Investigating the Effect of Patient-Related Factors on Computed Tomography Radiation Dose Using Regression and Correlation Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Dataset Description
2.3. Regression Analysis
3. Experimental Results
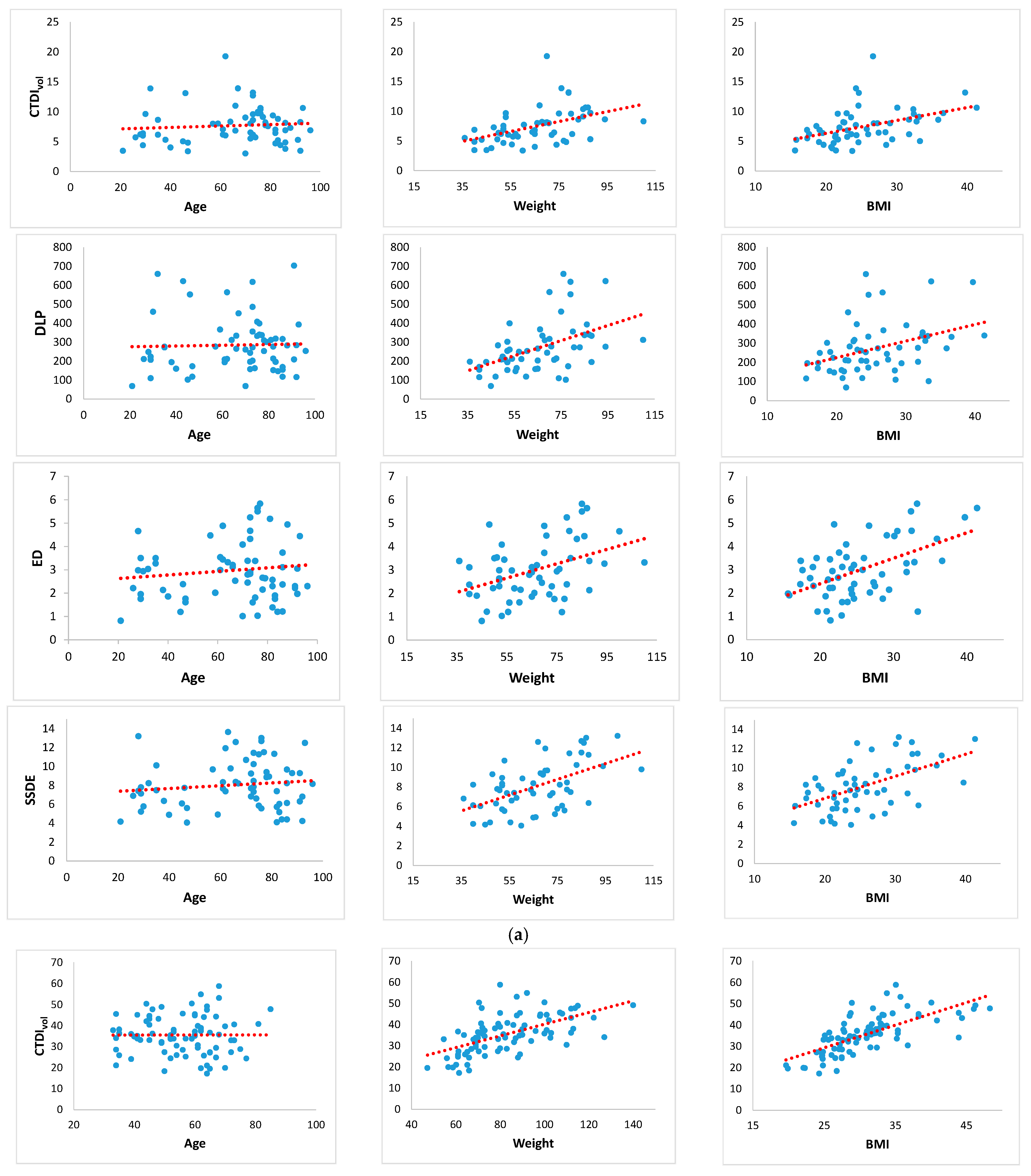
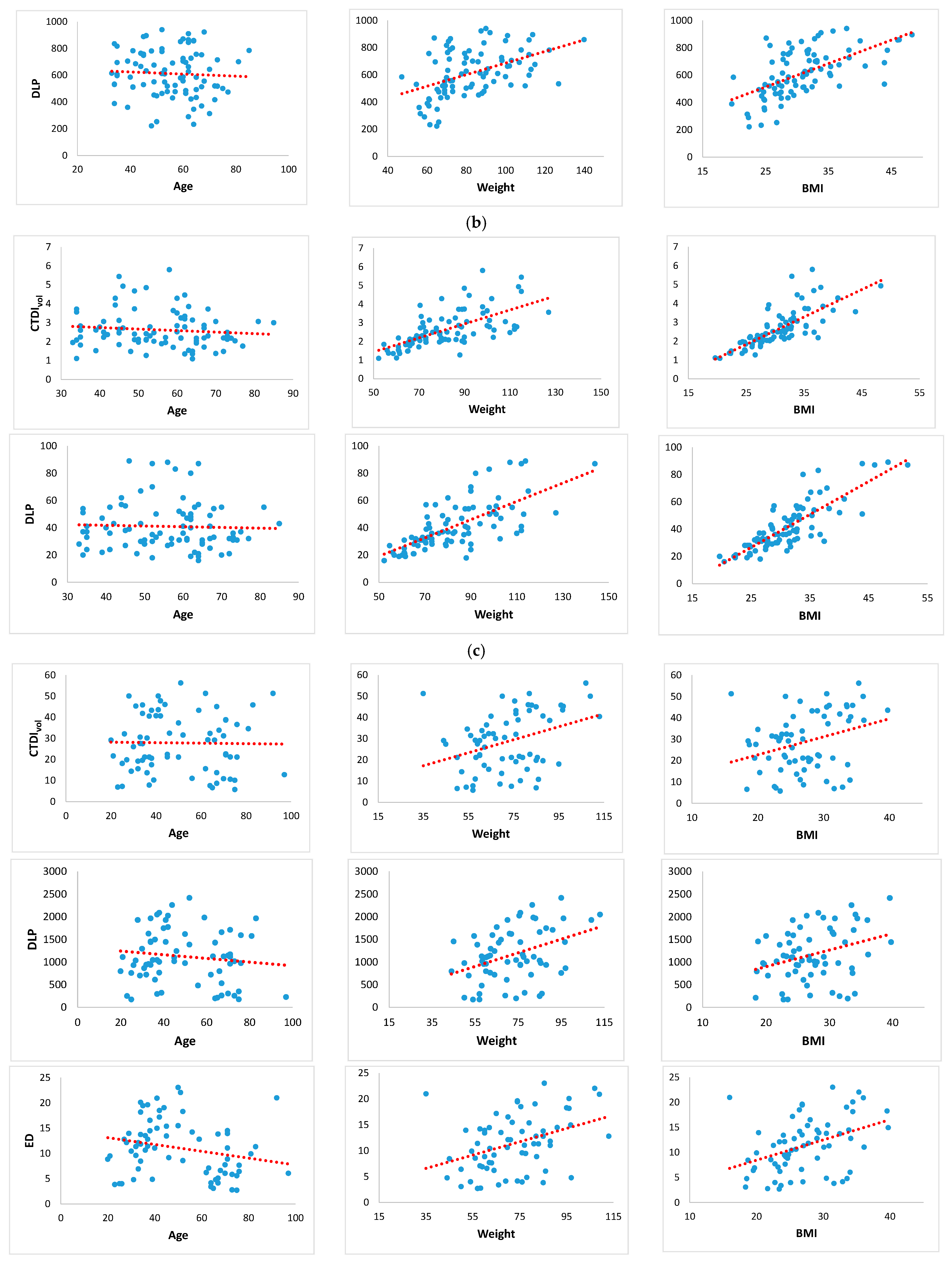
3.1. Computed Tomography Dose Index Volume (CTDIvol) Correlations
3.2. Dose Length Product (DLP) Correlations
3.3. Effective Dose (ED) Correlations
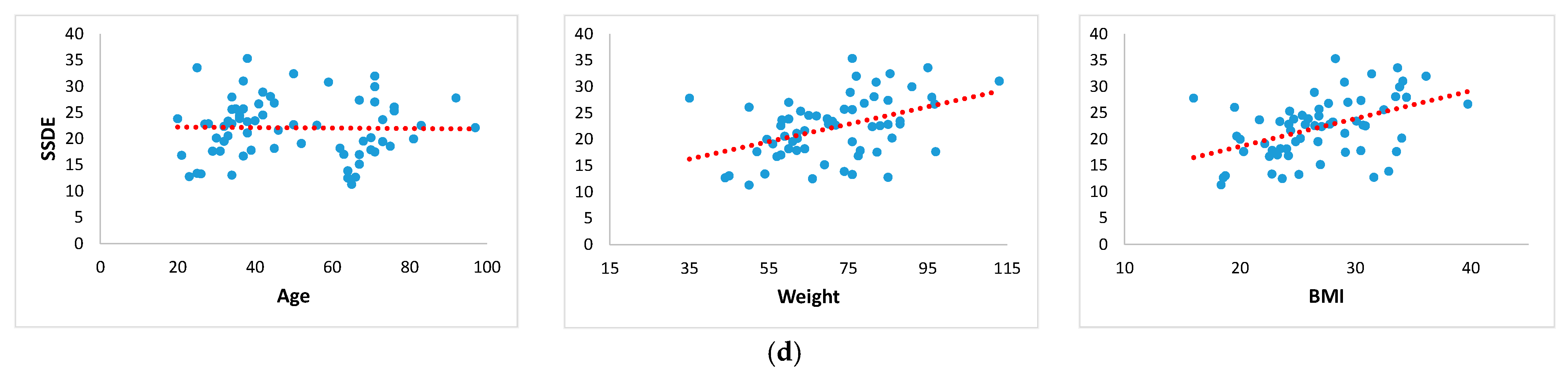
3.4. Size-Specific Dose Estimate (SSDE) Correlations
3.5. Plots of Linear Regression Models
3.6. Correlations between the CT Dose Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Power, S.P.; Moloney, F.; Twomey, M.; James, K.; O’Connor, O.J.; Maher, M.M. Computed Tomography and Patient Risk: Facts, Perceptions and Uncertainties. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.; Bouman, C.; Carmignato, S.; Cnudde, V.; Grimaldi, D.; Hagen, C.K.; Maire, E.; Manley, M.; Du Plessis, A.; Stock, S.R. X-Ray Computed Tomography. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubayr, N.; Alashban, Y. Estimation of Radiation Doses and Lifetime Attributable Risk of Radiation-Induced Cancer in the Uterus and Prostate from Abdomen Pelvis CT Examinations. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1094328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohmoudi, G.; Bahrami, A.; Rostampour, N.; Maskani, R.; Joukar, F.; Hosseinzadeh, A. Evaluation of Cancer Risk Induced by Radiation Exposure from Normal Head CT Scans. Front. Biomed. Technol. 2023, 10, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Over 75 Million CT Scans Are Performed Each Year and Growing Despite Radiation Concerns—iData Research. Available online: https://idataresearch.com/over-75-million-ct-scans-are-performed-each-year-and-growing-despite-radiation-concerns/ (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Dhou, S.; Dalah, E.; AlGhafeer, R.; Hamidu, A.; Obaideen, A. Regression Analysis between the Different Breast Dose Quantities Reported in Digital Mammography and Patient Age, Breast Thickness, and Acquisition Parameters. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalah, E.Z.; Dhou, S.; Mudalige, T.; Amin, F.; Obaideen, A. Challenges Estimating Patient Organs Doses Undergoing Enhanced Chest CT Examination: Exploratory Study. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2021, 7, 025019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalah, E.Z.; Alsuwaidi, J.S.; AlKtebi, R.S.; AlMulla, M.A.A.; Gupta, P. Establishing Protocol-Based Dose Metrics for Common Abdomen and Pelvis Computed Tomography Protocol. Curr. Med. Imaging 2024, 20, e220523217204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, W.; Ogden, K.M.; Khorasani, M.R. Converting Dose-Length Product to Effective Dose at CT. Radiology 2008, 248, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, J. Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE), Quality Factor (Q), and Radiation Weighting Factor (wR): ICRP Publication 92. Ann. ICRP 2003, 33, 1–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. How to Estimate Effective Dose for CT Patients. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1825–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binta, Y.I.; Suryani, S.; Abdullah, B. The Comparison of Size-Specific Dose Estimate (SSDE) in Chest CT Examination Calculated Based on Volumetric CT Dose Index (CTDIvol) Reference Phantom and Dose Length Product (DLP). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1763, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satharasinghe, D.M.; Jeyasugiththan, J.; Wanninayake, W.M.N.M.B.; Pallewatte, A.S. Size-Specific Dose Estimates (SSDEs) for Computed Tomography and Influencing Factors on It: A Systematic Review. J. Radiol. Prot. 2021, 41, R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAPM Reports—Size-Specific Dose Estimates (SSDE) in Pediatric and Adult Body CT Examinations. Available online: https://www.aapm.org/pubs/reports/detail.asp?docid=143 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Rajaraman, V.; Ponnusamy, M.; Halanaik, D. Size Specific Dose Estimate (SSDE) for Estimating Patient Dose from CT Used in Myocardial Perfusion SPECT/CT. Asia Ocean J. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2020, 8, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vano, E.; Frija, G.; Loose, R.; Paulo, G.; Efstathopoulos, E.; Granata, C.; Andersson, J.; the European Society of Radiology (ESR). Dosimetric Quantities and Effective Dose in Medical Imaging: A Summary for Medical Doctors. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boos, J.; Lanzman, R.S.; Heusch, P.; Aissa, J.; Schleich, C.; Thomas, C.; Sawicki, L.M.; Antoch, G.; Kröpil, P. Does Body Mass Index Outperform Body Weight as a Surrogate Parameter in the Calculation of Size-Specific Dose Estimates in Adult Body CT? Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, N.R.; Smith, H. Applied Regression Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The Coefficient of Determination R-Squared Is More Informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in Regression Analysis Evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Bindman, R.; Wang, Y.; Nelson, T.R.; Moghadassi, M.; Wilson, N.; Gould, R.; Seibert, A.; Boone, J.M.; Krishnam, M.; Lamba, R.; et al. Predictors of CT Radiation Dose and Their Effect on Patient Care: A Comprehensive Analysis Using Automated Data. Radiology 2017, 282, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, I.; Alikhani, B.; Wacker, F.; Raatschen, H.