Abstract
In recent years, wind energy has become remarkably popular among renewable energy sources due to its low installation costs and easy maintenance. Having high energy potential is of great importance in the selection of regions where wind energy investments will be made. In this study, the wind power potential in Çanakkale Province, located in the northwest of Türkiye, is examined, and the wind speed is estimated using hourly and daily data over a one-year period. The data, including 12 different meteorological parameters, were taken from the Turkish State Meteorological Service. The two-parameter Weibull and Rayleigh distributions, which are the most widely preferred models in wind energy studies, are employed to estimate the wind power potential using hourly wind speed data. The graphical method is implemented to calculate the shape (k) and scale (c) parameters of the Weibull distribution function. Daily average wind speed estimation is performed with artificial neural network–genetic algorithm (ANN-GA) and ANN–particle swarm optimization (ANN-PSO) hybrid approaches. The proposed hybrid ANN-GA and ANN-PSO algorithms provide correlation coefficient values of 0.94839 and 0.94042, respectively, indicating that the predicted and measured wind speed values are notably close. Statistical error indices reveal that the ANN-GA model outperforms the ANN-PSO model.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the energy consumption of countries has risen due to the rapid development of technology and population growth. The increasing need for energy and the depletion of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas have revealed the demand for renewable energy sources (RESs). Wind energy, which is one of the most widely used RESs, has attracted attention since it is a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels. Having high energy potential is of great importance in the selection of regions to be invested in wind energy. Therefore, the proper estimation of wind energy potential has become an important research issue that researchers have also focused on. Owing to the variable and unpredictable nature of wind energy, several methods have been developed to estimate wind speed and wind power potential using measured wind data.
There have been numerous research studies on the topic of wind speed estimation methods to realize investments effectively by evaluating the wind power potential of a region. Table 1 summarizes the prominent studies on wind speed estimation in the literature in terms of the time granularity, estimation method, and error metrics. It is seen that four main categories are highlighted for the estimation of wind power when the current studies are evaluated: (i) physical models, (ii) statistical models, (iii) artificial intelligence (AI)-based models, and (iv) hybrid approaches [1,2].
Physical models, which are based on the use of weather data such as temperature, humidity, pressure, terrain, and obstacles, are preferred to achieve more accurate results for long-term prediction. It should be noted here that Santhosh et al. [3] divided the wind speed forecasting process into four classes according to time horizons: very short-term, short-term, medium-term, and long-term. If the prediction is made for less than 30 min, it is called very short-term prediction; if it is 30 min to 6 h, it is called short-term prediction; if it is 6 h to 24 h, it is called medium-term prediction; and if it is 1 day to 7 days, it is called long-term prediction. These models require large computational resources, since complicated mathematical equations are implemented. Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) is one of the best-known examples of this type of model in the literature. Most of the early studies performed in the literature on wind speed estimation are based on physical models. A review of the use of NWP models for wind energy assessments is presented by Al-Yahyai et al. [4]. Statistical methods are generally appropriate for the short-term prediction of wind data. In statistical methods, large amounts of data are analyzed to determine the relationship between historical wind data and weather, and then this relationship is used to forecast future wind values. Unlike physical methods, there is no requirement to use complex mathematical equations in statistical methods. The Weibull and Rayleigh distribution models are the two most widely used types of this approach. Several studies have been conducted on the estimation of wind speed and wind power by using Weibull and Rayleigh probability density functions (PDFs) [5]. It has been emphasized in [6,7] that the Weibull function gave more accurate results in the estimation of wind energy potential when compared with the Rayleigh function. To determine the shape (k) and scale (c) parameters of the Weibull function, different techniques existing in the literature were reviewed, and the most frequently used techniques in the literature are the Maximum Likelihood Method (MLM) [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17], the Graphical Method (GM) [8,10,11,12,14,15,16,18,19], the Energy Pattern Factor Method (EPFM) [9,15,16,18,20] and the Least-Squares Regression (LSR) method [11,12,13,16].
Recent studies have shown that AI methods, which reveal the best prediction results in most cases, are one of the main interests in the topic of wind speed and wind power estimation. Many studies on wind speed and wind power estimation have been conducted using AI methods such as artificial neural networks (ANNs), deep learning, and machine learning. In studies by Brahimi et al. [21] and Dumitru et al. [22], a feedforward ANN is implemented to predict daily wind speeds using meteorological measurement data. Kumar and Malik [23] introduced a Generalized Regression Neural Network (GRNN) and Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) for long-term wind speed estimation. It has been shown that the GRNN gives a better result than the MLP as a result of the comparison of these two models using the mean square error (MSE) metric [23]. Navas et al. [24] developed a wind speed prediction model using different ANNs, such as the Multi-Layer Perceptron Neural Network (MLPNN) and Radial Basis Function Neural Network (RBFNN). Demolli et al. [25] performed wind power prediction based on daily wind speed data for different locations by using various machine learning algorithms, namely Least Absolute Shrinkage Selector Operator (LASSO) Regression, k-Nearest Neighbor Regression, Extreme Gradient Boost Regression, Random Forest Regression (RFR), and Support Vector Regression (SVR). Lawan et al. [26] proposed a topographic machine learning-based wind speed estimation model for the evaluation of onshore wind power potential and presented the comparison of the developed terrain-based ANN model and the Support Vector Machine (SVM).
