Multi-Layer Fusion 3D Object Detection via Lidar Point Cloud and Camera Image
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
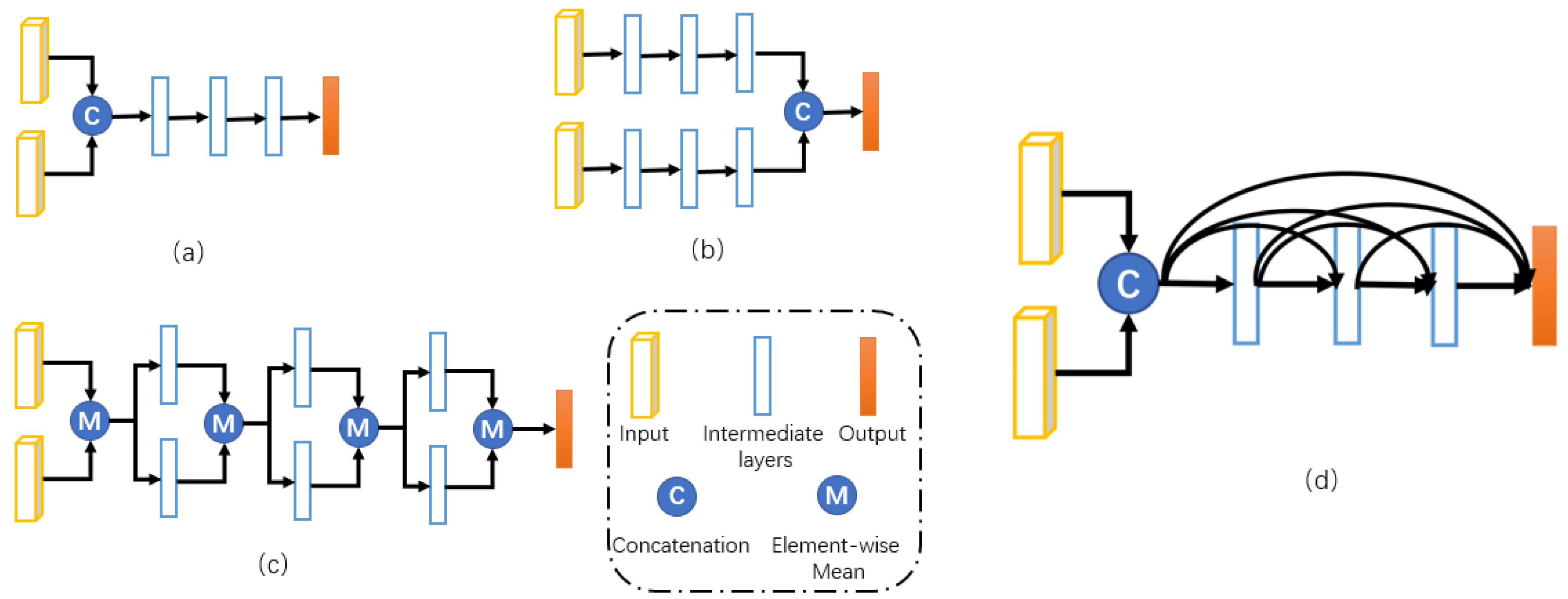
- A novel fusion method, D-fusion, is proposed, which can preserve the information of each layer of the fusion network to solve the problem of semantic loss and improve fusion performance.
