Estimating Tetrachloroethene Sorption Coefficients Based on Soil Properties in Organic-Poor Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Soil Samples
2.3. Sorption Experiments
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Development of Kd Prediction Models
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Soil Properties
3.2. Comparison of Measured and Estimated Linear Kd Values of Soil Samples
3.3. Statistical Data Analysis
3.4. Univariate and Multivariate Linear Regression
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Bowman, R.S. Sorption of Perchloroethylene by Surfactant-Modified Zeolite as Controlled by Surfactant Loading. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2278–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-G.; Park, J.-H. Effect of soil organic carbon on sorption and desorption of perchloroethylene in soils. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Gschwend, P.M.; Imboden, D.M. Environmental Organic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.W.; Feng, S.J.; Zheng, Q.T.; Chen, H.X.; Wei, H. Analytical model for the mitigation of VOC vapor with horizontal permeable reactive barrier in the contaminated site considering non-uniform source. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.T.; Porter, P.E.; Schmedding, D.W. Partition Equilibria of Non-Ionic Organic-Compounds between Soil Organic-Matter and Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1983, 17, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.T.; Peters, L.J.; Freed, V.H. A Physical Concept of Soil-Water Equilibria for Nonionic Organic Compounds. Science 1979, 206, 831–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, D.W.; Chiou, C.T.; Kile, D.E. Influence of soil organic matter composition on the partition of organic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karickhoff, S.W.; Brown, D.S.; Scott, T.A. Sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments. Water Res. 1979, 13, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Westall, J. Transport of Non-Polar Organic-Compounds from Surface-Water to Groundwater—Laboratory Sorption Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1981, 15, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.M.; Weber, W.J.J. A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments. 3. Effects of diagenetic processes on sorption energetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, W.P.; Roberts, P.V. Long-Term Sorption of Halogenated Organic-Chemicals by Aquifer Material. 1. Equilibrium. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Xing, B. Mechanisms of slow sorption of organic chemicals to natural particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Bjerg, P.L.; Zhang, F.; Broholm, M.M. Sorption of chlorinated solvents and degradation products on natural clayey tills. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, T.; Airey, D.W.; Leo, C.J. The diffusion and sorption of volatile organic compounds through kaolinitic clayey soils. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2003, 65, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarraya, I.; Fourmentin, S.; Benzina, M.; Bouaziz, S. VOC adsorption on raw and modified clay materials. Chem. Geol. 2010, 275, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelt-Hunt, S.L.; Burns, S.E.; Smith, J.A. Nonionic organic solute sorption onto two organobentonites as a function of organic-carbon content. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 266, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, C.T.; Shoup, T.D. Soil sorption of organic vapors and effects of humidity on sorptive mechanism and capacity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1985, 19, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, S.M.; Schmeltzer, J.S.; Kreamer, D.K. Sorption of benzene and trichloroethylene (TCE) on a desert soil: Effects of moisture and organic matter. Chemosphere 1996, 33, 961–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Chiou, C.T.; Kammer, J.A.; Kile, D.E. Effect of soil moisture on the sorption of trichloroethene vapor to vadose-zone soil at Picatinny Arsenal, New Jersey. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strenge, D.L.; Peterson, S.R. Chemical Data Bases for the Multimedia Environmental Pollutant Assessment System (MEPAS): Version 1; PNL-7145; Pacific Northwest Laboratory: Richland, WA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Werth, C.J.; Reinhardt, M. Effects of temperature on trichloroethylene desorption from silica gel and natural sediments. 2. Kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.M.; Evans, C.E.; Hayes, E.C. Porosity and pore size distribution in a sedimentary rock: Implications for the distribution of chlorinated solvents. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2017, 203, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poe, S.H.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Thibodeaux, L.J.; Springer, C. Equilibrium vapor phase adsorption of volatile organic chemicals on dry soils. J. Hazard Mater 1988, 19, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Diáková, K.; Aburto, F.; Doetterl, S.; Borovec, J. Sorption and desorption of organic matter in soils as affected by phosphate. Geoderma 2022, 405, 115377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüürmann, G.; Ebert, R.-U.; Kühne, R. Prediction of the sorption of organic compounds into soil organic matter from molecular structure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7005–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottosen, C.B.; Rønde, V.; McKnight, U.S.; Annable, M.D.; Broholm, M.M.; Devlin, J.F.; Bjerg, P.L. Natural attenuation of a chlorinated ethene plume discharging to a stream: Integrated assessment of hydrogeological, chemical and microbial interactions. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, G.; Gustafsson, Ö.; Bucheli, T.D.; Jonker, M.T.; Koelmans, A.A.; Van Noort, P.C. Extensive sorption of organic compounds to black carbon, coal, and kerogen in sediments and soils: Mechanisms and consequences for distribution, bioaccumulation, and biodegradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6881–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Allen-King, R.M.; Choung, S.; Feenstra, S.; Watson, R.; Kominek, M. A Practical Measurement Strategy to Estimate Nonlinear Chlorinated Solvent Sorption in Low f oc Sediments. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2013, 33, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Jia, J. Health risk assessment and distribution of VOCs during excavation processes for the remediation of contaminated sites. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 2073–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Gao, P.; Okoli, C.P.; Wang, P. Distribution, sources, and health risk assessment of VOCs/SVOCs in soils obtained from petrochemical-contaminated sites in Guangzhou, a subtropical coastal megacity in southern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boethling, R.S.; Mackay, D. Handbook of Property Estimation Methods for Chemicals: Environmental and Health Sciences; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; p. 481. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Standard Test Method for 24-h Batch-Type Measurement of Contaminant Sorption by Soils and Sediments; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Site Characterization for Subsurface Remediation. EPA/625/4-91/026; Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1991.
