A Two-Step Neurorehabilitation Program Utilizing Extended Reality and Telerehabilitation for Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study on Effectiveness, Adherence, and Technical Feasibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
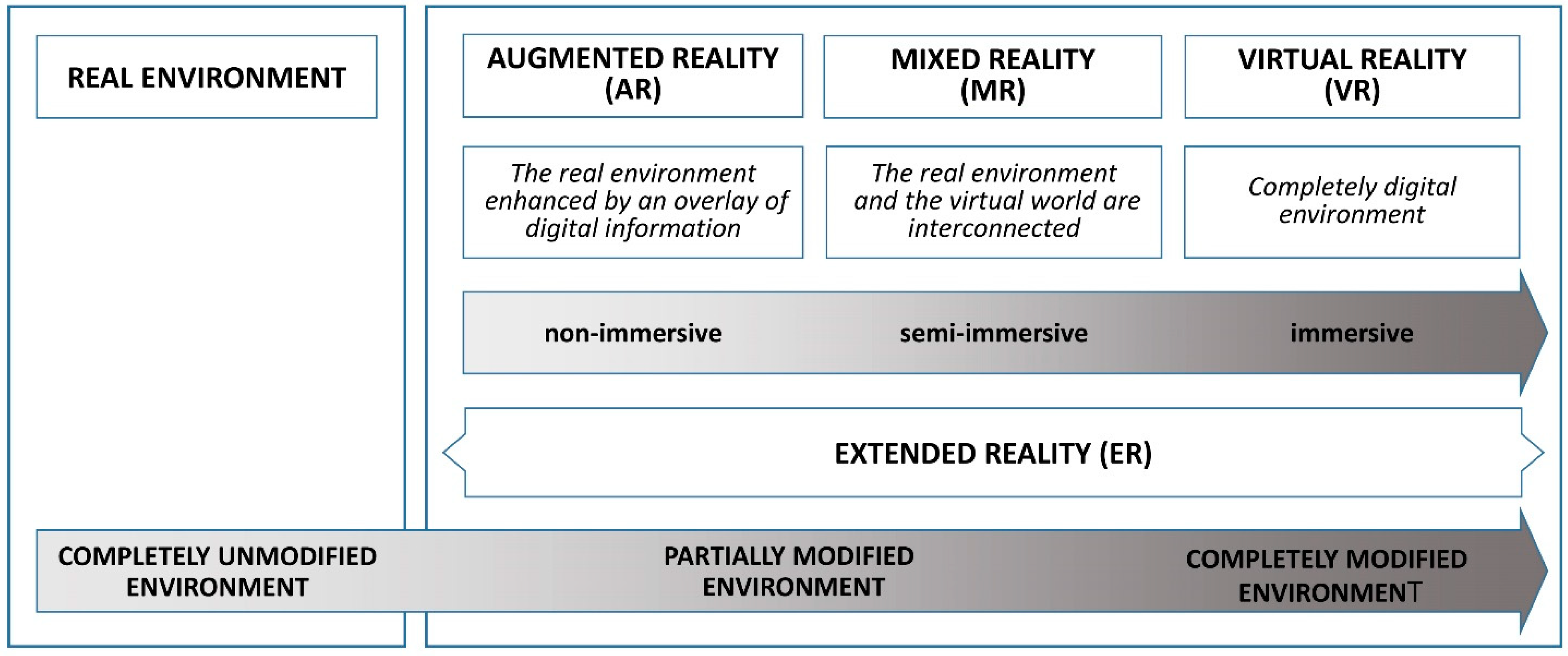
1.1. Background
1.2. Objectives and Hypotheses
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Participants
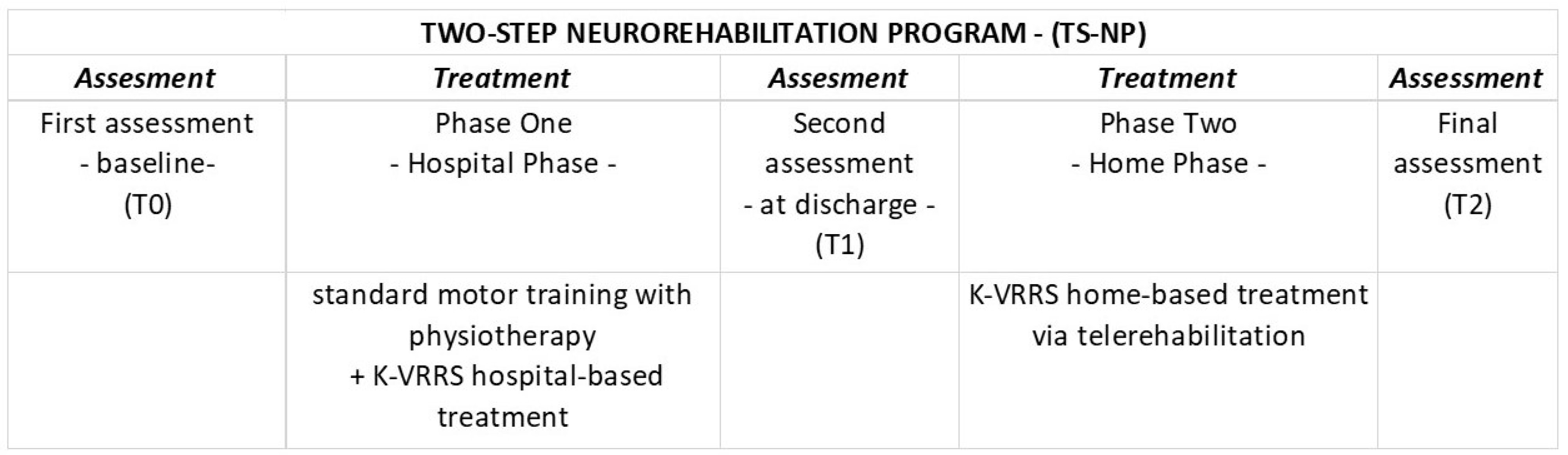
2.2. K-VRRS Technologies and Intervention
2.3. Evaluation Timeline and Outcome Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. Suppl. 2007, 109, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Christine, C.; Dolk, H.; Platt, M.J.; Colver, A.; Prasauskiene, A.; Krägeloh-Mann, I. Recommendations from the SCPE collaborative group for defining and classifying cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. Suppl. 2007, 109, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowska, M.; Sarecka-Hujar, B.; Kopyta, I. Cerebral Palsy: Current Opinions on Definition, Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification and Treatment Options. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health: Children & Youth Version: ICF-CY; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schiariti, V.; Longo, E.; Shoshmin, A.; Kozhushko, L.; Besstrashnova, Y.; Król, M.; Neri Correia Campos, T.; Náryma Confessor Ferreira, H.; Verissimo, C.; Shaba, D.; et al. Implementation of the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF) Core Sets for Children and Youth with Cerebral Palsy: Global Initiatives Promoting Optimal Functioning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.; Darrah, J.; Gordon, A.M.; Harbourne, R.; Spittle, A.; Johnson, R.; Fetters, L. Effectiveness of motor interventions in infants with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2016, 58, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinaro, A.; Fedrizzi, E.; Calza, S.; Pagliano, E.; Jessica, G.; Fazzi, E. Family-centred care for children and young people with cerebral palsy: Results from an Italian multicenter observational study. Child Care Health Dev. 2017, 43, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabacca, A.; Russo, L.; Losito, L.; Rinaldis, M.D.; Moro, G.; Cacudi, M.; Gennaro, L. The ICF-CY perspective on the neurorehabilitation of cerebral palsy: A single case study. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekteshi, S.; Monbaliu, E.; McIntyre, S.; Saloojee, G.; Hilberink, S.R.; Tatishvili, N.; Dan, B. Towards functional improvement of motor disorders associated with cerebral palsy. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabacca, A.; Vespino, T.; Di Liddo, A.; Russo, L. Multidisciplinary rehabilitation for patients with cerebral palsy: Improving long-term care. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2016, 9, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fanchiang, H.D.; Howard, A. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phys. Ther. 2018, 98, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Choromanski, L.; Kreuzer, T.; Stroppini, J. Exploring the Feasibility of a Virtual, Home-Based MusicGlove® Protocol for Children with Hemiparetic Cerebral Palsy. Open J. Occup. Ther. 2022, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, C.; Mohan, V.; Peirson, J.; Skinner, J.; Nethaji, K.S.; Kuhn, I. Effectiveness of virtual reality in the treatment of hand function in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review. J. Hand Ther. 2019, 32, 426–434.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboosi, M.E.; Al-Khathami, S.S.; El-Shamy, S.M. The effectiveness of tele-rehabilitation on improvement of daily living activities in children with cerebral palsy: Narrative review. Bull. Fac. Phys. Ther. 2021, 26, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.; Pang, Y.; Kim, J.H. The effectiveness of virtual reality for people with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: A meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, K.E.; Lange, B.; George, S.; Deutsch, J.E.; Saposnik, G.; Crotty, M. Virtual reality for stroke rehabilitation. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD008349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Reid, D. Virtual reality in pediatric neurorehabilitation: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, autism and cerebral palsy. Neuroepidemiology 2011, 36, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultheis, M.T.; Rizzo, A.A. The application of virtual reality technology in rehabilitation. Rehabil. Psychol. 2001, 46, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, A.; Slater, M. The building blocks of the full body ownership illusion. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewe, H.; Gottwald, J.M.; Bird, L.A.; Brenton, H.; Gillies, M.; Cowie, D. My Virtual Self: The Role of Movement in Children’s Sense of Embodiment. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2022, 28, 4061–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, G.; Mancuso, V.; Cavedoni, S.; Stramba-Badiale, C. Virtual reality in neurorehabilitation: A review of its effects on multiple cognitive domains. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2020, 17, 1035–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, M.; Wilbur, S. A framework for immersive virtual environments (FIVE): Speculations on the role of presence in virtual environments. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 1997, 6, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, P.L.; Kizony, R.; Feintuch, U.; Katz, N. Virtual reality in neurorehabilitation. Textb. Neural Repair Rehabil. 2006, 51, 182–197. [Google Scholar]
