Abstract
Accurate posture detection is the foundation for analyzing animal behavior, which can promote animal welfare. With the development of computer vision, such technology has been widely used in analyzing animal behavior without physical contact. However, computer vision technology for pig posture detection often suffers from problems of missed or false detection due to complex scenarios. To solve the problem, this study proposed a novel object detection model YOLOv5DA, which was based on YOLOv5s and designed for pig posture detection from 2D camera video. Firstly, we established the annotated dataset (7220 images) including the training set (5776 images), validation set (722 images), and test set (722 images). Secondly, an object detection model YOLOv5DA based on YOLOv5s was proposed to recognize pig postures (standing, prone lying, and side lying), which incorporated Mosaic9 data augmentation, deformable convolution, and adaptive spatial feature fusion. The comparative and ablation experiments were conducted to verify the model’s effectiveness and reliability. Finally, we used YOLOv5DA to detect the posture distribution of pigs. The results revealed that the standing posture was more frequent in the morning and afternoon and the side-lying posture was most common at noon. This observation demonstrated that the posture of pigs is influenced by temperature variations. The study demonstrated that YOLOv5DA could accurately identify three postures of standing, prone lying, and side lying with an average precision (AP) of 99.4%, 99.1%, and 99.1%, respectively. Compared with YOLOv5s, YOLOv5DA could effectively handle occlusion while increasing the mean precision (mAP) by 1.7%. Overall, our work provided a highly accurate, effective, low-cost, and non-contact strategy of posture detection in grouped pigs, which can be used to monitor pig behavior and assist in the early prevention of disease.
1. Introduction
The behaviors of pigs can reflect their growth conditions and comfort in the growing environment. Detecting pig behaviors can provide early warning of pig diseases, identify the factors affecting pig health, and prevent economic losses caused by widespread infection [1]. The accurate identification of pig postures serves as a crucial indicator of their behavior.
Pig posture detection can help predict the health and comfort of a pig [2], which can avoid the spread of disease and improve the profitability of pigs. Besides that, pig posture detection can improve the accuracy of pig body size measurement [3]. The change in temperature affects the posture of the pig. In general, pigs prefer to lie down under comfortable conditions, and at high ambient temperatures, they may be in postures of side lying [4]. Traditionally, identification of pig postures is often based on manual direct observation, which is not only cumbersome and inefficient but also easily causes stress in pigs. With the development of computer technologies, non-contact vision technology has been gradually applied in pig farming, and deep learning methods have been widely used in animal detection and tracking [5,6,7,8], which are accurate, low-cost, and stress-free methods.
In traditional posture detection methods, the collection of pigs’ posture and location information primarily relies on on-site observation or surveillance systems [9]. However, during the evaluation process, differences in the interpretation of postures inevitably arise due to the subjectivity of individual evaluators [10].
With the evolution of computer vision, object detection serves as a common method for posture detection. The goal of object detection is to accurately identify and enclose all the visible pigs within minimal bounding boxes, while simultaneously classifying each bounding box based on the specific behavior that needs to be extracted [11,12,13,14]. The R-FCN ResNet101 [15] method and the Faster R-CNN [16,17] technology can effectively detect the three basic postures of pigs—standing, lying on the side, and lying on the belly—with high accuracy. Additionally, Faster R-CNN [16] is capable of precisely identifying the sitting and sternal recumbent postures. The two-stage algorithmic framework, while exhibiting excellent precision, is comparatively slower in processing speed.
Therefore, there is a growing preference for single-stage methods. These methods simultaneously estimate object positions and classify categories in a single computational process, thereby significantly enhancing processing speed. The widely used YOLO series has achieved a superior balance between speed and accuracy among single-stage detection algorithms [18]. The YOLOv5 algorithm is utilized for initial pig detection, with the EfficientNet model then classifying pigs as “lying” or “not lying” [19]. YOLOX’s enhancements have notably boosted the detection and recognition of pigs’ various postures, day or night [20]. Additionally, the HE-Yolo model, an advanced version of YOLOv5, accurately identifies four key pig postures: standing, sitting, lying prone, and lying on one side [21]. However, current methods for pig posture detection often result in blurred or missed detection of the object box boundary due to occultation and adhesion of pigs, and their detection accuracy still needs to be further improved [18].
To address the above-mentioned issues, this study introduced an enhanced YOLOv5DA model derived from YOLOv5s, which generally has three improvements: Mosaic9 data augmentation [22], deformable convolution [23], and adaptive spatial feature fusion [24].
