Optimizing Internet of Things Honeypots with Machine Learning: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Honeypot
2.2. Internet of Things
2.3. Machine Learning
3. Comparison of Existing Surveys
4. Methodology
4.1. Research Design
4.2. Data Collection
(“iot” OR “internet of things”) AND “honeypot”
- Literature that did not address honeypots or was unrelated to IoT.
- Literature that lacked insights into machine learning techniques.
- Literature that focused narrowly on technologies outside the scope of our research.
- Literature that only focused on the hardware aspects of honeypots and did not incorporate machine learning.
4.3. Data Analysis
5. Findings
5.1. Interaction Honeypots
5.2. Machine Learning Techniques
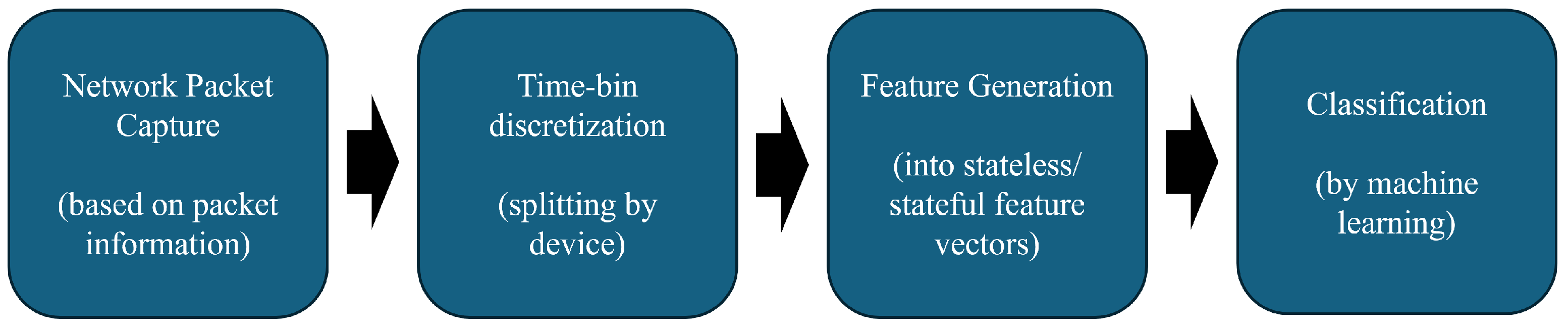
5.3. Detection Architecture
5.4. Machine Learning Classifiers
6. Discussion
6.1. Potential Advantages of Dynamic Honeypots in Internet of Things over Adaptative Honeypots
6.2. Combined Advantages of Multiple Machine Learning Techniques in Internet of Things Honeypots
6.3. Limitations
6.4. Future Research Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKinsey & Company. The Internet of Things: Catching Up to an Accelerating Opportunity. Report. 2021. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/mckinsey/business%20functions/mckinsey%20digital/our%20insights/iot%20value%20set%20to%20accelerate%20through%202030%20where%20and%20how%20to%20capture%20it/the-internet-of-things-catching-up-to-an-accelerating-opportunity-final.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- Kozlov, D.; Veijalainen, J.; Ali, Y. Security and Privacy Threats in IoT Architectures. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Body Area Networks, Oslo, Norway, 24–26 February 2012; pp. 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, N. Research of MQTT, CoAP, HTTP and XMPP IoT Communication Protocols for Embedded Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 XXIX International Scientific Conference Electronics (ET), Sozopol, Bulgaria, 16–18 September 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringer, M.L.; Chelmecki, C.A.; Fujinoki, H. A Survey: Recent Advances and Future Trends in Honeypot Research. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Inf. Secur. 2012, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pa, Y.M.P.; Suzuki, S.; Yoshioka, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Kasama, T.; Rossow, C. IoTPOT: A Novel Honeypot for Revealing Current IoT Threats. J. Inf. Process. 2016, 24, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Hussain, R.; Hassan, S.A.; Hossain, E. Machine Learning in IoT Security: Current Solutions and Future Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2020, 22, 1686–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.; Beyioku, K.; Yousefi, M. Securing Smart Cities Through Machine Learning: A Honeypot-Driven Approach to Attack Detection in Internet of Things Ecosystems. IET Smart Cities 2024, 6, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlin, C. Guidelines for Snowballing in Systematic Literature Studies and a Replication in Software Engineering. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering, London, UK, 13–14 May 2014; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Watson, R.T. Analyzing the Past to Prepare for the Future: Writing a Literature Review. MIS Q. 2002, 26, xiii–xxiii. [Google Scholar]
- Spitzner, L. Honeypots: Catching the Insider Threat. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–12 December 2003; pp. 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Pan, L.; Xiang, Y. Design Honeypots. In Honeypot Frameworks and Their Applications: A New Framework; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mokube, I.; Adams, M. Honeypots: Concepts, Approaches, and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual ACM Southeast Conference, Winston-Salem, NC, USA, 23–24 March 2007; pp. 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, N.; Shankar, P.; Arvind, P.V.; Singh, V. Intelligent Insight into IoT Threats: Leveraging Advanced Analytics with Honeypots for Anomaly Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 9th International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Pune, India, 5–7 April 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lingenfelter, B.; Vakilinia, I.; Sengupta, S. Analyzing Variation Among IoT Botnets Using Medium Interaction Honeypots. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–8 January 2020; pp. 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, S. IoT Security Challenges and Mitigations: An Introduction. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.14618. [Google Scholar]
