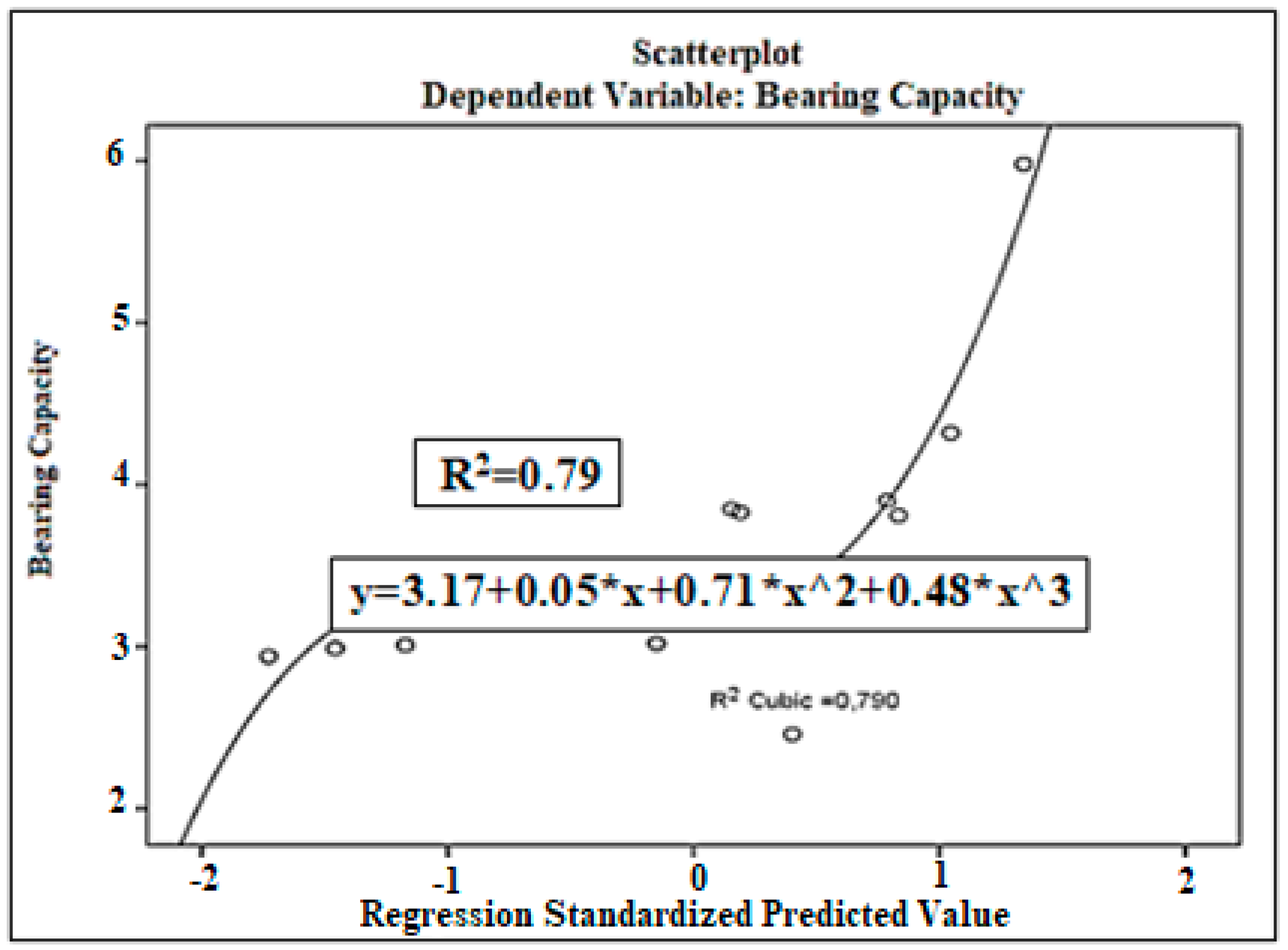
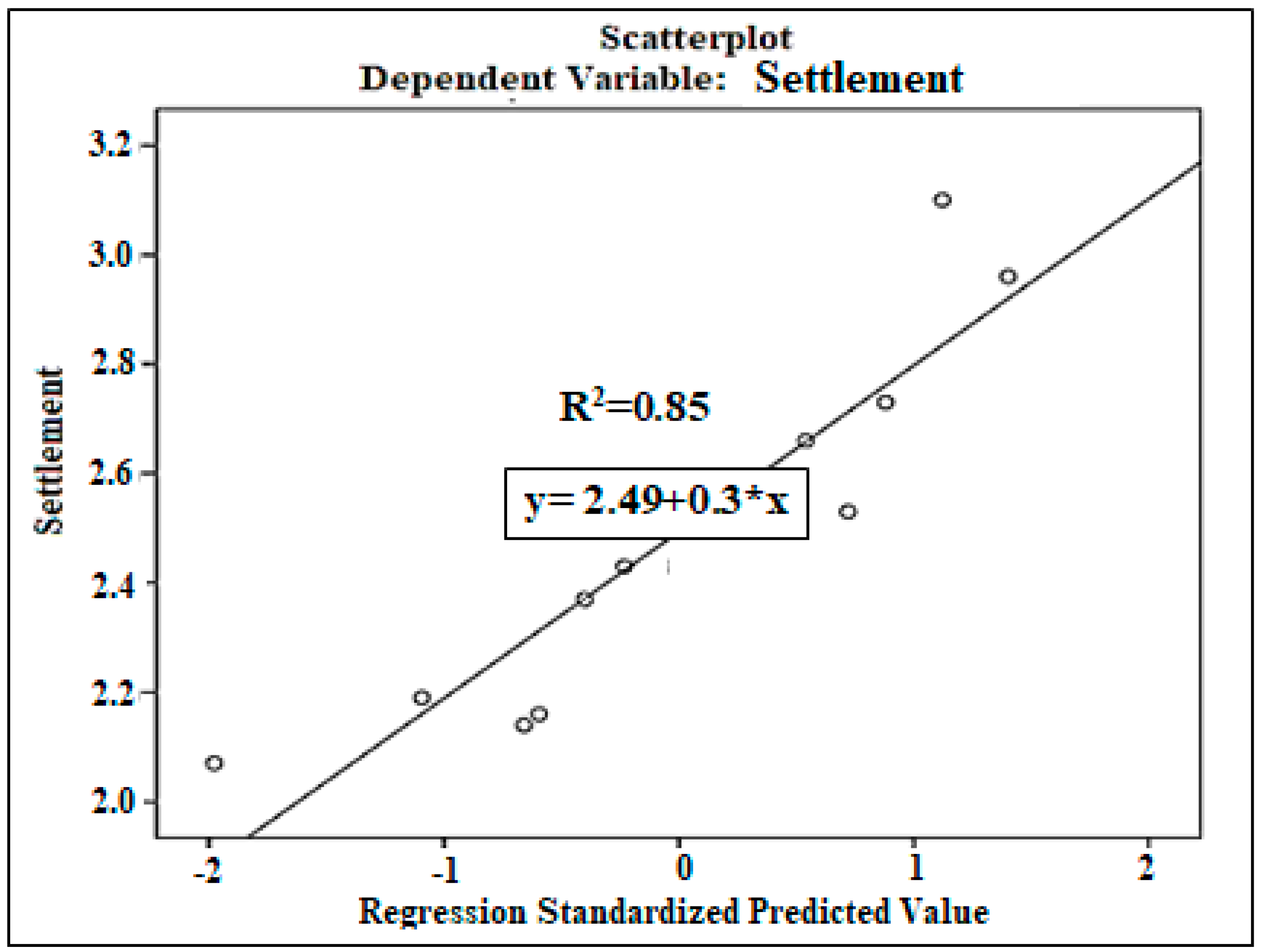
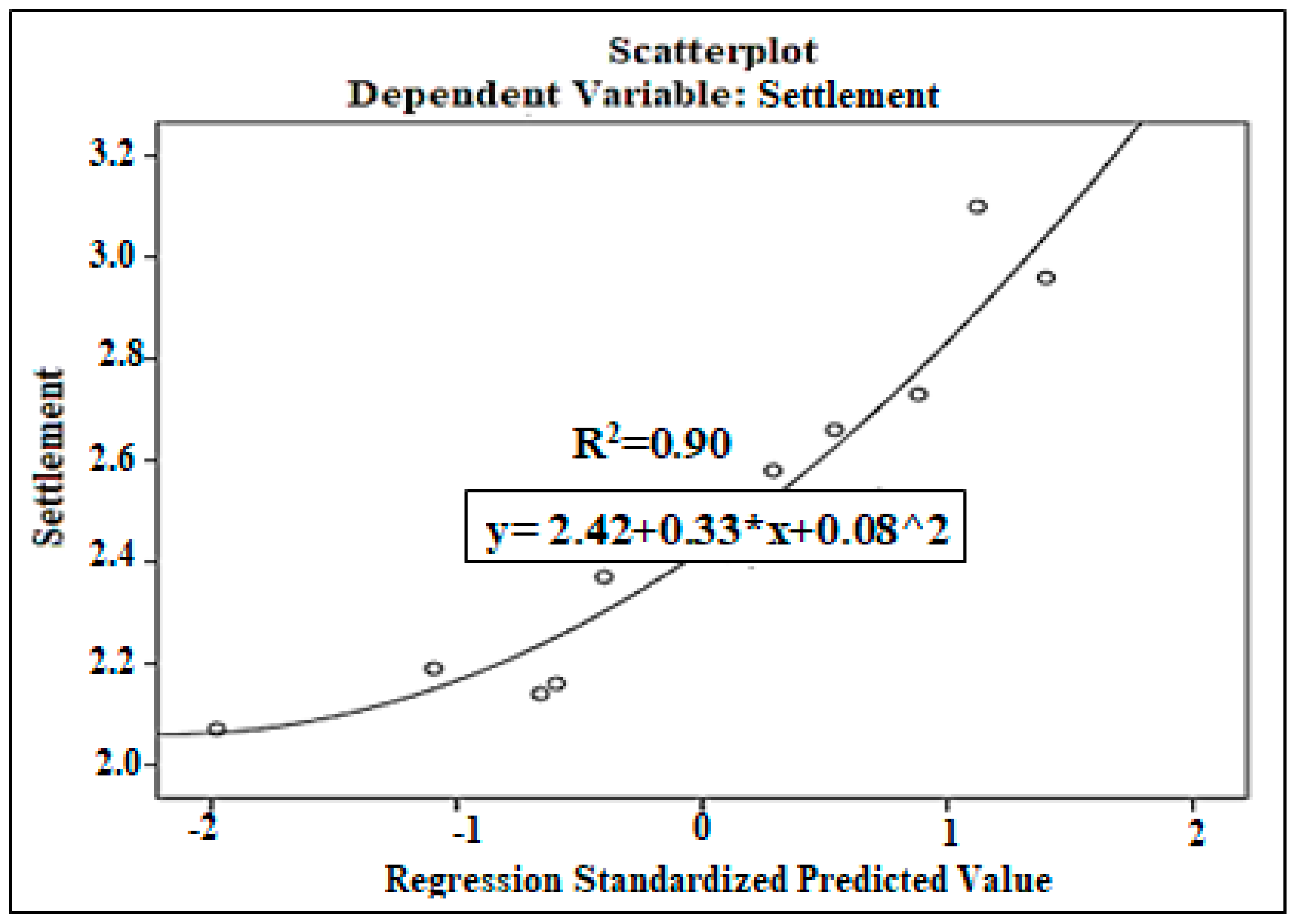
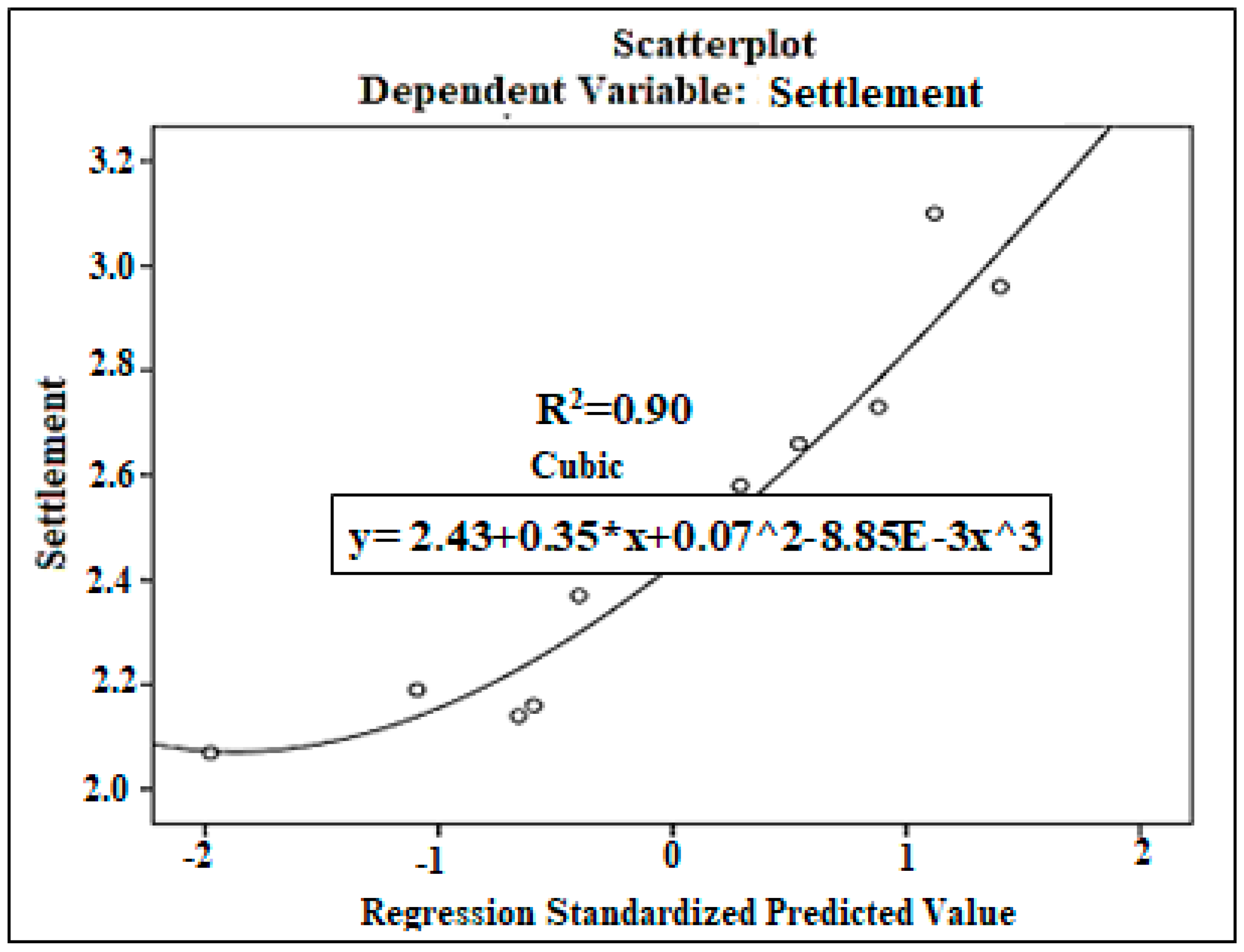
| N | Range | Min. | Max. | Mean Std. Error | Std. Deviation | Variance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Bearing Capacity (MPa) | 27 | 3.76 | 2.22 | 5.98 | 3.5052 | 0.19752 | 1.02635 | 1.053 |
| Settlement (cm) | 27 | 3.55 | 0.00 | 3.55 | 2.2964 | 0.14957 | 0.74783 | 0.559 |
| Excavation Level (m) | 27 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 3.00 | 2.0000 | 0.13868 | 0.72058 | 0.519 |
| Groundwater Level (m) | 27 | 5.00 | 2.00 | 7.00 | 3.9444 | 0.23010 | 1.19561 | 1.429 |
| Unit Volume Weight (g/cm3) | 27 | 0.40 | 1.73 | 2.13 | 1.8900 | 0.01963 | 0.10198 | 0.010 |
| Water Content (%) | 27 | 17.91 | 0.00 | 17.91 | 9.1452 | 0.80688 | 4.19266 | 17.578 |
| Sieve No. 10 (2.0 mm) | 27 | 18.70 | 43.80 | 62.50 | 51.3083 | 1.86562 | 6.46271 | 41.767 |
| Sieve No. 200 (0.074 mm) | 27 | 88.70 | 0.00 | 88.70 | 17.6081 | 3.60490 | 18.73159 | 350.872 |
| Internal Friction Angle (ø) | 27 | 20.00 | 0.00 | 20.00 | 12.9384 | 1.28065 | 6.40326 | 41.002 |
| Cohesion Coefficient (MPa) | 27 | 108 | 7 | 115 | 40.87 | 6.370 | 29.877 | 892.620 |
| Correlation Range (Can Be + and – Values) | Level of Relationship |
|---|---|
| 0.00–0.25 | Very weak relationship |
| 0.26–0.49 | Weak relationship |
| 0.50–0.69 | Moderate relationship |