- Brusseau, M.L.; Jessup, R.E.; Rao, P.S.C. Sorption kinetics of organic chemicals: Evaluation of gas-purge and miscible-displacement techniques. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 24, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukalska-Jaruga, A.; Bejger, R.; Smreczak, B.; Podlasiński, M. Sorption of organic contaminants by stable organic matter fraction in soil. Molecules 2023, 28, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozerski, G.E.; Kim, J.; Durham, J.A.; Townsend, B. Batch equilibrium experiments and modeling reveal weak temperature dependence of cyclic volatile methylsiloxane sorption in soil/sediment organic carbon-water systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 942, 173541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Creamer, A.E.; Cao, C.; Li, Y. Adsorption of VOCs onto engineered carbon materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán–Álvarez, J.C.; Prado, B.; Ferroud, A.; Juayerk, N.; Jiménez-Cisneros, B. Sorption, desorption and displacement of ibuprofen, estrone, and 17β estradiol in wastewater irrigated and rainfed agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, W.R. Technical Resource Document: Batch-Type Procedures for Estimating Soil Adsorption of Chemicals; Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1992.
- OECD. Test No. 106. Adsorption-Desorption using a batch equilibrium method. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development Publishing: Paris, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Addinsoft. XLSTAT Tutorials and Guides. 2018. Available online: https://www.xlstat.com (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Castaldi, P.; Santona, L.; Enzo, S.; Melis, P. Sorption processes and XRD analysis of a natural zeolite exchanged with Pb2+, Cd2+ and Zn2+ cations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Z. Chemistry of soil-type dependent soil matrices and its influence on behaviors of pharmaceutical compounds (PCs) in soils. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassman, S.A.; Lee, L.S. Sorption of three tetracyclines by several soils: Assessing the role of pH and cation exchange. