Research on Supply Chain Network Resilience: Considering Risk Propagation and Node Type
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Supply Chain Network Resilience
2.2. Supply Chain Network Risk Propagation
3. Supply Chain Network Risk Propagation Model and Resilience Metric
3.1. Supply Chain Network Risk Propagation Model
3.1.1. Supply Chain Networks with Tunable Parameters
3.1.2. SIS Model
3.2. Resilience Metric
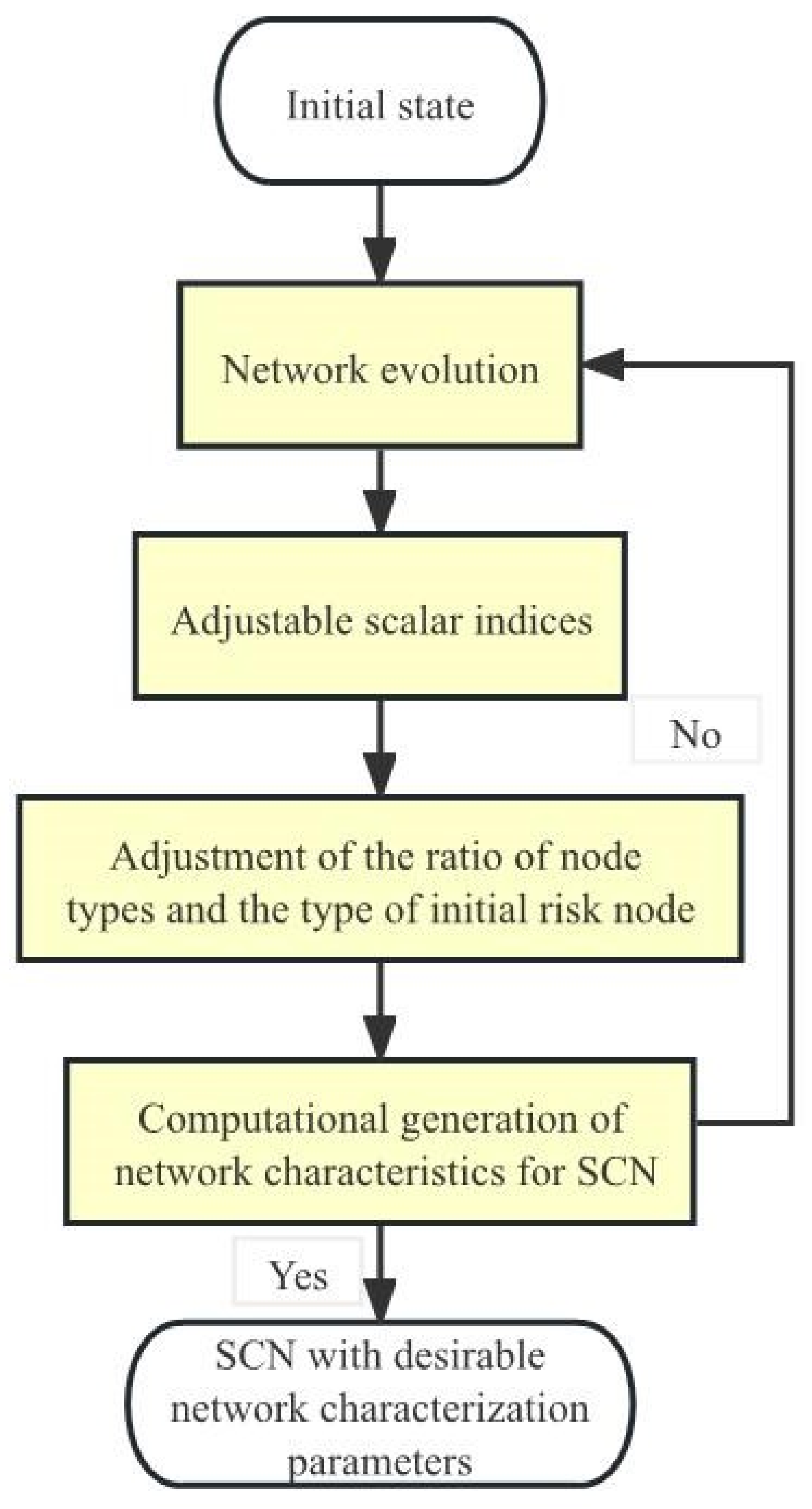
4. Numerical Simulation
4.1. Simulation Setup
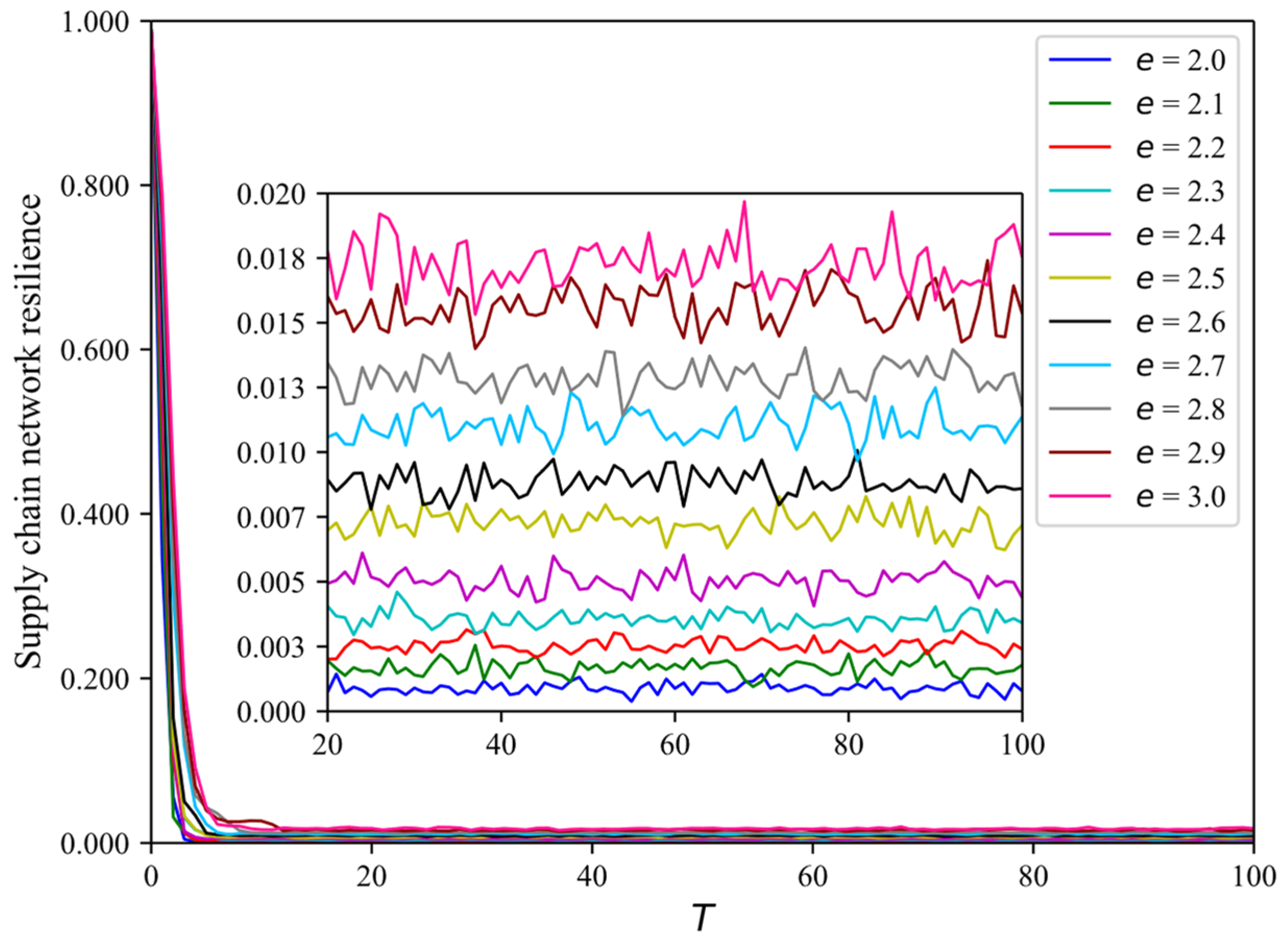
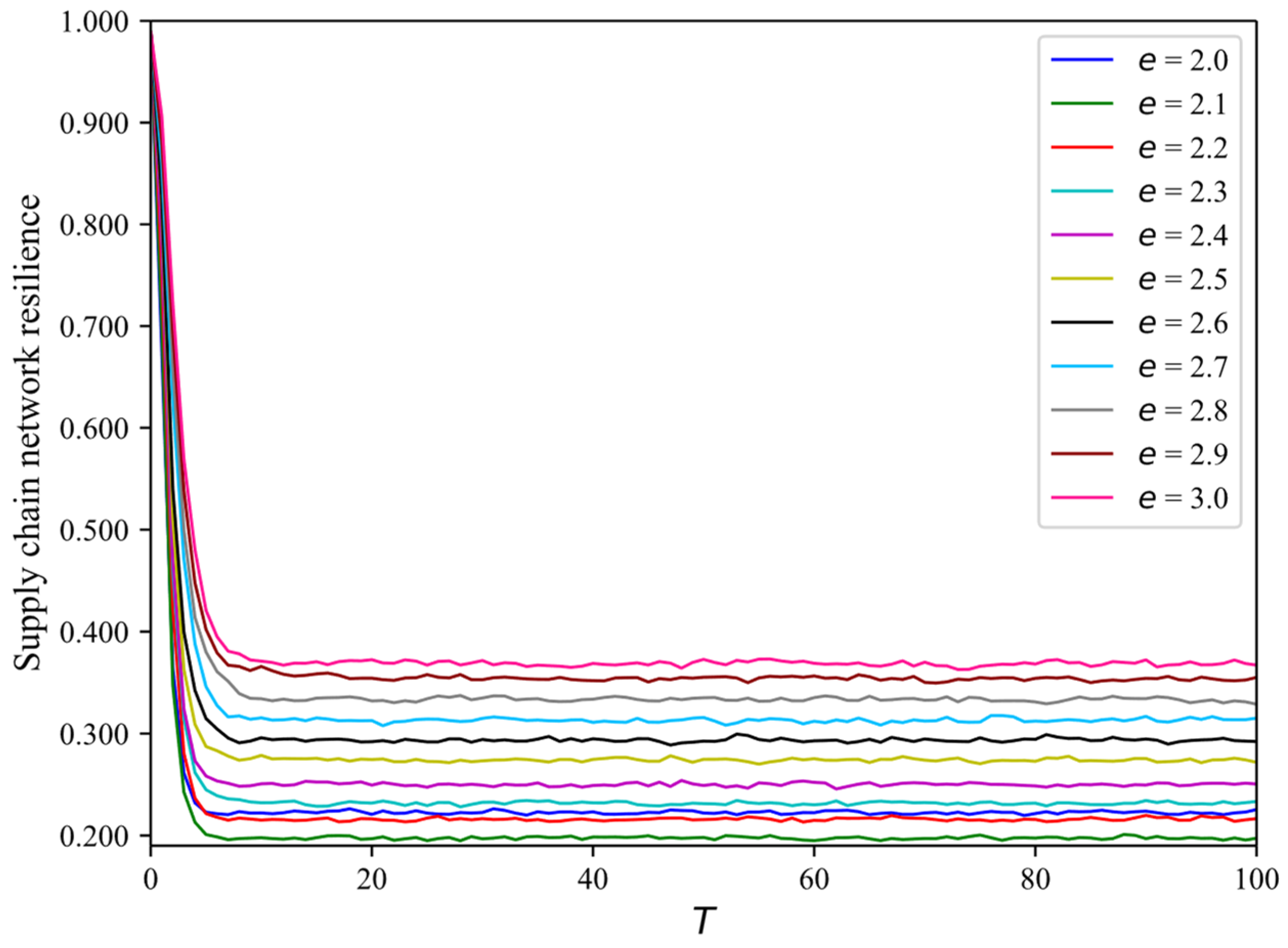