Various research papers have been published on the prediction of wind speed and wind power using hybrid approaches that combine statistical techniques, AI models, machine learning algorithms, deep learning algorithms, and optimization algorithms. Hybrid approaches that exploit the advantages of different techniques provide improved prediction accuracy and performance. Alencar et al. [27] presented a hybrid algorithm composed of the Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (SARIMA) and Neural Network (NN) for multi-step-ahead wind speed forecasting using explanatory variables. The suggested hybrid algorithm was verified by comparing it with other well-known techniques in the literature, such as the NN, SARIMA, and SARIMA + Wavelet. Mohammed et al. [28] utilized a short-time-period wind speed forecasting method based on Variational Mode Decomposition—ANN (VMD-ANN). Ozkan et al. [29] introduced a short-term wind power forecast model, Statistical Hybrid Wind Power (SHWIP), and compared it with well-known models such as the ANN and SVM in the literature. Zhang et al. [30] addressed a prediction model combined with an NN, Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), and SVR. Khosravi et al. [31] employed three machine learning algorithms called a Multi-Layer Feed-Forward Neural Network (MLFFNN), SVR with a Radial Basis Function (SVR-RBF), and the Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFISs) optimized with PSO (ANFIS-PSO) to estimate the wind speed, wind direction, and output power of a wind turbine. Asghar et al. [32] adopted a hybrid intelligence learning-based ANFIS to estimate the Weibull PDF with available wind speed data, and then compared the results with five well-known methods: the GM, the Empirical Method of Justus (EMJ), the Empirical Method of Lysen (EML), the Method of Moments (MOM), and the EPFM. Saeed et al. [33] introduced an AI optimization approach based on the Chebyshev metric to estimate the Weibull PDF parameters. This algorithm was then evaluated together with four different AI optimization algorithms (the Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO), Bat Optimization (BOA), the Genetic Algorithm (GA), and the Artificial Bee Colony (ABCOA)) to obtain the optimum Weibull distribution parameters. Aly et al. [34] proposed hybrid deep learning clustered models for the prediction of wind speed and wind power using various combinations of the Recurrent Kalman Filter (RKF), the Fourier Series (FS), the Wavelet Neural Network (WNN), and the ANN for optimal performance. Lin et al. [35] carried out a study using both time-series data and multivariate regression data to forecast wind speeds in Taiwan. The SARIMA method and the Least-Squares Support Vector Regression for Time Series with Genetic Algorithms (LSSVRTSGA) were applied to forecast wind speed in a time series, and the Least-Squares Support Vector Regression with Genetic Algorithms (LSSVRGA) and Deep Belief Network with Genetic Algorithms (DBNGA) models were utilized for the prediction of wind speed in a multivariate format. Fazelpour et al. [36] analyzed four methods (ANN with RBF, ANFIS, ANN-GA, and ANN-PSO) based on AI to forecast short-term wind speed data. An AI approach composed of a hybrid NN modified by GA and PSO, which functioned as a model predictor, was recommended to forecast maritime weather variables an hour ahead by Arifin et al. [37].
In this study, a comprehensive and detailed comparison is made by using four different wind speed and wind power estimation approaches. For the first time in the literature for the Çanakkale region, both hourly and daily wind speed estimations are realized using these four methods. Two different statistical methods are utilized to determine the hourly wind speed: the Weibull and Rayleigh distributions. In addition, the ANN-GA and ANN-PSO hybrid approaches are proposed for daily estimation. After evaluating the performances of these four methods separately, wind power density estimation is performed for all methods on a daily basis and a comparison is established. Meteorological data, including the average wind speed and direction at an altitude of 10 m, the wet bulb temperature, the actual pressure, the maximum and minimum temperature, the relative humidity, the average temperature, the total global solar radiation, the areal precipitation, the amount of cloudiness, the sea water temperature, and the hours of sunshine, are taken from the Turkish State Meteorological Service for a 12-month time frame and analyzed in detail.
There is a lack of publications on wind speed and wind power estimation for the Çanakkale region using hybrid and AI-based methods. It is found that the hybrid ANN-GA and ANN-PSO methods are not applied together with the Weibull and Rayleigh techniques and the performance comparison of these methods has not been presented previously in the few existing studies carried out for this region. With the aim of filling the gap in the literature, this paper is proposed and organized into four sections. After this introduction, which presents a comprehensive literature review, theoretical calculations and an analysis of wind data in Çanakkale are provided in Section 2. The analysis results and discussion are given in Section 3. Finally, the conclusions of this study are presented in Section 4.

Table 1.
Comparison of the time granularity, estimation method, and error metrics of the studies on wind speed forecasting.
Table 1.
Comparison of the time granularity, estimation method, and error metrics of the studies on wind speed forecasting.
| References | Measurement Period/Sampling Interval | Location | Proposed Estimation Method | Error Calculation Technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | June 2016–May 2017 | Brazil | SARIMA—NN | MAE, MAPE, RMSE |
| [28] | 15 min time interval | Liaoning, China | VMD—ANN | MAE, RMSE, R |
| [30] | 10 min time interval | China | PSO-SVR-NN | MAE, MAPE, RMSE |
| [31] | 2008–2016 | Bushehr, Iran | MLFFNN, SVR-RBF, ANFIS-PSO | RMSE, R, MSE |
| [26] | 2007–2016 | Sibu, Malaysia | Terrain-Based ANN | R, MAPE |
| [1] | 2013–2014 | Ankara, Türkiye | Weibull Function | - |
| [38] | 10 min periods, 30 min periods | Penglai, China | NN-Linear Combination | RMSE, MAE, MAPE |
| [24] | April 2006–March 2007 | Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India | MLPNN, RBFNN | R2, MSE |
| [21] | May 2013–July 2016 | Saudi Arabia | ANN | R, RMSE |
| [6] | 2000–2016 | Incheon, South Korea | Weibull and Rayleigh | RMSE, R2, X2 |
| [8] | 1995–2002,2012–2013 | Giruliai, Lithuania | Weibull—MLM, Weibull—MSSDM | RMSE, R2, X2 |
| [22] | 4 years | Romania | Feedforward ANN | RMSE |
| [39] | - | - | ANN with BP, ANN with ELM | RMSE, R2, R |
| [32] | - | - | ANFIS-Weibull | RMSE |
| [9] | 2004, 2005, 2006, 2009 | Florya, Yalova, Gebze, Biga | MUOM-Weibull | R2, KS, RMSE, X2, PDE |
| [40] | 2014, 2016 | Xinjiang, China | SSA, Hybrid Laguerre NN | RMSE, MAE |
| [18] | 2016–2018 | Northern Pakistan | MOM, EML, EMJ, EPFM, MMLM, GM | RMSE, R2, MBE |
