The Diagnostic Accuracy of Overnight Oximetry for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
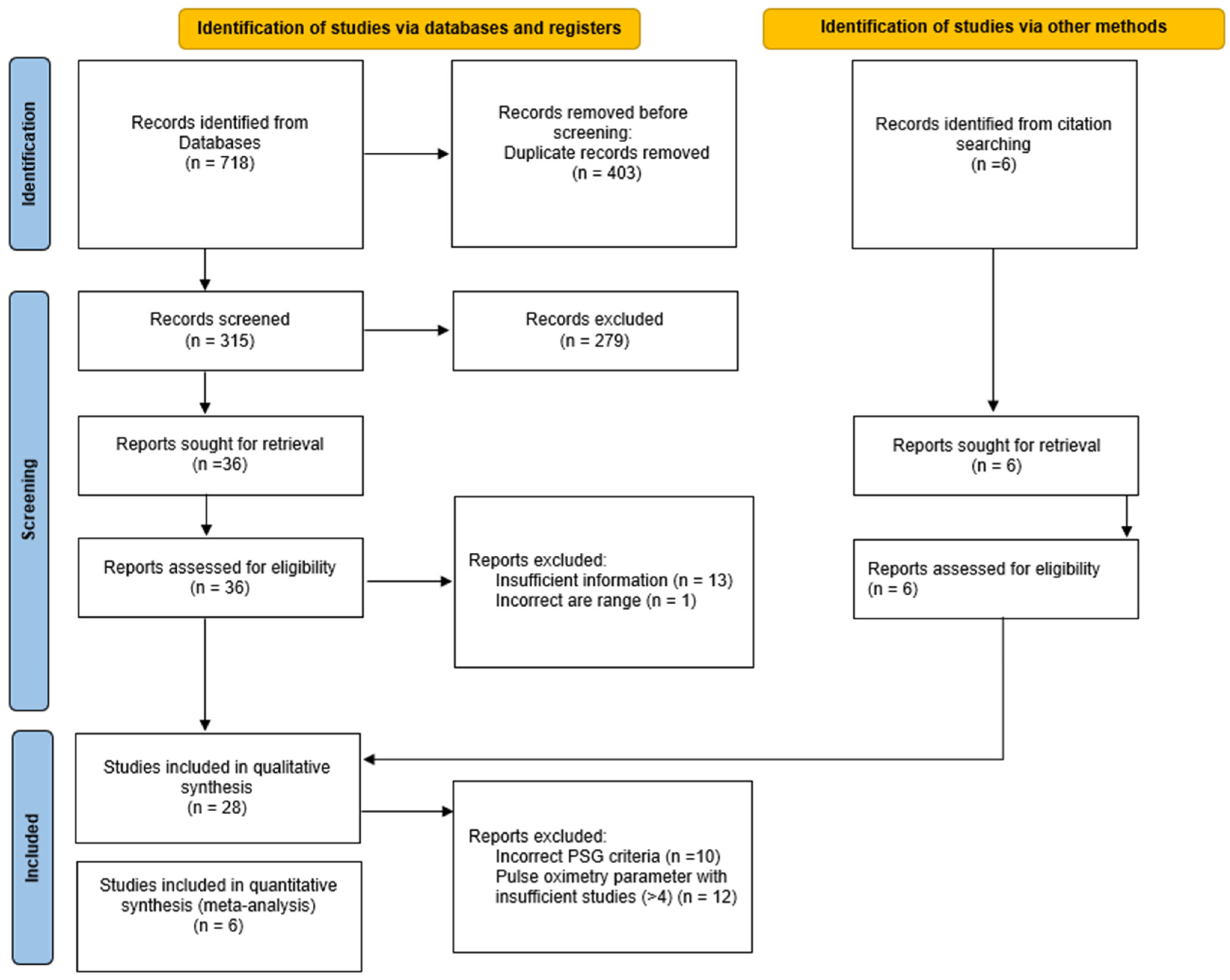
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
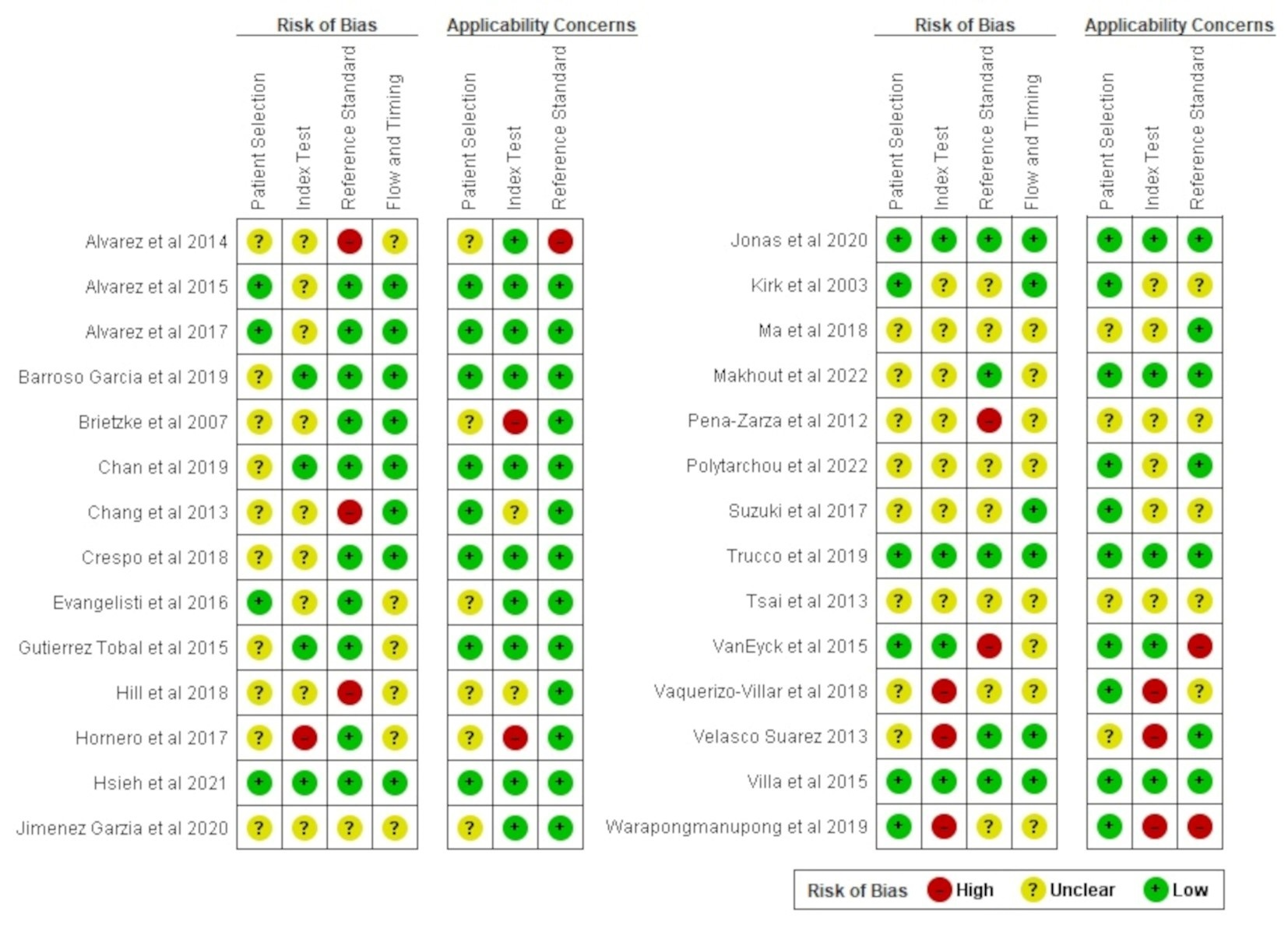
2.4. Assessment of Quality of Studies
2.5. Data Synthesis
2.6. Investigations of Heterogeneity
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Studies
3.2. Assessment of Quality of Studies
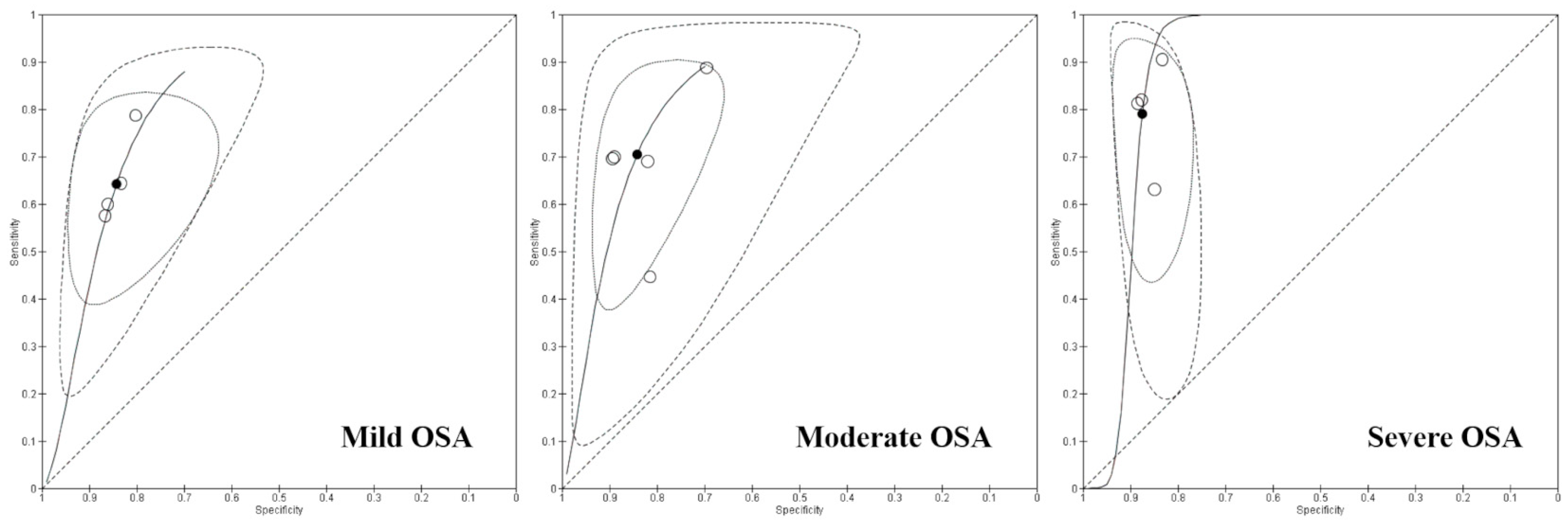
3.3. Data Synthesis and Findings
3.4. Heterogeneity of Included Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Thoracic Society. Standards and indications for cardiopulmonary sleep studies in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sateia, M.J. International classification of sleep disorders-third edition: Highlights and modifications. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, C.L.; Brooks, L.J.; Ward, S.D.; Draper, K.A.; Gozal, D.; Halbower, A.C.; Jones, J.; Lehmann, C.; Schechter, M.S.; Sheldon, S.; et al. Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e714–e755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaditis, A.G.; Alvarez, M.L.A.; Boudewyns, A.; Alexopoulos, E.I.; Ersu, R.; Joosten, K.; Larramona, H.; Miano, S.; Narang, I.; Trang, H.; et al. Obstructive sleep disordered breathing in 2- to 18-year-old children: Diagnosis and management. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luca Canto, G.; Singh, V.; Major, M.P.; Witmans, M.; El-Hakim, H.; Major, P.W.; Flores-Mir, C. Diagnostic capability of questionnaires and clinical examinations to assess sleep-disordered breathing in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2014, 145, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelet, D.; Julien-Marsollier, F.; Vacher, T.; Bellon, M.; Skhiri, A.; Bruneau, B.; Fournier, J.; Diallo, T.; Luce, V.; Brasher, C.; et al. Accuracy of the sleep-related breathing disorder scale to diagnose obstructive sleep apnea in children: A meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2019, 54, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incerti Parenti, S.; Fiordelli, A.; Bartolucci, M.L.; Martina, S.; D’Antò, V.; Alessandri-Bonetti, G. Diagnostic accuracy of screening questionnaires for obstructive sleep apnea in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2021, 57, 101464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-R.; Tu, Y.-K.; Chuang, L.-P.; Gordon, C.; Chen, N.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hasan, F.; Kurniasari, M.D.; Susanty, S.; Chiu, H.-Y. Diagnostic meta-analysis of the Pediatric Sleep Questionnaire OSA-18 and pulse oximetry in detecting pediatric obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Med. Rev. 2020, 54, 101355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Han, D. Diagnostic accuracy of level IV portable sleep monitors versus polysomnography for pediatric obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2021, 87, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luca Canto, G.; Pachêco-Pereira, C.; Aydinoz, S.; Major, P.W.; Flores-Mir, C.; Gozal, D. Diagnostic capability of biological markers in assessment of obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2015, 11, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Tobal, G.C.; Álvarez, D.