Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs), based on transformer architecture, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in natural language processing tasks, enabling machines to generate human-like text and engage in meaningful dialogues. However, the exponential increase in model parameters has led to limitations in inference speed and energy efficiency. Compute-in-memory (CIM) technology offers a promising solution to accelerate AI inference by performing analog computations directly within memory, potentially reducing latency and power consumption. At the same time, CIM has been successfully applied to accelerate Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs); however, the matrix–matrix multiplication (MatMul) operations inherent in the scaled dot-product attention of the transformer present unique challenges for direct CIM implementation. In this work, we propose InMemQK, a compute-in-memory-based attention accelerator that focuses on optimizing MatMul operations through software and hardware co-design. At the software level, InMemQK employs product quantization (PQ) to eliminate data dependencies. At the hardware level, InMemQK integrates energy-efficient time-domain MAC macros for ADC-free computations. Experimental results show InMemQK achieves 13.2×–13.9× lower power consumption than existing CIM-based accelerators.
1. Introduction
Large Language Models (LLMs), exemplified by ChatGPT [1], have found extensive applications across various domains, including AI-generated content (AIGC), medical diagnostics [2,3], and autonomous vehicles [4]. During inference, these models, based on the transformer architecture and its derivatives [5,6], generally require extensive computational density and frequent memory access. With the deceleration of Moore’s law, conventional processor-centric computing architectures are encountering limitations in both performance and energy efficiency. Against this backdrop, compute-in-memory (CIM) technology presents itself as a promising solution that fundamentally alleviates data movement bottlenecks.
Non-volatile memory (NVM) [7,8], characterized by high density, rapid access, and low power leakage, fulfills crucial requirements of LLMs for computational density and memory bandwidth. Researchers have successfully implemented CIM techniques based on NVM technologies like ReRAM to accelerate Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) [9] and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) [10]. Among these studies, time-domain CIM has garnered significant attention due to its capacity to minimize extensive AD/DA conversions prevalent in conventional CIM accelerators. Nevertheless, the distinctive scaled dot-product attention computation process in transformers poses challenges for directly applying these techniques. Additionally, effective management of intermediate results in matrix–matrix multiplication (MatMul) remains a significant challenge for CIM accelerators [11,12,13].
To address these challenges, we introduce InMemQK, an NVM-based software–hardware co-design module aimed at accelerating MatMul computations. From a software perspective, InMemQK utilizes product quantization (PQ) techniques to avoid writing intermediate results. We clustered intermediate computational results into codebooks to eliminate data dependencies and propose an optimized PQ quantization method based on reconstructed feature map loss to suppress accuracy degradation. In terms of hardware, we designed an attention score computation module using time-domain MAC macros. Compared with the voltage-domain interface, the peripheral circuit of the proposed method is very compact, which is crucial to achieving high energy efficiency and speed at the system level. Experiments show that the PQ-based InMemQK reduces power consumption by avoiding delays associated with writing intermediate results to the NVM array, thereby enhancing overall efficiency.
2. Transformer and CIM Accelerator
2.1. Transformer Model
Transformer architecture is primarily composed of an encoder and a decoder [14], with the block serving as their main constituent module. As illustrated in Figure 1a, a typical block consists of fully connected layers, self-attention layers, and a Feed-Forward Network (FFN). The multi-head self-attention layer incorporates three trainable matrices within its linear layers: the query matrix , the key matrix , and the value matrix . The query Q, key K, and value V are derived by multiplying the input sequence X = [,,…,] with the corresponding query, key, and value matrices. The computational expression is as follows:
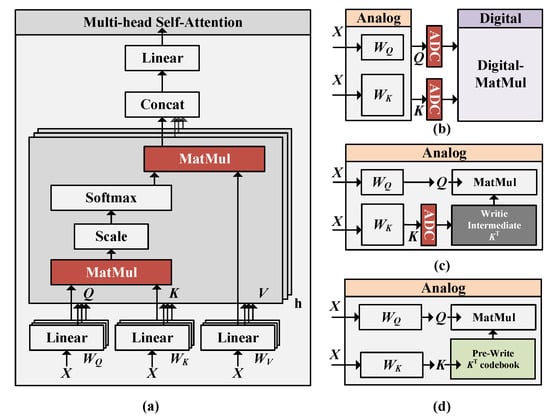
Figure 1.