| [10] | 2009–2013 | Hatay, Osmaniye, Türkiye | Weibull with GM, MLM, EML, EPM, MOM | RMSE, R2, MPE |
| [5] | January 2008–August 2011 | Osmaniye, Türkiye | Weibull and Rayleigh with GM | - |
| [19] | 2013 | Osmaniye, Türkiye | Weibull and Rayleigh with GM, MOM | - |
| [11] | 2008–2012 | Jubail, Saudi Arabia | Weibull with MLM, LSR | RMSE, R2, MAE, MBE |
| [7] | 12 months | Northern Morocco | Weibull and Rayleigh | RMSE, R2, MBE |
| [12] | September 2014 | Southern India | Weibull with GM, MOM, EMJ, EML, LSR, MLM, MMLM, PDM, AMLM | RMSE, MAPE, R2, X2 |
| [13] | Period of a year | Saudi Arabia | Weibull with MOM, LSR, MLM | MSE |
| [41] | 1971–2000 | Poland | Two and three-parameter Weibull | R2, SE |
| [42] | 2010–2014 | Bohawian, China | Weibull-AI (GWO, PSO, CS, EMJ, EML, EPFM, MLM) | RRMSE, R2 |
| [43] | September 2014 | Kayathar, Tamil Nadu, India | Weibull with nine different methods | RMSE, MAPE, R2, X2 |
| [44] | 1960–1978 | Faya-Largeau, Chad | Weibull | - |
| [33] | April 2016–December 2018 | Coastal region ofPakistan | Weibull-AI (GWO, BOA, GA, ABCOA) | RMSE, R2, MBE |
| [45] | 2009–2013 | Southern region of Türkiye(Adana, Osmaniye, Hatay) | Weibull with the PDM | R2, MPE, RMSE |
| [14] | Period of a year | Hawke’s Bay region of Pakistan | Weibull with EM, MLM, MMLM, EPM, GM | RMSE, R2 |
| [15] | 2007–2013 | Bafoussam, Cameroon | Weibull with EMJ, EML, MOM, GM, Mmab, MLM, EPFM, MMLM, EEM, AMLM | RMSE, R2, X2 |
| [16] | 2018 | İzmir, Türkiye | Weibull with GM, MLM, EPFM | RMSE, R2, X2 |
| [17] | 2014 | Lithuania | MLM, MMLM, WAsP, Rayleigh | MSE, R2, X2, RE |
| [20] | 2014–2018 | Punjab, Pakistan | Weibull with EPFM | RMSE, R2 |
| [25] | 4 years | Niğde, Cesme, Mamak, Bozcaada, and Silivri, Türkiye | Machine Learning Algorithms(LASSO, KNN, xGBoost, SVR, RFR) | RMSE, R2, MAE |
| [34] | - | - | Hybrid Deep Learning Models(RKF, FS, WNN, ANN) | MAPE, nRMSE |
| [35] | January 2017–December 2017 | Taiwan | DBNGA, SARIMA, LSSVRTSGA, LSSVRGA | MAPE, RMSE |
| [36] | Period of a year with 1 h intervals | Tehran, Iran | ANN-RBF, ANFIS, ANN-GA, ANN-PSO | RMSE, MSE |
| [37] | May 2014–April 2015 | Madura Strait, Java Sea | Hybrid NN-GA, NN-PSO | RMSE, MAPE, SDE, SSE |
| [46] | 24 h ahead | Beijing, China | PSO-ANN | - |
| [47] | March–May 2009 | Mongolia | ANN, Hybrid Model | RMSE |
| [23] | Period of a year | Western region of India | GRNN, MLP | MSE |
| [29] | 3 months | Türkiye | SHWIP | nMAE |
2. Methodology
2.1. Information about Study Region
Çanakkale Province, located in the Marmara region, is among the places with the highest wind energy potential in Türkiye [48]. There are 25 wind power plants in operation and 7 wind power plants under construction in the region. The total installed power of the operational power plants is 891 MW. At the end of June 2022, the installed power based on wind energy in Türkiye was 10.976 MW, approximately 8% of which is located in Çanakkale. In addition, the Saros Wind Power Plant, one of the ten largest wind power plants in Türkiye with an installed capacity of 138 MW, is located in this region. The hourly time-series wind data consist of the average wind speed and direction at an altitude of 10 m; the temperature, relative humidity, and actual pressure of Çanakkale are analyzed in detail for a 12-month period (2019 year). Çanakkale Province is one of the geopolitically strategic cities in Türkiye, which is located on the in the coast of the Aegean Sea in West Anatolia, and is surrounded by Balıkesir from east, the Aegean Sea in the west, Edirne in the northwest, and Tekirdag and the Marmara Sea in the north. The coordinates from the Northern Hemisphere are 40.14 north latitude and 26.40 east longitude. The altitude of Çanakkale is 2 m, and its distance from the sea is 12 km. The location of Çanakkale Province, as well as its annual average wind speed and annual average wind power density distribution, is shown in Figure 1.
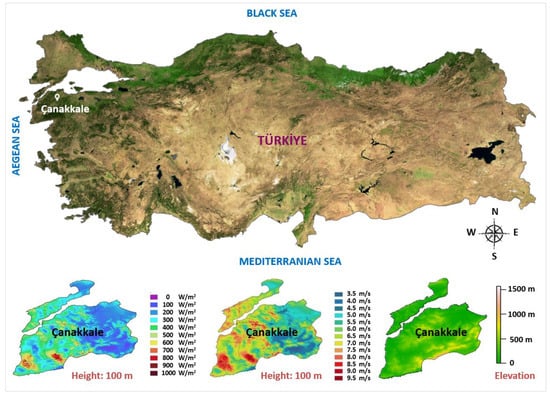
Figure 1.
Location, elevation, annual average wind speed, and wind power density distribution of Çanakkale [49].
2.2. Weibull and Rayleigh Distribution Functions
Weibull and Rayleigh are the two most widely used and simplest distribution models for estimating wind power potential by expressing the PDF of wind speed data. Several techniques have been used to attain the shape (k) and the scale (c) parameters, which play a significant role in the Weibull distribution function. Each of these techniques existing in the literature has advantages and drawbacks. In this study, GM, which is a practical and effective way to find these parameters, is preferred.
2.2.1. Weibull Distribution
The mean wind speed and standard deviation values of observed time-series wind data were calculated using Equations (1) and (2):
where v is wind speed, vm is the mean wind speed (m/s), σ is the standard deviation (m/s), and N is the number of hours within the time period. To evaluate the mean wind speed values accurately, it is essential to know the number of hours during a given time interval per month or year. Estimation of the wind power potential of any region is realized using previously measured data. In general, this process is performed through wind speed distribution functions. First of all, hourly wind speed values in a time-series format are observed and then converted into the frequency distribution format for probability modelling because of the convenience [5]. Weibull distribution can be defined as the PDF, fw(v), and the cumulative distribution function, Fw(v), as follows:
where fw(v) is the probability of a wind speed of v (m/s) occurring, v (m/s) is the measured wind speed, k (dimensionless) is the shape parameter, and c (m/s) is the scale parameter of the Weibull distribution. It is essential to know and interpret wind speed distributions for wind speed estimation. The data organized in the time-series format are rearranged in the frequency distribution format to make it more suitable for statistical analysis [5]. The following equation [5] describes the relationship between the Weibull scale parameter (c), the Weibull shape parameter (k), and the mean wind speed, vm:
Γ is the gamma function, which can be determined by the standard equation below:
By transforming Equation (4) into a logarithmic form, Equation (7) can be defined as
Here, if , , , and are assumed [50], a linear equation is obtained from the function. Then, is acquired from Equation (7). Furthermore, the equation of is computed from the equation of . Then, A and B are calculated using the Least-Squares Method:
Here, (average of x values) and (average of y values) are obtained from Equation (9):
A straight line should result when plotting against . The line’s slope is k and its y-axis intersection point is . The captured graph as an example for 2019 is given in Figure 2. Using wind speed data from Çanakkale Province, the Weibull parameters k and c in Equation (4) can be determined as 1.33 and 3.06, respectively.
