Abstract
Electrochemical disinfection in dentistry using boron-doped diamond (BDD) electrodes bears the potential risk of disturbing vital functions. Applying different arrays of BDD electrodes and an electrotome as reference, it was the goal of this animal study to compare their effects on an electrocorticogram (ECoG) and electrocardiogram (ECG). Following the trepanation of teeth in rats, the electrodes and electrotome were applied in a randomized manner while recording ECoG and ECG. The recordings were classified according to an electrophysiological significance score based on involvement, extent of disruption and duration. The scores obtained were compared by means of ANOVA followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (α = 0.05). Voltage type and electrode design had a significant influence on the detectable electrophysiological effects. The results seen with BDD electrodes ranged from no detectable electrophysiological effects to a pronounced effect. The application of the electrotome induced the most pronounced effects. Given that electrotomes are safe medical devices, despite evoking greater disturbance compared to BDD electrodes, regardless of their design, electrochemical disinfection may be considered a safe procedure.
1. Introduction
Electrochemical disinfection using boron-doped diamond electrodes has been shown to effectively reduce bacterial loads in both endodontic and peri-implant infections, while local host tissue reactions seem not to differ from conventional treatment protocols [1,2]. In contrast to being locally effective while not causing harm, the potential risks of electric currents interfering with body functions have not been investigated yet. Depotphoresis for endodontic treatment [3], transporting OH-ions and Cu compounds through apical canals of teeth [4,5] and thereby removing and inactivating organic material [6], seems to be well comparable from an electrical perspective, but reports on the general risks are not available.
The effects of electrical currents on the human body are governed by the exposure time, the intensity and frequency of the current and the path of the current in the body [7]. Ranked according to severity, these effects may range from no effect to pain sensation, muscle cramping, reversible respiratory problems and arrhythmia, to ventricular fibrillation, respiratory arrest and cardiac arrest (Figure 1). Thermal effects such as burns only occur at high current strengths, which normally already have dangerous effects on the human body. Consequently, the norm for the electrical safety of medical devices (VDE Norm EN 60601-1, VDE 0100-751) dictates much lower current limits compared to the consumer or industrial safety norm VDE 0100-710, 720 and 410. The patient auxiliary current, which is necessary for the function of a device, is specified in EN 60601 at a maximum of 0.5 mA [8].
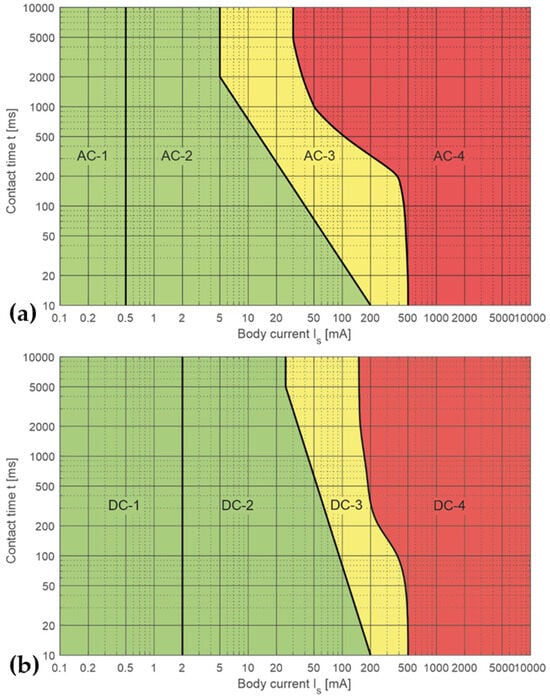
Figure 1.
Nomograms showing the influence of a current on the human body. The nomograms are divided into 4 sections, AC-1 to AC-4 and DC-1 to DC-4, describing body reactions as a result of the current and exposure time. Section 1: usually indiscernible; Section 2: clearly perceptible up to muscle cramping; Section 3: muscle cramping, respiratory problems; and Section 4: arrhythmia, ventricular fibrillation, respiratory arrest, cardiac arrest. (a) Effects of an alternating current (AC). (b) Effects of a direct current (DC).