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Reliability of machine learning to diagnose pediatric obstructive sleep apnea: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2022, 57, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouillette, R.T.; Morielli, A.; Leimanis, A.; Waters, K.A.; Luciano, R.; Ducharme, F.M. Nocturnal pulse oximetry as an abbreviated testing modality for pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Pediatrics 2000, 105, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trucco, F.; Rosenthal, M.; Bush, A.; Tan, H.-L. The McGill score as a screening test for obstructive sleep disordered breathing in children with co-morbidities. Sleep Med. 2020, 68, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brietzke, S.E.; Katz, E.S.; Roberson, D.W. Pulse transit time as a screening test for pediatric sleep-related breathing disorders. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-M.; Kang, C.-H.; Su, M.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Huang, E.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Hung, J.-C.; Niu, C.-K.; Liao, D.-L.; Yu, H.-R. Usefulness of desaturation index for the assessment of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannink, N.; Mathijssen, I.M.J.; Joosten, K.F.M. Use of ambulatory polysomnography in children with syndromic craniosynostosis. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2010, 21, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaditis, A.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gozal, D. Pediatric OSAS: Oximetry can provide answers when polysomnography is not available. Sleep Med. Rev. 2016, 27, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Wisniewski, S.; Diagnostic Test Accuracy Working Group; Bhandari, M.; Bossuyt, P.M. Guide to the contents of a Cochrane Diagnostic Test Accuracy Protocol. Cochrane Rev. 2013, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- McInnes, M.D.F.; Moher, D.; Thombs, B.D.; McGrath, T.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Clifford, T.; Cohen, J.F.; Deeks, J.J.; Gatsonis, C.; Hooft, L.; et al. Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies: The PRISMA-DTA Statement. JAMA 2018, 319, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Brooks, R.; Gamaldo, C.E.; Harding, S.M.; Lloyd, R.M.; Quan, S.F.; Troester, M.M.; Vaughn, B.V. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology, and Technical Specifications. Version 2.4; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2017; pp. 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.; Davenport, C.; Deeks, J.; Hyde, C.; Leeflang, M.; Scholten, R. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Chapter 11: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. Cochrane Rev. 2013, 1, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, D.; Gutierrez-Tobal, G.C.; Alonso, M.L.; Teran, J.; del Campo, F.; Hornero, R. Statistical and nonlinear analysis of oximetry from respiratory polygraphy to assist in the diagnosis of Sleep Apnea in children. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2014, 2014, 1860–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, D.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gutierrez-Tobal, G.C.; Crespo, A.; Philby, M.F.; Mohammadi, M.; del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Automated analysis of nocturnal oximetry as screening tool for childhood obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 2800–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, D.; Alonso-Álvarez, M.L.; Gutiérrez-Tobal, G.C.; Crespo, A.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Hornero, R.; Gozal, D.; Terán-Santos, J.; Del Campo, F. Automated Screening of Children With Obstructive Sleep Apnea Using Nocturnal Oximetry: An Alternative to Respiratory Polygraphy in Unattended Settings. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso-Garcia, V.; Gutierrez-Tobal, G.C.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Alvarez, D.; Vaquerizo-Villar, F.; del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Usefulness of Spectral Analysis of Respiratory Rate Variability to Help in Pediatric Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 4580–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-S.; Chan, E.-T.; Ng, D.-K.; Kwok, K.-L.; Yip, A.-F.; Leung, S.-Y. McGill oximetry score to predict risk of obstructive sleep apnea in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Respirol. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Wu, J.; Cao, L. Combination of symptoms and oxygen desaturation index in predicting childhood obstructive sleep apnea. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelisti, M.; Shafiek, H.; Rabasco, J.; Forlani, M.; Montesano, M.; Barreto, M.; Verhulst, S.; Villa, M.P. Oximetry in obese children with sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Med. 2016, 27–28, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobal, G.C.G.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Alvarez, D.; Crespo, A.; Philby, M.F.; Mohammadi, M.; Del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Analysis and classification of oximetry recordings to predict obstructive sleep apnea severity in children. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 4540–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.M.; E Elphick, H.; Farquhar, M.; Gringras, P.; Pickering, R.M.; Kingshott, R.N.; Martin, J.; Reynolds, J.; Joyce, A.; Gavlak, J.C.; et al. Home oximetry to screen for obstructive sleep apnoea in Down syndrome. Arch. Dis. Child. 2018, 103, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornero, R.