Abstract
In this study, prevention of fracture in vibration fatigue testing of automotive alternator heatsink blocks was investigated using an artificial neural network. Automotive components such as alternator heatsink blocks are subjected to high cyclic vibration fatigue loads throughout their lifespan, which can lead to the formation and propagation of fatigue cracks and ultimately component failure. The basic parameters affecting the resonant frequency of the heatsink blocks, including geometry and loading conditions, are determined. Data-driven decision making provides advanced predictive insights to analyze data for prediction and decisions using artificial intelligence approaches. An efficient artificial neural network model was defined to predict the resonance frequency in the vibration fatigue test. While the artificial neural network was trained to establish a functional relationship between the parameters and the resonance frequency, regression analysis was used to develop a predictive model to detect the resonance frequency of the heatsinks. The proposed approach aims to provide a comprehensive framework for preventing fracture problems in vibration fatigue tests of automotive alternator heatsinks and ultimately contribute to the reliable design and performance of these critical components. While the artificial neural network approach achieved high classification accuracy in predicting the new natural frequency, the regression model was also able to make accurate predictions. The results of this study showed that the time spent on design and simulation can be significantly reduced in preventing breakage problems that may occur before dynamic tests such as vibration tests of alternator components.
Keywords:
vibration; neural network; heatsink; fracture; fatigue; automotive; crack; regression; optimization 1. Introduction
The performance and reliability of alternators in vehicles are heavily dependent on effective thermal management strategies [1,2,3]. Alternators, responsible for converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, generate significant heat during operation, which can lead to thermal runaway and potential system failures if not properly addressed. Thermal management is a critical aspect of alternator design, as it ensures the efficient dissipation of heat generated by the alternator, thereby maintaining its optimal operating temperature and extending its lifespan.
The fundamental principle behind alternator heatsink design is to maximize the surface area available for heat transfer, thereby enhancing the rate of heat dissipation. This can be achieved through the incorporation of extended surfaces, like fins, which increase the contact area between the heatsink and the surrounding air. Extensive research has been conducted to optimize the design of heatsinks, with a focus on improving their thermal performance and reducing the overall size and weight of the cooling system. Alternator heatsinks manufactured with a large surface area for better cooling are produced in a thin structure, and therefore, when subjected to dynamic loads, they can be broken from certain regions if their natural frequency coincides with the excitation frequency. For this reason, in the R&D studies of alternators, breakage can occur, especially in the heatsink bolt connection regions during vibration tests.
This study investigates the prevention of fracture in the vibration fatigue testing of automotive alternator heatsink blocks using an artificial neural network. Automotive components, such as alternator heatsink blocks, are subjected to high-cycle vibration fatigue loads during their service life, which can lead to the formation and propagation of fatigue cracks and ultimately component failure. Artificial intelligence-based models are developed to predict the resonance frequency behavior of the heatsink blocks under vibration loading conditions. The results of this study demonstrate the effectiveness of using artificial neural networks in predicting the fatigue life and fracture behavior of automotive heatsink components, which can aid in the design and optimization of these critical thermal management systems [4].
Automotive components are subjected to various vibration loads during their service life, which can lead to the development of fatigue cracks and ultimately component failure. The fracture of materials subjected to fatigue loading is a prominent failure mechanism in engineering, accounting for up to 90% of all structural failures [5]. Accurately predicting the evolution of fatigue damage, including crack nucleation and growth, is crucial for the reliable design of automotive components.
To address this challenge, researchers have explored the use of advanced computational techniques, such as artificial neural networks and regression analysis, to predict the fatigue life and fracture behavior of automotive components under vibration loading [6]. Artificial neural networks have shown promise in modeling the complex nonlinear relationships between various parameters that influence the fatigue life of engineering components. Prediction using neural networks is very effective and important in practice [7].
In this research, we present a methodology for using artificial neural networks and regression analysis to predict the fracture behavior of automotive alternator heatsink blocks subjected to vibration fatigue testing. The proposed approach first identifies the key parameters that influence the resonance frequency of the heatsink blocks, such as geometry and loading conditions. An artificial neural network is then trained to establish a functional relationship between these parameters and the onset of fatigue fracture [8]. Additionally, artificial intelligence analysis is employed to develop a predictive model to detect the resonance frequency of the heatsink blocks, considering the identified critical parameters. The numerical implementation of this methodology leverages an efficient quasi-Newton monolithic solution strategy, which has been demonstrated to be effective in similar applications as reported in the literature [9].
The proposed approach aims to provide a comprehensive framework for the prevention of the fracture problem in vibration fatigue testing of automotive alternator heatsink blocks, ultimately contributing to the reliable design and performance of these critical components.