Transformer model structure and MatMul methods in CIM: (a) Multi-head self-attention module. (b) MatMul calculations in ISAAC, Timely [15], etc. (c) MatMul calculations in ReTransformer and (d) proposed MatMul methods.
Self-attention is calculated using scaled dot-product attention, while the multi-head attention mechanism enables the model to focus on various positions, thereby enhancing performance. The computational expression is
The initial step in self-attention involves computing token correlations by multiplying Q and K to produce the score matrix (S). In contrast to linear layers with fixed model parameters, the intermediate MatMul layers in transformers utilize input operands that are generated during runtime.
Traditional CIM accelerators (as shown in Figure 1b) use analog-to-digital conversion to transfer intermediate results from the analog domain to the digital domain, where digital matrix computation units are employed for correlation calculations. The literature [16] optimized MatMul via matrix decomposition (as shown in Figure 1c), which necessitates writing intermediate results K to the NVM array in real time, but it cannot circumvent the high power consumption associated with analog-to-digital conversion.
To tackle the issue of the challenges associated with adapting traditional CIM accelerators’ self-attention modules for in-memory computation, Figure 1d illustrates our proposed solution, which employs product quantization to cluster one operand of the MatMul into a codebook, pre-written to the NVM array. This approach mitigates the high programming power consumption and writes latency [17] associated with attention computation while significantly reducing AD conversions. It is worth noting that the MatMul between the softmax output and the value (V) in the attention module can also be approximated using this method.
2.2. Voltage-Domain MAC and Time-Domain MAC
NVM-based MAC macros have gained widespread adoption in compute-in-memory (CIM) systems owing to their capability to substantially decrease weight data transfer. NVM-MAC macros are primarily categorized into two types: time-domain MAC and voltage-domain MAC. Time-domain NVM-MAC has garnered growing interest in recent years, attributed to its advantages in energy efficiency and scalability.
Specifically, voltage-domain MAC designs, such as PRIME [18] and ISAAC [19], use ReRAM to accelerate the inference of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The computation process is shown in Figure 2a, taking ReRAM [20] as an example, where digital input signals are first converted to voltage signals, multiplication is performed by activating word lines, products are calculated based on Ohm’s law, and results are accumulated along each column according to Kirchhoff’s law. Nevertheless, these designs necessitate high power consumption and physically large analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs) to interface the intermediate results from the NVM array with digital circuits; notably, in the ISAAC design, the power consumption of ADCs accounts for 61% of the total chip power consumption. With the technology scaling down, the decreased supply voltage constrains the signal-to-noise ratio, imposing more stringent requirements for mitigating mismatch and thermal noise, often necessitating larger passive or active devices.
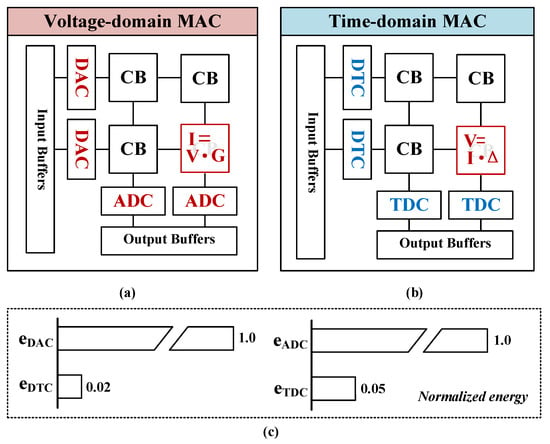
Figure 2.