An alternating current (AC) mainly acts by nerve irritation with frequencies > 200 Hz no longer causing muscle cramps due to their longer reaction time; the current is mainly determined by the capacity of the body (approx. 150 pF; EN 60601-1, VDE 0100-751 [9]). In addition, increasing frequencies lead to the skin effect, i.e., the current is concentrated on the surface of a conductor but does not use the entire conductor. Unipolar electrotomes (High-frequency (HF) surgery) apply a high-frequency current, which is conducted away from the patient via a counter-electrode. These high currents act by heating or vaporizing tissue and fluids, but would cause ventricular fibrillation when passing through the heart (VDE0100-410, Section 415), which can be avoided by the adequate positioning of the counter-electrode. Furthermore, AC devices may interfere with monitoring instruments as a consequence of the electromagnetic field evoked.
A direct current (DC), on the contrary, impairs nerve conduction, particularly in the case of small currents [7,10]. In addition, a DC always uses the entire body as a conductor and the current divides itself according to the resistance present in a specific region, with nerves and blood vessels having a low resistance, while bone, skin and fat tissue have high resistance [11]. The total internal resistance of the human body is approximately 1 kOhm [7]. As a rule, when the heart is in the path of the current, the current is considered more dangerous (VDE0100-410).
In order to maximize patient safety, a bipolar configuration avoiding a direct current path via the patient is preferred. In such a situation, only a small equalizing current can flow via the patient until the body capacity has adapted to the potential of the electrode. Since the patient, in most scenarios, is connected to ground potential at a high impedance (dissipative, 10 × 105 to 10 × 106 Ohm), the current to charge the capacitance is limited to a few nA.
While the problem of potential electromagnetic interference between dental instruments and patient assist systems has been addressed by several authors [12,13], vastly contradictive findings are described with an obvious dependence on manufacturer and type of device [14,15]. Only few reports on non-cardiac devices could be found showing that an electric pulp tester, apex locator and electrocautery unit did not profoundly damage cochlear implants, while it was possible to destroy the implant’s circuitry with an electrosurgical unit [16]. Similarly, the probability of damage to spinal cord stimulation by an apex locator, electric pulp tester or electrocautery unit was found to be negligible [17]. Only one report on the interactions between dental instruments and their surroundings was found, showing that mobile phones did not interfere with electronic working length determination [18].
Electrosurgery caused electromagnetic disturbances in an implantable cardioverter defibrillator [19,20], which hence seems to be contraindicated [21], while piezoelectric dental scalers [22], electronic apex locators and electric pulp testers [19,23,24] did not interfere. The exposure distance and lead-related parameters of the cardiac implantable electrical devices [12,13] seem to play an important role and, consequently, Gomez et al. [25] found electromagnetic interference in electronic apex locators and pacemakers when placed in close contact. Implanted cardiac pacemakers seem to be comparably robust in not interfering with numerous electronic dental instruments [26], including electronic apex locators and electric pulp testers [27]. However, an in vitro study also showed that electronic apex locators did not interfere with cardiac pacemaker function, while electronic pulp testers showed varying levels of background noise and the use of diathermy interfered with the pacing system [28].
It was the goal of this animal study to compare the potential disturbances of an electrocorticogram (ECoG) and electrocardiogram (ECG) caused by the use of an electrotome and the different arrays of boron-doped diamond electrodes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
This study was approved by the local governmental animal protection committee (Landesamt für Verbraucherschutz des Saarlandes; permission number: 08/2022) and conducted in accordance with the Directive 2010/63/EU and the NIH Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH Publication #85-23 Rev. 1985). A total of ten female Sprague-Dawley rats were allocated for this study and accommodated for 1 week prior to entering the experiment. Eight animals were used for the planned investigations. Two animals died prematurely due to complications during induction of anesthesia.
2.2. Surgical Procedure and Instrumentation
General anesthesia was induced by inhalation of isoflurane followed by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of ketamine (80 mg/kg) and xylazine (6 mg/kg), while intraoperative analgesia was achieved by subcutaneous carprofen (5 mg/kg) injection.