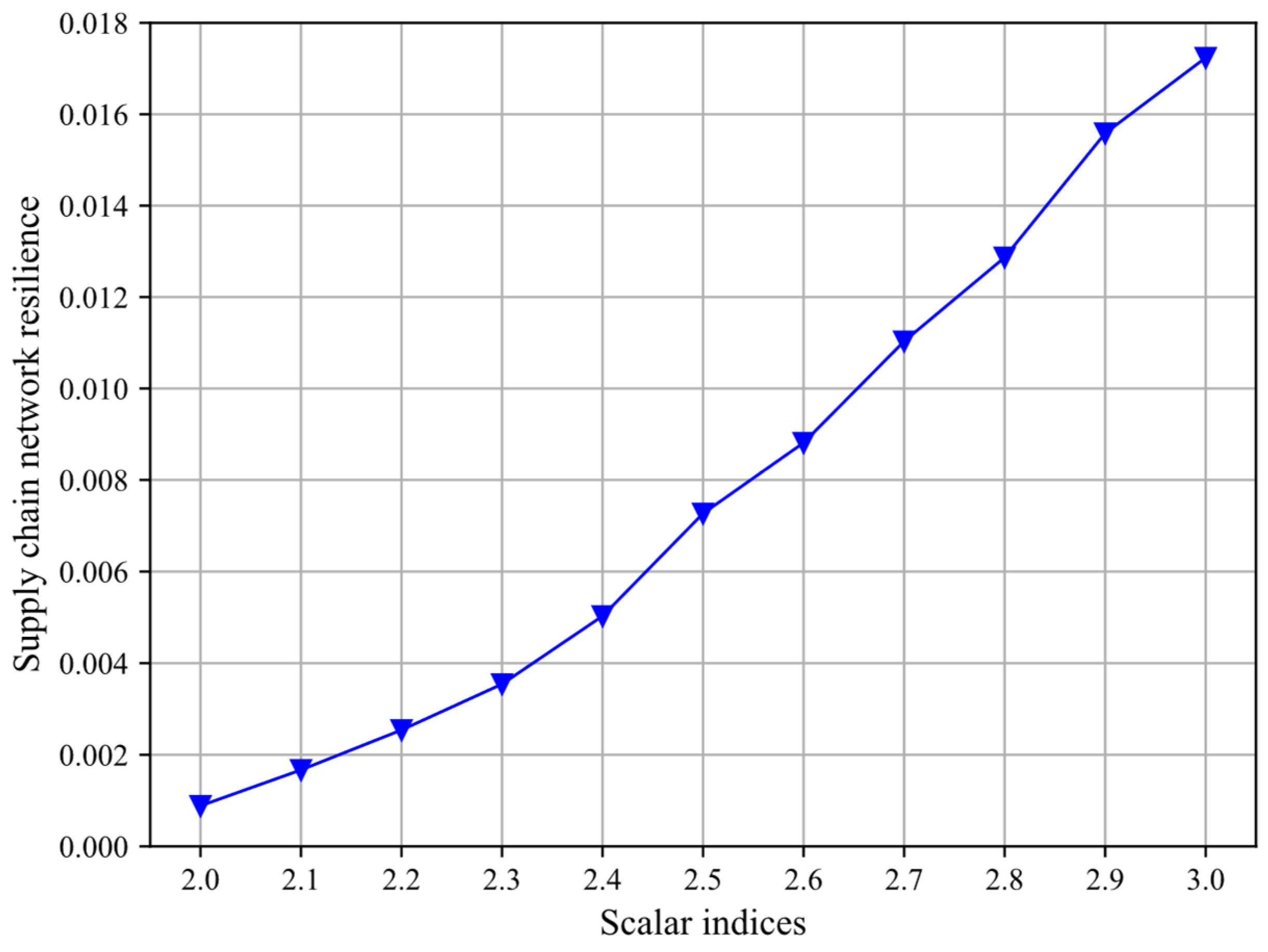
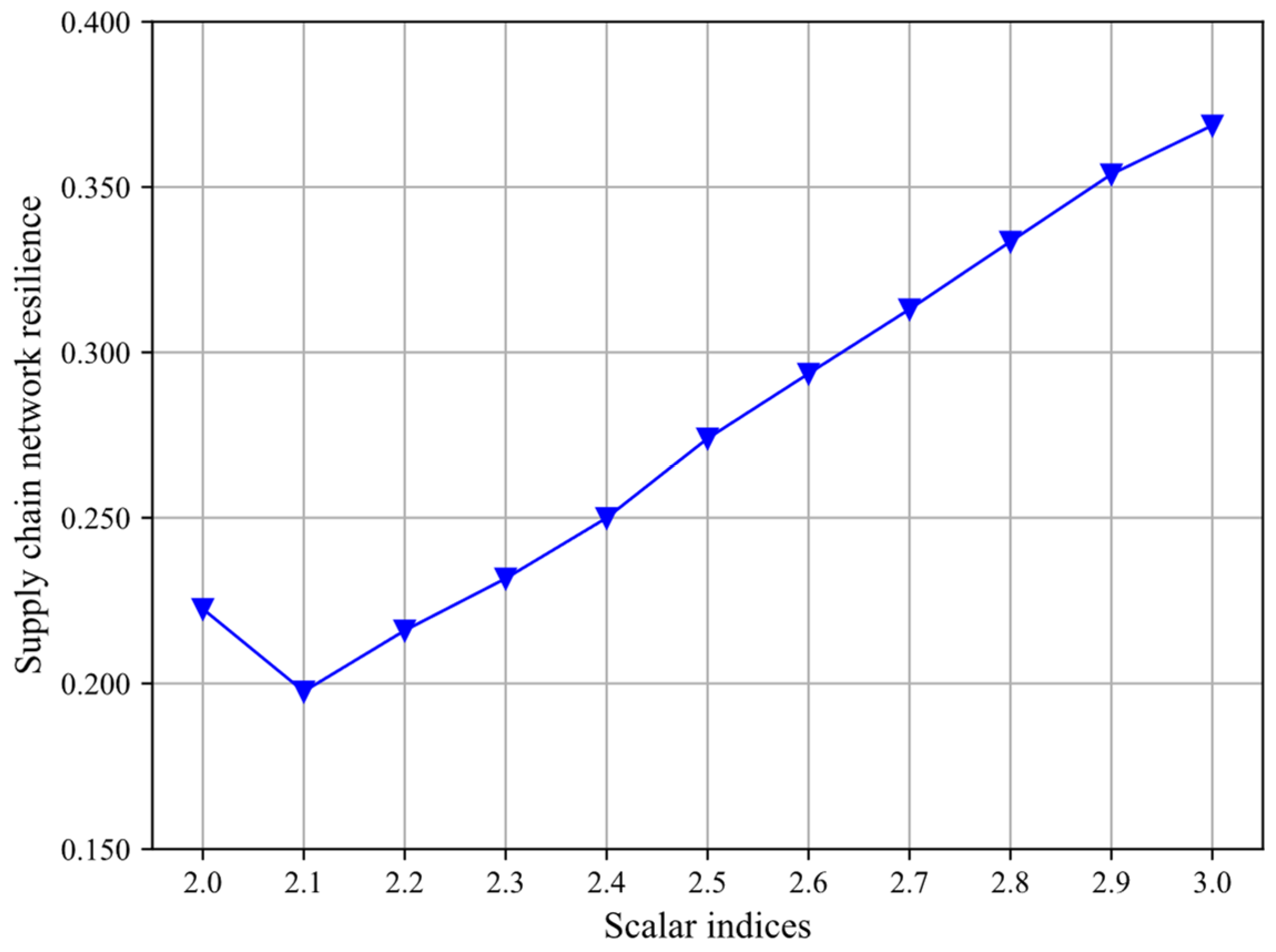
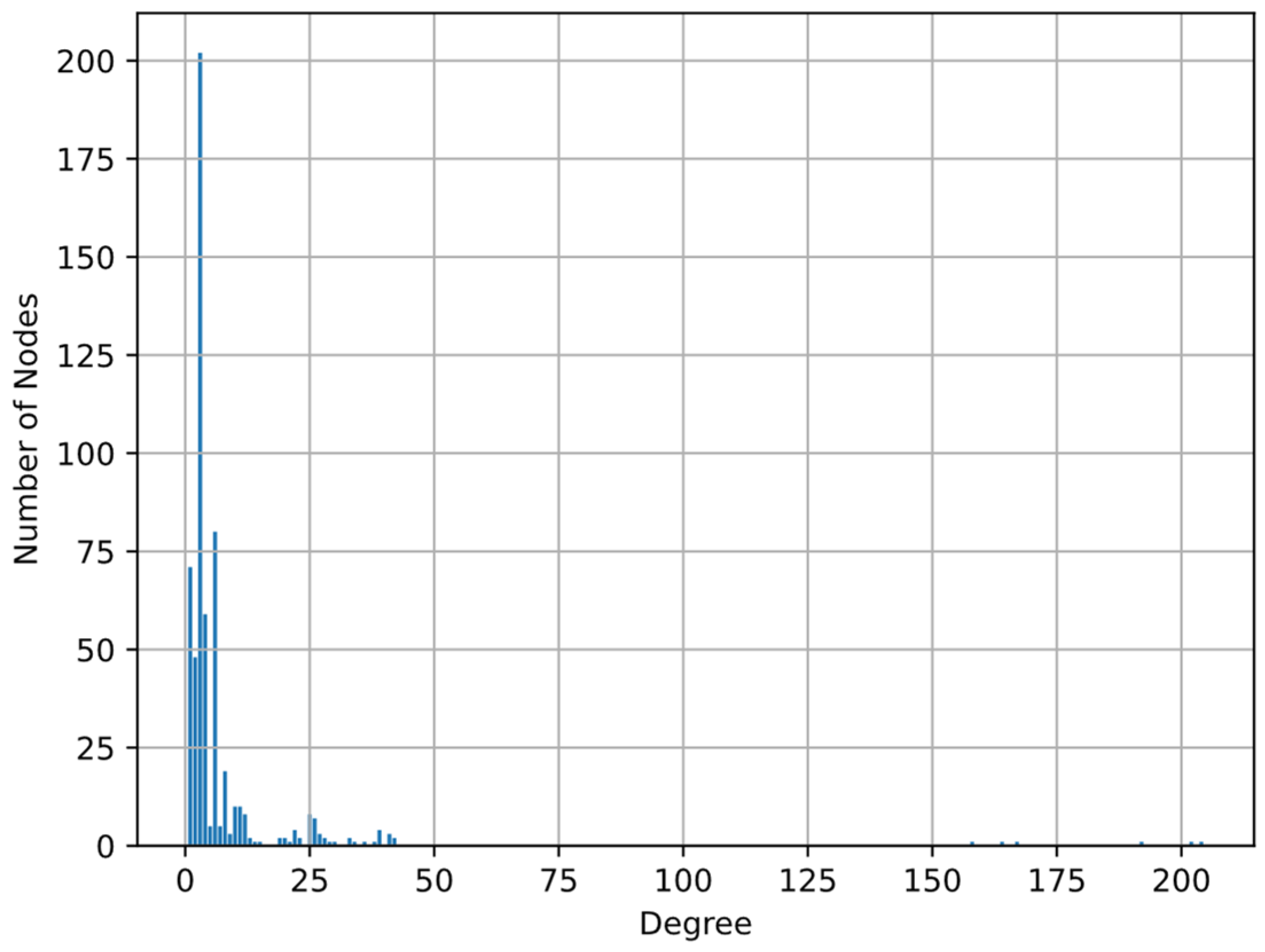
4.2. How Scalar Indices Affect SCNR
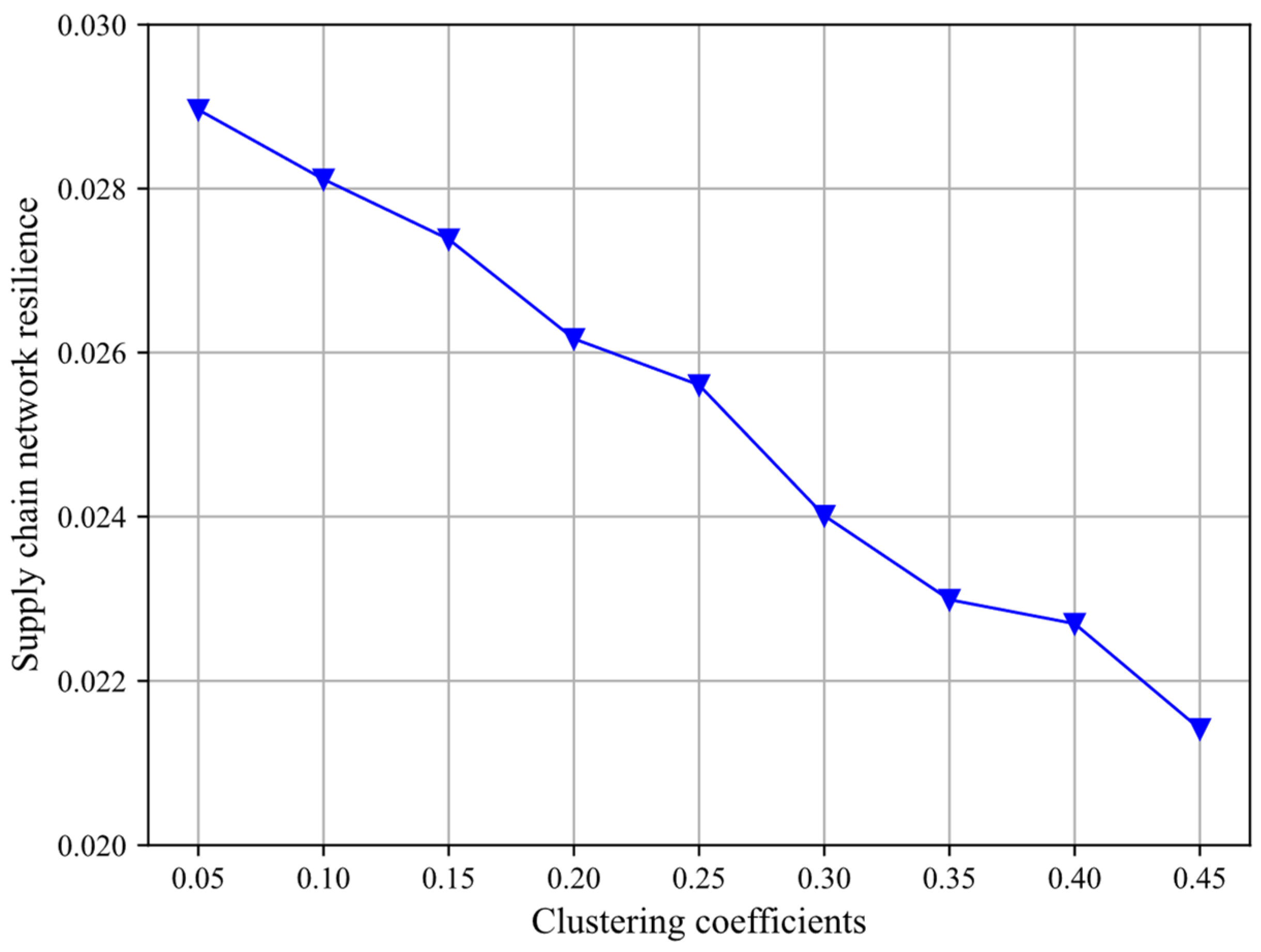