(a) Voltage-domain MAC based on Ohm’s law. (b) Time-domain MAC based on current integration. (c) The normalized energy of different interfaces, where , , , and denote the energy of one DAC, ADC, DTC, and TDC, respectively.
In contrast, the computational process of time-domain MAC is depicted in Figure 2b, where the distinction lies in utilizing pulse width as the input signal, representing neural network weights with programmable current sources, executing multiplication through current integration, and computing accumulated results based on the principle of charge conservation. Time-domain MAC not only substantially reduces energy consumption per conversion (as illustrated in Figure 2c) but also exhibits higher frequency in designs involving multi-input parallel computation and offers superior scalability [21,22].
In light of these advantages offered by time-domain MAC, this paper employs a design based on the time-domain NVM-MAC macro and presents the design and simulation verification of an InMemQK prototype module for time-domain MatMul.
3. Optimized Product Quantization and InMemQK Based on Time-Domain MAC
3.1. Background: Product Quantization
Product quantization (PQ) [23] is commonly employed to address similarity search or nearest neighbor search problems. Its fundamental approach involves compressing data by decomposing the original vector space into a Cartesian product of multiple low-dimensional vector spaces. As illustrated in Figure 3a, a D-dimensional vector is split into C (where C = 3 for demonstration purposes) distinct V-dimensional subvectors, and M centroids are derived by performing K-means clustering on N subvectors (as shown in Figure 3b, where M = 3 for demonstration purposes).
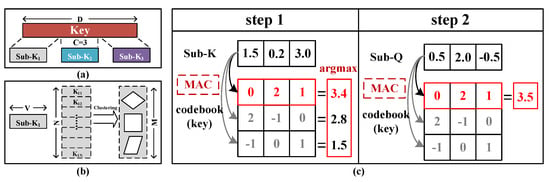
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of product quantization. (a) Vector splitting. (b) Clustering and representation. (c) Two steps of approximate MatMul.
Figure 3c illustrates the two-step approximate MatMul process based on product quantization. Taking the product quantization of the key as an example, we obtain a codebook(key). In the first step, the input subvector sub-K [1.5, 0.2, 3.0] is multiplied and accumulated (MAC) with the centroids in the codebook(key), and the maximum value 3.4 is found via argmax, with its index recorded. In the second step, the corresponding value is found in the codebook(key) based on this index, followed by a MAC operation with subvector sub-Q [0.5, 2.0, −0.5], ultimately obtaining an approximate multiplication result of 3.5 for sub-Q · sub-K. Finally, summing all subvector inner products provides the final approximate inner product result for . Given that the centroids are known, query vectors or key vectors can be pre-quantized into codebooks and subsequently written into NVM arrays.
3.2. ADC-Free InMemQK Module Design
Drawing from the time-domain method presented in the literature [24], we developed a time-domain vector–matrix multiplication (VMM) module. As illustrated in Figure 4a, inputs are encoded using pulse width, while weights are represented by programmable current sources constructed from NVM cells. Assuming the i-th current source is activated with current for an input duration of , the current integral over a unit period is the product of and . The dot product of N elements can be computed by summing the charges in a single column of the NVM array. NVM-CS cannot represent negative inputs or negative weights, whereas the query and key in the self-attention module exhibit both positive and negative representations.
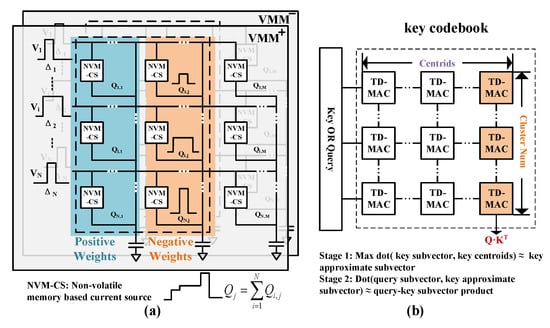
Figure 4.
(a) Time-domain multiplication–accumulation macro. (b) Two-stage MatMul calculation pipeline.