- (2)
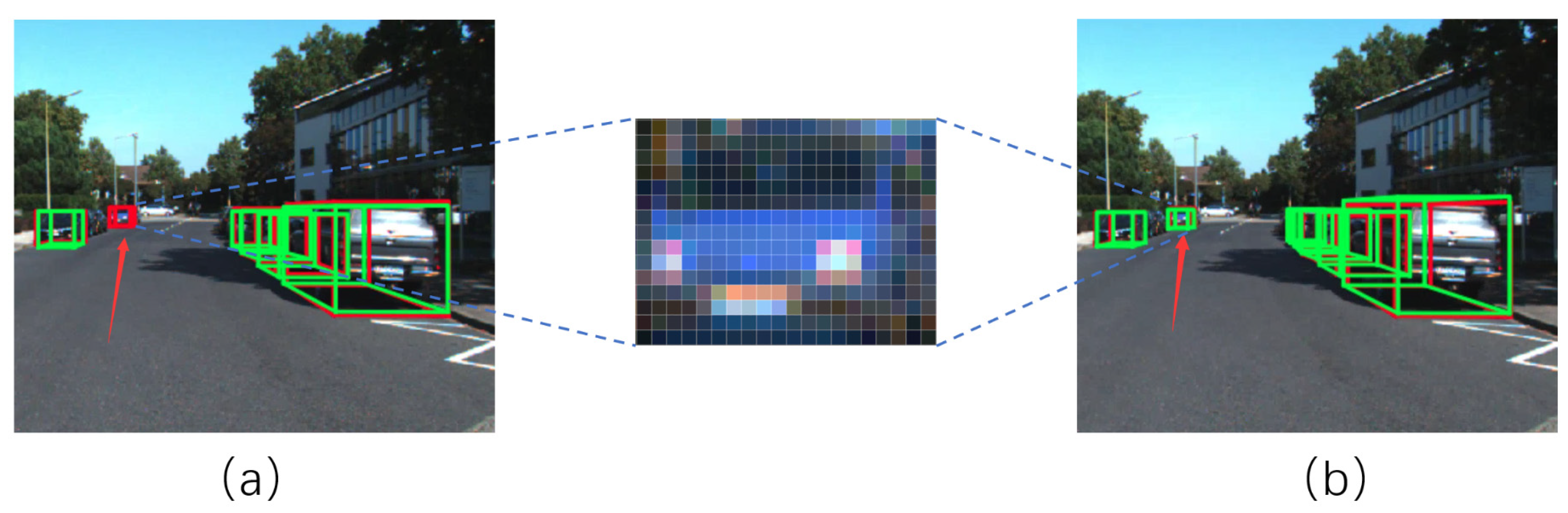
- We designed an adaptive fusion module (AFM) and applied it after using the feature extraction network, which effectively solves the problem of small-scale object loss in detection tasks.
- (3)
- An attention mechanism was introduced to optimize the efficiency of the feature extraction network.
- (4)
- We conducted comparative experiments on the challenging KITTI data set, and the results show that our network achieves satisfactory performance.
2. Related Works
2.1. Image-Based 3D Object Detection
2.2. Point Cloud-Based 3D Object Detection
2.3. Fusion-Based 3D Object Detection
2.4. Detection of Small Objects
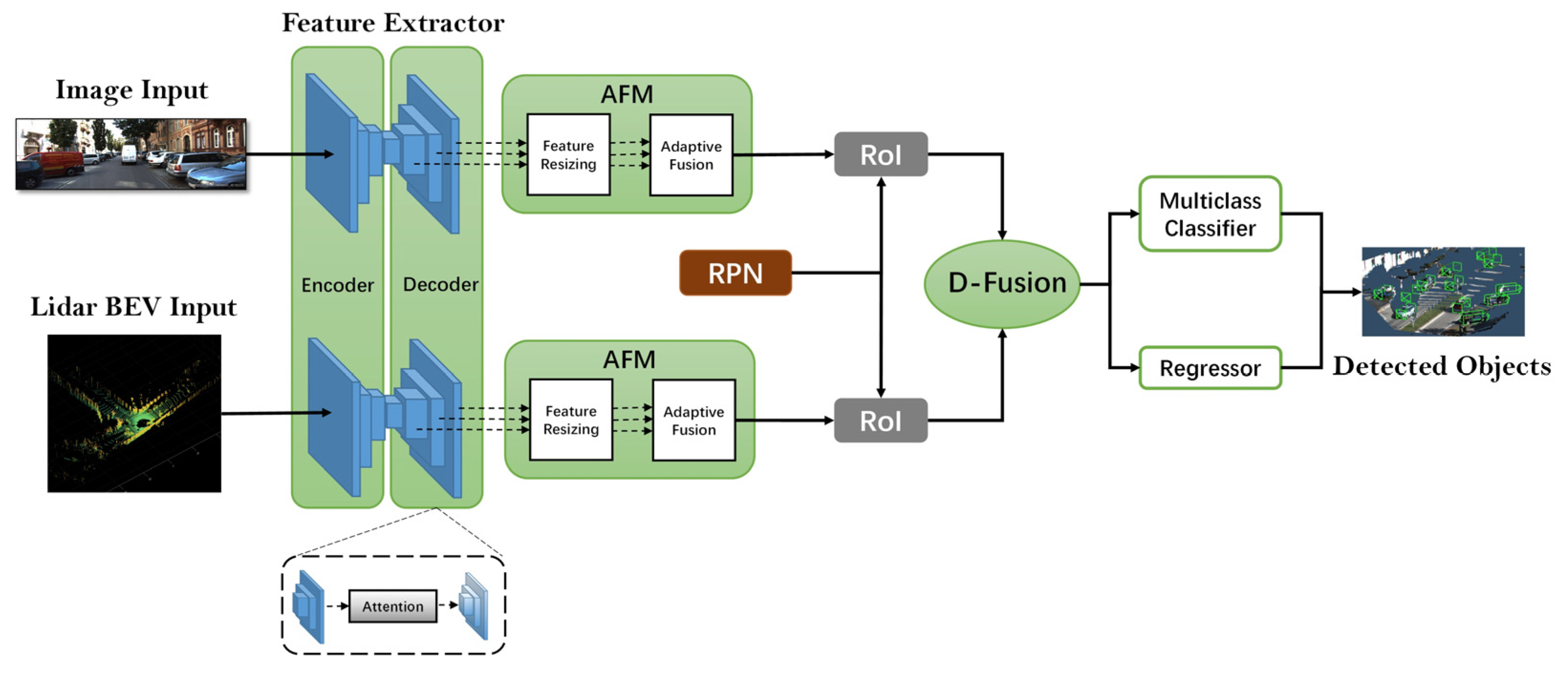
3. The Proposed Approach
3.1. Inputs
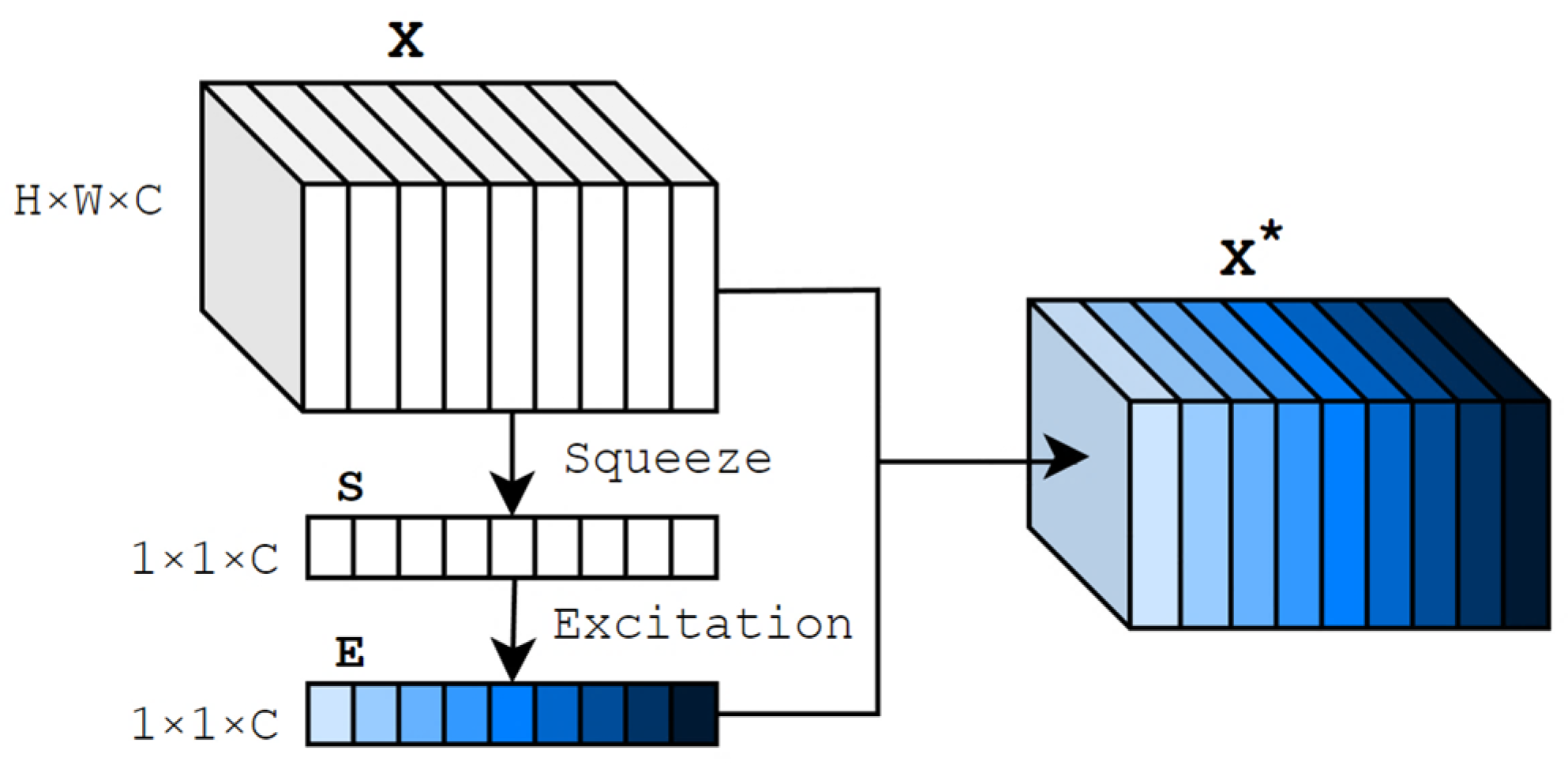
3.2. Feature Extractor
3.3. RPN
3.4. D-Fusion
3.5. Training
4. Experiment and Results
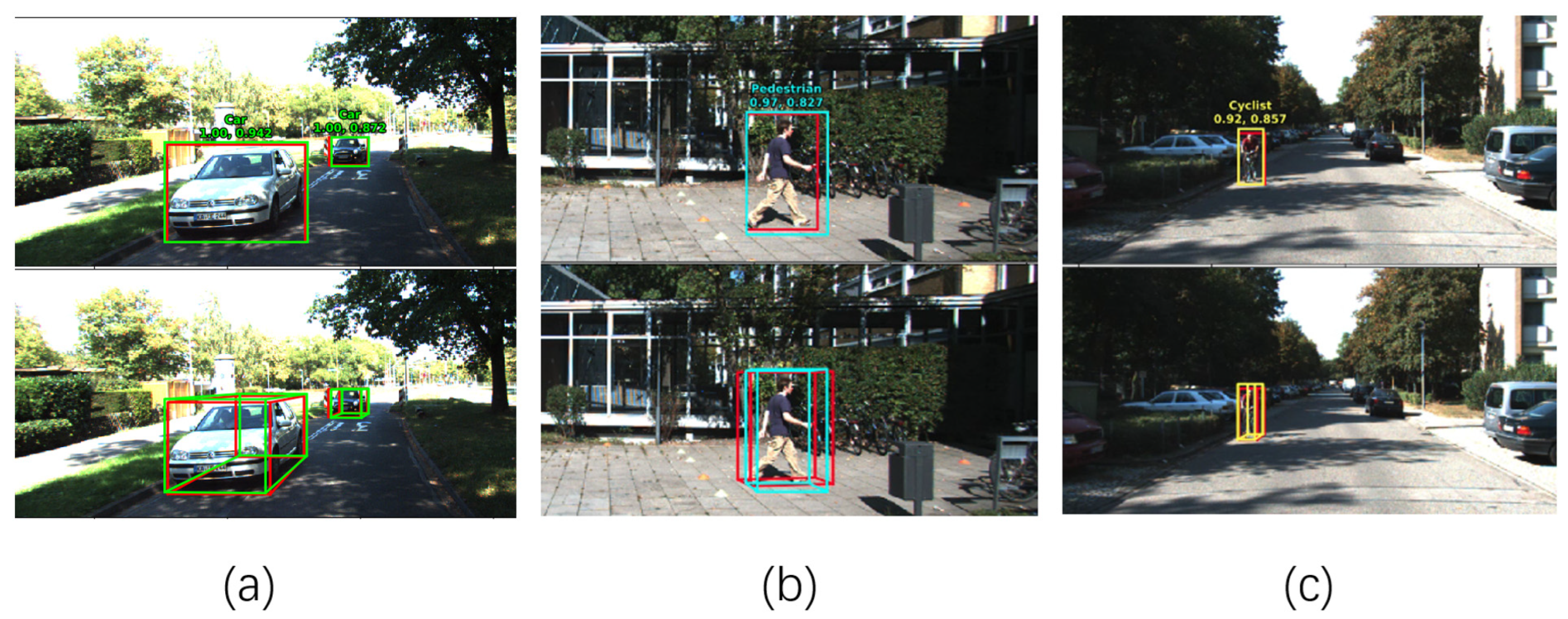
4.1. 3D Detection
4.2. The Effect of D-Fusion
4.3. The Effect of AFM and SENet
4.4. Ablation Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Kundu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, H.; Fidler, S.; Urtasun, R. Monocular 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2147–2156. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y. MonoGRNet: A Geometric Reasoning Network for Monocular 3D Object Localization. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hilton, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 8851–8858. [Google Scholar]
- Chabot, F.; Chaouch, M.; Rabarisoa, J.; Teuliere, C.; Chateau, T. Deep manta: A coarse-to-fine many-task network for joint 2d and 3d vehicle analysis from monocular image. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2040–2049. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Tóth, R. Smoke: Single-stage monocular 3d object detection via keypoint estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 996–997. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Kundu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, H.; Fidler, S.; Urtasun, R. 3d object proposals using stereo imagery for accurate object class detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Chen, Z. Multi-level fusion based 3d object detection from monocular images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2345–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Chen, Z. Confidence guided stereo 3D object detection with split depth estimation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 5776–5783. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.N.; Dai, H.; Ding, Y. Pseudo-stereo for monocular 3d object detection in autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 887–897. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, Y. SIDE: Center-based stereo 3D detector with structure-aware instance depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Jia, J. 3dssd: Point-Based 3D Single Stage Object Detector. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11037–11045. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Xiong, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z. Rangedet: In defense of range view for lidar-based 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2898–2907. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Tang, W.; Jiang, L.; Fu, C.W. SE-SSD: Self-Ensembling Single-Stage Object Detector From Point Cloud. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14489–14498. [Google Scholar]
- Vora, S.; Lang, A.H.; Helou, B.; Beijbom, O. Pointpainting: Sequential fusion for 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4604–4612. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Xiang, C.; Yu, Z.; Xu, G.; Yang, Z.; Cai, D.; He, X. PI-RCNN: An efficient multi-sensor 3D object detector with point-based attentive cont-conv fusion module. In Proceedings of the 2020 AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12460–12467. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Pointrcnn: 3d object proposal generation and detection from point cloud. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 770–779. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Caesar, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Beijbom, O. Pointpillars: Fast encoders for object detection from point clouds. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12697–12705. [Google Scholar]
- Sindagi, V.A.; Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. Mvx-net: Multimodal voxelnet for 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 7276–7282. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Liu, W.; Wu, C.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Frustum PointNets for 3D Object Detection from RGB-D Data. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 918–927. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, D.; Yurtsever, E.; Redmill, K.A.; Özgüner, Ü. Faraway-frustum: Dealing with lidar sparsity for 3D object detection using fusion. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 2646–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Kui, J. Frustum convnet: Sliding frustums to aggregate local point-wise features for a modal 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 4–8 November 2019; pp. 1742–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ma, H.; Wan, J.; Li, B.; Xia, T. Multi-view 3D Object Detection Network for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6526–6534. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, J.; Mozifian, M.; Lee, J.; Harakeh, A.; Waslander, S.L. Joint 3d proposal generation and object detection from view aggregation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y. SCANet: Spatial-channel attention network for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 1992–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Yang, B.; Wang, S.; Urtasun, R. Deep continuous fusion for multi-sensor 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 641–656. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.S.; Chen, H.H.; Hsiao, P.Y.; Fu, L.C.; Siao, S.M. CrossFusion net: Deep 3D object detection based on RGB images and point clouds in autonomous driving. Image Vis. Comput. 2020, 100, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Ma, C.; Ji, P.; Yang, X. Cross-modality 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikola, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 3772–3781. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Fragonara, L.Z.; Tsourdos, A. RoIFusion: 3D object detection from LiDAR and vision. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 51710–51721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Morris, D.; Radha, H. CLOCs: Camera-LiDAR object candidates fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 10386–10393. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.Y.; Liu, W.; Ranga, A.; Tyagi, A.; Berg, A.C. Dssd: Deconvolutional single shot detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.06659. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.S.; Astrid, M.; Yoon, H.J.; Lee, S.I. Small object detection using context and attention. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kisantal, M.; Wojna, Z.; Murawski, J.; Naruniec, J.; Cho, K. Augmentation for small object detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.07296. [Google Scholar]
- Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Vgg Convolutional Neural Networks Practical; Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2016; Volume 66. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Stiller, C.; Urtasun, R. Vision meets robotics: The kitti dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]


| Method | Class | AP3D (%) | APBEV (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Moderate | Hard | Easy | Moderate | Hard | ||
| MV3D | Car | 71.09 | 62.35 | 55.12 | 86.02 | 76.90 | 68.49 |
| AVOD | 73.59 | 65.78 | 58.38 | 86.80 | 85.44 | 77.73 | |
| AVOD-FPN | 81.94 | 71.88 | 66.38 | 88.53 | 83.79 | 77.90 | |
| F-PointNet | 81.20 | 70.39 | 62.19 | 88.70 | 84.00 | 75.33 | |
| SCANet | 83.63 | 74.47 | 67.78 | - | - | - | |
| MVX-Net | 83.20 | 72.70 | 65.20 | 89.20 | 85.90 | 78.10 | |
| ContFuse | 82.54 | 66.22 | 64.04 | 88.81 | 85.83 | 77.33 | |
| CrossFusion | 83.20 | 74.50 | 67.01 | 88.39 | 86.17 | 78.23 | |
| Ours | 85.58 | 75.37 | 68.83 | 89.59 | 86.62 | 79.52 | |
| MV3D | Ped | 39.48 | 33.69 | 31.51 | 46.13 | 40.74 | 38.11 |
| AVOD | 38.28 | 31.51 | 26.98 | 42.52 | 35.24 | 33.97 | |
| AVOD-FPN | 50.80 | 42.81 | 40.88 | 58.75 | 51.05 | 47.54 | |
| F-PointNet | 51.21 | 44.89 | 40.23 | 58.09 | 50.22 | 47.20 | |
| Ours | 53.87 | 51.27 | 45.99 | 62.00 | 56.19 | 49.97 | |
| MV3D | Cyc | 61.22 | 48.36 | 44.37 | 66.70 | 54.76 | 50.55 |
| AVOD | 60.11 | 44.90 | 38.80 | 63.66 | 47.74 | 46.55 | |
| AVOD-FPN | 64.00 | 52.18 | 46.61 | 68.09 | 57.48 | 50.77 | |