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gutiérrez-Tobal, G.C.; Philby, M.F.; Alonso-Álvarez, M.L.; Álvarez, D.; Dayyat, E.A.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Y.-S.; Kakazu, M.T.; et al. Nocturnal Oximetry-based Evaluation of Habitually Snoring Children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.-S.; Kang, C.-J.; Chuang, H.-H.; Zhuo, M.-Y.; Lee, G.-S.; Huang, Y.-S.; Chuang, L.-P.; Kuo, T.B.-J.; Yang, C.C.-H.; Lee, L.-A.; et al. Screening Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children with Snoring. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-García, J.; Gutiérrez-Tobal, G.C.; García, M.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Martín-Montero, A.; Álvarez, D.; del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R. Assessment of Airflow and Oximetry Signals to Detect Pediatric Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome Using AdaBoost. Entropy 2020, 22, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, C.; Thavagnanam, S.; Blecher, G.; Thambipillay, G.; Teng, A.Y. Comparison of nocturnal pulse oximetry with polysomnography in children with sleep disordered breathing. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, V.G.; Bohn, S.G.; Flemons, W.W.; Remmers, J.E. Comparison of home oximetry monitoring with laboratory polysomnography in children. Chest 2003, 124, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.-R.; Huang, J.-J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, H.-T.; Xiao, K.-L.; Zhang, Y.-T. Value of pulse oximetry watch for diagnosing pediatric obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2018, 138, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Zarza, J.A.; de Torres, B.O.-R.; Gil-Sanchez, J.A.; Figuerola-Mulet, J. Utility of the pediatric sleep questionnaire and pulse oximetry as screening tools in pediatric patients with suspected obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep Disord. 2012, 2012, 819035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Furukawa, T.; Sugimoto, A.; Kotani, R.; Hosogaya, R. Comparison of diagnostic reliability of out-of-center sleep tests for obstructive sleep apnea between adults and children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 94, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eyck, A.; Lambrechts, C.; Vanheeswijck, L.; Van Hoorenbeeck, K.; Haentjens, D.; Boudewyns, A.; De Winter, B.Y.; Van Gaal, L.; De Backer, W.; Verhulst, S.L. The role of nocturnal pulse oximetry in the screening for obstructive sleep apnea in obese children and adolescents. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquerizo-Villar, F.; Alvarez, D.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gutierrez-Tobal, G.C.; Barroso-Garcia, V.; Crespo, A.; del Campo, F.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R.; Vaquerizo-Villar, F.; et al. Utility of bispectrum in the screening of pediatric sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome using oximetry recordings. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 156, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, C.T.V.; Turienzo, J.M.F.; Len, F.; Mansilla, E. Pulse oximetry recording in children with adenotonsillar hypertrophy: Usefulness in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2013, 111, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.P.; Pietropaoli, N.; Supino, M.C.; Vitelli, O.; Rabasco, J.; Evangelisti, M.; Del Pozzo, M.; Kaditis, A.G. Diagnosis of Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Settings With Limited Resources. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warapongmanupong, S.; Preutthipan, A. Can standard deviation of overnight pulse oximetry be used to screen childhood obstructive sleep apnea. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 119, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, A.; Álvarez, D.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gutiérrez-Tobal, G.C.; Cerezo-Hernández, A.; Gozal, D.; Hornero, R.; del Campo, F. Assessment of oximetry-based statistical classifiers as simplified screening tools in the management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2018, 22, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhout, S.; Boudewyns, A.; Van Hoorenbeeck, K.; Verhulst, S.; Van Eyck, A. Nocturnal pulse oximetry as a possible screening method for obstructive sleep apnea in infants with laryngomalacia. Sleep Med. 2022, 90, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polytarchou, A.; Ohler, A.; Moudaki, A.; Koltsida, G.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L.; Gozal, D.; Kaditis, A.G. Nocturnal oximetry parameters as predictors of sleep apnea severity in resource-limited settings. J. Sleep Res. 2023, 32, e13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, G.M.; Kermack, A.S.; Davis, G.M.; Manoukian, J.J.; Brown, K.A.; Brouillette, R.T. Planning adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: The role of overnight oximetry. Pediatrics 2004, 113, e19–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urschitz, M.S.; Wolff, J.; Von Einem, V.; Urschitz-Duprat, P.M.; Schlaud, M.; Poets, C.F. Reference values for nocturnal home pulse oximetry during sleep in primary school children. Chest 2003, 123, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N | First Author, Year of Publication | Age | Population | Sample Size | PO Device | PO Criteria | PSG Device | PSG Criteria (Scoring Rules) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alvarez et al., 2014 [23] | 5.30 ± 2.55 y | Suspected OSA | 50 | Part of at-home RP (eXim Apnea Polygraph, Bitmed, Sibel S.A., Barcelona, Spain) | Avg SpO2 Min SpO2 ODI3 CT Statistical features Nonlinear features | Attended PSG (Deltamed Coherence 3NT version 3.0; Diagniscan, S.A.U., Group Werfen, Paris, France) | AHI ≥ 3/h (AASM 2007) |