- Sharmeela, C.; Sanjeevikumar, P.; Sivaraman, P.; Joseph, M. IoT, Machine Learning and Blockchain Technologies for Renewable Energy and Modern Hybrid Power Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, P.P.; Shah, S. A Review of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fourth International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, India, 16–18 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, R.; Jadhav, A.; Choudhary, G.; Dragoni, N.; Mishra, M.; Lalwani, P. ML-Based 5G Network Slicing Security: A Comprehensive Survey. Future Internet 2022, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.; Aris, A.; Canberk, B.; Uluagac, A.S. A Survey of Honeypots and Honeynets for Internet of Things, Industrial Internet of Things, and Cyber-Physical Systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 2351–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Shukla, H.; Goel, D. A Comprehensive Survey on DDoS Detection, Mitigation, and Defense Strategies in Software-Defined Networks. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 13129–13164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Pateriya, P.K. A Survey on Security Concerns in Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 14–15 June 2018; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, A.D.; Kumar, G.N.; Khorajiya, M. Survey of Snaring Cyber Attacks on IoT Devices with Honeypots and Honeynets. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT), Pune, India, 6–8 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, M.F.; Razali, M.N.; Mansor, F.Z.; Muruti, G.; Jamil, N. IoT Honeypot: A Review from Researcher’s Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Application, Information and Network Security (AINS), Langkawi, Malaysia, 21–22 November 2018; pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.; Vakkalanka, S.; Kuzniarz, L. Guidelines for Conducting Systematic Mapping Studies in Software Engineering: An Update. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2015, 64, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, A. Predication Attacks Based on Intelligent Honeypot Technique. Inf. Sci. Lett. 2023, 12, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; Kantarcioglu, M.; Vorobeychik, Y.; Kamhoua, C. IoTFlowGenerator: Crafting Synthetic IoT Device Traffic Flows for Cyber Deception. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.00925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chempavathy, B.; Deshmukh, V.M.; Datta, A.; Shiva, A.T.; Singh, G. An Exploration into Secure IoT Networks Using Deep Learning Methodologies. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference for Advancement in Technology (ICONAT), Goa, India, 21–22 January 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, P.J.; Hung, T.C. Enhanced Attack Blocking in IoT Environments: Engaging Honeypots and Machine Learning in SDN OpenFlow Switches. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2020, 23, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, K.A.; Papa, J.P.; Lisboa, C.O.; Munoz, R.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Internet of Things: A Survey on Machine Learning-Based Intrusion Detection Approaches. Comput. Netw. 2019, 151, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, V.; Ovasapyan, T.; Ivanov, D.V.; Konoplev, A.S.; Moskvin, D.A. Generation of Synthetic Data for Honeypot Systems Using Deep Learning Methods. Autom. Control Comput. Sci. 2022, 56, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, S.; Schukat, M.; Barrett, E. New Framework for Adaptive and Agile Honeypots. Etri J. 2020, 42, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghazi, A.; Rachid, A.M. Machine Learning and Datamining Methods for Hybrid IoT Intrusion Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Artificial Intelligence: Technologies and Applications (CloudTech), Marrakesh, Morocco, 24–26 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- El-Taie, M.; Kraidi, A.Y. A Deep Learning Framework for Securing IoT Against Malwares. J. Cybersecur. Inf. Manag. 2023, 11, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, J.; Aris, A.; Babun, L.; Uluagac, A.S. S-Pot: A Smart Honeypot Framework with Dynamic Rule Configuration for SDN. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2022–2022 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Liu, H.; Cao, G.; Zhu, S.; La Porta, T. HoneyIoT: Adaptive High-Interaction Honeypot for IoT Devices Through Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Security and Privacy in Wireless and Mobile Networks, Guildford, UK, 29 May–1 June 2023; pp. 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahsheh, K.M.; Chen, C.H. A Survey of Using Machine Learning in IoT Security and the Challenges Faced by Researchers. Informatica 2023, 47, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Automatic Identification of Honeypot Server Using Machine Learning Techniques. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2019, 2019, 2627608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, M.; Nakamura, A. A Heuristics and Machine Learning Hybrid Approach to Adaptive Cyberattack Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Computer, Data Sciences and Applications (ACDSA), Victoria, Seychelles, 1–2 February 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Eusufzai, F.; Azharuddin Redwan, M.; Ahmed, M.; Sabuj, S.R. Artificial Intelligence for Cyber Security: Performance Analysis of Network Intrusion Detection. In Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Cyber Security: Next Generation Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Janet, B.; Eswari, R. Multi Platform Honeypot for Generation of Cyber Threat Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 9th International Conference on Advanced Computing (IACC), Tiruchirappalli, India, 13–14 December 2019; pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layton, J.; Hu, F.; Hei, X. Survey of Machine Learning Defense Strategies. In AI, Machine Learning and Deep Learning; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Abdullah, A.; Jhanjhi, N. A Review on Honeypot-Based Botnet Detection Models for Smart Factory. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Abdullah, A.; Jhanjhi, N.; Kok, S. Classification of Botnet Attacks in IoT Smart Factory Using Honeypot Combined with Machine Learning. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Abdullah, A.; Jhanjhi, N.; Kok, S. Honeypot Coupled Machine Learning Model for Botnet Detection and Classification in IoT Smart Factory—An Investigation. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Subang Jaya, Malaysia, 25 November 2020; Volume 335, p. 04003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lang, B. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods for Intrusion Detection Systems: A Survey. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S. Detection of IoT Botnet Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Guangzhou, China, 27–30 July 2019; pp. 8381–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, V.; Singh, J. Malware Detection and Analysis Using Modern Honeypot Allied with Machine Learning: A Performance Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 6–8 July 2023; pp. 1539–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, I.M.M.; Rahardjo, B. Malware Detection Using Honeypot and Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th International Conference on Cyber and IT Service Management (CITSM), Jakarta, Indonesia, 6–8 November 2019; Volume 7, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mfogo, V.S.; Zemkoho, A.; Njilla, L.; Nkenlifack, M.; Kamhoua, C. AIIPot: Adaptive Intelligent-Interaction Honeypot for IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 34th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Toronto, ON, Canada, 5–8 September 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, M.; Abd Allah, A.M.; Hassanien, A.E. Developing an Efficient Feature Engineering and Machine Learning Model for Detecting IoT-Botnet Cyber Attacks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 91038–91052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashaei, A.; Akbari, M.E.; Lighvan, M.Z.; Charmin, A. Deep Learning Based Early Intrusion Detection in IIoT using Honeypot. Majlesi J. Electr. Eng. 2023, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pauna, A.; Bica, I.; Pop, F.; Castiglione, A. On the Rewards of Self-Adaptive IoT Honeypots. Ann. Telecommun. 2019, 74, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothumani, P.; Reddy, E.S. Network Intrusion Detection Using Ensemble Weighted Voting Classifier Based Honeypot Framework. J. Auton. Intell. 2024, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, W.B.; Aslam, B.; Abbas, H.; Afzal, H.; Khalid, S.B. A Deep Learning Assisted Personalized Deception System for Countering Web Application Attacks. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2022, 67, 103169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kapoor, S.; Sharma, R. Ransomware Detection, Prevention and Protection in IoT Devices Using ML Techniques Based on Dynamic Analysis Approach. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2023, 14, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinan, K.; Alsubhi, K.; Alzahrani, A.; Ashraf, M.U. Machine Learning-Based Botnet Detection in Software-Defined Network: A Systematic Review. Symmetry 2021, 13, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobana, M.; Poonkuzhali, S. A Novel Approach to Detect IoT Malware by System Calls Using Deep Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Innovative Trends in Information Technology (ICITIIT), Kottayam, India, 13–14 February 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, R.K.; Bashir, B.; Hota, C. Attack Detection and Forensics Using Honeypot in IoT Environment. In Proceedings of the Distributed Computing and Internet Technology: 15th International Conference, ICDCIT, Bhubaneswar, India, 10–13 January 2019; pp. 