Our primary contribution is the development of a model that can efficiently discern three distinct pig postures—standing, prone lying, and side lying—even in crowded and obstructed environments, using 2D camera video. Compared to other mainstream algorithms, our model achieves higher accuracy and faster detection speeds. Overall, YOLOv5DA can accurately identify different postures of pigs and effectively reduce missed or false detections. This can enhance the utilization of intelligent techniques within the realm of animal husbandry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
The data used were collected from a pig farm in Wuhan from 1 July 2021 to 1 October 2021, and the subjects were landrace pigs aged 90–180 days. The original RGB video of the experiment was collected by a Hikvision DS-2CD3346FWDA3-1 camera, placed about 3 m above the ground. This camera can capture video images at a resolution of 2560 * 1440. To ensure the diversity of data, we selected monitoring videos of four columns of live pigs for the experiment, with about ten pigs raised in each column.
2.2. Dataset Construction
To accurately recognize the different postures of pigs, we annotated a dataset with the following steps.
- (1)
- The captured surveillance videos were processed into frames, with one frame being extracted every two seconds and removal of similar images inside. After processing, a total of 7220 images were obtained.
- (2)
- The obtained images were annotated with the LabelMe annotation tool [25], which annotated the position of each pig and their posture categories (standing, side lying, and prone lying) in each picture [15]. As shown in Figure 1, we assigned the pigs in standing posture a yellow bounding box, the pigs in side-lying posture a green bounding box, and the pigs in prone-lying posture a light blue bounding box.
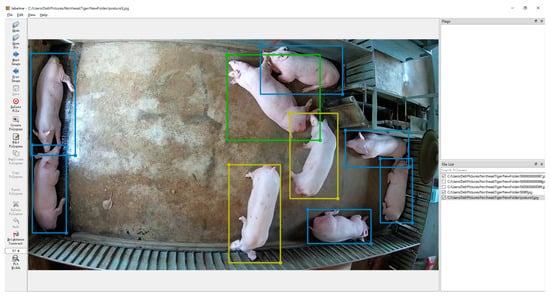 Figure 1. Examples of pig posture dataset annotation (the yellow bounding box represents the standing pig, the green bounding box represents the side-lying pig, and the light blue bounding box represents the prone-lying pig).
Figure 1. Examples of pig posture dataset annotation (the yellow bounding box represents the standing pig, the green bounding box represents the side-lying pig, and the light blue bounding box represents the prone-lying pig). - (3)
- The annotated images were then divided into the training set, validation set, and test set using the random sampling technique with an 8:1:1 ratio, which corresponded to 5,776, 722, and 722 pictures, respectively. Then, the total number of samples in the divided pictures and the number of samples from three different postures were counted, and the statistical results are shown in Table 1.
 Table 1. Datasets of pig posture detection.
Table 1. Datasets of pig posture detection.
2.3. YOLOv5
Among single-target detection algorithms, the YOLO series has been widely used owing to its simple network structure and fast detection speed [26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. The YOLO series is pivotal in object detection, noted for its efficiency and simplicity.
As the epitome of the YOLO series, YOLOv5 not only possesses faster inference speed but also has better detection performance. The YOLOv5 [22] series includes YOLOv5n, YOLOv5s, YOLOv5m, YOLOv5l, and YOLOv5x [33]. Here, we selected YOLOv5s with better detection performance as the base network for improvement. Figure 2 shows the network structure of YOLOv5s, which mainly consists of the Backbone, Neck, and Head. The Backbone module mainly consists of CBS, C3, and Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast (SPPF), and is mainly used for the extraction of image features. The Neck module is composed of a feature pyramid network (FPN) [34] and path aggregation network (PAN) [35], and is mainly used to fuse different scale features extracted from the Backbone to further learn richer semantic information. The Head module is set to adjust the number of channels of different scale feature maps to N × (C+5) by a 1 × 1 convolution. N denotes the number of anchors used in each different scale feature layer; C denotes the number of categories in the dataset; and 5 represents the four regression parameters (x, y, w, and h) and an object confidence score P. The main function of the Head is to convert the features extracted by the Neck into the final prediction results.