Also, the developed and optimized methodology, which is integrated as a parameter estimation method into the optimization process, has been used in alternator development studies, which have an important place in the automotive product development process. The results obtained have been compared in terms of accuracy with conventional methods such as regression [10]. The fact that the developed learning-based method has shown higher accuracy compared to other methods and produced better results as a result of optimization has both proven the success of the method in the alternator local resonance frequency estimation process and eliminated the experience-based calculation and design suggestions in the alternator design process, shortening the calculation times and introducing a new approach to the literature.
As a result, the development of AI models to predict the natural frequencies of vehicle components can provide significant advantages in addressing resonance-related issues and optimizing the design process [11,12].
The following sections will provide information on the breakage of the heatsink that occurred due to local natural frequency in the vibration fatigue test conducted for the alternator. Simulation studies will be used to shift the natural frequency that caused this breakage to higher frequencies, and a data set will be created for the prediction methods to use. The grid search method was used to obtain the best artificial neural network model. The high-accuracy ANN model designed significantly reduced the computational time and effort [13,14,15,16,17,18,19].
Since optimization problems in the field of engineering require a lot of design modifications and these designs are costly in terms of both time and workload, surrogate models are frequently used to obtain objective and constraint functions. In this study, the artificial neural network method was used in the surrogate modeling phase due to its good results in engineering problems, such as ball bearings and electrical machines, which can be achieved using machine learning methods [20,21,22,23].
In recent decades, many metaheuristic algorithms have been developed to improve the performance of the optimization studies to design better systems, and therefore, new optimization algorithms with enhanced search techniques have also been introduced to solve different optimization problems [24,25]. As stated above, the results of optimization can change depending on the structure of an applied problem and also due to the search techniques’ adaptability to the optimization algorithm according to the applied problem structure. Therefore, in this study, the new recent optimization algorithms are also used to see the effects of new optimization algorithms on the efficiency of the alternator heatsink design outcomes. In this section, each optimization method used in this paper is presented briefly. Only the fundamentals are presented, and readers who are interested by the optimization methods can see all the required knowledge in the cited paper.
The arithmetic optimization algorithm (AOA) was introduced by Abualigah et al. in 2021 [26]. The main inspiration for the presented algorithm was arithmetic operators such as division, multiplication, addition and subtraction, which are used in solving arithmetic problems. The AOA employs these arithmetic operators as a mathematical optimization to specify the most suitable element subjected to objectives and constraints from some set of competitor solutions.
The Aquila optimizer (Aquila) was presented by Abualigah et al. in 2021b [27]. The AO mimics the Aquila’s actions in nature during the technique of hunting the prey. The method consists of four basic steps, which are choosing the search area, contour flight, low flight and swooping by walk and catch prey.
The African vultures optimization algorithm (AVOA) is a new population-based algorithm, which was proposed by Abdollahzadeh et al. in 2021 [28]. The approach mimics the African vultures’ foraging and navigation techniques. The AVOA consists of four steps: specifying the best vulture in any group, the rate of starvation of vultures, exploration and exploitation. In the algorithm, two of the best alternatives are observed for the most powerful and best vultures, and other vultures attempt to reach the levels of the best.
The equilibrium optimizer (EO), proposed by Faramarzi et al. in 2020, is an algorithm that mimics control volume mass balance principles used to predict both dynamic and equilibrium conditions [29].
The genetic algorithm (GA) presented by Holland (1992) is one of the first population-based stochastic approaches proposed in history [30]. The GA is an optimization algorithm that operates using mechanisms similar to the evolutionary mechanisms observed in nature. The GA mimics the operation of natural selection where the best individuals are chosen for reproduction in order to create offspring of the following generation. The algorithm aims to obtain the best objective function by working with three essential evolution operators: selection, crossover and mutation.
Particle swarm optimization (PSO), presented by Kennedy and Eberhart (1995), is an optimization algorithm inspired by the movement of individuals in a bird flock or fish school [31]. Each particle has a position and speed within the region covered by the swarm. Each particle is affected by the best local position it reaches, as well as being directed towards the best-known positions in the updated search space, which is updated as other particles in the swarm reach the better position. Thus, it aims to reach the best solutions for the swarm.
2. The Proposed Approach
The proposed approach aims to develop an artificial intelligence-based prediction model to prevent resonance-related failures in the heatsink blocks of alternators subjected to dynamic loading tests.
The test specimens were subjected to controlled vibration loading conditions, and the onset of fatigue fracture was carefully monitored and recorded. In order to validate the proposed methodology, a series of modal analyses were conducted on a representative model of automotive alternator heatsink blocks.
The experimental data were used to train and validate the artificial neural network model, which was able to accurately predict the fracture behavior of the heatsink blocks. The regression analysis model was also validated by comparing its predictions of resonance frequency with the experimental observations, demonstrating a high degree of accuracy.