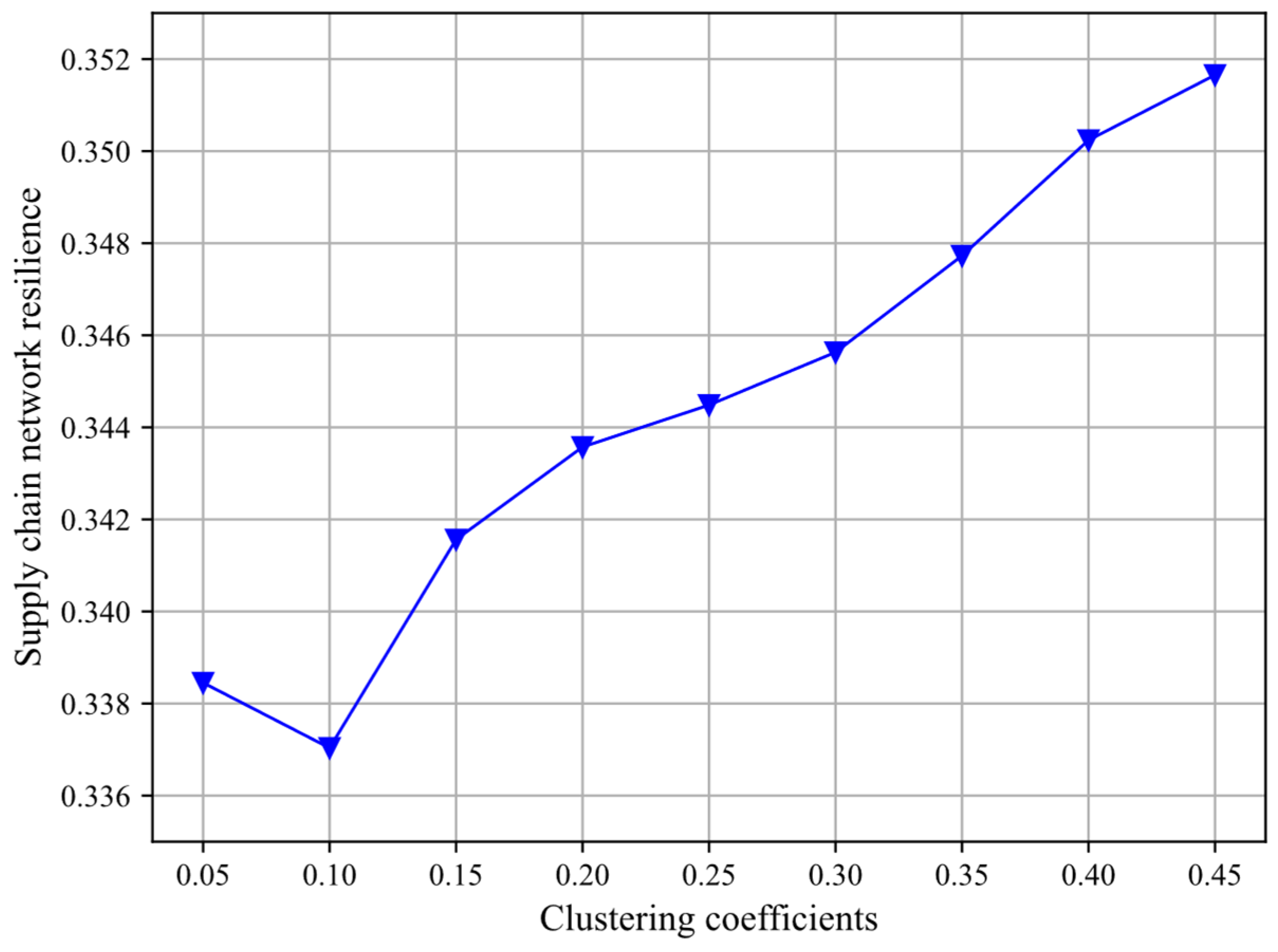
4.3. How Clustering Coefficients Affect SCNRs
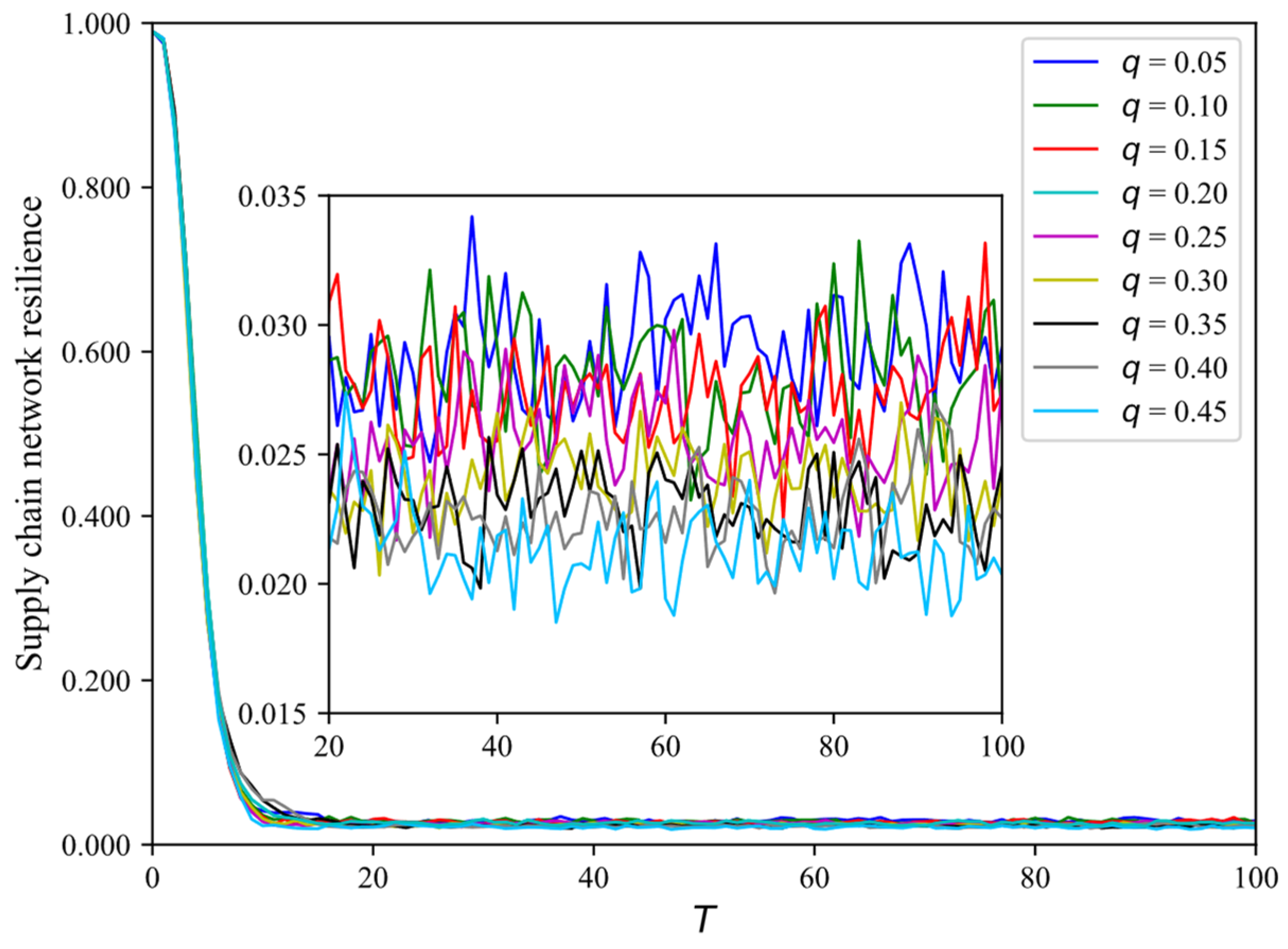
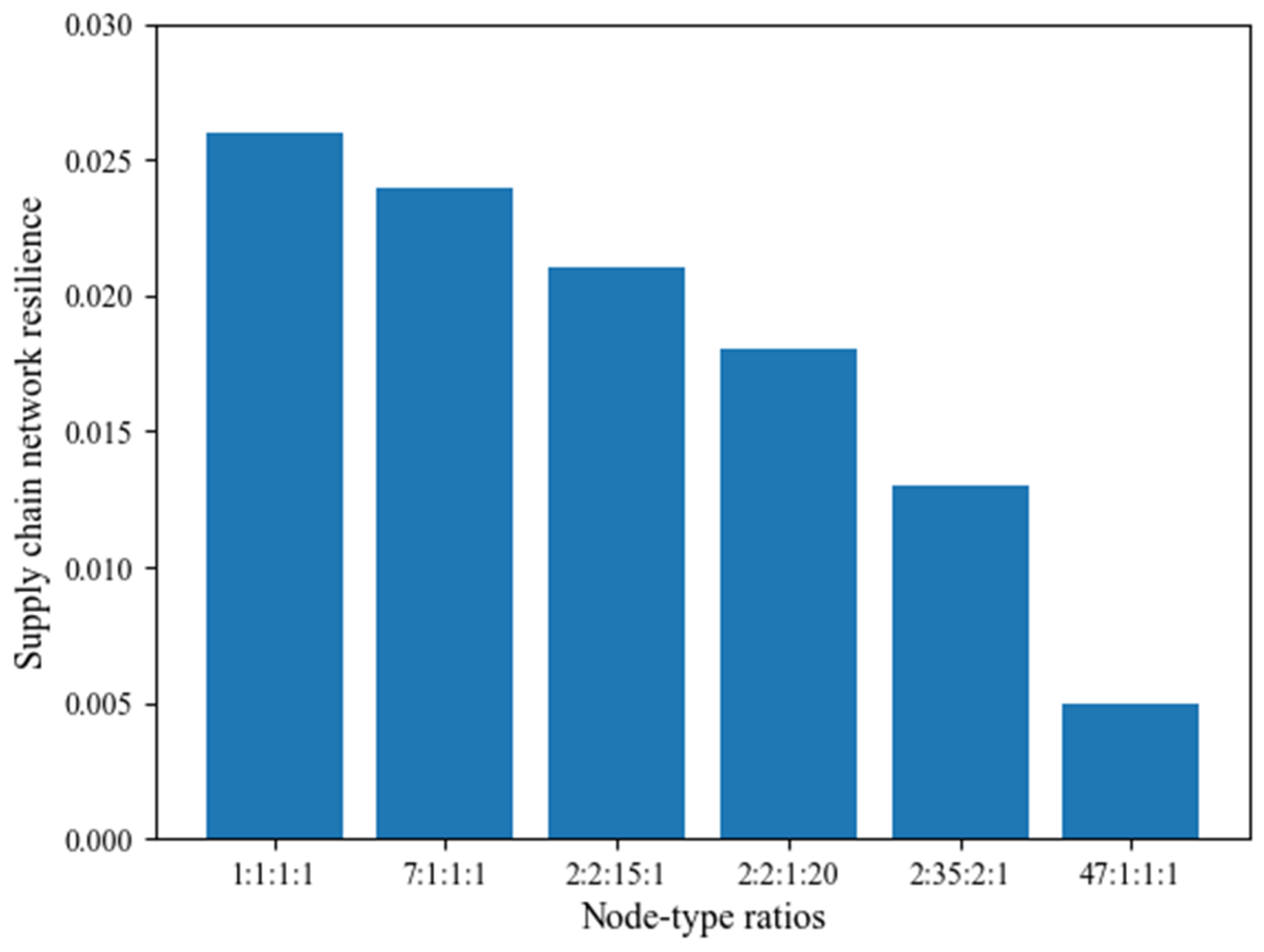