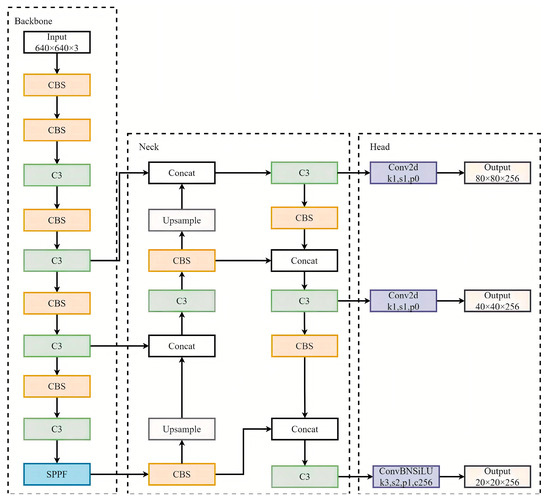
Figure 2.
YOLOv5s model structure [22].
2.4. YOLOv5DA
When pigs are housed in groups, it is common for live pigs to gather, shelter, and adhere, which often causes missed or false detections in the object detection model. This issue arises from the scarcity of small targets within the dataset, coupled with the YOLOv5 model’s constrained ability to extract features from irregularly shaped objects.
To further reduce the detection errors and missing rate of the object detection model, we made three improvements to YOLOv5s to obtain the YOLOv5DA model. Firstly, in data preprocessing, the Mosaic9 data augmentation method was used to increase the number of small targets in the dataset; secondly, deformable convolution was introduced into the feature extraction network (Backbone) for flexible sampling positions; finally, adaptive spatial feature fusion was introduced in the Head to adaptively learn the fusion weights of different scale features. In the following sections, we will provide detailed explanations of these three optimizations. The final model structure diagram is shown in Figure 3.
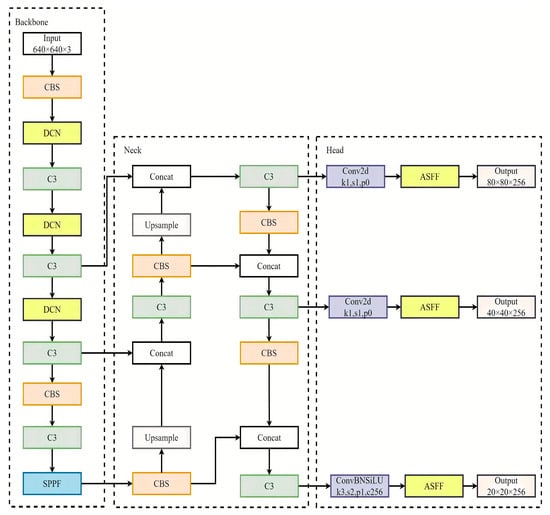
Figure 3.
YOLOv5DA model structure diagram.
- (1)
- Mosaic9 data augmentation
Group-housed pigs often gather and block each other, which will generate more small targets in the image [36], which may largely reduce the detection accuracy of object detection. To address this issue, we introduced the Mosaic9 data augmentation method in data preprocessing [22].
Figure 4 shows the specific implementation process. Firstly, this method randomly selects nine images from the training images of a batch size, and then each image is randomly cropped and zoomed. Finally, the nine cropped and zoomed images are reassembled into a new image, which is repeated multiple times to form multiple enhanced images for model training.
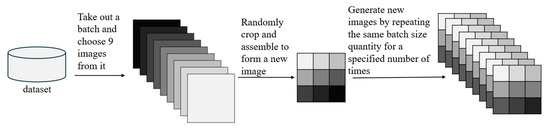
Figure 4.
Schematic Diagram of Mosaic9 Data Augmentation: Adapted from Reference [22].
The utilization of Mosaic9 data augmentation in the training set can augment the number of small targets in the dataset and enhance the background information of the samples [37]. Thereby it boosted the model’s generalization and detection capabilities for small targets, ultimately improving the object detection model’s performance.
- (2)
- Deformable convolution
Under group housing conditions, pigs tend to gather and block, which inevitably leads to irregular shapes of individuals. Traditional convolution always uses fixed-size convolution kernels for sampling at fixed positions in the feature map, which greatly limits the modeling’s ability to handle irregular objects. To address this issue, we introduced a more flexible deformable convolution (DC) [23] into the feature extraction network (Backbone).