Through the experimental validation, the proposed approach has been shown to be effective in preventing the fracture problem in the vibration fatigue testing of automotive alternator heatsink blocks. The integration of artificial neural networks and regression analysis has proven to be a powerful tool in capturing the complex nonlinear relationships between the critical parameters and the fracture behavior of these components.
The flowchart of the proposed approach is given in Figure 1.
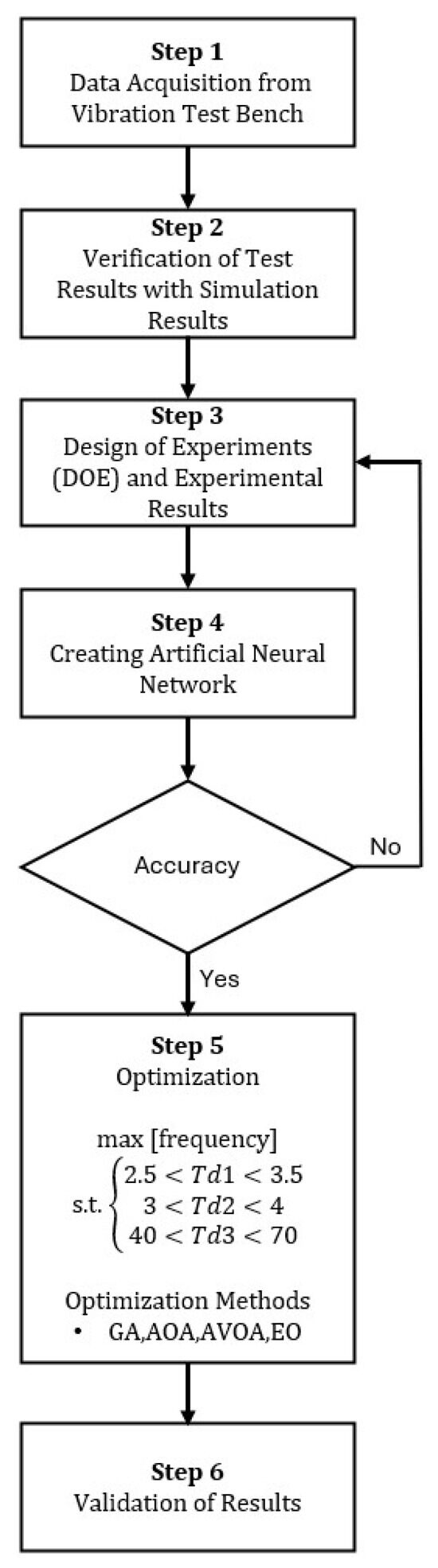
Figure 1.
Flowchart of proposed study.
Step 1 involves identifying the local resonance frequency obtained from the vibration test based on the road test data. In Step 2, the validation of the identified local mode is performed through modal test simulation. To provide data for the optimization methods to be used, Step 3 involves conducting numerous modal analysis simulations to obtain experimental data. Step 4 involves all the optimization studies. Step 5 involves studies on artificial neural network methods used to create a prediction model. The accuracy of the predictions obtained using the NN Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm and optimization results were compared, and the predictions were then obtained.
2.1. Data Measurement from Bench Test
To identify the natural frequencies of the alternator, a vibration fatigue test was conducted using a 40 kN electrodynamic shaker and a thermal chamber to simulate the environmental conditions. A vibration fatigue test was performed as sine sweep for 72 h in the frequency range of 100–500 Hz with constant 10 g amplitude. To detect the resonance frequencies before the durability test, a sine sweep test was performed in the frequency range of 100–1000 Hz at a sweep rate of 120 Hz/min with a 5 g peak acceleration.
Throughout the whole test, the alternator was rotated at 3000 rpm, and 90% of the nominal current produced at this speed was provided by an electronic load. Simultaneously, the alternator was maintained at a constant temperature of 100 °C inside the thermal chamber. The test setup is shown in Figure 2. The characterization was performed separately for the Y- and Z-axes of the alternator, and the acceleration versus frequency plot for the Z-axis characterization is shown in Figure 3.
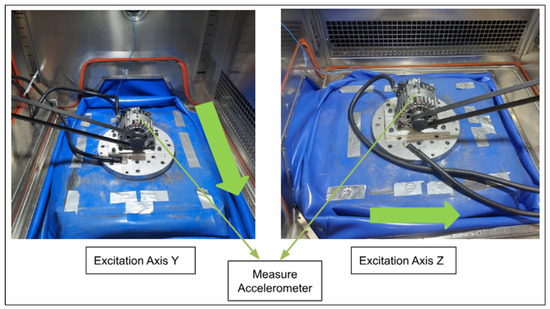
Figure 2.