| 2 | Alvarez et al., 2015 [24] | 6.95 ± 3.55 y | Suspected OSA | 176 | Part of reference PSG | ODI3 Statistical features Nonlinear features Spectral features | Digital PSG (Polysmith; Nihon Kohden America Inc., Irvine, CA, USA) | AHI ≥ 1/h AHI ≥ 3/h AHI ≥ 5/h (AASM 2007) |
| 3 | Alvarez et al., 2017 [25] | 3–13 y | Suspected OSA | 50 | Part of at-home RP (eXim Apnea Polygraph, Bitmed, Sibel S.A., Barcelona, Spain) | Avg SpO2 Min SpO2 ODI3 CT Statistical features | Attended PSG (Deltamed Coherence 3NT version 3.0; Diagniscan, S.A.U., Group Werfen, Paris, France) | OAHI ≥ 1/h OAHI ≥ 3/h OAHI ≥ 5/h (AASM 2007) |
| 4 | BarrosoGarcia et al., 2019 [26] | 6 y | Suspected OSA | 376 | Part of reference PSG | ODI3 Spectral features | Digital PSG (Polysmith; Nihon Kohden America Inc., Irvine, CA, USA) | AHI ≥ 1/h AHI ≥ 5/h AHI ≥ 10/h (AASM 2007) |
| 5 | Brietzke et al., 2007 [14] | 2–16 y | Sleep-related breathing disorders | 59 | Ambulatory device (Stowood Scientific Instruments, Oxford, England) | PTT | PSG (Bio-logic Systems Corporation, Mundelein, IL, USA) | AHI > 1/h AHI > 3/h AHI > 5/h (NIH Manual 1968) |
| 6 | Chan et al., 2019 [27] | 10.86 ± 4.22 y | Habitual snoring | 573 | Part of reference PSG | McGill Nadir SpO2 | Ambulatory PSG (Siesta, Compumedics) | AHI > 1/h AHI > 5/h (AASM 2007) |
| 7 | Chang et al., 2013 [28] | 1.8–12.8 y | Suspected OSA | 141 | Part of reference PSG | ODI3 | Standard PSG (Alice 5, Philips, Respironics, USA) | AHI > 5/h (AASM 2007) |
| 8 | Crespo et al., 2018 [45] | 1–13 y | Suspected OSA | 176 | Part of reference PSG | Statistical features ODI3 | Digital PSG (Polysmith; Nihon Kohden America Inc., CA, USA) | AHI ≥ 1/h AHI ≥ 3/h AHI ≥ 5/h (AASM 2012) |
| 9 | Evangelisti et al., 2016 [29] | 5.54–10.33 y 4.71–9 y | Suspected OSA (obese) Suspected OSA (non-obese) | 128 120 | Home nocturnal PO (Nonin Medical, Plymouth, MN, USA) | McGill ODI3 | Laboratory PSG (Grass Heritage polygraph; Natus Neurology IncorporatedeGrass Products, Warwick, RI, USA) | AHI ≥ 1/h 1/h ≤ AHI < 10/h AHI ≥ 5/h (AASM 2007) |
| 10 | Gutierrez-Tobal et al., 2015 [30] | 7.0 ± 3.6 y | Suspected OSA | 176 | Part of reference PSG | ODI3 MLP | Overnight PSG | AHI ≥ 1/h AHI ≥ 5/h (AASM 2012) |
| 11 | Hill et al., 2018 [31] | 0.5–6 y | Down syndrome | 161 | Home nocturnal PO Masimo Radical 7 device (Masimo, Irvine, CA, USA) | ODI3 Avg SpO2 Min SpO2 CT | Home CP (SOMNOtouch device; Somnomedics, Randersacker, Germany) | OAHI ≥ 5 (AASM 2012) |
| 12 | Hornero et al., 2017 [32] | 6.7 ± 4.4 y | Habitual snoring | 4191 | Part of reference PSG | Neural network analysis | Nocturnal PSG | AHI ≥ 1/h AHI ≥ 5/h (AASM 2012) |
| 13 | Hsieh et al., 2021 [33] | 6–10 y | OSA | 39 | Home nocturnal PO (3100WristOx, Nonin Medical, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) | ODI3 | Attended night PSG (Nicolet Biomedical Inc., Madison, WI, USA) | AHI ≥ 2/h (AASM 2012) |
| 14 | Jimenez-Garzia et al., 2020 [34] | 3–9 y | Suspected OSA | 390 | Part of reference PSG | ODI3 Nonlinear analysis Spectral analysis | Digital PSG (Nihon Kohden America Inc., Irvine, CA, USA) | AHI ≥ 1/h AHI ≥ 5/h AHI ≥ 10/h (AASM 2007) |
