Food Waste as Feedstock for Anaerobic Mono-Digestion Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- Physicochemical properties of FW collected from various sources, such as canteens, restaurants and cafeterias,
- (ii)
- The performance profile of the single-stage anaerobic mono-digestion process with the use of FW as a feedstock.
- (i)
- One of the most important challenge of the FW mono-digestion is the instability of the digester [38]. Therefore, deepening the knowledge of the FW parameters is required for ensuring high process performance.
- (ii)
- The performance of the AD process with the use of FW as a feedstock in strongly influenced by several operational parameters, such as temperature, pH, ratio between food waste and inoculum (I) (FW/I), and organic loading rate (OLR).
2. Physicochemical Properties of Food Wastes
3. Performance Profile of Single-Stage Anaerobic Mono-Digestion Process
3.1. Temperature and pH
3.2. Food Waste to Inoculum Ratio
3.3. Organic Loading Rate
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | anaerobic digestion |
| AM | animal manure |
| BNR | biological nutrient removal |
| C | carbon |
| C/N | carbon to nitrogen ratio |
| Co-AD | co-anaerobic digestion |
| CS | corn stover |
| CSTR | continuously stirred tank reactor |
| CM | chicken manure |
| C/N | carbon to nitrogen ratio |
| FW | food waste |
| FW/I | ratio between food waste to inoculum |
| H | hydrogen |
| HF-AnMBR | hollow fiber anaerobic membrane bioreactor |
| I | inoculum |
| KW | kitchen waste |
| N | nitrogen |
| NH4+-N | ammonium nitrogen |
| NI | no information |
| O | oxygen |
| OLR | organic loading rate |
| sCOD | soluble chemical oxygen demand |
| SS | sewage sludge |
| TS | total solids |
| VFA | volatile fatty acids |
| VS | volatile solids |
| VS/TS | ratio of volatile solids to total solids |
References
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X. The World Trends and Patterns of Grain Loss and Waste Research and Their Implications. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesković Moračanin, S.; Milijašević, M.; Borović, B.; Kureljušić, J. Food Loss and Waste: A Global Problem. Meat Technol. 2023, 64, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, A. Bioconversion of Food Industry Waste to Value Added Products: Current Technological Trends and Prospects. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 102935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat Statistics Explained. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Food_waste_and_food_waste_prevention_-_estimates (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/europe/news/detail/towards-a-food-waste-free-future/en (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sustainable-management-food/sustainable-management-food-basics (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Carmona-Cabello, M.; García, I.L.; Sáez-Bastante, J.; Pinzi, S.; Koutinas, A.A.; Dorado, M.P. Food Waste from Restaurant Sector—Characterization for Biorefinery Approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, H.K.; Figueroa-Torres, G.; Azapagic, A. The Extent of Food Waste Generation in the UK and Its Environmental Impacts. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chaudhary, A.; Mathys, A. Nutritional and Environmental Losses Embedded in Global Food Waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 160, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gnaoui, Y.; Sounni, F.; Bakraoui, M.; Karouach, F.; Benlemlih, M.; Barz, M.; El Bari, H. Anaerobic Co-Digestion Assessment of Olive Mill Wastewater and Food Waste: Effect of Mixture Ratio on Methane Production and Process Stability. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierowicz, J.; Dzienis, L.; Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M. Optimisation of Methane Fermentation as a Valorisation Method for Food Waste Products. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 144, 105913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsirichot, P.; Barroso-Ingham, B.; Hamilton, A.; Parroquin Gonzalez, M.; Romero Jimenez, R.; Hoeven, R.; Winterburn, J. Food Wastes for Bioproduct Production and Potential Strategies for High Feedstock Variability. Waste Manag. 2024, 184, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lee, Y.-W.; Jahng, D. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Piggery Wastewater: Focusing on the Role of Trace Elements. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5048–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A.A.; Tavares, F.; Alves, M.M.; Cavaleiro, A.J.; Pereira, M.A. Garden and Food Waste Co-Fermentation for Biohydrogen and Biomethane Production in a Two-Step Hyperthermophilic-Mesophilic Process. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 278, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Guan, W.; Song, N.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C. Effect of Yeast Addition on the Biogas Production Performance of a Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion System. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ouyang, W.; Lia, A. Essential Role of Trace Elements in Continuous Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Xiao, X.; Feng, L.; He, Y.; Liu, G. Evaluating Methane Production from Anaerobic Mono- and Co-Digestion of Kitchen Waste, Corn Stover, and Chicken Manure. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bożym, M.; Florczak, I.; Zdanowska, P.; Wojdalski, J.; Klimkiewicz, M. An Analysis of Metal Concentrations in Food Wastes for Biogas Production. Renew. Energy 2015, 77, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, N.; Pillay, P. Biogas Prediction and Design of a Food Waste to Energy System for the Urban Environment. Renew. Energy 2012, 41, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, W.; Gryta, M.; Grubecki, I.; Miłek, J. Biogas Production in AnMBRs via Treatment of Municipal and Domestic Wastewater: Opportunities and Fouling Mitigation Strategies. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Bano, A.; Singh, S.P.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, S.P.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Varjani, S. Different Stages of Microbial Community during the Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 2079–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.R.; Leong, H.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Anjum, H.; Chang, C.-K.; Show, P.L. Effects of Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste on Biogas Production and Environmental Impacts: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2921–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.M.; Wright, M.M. Anaerobic Digestion Fundamentals, Challenges, and Technological Advances. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2023, 8, 2819–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasapoor, M.; Young, B.; Brar, R.; Sarmah, A.; Zhuang, W.-Q.; Baroutian, S. Recognizing the Challenges of Anaerobic Digestion: Critical Steps toward Improving Biogas Generation. Fuel 2020, 261, 116497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, D.P.; Fujiwara, T.; Leu Tho, B.; Song Toan, P.P.; Hoang Minh, G. A Review of Anaerobic Digestion Systems for Biodegradable Waste: Configurations, Operating Parameters, and Current Trends. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksay, M.V.; Tabak, A. Mapping of Biogas Potential of Animal and Agricultural Wastes in Turkey. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 5345–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, M.C.; Braghieri, A.; Capece, A.; Napolitano, F.; Romano, P.; Galgano, F.; Altieri, G.; Genovese, F. Recent Updates on the Use of Agro-Food Waste for Biogas Production. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.C.; Wang, J. An Overview on Biogas Generation from Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Int. J. Green Energy 2016, 13, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimberg, S.J.; Hilderbrandt, D.; Kinnunen, M.; Rogers, S. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste through the Operation of a Mesophilic Two-Phase Pilot Scale Digester—Assessment of Variable Loadings on System Performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algapani, D.E.; Qiao, W.; Ricci, M.; Bianchi, D.; Wandera, S.M.; Adani, F.; Dong, R. Bio-Hydrogen and Bio-Methane Production from Food Waste in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion Process with Digestate Recirculation. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Yan, F.; Su, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H. High-Calorific Biogas Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste Using a Two-Phase Pressurized Biofilm (TPPB) System. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartini, S.; Nurika, I.; Paul, R.; Melville, L. Estimation of Biogas Production and the Emission Savings from Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit-Based Agro-Industrial Waste and Agricultural Crops Residues. Bioenergy Res. 2021, 14, 844–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capson-Tojo, G.; Rouez, M.; Crest, M.; Steyer, J.-P.; Delgenès, J.-P.; Escudié, R. Food Waste Valorization via Anaerobic Processes: A Review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 499–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Sun, S.; Yang, D.; Sheng, W.; Ma, Y.; He, W.; Li, G. Anaerobic Digestion: An Alternative Resource Treatment Option for Food Waste in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komilis, D.; Barrena, R.; Grando, R.L.; Vogiatzi, V.; Sánchez, A.; Font, X. A State of the Art Literature Review on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: Influential Operating Parameters on Methane Yield. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.; Li, Y. Solid State Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Yard Waste and Food Waste for Biogas Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 127, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.L.H.; Lo, I.M.C. Reviewing the Anaerobic Digestion and Co-Digestion Process of Food Waste from the Perspectives on Biogas Production Performance and Environmental Impacts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24435–24450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelsalam, E.M.; Samer, M.; Amer, M.A.; Amer, B.M.A. Biogas Production Using Dry Fermentation Technology through Co-Digestion of Manure and Agricultural Wastes. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 8746–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Elmashad, H.; Hartman, K.; Wang, F.; Liu, G.; Choate, C.; Gamble, P. Characterization of Food Waste as Feedstock for Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, F.H.; Makkawi, Y.T. A Review of Post-Consumption Food Waste Management and Its Potentials for Biofuel Production. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 7759–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanussen, H.; Loy, J.-P. Household Food Waste: A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Chall. 2024, 14, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuri, N.R.; Parthasarathy, P. An Insight into Seasonal Variations in Food Waste Characteristics and Associated Carbon Footprint Management. Kuwait J. Sci. 2024, 51, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, W.; Sheng, K.; Sanati, M. Comparison of High-Solids to Liquid Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Green Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 154, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Yu, Z. Effects of Thermal Pretreatment on the Biomethane Yield and Hydrolysis Rate of Kitchen Waste. Appl. Energy 2016, 172, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramaguru, G.; Kannan, M.; Lawrence, P.; Thamilselvan, D. Effect of Total Solids on Biogas Production through Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 63, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, X.C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of pH on Lactic Acid Production from Acidogenic Fermentation of Food Waste with Different Types of Inocula. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Lactic Acid Fermentation from Food Waste with Indigenous Microbiota: Effects of pH, Temperature and High OLR. Waste Manag. 2016, 52, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Shen, F.; Yuan, H.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Jaffu, M.; Chufo, A.; Li, X. Minimizing Asynchronism to Improve the Performances of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Corn Stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsha, S.S.V.; Soomro, A.F.; Baig, Z.T.; Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Murugavelh, S.; Antunes, E. Methane Production from Anaerobic Mono- and Co-Digestion of Kitchen Waste and Sewage Sludge: Synergy Study on Cumulative Methane Production and Biodegradability. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 3911–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad Lohani, S. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste with Cow Manure. Iran. J. Energy Environ. 2020, 11, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, J.D.; Murphy, J.D. Assessment of the Resource Associated with Biomethane from Food Waste. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Yan, X.; Ye, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation of Biogas Production from Different Biomass Wastes with/without Hydrothermal Pretreatment. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 3313–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Deng, L.; Li, H.; Zou, Z. Design and Efficiency Analysis of Biogas Engineering for the Mixture of Kitchen Waste and Garden Waste. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd Joint International Information Technology, Mechanical and Electronic Engineering Conference (JIMEC 2018), Chongqing, China, 15–16 December 2018; Atlantis Press: Chongqing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.W.; Kelvin Wong, S.W.; Dai, Y.; Tong, Y.W. Effect of Seed Sludge Source and Start-up Strategy on the Performance and Microbial Communities of Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Energy 2020, 203, 117922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Chaulagain, N.P.; Shrestha, K.R. Biogas Production for Organic Waste Management: A Case Study of Canteen’s Organic Waste in Solid Waste Management Technical Support Center, Lalitpur, Nepal. Nepal J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Borrion, A.; Li, H.; Li, J. Effects of Organic Composition on Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Loh, K.-C.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Y.W.; Dai, Y. Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste and Horticultural Waste in High-Solid System. Appl. Energy 2018, 209, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yin, J.; Shen, D.; Li, N. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste for Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) Production with Different Types of Inoculum: Effect of pH. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Xue, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, R. Effects of Ammonia on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: Process Performance and Microbial Community. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5749–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, F.; Xu, X.; Shao, L.; He, P. Importance of Storage Time in Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 45, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arelli, V.; Mamindlapelli, N.K.; Begum, S.; Juntupally, S.; Anupoju, G.R. Solid State Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge: Impact of Mixing Ratios and Temperature on Microbial Diversity, Reactor Stability and Methane Yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanatamskul, C.; Wattanayommanaporn, O.; Yamamoto, K. An On-Site Prototype Two-Stage Anaerobic Digester for Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge for Biogas Production from High-Rise Building. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Yuan, Z.; Zhen, F.; Wang, Y. Improved Biogas Production from Rice Straw by Co-Digestion with Kitchen Waste and Pig Manure. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2653–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, F.; Yuan, H.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, X. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Kitchen Waste and Fruit/Vegetable Waste: Lab-Scale and Pilot-Scale Studies. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.; Ren, F.; Wang, J.-Y.; Giannis, A. Effect of Pretreatment Techniques on Food Waste Solubilization and Biogas Production during Thermophilic Batch Anaerobic Digestion. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Anwar, N.; Ma, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, R. Effect of Organic Loading Rate on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste under Mesophilic and Thermophilic Conditions. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mao, L.; Nithya, K.; Loh, K.-C.; Dai, Y.; He, Y.; Wah Tong, Y. Optimizing Mixing Strategy to Improve the Performance of an Anaerobic Digestion Waste-to-Energy System for Energy Recovery from Food Waste. Appl. Energy 2019, 249, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.M.; Gogate, P.R. Intensifying the Biogas Production from Food Waste Using Ultrasound: Understanding into Effect of Operating Parameters. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 59, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Huang, Z.; Miao, H.; Xu, Z.; Ruan, W. Enhancing Biogas Generation Performance from Food Wastes by High-Solids Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion: Effect of pH Adjustment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 105, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linyi, C.; Yujie, Q.; Buqing, C.; Chenglong, W.; Shaohong, Z.; Renglu, C.; Shaohua, Y.; Lan, Y.; Zhiju, L. Enhancing Degradation and Biogas Production during Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste Using Alkali Pretreatment. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenmee, S.; Prasertboonyai, K. Potential Biogas Production Generated by Mono- and Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Fruit Waste (Durian Shell, Dragon Fruit and Pineapple Peel) in Different Mixture Ratio under Anaerobic Condition. Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2021, 77, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminzadeh, M.; Bardi, M.J.; Aminirad, H. A New Approach to Enhance the Conventional Two-Phase Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanapan, C.; Sinchai, L.; Tachapattaworakul Suksaroj, T.; Kantachote, D.; Ounsaneha, W. Biogas Production by Co-Digestion of Canteen Food Waste and Domestic Wastewater under Organic Loading Rate and Temperature Optimization. Environments 2019, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jahng, D. Long-Term Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste Stabilized by Trace Elements. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster-Carneiro, T.; Pérez, M.; Romero, L.I. Influence of Total Solid and Inoculum Contents on Performance of Anaerobic Reactors Treating Food Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6994–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Morais Andrade, M.M.; Alencar, B.R.A.; Leite, N.P.; Firmo, A.L.B.; Dutra, E.D.; De Sá Barretto Sampaio, E.V.; Menezes, R.S.C. Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Different Proportions of Food Waste and Fresh Bovine Manure. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczman, O.; Gueri, M.V.D.; De Souza, S.N.M.; Schirmer, W.N.; Alves, H.J.; Secco, D.; Buratto, W.G.; Ribeiro, C.B.; Hernandes, F.B. Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion of a Popular Restaurant in Southern Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valença, R.B.; Santos, L.A.D.; Firmo, A.L.B.; Silva, L.C.S.D.; Lucena, T.V.D.; Santos, A.F.D.M.S.; Jucá, J.F.T. Influence of Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3) on the Methane Generation Potential of Organic Food Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helenas Perin, J.K.; Biesdorf Borth, P.L.; Torrecilhas, A.R.; Santana Da Cunha, L.; Kuroda, E.K.; Fernandes, F. Optimization of Methane Production Parameters during Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Garden Waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 123130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Orobio, B.A.; Donoso-Bravo, A.; Ruiz-Sánchez, J.C.; Valencia-Molina, K.J.; Torres-Lozada, P. Effect of Inoculum on the Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste Accounting for the Concentration of Trace Elements. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasius, J.P.; Contrera, R.C.; Maintinguer, S.I.; Alves De Castro, M.C.A. Effects of Temperature, Proportion and Organic Loading Rate on the Performance of Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 27, e00503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Xi, J.; Yeung, M.; Ren, G. Characteristics and Mechanisms of H2S Production in Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 137977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, O.W.; Lu, J.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Nzihou, A.; Lyczko, N.; Minh, D.P. Effect of Oil Content on Biogas Production, Process Performance and Stability of Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion. Waste Biomass Valor 2018, 9, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dompara, I.; Maragkaki, A.; Papastefanakis, N.; Floraki, C.; Vernardou, D.; Manios, T. Effects of Different Materials on Biogas Production during Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnaoui, Y.E.; Karouach, F.; Bakraoui, M.; Barz, M.; Bari, H.E. Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: Effect of Thermal Pretreatment on Improvement of Anaerobic Digestion Process. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Guo, X.; Zuo, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. A Comparative Study of Thermophilic and Mesophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Wheat Straw: Process Stability and Microbial Community Structure Shifts. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainal, A.; Harun, R.; Idrus, S. Performance Monitoring of Anaerobic Digestion at Various Organic Loading Rates of Commercial Malaysian Food Waste. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 775676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyeman, F.O.; Tao, W. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Dairy Manure: Effects of Food Waste Particle Size and Organic Loading Rate. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Z.; Anwar, N.; Liu, G.; Zhang, R. Comparison of the Methane Production Potential and Biodegradability of Kitchen Waste from Different Sources under Mesophilic and Thermophilic Conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, N.; Zhang, T.; Yin, D.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Ren, G.; Feng, Y. Effect of Initial pH on Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Kitchen Waste and Cow Manure. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wu, G.; Zhan, X. Impact of Total Solids Content on Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Pig Manure and Food Waste: Insights into Shifting of the Methanogenic Pathway. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, M.; Zeshan; Yousaf, S.; Haider, M.R.; Malik, R.N. High-Solids Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Rice Husk at Different Organic Loading Rates. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Zeng, G.; Yang, Q. Potential Impact of Salinity on Methane Production from Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion. Waste Manag. 2017, 67, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.; Chen, X.; Pan, J.; Kloss, R.; Wei, Y.; Ying, Y. Effect of Ammonia and Nitrate on Biogas Production from Food Waste via Anaerobic Digestion. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 116, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, K.; Ma, J.; Ifran, M.; Li, A. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge, Food Waste and Yard Waste: Synergistic Enhancement on Process Stability and Biogas Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oduor, W.W.; Wandera, S.M.; Murunga, S.I.; Raude, J.M. Enhancement of Anaerobic Digestion by Co-Digesting Food Waste and Water Hyacinth in Improving Treatment of Organic Waste and Bio-Methane Recovery. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Xie, S.; Yu, L.; Zhen, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Frear, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Z. pH Shaped Kinetic Characteristics and Microbial Community of Food Waste Hydrolysis and Acidification. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 146, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, C. Treatment of Cattle Manure by Anaerobic Co-Digestion with Food Waste and Pig Manure: Methane Yield and Synergistic Effect. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakahmad, A.; Ahmad Basri, N.E.; Md Zain, S. Production of Renewable Energy by Transformation of Kitchen Waste to Biogas, Case Study of Malaysia. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Symposium on Business, Engineering and Industrial Applications (ISBEIA), Langkawi, Malaysia, 25–28 September 2011; IEEE: Langkawi, Malaysia, 2011; pp. 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Yuan, H.; Pang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhu, B.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Yu, L.; Li, X. Performances of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Fruit & Vegetable Waste (FVW) and Food Waste (FW): Single-Phase vs. Two-Phase. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepanraj, B.; Sivasubramanian, V.; Jayaraj, S. Effect of Substrate Pretreatment on Biogas Production through Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 26522–26528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hussain, A.; Dubey, S.K. Methane Formation from Food Waste by Anaerobic Digestion. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2016, 6, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamodharan, K.; Kumar, V.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Effect of Different Livestock Dungs as Inoculum on Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion and Its Kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 180, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Xiao, G.; Peng, L.; Su, H.; Tan, T. The Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Cattle Manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Effects of Alkalinity Sources on the Stability of Anaerobic Digestion from Food Waste. Waste Manag. Res. 2015, 33, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikrant, D.; Shekhar, P. Generation of Biogas from Kitchen Waste -Experimental Analysis. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2013, 68, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Rakić, N.; Šušteršič, V.; Gordić, D.; Jovičić, N.; Bošković, G.; Bogdanović, I. Characteristics of Biogas Production and Synergistic Effect of Primary Sludge and Food Waste Co-Digestion. Bioenergy Res. 2023, 17, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Chen, S.; Li, X. Biogas Production from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste with Dairy Manure in a Two-Phase Digestion System. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Dong, B.; Jin, J.; Dai, X. Effect of Increasing Total Solids Contents on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste under Mesophilic Conditions: Performance and Microbial Characteristics Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-J.; Kobayashi, T.; Kuramochi, H.; Li, Y.-Y.; Xu, K.-Q. Improved Biogas Production from Food Waste by Co-Digestion with de-Oiled Grease Trap Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.; Song, N.; Chang, Q.; Gao, M.; Sonomoto, K. Effect of Ethanol Pre-Fermentation and Inoculum-to-Substrate Ratio on Methane Yield from Food Waste and Distillers’ Grains. Appl. Energy 2015, 155, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-W.; Han, S.-K.; Shin, H.-S. The Optimisation of Food Waste Addition as a Co-Substrate in Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge. Waste Manag. Res. 2003, 21, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kusch-Brandt, S.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C. Effect of Pasteurisation on Methane Yield from Food Waste and Other Substrates in Anaerobic Digestion. Processes 2020, 8, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Nagao, N.; Tajima, N.; Niwa, C.; Matsuyama, T.; Toda, T. The Effect of the Labile Organic Fraction in Food Waste and the Substrate/Inoculum Ratio on Anaerobic Digestion for a Reliable Methane Yield. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 157, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan-jiang, P.; Jie, L.; Feng-mei, S.; Su, W.; Ya-bing, G.; Da-lei, Z. High-Solid Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Rice Straw for Biogas Production. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. (Engl. Ed.) 2014, 21, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbeshbishy, E.; Nakhla, G.; Hafez, H. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) of Food Waste and Primary Sludge: Influence of Inoculum Pre-Incubation and Inoculum Source. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampio, E.; Ervasti, S.; Paavola, T.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.; Rintala, J. Anaerobic Digestion of Autoclaved and Untreated Food Waste. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tampio, E.A.; Blasco, L.; Vainio, M.M.; Kahala, M.M.; Rasi, S.E. Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) and Methane from Food Waste and Cow Slurry: Comparison of Biogas and VFA Fermentation Processes. GCB Bioenergy 2019, 11, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Qiao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zou, T.; Lin, M.; Dong, R. Balancing Acidogenesis and Methanogenesis Metabolism in Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste under a High Loading Rate. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Dennehy, C.; Lawlor, P.G.; Hu, Z.; McCabe, M.; Cormican, P.; Zhan, X.; Gardiner, G.E. Inhibition of Volatile Fatty Acids on Methane Production Kinetics during Dry Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Pig Manure. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Shim, J.; Park, S.J. Composting Process and Gas Emissions during Food Waste Composting under the Effect of Different Additives. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.G.; Han, G.; Lee, J.; Cho, K.; Jeon, E.-J.; Lee, C.; Hwang, S. Characterization of Food Waste-Recycling Wastewater as Biogas Feedstock. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Banks, C.J.; Heaven, S. Co-Digestion of Source Segregated Domestic Food Waste to Improve Process Stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, V.; Somitsch, W.; Schnitzhofer, W. The Anaerobic Fermentation of Food Waste: A Comparison of Two Bioreactor Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 34, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gioannis, G.; Muntoni, A.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Spiga, D. Energy Recovery from One- and Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Gong, C.; Li, M. Volatile Fatty Acids Production from Food Waste: Effects of pH, Temperature, and Organic Loading Rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukitawesa; Patinvoh, R.J.; Millati, R.; Sárvári-Horváth, I.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Factors Influencing Volatile Fatty Acids Production from Food Wastes via Anaerobic Digestion. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadka, A.; Parajuli, A.; Dangol, S.; Thapa, B.; Sapkota, L.; Carmona-Martínez, A.A.; Ghimire, A. Effect of the Substrate to Inoculum Ratios on the Kinetics of Biogas Production during the Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Energies 2022, 15, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Hiro, Y.; Hojo, T.; Li, Y.-Y. Upgrading Methane Fermentation of Food Waste by Using a Hollow Fiber Type Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Wang, N.; Yuan, T.; Lü, F.; He, P.; Xu, Q. Effect of Nickel-Containing Activated Carbon on Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiarto, Y.; Sunyoto, N.M.S.; Zhu, M.; Jones, I.; Zhang, D. Effect of Biochar Addition on Microbial Community and Methane Production during Anaerobic Digestion of Food Wastes: The Role of Minerals in Biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariunbaatar, J.; Scotto Di Perta, E.; Panico, A.; Frunzo, L.; Esposito, G.; Lens, P.N.L.; Pirozzi, F. Effect of Ammoniacal Nitrogen on One-Stage and Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Meng, S.; Chen, G.; Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Co-Digestion of Garden Waste, Food Waste, and Tofu Residue: Effects of Mixing Ratio on Methane Production and Microbial Community Structure. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisgativa, H.; Tremier, A.; Dabert, P. Characterizing the Variability of Food Waste Quality: A Need for Efficient Valorisation through Anaerobic Digestion. Waste Manag. 2016, 50, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte, J.-C.; Trably, E.; Escudié, R.; Hamelin, J.; Steyer, J.-P.; Bernet, N.; Delgenes, J.-P.; Dumas, C. Total Solids Content: A Key Parameter of Metabolic Pathways in Dry Anaerobic Digestion. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, W.L.; Chan, Y.J.; Tiong, T.J.; Chong, W.C.; Kiatkittipong, W.; Kiatkittipong, K.; Mohamad, M.; Daud, H.; Suryawan, I.W.K.; Sari, M.M.; et al. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste with Sewage Sludge: Simulation and Optimization for Maximum Biogas Production. Water 2022, 14, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdeș, M.; Zăbavă, B.Ș.; Paraschiv, G.; Ionescu, M.; Dincă, M.N.; Moiceanu, G. Food Waste Management for Biogas Production in the Context of Sustainable Development. Energies 2022, 15, 6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casallas-Ojeda, M.R.; Marmolejo-Rebellón, L.F.; Torres-Lozada, P. Identification of Factors and Variables That Influence the Anaerobic Digestion of Municipal Biowaste and Food Waste. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 2889–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Miao, H.; Huang, Z.; Gao, S.; Ruan, W. In Situ Volatile Fatty Acids Influence Biogas Generation from Kitchen Wastes by Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; McAdam, E.; Zhang, Y.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.; Longhurst, P. Ammonia Inhibition and Toxicity in Anaerobic Digestion: A Critical Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakakubo, R.; Møller, H.B.; Nielsen, A.M.; Matsuda, J. Ammonia Inhibition of Methanogenesis and Identification of Process Indicators during Anaerobic Digestion. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 25, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondusamy, D.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Pre-Treatment and Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste for High Rate Methane Production—A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mashad, H.M.; Zhang, R. Biogas Production from Co-Digestion of Dairy Manure and Food Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4021–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Rojas-Downing, M.M.; Zhong, Y.; Saffron, C.M.; Liao, W. Life Cycle and Economic Assessment of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Dairy Manure and Food Waste. Ind. Biotechnol. 2015, 11, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.R.; Zeshan; Yousaf, S.; Malik, R.N.; Visvanathan, C. Effect of Mixing Ratio of Food Waste and Rice Husk Co-Digestion and Substrate to Inoculum Ratio on Biogas Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Shahazi, R.; Nova, S.N.B.; Uddin, M.R.; Hossain, M.S.; Yousuf, A. Biogas Production from Anaerobic Co-Digestion Using Kitchen Waste and Poultry Manure as Substrate—Part 1: Substrate Ratio and Effect of Temperature. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 6635–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Oh, B.R.; Chun, Y.N.; Kim, S.W. Effects of Temperature and Hydraulic Retention Time on Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamanzadeh, M.; Hagen, L.H.; Svensson, K.; Linjordet, R.; Horn, S.J. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste—Effect of Recirculation and Temperature on Performance and Microbiology. Water Res. 2016, 96, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, R.; El-Mashad, H.M.; Dong, R. Effect of Feed to Inoculum Ratios on Biogas Yields of Food and Green Wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5103–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerholm, M.; Liu, T.; Schnürer, A. Comparative Study of Industrial-Scale High-Solid Biogas Production from Food Waste: Process Operation and Microbiology. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 122981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, N.; Davidsson, Å.; La Cour Jansen, J.; Nielsen, J.L. Characterisation of Microbial Communities for Improved Management of Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Waste Manag. 2020, 117, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baştabak, B.; Koçar, G. A Review of the Biogas Digestate in Agricultural Framework. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmohamadsadeghi, S.; Karimi, K.; Tabatabaei, M.; Aghbashlo, M. Biogas Production from Food Wastes: A Review on Recent Developments and Future Perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.K.; Suja, F.B.; Zain, S.M.; Pramanik, B.K. The Anaerobic Digestion Process of Biogas Production from Food Waste: Prospects and Constraints. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 8, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

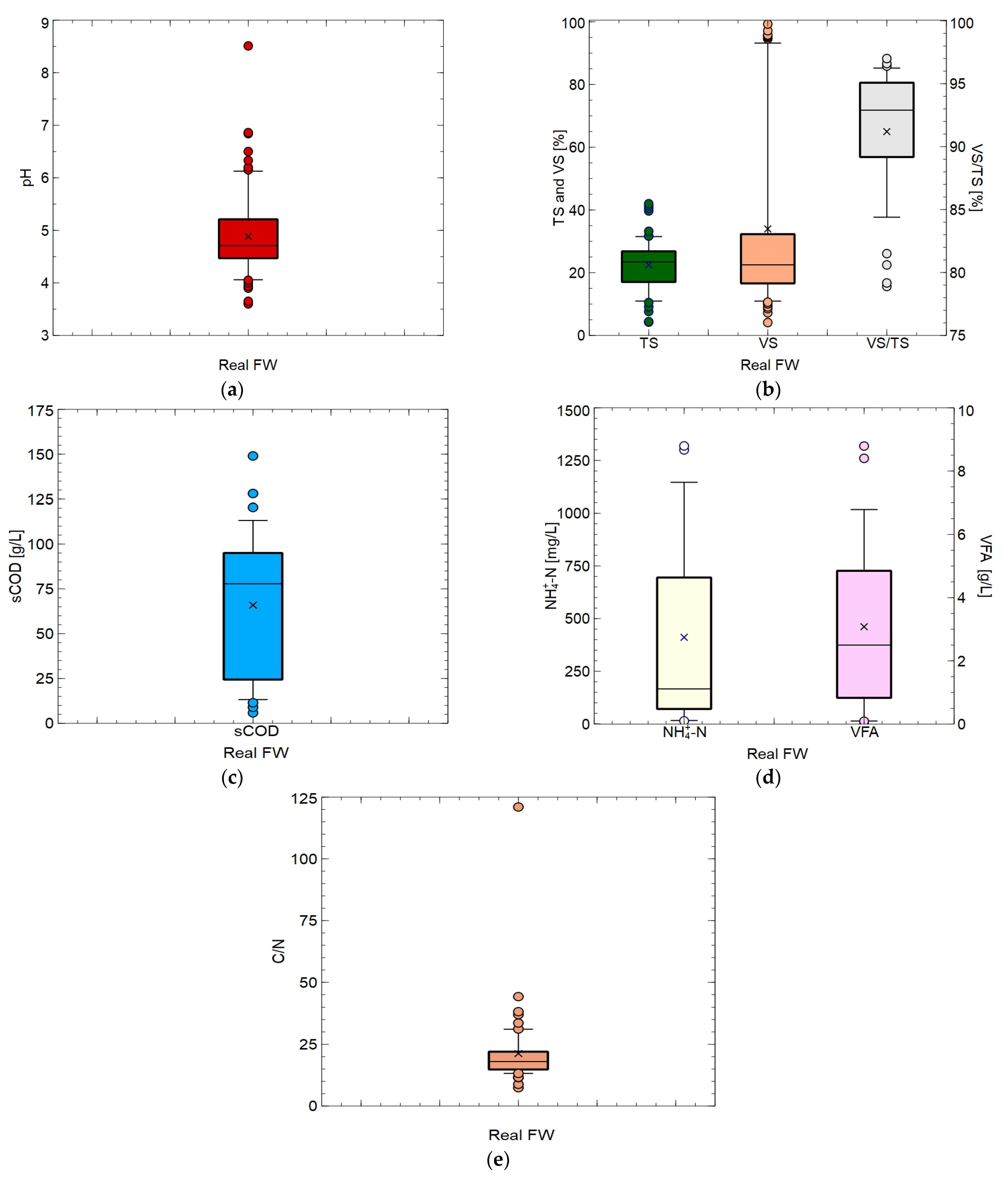
| Source | pH [-] | TS [%] or [g/L] | VS [%] or [g/L] | VS/TS [%] | sCOD [g/L] | VFA [g/L] | NH4+-N [mg/L] | C [%] | N [%] | H [%] | O [%] | C/N [-] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| canteen | 4.70 | 25.7 ± 0.03 | 24.0 ± 0.03 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 49.1 ± 0.04 | 2.10 ± 0.14 | 7.23 ± 0.15 | 30.2 ± 0.17 | 23.5 ± 1.6 | [15] |
| canteen | 4.51 ± 0.01 | 26.9 ± 0.3 | 25.2 ± 0.3 | 93.6 ± 0.5 | NI | NI | NI | 46.3 ± 0.7 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | NI | NI | 22.0 ± 1.1 | [43] |
| canteen | NI | 10.5 ± 1.5 | 9.1 ± 1.3 | NI | 84 | 1.882 ± 0.262 | 40 ± 8.2 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [30] |
| canteen | 6.86 ± 0.06 | 22.73 ± 0.05 | 21.01 ± 0.04 | 92.42 ± 0.06 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [31] |
| canteen | 6.86 ± 0.06 | 22.73 ± 0.05 | 21.01 ± 0.04 | 92.42 ± 0.06 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [31] |
| canteen | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 19.1 ± 1.1 | 93.2 ± 1.4 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 46.1 ± 1.6 | 3.2 ± 0.4 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 37.8 ± 1.6 | 13.7 ± 0.9 | [44] |
| canteen | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 19.1 ± 1.1 | 93.2 ± 1.4 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 46.1 ± 1.6 | 3.2 ± 0.4 | 7.0 ± 0.2 | 37.8 ± 1.6 | 13.7 ± 0.9 | [44] |
| canteen | NI | NI | NI | NI | 152 | NI | NI | 46.19 | 1.94 | 12.05 | 39.58 | 23.72 | [45] |
| canteen | 4.3 | 4.3 ± 0.3 | NI | 96.4 ± 7.6 | 11.0 ± 1.4 | 3.6 ± 0.9 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [46] |
| canteen | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 20 ± 1.2 | NI | 96.4 ± 0.3 | 71.9 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [47] |
| canteen | 5.02 | 22.71 | 20.72 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 18.9 | [48] |
| canteen | NI | 16.60 ± 0.9 | 94.52 ± 2.9 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 54.05 ± 0.26 | 2.87 ± 0.20 | 6.59 ± 0.29 | 35.72 ± 1.6 | 18.83 | [49] |
| canteen | 5.2 | 19.9 | 90.2 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 15.9 | [50] |
| canteen | 4.1 | 29.4 | 95.3 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 49.58 | 3.53 | 7.32 | 34.88 | 14.2 | [51] |
| canteen | 4.41 | 19.71 | 17.04 | 86.45 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [52] |
| canteen | 4.51 ± 0.01 | NI | NI | 93.6 ± 0.5 | NI | NI | - | 46.3 ± 0.7 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | NI | NI | 22.0 ± 1.1 | [53] |
| canteen | 4.3 | 33.2 | 22.5 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 21 | [54] |
| canteen | 5.99 | 14.00 | 99.26 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 34.61 | 1.75 | NI | NI | 19.85 | [55] |
| canteen | NI | 17.2–24.7 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 45.5–51.5 | 2.6–5.3 | 6.8–7.5 | NI | 9.7–18.1 | [56] |
| canteen | NI | 29.32 | 26.03 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 50.48 | 2.84 | NI | NI | 17.77 | [57] |
| canteen | 6.1 | 24.0 | NI | 96.2 | 25.2 | NI | NI | NI | 1.8 | NI | NI | 22 | [58] |
| canteen | 5.02 ± 0.03 | 24.30 ± 2.11 | 22.50 ± 1.32 | NI | 103.53 ± 0.31 | NI | 96 ± 3.5 | 53.39 ± 1.22 | 2.31 ± 0.42 | 6.93 ± 0.71 | 29.75 ± 0.25 | NI | [59] |
| canteen | 6.33 ± 0.07 | 24.13 ± 1.04 | 88.22 ± 3.78 | NI | NI | 0 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [60] |
| canteen | 5.1 ± 0.1 | 25 ± 0.6 | 21 ± 1 | NI | 63 ± 1 | 5.4 ± 0.2 | NI | 40.2 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | NI | 26.8 | [61] |
| canteen | 4.5 | 74,520 | 69,688 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [62] |
| canteen | 4.40 | 20.23 | 18.16 | 90 | NI | - | - | NI | NI | NI | NI | 14.6 | [63] |
| canteen | 5.08 ± 0.07 | 22.17 ± 1.57 | 17.87 ± 1.28 | 80.60 | NI | NI | NI | 32.85 | 2.35 | NI | NI | 13.98 | [64] |
| canteen | 5.1 ± 0.4 | NI | NI | 93.51 ± 1.7 | 8.95 ± 1.24 | NI c | 16 ± 0.5 | 47.2 | 2.7 | 7.4 | - | 17.5 | [65] |
| canteen | 5.02 ± 0.03 | 24.30 ± 2.11 | 22.50 ± 1.32 | NI | 103.53 ± 0.31 | NI | 96.0 ± 3.5 | 53.39 ± 1.22 | 2.31 ± 0.42 | 6.93 ± 0.71 | 29.50 ± 0.25 | NI | [66] |
| canteen | NI | 31.70 ± 1.20 | 29.59 ± 2.37 | 93.34 ± 1.54 | NI | NI | NI | 47.08 ± 2.01 | 3.02 ± 0.32 | 7.04 ± 1.11 | NI | 15.58 ± 1.87 | [67] |
| canteen | 6.2 ± 0.2 | 42 ± 3 | 65 ± 3 | NI | 11.450 ± 0.002 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [68] |
| canteen | NI | 24.87 | 23.87 | 95.98 | NI | NI | NI | 56.74 | 2.98 | NI | NI | 19.04 | [69] |
| canteen | 6.15 ± 0.02 | 22.68 ± 0.37 | 20.35 ± 0.29 | 89.77 ± 3.88 | 128.064 ± 0.676 | NI | 1319 ± 376 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 20.01 ± 0.09 | [70] |
| canteen | 5.63–5.96 | 20.66–22.29 | 20.04–21.62 | 95.82–96.70 | 85.880–135.808 | NI | 1143–1343 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 18.93–20.31 | [70] |
| canteen | 4.62 | 41.33 ± 0.28 | 35.41 ± 1.38 | 85.68 | NI | NI | NI | 46.20 | 1.89 | NI | NI | 24.44 | [71] |
| canteen | 5.34 ± 0.32 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 22.31 ± 0.01 | 2.33 ± 0.3 | NI | NI | NI | [72] |
| canteen | 5.21 ± 0.12 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 21.52 ± 3.10 | [73] |
| restaurant | 4.50 ± 0.02 | 16.8 ± 0.4 | 13.7 ± 0.1 | 81.5 | NI | 4.3 ± 0.7 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [10] |
| restaurant | NI | 18.1 | 17.1 | 94 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 13.2 | [74] |
| restaurant | 6.5 ± 0.2 | 18.1 ± 0.6 | 17.1 ± 0.6 | 94 ± 1 | 106.6 ± 5.3 | NI | NI | 46.67 | 3.54 | 6.39 | 36.39 | 13.2 ± 0.2 | [13] |
| restaurant | 4.7 | 26.3 | 22.7 | 86.3 | NI | 8.4 | NI | 52.9 | 2.6 | 7.9 | 26.0 | 20.3 | [17] |
| restaurant | 5.9 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.49 | 130 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 37 | [75] |