Figure 5 shows the specific implementation process of deformable convolution. Firstly, based on the input image, traditional convolutional kernels are used to extract the feature maps. Secondly, the acquired feature maps are fed into the model as input, and an additional convolutional layer is incorporated to generate the deformation offset required for deformable convolution. Among them, the offset layer is 2N, where 2 indicates the 2D offsets X and Y, respectively, and N is the number of channels. Then, the offset of the obtained deformable convolution deformation is added to the feature map extracted in the first step to obtain the offset position. Next, the bilinear interpolation algorithm is used to obtain the pixels at each position after the offset to obtain the output feature map. Finally, the newly obtained output feature map is used as input data to the next layer for subsequent feature extraction. During training, the convolutional kernels used to generate feature maps extracted in the first step and offsets extracted in the second step are synchronously learned. Learning of the offset is achieved through backpropagation using bilinear interpolation algorithms. The expression of the output feature map is shown in Equation (1), where represents the offset of convolutional kernel elements relative to the center of the convolutional kernel, indicates the set of all , represents the coordinates of the convolutional kernel center relative to the upper left corner of the input feature map, represents an offset of deformable convolution deformation, usually in decimal places. presents a weight function, in which is used as input to output the weight of the coordinate position , and the weight corresponding to each coordinate is known. represents the original coordinate value plus the generated offset coordinate value, which results in a new coordinate value. means to input the new coordinate value and output the pixel corresponding to its coordinates obtained by bilinear interpolation. The expression of is shown in Equation (2), where represents the coordinates of all pixels in the image and stands for the input of a coordinate value and the output of its corresponding pixel value. The pixel values corresponding to each integer coordinate are known. represents the weight corresponding to coordinate . The expression of is shown in Equation (3), where and represent the abscissa of pixel point and p in the image, respectively. and indicate the vertical coordinates of pixel point and p in the image, respectively. represents the calculated weight. The expression of is shown in Equation (4), which means that when the difference between two coordinate values is between 0 and 1, the weight is 1 minus their difference, and if their difference is greater than 1, the weight is 0.
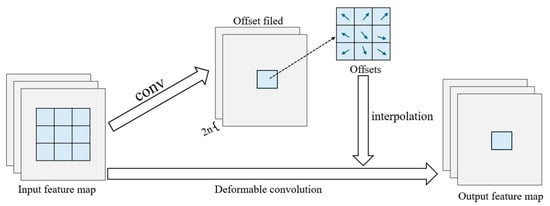
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of deformable convolution operation: Adapted from Reference [23].
Compared with traditional convolution, deformable convolution increases the learnable coordinate offsets, making the sampling position flexible, and thus the extracted features can better match the shape of the target object [38], which greatly improves the modeling ability of the model for irregular objects [39].
- (3)
- Adaptive Spatial Feature Fusion
Mainstream research usually uses a feature pyramid structure to utilize semantic information at high levels and spatial information at low levels. YOLOv5s adopts a feature pyramid structure attached to a bottom-up path aggregation network to learn richer semantic information. However, it fails to consider the varying significance of features across different resolutions during the process of multi-scale feature fusion. Direct addition of elements from adjacent feature layers or concatenating feature layers into the depth direction usually cannot achieve the best detection performance [40]. To address this issue, we introduced adaptive spatial feature fusion [24] in the Head.
Figure 6 shows the diagram of this structure, which is mainly completed in two steps: size adjustment and adaptive fusion. Size adjustment is mainly achieved through three operations: up sampling, maximum pooling, and down sampling. For up sampling, the method first uses a 1 × 1 convolution to adjust the number of channels to the same size and then employs the nearest neighbor interpolation to enlarge the size. For 1/2 rate down sampling, it directly uses a 3 × 3 convolution with a step of 2 to complete. For 1/4 rate down sampling, it first uses a maximum pooling with a step of 2 and then processes it using a 3 × 3 convolution with a step of 2. Adaptive fusion starts with the adaptive fusion of features at different scales after size adjustment. The fusion process is shown by taking ASFF-1 in Figure 6 as an example. The fusion formula is shown in expression (5), where and respectively represent the features from level 2 and level 3, which are scaled to generate feature maps of the same size as . For weight parameters , and , the feature maps of level 1, level 2, and level 3 after scaling are processed through a 1 × 1 convolution to obtain , , and . Then, the obtained , , and are adjusted to range within [0, 1] using the softmax function as shown in expression (6), making their sum 1.
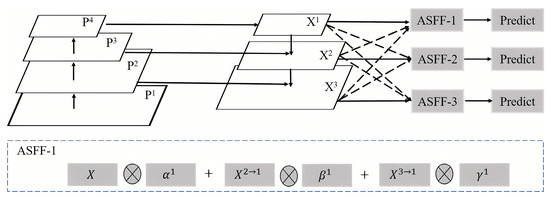
Figure 6.
Adaptive spatial feature fusion structure diagram [24].
Spatial feature fusion can adaptively learn the fusion weights of different scale features, allowing the model to filter invalid information and retain valid information. This enabled the model to fully utilize features at different scales [41], thereby improving the feature extraction and the detection ability of the model in complex scenarios [42].