| 15 | Jonas et al., 2020 [35] | 4.75–38.5 mo | Suspected OSA | 110 | Hospital or at home PO | McGill | Laboratory PSG (Compumedics, Melbourne, Australia) | MOAHI ≥ 1 MOAHI ≥ 5 (NR) |
| 16 | Kirk et al., 2003 [36] | 4–18 y | Suspected OSA | 58 | At home portable monitor (SnoreSat, SagaTech Electronics, Calgary, AB, Canada) | DI | Laboratory PSG (Sandman NT; Nellcor Puritan Bennett; Ottawa, ON, Canada) | AHI > 5/h (ATS 1996) |
| 17 | Ma et al., 2018 [37] | 4–16 y | Snoring | 32 | PO Watch (CloudCare Healthcare Co., Ltd., Chengdu, China) | ODI4 | Laboratory PSG | AHI > 1/h AHI > 5/h AHI > 10/h AHI > 15/h AHI > 20/h (AASM 2012) |
| 18 | Makhout et al., 2022 [46] | 3.72 ± 0.26 y | Laryngomalacia | 53 | Nocturnal PO during PSG | McGill | Laboratory PSG | OAHI ≥ 2/h (AASM 2007) |
| 19 | PenaZarza et al., 2012 [38] | 2–15 y | Suspected OSA | 98 | Home nocturnal PO (3DI Pulsox Minolta) | McGill | Home Nocturnal Polygraphy (Sleepscreen, Viasys Healthcare GmBH, Hoechberg, Leibnizstr, Germany) | AHI ≥ 3/h AHI ≥ 5/h AHI ≥ 10/h (AASM 2007) |
| 20 | Polytarchou et al., 2022 [47] | 3.9–9.1 y | Suspected OSA | 98 | Part of reference PSG | ODI3 McGill | Laboratory PSG (EMBLA S4500 System) | AHI ≥ 5/h (AASM 2012) |
| 21 | Suzuki et al., 2017 [39] | 7 ± 2.6 y | Suspected OSA | 119 | Home nocturnal PO (PMP-200GplusX, Philips Respironics, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) | ODI3 | Type 1 laboratory overnight PSG (Alice 6, Philips Respironics, Pittsburgh, PA, USA) | AHI < 1/h AHI < 5/h AHI < 10/h (AASM 2016) |
| 22 | Trucco et al., 2019 [13] | 2.4–7.9 y | Suspected OSA | 312 | Transcutaneous monitoring (CombiM monitor, Radiometer, Copenhagen, Denmark | McGill | CP (SOMNOScreen™ plus, SOMNOmedics, Germany) | OAHI ≥ 1/h OAHI ≥ 5/h (NR) |
| 23 | Tsai et al., 2013 [15] | 7.18 ± 2.57 y | Suspected OSA | 148 | Part of reference PSG | DI | Overnight laboratory PSG (Sandman EliteTM, Nellcor Puritan Bennett [Melville] Ltd., Canada) | AHI ≥ 1/h AHI ≥ 5/h AHI ≥ 10/h (AASM 2007) |
| 24 | VanEyck et al., 2015 [40] | 6–17 y | Suspected OSA (obese) | 130 | Part of reference PSG (Xpod, Nonin, MN, USA) | ODI | Overnight laboratory PSG | OAHI ≥ 2/h (AASM 2007) |
| 25 | Vaquerizo-Villar et al., 2018 [41] | 0–13 y | Suspected OSA | 298 | Part of reference PSG | Bispectrum analysis | Overnight laboratory PSG (Polysmith; Nihon Kohden America Inc., CA, USA). | AHI ≥ 5/h AHI ≥ 10/h (NR) |
| 26 | Velasco Suarez 2013 [42] | 2–16 y | Suspected OSA | 167 | Part of reference PSG. PO (NONIN 8008JFW) | Visual analysis | Digital PSG (Akonic Neurotrace) | AHI ≥ 1/h (NR) |
| 27 | Villa et al., 2015 [43] | 5.93 ± 2.97 | Suspected OSA (SCR-positive) | 236 | First night PO (Nonin 2500A; NoninMedical) | McGill | Second night PSG (GrassHeritage; GrassTechnologies, Fort Myers, FL, USA) | 1/h ≤ AHI ≤ 5/h AHI > 5/h (AASM 2007) |