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7452–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karickhoff, S.W. Organic Pollutant Sorption in Aquatic Systems. J. Hydraul. Eng. Asce 1984, 110, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaGrega, M.D.; Buckingham, P.L.; Evans, J.C. Hazardous Waste Management; Waveland Press: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kret, E.; Kiecak, A.; Malina, G.; Nijenhuis, I.; Postawa, A. Identification of TCE and PCE sorption and biodegradation parameters in a sandy aquifer for fate and transport modelling: Batch and column studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9877–9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen-King, R.M.; Grathwohl, P.; Ball, W.P. New modeling paradigms for the sorption of hydrophobic organic chemicals to heterogeneous carbonaceous matter in soils, sediments, and rocks. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 985–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yu, Z.; Fu, J. Effects of organic matter heterogeneity on sorption and desorption of organic contaminants by soils and sediments. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 955–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenny, S.; Abdelgawad, I. Statistical Significance; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Allen-King, R.M.; Groenevelt, H.; Warren, C.J.; Mackay, D.M. Non-linear chlorinated-solvent sorption in four aquitards. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1996, 22, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen-King, R.M.; Groenevelt, H.; Mackay, D.M. Analytical Method for the Sorption of Hydrophobic Organic Pollutants in Clay-Rich Materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Reinhard, M. Sorption of Trichloroethylene in Hydrophobic Micropores of Dealuminated Y Zeolites and Natural Minerals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7694–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, C.; Deng, D.; Li, Y.; Luo, L. Factors affecting sorption behaviors of tetracycline to soils: Importance of soil organic carbon, pH and Cd contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, F.; Wang, M.K.; Fu, Q.L.; Zhu, J. The properties of clay minerals in soil particles from two Ultisols, China. Clays Clay Miner. 