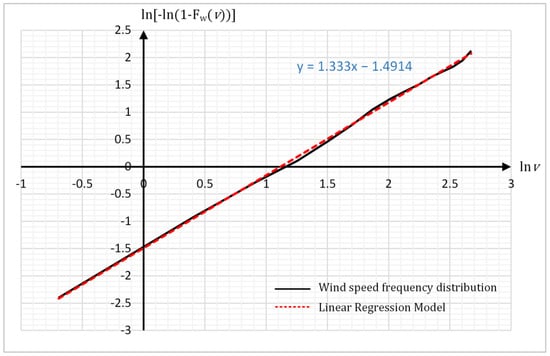
Figure 2.
Graphical method of determining Weibull parameters.
The calculated parameters of shape (k), scale (c), the mean wind speed (vm), and the standard deviation are listed by month in Table 2. The scale factor, c, ranges from 2.45 to 4.04 m/s, according to the Weibull parameters outlined in Table 1, while the shape factor, k, is between 0.95 and 2.12. October and November have the lowest values of the scale parameter, indicating that they are the least windy months of the year. The value of the scale parameter is lowest in January and February, which means that these two months are the windiest months of 2019 year in Çanakkale Province.

Table 2.
The monthly average mean wind speed, standard deviation, and Weibull parameters calculated using wind speed data of Çanakkale Province.
2.2.2. Rayleigh Probability Density Function
Another statistical approach used to determine the wind speed, and thus, the wind power potential, is the Rayleigh distribution function. The situation where the shape parameter is equal to 2 in the Weibull function is accepted as a Rayleigh distribution [6]. The PDF of the Rayleigh model, , is as given below:
2.3. Calculations of Wind Power
The wind power, P(v), whose unit is Watts, passing through a blade sweep area (A) at speed v rises as the cube of its velocity, and is calculated as follows [5,6,51]:
where is the standard air density ( kg/m3). The wind power density per unit area (W/m2) in a region is obtained with the following formula for the Weibull function [5]:
The wind power density per unit area (W/m2) in a region for the Rayleigh function is expressed as follows [5]:
The wind power densities of the Weibull and Rayleigh functions were calculated using the equations above. The monthly variation in the mean wind power densities, based on the Weibull and Rayleigh distribution functions, as well as actual (measured) data for Çanakkale, are illustrated in Figure 3. As stated in the literature [6,7], and as seen from the figure, the Weibull PDF provides results that are closer to the actual value for wind power density estimation than the Rayleigh PDF.
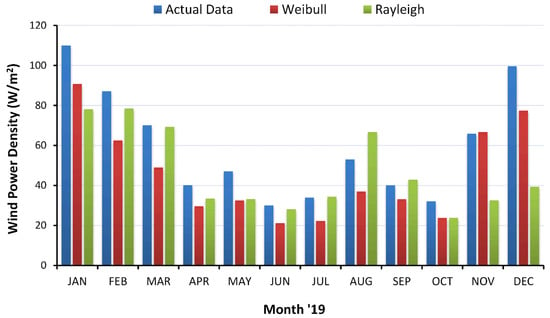
Figure 3.
Monthly variation in mean wind power densities (W/m2) for the Çanakkale Province.
2.4. ANN-Based Hybrid Models for Wind Speed Estimation
ANNs are intelligent systems that work by mimicking the biological nervous system and are inspired by the electrochemical information processing technique of the human brain. An ANN model is comprised of neurons that use inputs across the network and transform inputs using transfer functions to produce results [52]. In this study, a Multi-Layer Feed-Forward Backpropagation ANN structure, as demonstrated in Figure 4, is utilized for the estimation of wind speed. Each cell in an ANN is called a neuron, which connect with each other through connections of different weights. Sets of neurons form layers that are divided into three layers: input, output, and hidden. As seen in Figure 4, 12 neurons (x1, x2, x3, …, x12) representing the wind direction, wet bulb temperature, actual pressure, maximum and minimum temperature, relative humidity, average temperature, total global solar radiation, areal precipitation, amount of cloudiness, sea water temperature and hours of sunshine are used in the input layer, whereas one neuron (y1) is employed In the output layer, denoting the daily average wind speed.
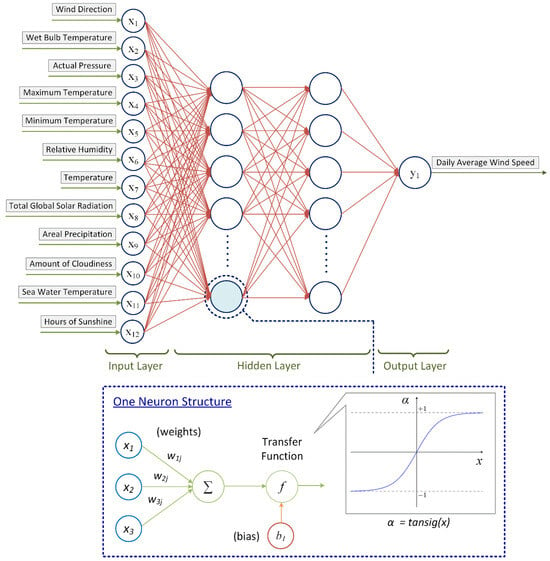
Figure 4.
Feed-forward backpropagation ANN structure with two hidden layers.