Alternator resonance frequency characterization test setup.
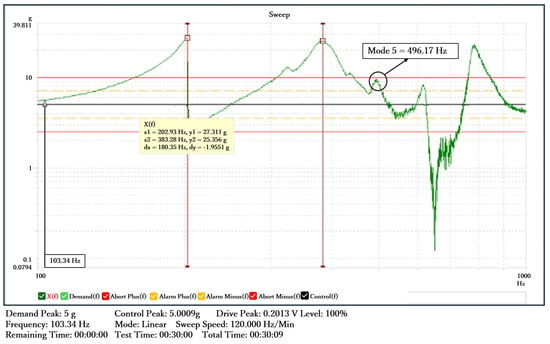
Figure 3.
Resonance frequency characterization test results of alternator at Z-axis.
The first five natural frequencies obtained from the characterization test are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
First 5 resonance frequencies of alternator.
Following the characterization test, a vibration fatigue test was performed on the component according to the alternator life test specification, with a 10 g peak sine sweep vibration applied in the Z-axis direction for 72 h in the frequency range of 100–500 Hz. The effect of the local mode in the B+ region resulted in fracture occurring in the heatsink bolt area, as shown in Figure 4.
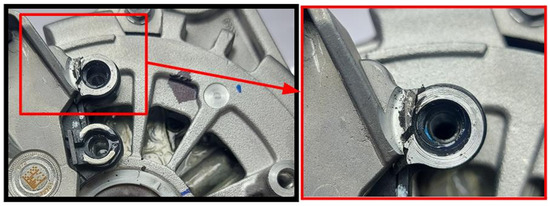
Figure 4.
Heatsink fracture after durability test.
2.2. Verification of Results with Simulation
To identify the regional modal shape causing the fracture, a modal test simulation was performed on the alternator model, and the von Mises stress values at the fracture location were obtained. The modal test simulation revealed that the fifth mode at 496.17 Hz observed in the vibration test was a local mode in the heatsink B+ zone, which matched the local mode detected at 460.21 Hz, as shown in Figure 5.
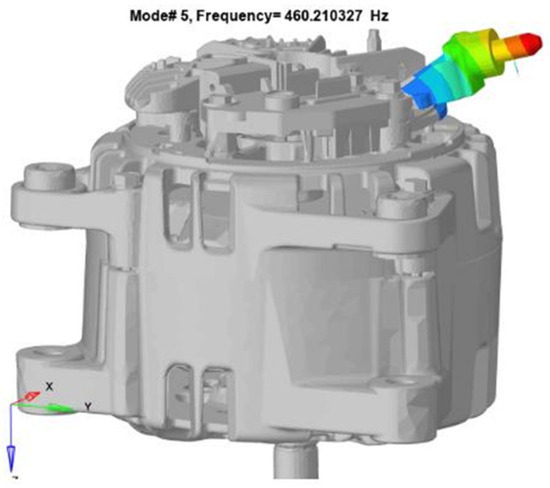
Figure 5.
Alternator heatsink B+ zone local resonance modal shape.
The simulation study (Figure 6) confirmed that the fracture observed during the test was due to the high stress at the heatsink bolt hole caused by the 10 g excitation at the local natural frequency in the Z-axis direction.
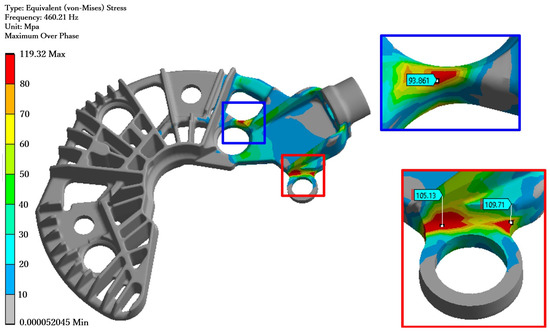
Figure 6.
Alternator heatsink analysis with ANSYS 2019 R2.
2.3. Other Design and Simulation Studies
The frequency range of 100–500 Hz defined for the alternator vibration test covers a wide range of frequencies that can affect the alternator in a vehicle. The local mode at 496 Hz, which caused the fracture, is very close to the upper limit of 500 Hz, so it was considered appropriate to shift the heatsink natural frequency above 700 Hz, considering the damping effect. To shift the natural frequency to a higher frequency, the impact of the heatsink design and the loads on the part were considered, and the parameters that can be modified were identified. To provide data for the neural network and optimization studies, 60 new designs were created, with increased thickness of the heatsink bolt hole and both the B+ cross-section geometries. In the modal analysis simulation of the 60 new designs, the effect of reducing the weight of the 70 g B+ cable, which also affects the frequency shift due to its local impact, was also investigated. The design and simulation studies at this stage were carried out only on the heatsink CAD geometry, along with the determination of the contacts and boundary conditions on the heatsink. The simulation result based on the heatsink CAD data under test conditions showed that the heatsink natural frequency is 500.09 Hz, which is very close to the 496.17 Hz natural frequency detected in the characterization test. The modal analysis simulation performed for the heatsink is shown in Figure 7 [32].