For instrumentation, the animals’ foreheads and backs were shaved. ECG was recorded as Lead I using stainless steel needle electrodes inserted into both forelegs and hindlegs. The animals were placed in a sphinx position with the head fixed in a custom-made stereotactic frame. The head was fixed by ear bars placed in the auditory canals, mouth bars and nose pieces. The skull was exposed and burr holes were made for the insertion of four electrocorticographic screw electrodes for bilateral unipolar leads from the primary somatosensory cortex (reference, nasal bone) [29]. Electrodes were covered with glass ionomer dental cement (Ketac Cem, 3 M, Seefeld, Germany) in order to fix in place and insulate electrodes throughout the experiment. The first molars in the maxilla and—where possible—also in the mandible were then trepanned until bleeding occurred.
2.3. Experimental Protocols
After completion of the instrumentation, the animals were removed from the stereotactic apparatus and placed in the pronation position. A three-minute recording of the initial conditions was first made from each animal. Subsequently, the opened tooth cavities were continuously rinsed with physiological saline solution. The various stimulators ((i) a Boron-doped diamond electrode (9 V) consisting of a 50 µm BDD placed inside the cannula (Figure 2), (ii) a Boron-doped diamond electrode (9 V) consisting of a 50 µm BDD placed outside the cannula (Figure 3), (iii) a monopolar electrotome electrode, set at maximum intensity (Coagulation electrode: Sirona “No. 5”, hf surg, Hager & Werken, Duisburg) and (iv) an electric shortcut electrode consisting of two “Figure 2” electrically interconnected electrotome coagulation electrodes) were introduced in a random order into one of the opened cavities for a period of <20 s. The electrode activity of the Boron-doped diamond electrodes i and ii was verified by a visual verification of intracavitary gas bubble production. The application of physiological saline solution into opened tooth cavities did not cause any changes in the recorded electrophysiological parameters. At the end of the experiment, the animals were sacrificed by an overdose of Pentobarbital (400–800 mg/kg i.p.).
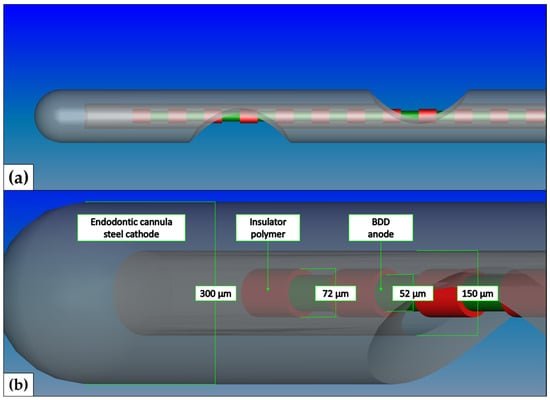
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of Boron-doped diamond electrode—inside. The anode consisted of a 50 µm niobium wire coated with 1 µm boron-doped diamond. The cathode consisted of an endodontic needle (0.3 × 25 mm, transcodent, Sulzer GmbH, Munich, Germany). The anode and cathode were separated by a thin polymeric layer. (a) CAD schematic overview (FreeCAD, version 0.18, http://www.freecadweb.org/, accessed on 11 December 2023) of the irrigation needle. (b) In-depth view of the electrolytically active tip of the BDD electrode type i probe.
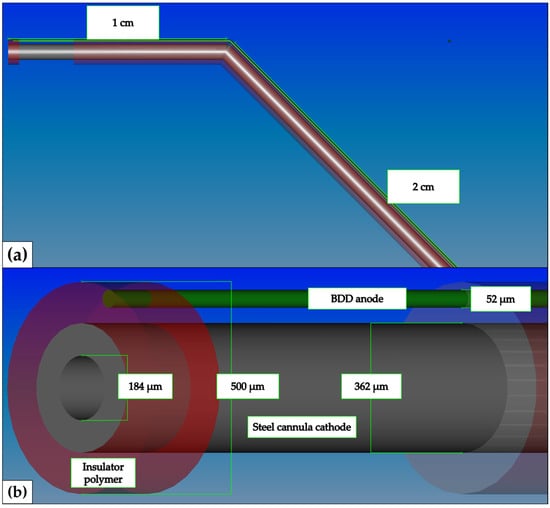
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration of Boron-doped diamond electrode—outside. The anode consisted of a 50 µm niobium wire coated with 1µm boron-doped diamond. The cathode consisted of an endodontic needle (28 G, VMK Endoneedle, Vedefar N.V, Dilbeek, Belgium). The anode and cathode were separated by a thin polymeric layer. (a) CAD schematic overview (FreeCAD, version 0.18, http://www.freecadweb.org/, accessed on 11 December 2023) of the kinked endodontic needle. (b) In-depth view of the electrolytically active tip of the BDD electrode type ii probe.