2017, 65, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberhauer, G.; Pfeiffer, L.; Gerzabek, M.H. Influence of molecular structure on sorption of phenoxyalkanoic herbicides on soil and its particle size fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3722–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, P.; Nilda, M.A.; Pablo, Z.; Maria, B.V. Effect of clay minerals and organic matter on the Cation Exchange Capacity of silt fraction. J. Plant Nutri. Soil Sci. 2000, 163, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Kobayashi, T. Investigating the Effects of Long-Term Sorption of Chlorinated Volatile Organic Compounds into Sandy Soils on the Difficulty of Desorption. J. Environ. Eng. 2024, 150, 4023098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

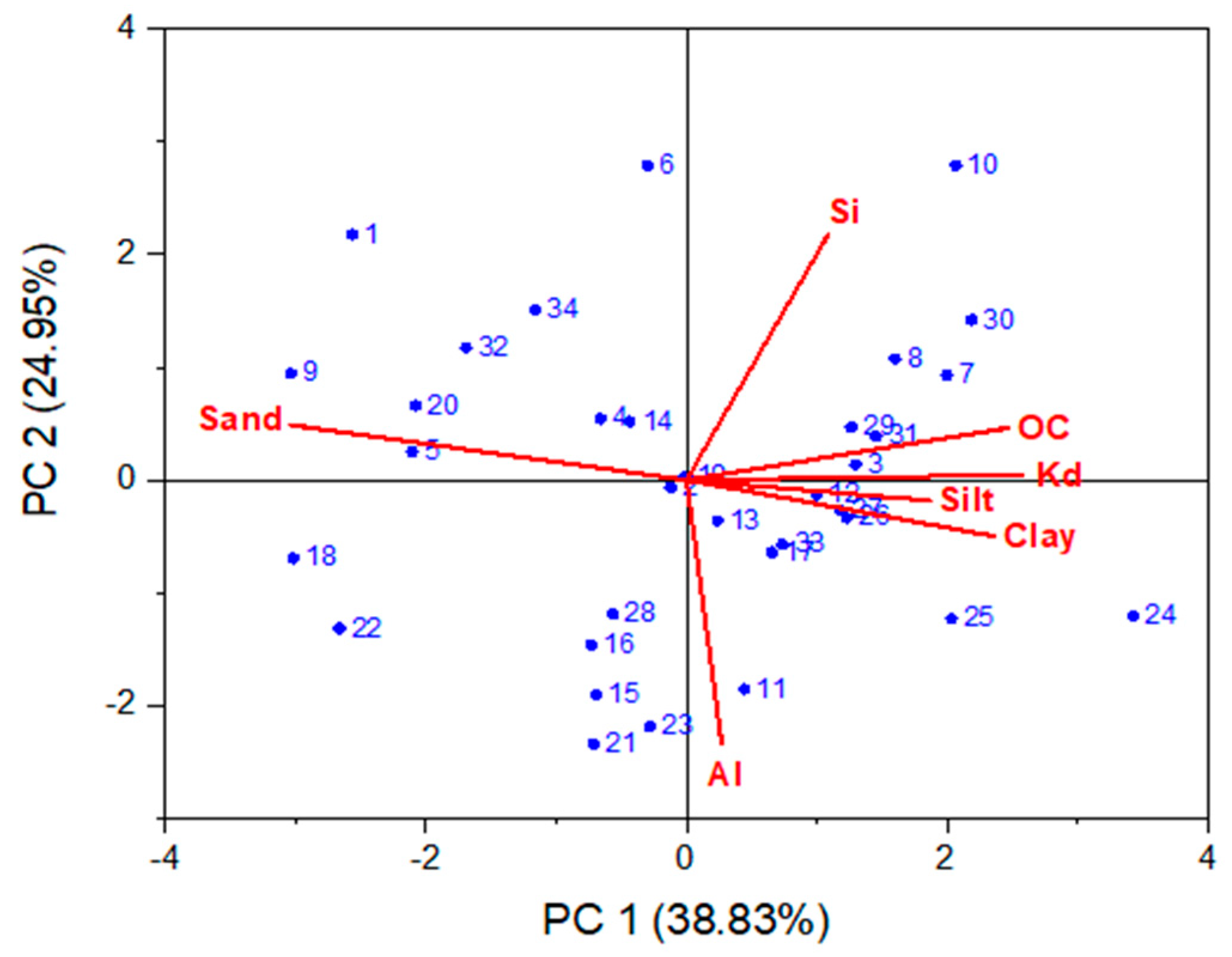
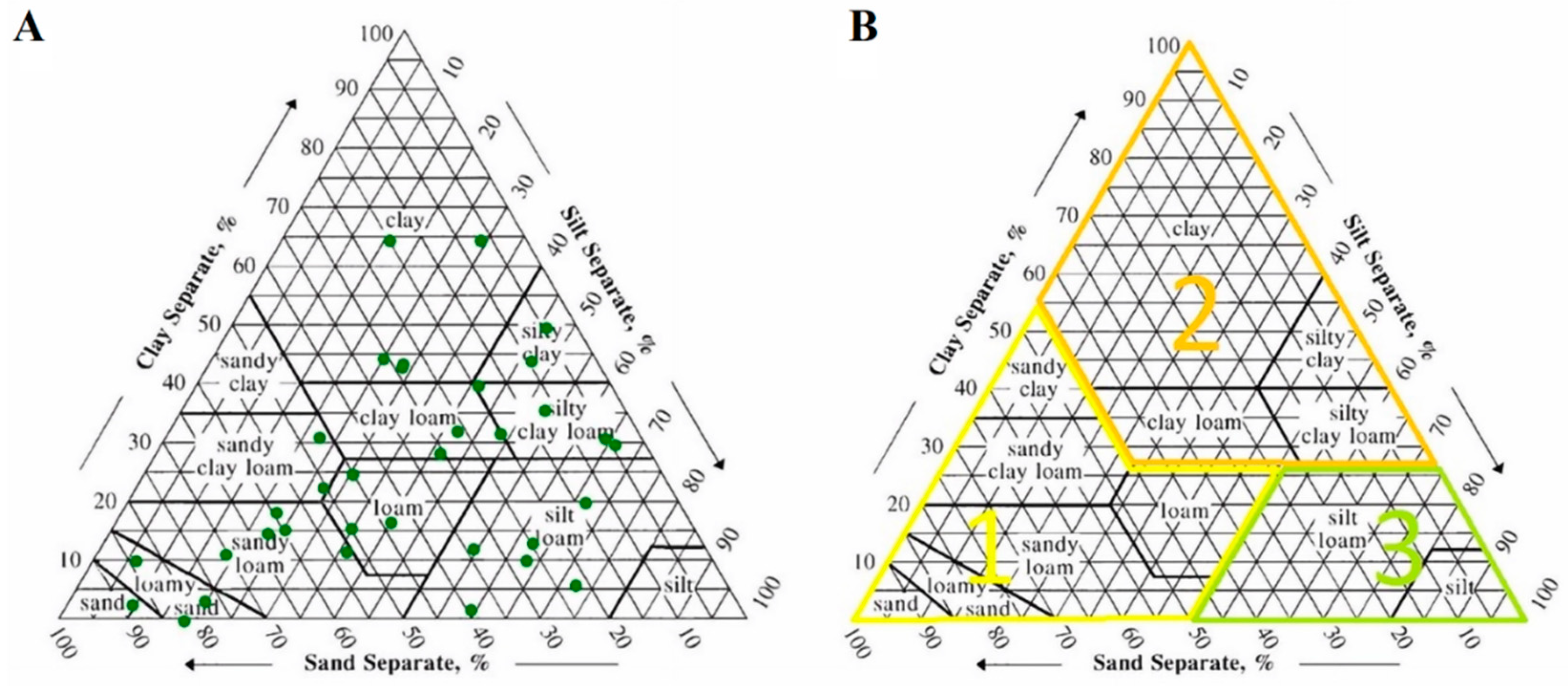
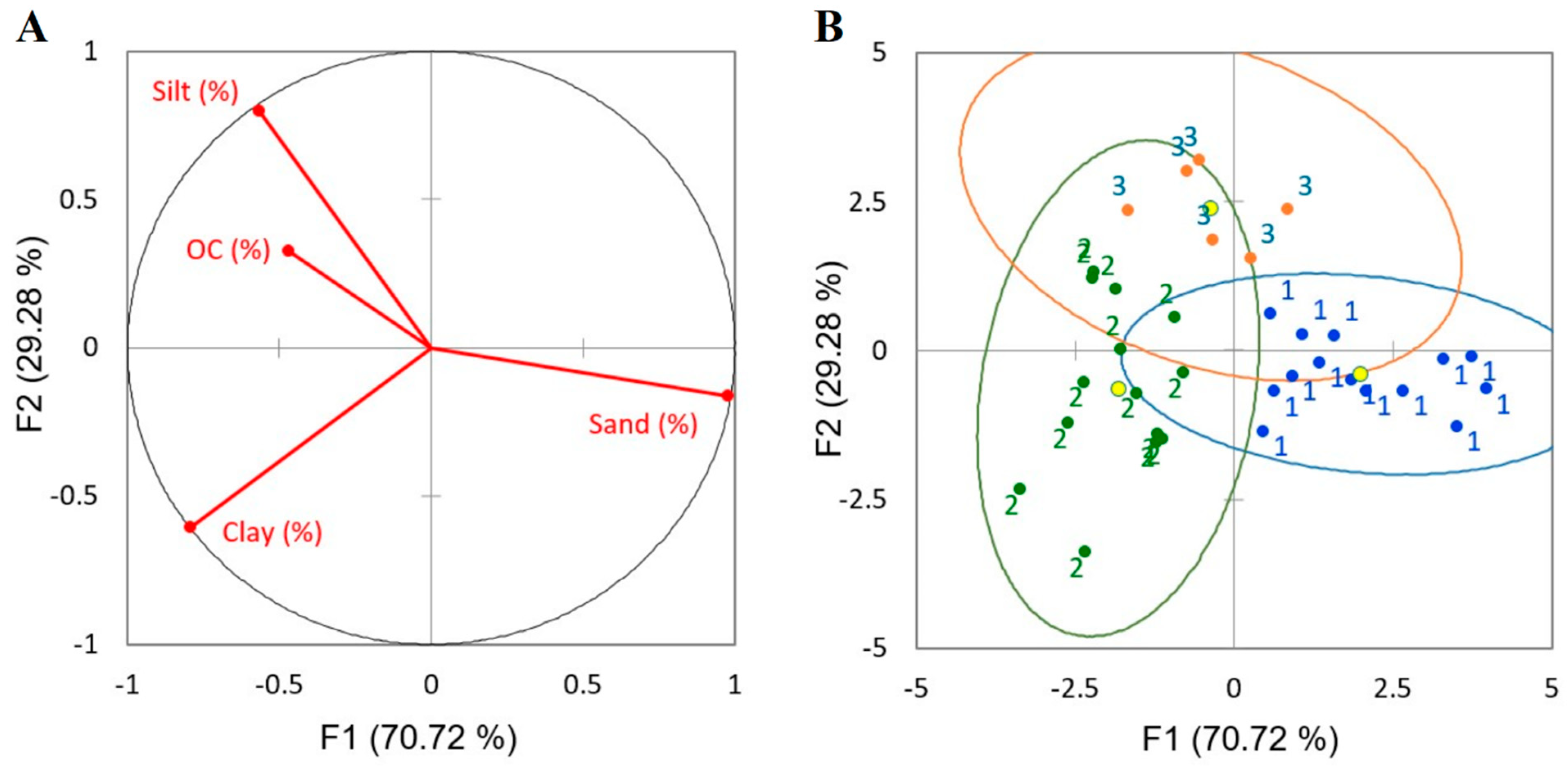
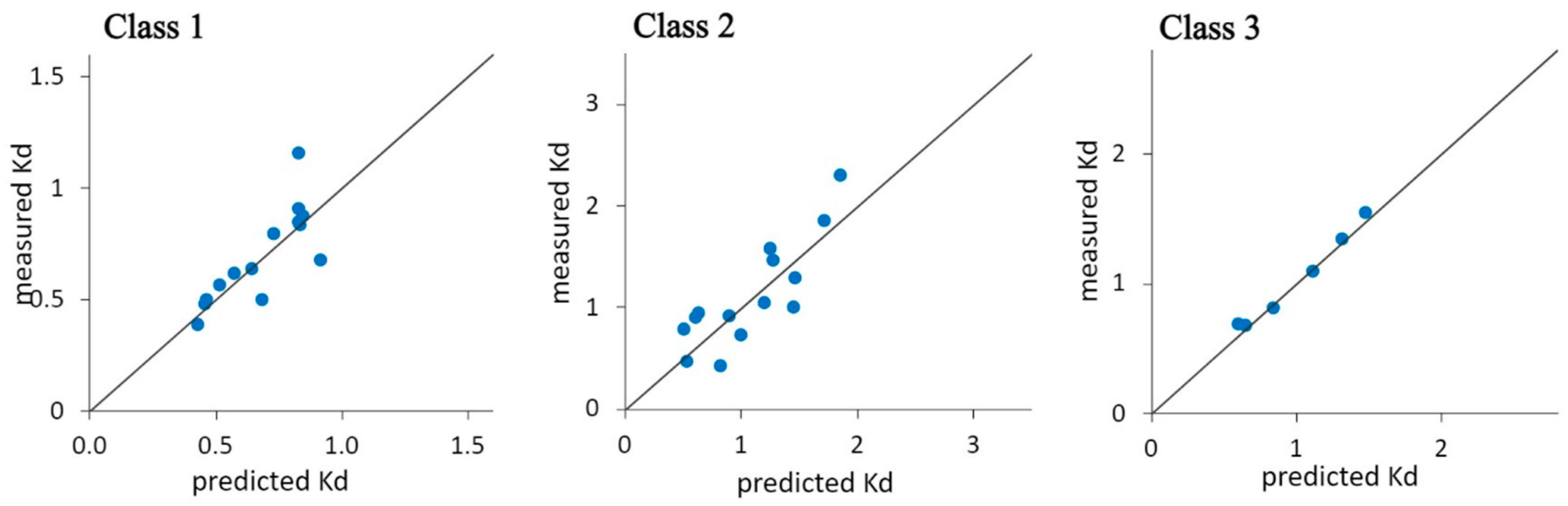
| No. | Site of Origin | Samp. Depth (m) | Soil Texture | Distribution of Soil Particles ≤ 2 mm | ρs | ρb | ε | Elemental Composition | SSA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | Silt | Sand | OC | Si | Al | ||||||||
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (g cm−3) | (g cm−3) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (m2 g−1) | ||||
| 1 | Chotikov | 4.30 | loamy sand | 10.3 | 5.1 | 84.6 | 2.54 | 1.38 | 45.8 | 0.12 | 37.67 | 6.52 | 17.62 |
| 2 | Vestec | 2.00 | silt loam | 2.0 | 58.0 | 40.0 | 2.69 | 1.15 | 57.3 | 0.23 | 33.44 | 10.98 | 10.27 |
| 3 | Vestec | <0.50 | silt loam | 6.1 | 71.2 | 22.7 | 2.54 | 1.20 | 52.8 | 0.42 | 34.27 | 10.63 | |
| 4 | Liberec | 3.50 | loam | 25.0 | 29.2 | 45.8 | 2.58 | 1.21 | 53.0 | 0.12 | 35.08 | 9.24 | 13.64 |
| 5 | Liberec | 3.00 | sandy loam | 11.3 | 17.7 | 71.0 | 2.53 | 1.25 | 50.5 | 0.07 | 34.20 | 10.71 | 10.52 |
| 6 | Kladno | 3.00 | sandy clay loam | 21.8 | 27.3 | 50.9 | 2.43 | 1.00 | 59.1 | 0.25 | 40.65 | 5.30 | |