| F-PointNet | 71.96 | 56.77 | 50.39 | 75.38 | 61.96 | 54.68 | |
| Ours | 68.66 | 42.23 | 41.71 | 68.28 | 46.48 | 40.64 | |
| Method | Class | AP3D (%) | APBEV (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Moderate | Hard | Easy | Moderate | Hard | ||
| Early fusion | Car | 82.12 | 73.87 | 67.70 | 88.50 | 86.07 | 79.03 |
| Late fusion | 70.28 | 56.48 | 55.85 | 86.47 | 77.17 | 70.03 | |
| Deep fusion | 82.86 | 73.42 | 67.30 | 89.07 | 85.91 | 78.99 | |
| D-fusion (Ours) | 85.58 | 75.37 | 68.83 | 89.59 | 86.62 | 79.52 | |
| Early fusion | Ped | 45.60 | 40.75 | 35.07 | 48.71 | 43.42 | 37.23 |
| Late fusion | 48.77 | 43.75 | 37.20 | 52.64 | 46.55 | 45.16 | |
| Deep fusion | 47.16 | 40.85 | 35.21 | 54.43 | 47.69 | 41.83 | |
| D-fusion (Ours) | 53.87 | 51.27 | 45.99 | 62.00 | 56.19 | 49.97 | |
| Early fusion | Cyc | 49.62 | 32.1 | 31.57 | 50.09 | 32.49 | 31.89 |
| Late fusion | 65.19 | 40.71 | 40.32 | 65.72 | 41.35 | 40.73 | |
| Deep fusion | 46.22 | 29.07 | 23.66 | 47.16 | 29.66 | 29.37 | |
| D-fusion (Ours) | 68.66 | 42.23 | 41.71 | 68.28 | 46.48 | 40.64 | |
| Method | Class | AP3D (%) | APBEV (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Moderate | Hard | Easy | Moderate | Hard | ||
| FPN | Car | 83.25 | 74.55 | 67.46 | 89.24 | 86.57 | 78.81 |
| AFM | 84.71 | 74.79 | 68.17 | 89.77 | 86.84 | 79.34 | |
| AFM and SENet | 85.12 | 75.65 | 68.78 | 89.74 | 86.66 | 79.39 | |
| FPN | Ped | 47.33 | 41.23 | 35.29 | 55.40 | 48.57 | 42.27 |
| AFM | 61.32 | 54.47 | 47.62 | 59.30 | 52.60 | 46.17 | |
| AFM and SENet | 50.69 | 45.17 | 39.88 | 57.01 | 50.37 | 44.09 | |
| FPN | Cyc | 48.48 | 31.25 | 25.66 | 49.16 | 31.75 | 25.92 |
| AFM | 66.65 | 40.97 | 40.46 | 67.21 | 40.80 | 40.51 | |
| AFM and SENet | 68.03 | 41.88 | 41.45 | 69.20 | 42.71 | 41.74 | |
| Method | Class | AP3D (%) | APBEV (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Moderate | Hard | Easy | Moderate | Hard | ||
| D-fusion | Car | 83.99 | 74.93 | 68.08 | 89.41 | 80.12 | 79.21 |
| AFM | 84.52 | 74.60 | 68.00 | 89.33 | 86.37 | 79.32 | |
| SENet | 82.90 | 73.40 | 66.98 | 88.59 | 85.73 | 78.65 | |
| D-fusion and AFM | 85.11 | 75.70 | 68.64 | 89.19 | 86.56 | 79.29 | |