2.4. Data Acquisition and Analyses
Unipolar ECoG and ECG signals were amplified (4-Channel EEG or ECG Amplifiers, Biovision, Wehrheim, Germany), filtered (time constant was 0.1 s, cut-off frequency was 1000 Hz), fed into a multi-channel recording device (GJB Datentechnik Bolten & Jannek GbR, Ilmenau, Germany) and stored after A/D conversion continuously on hard disc at 1000 Hz. In order to reveal the electrocorticographic activity, the signals derived from head screw electrodes were bandpass filtered (0.5–45 Hz) and stored. The instantaneous heart rate (HR) was derived from the reciprocal RR interval time series. Therefore, the individual R-waves, with the R-wave peak as the trigger point, were sequentially recognized (ATISApro®, GJB Datentechnik GmbH, Langewiesen, Germany). Accurate R-wave peak detection was verified by visual inspection. The distance of consecutive R wave peaks was measured by a precision of 1 ms. The series of R-R intervals (T1, T2, T3 … Tn) was stored as a function of the beat number. This series constitutes the RR interval time series (measured in ms). The reciprocal of this series represents the instantaneous HR (in beats per minute) and this was stored simultaneously to the electrocorticographic activity (ECoG, in µV) [30].
The types of stimulation were administered in a predetermined order. The times at which the stimuli were applied and their effects on ECoG, ECG and heart rate were recorded and subsequently evaluated semi-quantitatively. Specifically, in each case of stimulation, immediate reactions in the ECoG recordings, as well as in the ECG curve or the instantaneous heart rate (e.g., induced arrhythmias), were checked and, if necessary, the extent and duration of the electrophysiological events were classified (Table 1).

Table 1.
Electrophysiological significance score.
2.5. Statistics
Values are given as medians as well as the first quartile and third quartile. Comparisons between groups were made via one-way analysis of variance on ranks. Post hoc comparisons were made with the Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Differences in frequencies were considered significant at p values < 0.05.
3. Results
The effects of the different electrode-mediated DC or AC applications on intracavitary rat pulps showed that both the voltage type and the electrode design had a significant influence on the biological effects.
As shown in Table 2 and Figure 4a,b, the design of the BDD electrodes was crucial for the intensity of the electrophysiological effects. We found no detectable electrophysiological effects when using the inside BDD electrode (type i), which proves that this design of a BDD electrode is safe to use for endodontic electrochemical disinfection in living organisms. In contrast, the other BDD electrode design tested caused significant to serious effects. Significant and potentially dangerous effects were observed when using the outside BDD electrode (type ii) (Figure 4b, Table 2, p < 0.01). Generalized ECoG disorders occurred in almost all applications when using the type ii BDD electrode. Furthermore, we found short-term epilepsy-like discharges in the ECoG (Figure 4b). In addition, ECG disturbances and even brief heartbeat interruptions occurred, so this type of electrode must be considered potentially dangerous when used in living organisms. The use of the AC-operated electrotome (type iii) as a legally approved cutting and coagulation instrument in oral surgery was used as a reference for documenting the sensitivity of electrophysiological parameter detection. The use of the electrotome induced the strongest effects on ECoG and ECG recordings (Figure 4c, Table 2). However, it should be noted that the high-frequency AC application led to strong electromagnetic interferences, which always overdrive the ECG and ECG amplifiers during electrotome stimulation. Electric shortcuts (type iv) induced merely minor ECoG changes (Figure 4d, Table 2).

Table 2.
Effect of intracavitary pulp stimulation on ECG and ECoG.