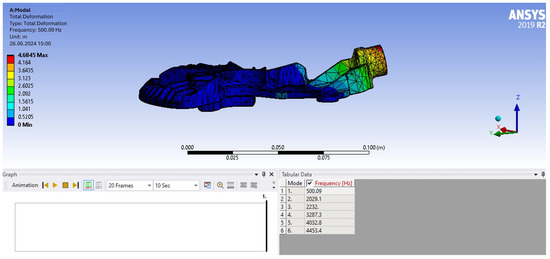
Figure 7.
Heatsink modal analysis with ANSYS 2019 R2.
3. Optimization of Alternator Heatsink
In this section, the alternator heatsink optimization model was explained. The optimization process consists of creating an experimental design with the Latin hypercube method, developing a surrogate model with artificial neural networks and performing optimization with six different optimization algorithms.
3.1. Design of the Experiment
Data-driven decision making provides enhanced predictive insights to analyze data for prediction and decisions using artificial intelligence approaches. In the first stage of the optimization process, three design variables were determined: the cross-sectional thickness of the alternator B+ region (Td1), the thickness of the bolt hole (Td2) and the weight of the alternator B+ cable (Td3). Heatsink natural frequency values are also the output collected by modal analyses performed with experimental sets. With the determined design variables, 60 experimental designs were created with the Latin hypercube method, twenty times the number of design variables. Table 2 shows the variation parameters in the 60 designs prepared and the new natural frequency values obtained as a result of the modal analysis simulation for each design and each different cable weight.

Table 2.
Heatsink natural frequency values regarding parameter changes.
3.2. Surrogate Modeling
In this study, an artificial neural network-based regression model was developed and the grid search method was used for hyperparameter selection to optimize model performance. In this context, four basic hyperparameters affecting the learning process of the model were evaluated: learning rate, training function, number of layers and number of neurons. Learning rate was determined between 0.002 and 0.02 with 0.002 increments; Levenberg–Marquardt, Bayesian regularization and scaled conjugate gradient algorithms were preferred as training functions, respectively. In order to expand the capacity of the model, the number of neurons in each hidden layer was changed between 2 and 20, and the number of layers was kept between 1 and 3. These combinations were examined to evaluate the effect of each parameter on the accuracy and generalizability of the regression model, and the parameter sets providing the most appropriate performance were systematically determined.
There are different cross-validation methods such as k-fold, hold-out and leave-one-out to evaluate the reliability of the surrogate model in the literature. In this study, the k-fold method is frequently preferred in engineering problems because it provides more reliable and stable results by testing the generalization performance of the model in a balanced way on the entire data set. In the k-fold method, the data set is divided into k equal subsets and each subset is used as test data in turn, while the remaining subsets are used for training the model. Thus, the model is tested repeatedly on different parts of the data set, and a more balanced performance evaluation is made. When determining the k value, a suitable balance should be provided between processing time and accuracy evaluation. “k” values at medium levels such as 5 and 10 keep the processing cost low and reliably reflect the overall performance of the model. The “k” value was selected as 5 in this study.
Single-layer perceptron (SLP) is a basic artificial neural network model used for pattern recognition and classification tasks. SLP consists of a single layer of interconnected nodes or neurons, where each neuron takes multiple inputs, applies a weighted sum to those inputs and produces a single output. The weights associated with each input represent the strength of the connection between the input and the neuron [33]. The single-layer perceptron is described by the following equation:
where are the inputs, are the weights, is the bias and is the output [34]. Figure 8 shows the architecture of the single-layer perceptron network used in this study.
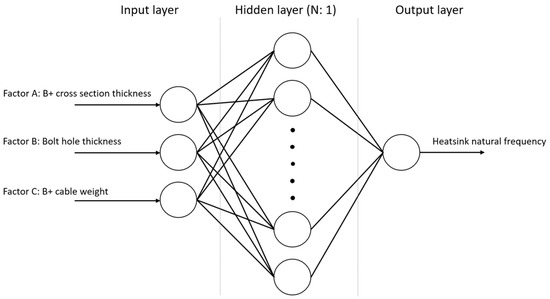
Figure 8.
NN architecture.