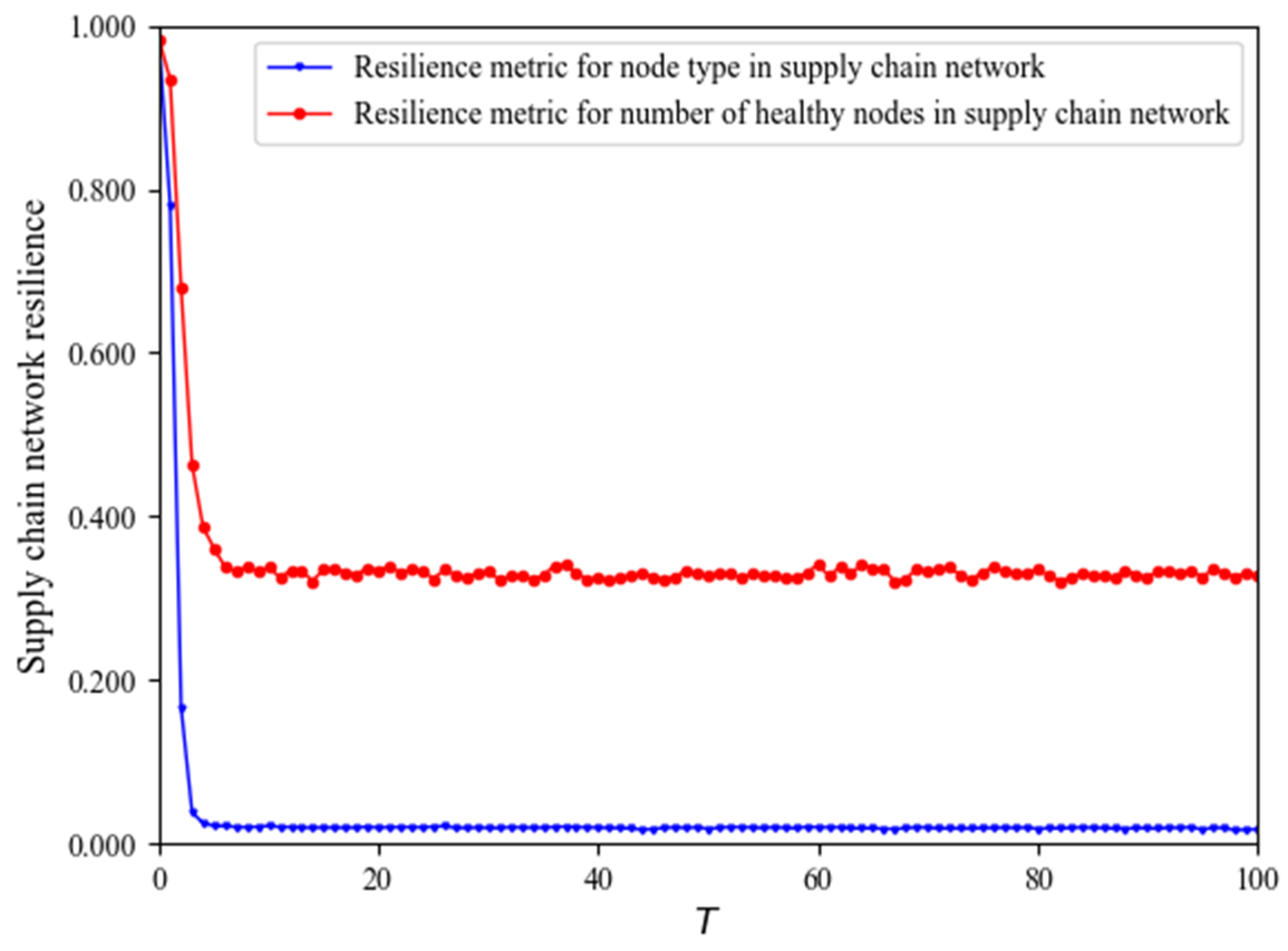
4.4. How Node-Type Ratios Affect SCNR
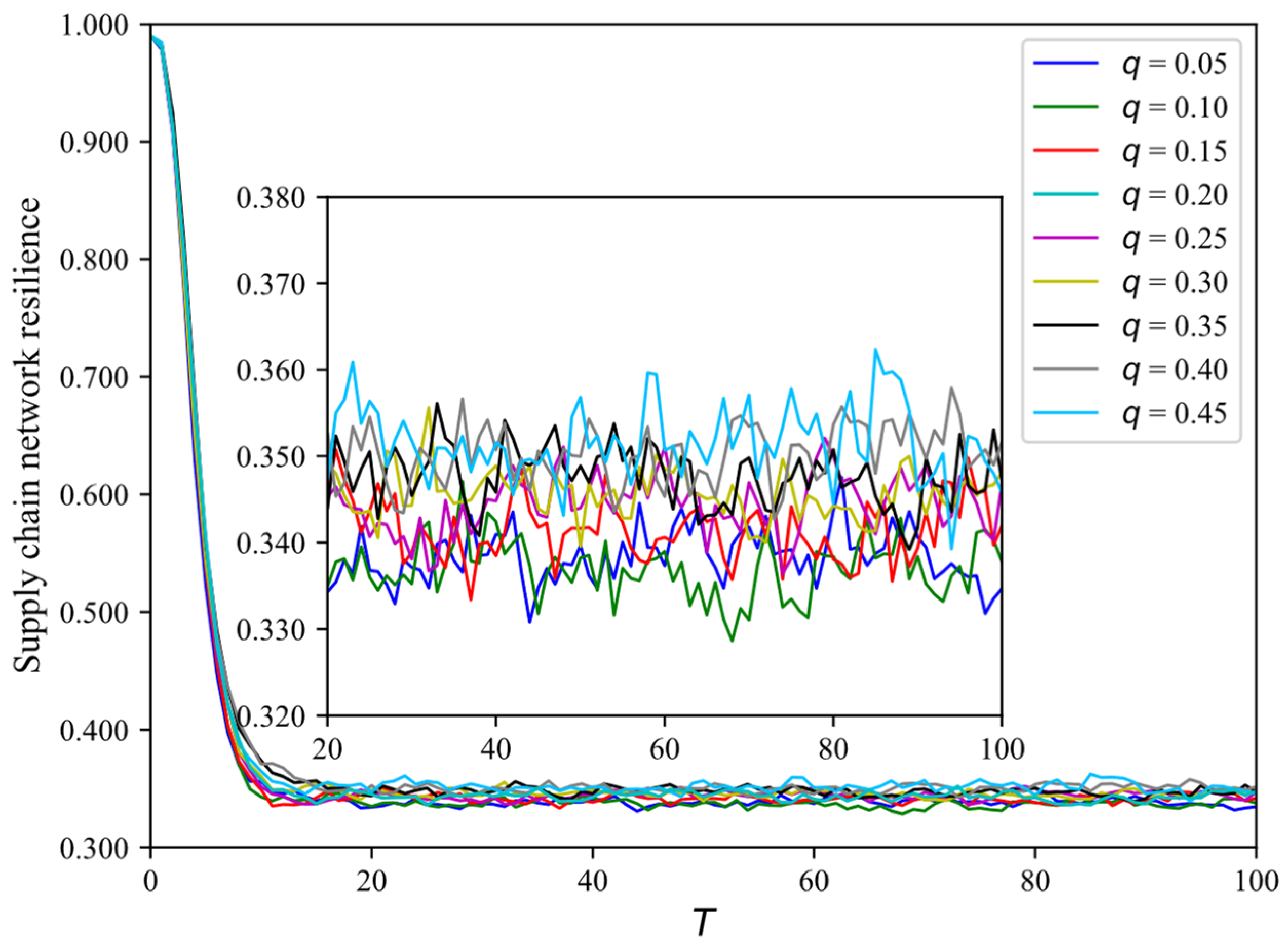
4.5. How the Types of Nodes Initially Infected Affect SCNR
5. Discussion
- (1).