Each neuron’s input is determined by adding a bias term to the weighted sum of its previous layer’s outputs [53]. The inputs of each neuron are processed by a transfer function, from which the linked neuron’s output is produced. The sigmoid and hyperbolic tangent functions are the most frequently used activation functions [52]. The hyperbolic tangent sigmoid (tansig) is preferred as the transfer function in that configuration because the relation between input and output neurons is nonlinear. Equation (14) can be employed to mathematically define the output of the network.
where xi represents the input values and ŷ is the output values of the network; wij represents the weights used to establish connections between the ith node of the input layer and the jth node of the first hidden layer; wjk is the weights used to establish connections between the first and second hidden layers; and wks denotes the weights used to establish connections between the output layer and the second hidden layer. The transfer function is represented by f1, f2, and f3, whereas the biases on the nodes of the first hidden, second hidden, and output layers are indicated by φj, φk, and φs, respectively.
One of the main objectives and novelties of this study is to introduce two hybrid approaches consisting of ANNs’ dual combinations with GA and PSO algorithms to predict the wind speed and wind power potential. These hybrid approaches are more effective than the conventional ANN method alone. To overcome the lack of a single ANN model, the parameters of the ANN model are optimized by GA and PSO, resulting in higher prediction performance. Most recent studies have focused on hybrid approaches, where an ANN and metaheuristic optimization methods have been combined [54,55,56,57].
A network of interconnected artificial neurons that have been trained utilizing a learning algorithm is known as an ANN. In the ANN-GA hybrid model, a GA is used as a learning algorithm and trains the ANN in order to optimize the estimation technique. Similarly, in the ANN-PSO hybrid model, PSO is employed as a learning algorithm and trains the ANN to optimize the model and learning parameters. Figure 5 illustrates the flowchart of the presented hybrid ANN-GA and ANN-PSO algorithms. The performance of the ANN model depends on the number of hidden layers, the number of neurons in hidden layer, the rate division of the data (training and testing), the number of iterations, and the training function. The coefficient of determination (R2), mean square error (MSE), root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) are used to evaluate the accuracy of the presented models. The presented models are implemented using MATLAB software (2022b version). The ANN design parameters for MATLAB implementation are listed in Table 3.
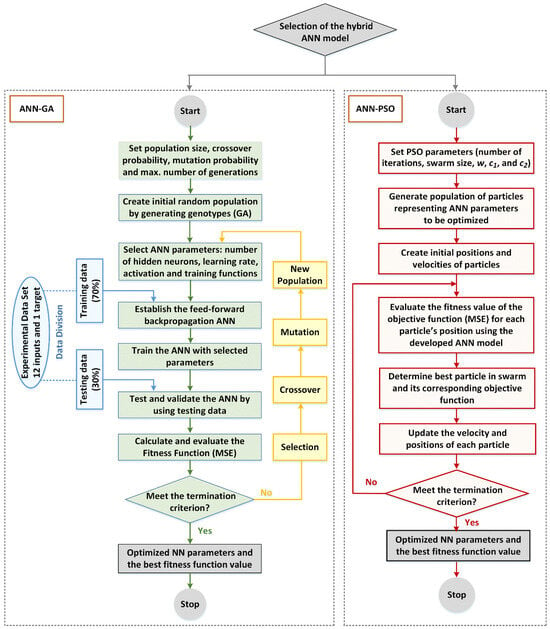
Figure 5.
Flowchart of the hybrid ANN-GA and ANN-PSO algorithms [53].

Table 3.
ANN design specifications for MATLAB implementation.
3. Results and Discussions
The main purpose of this study is to examine the Weibull and Rayleigh distribution functions, which are statistical methods for the daily average wind speed and wind power potential estimation of Çanakkale Province, as well as the hybrid artificial intelligence-based ANN-GA and ANN-PSO methods, and then to present a comparison of these four methods. The gap in the literature was filled by using the ANN-GA and ANN-PSO methods for the first time to estimate the wind speed and wind power density in Çanakkale Province. The statistical error indices listed in Table 4 were used to evaluate the accuracy of the presented estimation techniques and to determine the error rates. The error rates were calculated with the formulas for the five most commonly used statistical error indices given in this table: R2, MSE, RMSE, MAE, and MAPE. In these formulas, n is the number of observations, yi and xi represent the estimated and measured test data, respectively, and zi represents the mean of the measured data.

Table 4.
The mathematical formulas of the statistical error indicators.
Figure 6 depicts the mean, minimum, and best fitness values (MSE) in relation to the generation size of the GA. The best MSE for the testing data was reached during the GA’s 52nd iteration as 0.3653, while the correlation was computed as 0.94839. Figure 7 demonstrates the linear correlation between the actual and estimated outcomes for the training and testing data. As seen in that figure, the regression line of the test and the estimated data are provided as y = 0.81 × T + 0.62. The error between the estimated result and actual data and a comparison of them are also shown in Figure 7. As can be observed from the figure, the error graph has a few peak points, but overall, the error rate is close to zero, which leads one to deduce that the proposed ANN-GA algorithm performs successfully.
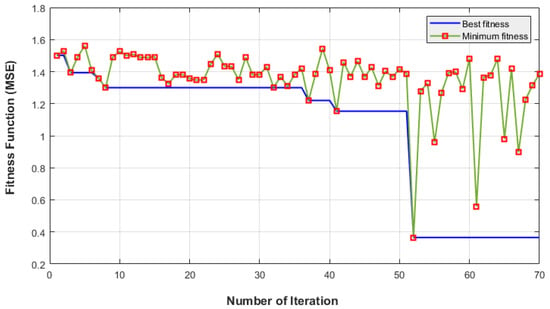
Figure 6.
The minimum and best values of fitness with respect to the generation size of GA.
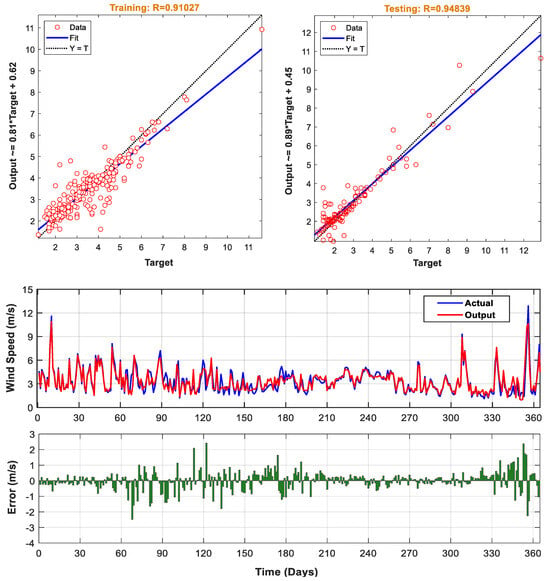
Figure 7.
Correlation between target and predicted results for the training and test data (ANN-GA).