| 0.70–0.89 | High relationship |
| 0.90–1.00 | Very high relationship |
| Bearing Capacity (MPa) | Excavation Level (m) | Ground Water Level (m) | Unit Volume Weight (g/cm3) | Water Content (%) | Sieve No. 10 (2 mm) | Sieve No. 200 (0.074 mm) | Internal Friction Angle | Cohesion Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bearing Capacity (MPa) | Correlation | 1 | 0.033 | −0.146 | −0.078 | 0.272 | 0.132 | 0.356 | −0.039 | 0.163 |
| Sig. | 0.871 | 0.468 | 0.699 | 0.170 | 0.682 | 0.069 | 0.853 | 0.468 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Excavation Level (m) | Correlation | 0.033 | 1 | 0.067 | 0.047 | −0.121 | −0.347 | 0.145 | 0.036 | −0.094 |
| Sig. | 0.871 | 0.740 | 0.816 | 0.547 | 0.270 | 0.471 | 0.864 | 0.676 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Ground water level (m) | Correlation | −0.146 | 0.067 | 1 | −0.457 * | −0.094 | −0.642 * | 0.323 | −0.225 | 0.190 |
| Sig | 0.468 | 0.740 | 0.016 | 0.639 | 0.024 | 0.101 | 0.279 | 0.397 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Unit Vol. Weight (g/cm3) | Correlation | −0.078 | 0.047 | −0.457 * | 1 | 0.051 | 0.632 * | −0.297 | 0.402 * | −0.210 |
| Sig. | 0.699 | 0.816 | 0.016 | 0.802 | 0.028 | 0.132 | 0.046 | 0.347 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Water Content (%) | Correlation | 0.272 | −0.121 | −0.094 | 0.051 | 1 | 0.297 | −0.158 | 0.269 | 0.028 |