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Li, J.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.A.; Wang, L.; Li, B. Modeling and Clustering Attacker Activities in IoT Through Machine Learning Techniques. Inf. Sci. 2019, 479, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Bu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J. Application of Artificial Intelligence Technology in Honeypot Technology. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Endogenous Security, Nanjing, China, 21–22 April 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, A.Z.; Liu, G.; Ou, X.; Singhal, A. Revealing Human Attacker Behaviors Using an Adaptive Internet of Things Honeypot Ecosystem. In IFIP International Conference on Digital Forensics; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, C.W.; Chen, S.W.; Ban, T.; Kuo, S.Y. Machine Learning Framework to Analyze IoT Malware Using ELF and Opcode Features. Digit. Threat. Res. Pract. 2020, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsemogne, O.; Hayel, Y.; Kamhoua, C.; Deugoué, G. Game-Theoretic Modeling of Cyber Deception Against Epidemic Botnets in Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 2678–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluchamy, S.; Kathavarayan, R.S. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Building Honeypots Against Runtime DoS Attack. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 3981–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, R.; Jain, A.K. A Honeypot with Machine Learning Based Detection Framework for Defending IoT Based Botnet DDoS Attacks. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 23–25 April 2019; pp. 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dou, Y.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J. IoTCMal: Towards a Hybrid IoT Honeypot for Capturing and Analyzing Malware. In Proceedings of the ICC 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 7–11 June 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Cao, C.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K. Game Analysis and Decision Making Optimization of Evolutionary Dynamic Honeypot. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2024, 119, 109534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, J. Brief Industry Paper: Catching IoT Malware in the Wild Using HoneyIoT. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 27th Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium (RTAS), Nashville, TN, USA, 18–21 May 2021; pp. 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kakei, S.; Saito, S. Firmpot: A Framework for Intelligent-Interaction Honeypots Using Firmware of IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2021 Ninth International Symposium on Computing and Networking Workshops (CANDARW), Matsue, Japan, 23–26 November 2021; pp. 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.N.; Guo, W.K.; Liu, Y.Z.; Cao, Y.P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.F. An Automatic Features Extraction Model of IDS for IoT. In International Conference on Computer Engineering and Networks; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinly, S.S.S.; Raja, R.S. Investigation of Machine Learning Techniques in Intrusion Detection System for IoT Network 2020. In Proceeding of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Sustainable Systems (ICISS), Thoothukudi, India, 3–5 December 2020; pp. 1164–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Benerradi, J.; Clos, J.; Landowska, A.; Valstar, M.F.; Wilson, M.L. Benchmarking framework for machine learning classification from fNIRS data. Front. Neuroergon. 2023, 4, 994969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machine Learning Models Organization Practical Guide: Deploying Machine Learning Models in Real-World. 2023. Available online: https://machinelearningmodels.org/practical-guide-deploying-machine-learning-models-in-real-world/ (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Paleyes, A.; Urma, R.G.; Lawrence, N.D. Challenges in Deploying Machine Learning: A Survey of Case Studies. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, C.; Paleyes, A.; Thodoroff, P.; Lawrence, N.D. Real-world Machine Learning Systems: A Survey from a Data-Oriented Architecture Perspective. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.04810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author | Year | ML Techniques | Honeypot Technology | IoT Enviroment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dangi [18] | 2022 | X | ||
| Franco [19] | 2021 | X | X | |
| Jain [20] | 2024 | X | ||
| Kaur [21] | 2018 | X | partly | |
| Oza [22] | 2018 | X | X | |
| Razali [23] | 2018 | X | X | |
| This paper | 2025 | X | X | X |