| D-fusion and SENet | 84.45 | 74.80 | 67.64 | 89.53 | 80.13 | 79.05 | |
| AFM and SENet | 85.12 | 75.65 | 68.78 | 89.74 | 86.66 | 79.39 | |
| D-fusion and AFM and SENet | 85.58 | 75.37 | 68.83 | 89.59 | 86.72 | 79.52 | |
| D-fusion | Ped | 53.98 | 48.44 | 41.90 | 57.95 | 51.97 | 45.09 |
| AFM | 59.27 | 52.56 | 46.14 | 61.35 | 54.54 | 47.64 | |
| SENet | 47.33 | 41.23 | 35.29 | 55.40 | 48.57 | 42.27 | |
| D-fusion and AFM | 53.98 | 48.78 | 42.87 | 57.13 | 51.41 | 45.09 | |
| D-fusion and SENet | 53.84 | 50.65 | 45.14 | 58.79 | 53.42 | 47.65 | |
| AFM and SENet | 54.02 | 43.79 | 41.83 | 54.83 | 49.23 | 43.23 | |
| D-fusion and AFM and SENet | 53.87 | 51.27 | 45.99 | 62.00 | 56.19 | 49.97 | |
| D-fusion | Cyc | 68.07 | 41.84 | 41.22 | 58.61 | 40.46 | 39.90 |
| AFM | 66.65 | 40.97 | 40.46 | 67.21 | 40.80 | 40.51 | |
| SENet | 48.48 | 31.25 | 25.66 | 49.16 | 31.75 | 25.92 | |
| D-fusion and AFM | 69.11 | 43.42 | 42.40 | 69.72 | 43.95 | 42.95 | |
| D-fusion and SENet | 61.19 | 41.38 | 34.57 | 61.70 | 41.67 | 34.81 | |
| AFM and SENet | 67.93 | 42.11 | 41.07 | 68.53 | 42.31 | 41.92 | |
| D-fusion and AFM and SENet | 68.66 | 42.23 | 41.71 | 68.28 | 46.48 | 40.64 | |
| Architecture | Number of Parameters |
|---|---|
| Base Model | 26,265,899 |
| Backbone (Image and Lidar) | 9,366,336 & 9,366,336 |
| AFM | 64,515 |
| SENet | 717,440 |
| D-fusion | 12,589,056 |
| Total | 38,854,955 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Hu, H. Multi-Layer Fusion 3D Object Detection via Lidar Point Cloud and Camera Image. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041348
Guo Y, Hu H. Multi-Layer Fusion 3D Object Detection via Lidar Point Cloud and Camera Image. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(4):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041348
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yuhao, and Hui Hu. 2024. "Multi-Layer Fusion 3D Object Detection via Lidar Point Cloud and Camera Image" Applied Sciences 14, no. 4: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041348
APA StyleGuo, Y., & Hu, H. (2024). Multi-Layer Fusion 3D Object Detection via Lidar Point Cloud and Camera Image. Applied Sciences, 14(4), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14041348