-J. Intraindividual Variation of Dose Parameters in Oncologic CT Imaging. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Sanchez, A.-J.; Garcia Angosto, E.; Llor, J.L.; Serna Berna, A.; Ramos, D. Machine Learning Techniques Applied to Dose Prediction in Computed Tomography Tests. Sensors 2019, 19, 5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christner, J.A.; Braun, N.N.; Jacobsen, M.C.; Carter, R.E.; Kofler, J.M.; McCollough, C.H. Size-Specific Dose Estimates for Adult Patients at CT of the Torso. Radiology 2012, 265, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, P.D.; Chawke, L.; Twomey, M.; Murphy, K.P.; O’Neill, S.B.; McWilliams, S.R.; James, K.; Kavanagh, R.G.; Sullivan, C.; Chan, F.E.; et al. Body Composition Determinants of Radiation Dose during Abdominopelvic CT. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, P.; Priya, S.; Eskandari, A.; Mullan, A.; Aggarwal, T.; Narayanasamy, S.; Parashar, K.; Bhat, A.P.; Sieren, J.C. Factors Affecting Radiation Dose in Computed Tomography Angiograms for Pulmonary Embolism: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2020, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.N.; Lodwick, D.L.; Adler, B.; Lee, C.; Minneci, P.C.; Deans, K.J. Patient Characteristics Associated with Differences in Radiation Exposure from Pediatric Abdomen-Pelvis CT Scans: A Quantile Regression Analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 85, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, K.W.; Kwon, H.-J.; Lee, J.; Koo, K.; Song, G.-W.; Lee, S.-G. Relationship of Body Mass Index and Abdominal Fat with Radiation Dose Received during Preoperative Liver CT in Potential Living Liver Donors: A Cross-Sectional Study. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 2206–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, S.; Kavanagh, R.G.; Carey, B.W.; Moore, N.; Maher, M.; O’Connor, O.J. Using Body Mass Index to Estimate Individualised Patient Radiation Dose in Abdominal Computed Tomography. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svahn, T.M.; Sjöberg, T.; Ast, J.C. Dose Estimation of Ultra-Low-Dose Chest CT to Different Sized Adult Patients. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4315–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Luo, K.; He, X. Size-Specific Dose Estimates of Radiation Based on Body Weight and Body Mass Index for Chest and Abdomen-Pelvic CTs. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, e6046501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deevband, M.R.; Nasab, S.M.B.H.; Mohammadi, H.; Salimi, Y.; Mostaar, A.; Deravi, N.; Fathi, M.; Vakili, K.; Yaghoobpoor, S.; Ghorbani, M. Body-Mass Index-Based Effective Dose Determination in Commonly Performed Computed Tomography Examinations in Adults. Front. Biomed. Technol. 2022, 9, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jarrah, M.A.; Al-Jarrah, A.; Jarrah, A.; AlShurbaji, M.; Magableh, S.K.; Al-Tamimi, A.-K.; Bzoor, N.; Al-Shamali, M.O. Accurate Reader Identification for the Arabic Holy Quran Recitations Based on an Enhanced VQ Algorithm. Rev. D’intelligence Artif. 2022, 36, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShurbaji, M.; Kader, L.A.; Hannan, H.; Mortula, M.; Husseini, G.A. Comprehensive Study of a Diabetes Mellitus Mathematical Model Using Numerical Methods with Stability and Parametric Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebelego, I.-K.; Acho, S.; van der Merwe, B.; Rae, W.I.D. Factors Influencing Size-Specific Dose Estimates of Selected Computed Tomography Protocols at Two Clinical Practices in South Africa. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2023, 199, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiniger, B.; Klippel, C.; Teichgräber, U.; Reichenbach, J.R.; Fiebich, M. Can The Size-Specific Dose Estimate Be Derived From The Body Mass Index? A Feasibility Study. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2022, 198, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, H.O.; Almisned, F.; Erguzel, T.T.; Abuzaid, M.M.; Elshami, W.; Ene, A.; Issa, S.A.M.; Zakaly, H.M.H. Prediction of Dose Length Product for Chest CT Examinations Using Artificial Neural Networks (ANN). 2022, preprint. [CrossRef]
- Juszczyk, J.; Badura, P.; Czajkowska, J.; Wijata, A.; Andrzejewski, J.; Bozek, P.; Smolinski, M.; Biesok, M.; Sage, A.; Rudzki, M.; et al. Automated Size-Specific Dose Estimates Using Deep Learning Image Processing. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 68, 101898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vañó, E.; Miller, D.L.; Martin, C.J.; Rehani, M.M.; Kang, K.; Rosenstein, M.; Ortiz-López, P.; Mattsson, S.; Padovani, R.; Rogers, A. ICRP Publication 135: Diagnostic Reference Levels in Medical Imaging. Ann. ICRP 2017, 46, 1–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CT Exam | No. of Patients (Male, Female) | Average Age (Range) | Average Weight (Range) | Average BMI (Range) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest | 68 (37, 31) | 65.3 (21–96) | 66.4 (36–110) | 25.5 (15.6–41.4) |
| Cardiac Angiogram | 91 (49, 42) | 55.7 (33–85) | 83.8 (47–144) | 31.2 (19.6–51.6) |
