A Multi-Path Semantic Segmentation Network Based on Convolutional Attention Guidance
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A multi-path convolutional self-attention structure is proposed to enhance the learning of advanced semantic information. It also integrates global information and focuses more on the boundary information.
- (2)
- A spatial and channel reconstruction module is developed to reinforce feature interaction, which also eliminates redundant information.
- (3)
- Extensive experiments are conducted on mainstream datasets, where our model exhibits superior performances against other popular methods.
2. Related Works
2.1. Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Multi-Scale Blocks
2.3. Multi-Path Structure
3. Method
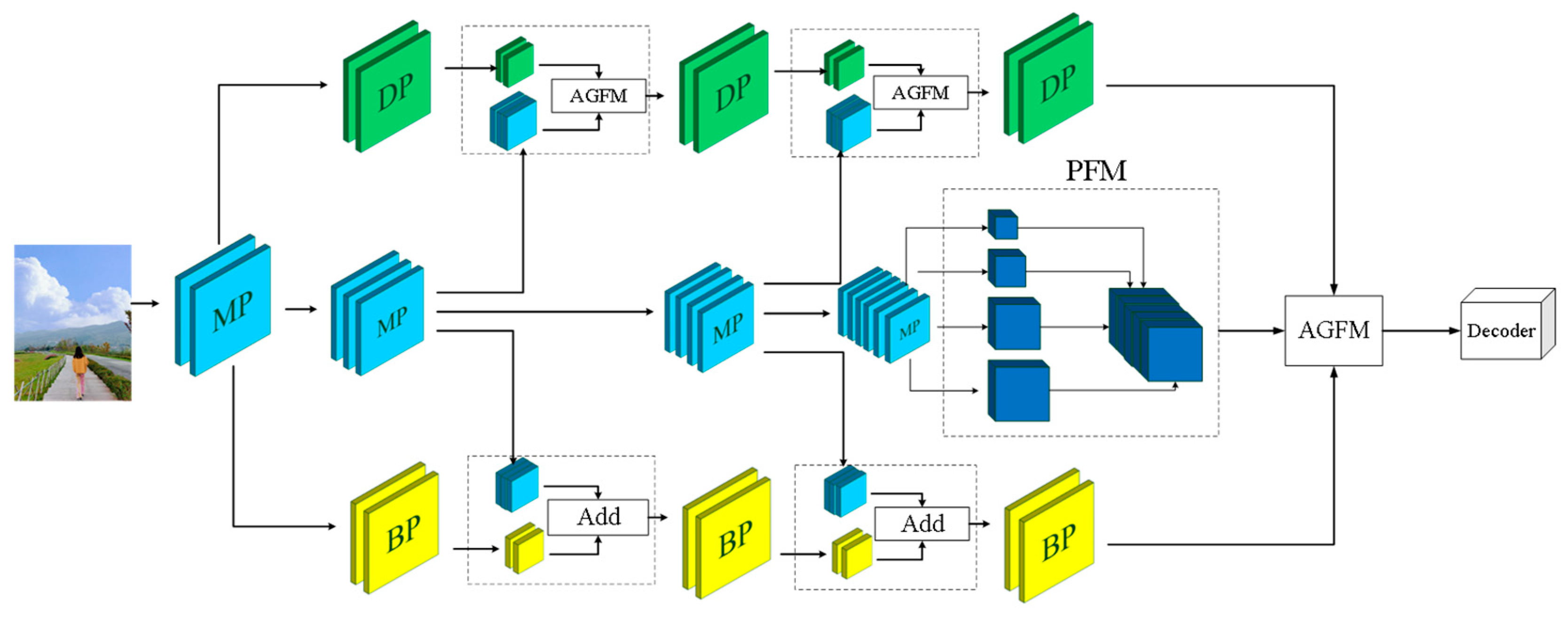
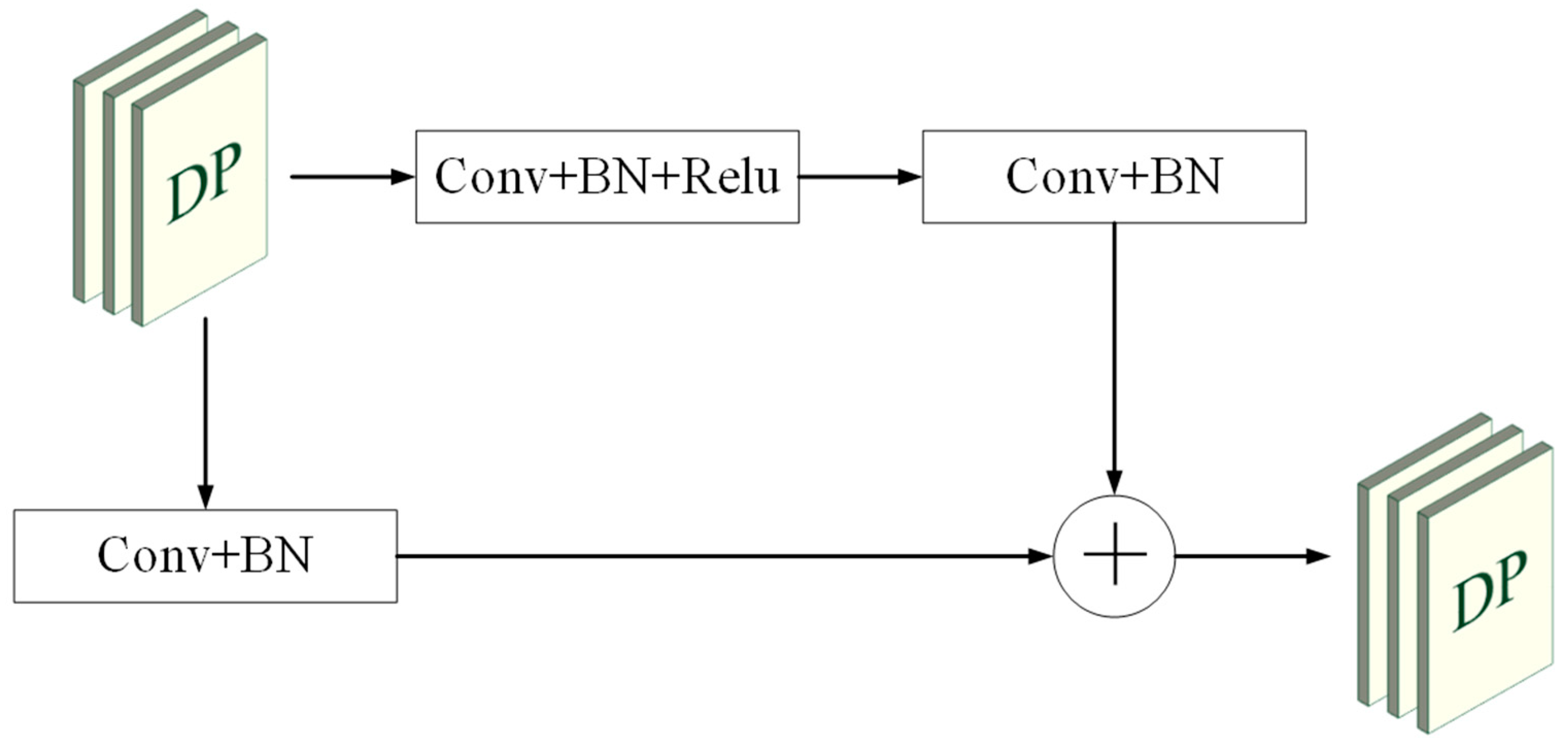
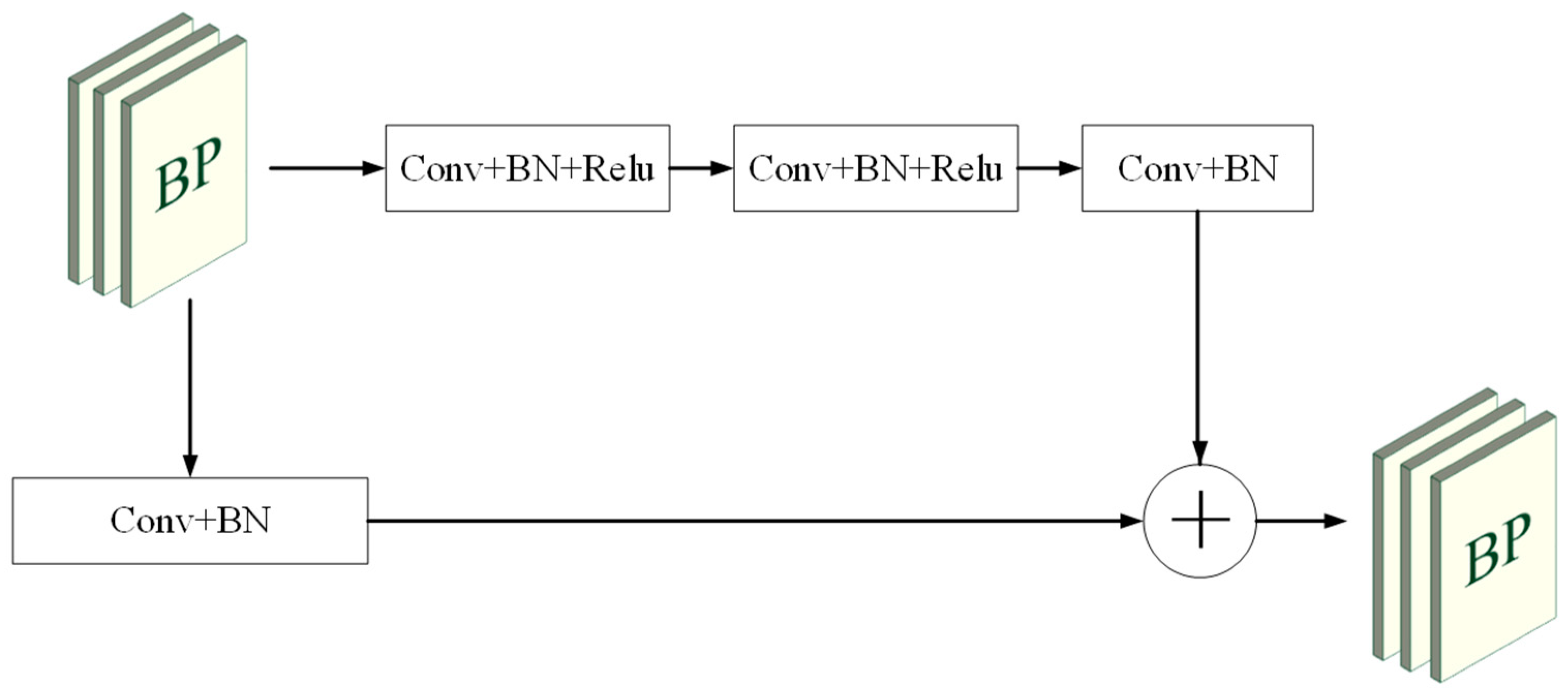
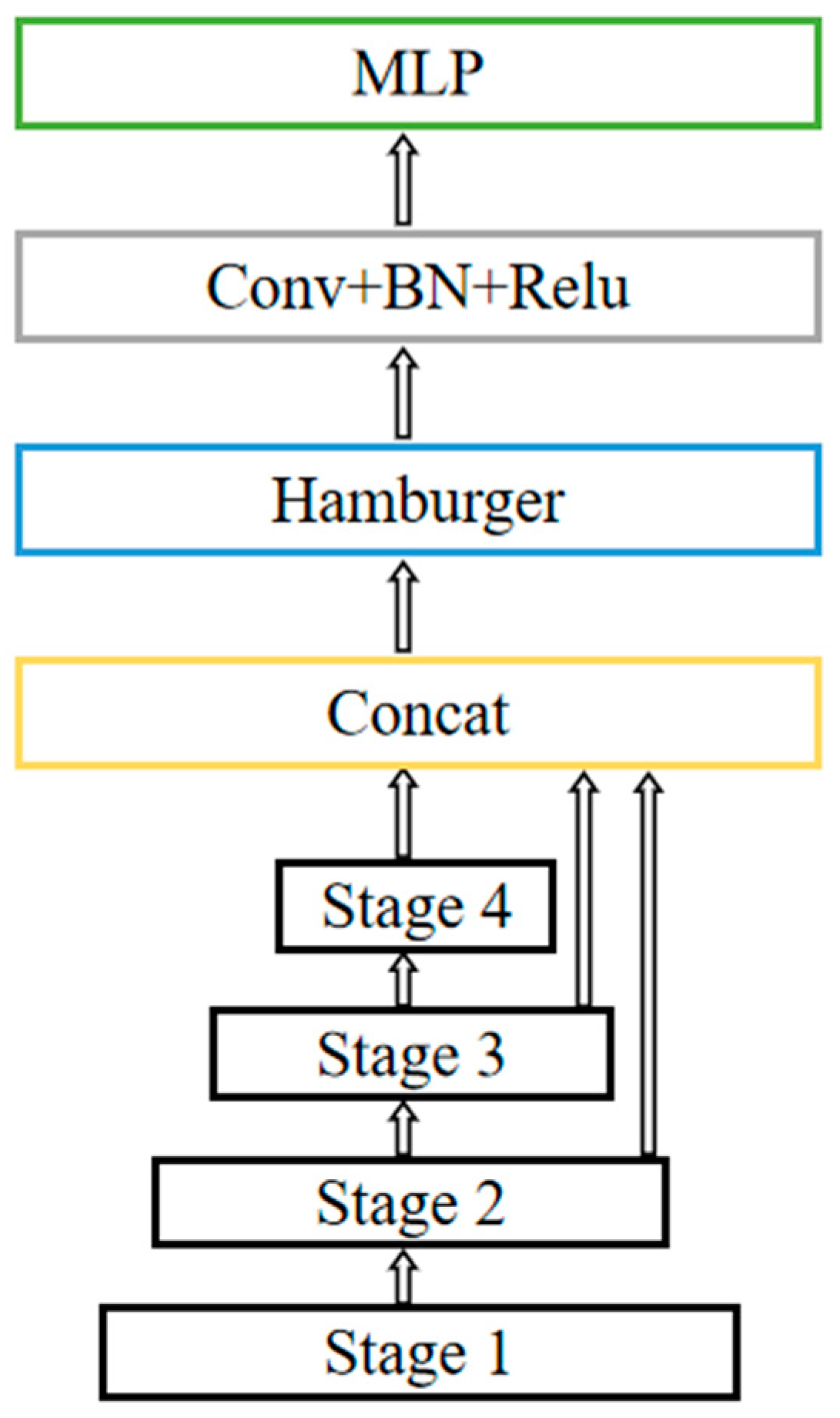
3.1. Overall Architecture
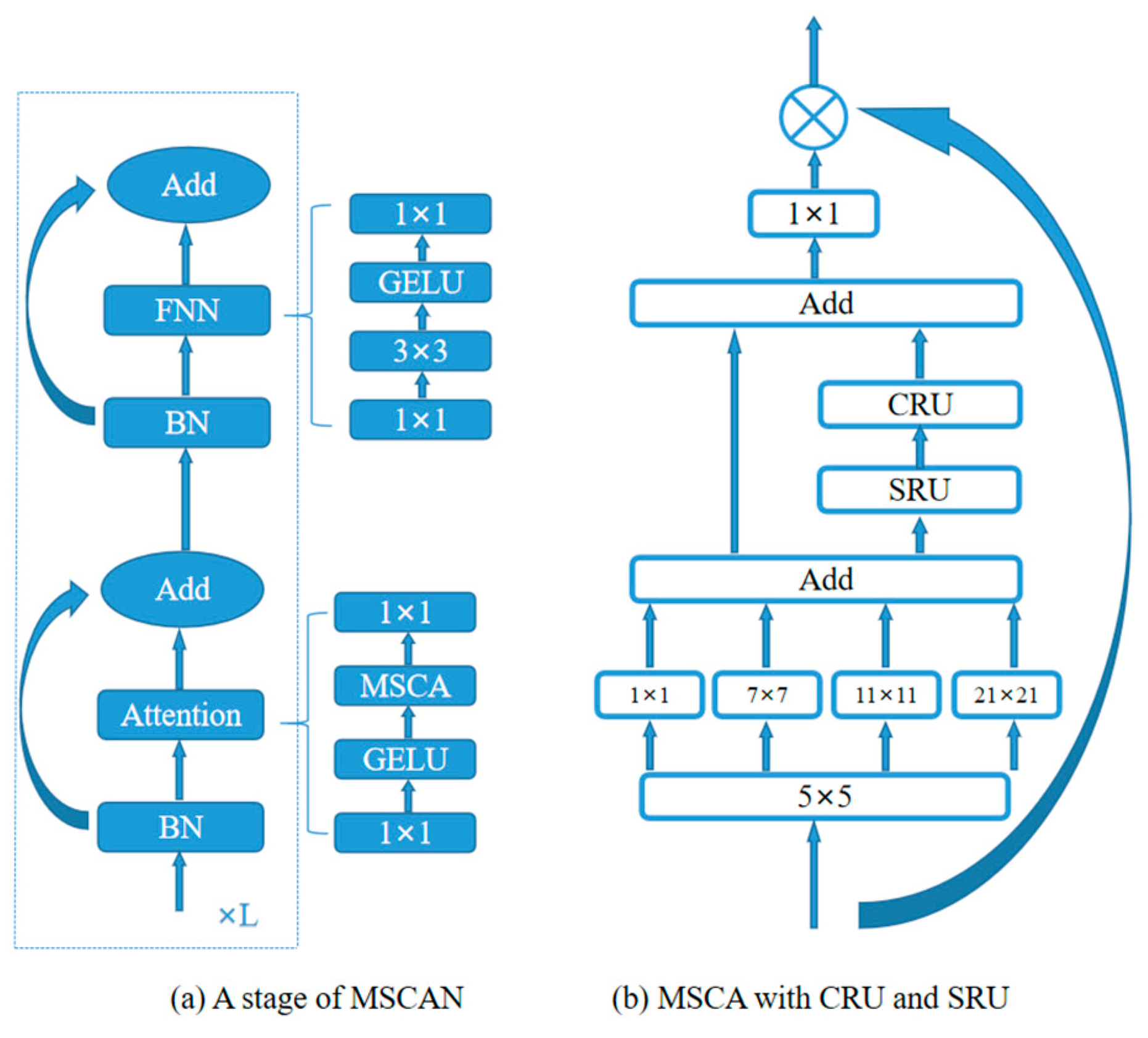
3.2. Convolutional Attention
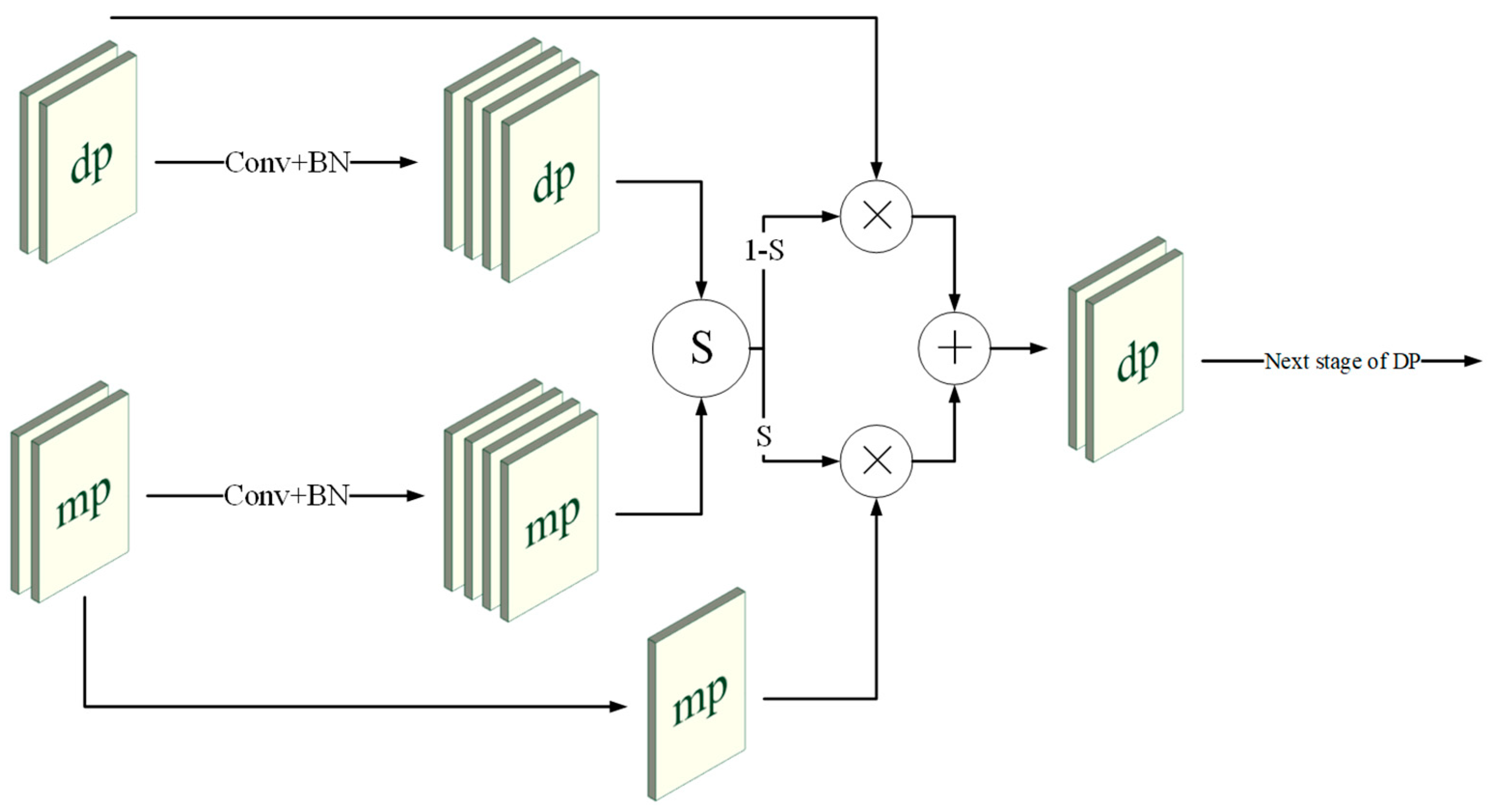
3.3. Multi-Path and Attention-Guided Fusion Module
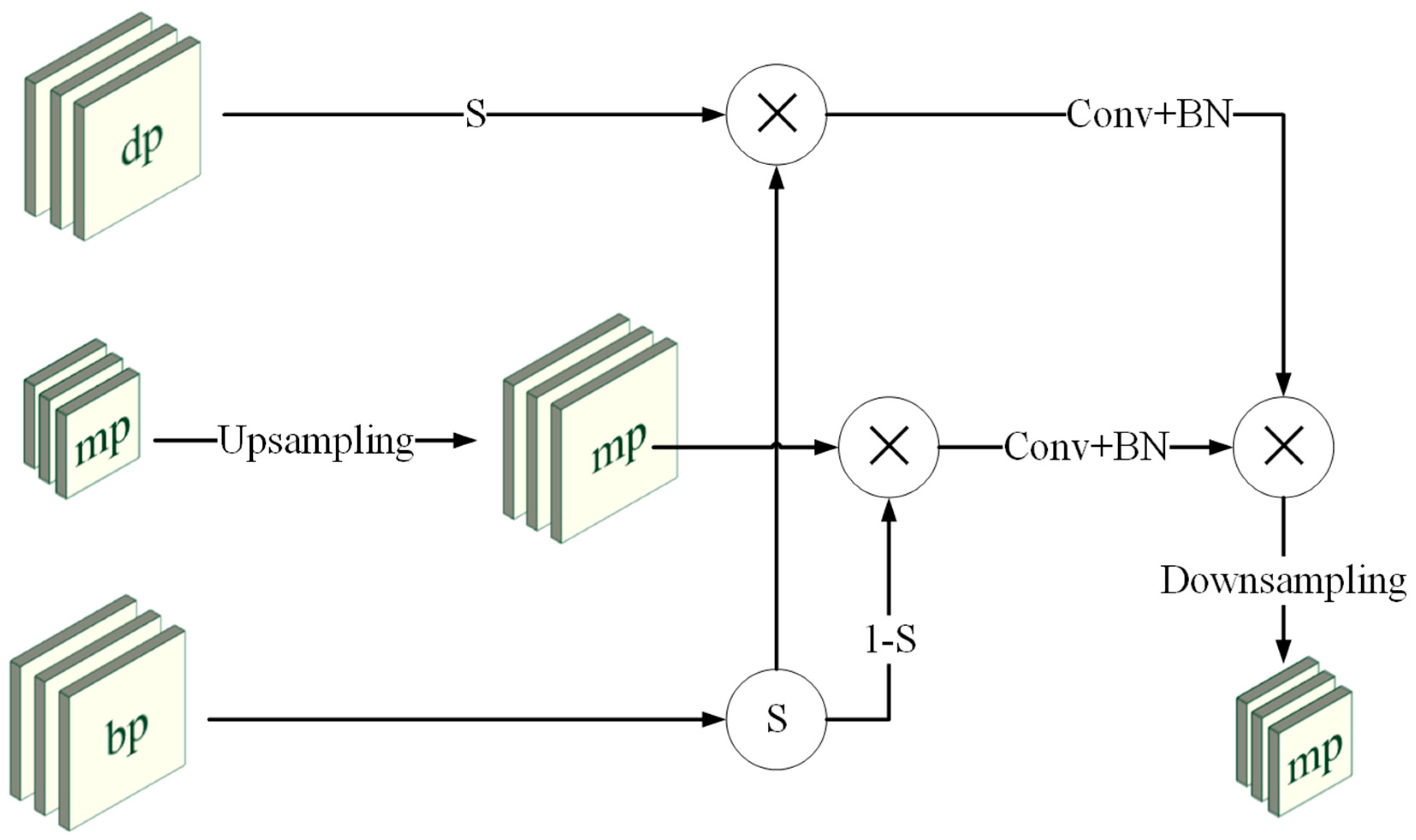
3.4. Architecture of the Decoder
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets and Experimental Setup
4.2. Comparison to State-of-the-Art and Analysis
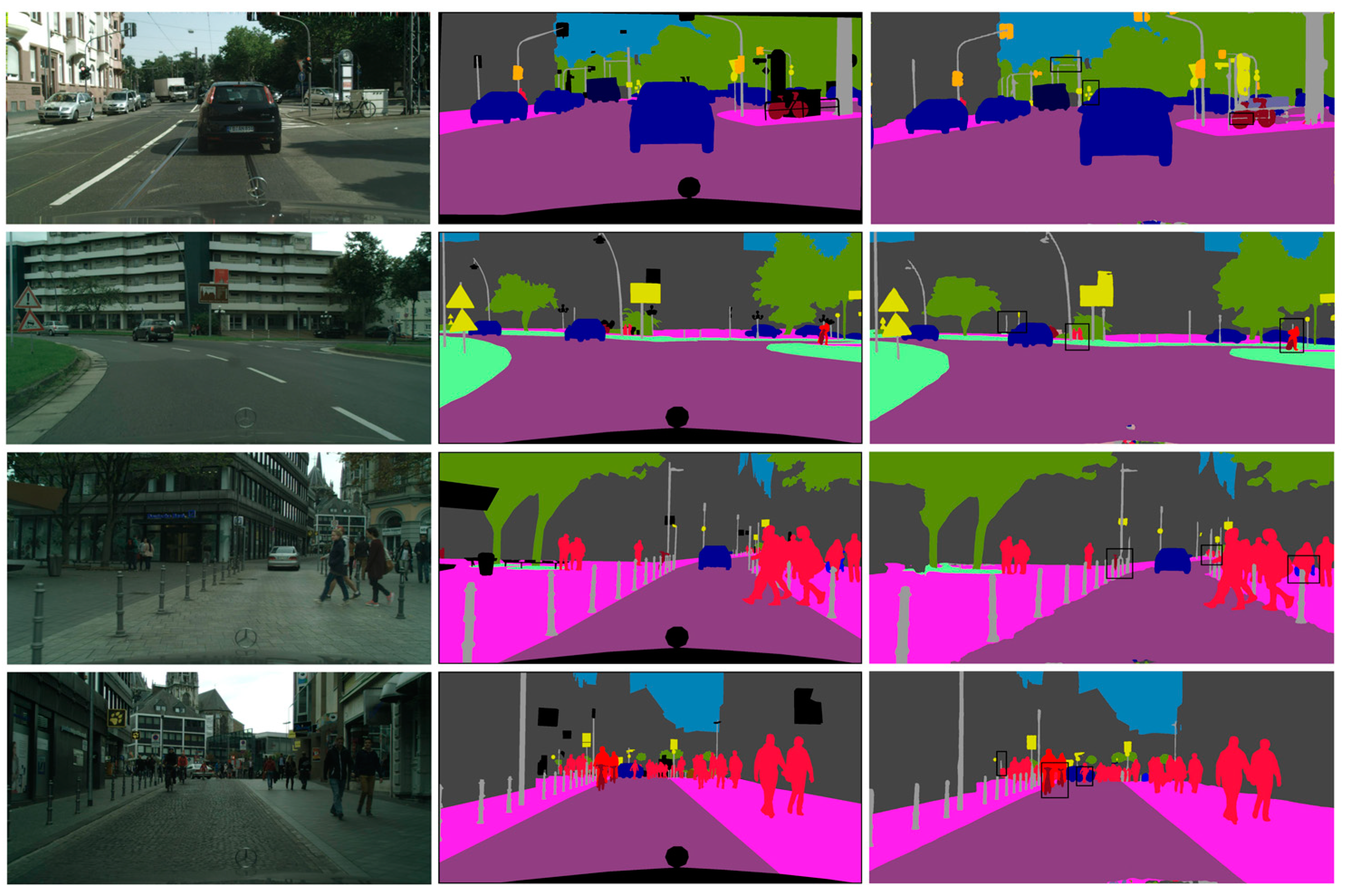