| 28 | Warapongmanupong et al., 2019 [44] | 6.7 ± 3.2 y | Snoring adenotonsillar hypertrophy | 457 | Part of reference PSG (Masimo SET Radical-7) | SpO2 SD | Overnight laboratory PSG (Grael system) | AHI ≥ 1.5/h AHI ≥ 5/h (AASM 2012) |
| N | First Author, Year of Publication | Sample Size | Prevalence | Severity | True Positive | False Positive | False Negative | True Negative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alvarez et al., 2015 [24] | 176 | 83.0 | Mild OSA | 94 | 5 | 52 | 25 |
| 40.3 | Moderate OSA | 63 | 32 | 8 | 73 | |||
| 2 | Barroso Garcia et al., 2019 [26] | 376 | 80.9 | Mild OSA | 182 | 10 | 122 | 62 |
| 37.5 | Moderate OSA | 98 | 25 | 43 | 210 | |||
| 21.3 | Severe OSA | 65 | 34 | 15 | 262 | |||
| 3 | Gutierrez-Tobal et al., 2015 [30] | 176 | 42.6 | Mild OSA | 59 | 20 | 16 | 81 |
| 40.3 | Moderate OSA | 49 | 19 | 22 | 86 | |||
| 4 | Hsieh et al., 2021 [33] | 39 | 53.8 | Severe OSA | 19 | 3 | 2 | 15 |
| 5 | Jimenez-Garzia et al., 2020 [34] | 390 | 80.8 | Mild OSA | 181 | 10 | 134 | 65 |
| 37.4 | Moderate OSA | 102 | 27 | 44 | 217 | |||
| 21.3 | Severe OSA | 68 | 38 | 15 | 269 | |||
| 6 | Suzuki et al., 2017 [39] | 119 | 54.8 | Moderate OSA | 30 | 10 | 36 | 43 |
| 38.5 | Severe OSA | 29 | 11 | 17 | 62 |
| Number of Studies | Number of Participants | Sensitivity (95% Confidence Interval) | Specificity (95% Confidence Interval) | Positive Predictive Value (95% Confidence Interval) | Negative Predictive Value (95% Confidence Interval) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild OSA | 4 | 1118 | 61% (58–65%) | 84% (79–88%) | 91% (88–93%) | 46% (44–49%) |
| Moderate OSA | 5 | 1237 | 69% (65–73%) | 85% (82–87%) | 77% (73–80%) | 79% (77–81%) |
| Severe OSA | 4 | 924 | 79% (73–84%) | 88% (85–90%) | 76% (72–80%) | 89% (87–91%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Incerti Parenti, S.; Bartolucci, M.L.; Fiordelli, A.; Gigola, P.; Paganelli, C.; Alessandri-Bonetti, G. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Overnight Oximetry for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10208. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210208
Incerti Parenti S, Bartolucci ML, Fiordelli A, Gigola P, Paganelli C, Alessandri-Bonetti G. The Diagnostic Accuracy of Overnight Oximetry for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(22):10208. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210208
Chicago/Turabian StyleIncerti Parenti, Serena, Maria Lavinia Bartolucci, Andrea Fiordelli, Pierangelo Gigola, Corrado Paganelli, and Giulio Alessandri-Bonetti. 2024. "The Diagnostic Accuracy of Overnight Oximetry for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Applied Sciences 14, no. 22: 10208. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210208
APA StyleIncerti Parenti, S., Bartolucci, M. L., Fiordelli, A., Gigola, P., Paganelli, C., & Alessandri-Bonetti, G. (2024). The Diagnostic Accuracy of Overnight Oximetry for Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Applied Sciences, 14(22), 10208. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210208