| Cardiac Calcium Score | 94 (48, 46) | 56.1 (33–85) | 83.9 (52–144) | 31.5 (19.6–51.6) |
| Abdomen/Pelvis | 73 (31, 42) | 48.4 (20–92) | 72.9 (35–113) | 27.4 (16–39.7) |
| CT Exam | Statistics | DLP (in mGy.cm) | CTDIvol (in mGy) | ED (in mSv) | SSDE (in mGy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest | Mean | 316.76 | 9.03 | 3.32 | 8.53 |
| Range | 69–1013 | 3.01–28.73 | 0.82–15.05 | 3.59–25.3 | |
| Std. | 197.16 | 5.42 | 2.12 | 3.7 | |
| Number of Outliers | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | |
| Cardiac Angiogram | Mean | 654.1 | 37.1 | - | - |
| Range | 222–1494 | 13.4–71.8 | - | - | |
| Std. | 241.1 | 11.5 | - | - | |
| Number of Outliers | 5 | 7 | - | - | |
| Cardiac Calcium Score | Mean | 44.5 | 2.93 | - | - |
| Range | 16–121 | 1.1–7.8 | - | - | |
| Std. | 22.62 | 1.44 | - | - | |
| Number of Outliers | 5 | 7 | - | - | |
| Abdomen/Pelvis | Mean | 1156.4 | 27.5 | 11.53 | 22.71 |
| Range | 58–2750 | 2.96–65.51 | 2.7–32.72 | 9.9–43.72 | |
| Std. | 660.5 | 14.39 | 6.23 | 7.2 | |
| Number of Outliers | 3 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| CTDIvol (mGy) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT Exam | Evaluation Metric | Linear | Multiple Linear | ||
| X1: BMI | X1: Weight | X1: Age | All Parameters (X1: BMI, X2: Weight, X3: Age) | ||
| Chest | R2 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.23 |
| RMSE | 18.60 | 59.75 | 61.47 | 2.58 | |
| MAE | 17.82 | 57.88 | 58.04 | 1.76 | |
| MAPE | 70.13 | 93.81 | 86.87 | 23.57 | |
| Eq. | = 0.87 X1 + 18.80 | = 2.44 X1 + 47.13 | = 0.52 X1 + 61.73 | = 0.81 + 0.09 * X1 + 0.05 X2 + 0.01 X3 | |
| r | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.08 | 0.48 | |
| p-value | 9.38 × 10−4 | 5.56 × 10−4 | 5.46 × 10−1 | 1.80 × 10−4 | |
| Cardiac Angiogram | R2 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.49 |
| RMSE | 7.96 | 50.01 | 25.09 | 6.43 | |
| MAE | 6.12 | 47.56 | 20.73 | 4.92 | |
| MAPE | 19.99 | 56.65 | 34.55 | 14.09 | |
| Eq. | = 0.46 X1 + 14.60 | = 1.20 X1 + 40.30 | = 0.00 X1 + 55.25 | = −0.14 + 1 X1 + 0.02 X2 + 0.05 X3 | |
| r | 0.70 | 0.58 | 0.00 | 0.70 | |
| p-value | 1.70 × 10−13 | 9.08 × 10−9 | 9.78 × 10−1 | 1.27 × 10−13 | |
| Cardiac Calcium Score | R2 | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.59 |
| RMSE | 28.17 | 80.59 | 54.40 | 0.62 | |
| MAE | 27.82 | 78.96 | 52.92 | 0.42 | |
| MAPE | 91.56 | 96.81 | 94.98 | 15.12 | |
| Eq. | = 0.15 X1 −1.80 | = 0.04 X1 −0.43 | = −0.01 X1 + 3.07 | = −1.86 + 0.12 X1 + 0.01 X2 + 0 X3 | |
| r | 0.76 | 0.64 | −0.10 | 0.77 | |
| p-value | 1.24 × 10−17 | 1.83 × 10−11 | 3.40 × 10−1 | 4.22 × 10−18 | |
| Abdomen/Pelvis | R2 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.17 |