| restaurant | 4.8 | 29.2 | 92.5 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 46.8 | 4.04 | 5.6 | NI | 11.6 | [76] |
| restaurant | 5.98 | 15.28 | 13.02 | 85.21 | NI | NI | NI | 7.23 | 0.46 | NI | NI | 15.72 | [77] |
| restaurant | 5.1 ± 0.07 | 29 ± 0.32 | 95 ± 0.04 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 14 ± 0.12 | [78] |
| restaurant | 4.3 | 9.11 | 8.53 | 93.6 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [79] |
| restaurant | 5.6 ± 0.1 | NI | NI | 80 | NI | 3.650 ± 0.235 | 86 ± 63 | 37.3 ± 2.0 | 1.71 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.30 | 32.7 ± 1.1 | 33.6 | [80] |
| restaurant | 4.53 ± 0.06 | 19.59 ± 1.02 | 15.46 ± 0.86 | 78.89 ± 0.57 | NI | 1.98 ± 0.03 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 23.5 ± 0.45 | [81] |
| restaurant | 3.9 | 28.90 | 28.0 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [82] |
| restaurant | 4.87 ± 0.05 | 14.3 ± 2.50 | 13.1 ± 2.23 | 91.90 ± 1.06 | 39.083 ± 33.276 | NI | 166 | 51.12 ± 1.0 | 2.74 ± 0.07 | 7.2 ± 0.25 | 30.41 ± 0.04 | 18.68 ± 0.11 | [83] |
| restaurant | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 22.621 ± 0.231 | 21.689 ± 0.195 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [84] |
| restaurant | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 16.5 ± 0.3 | 15.2 ± 0.7 | NI | 47.7 ± 1.7 | 5.8 ± 2.3 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [85] |
| restaurant | NI | 25.94 ± 1.12 | 24.59 ± 0.84 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 51.1 ± 1.4 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 7.4 ± 0.7 | 37.0 ± 1.6 | 17.5 ± 1.5 | [86] |
| restaurant | 4.5 | 0.725 | 0.048 | NI | 149 | NI | 213 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 121 | [87] |
| restaurant | 4.4 | NI | 29.3 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 48.4 | 3.8 | NI | NI | NI | [88] |
| restaurant and cafeteria | 3.94–4.85 | 13.95–24.30 | 11.47–21.44 | NI | NI a | NI | NI b | 43.36–53.01 | 2.39–4.13 | 6.09–7.84 | NI | NI | [89] |
| cafeteria | 4.2 ± 0.23 | 23.19 ± 0.54 | 95.69 ± 1.27 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 31.18 ± 1.37 | [90] |
| cafeteria | 4.93 ± 0.02 | 40.52 ± 0.38 | 39.96 ± 0.30 | 96.2 | 126.8 | 8.79 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [91] |
| cafeteria | NI | 27.45 | 91.99 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 3.04 | NI | NI | 16.81 | [92] |
| cafeteria | 6.5 ± 0.1 | 24.9 ± 1.2 | 18.8 ± 1.1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [93] |
| cafeteria | 4.51 ± 0.01 | 27.59 ± 0.13 | 25.91 ± 0.13 | 93.90 ± 0.07 | NI | NI | 1125.08 ± 9.65 | 46.28 ± 0.02 | 2.23 ± 0.13 | 7.27 ± 0.02 | NI | NI | [94] |
| cafeteria | NI | 23.9 ± 0.1 | 21.8 ± 0.1 | 91.3 ± 0.3 | NI | NI | NI | 45.7 ± 0.1 | 2.8 ± 0.0 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | NI | 16.3 ± 0.2 | [95] |
| cafeteria | 5.8 ± 0.34 | 60.78 ± 0.73 | 54.12 ± 0.97 | 89.05 | 85 ± 2.32 | NI | 970 ± 50 | 45.97 ± 0.48 | 2.66 ± 0.24 | 16.44 ± 0.69 | 18.56 ± 0.92 | 17.28 ± 0.57 | [96] |
| cafeteria | NI | 31.67 ± 0.30 | 29.98 ± 0.31 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 46.47 ± 0.06 | 2.99 ± 0.21 | 7.14 ± 0.06 | 36.05 ± 0.15 | NI | [97] |
| cafeteria | 4.5 | 12.64 | 12.06 | 95.4 | 52.3 | NI | NI | 53.6 | 3.0 | 7.9 | 32.9 | 17.9 | [98] |
| cafeteria | NI | 14.8 | 89.5 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 38.2 | [99] |
| cafeteria | NI | 22.61 | 17.90 | 79.17 | NI | NI | NI | 30.25 | 2.63 | NI | NI | 11.50 | [100] |
| hostel | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 49.96 | 1.13 | NI | NI | 44.21 | [101] |
| hostel | 5.6 | 25.9 | 55.59 | NI | NI | 0.09 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [102] |
| hostel | 5.02–6.64 | 24.6 ± 3.6 | 20.3 ± 3.2 | 76–86 | 78.4 ± 6.2 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [103] |
| distribution points of big retail chains | 6.84 ± 0.1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.3601 ± 0.0071 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 7.4 ± 0.5 | [11] |
| distribution points of big retail chains | 8.51 ± 0.2 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.1001 ± 0.0033 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 14.7 ± 0.3 | [11] |
| waste management company | NI | 30.90 ± 0.07 | 26.35 ± 0.14 | 85.30 ± 0.65 | NI | NI | NI | 46.78 ± 1.15 | 3.16 ± 0.22 | NI | NI | 14.8 | [39] |
| university | 5.2 ± 0.3 | 18.5 ± 0.1 | 17.0 ± 0.1 | 92.0 | NI | NI | NI | 46.5 ± 1.5 | 2.2 ± 0.3 | NI | NI | 21.1 | [104] |
| university | 5.2 ± 0.3 | NI | - | 96.2 ± 0.5 | 5.84 ± 0.05 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 14 ± 1.5 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [105] |
| leftovers at households | 4–7.1 | 80–110 | 68–93 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [106] |
| student dorm | 5.41 ± 0.13 | 39.67 ± 0.37 | 34.83 ± 0.21 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [107] |
| dining center | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 291 ± 0.8 | 260 ± 0.1 | NI | NI | NI | 1300 ± 100 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [108] |
| dining room | 4.72 ± 0.21 | 26.56 ± 0.6 | NI | 94.76 ± 3.9 | NI | NI | 538 ± 24 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 13.4 ± 0.6 | [109] |
| dining hall | 3.65 ± 0.06 | 7.62 ± 0.29 | 7.21 ± 0.29 | 94.6 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [110] |
| dining hall | NI | 25.5 | 24.1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 43.2 | 2.4 | NI | NI | 18 | [111] |
| dining hall | NI | 4.24 | 4.10 | 97.0 | NI | NI | NI | 45.7 | 2.2 | 6.7 | NI | 20.8 | [112] |
| environmental services provider | 4.71 ± 0.01 | 23.7 ± 0.1 | 21.7 ± 0.1 | NI | NI | NI | - | 47.9 ± 0.5 | 3.42 ± 0.04 | 7.03 ± 0.26 | 34.3 ± 2.5 | NI | [113] |
| garbage collection company | - | 4.4 | 4.1 | 96 | 22 | NI | NI | 45 | NI | NI | NI | NI | [114] |
| garbage collection company | - | 10.5 | 10.1 | 93 | 20 | NI | NI | 45 | NI | NI | NI | NI | [114] |
| company Jinquan Environmental Protection Co., Ltd. | 5.4 | 29.65 ± 0.05 | 28.76 ± 0.05 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 20 | [115] |
| Dufferin Organaics Processing Facility | 4.6 ± 0.2 | NI | NI | NI | 60.30 ± 0.35 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [116] |
| digestion plant | 4.96 ± 0.16 | 24.75 ± 0.47 | 22.99 ± 0.45 | 92.9 | 98.2 ± 6.5 | NI d | 0.32 ± 0.12 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [117] |
| local waste treatment facility | 4.2 | 30.4 | 28.1 | 92.5 | 120.4 | 2.5 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [118] |
| FW treatment industrial plant | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 75.1 ± 7.1 | 67.5 ± 3.5 | NI | NI | NI | 208 ± 74 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [119] |
| FW treatment industrial plant | 4.5 | 29.38 | 28.37 | 96.6 | 92.6 | 3.007 | 386 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [120] |
| municipal waste collection station | 4.9 ± 0.1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 44.9 ± 0.1 | 5.1 ± 0.03 | NI | NI | 8.8 ± 0.1 | [121] |
| landfill site | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 97,300 ± 28,100 | 82,000 ± 23,900 | NI | 92.4 ± 22.4 | 5.4 ± 2.8 | 630 ± 420 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [122] |
| digestion facility | 4.71 ± 0.01 | 23.74 ± 0.08 | 91.44 ± 0.39 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 47.6 ± 0.5 | 3.44 ± 0.04 | 7.04 ± 0.63 | 33.3 ± 2.6 | [123] | |