To realize signed MatMul, we employ a differential structure to implement VMM, using and to handle the positive and negative paths separately. The expression for the positive path is given by
Specifically, for , we have = and = 0, while for , we have = 0 and = , and the same for Q. Similarly, the expression for the negative path is
As depicted in Figure 4b, our proposed InMemQK computation module implements an approach where keys are quantized into codebooks. During stage 1, the distances between and the centroids in the key codebook are computed. Given that the distance from the key to all centroids remains constant, the minimum L2 distance between the subvector and centroids can be equivalently represented as the maximum inner product between the key subvector and . In stage 2, utilizing the maximum inner product index identified in stage 1, the approximate inner product between the input tensor and is computed. The inner product calculation of and is accomplished by utilizing the crossbar array structure, with the activated centroid word lines serving as weights. Lastly, the inner product of and is calculated, and the inner products of C subvectors are aggregated to yield the approximate MatMul result of .
3.3. Hierarchical Feature Reconstruction and Reverse Layer-Wise Fine-Tuning
Substitution of approximate matrix multiplication (AMM), based on the L2 norm distance metric PQ, typically results in decreased model performance. Experiments [25] show model accuracy diminishes as the number of AMM replacement layers increases. This is because the K-means clustering algorithm uses a greedy algorithm to minimize Euclidean distance between original data and centroids in the subvector space, which may lead to local optima.
To address this issue, we propose a hierarchical feature reconstruction (HFR) algorithm. This algorithm employs mean squared error (MSE) to quantify the disparity between keys before and after quantization and utilizes gradient descent to optimize the loss function. The algorithm’s pseudo-code is presented in Algorithm 1. Following hierarchical feature reconstruction, nearly every layer of the network model approaches an optimal solution. Nevertheless, this still diverges from the ultimate objective of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), which aims to minimize the overall loss function. Furthermore, fine-tuning the model using soft-PQ techniques [26] fails to fully restore accuracy. This is attributed to the accumulated errors in the approximate attention module, which causes the distribution of quantized model parameters to deviate substantially from that of the pre-trained model, whereas model fine-tuning depends on well-initialized parameters [27].
| Algorithm 1 Optimized product quantization. |
|
To tackle this challenge, we introduced a reverse layer-wise fine-tuning (RL-FT) algorithm. This algorithm leverages the characteristic that the error magnitude increases with the number of quantization layers, fine-tuning the centroids in the codebooks layer by layer from back to front. To enhance fine-tuning efficiency, we initiate the RL-FT from the N-th last layer, where N (commonly set to 6) is the layer index where the PQ accuracy drops below 95% of the original accuracy. First, we load the codebooks from the N-th layer to the 12-th layer and freeze its parameters, then fine-tune the codebooks of the (N-1)-th layer, continuing in this manner by loading the codebooks from the (N-1)-th layer to the 12-th layer and fine-tuning the (N-2)-th layer.
During this process, we incorporated the soft-PQ technique, employing softmax to approximate argmax to circumvent non-differentiability issues. Furthermore, we considered the variations and resolution of NVM devices, simulating the non-ideal behavior of real devices by quantizing the centroids and introducing Gaussian noise. Comprehensive results are presented in Section 4.2.
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Experiment Methodologies and Settings Dataset and Models
We conducted experiments to validate the effectiveness of InMemQK in natural language processing (NLP) tasks [28]. The models used were BERT-Base [29] (approximately 100 million parameters), consisting of 12 layers and 12 self-attention heads, with an embedding dimension of 768; ALBERT [30] (with approximately 11 million parameters for the base configuration), which reduces the number of parameters by factorizing the embedding parameters and sharing weights across layers; and RoBERTa [31] (approximately 125 million parameters), an optimized version of BERT that uses dynamic masking and trains on larger datasets with longer sequences. All three models are evaluated on 8 tasks from the GLUE dataset [32], with default sequence lengths of 64 or 128. We report the Matthews correlation coefficient for the COLA task, F1 score for the MRPC task, Spearman correlation for the STS-B task, and accuracy for the other tasks. All of these metrics are positively correlated with model performance.