| RMSE | 13.01 | 46.90 | 32.44 | 12.34 | |
| MAE | 11.11 | 44.26 | 25.46 | 10.61 | |
| MAPE | 42.22 | 60.79 | 46.18 | 37.92 | |
| Eq. | = 0.12 X1 + 23.83 | = 0.42 X1 + 60.38 | = −0.02 X1 + 50.66 | = −3.27 + −0.19 X1 + 0.4 X2 + 0.17 X3 | |
| r | 0.32 | 0.36 | −0.02 | 0.42 | |
| p-value | 8.69 × 10−3 | 2.52 × 10−3 | 8.86 × 10−1 | 3.85 × 10−4 | |
| DLP (mGy.cm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT Exam | Evaluation Metric | Linear | Multiple Linear | ||
| X1: BMI | X1: Weight | X1: Age | All Parameters (X1: BMI, X2: Weight, X3: Age) | ||
| Chest | R2 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 0.24 |
| RMSE | 278.74 | 241.19 | 261.54 | 115.94 | |
| MAE | 246.12 | 205.70 | 219.17 | 82.71 | |
| MAPE | 977.52 | 312.39 | 392.03 | 29.60 | |
| Eq. | = 0.02 X1 + 20.74 | = 0.06 X1 + 49.76 | = 0.00 X1 + 64.59 | = −2.48 −0.62 X1 + 4.11 X2 + 0.32 X3 | |
| r | 0.39 | 0.49 | 0.03 | 0.49 | |
| p-value | 3.27 × 10−3 | 1.48 × 10−4 | 8.22 × 10−1 | 1.22 × 10−4 | |
| Cardiac Angiogram | R2 | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.35 |
| RMSE | 605.98 | 554.89 | 583.90 | 138.45 | |
| MAE | 582.00 | 529.96 | 557.57 | 108.57 | |
| MAPE | 1895.46 | 653.77 | 1075.71 | 18.39 | |
| Eq. | = 0.02 X1 + 18.26 | = 0.05 X1 + 52.01 | = 0.00 X1 + 57.64 | = 114 + 19.48 X1 −0.91 X2 −0.46 X3 | |
| r | 0.59 | 0.46 | −0.06 | 0.59 | |
| p-value | 1.86 × 10−9 | 7.33 × 10−6 | 6.08 × 10−1 | 1.53 × 10−9 | |
| Cardiac Calcium Score | R2 | 0.68 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 0.68 |
| RMSE | 16.31 | 43.79 | 26.17 | 9.76 | |
| MAE | 11.45 | 41.56 | 22.49 | 7.22 | |
| MAPE | 34.04 | 51.21 | 77.52 | 17.26 | |
| Eq. | = 2.42 X1 −33.91 | = 0.67 X1 −14.26 | = −0.05 X1 −33.91 | = −37.36 + 2.19 X1 + 0.09 X2 + 0.05 X3 | |
| r | 0.82 | 0.69 | −0.04 | 0.83 | |
| p-value | 3.39 × 10−23 | 5.01 × 10−14 | 7.26 × 10−1 | 2.28 × 10−23 | |
| Abdomen/Pelvis | R2 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.17 |
| RMSE | 1278.41 | 1236.02 | 1226.73 | 521.47 | |
| MAE | 1143.78 | 1098.39 | 1074.49 | 420.42 | |
| MAPE | 4200.92 | 1515.99 | 2551.55 | 36.68 | |
| Eq. | = 0.00 X1 + 24.04 | = 0.01 X1 + 60.48 | = 0.00 X1 + 53.77 | = −93.35 −9.31 X1 + 17.99 X2 + 4.3 X3 | |
| r | 0.32 | 0.40 | −0.13 | 0.41 | |
| p-value | 7.76 × 10−3 | 9.25 × 10−4 | 2.92 × 10−1 | 5.49 × 10−4 | |
| ED (mSv) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT Exam | Evaluation Metric | Linear | Multiple Linear | ||
| X1: BMI | X1: Weight | X1: Age | All Parameters (X1: BMI, X2: Weight, X3: Age) | ||
| Chest | R2 | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.30 |
| RMSE | 23.01 | 64.97 | 66.44 | 1.03 | |
| MAE | 22.39 | 62.97 | 63.64 | 0.86 | |