| biogas plant | 4.05 ± 0.28 | 12.02 ± 2.03 | 10.61 ± 1.79 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | [124] |
| Scale | AD Conditions | Process Performance | Ref. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FW/I on a VS Basis | T [°C] | pH | OLR [g VS/L] or [g VS/L/d] | Biogas Production Rate [L/d] or [L/L/d] | Specific Biogas Yield [L/g VS] | CH4 Content in Biogas [%] | Specific CH4 Yield [L/g VS] | ||
| lab | 1.5; 3.0 | 37 | 8.0→7.4 | 3 | NI | 1.142 | 60 | about 0.180; 0.670 | [17] |
| lab | NI | 50 ± 2 | 7.57 | 6.8; 10.5 | NI | NI | 73.14 ± 3.64 | 0.425; 0.445 | [39] |
| lab | NI | 30 | NI | NI | 0.150; 0.162; 0.143; 0.129; 0.109 | NI | 60.2–64.9 | NI | [45] |
| lab | 1:3 | 37 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.314; 0.358; 0.467 | [51] |
| lab | NI | 35; 36–40; 41–45; 46–50; 51–55; 55 | 7.48→6.93; 6.95 ± 0.10; 7.0–7.5; 7.14→4.73;7.82→7.46; 7.27 ± 0.12; 7.0–7.5; 7.68–7.09 | 0.0667–0.5336 | 0.057 ± 0.020; 0.082 ± 0.024; 0.233 ± 0.063; 0.528 ± 0.132; 0.610 ± 0.165; 0.615 ± 0.120; 0.574 ± 0.074; 0.507 ± 0.091; 0.349 ± 0.087; 0.609 ± 0.167; 0.542 ± 0.101; 0.502 ± 0.152; 0.237 ± 0.075; 0.130 ± 0.027; 0.318 ± 0.344; 0.192 ± 0.023; 0.119 ± 0.034; 0.143 ± 0.052; 0.193 ± 0.039; 0.068 ± 0.064; 0.109 ± 0.029; 0.133 ± 0.030; 0.316 ± 0.072; 0.531 ± 0.167; 0.584 ± 0.122; 0.619 ± 0.185; 0.519 ± 0.147; 0.505 ± 0.087; 0.498 ± 0.033; 0.693 ± 0.203; 0.505 ± 0.132; 0.576 ± 0.141; 0.395 ± 0.158; 0.194 ± 0.032; 0.447 ± 0.397; 0.365 ± 0.120; 0.632 ± 0.203; 0.511 ± 0.118; 0.413 ± 0.116 | NI | NI | NI | [54] |
| lab | 1:2 | 37 | 7.79–7.99 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.385–0.627 | [56] |
| lab | 1:2 | 35 ± 1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.285 ± 0.008; 0.308 ± 0.031; 0.530 ± 0.197; 0.466 ± 0.106; 0.418 ± 0.119; 0.618 ± 0.012; 0.696 ± 0.043; 0.639 ± 0.174 | [60] |
| lab | NI | 37 ± 1; 55 ± 1 | NI | 1.5; 1; 1.5; 2.5; 5; 7.5; 10 | 0.3; 0.4; 0.03; 0.03; 0.150; 0.100 | NI | 56.0−58.0; 54.0; 56.0; 3.4; 2.3; 1.8; 0.1; 55.0−57.0; 55.0; 56.7; 59.0; 58.6; 57.0; 55.7 | 0.38673; 0.37057; 0.51267; 0.55140; 0.54139; 0.44393; 0.401 | [66] |
| lab | 1:10 | 37 ± 2 | 6.5–7.5 | NI | NI | 0.249 ± 0.00022 | 69 ± 0.32 | 0.086 ± 0.00061 | [78] |
| lab | 1 | 37 | 7.0 | 0.15; 0.30; 0.45; 0.60; 0.90 | NI | NI | NI | 0.869; 0.348–0.837; 0.740; 0.654; 0.348 | [81] |
| lab | 1 | 55 | 7.0 | 0.15; 0.30; 0.45; 0.60; 0.90 | NI | NI | NI | 0.735; 0.670; 0.568; 0.500; 0.338 | [81] |
| lab | 2 | 37 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 52 | NI | [82] |
| lab | NI | 37 | 7.6 ± 0.21 | 1.42→2.10 | NI | NI | NI | 0.30952 | [85] |
| lab | 1:300; 1:150; 1:100; 1:75; 1:60; 1:30 | 38 ± 2 | 7.05; 6.98; 7.01; 6.97; 6.99; 7.14 | 0.38; 0.77; 1.15; 1.53; 1.92; 3.83 | NI | NI | 70; 51; 65; 79; 81; 52 | NI | [87] |
| lab | 1:300; 1:150; 1:100; 1:75; 1:60; 1:30 | 38 ± 2 | 6.6–6.7 | 1.3; 2; 4; 6; 7; 8 | NI | NI | 72; 68; 63; 85; 42; 42; 36 | NI | [87] |
| lab | 0.6 | 37 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.4911; 0.4361; 0.3532; 0.4824; 0.4397; 0.5384; 0.5652 | [89] |
| lab | 0.6 | 55 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.4971; 0.4308; 0.3739; 0.5127; 0.4445; 0.5512; 0.5747 | [89] |
| lab | NI | 35 ± 1 | 7.0 ± 0.1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.2533; 0.1977; 0.0503; 0.0227 | [93] |
| lab | 1:1 | 37 | NI | NI | NI | 0.35785 ± 0.024 | 53 ± 4.35 | NI | [96] |
| lab | NI | 50 | 7.0 | NI | NI | NI | 62.03 | NI | [101] |
| lab | NI | 30 ± 2; 50 ± 2; 15 ± 2 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI a | [102] |
| lab | NI | 37 ± 1 | 7.1–7.5 | 8; 10 | NI | NI | NI | 0.251; 0.197; 0.1948; 0.1562; 0.1202 | [105] |
| lab | NI | 35 | 7.39 ± 0.08; 7.68 ± 0.06; 7.82 ± 0.09 | 2.35; 7.01; 9.41 | NI | 0.70 ± 0.02; 0.76 ± 0.01; 0.87 ± 0.02 | 52.5 ± 2.1; 54.2 ± 2.7; 55.1 ± 2.6 | 0.37 ± 0.01; 0.41 ± 0.01; 0.48 ± 0.01 | [109] |
| lab | NI | 36 ± 1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.475 ± 0.031 | [113] |
| lab | 1:2 | 37 | 7.7; 7.3 ± 0.01; 7.7 ± 0.03; 7.6 ± 0.03; 7.7 ± 0.01 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 0.435 | [117] |
| lab | NI | 50 ± 1 | 7.6 ± 0.1; 7.7 ± 0.1; 7.7→7.3; 7.6 ± 0.1 | 4.2→5.4; 7.3; 10.0; 10.0 | 2.6 ± 0.2; 3.9 ± 0.2; 5.4→4.4; 5.3 ± 0.2 | NI | 59.0 ± 1.1; 58.0 ± 0.5; 54.4 ± 0.2; 55.1 ± 0.4 | NI b | [119] |
| lab | NI | 40 | NI | 0.6; 1.2; 1.7; 2.3; 3.5; 4.9; 5.3; 6.0; 6.7; 7.3; 9.1; 12.8; 16.4; 20.1 | NI | NI | NI | 0.431 ± 0.122; 0.336 ± 0.044; 0.509 ± 0.082; 0.437 ± 0.048; 0.315 ± 0.020; 0.302 ± 0.022; 0.408 ± 0.053; 0.483 ± 0.057; 0.500 ± 0.106; 0.503 ± 0.026; 0.377 ± 0.094; 0.315 ± 0.037; 0.284 ± 0.023; 0.154 ± 0.075 | [124] |
| lab | NI | 40 | NI | 0.5; 1.1; 1.6; 2.7; 3.8; 5.2; 6.6; 8.2; 10.1; 12.4; 14.6 | NI | NI | NI | 0.208 ± 0.052; 0.211 ± 0.029; 0.248 ± 0.034; 0.287 ± 0.031; 0.332 ± 0.056; 0.405 ± 0.050; 0.391 ± 0.059; 0.440 ± 0.033; 0.403 ± 0.046; 0.321 ± 0.024; 0.233 ± 0.075 | [124] |
| lab | 1:2 | 39 ± 1 | 7.3–7.8 | NI | NI | NI | 66 | 0.3286 | [125] |
| lab | 1; 3 | 37 | uncontrolled; 4; 5; 6 | 1.0 | NI | NI | NI | 0.0003; 0.0003; 0.017; 0.0008; 0; 0001; 0.0001; 0.0001; 0.0006; 0.0033; 0.0062; 0.00009; 0.0004; 0.0004 | [127] |
| lab | 0.5: 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6 | 35 ± 0.5 | 7.84→7.21; 7.79→7.19; 7.70→7.19; 7.71→7.37; 7.58→7.52; 7.47→7.60; 7.45→7.86 | NI | NI | 0.46401; 0.67437; 0.63888; 0.55513; 0.57014; 0.55158; 0.55678 | NI | NI | [128] |
| lab | NI | mesophilic conditions | 7.2 | NI c | 19.6 ± 3.0; 36.3 ± 4.5; 54.0 ± 6.0; 67.5 ± 9.0 | NI | 60.9 ± 0.2; 60.5 ± 0.3; 59.1 ± 0.4; 58.9 ± 0.3 | NI d | [129] |
| lab | NI | 40; 45; 50; 55 | NI | NI | 7.3; 6.1; 8.7; 7.4; 10.4; 8.6; 6.8; 5.6 | NI | 61.6; 65.6; 63.2; 66.2; 64.4; 67.4; 54.4; 58.9 | NI e | [147] |
| lab | NI | 37; 55 | 7.7 ± 0.1; 8 ± 0.1; 7.8 ± 0.2; 8 ± 0.1 | 1–3 | NI | NI | 63; 62; 62, 58 | 0.480 ± 0.033; 0.475 ± 0.029; 0.448 ± 0.044; 0.401 ± 0.045 | [148] |
| lab | 1.6; 3.1; 4.0; 5.0 | 50 ± 2 | 7.2→7.6; 7.3→7.4; 7.3→7.6; 7.2→7.6; 7.4→7/6 | 6.5; 12.5; 16; 20; 12.5 | NI | 0.778; 0.742; 0.784; 0.396; 0.430 | 65.6; 67.6; 66.1; 63.7; 56.9 | 0.510; 0.502; 0.518; 0.252; 0.245 | [149] |
| industrial | 3 | 39; 42; 54; 52→38 | 7.9 ± 0.1; 8.1 ± 0.04; 7.9 ± 0.1; 8.0 ± NI; 8.3 ± 0.1 | 6.4; 5.5; 5.9; 8.3; 5.8 | NI | NI | 58 ± 0.2; 59 ± 0.4; 61 ± 0.1; 61 ± 0.1; 57 ± 0.2 | 0.44 ± 0.15; 0.40 ± 0.01; 0.52 ± 0.05; 0.60 ± 0.12; 0.42 ± 0.12 | [150] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomczak, W.; Daniluk, M.; Kujawska, A. Food Waste as Feedstock for Anaerobic Mono-Digestion Process. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10593. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210593
Tomczak W, Daniluk M, Kujawska A. Food Waste as Feedstock for Anaerobic Mono-Digestion Process. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(22):10593. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210593
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomczak, Wirginia, Monika Daniluk, and Anna Kujawska. 2024. "Food Waste as Feedstock for Anaerobic Mono-Digestion Process" Applied Sciences 14, no. 22: 10593. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210593
APA StyleTomczak, W., Daniluk, M., & Kujawska, A. (2024). Food Waste as Feedstock for Anaerobic Mono-Digestion Process. Applied Sciences, 14(22), 10593. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210593