| Sig. | 0.170 | 0.547 | 0.639 | 0.802 | 0.348 | 0.431 | 0.193 | 0.903 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Sieve No. 10 (2 mm) | Correlation | 0.132 | −0.347 | −0.642 * | 0.632 * | 0.297 | 1 | −0.687 * | −0.588 * | −0.596 * |
| Sig. | 0.682 | 0.270 | 0.024 | 0.028 | 0.348 | 0.014 | 0.044 | 0.041 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Sieve No. 200 (0.074 mm) | Correlation | 0.356 | 0.145 | 0.323 | −0.297 | −0.158 | −0.687 * | 1 | −0.567 ** | −0.010 |
| Sig. | 0.069 | 0.471 | 0.101 | 0.132 | 0.431 | 0.014 | 0.003 | 0.963 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Internal Friction Angle (ø) | Correlation | −0.039 | 0.036 | −0.225 | 0.402 * | 0.269 | −0.588 * | −0.567 ** | 1 | 0.322 |
| Sig.) | 0.853 | 0.864 | 0.279 | 0.046 | 0.193 | 0.044 | 0.003 | 0.144 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Cohesion Coefficient (MPa) | Correlation | 0.163 | −0.094 | 0.190 | −0.210 | 0.028 | −0.596 * | −0.010 | 0.322 | 1 |
| Sig. | 0.468 | 0.676 | 0.397 | 0.347 | 0.903 | 0.041 | 0.963 | 0.144 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Model Summary b | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate | Change Statistics | ||||
| R Square Change | F Change | df1 | df2 | Sig. F Change | |||||
| 1 | 0.678 a | 0.460 | −0.979 | 1.29345 | 0.460 | 0.320 | 8 | 3 | 0.912 |
| ANOVA a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| 1 | Regression | 4.279 | 8 | 0.535 | 0.320 | 0.912 b |