- Better structure of an SCN is very important to improve its resilience
- (2).
- The ratio of node types in an SCN has a significant impact on SCNR
- (3).
- The two infection methods of the initial node type do not affect SCNR
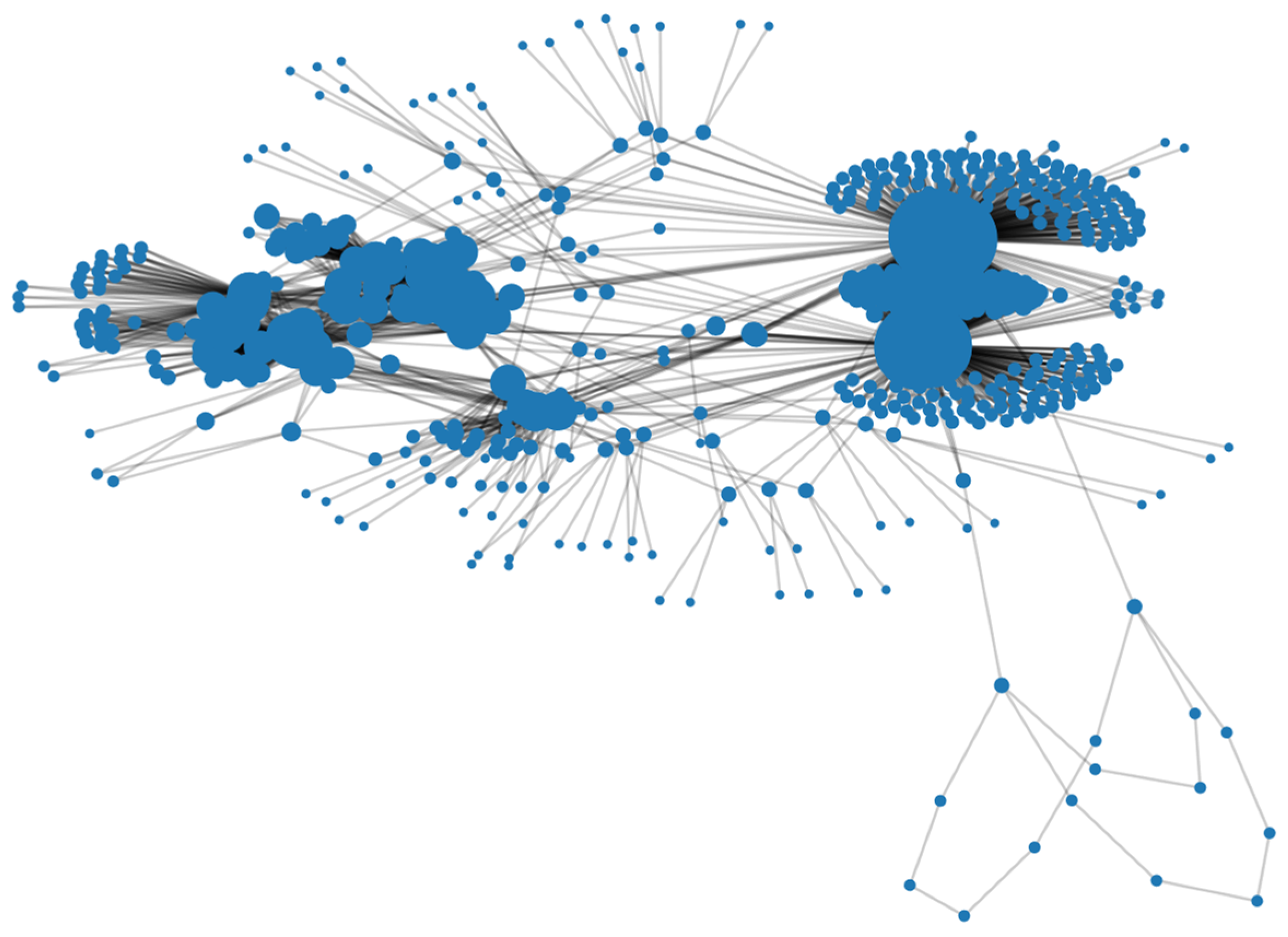
6. Case Study
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A. OR-methods for coping with the ripple effect in supply chains during COVID-19 pandemic: Managerial insights and research implications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 232, 107921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wang, Q.; Olson, D.L. Industry classification based on supply chain network information using graph neural networks. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2023, 13, 09849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibe, K.P.; Blackhurst, J. Supply chain disruption propagation: A systemic risk and normal accident theory perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 561, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.M.; Lim, M.K.; Cui, L.; Wang, Y.Z. Modelling of risk transmission and control strategy in the transnational supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.H.; Huo, B.F. Supply chain elasticity research: Theory and influence mechanism. Supply. Chain Manag. 2020, 1, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.; Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A. Review of quantitative methods for supply chain resilience analysis. Transport. Res. E Logist. Transport. Rev. 2019, 125, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidi, S.; Kermad, L.; Hamani, N.; Zidi, H. Reconfigurable Supply Chain Selection: Literature Review, Research Roadmap and New Trends. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hou, F.; Kang, M. Using Building Information Modeling to Enhance Supply Chain Resilience in Prefabricated Buildings: A Conceptual Framework. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarik, M.S.; Naghavi, N.; Mubarik, M.; Kusi-Sarpong, S.; Khan, S.A.; Zaman, S.I.; Kazmi, S.H.A. Resilience and cleaner production in industry 4.0: Role of supply chain mapping and visibility. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrjerdi, Y.Z.; Shafiee, M. A resilient and sustainable closed-loop supply chain using multiple sourcing and information sharing strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzauskas, V.; Burinskiene, A.; Krisciunas, A. Application of information-sharing for resilient and sustainable food delivery in last-mile logistics. Mathematics 2023, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Hansen, D.W.; Chen, Z.Y. Leveraging digital twins to support industrial symbiosis networks: A case study in the norwegian wood supply chain collaboration. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmer, J.; Bugert, N.; Lasch, R. Analysis of resilience strategies and ripple effect in blockchain-coordinated supply chains: An agent-based simulation study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 228, 107882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Bryde, D.J.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Papadopoulos, T. Blockchain technology for enhancing swift-trust, collaboration and resilience within a humanitarian supply chain setting. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 3381–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zobel, C.W. Exploring supply chain network resilience in the presence of the ripple effect. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 228, 107693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zobel, C.W.; Seref, O.; Chatfield, D. Network characteristics and supply chain resilience under conditions of risk propagation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 223, 107529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortt, R.; Stolwijk, C.; Punter, M. Implementing Industry 4.0: Assessing the current state. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022, 31, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieske, A.; Birkel, H. Improving supply chain resilience through industry 4.0: A systematic literature review under the impressions of the COVID-19 pandemic. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 158, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinagi, C.; Reklitis, P.; Trivellas, P.; Sakas, D. The impact of industry 4.0 technologies on key performance indicators for a resilient supply chain 4.0. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A. A digital supply chain twin for managing the disruption risks and resilience in the era of Industry 4.0. Prod. Plan. Control 2021, 32, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qader, G.; Junaid, M.; Abbas, Q.; Mubarik, M.S. Industry 4.0 enables supply chain resilience and supply chain performance. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2022, 185, 122026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A.; Sokolov, B. The impact of digital technology and Industry 4.0 on the ripple effect and supply chain risk analytics. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Q.; Yuan, X.J.; Deng, D.S. Research on supply network resilience considering the ripple effect with collaboration. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 5553–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Zhou, H.; Jin, X.D. Risk transmission in complex supply chain network with multi-drivers. Chaos. Soliton. Fract. 2021, 143, 110259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Han, X.; Duan, X.Y. Supply chain network resilience by considering disruption propagation: Topological and operational perspectives. IEEE. Syst. J. 2022, 16, 5305–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Li, W.; Wu, J.; Chai, L.H. Eco-industrial parks’ structural characteristics and mechanisms: A case of Xinzhuang and comparison studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basole, R.C.; Bellamy, M.A. Supply network structure, visibility, and risk diffusion: A computational approach. Decision. Sci. 2014, 45, 753–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Kumar, A.; Harrison, T.P.; Yen, J. Analyzing the resilience of complex supply network topologies against random and targeted disruptions. IEEE. Syst. J. 2011, 5, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.P.; Chen, Z.L.; Zhao, X.D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.J. Robust analysis of cascading failures in complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2021, 583, 126320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Q.; Long, W.; Li, Y.Y.; Deng, D.S. Robustness of interdependent supply chain networks against both functional and structural cascading failures. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2022, 586, 126518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Q.; Deng, D.S.; Long, W.; Li, Y.Y.; Yu, X.J. Research on the robustness of interdependent supply networks with tunable parameters. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 158, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffray, N.; Bouchet, R.; Brechet, Y. Derivation of anisotropic matrix for bi-dimensional strain-gradient elasticity behavior. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 2009, 46, 440–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rudolph, A.; Sanchez-Pinsach, D.; Frey, D.; Opisso, E.; Cisek, K.; Kelleher, J.D. Know an Emotion by the Company It Keeps: Word Embeddings from Reddit/Coronavirus. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchi, S.; Licinio, J. Resilience and psychological distress in psychology and medical students. Acad. Psychiatr. 2017, 41, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bona, S.; Silva-Afonso, A.; Gomes, R.; Matos, R.; Rodrigues, F. Nature-Based Solutions in Urban Areas: A European Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombe, R.; Smuts, H. Agricultural Social Networks: An Agricultural Value Chain-Based Digitalization Framework for an Inclusive Digital Economy. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, R. Is China’s economic growth decoupled from carbon emissions? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleizadeh, A.A.; Ahmadzadeh, K.; Sarker, B.R.; Ghavamifar, A. Designing an optimal sustainable supply chain system considering pricing decisions and resilience factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 129895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarov, S.Y.; Holcomb, M.C. Understanding the concept of supply chain resilience. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2009, 20, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, R.; Gholamrezaei, A.; Kadłubek, M.; Afshar, M.; Ali, S.S.; Kheiri, K. A robust and resilience machine learning for forecasting agri-food production. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, K.A.D.; Flynn, B.B.; Paiva, E.L.; Awaysheh, A. Achieving risk resilience in an environment of mistrust: Supply chain piracy of physical goods. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2024, 44, 565–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A.; Sokolov, B.; Ivanova, M. Literature review on disruption recovery in the supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 6158–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Linderman, K. Supply network disruption and resilience: A network structural perspective. J. Oper. Manag. 2015, 33, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, L.V.; Atan, Z.; Peng, P.; Rong, Y.; Schmitt, A.J.; Sinsoysal, B. OR/MS models for supply chain disruptions: A review. IIE Trans. 2016, 48, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Q.; Long, W.; Li, Y.Y.; Deng, D.S.; Wei, Y.L.; Liu, H.G. Research on supply network resilience considering random and targeted disruptions simultaneously. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 6670–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.G.; Jin, S.Z. Resilience assessment of the lithium supply chain in China under impact of new energy vehicles and supply interruption. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.Y.; Cao, H.B.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, P.G.; Song, Q.B.; Yang, J.X.; Sun, Z. Rethinking Chinese supply resilience of critical metals in lithium-ion batteries. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Zhang, X.Y. Research on supply chain risk transmission mechanism based on improved SIRS model. Math. Prob. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9502793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.A.; Guo, H.Y.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Xie, X.X. A new model for supply chain risk propagation considering herd mentality and risk preference under warning information on multiplex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 545, 12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D. Predicting the impacts of epidemic outbreaks on global supply chains: A simulation-based analysis on the coronavirus outbreak (COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2) case. Transport. Res. E Logist. Transport. Rev. 2020, 136, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Xia, C.Y.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, G.R. Epidemic propagation with positive and negative preventive information in multiplex networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 51, 1454–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.T.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.F.; Shao, L.J. Spatiotemporal patterns of risk propagation in complex financial networks. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.B.; Chen, D.L.; Wang, L.Q.; Han, C.Q. Credit risk diffusion in supply chain finance: A complex networks perspective. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadge, A.; Er, M.; Ivanov, D.; Chaudhuri, A. Visualisation of ripple effect in supply chains under long-term, simultaneous disruptions: A system dynamics approach. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 6173–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Bhamra, R.; Liu, Z.; Pan, Y. Risk propagation and supply chain health control based on the SIR epidemic model. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, M. Mathematical modelling of inventory and process outsourcing for optimization of supply chain management. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.; Garcia, S.; Rajtmajer, S.; Grady, C.; Mejia, A. Fragility of a multilayer network of intranational supply chains. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2020, 5, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Ivanov, D. A multi-layer bayesian network method for supply chain disruption modelling in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 5258–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.P.; Mu, D.; Wang, C.; Ren, H.Y.; Ghadimi, P. Topological structure and COVID-19 related risk propagation in TFT-LCD supply networks. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 2758–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmer, R.; Griffis, S.E. Structural characteristics of complex supply chain networks. J. Bus. Logist. 2021, 42, 264–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.D.; Dai, Y.F. Evolution of the complex supply chain network based on deviation from the power-law distribution. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Mahajan, Y.; Kang, B.W.; Moore, T.J.; Cho, J.H. A survey on centrality metrics and their network resilience analysis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 104773–104819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme, P.; Kim, B.J. Growing scale-free networks with tunable clustering. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 026107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hasan, M.; Dave, V.S. Triangle counting in large networks: A review. Wires. Data. Min. Knowl. 2018, 8, e1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Castellano, C.; Van Mieghem, P.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Tang, M.; Liu, Y.; Lai, Y.C. Machine learning dynamical phase transitions in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 052312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishehchi Fayyaz, M.; Rasouli, M.R.; Amiri, B. A data-driven and network-aware approach for credit risk prediction in supply chain finance. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2021, 121, 785–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Xue, H.F.; Yuen, K.F.; Sun, Q.P.; Zhao, S.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Huang, K. Assessing the vulnerability of logistics service supply chain based on complex network. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, S.P. Data set real world multiechelon supply chains used for inventory optimization. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2008, 10, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, S.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Li, M.; Shi, X. Research on Supply Chain Network Resilience: Considering Risk Propagation and Node Type. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072675
Xue S, Li J, Yu J, Li M, Shi X. Research on Supply Chain Network Resilience: Considering Risk Propagation and Node Type. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(7):2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072675
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Shuaihao, Jia Li, Jiaxin Yu, Minghui Li, and Xiaoqiu Shi. 2024. "Research on Supply Chain Network Resilience: Considering Risk Propagation and Node Type" Applied Sciences 14, no. 7: 2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072675
APA StyleXue, S., Li, J., Yu, J., Li, M., & Shi, X. (2024). Research on Supply Chain Network Resilience: Considering Risk Propagation and Node Type. Applied Sciences, 14(7), 2675. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072675