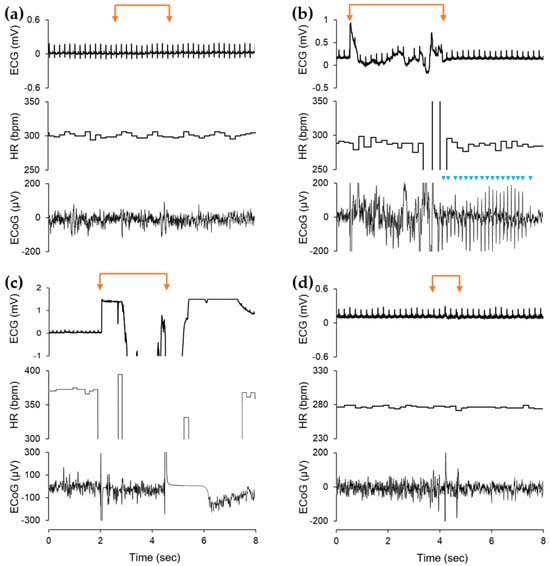
Figure 4.
Electrophysiological effects of intracavitary stimulation by three differently designed BDD electrodes in comparison with electrotome stimulation and short-circuit effects (representative examples). Note that (a) the BDD electrodes inside (i) had no visible effects on ECoG and ECG, while (b) BDD electrodes located outside (ii) had significantly stronger electrophysiological effects and even led to short-term epilepsy-like discharges in the ECoG (blue arrowheads). (c) The application of AC electrotome (iii) stimulation resulted in the greatest effects on ECoG and ECG, with transient overdrive of ECG and ECG amplifiers. (d) Electric shortcuts (iv) induced merely minor ECoG changes. (ECG, electrocardiogram; HR, heart rate; ECoG, electrocorticogram; orange-colored double arrows indicate stimulation periods).
4. Discussion
Our own previous work [1,2] on BDD electrodes, as well as the previous work of Ochiai et al. [31], showed that flexible BDD electrodes may be applied for electrochemical disinfection in dental root canal treatment. During these proof-of-concept and preliminary studies, the disinfective effect of BDD-processed electrolytes on microbial contaminations was proven using different prototypes. This animal study aimed to explore the potential generalized effects of prototype BDD electrodes intended for electrochemical disinfection [1,2] during endodontic treatment. Therefore, the focus of this study was not solely put on the electrophysiological effects, but also on design-dependent solutions for possible disturbances caused by different prototypes. With the final arrangement of the anode/cathode not yet determined, two different designs were applied. The design of the electrodes did have an effect on ECoG and ECG, with the anode (BDD-coated Nb wire) positioned inside the cathode (cannula) showing least interference. As expected, in this configuration, the electric current follows the path of least resistance and not affecting host tissues. With respect to the prototype design presented by Ochiai et al. [31] and our previously presented designs [1,2] this new generation of prototypes can be determined as suitable for use for electrochemical endodontic disinfection in living organisms. In contrast, it has been proven that, when BDD electrodes are used, design-related unshielded contact with body fluids leads to significant cerebral and cardiac effects (see Table 2, Figure 4b). Therefore, the main goal of the study was achieved by demonstrating that a design of the BDD electrodes for endodontic electrochemical disinfection could be developed that did not demonstrably cause any relevant electrophysiological cardiac or cerebral consequences in the living mammalian organism. Additionally, we also suggest that designs with direct contact between BDD anodes and patient tissue may lead to effects on human patients if DC currents higher than 20 mA are applied (Figure 1).