The surrogate model to be used in the study was implemented with the MATLAB program (version R2024a) using artificial neural networks and the k-fold crossover method [35]. The performance of the surrogate model was examined using the MATLAB “R-value”. The closer the “R-value” is to 1, the higher the accuracy of the model. Table 3 shows the R-values for f-folds. All values are above 0.997. These results can be used with high accuracy in the optimization phase of the created model.

Table 3.
R-values for k-folds.
Figure 9 shows the R-values of the artificial neural network surrogate model. The hyperparameters of the neural network surrogate model are as follows: learning rate is 0.01, training function is Bayesian regularization, number of neurons is 20, and number of layers is 1. The data set was split: 20% was used for testing and 80% for training.
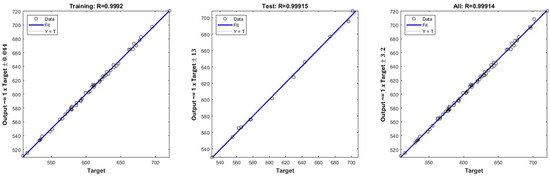
Figure 9.
MATLAB R-values.
In addition, a prediction model was created using MATLAB Simulink using the Levenberg–Marquardt artificial intelligence model with the highest accuracy. In addition, a high-accuracy artificial neural network model was created using the Levenberg–Marquardt training function via MATLAB Simulink. The model utilizes the alternator heatsink geometry and cable weight information as inputs and produces an estimate of the natural frequency of the heatsink as the output. Figure 10 shows this prediction model.
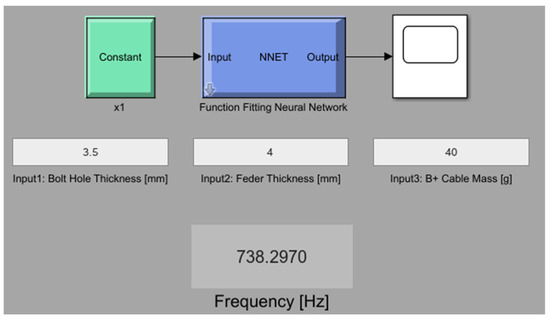
Figure 10.
MATLAB Simulink prediction model.
3.3. Optimization
In this section, the alternator heatsink was optimized with six different optimization algorithms and the optimization methods were compared. An objective surrogate model was developed by using the artificial neural network (ANN). Finally, the methods are compared both quantitatively and qualitatively.
In Figure 11, the convergence curves of each optimization method run twenty times are given. When the curves are examined, it is seen that each method exhibits different characteristics. In general, it can be said that method 6 converges very quickly. While convergence occurred with a small change after approximately 50 iterations in the AOA, the initial values in the Aquila, AVOA, EO and PSO algorithms started from worse values in some runs. The GA started from the best point in all runs and converged very quickly.
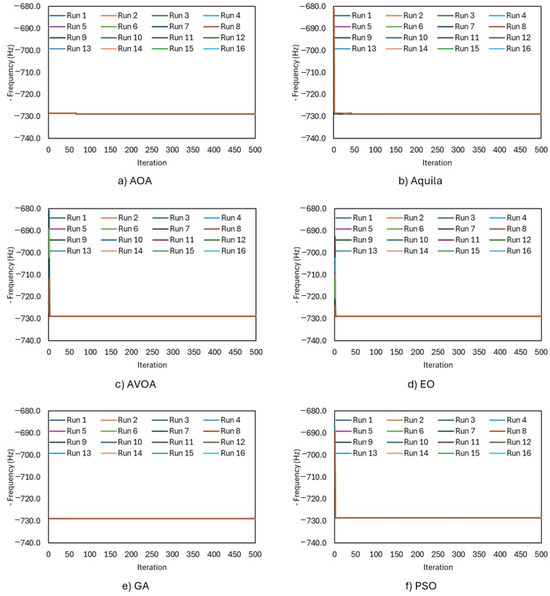
Figure 11.
Convergence curves of each optimization algorithm.
Optimization was performed on a computer with an AMD Ryzen 7 3750H processor, a Radeon Vega Mobile Gfx 2.30 GHz graphics card and 16 GB of RAM.
In Figure 12, the convergence curves of the best objective function of each optimization are given. In the graph, the fastest convergence occurs in the AVOA, GA and PSO, followed by the EO with a very small delay. Although PSO converges very quickly, its optimum value is worse than other methods. Aquila and the AOA have good optimum values, although they converge somewhat late.
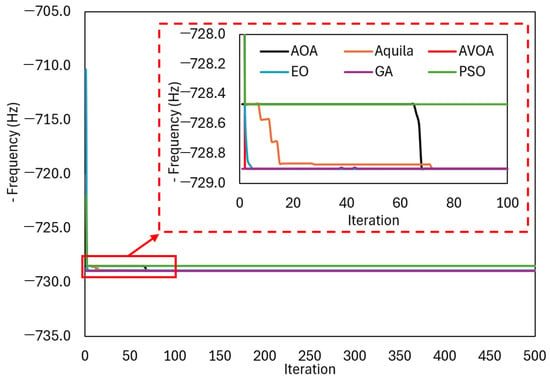
Figure 12.