| Residual | 5.019 | 3 | 1.673 | |||
| Total | 9.298 | 11 | ||||
| Coefficients a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval for B | |||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | −16.430 | 124.229 | −0.132 | 0.903 | −411.784 | 378.923 | |
| Excavation level | 0.471 | 1.986 | 0.379 | 0.237 | 0.828 | −5.849 | 6.792 | |
| Groundwater level | 2.202 | 6.519 | 1.298 | 0.338 | 0.758 | −18.545 | 22.950 | |
| Unit weight | 10.094 | 35.070 | 0.683 | 0.288 | 0.792 | −101.514 | 121.702 | |
| Water content | −0.088 | 0.194 | −0.428 | −0.454 | 0.681 | −0.705 | 0.529 | |
| Sieve No. 10 | 0.125 | 0.122 | 0.879 | 1.029 | 0.379 | −0.262 | 0.512 | |
| Sieve No. 200 | 0.272 | 0.202 | 0.937 | 1.346 | 0.271 | −0.371 | 0.915 | |
| Internal friction angle | −1.628 | 12.123 | −3.138 | −0.134 | 0.902 | −40.208 | 36.951 | |
| Cohesion | 0.110 | 1.045 | 2.160 | 0.106 | 0.923 | −3.214 | 3.435 | |
| Settlement | Excavation Level | Groundwater Level | Unit Volume Weight | Water Content | Sieve No. 10 | Sieve No. 200 | Internal Friction Angle | Cohesion Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Settlement | Correlation | 1 | −0.402 * | 0.004 | −0.240 | −0.052 | −0.303 | −0.310 | −0.002 | 0.334 |
| Sig. | 0.046 | 0.986 | 0.247 | 0.806 | 0.338 | 0.132 | 0.993 | 0.150 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Excavation Level | Correlation | −0.402 * | 1 | 0.067 | 0.047 | −0.121 | −0.347 | 0.145 | 0.036 | −0.094 |