| MAPE | 88.14 | 95.35 | 94.90 | 28.79 | |
| Eq. | = 2.51 X1 + 17.88 | = 5.48 X1 + 49.58 | = 1.85 X1 + 60.15 | = 0.18 + 0.12 X1 − 0.01 X2 + 0 X3 | |
| r | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.54 | |
| p-value | 3.28 × 10−5 | 1.70 × 10−3 | 3.40 × 10−1 | 1.48 × 10−5 | |
| Abdomen/Pelvis | R2 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.17 |
| RMSE | 16.90 | 62.76 | 44.54 | 4.90 | |
| MAE | 16.01 | 60.97 | 39.32 | 3.82 | |
| MAPE | 58.96 | 83.96 | 74.02 | 35.87 | |
| Eq. | = 0.39 X1 + 22.79 | = 1.15 X1 + 59.23 | = −0.83 X1 + 59.59 | = 1.17 + 0.32 X1 + 0.03 X2 −0.02 X3 | |
| r | 0.40 | 0.38 | −0.24 | 0.42 | |
| p-value | 9.22 × 10−4 | 1.42 × 10−3 | 4.83 × 10−2 | 4.91 × 10−4 | |
| SSDE (mGy) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT Exam | Evaluation Metric | Linear | Multiple Linear | ||
| X1: BMI | X1: Weight | X1: Age | All Parameters (X1: BMI, X2: Weight, X3: Age) | ||
| Chest | R2 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0.40 |
| RMSE | 18.02 | 59.88 | 60.94 | 1.92 | |
| MAE | 17.32 | 57.91 | 57.36 | 1.63 | |
| MAPE | 67.79 | 87.49 | 86.01 | 20.35 | |
| Eq. | = 1.30 X1 + 14.87 | = 3.55 X1 + 37.38 | = 0.98 X1 + 57.49 | = 0.7 + 0.12 X1 + 0.04 X2 + 0.02 X3 | |
| r | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.12 | 0.63 | |
| p-value | 1.23 × 10−5 | 2.30 × 10−5 | 3.40 × 10−1 | 1.57 × 10−7 | |
| Abdomen/Pelvis | R2 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.23 |
| RMSE | 7.28 | 51.07 | 34.05 | 4.99 | |
| MAE | 5.76 | 49.25 | 27.83 | 3.98 | |
| MAPE | 21.47 | 68.06 | 49.68 | 17.97 | |
| Eq. | = 0.40 X1 + 18.04 | = 1.15 X1 + 46.01 | = −0.05 X1 + 50.71 | = 6.25 + 0.32 X1 + 0.08 X2 + 0.03 X3 | |
| r | 0.46 | 0.44 | −0.01 | 0.48 | |
| p-value | 1.33 × 10−4 | 3.20 × 10−4 | 9.04 × 10−1 | 5.23 × 10−5 | |
| CTDIVol as Output Variable () with | DLP as Output Variable () with | ED as Output Variable () with | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT Exam | Evaluation Metric | X1: DLP | X1: ED | X1: SSDE | X1: ED | X1: SSDE | X1: SSDE |
| Chest | R2 | 0.85 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.68 |
| RMSE | 294.94 | 5.47 | 2.44 | 300.25 | 295.55 | 5.17 | |
| MAE | 268.43 | 4.83 | 1.94 | 273.25 | 268.32 | 4.94 | |
| MAPE | 97.06 | 193.59 | 25.89 | 98.84 | 96.80 | 63.28 | |
| Eq. | = 38.50 X1 − 22.14 | = 0.21 X1 + 1.30 | = 0.49 X1 + 4.08 | = 45.05 X1 + 144.52 | = 22.91 X1 + 96.15 | = 1.61 X1 + 3.15 | |
| r | 0.92 | 0.51 | 0.61 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.82 | |
| p-value | 4.86 × 10−26 | 2.17 × 10−5 | 1.55 × 10−7 | 3.52 × 10−4 | 3.66 × 10−4 | 2.77 × 10−16 | |
| Cardiac Angiogram | R2 | 0.74 | - | - | - | - | - |