| Category | Hits | Relevant Literature | Selected Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACM | 40 | 40 | 34 |
| IEEE Xplore | 219 | ||
| Scopus | 246 | ||
| DTU Find | 265 | ||
| Backward | 1314 | 28 | 10 |
| Forward | 674 | 53 | 5 |
| Total | 49 |
| Author | Year | Interaction Honeypots | Machine Learning Technique | Detection Architecture | Classifiers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Interaction | High Interaction | Supervised | Unsupervised | Reinforcement | Malware Detection | Adaptive Honeypots | Method | Framework | ||
| Alshahrani [25] | 2023 | X | X | |||||||
| Bao [26] | 2023 | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Bringer [4] | 2012 | X | X | |||||||
| Chempayathy [27] | 2022 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Chuang [28] | 2020 | X | ||||||||
| Da Costa [29] | 2019 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Danilov [30] | 2022 | X | X | |||||||
| Dara [13] | 2024 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Dowling [31] | 2020 | X | X | X | X | |||||
| El Ghazi [32] | 2020 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| El-Taie [33] | 2023 | X | X | |||||||
| Franco [34] | 2022 | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Guan [35] | 2023 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Harahsheh [36] | 2023 | X | X | |||||||
| Huang [37] | 2019 | X | ||||||||
| Iwabuchi [38] | 2024 | X | ||||||||
| Khan [39] | 2022 | X | ||||||||
| Kumar [40] | 2019 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Layton [41] | 2023 | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Lee [42] | 2020 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Lee [43] | 2021 | X | X | |||||||
| Lee [44] | 2021 | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Lingenfelter [14] | 2020 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Liu [45] | 2019 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Liu [46] | 2019 | X | ||||||||
| Mahajan [47] | 2023 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Matin [48] | 2019 | X | X | |||||||
| Mfogo [49] | 2023 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Panda [50] | 2021 | X | ||||||||
| Pashaei [51] | 2023 | X | X | |||||||
| Pauna [52] | 2019 | X | X | |||||||
| Pothumani [53] | 2024 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Shahid [54] | 2022 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Sharma [55] | 2023 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Shinan [56] | 2021 | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Shobana [57] | 2020 | X | X | |||||||
| Shrivastava [58] | 2019 | X | X | |||||||
| Sun [59] | 2019 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Sun [60] | 2022 | X | X | |||||||
| Tabari [61] | 2023 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Tien [62] | 2020 | X | X | |||||||
| Tsemogne [63] | 2021 | X | ||||||||
| Veluchamy [64] | 2022 | X | ||||||||
| Vishwakarma [65] | 2019 | X | ||||||||
| Wang [66] | 2020 | X | X | X | ||||||
| Wang [67] | 2024 | X | X | |||||||
| Xu [68] | 2021 | X | X | |||||||
| Yamamoto [69] | 2021 | X | X | |||||||
| Yu [70] | 2022 | X | X | |||||||
| 13 | 18 | 24 | 16 | 7 | 14 | 15 | 14 | 9 | ||
| Learning Type | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | FPR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised learning | 0.953 (Weka), | 0.82 [37] | 0.82 [37] | 0.219 (Weka), |
| 0.96 (R-Studio) [44] | 0.2667 (R-Studio) [44] | |||
| Unsupervised learning | 100% (CNN + ScS), | 100% micro and macro (CNN + ScS), | 100% micro and macro (CNN + ScS), | Not explicitly given; |
| 100% (DMLP + ScS) [50] | 100% micro and macro (DMLP + ScS) [50] | 100% micro and macro (DMLP + ScS) [50] | noted issue with unclassified instances [50] | |
| Reinforcement learning | Highest average reward (A2C, PPO) [35] | - | - | -1 reward for incorrect response, used as FPR proxy [35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lanz, S.; Pignol, S.L.-R.; Schmitt, P.; Wang, H.; Papaioannou, M.; Choudhary, G.; Dragoni, N. Optimizing Internet of Things Honeypots with Machine Learning: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105251
Lanz S, Pignol SL-R, Schmitt P, Wang H, Papaioannou M, Choudhary G, Dragoni N. Optimizing Internet of Things Honeypots with Machine Learning: A Review. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105251
Chicago/Turabian StyleLanz, Stefanie, Sarah Lily-Rose Pignol, Patrick Schmitt, Haochen Wang, Maria Papaioannou, Gaurav Choudhary, and Nicola Dragoni. 2025. "Optimizing Internet of Things Honeypots with Machine Learning: A Review" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105251
APA StyleLanz, S., Pignol, S. L.-R., Schmitt, P., Wang, H., Papaioannou, M., Choudhary, G., & Dragoni, N. (2025). Optimizing Internet of Things Honeypots with Machine Learning: A Review. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105251