| Sig. | 0.046 | 0.740 | 0.816 | 0.547 | 0.270 | 0.471 | 0.864 | 0.676 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Ground water Level | Correlation | 0.004 | 0.067 | 1 | −0.457 * | −0.094 | −0.642 * | 0.323 | −0.225 | 0.190 |
| Sig | 0.986 | 0.740 | 0.016 | 0.639 | 0.024 | 0.101 | 0.279 | 0.397 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Unit Volume Weight | Correlation | −0.240 | 0.047 | −0.457 * | 1 | 0.051 | 0.632 * | −0.297 | 0.402 * | −0.210 |
| Sig. | 0.247 | 0.816 | 0.016 | 0.802 | 0.028 | 0.132 | 0.046 | 0.347 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Water Content | Correlation | −0.052 | −0.121 | −0.094 | 0.051 | 1 | 0.297 | −0.158 | 0.269 | 0.028 |
| Sig. | 0.806 | 0.547 | 0.639 | 0.802 | 0.348 | 0.431 | 0.193 | 0.903 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Sieve No. 10 | Correlation | −0.303 | −0.347 | −0.642 * | 0.632 * | 0.297 | 1 | −0.687 * | −0.588 * | −0.596 * |
| Sig. | 0.338 | 0.270 | 0.024 | 0.028 | 0.348 | 0.014 | 0.044 | 0.041 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Sieve No. 200 | Correlation | −0.310 | 0.145 | 0.323 | −0.297 | −0.158 | −0.687 * | 1 | −0.567 ** | −0.010 |
| Sig. | 0.132 | 0.471 | 0.101 | 0.132 | 0.431 | 0.014 | 0.003 | 0.963 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Internal Friction Angle | Correlation | −0.002 | 0.036 | −0.225 | 0.402 * | 0.269 | −0.588 * | −0.567 ** | 1 | 0.322 |