Best convergence curve of each optimization.
In Table 4, the best value, mean value, standard deviation and total CPU time results obtained by running each optimization 20 times are presented. For the alternator heatsink optimization problem, the standard deviations of all optimization algorithms are very low, which shows that they converge to the same value every time. In terms of the best value, other methods except PSO gave the same optimum value. When the total CPU times were examined, the Aquila optimizer gave the longest time, followed by PSO. The remaining four methods gave very close times. Considering both speed and accuracy, the AOA, AVOA, EO and GA are the most suitable methods for the alternator heatsink optimization problem.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of the optimization algorithms.
In Table 5, the best values of each optimization and the results of the finite element analysis performed at these values are compared. According to the results, the largest relative error is 1.672%. Also, the largest relative error is 1.350% for the MATLAB Simulink model which was created by Levenberg–Marquardt. A 10% error is an acceptable margin of error in engineering studies [36]. Thus, it can be said that the use of metamodels created by the ANN method in optimization gives results with sufficient accuracy.

Table 5.
Comparison of the optimum solutions.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, in this study, the effectiveness of artificial neural network methods in predicting and classifying faults in automotive alternator cooling blocks subjected to vibration fatigue testing was demonstrated. The artificial neural network approach was able to achieve high classification accuracy in predicting the new natural frequency. The results of this study showed that the time spent on design and simulation can be significantly reduced in preventing breakage problems that may occur before dynamic tests such as vibration tests of alternator components. The integration of artificial neural networks and optimization has enabled the development of a comprehensive framework for accurately predicting the natural frequency and fracture behavior of these critical components.
The neural network model demonstrated a high degree of accuracy in predicting the new resonant frequency of the component, capturing the complex nonlinear relationships between the key parameters and the fracture behavior.
The contribution of this study using AI and optimization in resonance frequency prediction is as follows:
- In rotating machines used in vehicles, each component within the machine is subjected to excitation at different frequencies, both from the machine itself and from the effects of the vehicle. This situation, frequently encountered in vibration tests of components, leads to breakage, cracking and separation, necessitating product redesign and resolution of the resonance-related problems. The required redesign and simulation studies result in significant time losses and high costs. Developing artificial intelligence models that can predict the natural frequency of similar components can be used as an important time-saving and cost-reduction method in addressing recurrent resonance-related breakage and cracking problems.
- ANN and MATLAB Simulink regression models provided accurate approximations compared to the finite element analysis, while significantly reducing computation time and effort.
- Six of the methods used for the alternator heatsink optimization problem, except PSO, gave the same value and were found to be suitable for the alternator heatsink optimization problem.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.K. and F.Ö.; Methodology, D.K., E.İ.A., E.B. and F.Ö.; Software, D.K.; Analysis, D.K.; Validation, D.K.; Data curation, D.K. and A.E.; Writing—original draft, D.K.; Writing—review & editing, D.K., E.İ.A., E.B., A.E., İ.K. and F.Ö.; Supervision, F.Ö. and İ.K.; Project administration, D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Valeo Automotive, Bursa.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Adem Egi was employed by the company Valeo Elektrik Sistemleri A.S. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Karthik, C.A.; Kalita, P.; Cui, X.; Peng, X. Thermal management for prevention of failures of lithium ion battery packs in electric vehicles: A review and critical future aspects. Energy Storage 2020, 2, e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Cao, W. Research on parameter estimation methods of fatigue life distribution model of automotive chassis parts. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2022, 14, 168781322211177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Jia, L.; Ding, Y.; Dang, C.; Li, X. A review on lithium-ion power battery thermal management technologies and thermal safety. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 26, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarı, İ.; Yalcin, F.S. CFD Analyses of a Notebook Computer Thermal Management System and a Proposed Passive Cooling Alternative. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2010, 33, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golahmar, A.; Niordson, C.F.; Martínez-Pañeda, E. A phase field model for high-cycle fatigue: Total-life analysis. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 170, 107558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, I.; Nikitin, A.; Wang, C. Calculation of fatigue fracture in structural elements using a multimode damage model. In Proceedings of the XXII International Conference on Computational Mechanics and Modern Applied Software Systems (CMMASS 2021), Alushta, Crimea, 4–13 September 2021; EDP Sciences: Ulis, France, 2022; Volume 362, p. 01018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Han, C.