4.3. Visualization
4.4. Ablation Experiment
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected crfs. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.7062. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Feng, J.; Xiang, T.; Torr, P.H.; et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a equence-to-sequence perspective with Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6881–6890. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. Segformer: Simple and effificient design for semantic segmentation with Transformers. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Lu, C.Z.; Hou, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Segnext: Rethinking convolutional attention design for semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 1140–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Lu, C.Z.; Liu, Z.N.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Visual attention network. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.09741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Guo, M.H.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Wei, K.; Lin, Z. Is attention better than matrix decomposition? In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 3–7 May 2021.
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertasius, G.; Shi, J.; Torresani, L. Semantic segmentation with boundary neural fifields. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3602–3610. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.H.; Cheng, M.M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Torr, P. Res2net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Fu, R.; Huang, L.; Lin, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Hrformer: High-resolution vision Transformer for dense predict. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 7281–7293. [Google Scholar]
- Strudel, R.; Garcia, R.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Segmenter: Transformer for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 7262–7272. [Google Scholar]
- Ranftl, R.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Koltun, V. Vision Transformers for dense prediction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 12179–12188. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Willette, J.; Huang, S.J. Mpvit: Multi-path vision Transformer for dense predtion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7287–7296. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; Lai, S.; Huang, J.; Wei, X.; Chai, Z.; Luo, J.; Wei, X. Rethinking bisenet for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9716–9725. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2015), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective kernel networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; Volume 5, pp. 510–519. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Pan, H.; Sun, W.; Jia, Y. Deep dual-resolution networks for real-time and accurate semantic segmentation of road scenes. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.06085. [Google Scholar]
- Orsic, M.; Kreso, I.; Bevandic, P.; Šegvić, S. In defense of pre-trained imagenet architectures for real-time semantic segmentation of road-driving images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12607–12616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Scene parsing through ade20k dataset. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 633–641. [Google Scholar]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Caesar, H.; Uijlings, J.; Ferrari, V. Coco-stuff: Thing and stuff classes in context. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1209–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inform. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 8026. [Google Scholar]
- Contributors, M. MMSegmentation: Openmmlab Semantic seg213mentation Toolbox and Benchmark. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmsegmentation (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jegou, H. Training data efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2021), Online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 10347–10357. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Guo, H.; Huang, R. Fully attentional network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 2280–2288. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Cai, J.; Pan, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Tao, D.; Zhuang, B. Dynamic Focus-aware Positional Queries for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 11299–11308. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Hayat, M.; Cai, J. Transformer scale gate for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 3051–3060. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A. Per-pixel classification is not all you need for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS 2021, Online, 6–14 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Wang, P.; Wang, F. Head-free lightweight semantic segmentation with linear transformer. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.04648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Liang, Z.; Wu, S.; He, J.; Chen, K.; Tian, S. Structtoken: Rethinking semantic segmentation with structural prior. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 5655–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Pei, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zheng, L.; Fu, Z. Multi-Pooling Context Network for Image Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Bhattacharyya, S.P. PIDNet: A Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Network Inspired by PID Controllers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 19529–19539. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, C.; Tran, A.T.; Luu, K.; Hoai, M. Progressive semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16755–16764. [Google Scholar]
- Nirkin, Y.; Wolf, L.; Hassner, T. Hyperseg: Patch-wise hypernetwork for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4061–4070. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Liang, J.; Gong, Z.; Jiang, Z. LightSeg: Local Spatial Perception Convolution for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | Params (M) | Backbone | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segformer-B0 [6] | 3.8 | MiT | 38.0 |
| MaskFormer [40] * | 42 | Swin | 46.5 |
| Segformer-B1 [6] | 13.7 | MiT | 43.1 |
| HRFormer-S [14] | 13.5 | - | 45.1 |
| HRFormer-B [14] * | 56.2 | - | 45.9 |
| AFFormer-base [41] | 3.0 | - | 41.8 |
| SegNext-B [7] * | 27.6 | MSCAN-B | 46.72 |
| SETR-MLA-DeiT [5] | 92.59 | T-Base | 46.15 |
| StructToken-PWE [42] * | 38 | ViT-S/16 | 46.6 |