| Sig.) | 0.993 | 0.864 | 0.279 | 0.046 | 0.193 | 0.044 | 0.003 | 0.144 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Cohesion Coefficient | Correlation | 0.334 | −0.094 | 0.190 | −0.210 | 0.028 | −0.596 * | −0.010 | 0.322 | 1 |
| Sig. | 0.150 | 0.676 | 0.397 | 0.347 | 0.903 | 0.041 | 0.963 | 0.144 | ||
| N | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 | |
| Model Summary b | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | R | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate | Change Statistics | ||||
| R Square Change | F Change | df1 | df2 | Sig. F Change | |||||
| 1 | 0.920 a | 0.846 | 0.435 | 0.24882 | 0.846 | 2.058 | 8 | 3 | 0.299 |
| ANOVA a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
| 1 | Regression | 1.019 | 8 | 0.127 | 2.058 | 0.299 b |
| Residual | 0.186 | 3 | 0.062 | |||
| Total | 1.205 | 11 | ||||
| Coefficients a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval for B | |||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| 1 | (Constant) | 2.304 | 23.898 | 0.096 | 0.929 | −73.750 | 78.358 | |
| Excavation level | −0.122 | 0.382 | −0.271 | −0.318 | 0.771 | −1.338 | 1.094 | |
| Groundwater level | −1.673 | 1.254 | −2.739 | −1.334 | 0.274 | −5.664 | 2.318 | |
| Unit weight | −13.494 | 6.746 | −2.536 | −2.000 | 0.139 | −34.964 | 7.976 | |
| Water content | 0.067 | 0.037 | 0.908 | 1.802 | 0.169 | −0.051 | 0.186 | |