Experiments were conducted on an Nvidia RTX 3090 GPU, using PyTorch version 1.12 as the deep learning framework and fine-tuning pre-trained models from the Huggingface library [33]. The optimizer was Adam with a learning rate of and a batch size of 32, and the fine-tuning process lasted for 10 epochs. The codebook learning rate was set to 0.01, and the temperature learning rate for soft-PQ was set to 0.1. It is worth noting that we perform product quantization on the last dimension (D = 768) of the key (with dimensions [Batch, , ]). Each key vector is split into 24 (M = 24) subvectors, each with a dimension of 32 (V = 32). We plan to explore additional segmentation methods in the future.
4.2. Algorithm Simulation Results
We first verified the effectiveness of the proposed HFR algorithm. Specifically, we performed product quantization (PQ) on the key and value matrices in the BERT model and progressively replaced the MatMul calculations ( and ) in 10 attention layers from back to front. Initially, we implemented PQ using the L2 distance metric as the default approach (denoted as “L2” in Table 1). As shown in Table 1 (L2), when L2 distance is used as the default metric for PQ, performance on most datasets in the GLUE benchmark drops significantly, especially on the COLA dataset, where the Matthews correlation coefficient drops to 0.07. Next, we applied the proposed HFR algorithm to optimize the centroids of PQ, which were initialized using the L2 metric (denoted as “HFR” in Table 1). This optimization significantly improved accuracy, recovering 68–93% of the original performance. Finally, we applied RL-FT on top of the HFR optimization to further reduce quantization error and mitigate the impact of device non-idealities, improving overall model performance further (denoted as “RL-FT” in Table 1). The same progressive methodology (L2, HFR, RL-FT) was also applied to ALBERT and RoBERTa, achieving consistent improvements in accuracy.

Table 1.
Optimized product quantization attention performance and comparison.
It is worth noting that we introduced 10% Gaussian noise in the experiment to simulate manufacturing variation in NVM devices. As shown in Table 1 (HFR*), even with the introduction of device variation, the BERT model’s performance did not degrade significantly. This might be because we utilized centroids stored in a codebook, where slight input signal jitters did not notably affect computational accuracy.
To align with the designed time-domain MAC circuit, we quantized the codebook centroids to 6 bits, considering the limited precision requirements of NVM. To mitigate accuracy loss, we used RL-FT and PyTorch’s quantization-aware training (QAT). Table 1 (RL-FT) shows model performance after considering device variation and quantization using these methods.
4.3. InMemQK Performance of MatMul Optimization
To evaluate the performance of the proposed method, we built the proposed InMemQK based on the same parameter settings from the reliable time-domain accelerator Timely (T-MAC) and compared it with the 2024 digital multiply–accumulate macro (D-MAC) [34]. The D-MAC introduces a multi-precision adaptive accumulator (MPAA) and an SRAM buffer for serial–parallel conversion (SPBUF), effectively minimizing peripheral circuit and intermediate buffer area overhead while supporting multi-precision operations. As shown in Figure 5a, whether in terms of energy efficiency or area efficiency, InMemQK has significant advantages over the D-MAC, thanks to the inherent advantages of the in-memory computing architecture. Its energy efficiency is 184.9 times better than and its area efficiency is 15.8 times that of the D-MAC.
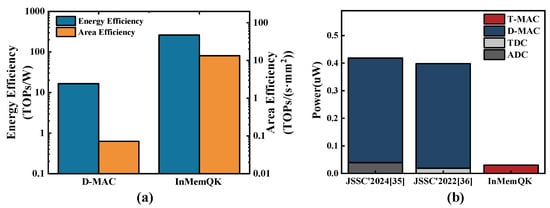
Figure 5.