| FLANet [37] | - | HRNetW48 | 46.99 |
| MPViT [22] * | 52 | MPViT-S | 46.52 |
| FASeg [38] * | 51 | R50 | 47.5 |
| TSG [39] | 72 | Swin-T | 47.5 |
| MPCNet [43] | - | R101 | 38.04 |
| MCAG (OURS) | 36 | MSCAN-B | 47.7 |
| Method | Params (M) | Backbone | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segformer-B0 [6] | 3.8 | MiT | 78.1 |
| SETR [5] | 311 | ViT-L | 79.3 |
| MagNet [45] | - | - | 67.57 |
| HyperSeg-S [46] | 10.2 | EfficientNet-B1 | 78.1 |
| AFFormer-base [41] | 3.0 | - | 78.7 |
| HRFormer-S [14] | 13.5 | - | 81.0 |
| SegNext-B [7] * | 27.6 | MSCAN-B | 82.0 |
| FLANet [37] | - | HRNetW48 | 79.7 |
| FASeg [38] * | 67 | R50 | 78.5 |
| StructToken-PWE [42] * | 364 | ViT-L/16 | 81.2 |
| PIDNet-L [44] | 36.9 | - | 80.6 |
| MPCNet [43] | - | R101 | 78.24 |
| LightSeg [47] | 2.44 | - | 76.8 |
| TSG [39] | 72 | Swin-T | 75.8 |
| MCAG (OURS) | 36 | MSCAN-B | 82.51 |
| Method | Param (M) | Backbone | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HRFormer-B [14] * | 56.2 | - | 43.3 |
| HRFormer-S [14] | 13.5 | - | 38.9 |
| AFFormer-base [41] | 3.0 | - | 35.1 |
| SegNext-B [7] * | 27.6 | MSCAN-B | 43.5 |
| SETR [5] * | 311 | ViT-L | 42.7 |
| MCAG (OURS) | 36 | MSCAN-B | 43.6 |
| Method | Mirror | Seat | Lamp | Box | Book | Pillow | Oven |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SegNext-B [7] * | 65.29 | 56.70 | 60.34 | 25.90 | 45.09 | 65.41 | 53.10 |
| MCAG (OURS) | 65.99 | 58.09 | 62.45 | 27.39 | 46.93 | 69.63 | 55.34 |
| Multiple Paths | Attention Guidance | Parallel Aggregation | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 47.70 |
| ✓ | ✓ | 47.55 | |
| ✓ | 46.94 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 47.30 | |
| 46.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, C.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y. A Multi-Path Semantic Segmentation Network Based on Convolutional Attention Guidance. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052024
Feng C, Hu S, Zhang Y. A Multi-Path Semantic Segmentation Network Based on Convolutional Attention Guidance. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(5):2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052024
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Chenyang, Shu Hu, and Yi Zhang. 2024. "A Multi-Path Semantic Segmentation Network Based on Convolutional Attention Guidance" Applied Sciences 14, no. 5: 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052024
APA StyleFeng, C., Hu, S., & Zhang, Y. (2024). A Multi-Path Semantic Segmentation Network Based on Convolutional Attention Guidance. Applied Sciences, 14(5), 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052024