| Sieve No. 10 | −0.057 | 0.023 | −1.114 | −2.439 | 0.093 | −0.131 | 0.017 | |
| Sieve No. 200 | −0.062 | 0.039 | −0.589 | −1.582 | 0.212 | −0.185 | 0.062 | |
| Internal friction angle | 3.617 | 2.332 | 19.366 | 1.551 | 0.219 | −3.804 | 11.039 | |
| Cohesion | −0.348 | 0.201 | −18.907 | −1.730 | 0.182 | −0.987 | 0.292 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Güner, A.B.S.; Özgan, E. Statistical Analysis of Soil Parameters Affecting the Bearing Capacity and Settlement Behaviour of Gravel Soils. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5271. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105271
Güner ABS, Özgan E. Statistical Analysis of Soil Parameters Affecting the Bearing Capacity and Settlement Behaviour of Gravel Soils. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5271. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105271
Chicago/Turabian StyleGüner, Ayşe Bengü Sünbül, and Ercan Özgan. 2025. "Statistical Analysis of Soil Parameters Affecting the Bearing Capacity and Settlement Behaviour of Gravel Soils" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5271. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105271
APA StyleGüner, A. B. S., & Özgan, E. (2025). Statistical Analysis of Soil Parameters Affecting the Bearing Capacity and Settlement Behaviour of Gravel Soils. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5271. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105271