The investigations carried out revealed that it is obviously essential to prevent the spread of direct current to induce electrochemical disinfection as best as possible. Previous studies have already shown that direct currents in the µA range lead to changes in cortical polarization in rat brains with drastic consequences for cerebral excitability [32,33]. Direct current effects on the heart muscle seem rather unlikely because, due to the anatomical conditions, the heart is hardly in the direct area of influence of potential current flows. In addition, the expected current intensities are several orders of magnitude smaller than those that occur in electrical accidents with heart muscle damage. The recorded ECG effects are most likely caused by electromagnetic interferences when switching on and/or off or possibly by motion artifacts. Altogether, the applicability of DC-driven electrochemical disinfection requires a high level of safety in terms of DC shielding. This also applies to an artificial technical failure with a subsequent electric shortcut. Even if the results listed here only documented minor electrophysiological effects when using the electric shortcut electrode, it must be taken into account that the animals examined were under general anesthesia. The avoidance of pain and affliction in animal experiments is, in addition to the fundamental ethical, practical and physiological reasons, a basic legal requirement for the approval of such studies and is required to ensure that animal welfare is indispensable for good scientific practice [34]. Therefore, we have to state that cerebral excitability, information processing and metabolic activity are significantly reduced and, therefore, the susceptibility of the ECoG to electrical disturbances might be less sensitive [35,36,37]. Of course, the combination of ketamine and xylazine used here for general anesthesia resulted in a global reduction in cerebral glucose metabolism. However, this reduction in brain metabolism was relatively smaller in the primary somatosensory cortex, the region where dental pulp neuronal afferents are primarily processed and one’s own ECoG recordings are made [38]. Therefore, ECoG susceptibility may be less affected than expected. Furthermore, the use of this combination anesthesia is widely used in anesthesia for laboratory animals [39] and offers clear advantages, namely the availability of different routes of administration, such as intraperitoneal and intramuscular applications, sufficient surgical anesthesia time and also good pain relief in rats [40].
The maximum effect on recorded electrophysiological parameters was observed with the electrotome, which was applied in the maximum of possible settings for use in humans. When assessing the biological effect, it must be taken into account that the mode of operation of the electrotome for cutting or coagulating biological tissue is fundamentally different from that of the BDD electrodes for endodontal electrochemical disinfection. As already mentioned above, the electrochemical process for electrolysis with radical production for local disinfection is caused by a direct current. This can potentially lead to an electrical current flowing through brain and heart, with potentially fatal consequences. In contrast, the electrotome works with a high-frequency alternating current, which, due to the design used, does not lead to a transmitted current flow. Serious functional consequences, especially on the heart, such as fatal cardiac arrhythmias, are prevented by the high frequency used. The effects of the use of the electrotome recorded in the experiment are most likely caused by electromagnetic interferences, which always overdrive the ECG and ECG amplifiers during electrotome stimulation. Therefore, comparing the recorded effects of the AC-driven electrotome with those of the DC-driven BDD electrodes is not appropriate.
Given that the electrotome can safely be applied in human patients, it may be inferred that the BDD electrodes would be safe, too. Electrotomes have been used previously as a reference system for evaluating a plasma discharge device with respect to local tissue reaction [41], as well as energy-based surgical devices for thyroid surgery [42].
As already pointed out, AC and DC show different modes of interaction with the human body. Consequently, the comparison between instruments working on AC vs. DC may be seen as a limitation of this study. It might have been more relevant to use the GalvoSurge device (GalvoSurge Dental AG, Widnau, Switzerland), which, however, would have required adaptation to fit the rat animal model [43]. In the same context, the electrotome was used for this relative comparison, which is also reflected in the scoring system established here.