| RMSE | 593.64 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MAE | 572.96 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MAPE | 94.13 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Eq. | = 0.04 X1 + 7.83 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| r | 0.86 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| p-value | 1.26 × 10−24 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Cardiac Calcium Score | R2 | 0.90 | - | - | - | - | - |
| RMSE | 39.48 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MAE | 36.77 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| MAPE | 93.31 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Eq. | = 15.60 X1 − 1.03 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| r | 0.95 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| p-value | 3.07 × 10−44 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Abdomen/Pelvis | R2 | 0.83 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.54 |
| RMSE | 1199.77 | 19.67 | 11.93 | 1217.96 | 1208.01 | 11.65 | |
| MAE | 1070.05 | 16.24 | 10.18 | 1086.03 | 1074.99 | 11.04 | |
| MAPE | 97.39 | 192.24 | 49.83 | 98.81 | 97.25 | 52.41 | |
| Eq. | = 40.03 X1 + 32.66 | = 0.16 X1 + 6.29 | = 0.21 X1 + 15.95 | = 62.26 X1 + 436.46 | = 61.14 X1 − 226.39 | = 0.77 X1 + 13.43 | |
| r | 0.91 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.73 | |
| p-value | 8.48 × 10−26 | 6.20 × 10−4 | 1.08 × 10−5 | 1.58 × 10−6 | 5.05 × 10−7 | 3.91 × 10−12 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlShurbaji, M.; El Haout, S.; Chanchal, A.; Dhou, S.; Dalah, E. Investigating the Effect of Patient-Related Factors on Computed Tomography Radiation Dose Using Regression and Correlation Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031071
AlShurbaji M, El Haout S, Chanchal A, Dhou S, Dalah E. Investigating the Effect of Patient-Related Factors on Computed Tomography Radiation Dose Using Regression and Correlation Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(3):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031071
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlShurbaji, Mohammad, Sara El Haout, Akchunya Chanchal, Salam Dhou, and Entesar Dalah. 2024. "Investigating the Effect of Patient-Related Factors on Computed Tomography Radiation Dose Using Regression and Correlation Analysis" Applied Sciences 14, no. 3: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031071
APA StyleAlShurbaji, M., El Haout, S., Chanchal, A., Dhou, S., & Dalah, E. (2024). Investigating the Effect of Patient-Related Factors on Computed Tomography Radiation Dose Using Regression and Correlation Analysis. Applied Sciences, 14(3), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031071