Figure 8 represents the mean, minimum, and best fitness values (MSE) in relation to the generation size of PSO. The best MSE for the testing data was 0.4721, while the correlation was obtained as 0.94042. Figure 9 illustrates the linear correlation between the actual and estimated values for the training and testing data. The regression line of the test and the predicted data are provided as y = 0.78 × T + 0.81. The error between the predicted and actual results and a comparison between them is also shown in that figure. According to Figure 9, the test and training errors are both quite low, which implies that the suggested ANN-PSO technique works satisfactorily.
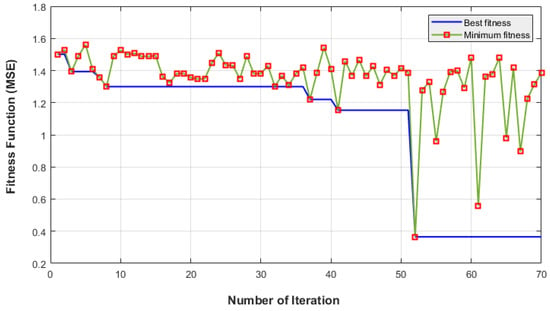
Figure 8.
The minimum and best values of fitness with respect to the generation size of PSO.
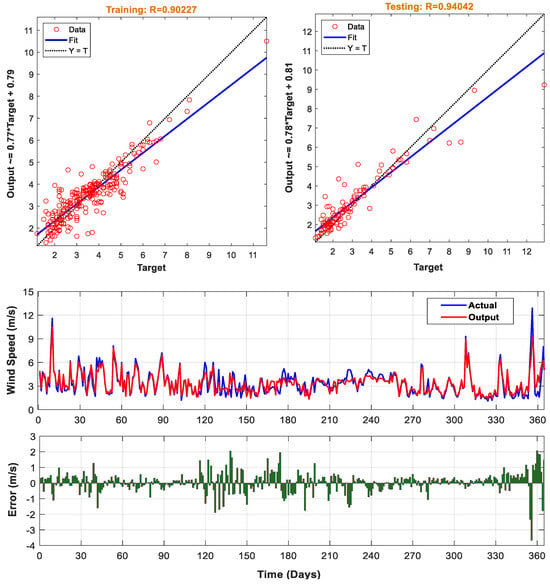
Figure 9.
Correlation between target and predicted results for the training and test data (ANN-PSO).
The comparison graph for the prediction of the 2019 daily wind power density for the Weibull distribution, Rayleigh distribution, hybrid ANN-GA, and ANN-PSO algorithms is depicted in Figure 10. The estimated and measured (actual) wind power density results are shown and compared in the figure. The actual wind power density is represented by the blue curve, while the ANN-GA, ANN-PSO, Rayleigh, and Weibull results are represented by green, red, purple, and yellow curves, respectively. As can be seen from Figure 10, the Weibull distribution, which is one of the statistical methods, shows a superior performance compared to the Rayleigh distribution. However, it is understood that ANN-based hybrid algorithms give much better results in WP estimation than these two statistical methods. Then, considering Table 5, when the proposed ANN-based hybrid techniques were evaluated internally, it was observed that the ANN-GA model performed superior to the ANN-PSO model. According to Table 5, an MSE of 0.3653, an RMSE of 0.6044, an MAE of 0.3994, and an MAPE of 16.66% were obtained, and a correlation of 94.839% was achieved for the ANN-GA model. For the ANN-PSO model, an MSE of 0.4721, an RMSE of 0.6871, an MAE of 0.4304, and an MAPE of 17.07% were acquired, and a correlation of 94.042% was accomplished. The results show that the proposed ANN-GA model improves the prediction accuracy better than ANN-PSO. As a result, it is understood that the ANN-GA method has the best prediction results among the four methods for wind speed and wind power density.
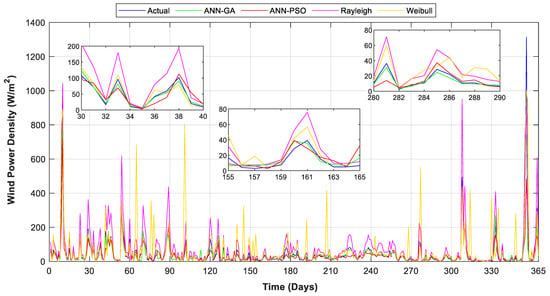
Figure 10.
Prediction of daily wind power density for ANN-GA, ANN-PSO, Weibull distribution, and Rayleigh distribution.

Table 5.
The statistical error performance result of ANN-based hybrid models.
Moreover, Table 5 is given to compare the performance of the presented ANN-based hybrid estimation techniques in this study. The performance of the proposed algorithms was evaluated using error metrics such as R2, RMSE, MSE, MAE, and MAPE. The range of RMSE, MSE, and MAE is (0, +∞); smaller values of these parameters mean that the estimation model has higher accuracy. In addition, 10% < MAPE < 20% indicates a good prediction result. As understood from Table 5, ANN-GA exhibited a more satisfactory performance compared to ANN-PSO.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, a performance comparison of statistical methods and ANN-based hybrid methods for daily average wind speed and wind power estimation in Çanakkale is presented. Four estimation techniques were used: Weibull distribution, Rayleigh distribution, ANN-GA, and ANN-PSO algorithms. The accuracy of the proposed hybrid ANN-based methods was calculated using the statistical error indices R2, RMSE, MSE, MAE, and MAPE. Among the statistical methods presented, the Weibull distribution yielded better results than the Rayleigh distribution, whereas the ANN-GA gave better results than ANN-PSO. The obtained results of R2, MSE, RMSE, MAE, and MAPE were 0.896, 0.3653, 0.6044, 0.3994, and 16.66%, respectively, for the ANN-GA model. It was seen that the ANN-GA model realized the wind speed and wind power density estimation of Çanakkale Province with 94.839% accuracy. The results indicate that the proposed hybrid approaches provide reasonable wind speed and wind power density predictions. Consequently, thanks to the presented study, it is expected that better planning and a more effective evaluation can be made for investments in the wind sector in the region. In further studies, by using different AI-based hybrid methods to predict the wind speed of the region and more favorable datasets, results with higher accuracy can be achieved.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.K.; Methodology, T.K. and E.E.; Software, T.K. and E.E.; Validation, T.K.; Writing—original draft, T.K. and E.E.; Writing—review & editing, T.K. and E.E.; Project administration, T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy and ethical restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| ABCOA | Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AMLM | Alternative Maximum Likelihood Method |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| BOA | Bat Optimization Algorithm |
| BP | Back-Propagation |
| CS | Cuckoo Search Algorithm |
| DBNGA | Deep Belief Network with Genetic Algorithms |
| EEM | Equivalent Energy Method |
| ELM | Extreme Learning Machine |
| EM | Empirical Method |
| EMJ | Empirical Method of Justus |
| EML | Empirical Method of Lysen |
| EPFM | Energy Pattern Factor Method |
| EPM | Energy Pattern Method |
| FS | Fourier Series |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GM | Graphical Method |
| GRNN | Generalized Regression Neural Network |
| GWO | Gray Wolf Optimizer |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbor |
| KS | Kolmogorov–Smirnov Distance |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage Selector Operator |
| LSR | Least-Squares Regression |
| LSSVRGA | Least-Squares Support Vector Regression with Genetic Algorithms |
| LSSVRTSGA | Least-Squares Support Vector Regression for Time Series with Genetic Algorithms |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| MBE | Mean Bias Error |
| MLFFNN | Multi-Layer Feed-Forward Neural Network |
| MLM | Maximum Likelihood Method |
| MLP | Multi-Layer Perceptron |
| MLPNN | Multi-Layer Perceptron Neural Network |
| Mmab | Mabchour’s Method |
| MMLM | Modified Maximum Likelihood Method |
| MOM | Method of Moments |
| MPE | Mean Percentage Error |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| MSSDM | Mean Speed and Standard Deviation Method |
| MUOM | Method of Multi-Objective Moments |
| nMAE | Normalized Mean Absolute Error |
| NN | Neural Network |
| NWP | Numerical Weather Prediction |
| nRMSE | Normalized Root Mean Square Error |
| PDE | Power Density Error |
| Probability Distribution Function | |
| PDM | Power Density Method |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| R | Correlation Coefficient |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| RBF | Radial Basis Function |