Further limitations include the fact that general anesthesia could not be standardized, resulting in initial heart rates of <250 bpm up to >350 bpm. Given that multiple applications were made in each animal, these factors should have only had a minor impact on the evaluation of the electrophysiological effects of the electrodes examined. A critical aspect was also the application of saline both during trepanation as well as during electrode application causing asphyxia. A better approach would have been to intubate the animals via a tracheostoma, which was not carried out for technical reasons as well as due to time constraints.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K. (Matthias Karl), M.W.L. and R.B.; methodology, R.B.; formal analysis, R.B.; investigation, M.K. (Maximilian Koch) and R.B.; resources, A.B. and M.K. (Matthias Karl); writing—original draft preparation, R.B., J.R., M.K. (Matthias Karl) and M.K. (Maximilian Koch); writing—review and editing, A.B., M.K. (Matthias Karl) and M.K. (Maximilian Koch); visualization, J.R., M.K. (Maximilian Koch) and R.B.; supervision, A.B. and M.K. (Matthias Karl); project administration, M.K (Matthias Karl). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the local governmental animal protection committee (Landesamt für Verbraucherschutz des Saarlandes; permission number: 08/2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
A. Burkovski and M. Karl declare a conflict of interest as inventors of BDD-mediated electrochemical disinfection. All other authors have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Böhm, A.L.; Koch, M.; Rosiwal, S.; Burkovski, A.; Karl, M.; Grobecker-Karl, T. Electrochemical Disinfection of Experimentally Infected Teeth by Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Palarie, V.; Koch, L.; Burkovski, A.; Zulla, M.; Rosiwal, S.; Karl, M. Preclinical Testing of Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes for Root Canal Disinfection-A Series of Preliminary Studies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enginalev, A.; Gura, E. Electrochemical preparation and treatment of the root canals using depotphoresis materials as galvanic post elements. ZWR 1985, 94, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knappwost, A.; Rudelt, H.G.; Fraber, R. Simulation studies on depot iontophoresis. Dtsch. Zahnarztl. Z. 1977, 32, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knappwost, A. New developments in depot inotophoresis of copper compounds. Dtsch. Zahnarztl. Z. 1977, 32, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knappwost, A.; Gura, E. Preparation of not completely accessible root canals by means of depot iontophoresis with an exterior iontrophoresis device. Dtsch. Zahnarztl. Z. 1979, 34, 477–479. [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer, G. VDE0100 und Die Praxis, 13th ed.; B. G. Teubner Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2010; pp. 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- DIN e.V. (Hrsg.). VDE 0100-410:2018-10, Errichten von Niederspannungsanlagen. In Teil 4.41—Schutzmaßnahmen—Schutz Gegen Elektrischen Schlag; VDE Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN 60601-1:2022-11; Medical Electrical Equipment—Part 1: General Requirements for Basic Safety and Essential Performance (IEC 60601-1:2005 + Cor1:2006 + Cor2:2007 + A1:2012 + A1:2012/Cor1:2014 + A2:2020); German Version EN 60601-1:2006 + Cor.:2010 + A1:2013 + AC:2014 + A1:2013/AC:2014 + A12:2014 + A2:2021. DIN Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2022.
- Biegelmeier, G.; Kieback, D.; Kiefer, G.; Krefter, K.-H. Schutz in Elektrischen Anlagen Band 1: Gefahren Durch Den Elektrischen Strom, 2nd ed.; VDE Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Dössel, O. Impedanz-Tomographie. In Bildgebende Verfahren in der Medizin, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Xie, R.; Deng, X. Electromagnetic interference effect of dental equipment on cardiac implantable electrical devices: A systematic review. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 43, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadalti, M.T.S.; da Cunha, A.J.L.A.; Araújo, M.C.P.; Moraes, L.G.B.; Risso, P.A. Electromagnetic interference of dental equipment with implantable cardioverter defibrillators. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2017, 75, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, U.; Studer, M.; Merkle, A.; Graf, H.; Simona, C. Effect of electrically powered dental devices on cardiac parameter function in humans. Parodontologie 1991, 2, 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda-Rius, J.; Lahor-Soler, E.; Brunet-Llobet, L.; Sabaté de la Cruz, X. Risk of electromagnetic interference induced by dental equipment on cardiac implantable electrical devices. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 124, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; West, L.A.; Liewehr, F.R.; Rueggeberg, F.A.; Sharpe, D.E.; Potter, B.J. Impact of dental devices on cochlear implants. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.; Vender, J.R.; Causey, M.S.; Roberts, J.R.; Loushine, R.J.; Morris, W.J.; Looney, S.W. The impact of dental devices on neurostimulators. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, P.; Shankargouda, S.; Dicksit, D.D.; Mahdey, H.M.; Muzaffar, D.; Arora, S. Evaluation of Interference of Cellular Phones on Electronic Apex Locators: An In Vitro Study. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idzahi, K.; de Cock, C.C.; Shemesh, H.; Brand, H.S. Interference of electronic apex locators with implantable cardioverter defibrillators. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, K.R.; Nikdel, K.; Guillaume, G.; Letra, A.M.; Silva, R.M.; Dorn, S.O. Evaluating the effects of different dental devices on implantable cardioverter defibrillators. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, H.S. Can dental equipment interfere with correct functioning of an ICD? Ned. Tijdschr. Voor Tandheelkd. 2022, 129, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorana, C.; Grossi, G.B.; Garramone, R.A.; Manfredini, R.; Santoro, F. Do ultrasonic dental scalers interfere with implantable cardioverter defibrillators? An in vivo investigation. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.L.; Broberg, C.; Baumgartner, J.C.; Harris, C.; Kron, J. Safety of electronic apex locators and pulp testers in patients with implanted cardiac pacemakers or cardioverter/defibrillators. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, R.R.; Ede, E.N.; Dorn, S.O.; Kuttler, S. Effect of electronic apex locators on cardiac pacemaker function. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, G.; Duran-Sindreu, F.; Jara Clemente, F.; Garofalo, R.R.; Garcia, M.; Bueno, R.; Roig, M. The effects of six electronic apex locators on pacemaker function: An in vitro study. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Mir, I.; Miranda-Rius, J.; Trucco, E.; Lahor-Soler, E.; Brunet-Llobet, L.; Domingo, R.; Tolosana, J.M.; Mont, L. In-vivo compatibility between pacemakers and dental equipment. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 126, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, C.W.; Bramwell, J.D.; Hutter, J.W. Use of an electronic apex locator on a cardiac pacemaker patient. J. Endod. 1996, 22, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriman, N.; Prabhakar, V.; Bhuvaneswaran, J.S.; Subha, N. Interference of apex locator, pulp tester and diathermy on pacemaker function. J. Conserv. Dent. 2015, 18, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapin, J.K.; Lin, C.S. Mapping the body representation in the SI cortex of anesthetized and awake rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 229, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndongson-Dongmo, B.; Lang, G.P.; Mece, O.; Hechaichi, N.; Lajqi, T.; Hoyer, D.; Brodhun, M.; Heller, R.; Wetzker, R.; Franz, M.; et al. Reduced ambient temperature exacerbates SIRS-induced cardiac autonomic dysregulation and myocardial dysfunction in mice. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2019, 114, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochiai, T.; Ishii, Y.; Tago, S.; Hara, M.; Sato, T.; Hirota, K.; Nakata, K.; Murakami, T.; Einaga, Y.; Fujishima, A. Application of Boron-Doped Diamond Microelectrodes for Dental Treatment with Pinpoint Ozone-Water Production. ChemPhysChem 2013, 14, 2094–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, F.; Fechner, R.; Haschke, W. Initiation of spreading depression can be blocked by transcortical polarization of rat cerebral cortex. Int. J. Neurosci. 1996, 86, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, F.; Fechner, R.; Haschke, W.; Fanardijan, V.V. Transcortical polarization in rat inhibits spreading depression. Int. J. Neurosci. 1994, 75, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar]
- Franks, N.P. General anaesthesia: From molecular targets to neuronal pathways of sleep and arousal. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasch, M.G.; Walter, B.; Friedrich, H.; Hoyer, D.; Eiselt, M.; Bauer, R. Detecting the signature of reticulothalamocortical communication in cerebrocortical electrical activity. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 1969–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, B.; Eiselt, M.; Cumming, P.; Xiong, G.; Hinz, R.; Uthe, S.; Brust, P.; Bauer, R. Resistance of brain glucose metabolism to thiopental-induced CNS depression in newborn piglets. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2013, 31, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prando, S.; Carneiro, C.G.; Otsuki, D.A.; Sapienza, M.T. Effects of ketamine/xylazine and isoflurane on rat brain glucose metabolism measured by (18) F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2019, 49, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, C.A.; Flecknell, P.A. Anaesthesia and post-operative analgesia following experimental surgery in laboratory rodents: Are we making progress? Altern. Lab. Anim. 2005, 33, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitrago, S.; Martin, T.E.; Tetens-Woodring, J.; Belicha-Villanueva, A.; Wilding, G.E. Safety and efficacy of various combinations of injectable anesthetics in BALB/c mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2008, 47, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Justan, I.; Tichý, F.; Slavícek, P. A new type of plasma knife and its effect on biological issues-a pilot study. Acta Chir. Plast. 2010, 52, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Cao, J.; Yan, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, T.; Han, L.; Ye, C.; Zheng, S.; Wang, S.; Ye, Y.; et al. Comparison of the safety of electrotome, Harmonic scalpel, and LigaSure for management of thyroid surgery. Head Neck 2017, 39, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratka, C.; Weigl, P.; Henrich, D.; Koch, F.; Schlee, M.; Zipprich, H. The Effect of In Vitro Electrolytic Cleaning on Biofilm-Contaminated Implant Surfaces. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).