| 7 | Kladno | 2.50 | clay loam | 32.0 | 47.4 | 20.6 | 2.48 | 1.11 | 55.3 | 0.81 | 35.18 | 8.62 | |
| 8 | Kladno | 3.50 | silt loam | 20.2 | 65.7 | 14.1 | 2.39 | 1.25 | 47.5 | 0.58 | 36.78 | 8.63 | |
| 9 | Svetla n. S. | 0.30 | sand | 2.8 | 8.3 | 88.9 | 2.62 | 1.11 | 57.6 | 0.15 | 33.34 | 8.48 | 0.41 |
| 10 | Kladno | 0.60 | clay loam | 28.6 | 40.2 | 31.2 | 2.52 | 1.00 | 60.3 | 0.65 | 40.65 | 5.57 | 40.81 |
| 11 | N. Bydzov | silty clay | 50.0 | 44.8 | 5.2 | 2.54 | 1.29 | 49.3 | 0.06 | 31.97 | 13.95 | ||
| 12 | N. Bydzov | silty clay | 44.3 | 45.7 | 10.0 | 2.59 | 1.20 | 53.7 | 0.28 | 33.28 | 9.29 | 6.89 | |
| 13 | Litvinov | silty clay loam | 35.8 | 51.9 | 12.3 | 2.53 | 1.43 | 43.5 | 0.10 | 33.81 | 10.28 | 1.56 | |
| 14 | Jihlava | 1.30 | sandy clay loam | 31.3 | 21.2 | 47.5 | 2.40 | 1.21 | 49.6 | 0.20 | 35.68 | 9.89 | 26.79 |
| 15 | Jihlava | 5.00 | loam | 16.9 | 38.9 | 44.2 | 2.50 | 1.23 | 50.9 | 0.32 | 27.92 | 14.01 | 36.96 |
| 16 | Jihlava | 1.20 | sandy loam | 18.4 | 21.4 | 60.2 | 2.56 | 1.05 | 59.0 | 0.50 | 28.60 | 13.82 | |
| 17 | Slany | 0.30 | clay | 43.2 | 27.3 | 29.5 | 2.53 | 1.14 | 55.1 | 0.31 | 33.29 | 12.00 | 46.02 |
| 18 | Struharov | 1.90 | loamy sand | < 0.1 | 17.3 | 82.7 | 2.45 | 1.25 | 49.0 | 0.07 | 29.73 | 11.75 | 10.24 |
| 19 | Jihlava | 1.50 | clay loam | 32.3 | 40.8 | 26.9 | 2.54 | 1.15 | 54.7 | 0.14 | 30.36 | 7.14 | 41.91 |
| 20 | Jihlava | 7.50 | sandy loam | 15.0 | 22.0 | 63.0 | 2.45 | 1.08 | 55.8 | <0.05 | 30.39 | 6.11 | 18.46 |
| 21 | Jihlava | 10 | silt loam | 11.8 | 52.7 | 35.5 | 2.41 | 1.05 | 56.6 | 0.24 | 25.23 | 13.38 | 21.24 |
| 22 | Struharov | 2.00 | loamy sand | 3.5 | 18.6 | 77.9 | 2.51 | 1.25 | 50.1 | 0.11 | 28.56 | 13.14 | |
| 23 | Jihlava | 1.20 | silt loam | 13.3 | 61.4 | 25.3 | 2.61 | 1.11 | 57.5 | 0.16 | 28.14 | 14.26 | |
| 24 | Chomutov | clay | 64.9 | 27.9 | 7.2 | 2.05 | 0.80 | 61.0 | 0.50 | 33.25 | 13.51 | ||
| 25 | Chomutov | clay | 64.9 | 14.7 | 20.4 | 2.46 | 1.00 | 59.4 | 0.30 | 33.60 | 13.72 | 64.39 | |
| 26 | Slany | clay | 43.2 | 27.3 | 29.5 | 2.56 | 1.25 | 51.2 | 0.37 | 33.62 | 11.28 | 46.65 | |
| 27 | Chomutov | clay | 44.8 | 23.9 | 31.3 | 2.54 | 1.18 | 53.6 | 0.46 | 33.84 | 11.43 | ||