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Cai, E.; Zhang, P. Surface roughness prediction of large shaft grinding via attentional CNN-LSTM fusing multiple process signals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 4925–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Abdullah, S.; Schramm, D.; Omar, M.Z.; Haris, S.M.; Brückmann, T.; Kracht, F.E. Characterizing Spring Durability for Automotive Ride Using Artificial Neural Network Analysis. Int. J. Eng. Technol. (UAE) 2018, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejsa, M.; Brožovský, J.; Lehner, P.; Seitl, S.; Kala, Z.; Krejsa, V. Probabilistic fatigue analysis of existing steel structure. In Proceedings of the 4th International Scientific Conference Structural and Physical Aspects of Construction Engineering (SPACE 2019), Strbske Pleso, Slovakia, 13–15 November 2019; EDP Sciences: Ulis, France, 2020; Volume 310, p. 00012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Topaloğlu, A.; Kaya, N.; Öztürk, F. Predictions of the design decisions for vehicle alloy wheel rims using neural network. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2023, 237, 2913–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, G. Finite Element Modeling and Vibration Analysis of Sprag Clutch-Flexible Rotor System. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitzer, S.; Obermeyer, J.; Mistry, R. The Effects of Structural and Localized Resonances on Induction Motor Performance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Villar, K.K.; Herbert-Acero, J.F. A Metaheuristic-Based Approach for the Capacitated Supply Chain Network Design Problem Including Imperfect Quality and Rework. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2014, 9, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Chandra, A.; Shalivahan, S.; Singh, R.K. Grey wolf optimizer: A new strategy to invert geophysical data sets. Geophys. Prospect. 2018, 66, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükoglu, I.; Öztürk, N. A differential evolution approach for the vehicle routing problem with backhauls and time windows. J. Adv. Transp. 2014, 48, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ene, S.; Küçükoglu, I.; Aksoy, A.; Öztürk, N. A hybrid metaheuristic algorithm for the green vehicle routing problem with a heterogeneous fleet. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2016, 71, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçükoglu, I.; Öztürk, N. Two-stage optimization method for material flow and allocation management in cross-docking networks. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 410–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallagnol, V.A.F.; Berg, J.V.D.; Mous, L. Portfolio management using value at risk: A comparison between genetic algorithms and particle swarm optimization. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 766–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Abualigah, L.; Jia, H. An Improved Teaching-Learning-Based Optimization Algorithm with Reinforcement Learning Strategy for Solving Optimization Problems. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1535957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankar, P.K.; Sharma, S.C.; Harsha, S.P. Fault diagnosis of ball bearings using machine learning methods. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 1876–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.; Sathiyasekar, K.; Padmanaban, S.; Chokkalingam, B. Insulation condition assessment of high-voltage rotating machines using hybrid techniques. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bıçakçı, S.; Çoramık, M.; Güneş, H.; Çıtak, H.; Ege, Y. A New Artificial Neural Network-Based Failure Determination System for Electric Motors. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çallı, M.; Albak, E.İ.; Öztürk, F. Prediction and optimization of the design and process parameters of a hybrid DED product using artificial intelligence. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albak, E.İ.; Solmaz, E.; Kaya, N.; Öztürk, F. Impact attenuator conceptual design using lightweight materials and meta-modeling technique. Mater. Test. 2019, 61, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Mohamed, R.; Jasser, M.B.; Hezam, I.M.; Mohamed, A.W. Developments on metaheuristic-based optimization for numerical and engineering optimization problems: Analysis, design, validation, and applications. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 78, 175–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Diabat, A.; Mirjalili, S.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Gandomi, A.H. The arithmetic optimization algorithm. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 376, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Yousri, D.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Ewees, A.A.; Al-qaness, M.A.; Gandomi, A.H. Aquila Optimizer: A novel meta-heuristic optimization Algorithm. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 157, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahzadeh, B.; Gharehchopogh, F.S.; Mirjalili, S. African vultures optimization algorithm: A new nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 158, 107408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, A.; Heidarinejad, M.; Stephens, B.; Mirjalili, S. Equilibrium optimizer: A novel optimization algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 191, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems: An Introductory Analysis with Applications to Biology, Control, and Artificial Intelligence; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95 International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- ANSYS 2019 R2. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/ (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Staudemeyer, R.C.; Morris, E.R. Understanding LSTM—A tutorial into Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09586. [Google Scholar]
- Almási, A.-D.; Woźniak, S.; Cristea, V.; Leblebici, Y.; Engbersen, T. Review of advances in neural networks: Neural design technology stack. Neurocomputing 2016, 174, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB R2024a. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/matlab.html (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Shu, C.; Zhao, S.; Hou, S. Crashworthiness analysis of two-layered corrugated sandwich panels under crushing loading. Thin Walled Struct. 2018, 133, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).