| RBFNN | Radial Basis Function Neural Network |
| RE | Relative Error |
| RES | Renewable Energy Sources |
| RFR | Random Forest Regression |
| RKF | Recurrent Kalman Filter |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| RRMSE | Relative Root Mean Square Error |
| SARIMA | Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average |
| SDE | Standard Deviation of Error |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SHWIP | Statistical Hybrid Wind Power |
| SSA | Singular Spectrum Analysis |
| SSE | Sum Squared Error |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| VMD | Variational Mode Decomposition |
| WNN | Wavelet Neural Network |
| X2 | Chi-Square Error |
| xGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boost |
References
- Kaplan, O.; Temiz, M. A Novel Method Based on Weibull Distribution for Short-Term Wind Speed Prediction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 17793–17800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, A.M.; Leahy, P.G.; Marvuglia, A.; McKeogh, E.J. Current Methods and Advances in Forecasting of Wind Power Generation. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, M.; Venkaiah, C.; Kumar, D.V. Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Approach Using Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition and Deep Boltzmann Machine. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2019, 19, 100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yahyai, S.; Charabi, Y.; Gastli, A. Review of the Use of Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) Models for Wind Energy Assessment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 3192–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniktepe, B.; Koroglu, T.; Savrun, M.M. Investigation of Wind Characteristics and Wind Energy Potential in Osmaniye, Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Lee, S.M.; Jang, C.M. Statistical Analysis of Wind Characteristics Using Weibull and Rayleigh Distributions in Deokjeok-do Island–Incheon, South Korea. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidaoui, H.; El Abbassi, I.; El Bouardi, A.; Darcherif, A. Wind Speed Data Analysis Using Weibull and Rayleigh Distribution Functions, Case Study: Five Cities Northern Morocco. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 32, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katinas, V.; Marčiukaitis, M.; Gecevičius, G.; Markevičius, A. Statistical Analysis of Wind Characteristics Based on Weibull Methods for Estimation of Power Generation in Lithuania. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta, I.; Arik, I.; Yenilmez, I.; Kantar, Y.M. A New Estimation Approach Based on Moments for Estimating Weibull Parameters in Wind Power Applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 164, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, Y.A. Determination of the Best Weibull Methods for Wind Power Assessment in the Southern Region of Turkey. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2017, 11, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baseer, M.A.; Meyer, J.P.; Rehman, S.; Alam, M.M. Wind Power Characteristics of Seven Data Collection Sites in Jubail, Saudi Arabia Using Weibull Parameters. Renew. Energy 2017, 102, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, P.K.; Ahmed, S.; Warudkar, V. Study of Different Parameters Estimation Methods of Weibull Distribution to Determine Wind Power Density Using Ground Based Doppler SODAR Instrument. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2299–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, M.M.; Abo-khalil, A.G.; Praveen, R.P. Wind Speed Characteristics and Energy Potential for Selected Sites in Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2021, 33, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulio, Z.H.; Jiang, W.; Rehman, S. Techno-Economic Assessment of Wind Power Potential of Hawke’s Bay Using Weibull Parameter: A Review. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 26, 100375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapen, P.T.; Gouajio, M.J.; Yemélé, D. Analysis and Efficient Comparison of Ten Numerical Methods in Estimating Weibull Parameters for Wind Energy Potential: Application to the City of Bafoussam, Cameroon. Renew. Energy 2020, 159, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, A.; Gokcek, M.; Uçar, H.; Arabacı, E.; Akyüz, A. Analysis of Wind Energy Potential and Weibull Parameter Estimation Methods: A Case Study from Turkey. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katinas, V.; Gecevicius, G.; Marciukaitis, M. An Investigation of Wind Power Density Distribution at Location with Low and High Wind Speeds Using Statistical Model. Appl. Energy 2018, 218, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.K.; Salam, A.; Rehman, A.U.; Saeed, M.A. Comparison of Six Different Methods of Weibull Distribution for Wind Power Assessment: A Case Study for A Site in the Northern Region of Pakistan. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 36, 100541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, Y. Rayleigh ve Weibull Dağılımları Kullanılarak Osmaniye Bölgesinde Rüzgar Enerjisinin Değerlendirilmesi. Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Enstitüsü Derg. 2016, 20, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumair, M.; Aized, T.; Gardezi, S.A.R.; Ur Rehman, S.U.; Rehman, S.M.S. Wind Potential Estimation and Proposed Energy Production in Southern Punjab Using Weibull Probability Density Function and Surface Measured Data. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2021, 39, 2150–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahimi, T.; Alhebshi, F.; Alnabilsi, H.; Bensenouci, A.; Rahman, M. Prediction of Wind Speed Distribution Using Artificial Neural Network: The Case of Saudi Arabia. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 163, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, C.D.; Gligor, A. Daily Average Wind Energy Forecasting Using Artificial Neural Networks. Procedia Eng. 2017, 181, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Malik, H. Generalized Regression Neural Network Based Wind Speed Prediction Model for Western Region of India. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 93, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, R.K.B.; Prakash, S.; Sasipraba, T. Artificial Neural Network Based Computing Model for Wind Speed Prediction: A case study of Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 542, 123383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demolli, H.; Dokuz, A.S.; Ecemis, A.; Gokcek, M. Wind Power Forecasting Based on Daily Wind Speed Data Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 198, 111823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawan, S.M.; Abidin, W.A.W.Z.; Masri, T. Implementation of A Topographic Artificial Neural Network Wind Speed Prediction Model for Assessing Onshore Wind Power Potential in Sibu, Sarawak. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencar, D.B.; Affonso, C.M.; Oliveira, R.C.; Jose Filho, C.R. Hybrid Approach Combining SARIMA and Neural Networks for Multi-Step Ahead Wind Speed Forecasting in Brazil. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 55986–55994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, G.; Zhang, Y.; Han, A. Performance Comparison of ANNs Model with VMD for Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 12, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, M.B.; Karagoz, P. A Novel Wind Power Forecast Model: Statistical Hybrid Wind Power Forecast Technique (SHWIP). IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Guo, Y. Wind Power Prediction Based on PSO-SVR and Grey Combination Model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 136254–136267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Koury, R.N.N.; Machado, L.; Pabon, J.J.G. Prediction of Wind Speed and Wind Direction Using Artificial Neural Network, Support Vector Regression and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2018, 25, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.B.; Liu, X. Estimation of Wind Speed Probability Distribution and Wind Energy Potential Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Methodology. Neurocomputing 2018, 287, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.A.; Ahmed, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W. An Optimal Approach of Wind Power Assessment Using Chebyshev Metric for Determining the Weibull Distribution Parameters. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 37, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, H.H. A Novel Deep Learning İntelligent Clustered Hybrid Models for Wind Speed and Power Forecasting. Energy 2020, 213, 118773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.P.; Pai, P.F.; Ting, Y.J. Deep Belief Networks with Genetic Algorithms in Forecasting Wind Speed. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 99244–99253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazelpour, F.; Tarashkar, N.; Rosen, M.A. Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Using Artificial Neural Networks for Tehran, Iran. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2016, 7, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, S.; Mahistha, D.S.P.; Ukhti, M.F.; Kurniawan, M.R.; Aisjah, A.S. Optimization of Neural Network Based on Hybrid Method of Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization for Maritime Weather Forecasting in Buoyweather Station Type II. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2088, 020035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, N.; Lu, H. A Novel System Based on Neural Networks with Linear Combination Framework for Wind Speed Forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 181, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petković, D.; Nikolić, V.; Mitić, V.V.; Kocić, L. Estimation of Fractal Representation of Wind Speed Fluctuation by Artificial Neural Network with Different Training Algorothms. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2017, 54, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ma, P. Wind Power Forecasting Based on Singular Spectrum Analysis and A New Hybrid Laguerre Neural Network. Appl. Energy 2020, 259, 114139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wais, P. Two and Three-Parameter Weibull Distribution in Available Wind Power Analysis. Renew. Energy 2017, 103, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Q.; Ma, X. Comparison of Seven Methods for Determining the Optimal Statistical Distribution Parameters: A Case Study of Wind Energy Assessment in the Large-Scale Wind Farms of China. Energy 2018, 164, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, P.K.; Ahmed, S.; Warudkar, V. Comparative Analysis of Weibull Parameters for Wind Data Measured from Met-Mast and Remote Sensing Techniques. Renew. Energy 2018, 115, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulouknga, M.H.; Doka, S.Y.; Revanna, N.; Djongyang, N.; Kofane, T.C. Analysis of Wind Speed Data and Wind Energy Potential in Faya-Largeau, Chad, Using Weibull Distribution. Renew. Energy 2018, 121, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, Y.A. Performance Assessment of Power Density Method for Determining the Weibull Distribution Coefficients at Three Different Locations. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2018, 63, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eseye, A.T.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, D.; Li, H.; Jingfu, G. A Double-Stage Hierarchical Hybrid PSO-ANN Model for Short-Term Wind Power Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data Analysis (ICCCBDA), Chengdu, China, 28–30 April 2017; pp. 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, X. A Hybrid Strategy of Short Term Wind Power Prediction. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duden Örgen, F.K.; Altıntaş, A.; Yaşar, S.; Öztürk, M.; Çiftçi, E.; Tuncer, A.D. Software-Based Wind Energy Potential Assessment: A Case Study from Western Turkey. J. Polytech. 2023, 26, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://repa.enerji.gov.tr/REPA/ (accessed on 30 December 2023).
- Karsli, V.M.; Gecit, C. An Investigation on Wind Power Potential of Nurdaǧı-Gaziantep, Turkey. Renew. Energy 2003, 28, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, O. Technoeconomic Aanalysis of Electricity Generation from Wind Energy in Kutahya, Turkey. Energy 2010, 35, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, A.; Turkoglu, A. An Intelligent Prediction of Self-Produced Energy. In Sustainable Future Energy Technology and Supply Chains; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boga, C.; Koroglu, T. Proper Estimation of Surface Roughness Using Hybrid Intelligence Based on Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 70, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Fu, W.; Wang, K.; Fang, P.; Chen, T.; Zou, F. A Blended Approach Incorporating TVFEMD, PSR, NNCT-Based Multi-Model Fusion and Hierarchy-Based Merged Optimization Algorithm for Multi-Step Wind Speed Prediction. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 230, 113680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zhang, K.; Wang, K.; Wen, B.; Fang, P.; Zou, F. A Hybrid Approach for Multi-Step Wind Speed Forecasting Based on Two-Layer Decomposition, Improved Hybrid DE-HHO Optimization and KELM. Renew. Energy 2021, 164, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Chang, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Zuo, H.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B. A Combined Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Model Based on CNN–RNN and Linear Regression Optimization Considering Error. Renew. Energy 2022, 200, 788–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeksiz, C.; Tan, M. Wind Speed Estimation Using Novelty Hybrid Adaptive Estimation Model Based on Decomposition and Deep Learning Methods (ICEEMDAN-CNN). Energy 2022, 249, 123785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).