| 28 | Jihlava | 0.80 | loam | 15.7 | 33.7 | 50.6 | 2.42 | 1.08 | 55.5 | 0.25 | 29.08 | 12.27 | |
| 29 | Holesov | 1.20 | silty clay loam | 30.0 | 65.0 | 5.0 | 4.09 | 1.34 | 67.3 | 0.26 | 35.94 | 8.99 | 28.35 |
| 30 | Holesov | 0.50 | silt loam | 10.3 | 61.9 | 27.8 | 2.32 | 1.21 | 47.6 | 0.81 | 35.80 | 7.99 | 13.95 |
| 31 | Holesov | 0.60 | silty clay loam | 31.0 | 63.0 | 6.0 | 2.49 | 1.40 | 43.8 | 0.31 | 35.70 | 9.27 | 16.53 |
| 32 | Holesov | 6.50 | sandy loam | 15.5 | 24.2 | 60.3 | 2.43 | 1.33 | 45.2 | 0.10 | 35.62 | 7.86 | |
| 33 | Holesov | 3.00 | silty clay | 40.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 2.45 | 1.25 | 49.2 | 0.22 | 34.20 | 11.86 | 35.81 |
| 34 | Holesov | 6.00 | sandy loam | 11.7 | 35.1 | 53.2 | 2.60 | 1.25 | 51.8 | <0.05 | 36.94 | 7.28 | |
| No. | Kd (L kg−1) Estimated | Linear Regression | No. | Kd (L kg−1) Estimated | Linear Regression | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kd (L kg−1) Measured | R2 | Sum of Sq. | Kd (L kg−1) Measured | R2 | Sum of Sq. | ||||||||
| 1 | 0.44 | 0.49 | ± | 0.04 | 0.991 | 62 | 18 | 0.25 | 0.47 | ± | 0.07 | 0.946 | 382 |
| 2 | 0.84 | 1.08 | ± | 0.11 | 0.963 | 994 | 19 | 0.51 | 0.92 | ± | 0.29 | 0.92 | 420 |
| 3 | 1.52 | 1.33 | ± | 0.20 | 0.954 | 1044 | 20 | 0.18 | 0.63 | ± | 0.32 | 0.97 | 363 |
| 4 | 0.44 | 0.83 | ± | 0.09 | 0.99 | 179 | 21 | 0.87 | 0.66 | ± | 0.17 | 0.899 | 1262 |
| 5 | 0.25 | 0.61 | ± | 0.10 | 0.971 | 135 | 22 | 0.40 | 0.56 | ± | 0.26 | 0.973 | 247 |
| 6 | 0.91 | 0.90 | ± | 0.08 | 0.887 | 1455 | 23 | 0.58 | 0.67 | ± | 0.06 | 0.944 | 710 |
| 7 | 2.94 | 0.98 | ± | 0.11 | 0.946 | 1261 | 24 | 1.82 | 2.27 | ± | 0.18 | 0.983 | 937 |
| 8 | 2.11 | 0.80 | ± | 0.07 | 0.957 | 994 | 25 | 1.09 | 1.83 | ± | 0.32 | 0.921 | 4601 |
| 9 | 0.54 | 0.38 | ± | 0.06 | 0.89 | 251 | 26 | 1.34 | 1.44 | ± | 0.19 | 0.929 | 2203 |
| 10 | 2.36 | 1.55 | ± | 0.99 | 0.877 | 899 | 27 | 1.67 | 1.26 | ± | 0.19 | 0.976 | 788 |
| 11 | 0.22 | 0.40 | ± | 0.03 | 0.993 | 35 | 28 | 0.91 | 1.15 | ± | 0.16 | 0.958 | 1056 |
| 12 | 1.02 | 0.71 | ± | 0.14 | 0.879 | 1777 | 29 | 0.94 | 0.76 | ± | 0.10 | 0.941 | 924 |
| 13 | 0.36 | 0.44 | ± | 0.04 | 0.96 | 241 | 30 | 2.94 | 1.53 | ± | 0.12 | 0.961 | 1722 |