- Piron, L.; Turolla, A.; Agostini, M.; Zucconi, C.; Cortese, F.; Zampolini, M.; Zannini, M.; Dam, M.; Ventura, L.; Battauz, M.; et al. Exercises for paretic upper limb after stroke: A combined virtual-reality and telemedicine approach. J. Rehabil. Med. 2009, 41, 1016–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, M.C. A meta-analysis and systematic literature review of virtual reality rehabilitation programs. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 70, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuara, A.; Fabbri-Destro, M.; Scalona, E.; Lenzi, S.E.; Rizzolatti, G.; Avanzini, P. Telerehabilitation in response to constrained physical distance: An opportunity to rethink neurorehabilitative routines. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.A.; Buckwalter, J.G.; van der Zaag, C. Virtual environment applications in clinical neuropsychology. In Handbook of Virtual Environments; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 1067–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Levac, D.E.; Huber, M.E.; Sternad, D. Learning and transfer of complex motor skills in virtual reality: A perspective review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.L.; Tunik, E.; Adamovich, S.V.; Boyd, L.A. Neuroplasticity and virtual reality. In Virtual Reality for Physical and Motor Rehabilitation; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kleim, J.A.; Jones, T.A. Principles of experience-dependent neural plasticity: Implications for rehabilitation after brain damage. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. JSLHR 2008, 51, S225–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.N.; Rosie, J.A. Virtual reality games for movement rehabilitation in neurological conditions: How do we meet the needs and expectations of the users? Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelman, K.D.; Hartman, L.M. Telerehabilitation: Policy issues and research tools. Int. J. Telerehabilit. 2009, 1, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchitella, L.; Amendola, S.; Barraco, G.; Scoditti, S.; Gallo, I.; Oliva, M.C.; Trabacca, A. A narrative review of the use of a cutting-edge virtual reality rehabilitation technology in neurological and neuropsychological rehabilitation. NeuroRehabilitation 2023, 53, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkman, M.; Kirk, U.; Kemp, S. NEPSY-II, Italian Version; Giunti OS Organizzazioni Speciali: Firenze, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Urgesi, C.; Campanella, F.; Fabbro, F. NEPSY-II. Contributo Alla Taratura Italiana; Giunti OS: Firenze, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Orsini, A.; Pezzuti, L.; Picone, L. WISC-IV: Contributo Alla Taratura Italiana, WISC-IV Italian ed.; Giunti OS: Firenze, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence, 4th ed.; The Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, M.; Johnson, L.; Reddihough, D. The Melbourne Assessment 2; Royal Children’s Hospital: Melbourne, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa-Rizzotto, M.; Visonà Dalla Pozza, L.; Corlatti, A.; Luparia, A.; Marchi, A.; Molteni, F.; Facchin, P.; Pagliano, E.; Fedrizzi, E. A new scale for the assessment of performance and capacity of hand function in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy: Reliability and validity studies. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 50, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.E. Movement Assessment Battery for Children, 2nd ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Varni, J.W.; Burwinkle, T.M.; Berrin, S.J.; Sherman, S.A.; Artavia, K.; Malcarne, V.L.; Chambers, H.G. The PedsQL in pediatric cerebral palsy: Reliability, validity, and sensitivity of the Generic Core Scales and Cerebral Palsy Module. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, J. SUS: A quick and dirty usability scale. In Usability Evaluation in Industry; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Menici, V.; Barzacchi, V.; Filogna, S.; Beani, E.; Tinelli, F.; Cioni, G.; Sgandurra, G. Tele-Rehabilitation for Postural Control by Means of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation System in an Adolescent with Motor Disorder: A Case Study. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 720677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraco, G.; Macchitella, L.; Accogli, G.; Pirani, G.; Nicolardi, V.; Trabacca, A. Exploring the Application and Usability of Emerging Technologies in Neuromotor Rehabilitation for a Patient with 5Q-Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 2 Receiving a Gene-Based Therapy: A Single Case Study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Extended Reality, Lecce, Italy, 4–7 September 2024; pp. 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri, I.; Chiappedi, M.; Meriggi, P.; Mazzola, M.; Grandi, A.; Angelini, L. Rehabilitation of children with hemiparesis: A pilot study on the use of virtual reality. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 695935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangor, A.; Kortum, P.T.; Miller, J.T. An empirical evaluation of the system usability scale. Intl. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2008, 24, 574–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sex N (%) | |
| Male | 5 (71.4%) |
| Female | 2 (28.6%) |
| Age | |
| Mean age (Standard Deviation) | 6.82 (2.08) |
| Age range | 4.25–10.6 |
| QI Mean (Standard Deviation) | 88 (16.2) |