(a) Performance comparison with D-MAC. (b) InMemQK power saving over JSSC’2024, JSSC’2022 (only mapping relevance computing).
Moreover, it should be noted that InMemQK, compared to the D-MAC, can avoid certain analog-to-digital conversion demands, thus further lowering power consumption. Figure 5b illustrates that in traditional in-memory accelerators (JSSC’2024 [35] and JSCC’2022 [36]), analog signals Q and K produced by the in-memory array must undergo quantization via ADC and TDC before being processed by the digital acceleration module, incurring extra power consumption and further diminishing energy efficiency. InMemQK, however, these can be directly integrated adjacent to the in-memory array, avoiding these additional conversions. Compared to JSSC’2024, power consumption is reduced by 13.9 times; compared to JSSC’2022, power consumption is reduced by 13.2 times.
5. Conclusions
In this work, we propose InMemQK to accelerate the correlation computation operations of the model’s attention module. InMemQK optimizes MatMul operations using product quantization (PQ), enabling intermediate results in CIM accelerators to perform approximate matrix computations directly in the analog domain without analog-to-digital conversion. We also introduce an optimized PQ algorithm and fine-tuning technique to mitigate the impact of approximate matrix calculations on model performance. Finally, we develop an approximate module for correlation computation using a codebook based on time-domain multiply–accumulate (MAC) operations. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can effectively substitute the correlation computations in the last 10 layers of the BERT model, offering a 13.2×–13.9× improvement in power consumption compared to conventional CIM accelerators.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.F. and Y.C.; methodology, P.F. and Y.C.; software, P.F.; validation, J.Y. and H.Y.; formal analysis, H.Y.; investigation, Y.X. and P.F.; resources, G.C. and H.L.; data curation, Z.J. and P.F.; writing—original draft, P.F.; writing—review and editing, P.F. and Z.J.; visualization, P.F. and Z.J.; supervision, W.X., H.L. and G.C.; project administration, W.X., H.L. and G.C.; funding acquisition, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China 92364202 and in part by the CAS Strategic Leading Science and Technology Project XDB44000000.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wu, T.; He, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, K.; Han, Q.L.; Tang, Y. A brief overview of ChatGPT: The history, status quo and potential future development. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Chen, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Zhang, D. Ds-transunet: Dual swin transformer u-net for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmaz, O.; Yurt, M.; Çukur, T. ResViT: Residual vision transformers for multimodal medical image synthesis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 2598–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teeneti, C.R.; Truscott, T.T.; Beal, D.N.; Pantic, Z. Review of wireless charging systems for autonomous underwater vehicles. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 46, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.; Fu, D.; Ermon, S.; Rudra, A.; Ré, C. FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 16344–16359. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. Mobilevit: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdioui, S.; Pouyan, P.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Raychowdhur, A.; Yoon, I. Test and reliability of emerging non-volatile memories. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 26th Asian Test Symposium (ATS), Taipei, Taiwan, 27–30 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Gu, P.; Boxun, L.; Tang, T.; Yin, X.; Huangfu, W.; Yu, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Technological exploration of RRAM crossbar array for matrix-vector multiplication. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kombrink, S.; Mikolov, T.; Karafiát, M.; Burget, L. Recurrent neural network based language model. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association INTERSPEECH 2011, Florence, Italy, 27–31 August 2011; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Mao, S.; Wang, G. Optimized content caching and user association for edge computing in densely deployed heterogeneous networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2020, 21, 2130–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, C.J.; Xue, C.X.; Hung, J.M.; Chang, F.C.; Chang, M.F. Challenges and trends of SRAM-based computing-in-memory for AI edge devices. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 1773–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Huang, S.; Jiang, H.; Lu, A.; Yu, S. DNN+ NeuroSim V2. 0: An end-to-end benchmarking framework for compute-in-memory accelerators for on-chip training. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2020, 40, 2306–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Xu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Xie, Y.; Lin, Y. Timely: Pushing data movements and interfaces in pim accelerators towards local and in time domain. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM/IEEE 47th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Valencia, Spain, 30 May–3 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yan, B.; Li, H.; Chen, Y. ReTransformer: ReRAM-based processing-in-memory architecture for transformer acceleration. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, Virtual, 2–5 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sheu, S.-S.; Chang, M.-F.; Lin, K.-F.; Wu, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chiu, P.-F.; Kuo, C.-C.; Yang, Y.-S.; Chiang, P.-C.; Lin, W.-P.; et al. A 4 Mb embedded SLC resistive-RAM macro with 7.2 ns read-write random-access time and 160 ns MLC-access capability. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, P.; Li, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y. Prime: A novel processing-in-memory architecture for neural network computation in reram-based main memory. ACM SIGARCH Comput. Archit. News 2016, 44, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, A.; Nag, A.; Muralimanohar, N.; Balasubramonian, R.; Strachan, J.P.; Hu, M.; Williams, R.S.; Srikumar, V. ISAAC: A convolutional neural network accelerator with in-situ analog arithmetic in crossbars. ACM SIGARCH Comput. Archit. News 2016, 44, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Xu, J.; Hu, E.; Samanta, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Realization of artificial neuron using MXene bi-directional threshold switching memristors. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2019, 40, 1686–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Wang, J.; Lian, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, K.; Sirakoulis, G.; et al. Time-domain computing in memory using spintronics for energy-efficient convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Freye, F.; Lou, J.; Bengel, C.; Menzel, S.; Wiefels, S.; Gemmeke, T. Memristive devices for time domain compute-in-memory. IEEE J. Explor.-Solid-State Comput. Devices Circuits 2022, 8, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herve, J.; Douze, M.; Schmid, C. Product quantization for nearest neighbor search. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 33, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, B.; Mahmoodi, M.R.; Strukov, D.B. Energy-efficient time-domain vector-by-matrix multiplier for neurocomputing and beyond. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2019, 66, 512–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, T.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, Q.; Cai, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M. Lut-nn: Empower efficient neural network inference with centroid learning and table lookup. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Madrid, Spain, 2–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wilder, B.; Ewing, E.; Dilkina, B.; Tambe, M. End to end learning and optimization on graphs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 2620. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Qixuan, Z.; Luo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.Q. Towards understanding the condensation of neural networks at initial training. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 2184–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Otter, D.W.; Medina, J.R.; Kalita, J.K. A survey of the usages of deep learning for natural language processing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 604–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z. Albert: A lite bert for self-supervised learning of language representations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11942. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A. GLUE: A multi-task benchmark and analysis platform for natural language understanding. arxiv 2018, arXiv:1804.07461. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, T.; Debut, L.; Sanh, V.; Chaumond, J.; Delangue, C.; Moi, A.; Cistac, P.; Rault, T.; Louf, R.; Funtowicz, M.; et al. Transformers: State-of-the-art natural language processing. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, Virtual, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, W.; Mo, K.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Cheng, B.; Pan, B. RDCIM: RISC-V Supported Full-Digital Computing-in-Memory Processor with High Energy Efficiency and Low Area Overhead. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 1719–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-H.; Wen, T.-H.; Khwa, W.-S.; Huang, W.-H.; Ke, Z.-E.; Chin, Y.-H.; Wen, H.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hsu, W.-T.; Lele, A.S.; et al. A 22 nm Floating-Point ReRAM Compute-in-Memory Macro Using Residue-Shared ADC for AI Edge Device. IEEE J.-Solid-State Circuits 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, J.-M.; Wen, T.-H.; Huang, Y.-H.; Huang, S.-P.; Chang, F.-C.; Su, C.-I.; Khwa, W.-S.; Lo, C.-C.; Liu, R.-S.; Hsieh, C.-C.; et al. 8-b precision 8-Mb ReRAM compute-in-memory macro using direct-current-free time-domain readout scheme for AI edge devices. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2022, 58, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).