| 14 | 0.73 | 0.87 | ± | 0.11 | 0.96 | 779 | 31 | 1.13 | 0.88 | ± | 0.11 | 0.912 | 1781 |
| 15 | 1.16 | 0.67 | ± | 0.15 | 0.973 | 755 | 32 | 0.36 | 0.49 | ± | 0.02 | 0.997 | 22 |
| 16 | 1.82 | 0.84 | ± | 0.22 | 0.955 | 834 | 33 | 0.80 | 0.89 | ± | 0.07 | 0.984 | 310 |
| 17 | 1.13 | 1.02 | ± | 0.10 | 0.981 | 170 | 34 | 0.18 | 0.79 | ± | 0.07 | 0.982 | 289 |
| Variable | Number of Samples | Mean | Standard Deviation | Variance | Minimum | Median | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kd (L kg−1) | 34 | 0.92 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 0.84 | 2.27 |
| OC (%) | 34 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.81 |
| Clay (%) | 34 | 24.9 | 17.2 | 296.8 | 0.0 | 21.0 | 64.9 |
| Silt (%) | 34 | 36.8 | 18.1 | 326.7 | 5.1 | 34.4 | 71.2 |
| Sand (%) | 34 | 38.3 | 24.5 | 598.7 | 5.0 | 31.2 | 88.9 |
| Si (%) | 34 | 33.41 | 3.51 | 12.32 | 25.23 | 33.71 | 40.65 |
| Al (%) | 34 | 10.27 | 2.65 | 7.05 | 5.30 | 10.46 | 14.26 |
| ρs (g cm−3) | 34 | 2.54 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 2.05 | 2.53 | 4.09 |
| ρb (g cm−3) | 34 | 1.18 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.80 | 1.21 | 1.43 |
| ε (%) | 34 | 53.2 | 5.4 | 29.1 | 43.5 | 53.3 | 67.3 |
| SSA (m2 g−1) | 21 | 24.2 | 17.1 | 289.9 | 0.4 | 19.9 | 64.4 |
| Variables | Chi-Squared Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| OC | 8.394 | 0.015 |
| Clay | 23.362 | <0.001 |
| Silt | 19.061 | <0.001 |
| Sand | 24.964 | <0.001 |
| Si | 0.218 | 0.890 |
| Al | 0.976 | 0.614 |
| ρs | 0.435 | 0.813 |
| ρb | 0.500 | 0.829 |
| ε | 0.520 | 0.771 |
| SSA | 3.889 | 0.143 |
| OC (%) | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | Kd (L kg−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Std. Dev. | Variance | Min | Median | Max |
| 1 | 0.17 | 14.22 | 22.87 | 62.92 | 0.69 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.38 | 0.65 | 1.15 |
| 2 | 0.34 | 41.78 | 39.99 | 18.21 | 1.10 | 0.53 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.95 | 2.27 |
| 3 | 0.41 | 10.61 | 61.81 | 27.58 | 1.01 | 0.36 | 0.13 | 0.66 | 0.94 | 1.53 |