| Side of motor impairment N (%) | |
| Right | 4 (57.1%) |
| Left | 3 (42.9%) |
| GMFCS N (%) | |
| Level 1 | 3 (42.9%) |
| Level 2 | 4 (57.1%) |
| MACS N (%) | |
| Level 1 | 1 (14.3%) |
| Lecel 2 | 6 (85.7%) |
| VFCS N (%) | |
| Level 1 | 7 (100%) |
| Level 2 | 0 (0%) |
| Mean (Standard Deviation) | Mean (Standard Deviation) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
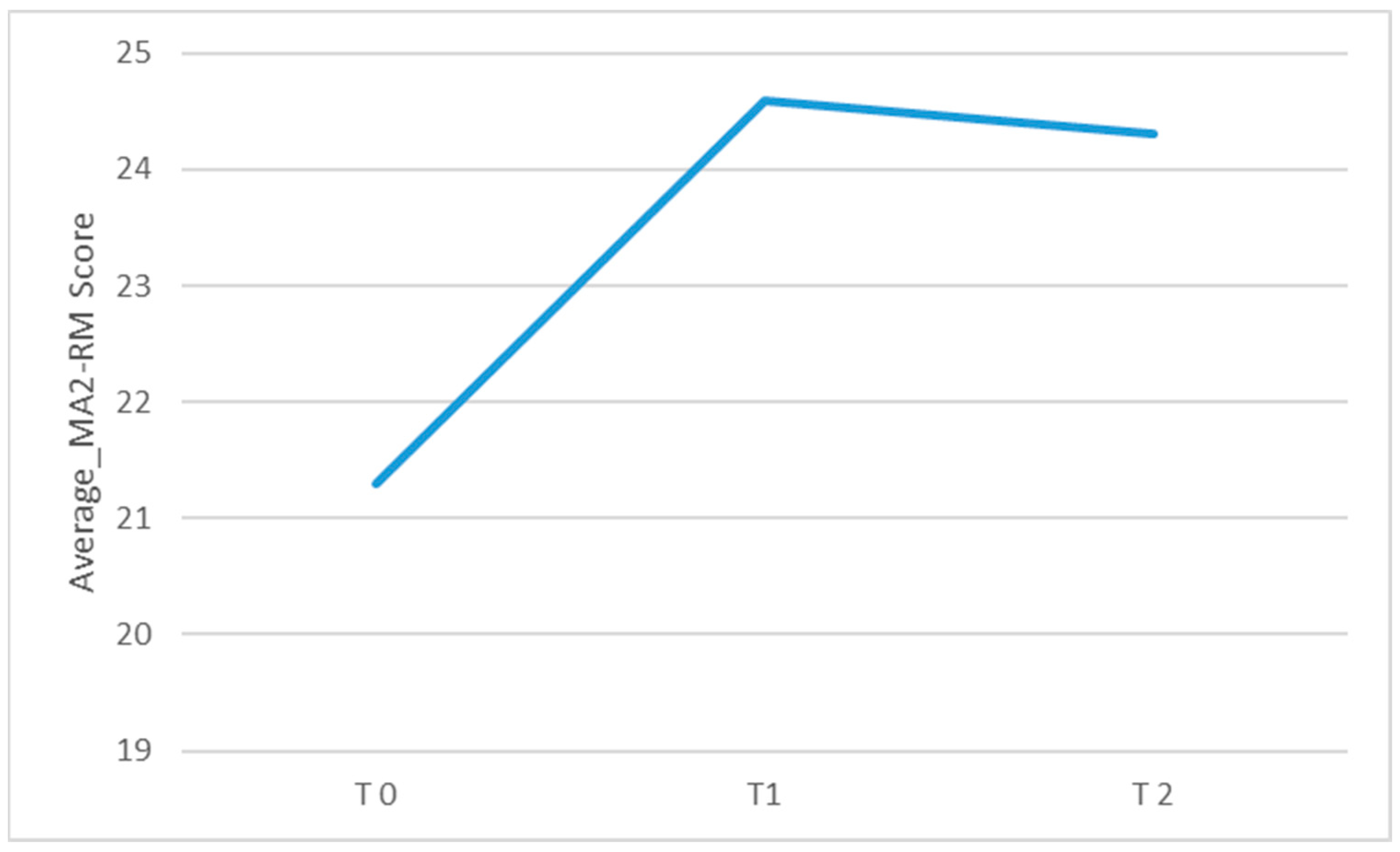
| MA2-RM_T0 | 21.3 (3.40) | MA2-RM_T1 | 24.6 (2.51) | 6.55 | <0.001 |
| MA2-RM_T0 | 21.3 (3.40) | MA2-RM_T2 | 24.3 (2.81) | 5.24 | <0.001 |
| MA2-RM_T1 | 24.6 (2.51) | MA2-RM_T2 | 24.3 (2.81) | 1.31 | 0.215 |
| MA2-FLU_T0 | 11.3 (3.15) | MA2-FLU_T1 | 14.6 (3.82) | 2.799 | 0.016 |
| MA2-FLU_T0 | 11.3 (3.15) | MA2-FLU_T2 | 14.9 (3.44) | 2.974 | 0.012 |
| MA2-FLU_T1 | 14.6 (3.82) | MA2-FLU_T2 | 14.9 (3.44) | 0.175 | 0.864 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macchitella, L.; Accogli, G.; Barraco, G.; Nicolardi, V.; Pirani, G.; Ferrante, C.; Oliva, M.C.; Fanizza, I.; Gallo, I.; De Rinaldis, M.; et al. A Two-Step Neurorehabilitation Program Utilizing Extended Reality and Telerehabilitation for Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study on Effectiveness, Adherence, and Technical Feasibility. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411961
Macchitella L, Accogli G, Barraco G, Nicolardi V, Pirani G, Ferrante C, Oliva MC, Fanizza I, Gallo I, De Rinaldis M, et al. A Two-Step Neurorehabilitation Program Utilizing Extended Reality and Telerehabilitation for Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study on Effectiveness, Adherence, and Technical Feasibility. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(24):11961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411961
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacchitella, Luigi, Giuseppe Accogli, Giulia Barraco, Valentina Nicolardi, Greta Pirani, Camilla Ferrante, Maria Carmela Oliva, Isabella Fanizza, Ivana Gallo, Marta De Rinaldis, and et al. 2024. "A Two-Step Neurorehabilitation Program Utilizing Extended Reality and Telerehabilitation for Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study on Effectiveness, Adherence, and Technical Feasibility" Applied Sciences 14, no. 24: 11961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411961
APA StyleMacchitella, L., Accogli, G., Barraco, G., Nicolardi, V., Pirani, G., Ferrante, C., Oliva, M. C., Fanizza, I., Gallo, I., De Rinaldis, M., & Trabacca, A. (2024). A Two-Step Neurorehabilitation Program Utilizing Extended Reality and Telerehabilitation for Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study on Effectiveness, Adherence, and Technical Feasibility. Applied Sciences, 14(24), 11961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411961