| Linear Regression Model | Units of x | Standard Error | Observations | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | Slope | ||||||
| Kd(PCE) = 0.475 + 0.016 SSA | m2 g1 | 0.104 | 0.003 | 21 | 0.511 | 0.271 | 24.5 |
| fOC | - | 0.101 | 29.0 | 34 | 0.378 | 0.343 | 28.4 |
| fClay | - | 0.114 | 0.38 | 34 | 0.260 | 0.374 | 34.1 |
| fSilt | - | 0.094 | 0.23 | 34 | 0.008 | 0.433 | 39.3 |
| fSand | - | 0.127 | 0.28 | 34 | 0.180 | 0.394 | 34.4 |
| Class | Model | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kd(PCE) = 1.22 + 34.9fOC + 0.05fClay − 0.94fSand | ||||||||||
| 2 | Kd(PCE) = −0.74 + 131.5fOC + 2.87fClay + 1.01fSand | ||||||||||
| 3 | Kd(PCE) = 1.44 + 115.3fOC − 5.37fClay − 1.17fSand | ||||||||||
| Standard Error | Observations | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | |||||||
| Intercept | X1 | X2 | X3 | ||||||||
| 1 | 0.41 | 34.96 | 0.85 | 0.47 | 14 | 0.636 | 0.147 | 11.3 | |||
| 2 | 0.41 | 46.97 | 0.78 | 0.95 | 14 | 0.698 | 0.329 | 28.8 | |||
| 3 | 0.24 | 14.40 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 6 | 0.985 | 0.070 | 3.8 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rippelová, V.; McGachy, L.; Janků, J.; Kroužek, J. Estimating Tetrachloroethene Sorption Coefficients Based on Soil Properties in Organic-Poor Soils. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11761. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411761
Rippelová V, McGachy L, Janků J, Kroužek J. Estimating Tetrachloroethene Sorption Coefficients Based on Soil Properties in Organic-Poor Soils. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(24):11761. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411761
Chicago/Turabian StyleRippelová, Veronika, Lenka McGachy, Josef Janků, and Jiří Kroužek. 2024. "Estimating Tetrachloroethene Sorption Coefficients Based on Soil Properties in Organic-Poor Soils" Applied Sciences 14, no. 24: 11761. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411761
APA StyleRippelová, V., McGachy, L., Janků, J., & Kroužek, J. (2024). Estimating Tetrachloroethene Sorption Coefficients Based on Soil Properties in Organic-Poor Soils. Applied Sciences, 14(24), 11761. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411761