2.5. Experimental Environment
For pig posture detection experiments, the experimental environment used in this study is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Configuration information of the experimental environment.
In the training process of the pig posture detection model, to reduce memory occupation, all images were uniformly scaled to 640 × 640. To optimize the model, the stochastic gradient descent (SGD) optimizer was employed. SGD is an optimization method that tweaks model settings based on the loss function’s gradient. The initial learning rate (the learning rate controls how much the model’s settings change with each update) was 0.01, and the momentum (momentum helps speed up learning by combining past and current adjustments) was 0.937. All models were trained for 210 rounds, and the rest of the hyperparameters were set by the model default.
2.6. Performance Evaluation
For pig posture detection, this study employed multiple indicators to evaluate the performance of the model, including intersection over union (IoU), precision, recall, average precision (AP), mean average precision (mAP), parameters (Params), and floating point operations (FLOPs). IoU is mainly used to measure the degree of overlap between predicted and manually annotated bounding boxes. Its value ranges from 0 to 1, with a value closer to 1 indicating that the predicted bounding box is closer to the real bounding box [43]. Precision quantifies the accuracy of model predictions by measuring the proportion of correct predictions among all detected targets. Recall measures the effectiveness of the model by indicating the proportion of correct predictions among all positive samples [44]. AP, which is defined as the integration of precision and recall, refers to the area under the P-R curve plotted with recall as the x-axis and precision as the y-axis [45], and mAP is obtained by averaging multiple categories of AP. In pig posture detection experiments, unless otherwise specified, the parameters are taken by default. AP represents the average accuracy calculated when the IoU is equal to 0.5, and mAP indicates the average accuracy calculated at intervals of 0.05 for IoU from 0.5 to 0.95. Params are indicators to measure the space complexity of the model [46]. FLOPs are used to measure the time complexity of models [47]. In experiments, GFLOPs are often used as the unit of measurement for FLOPs.
3. Results
3.1. Training Evaluation
We trained our pig posture model with all images at 640 × 640. We used SGD with a learning rate of 0.01 and momentum of 0.937, training for 210 epochs, and kept other settings at their defaults. Figure 7 illustrates the training loss fluctuation of the object detection model, highlighting that YOLOv5DA experiences a swift initial reduction in loss, followed by a slow stabilization, and ultimately achieves convergence as the iteration count increases.
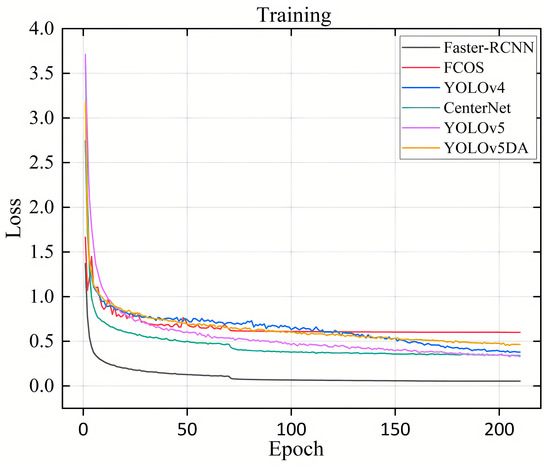
Figure 7.
Loss curve of the object detection model.
Figure 8 displays the mAP of the object detection model on the validation set. The results demonstrated that as the number of iterations increased, all models exhibited continuous improvement in mAP and ultimately converged to higher accuracy. It is worth noting that the YOLOv5DA model can converge with the highest accuracy.
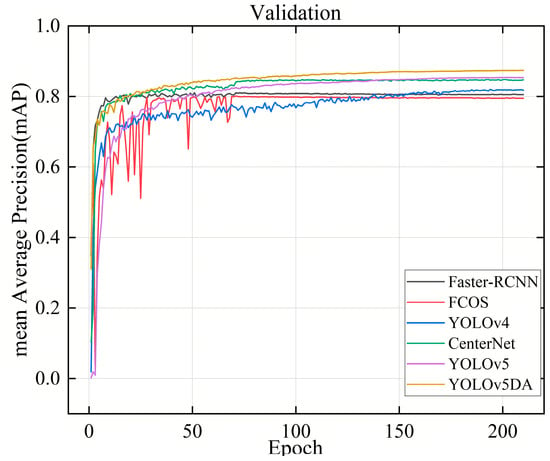
Figure 8.
mAP curve of the object detection model.
3.2. Results and Analysis of Ablation Experiments
We have made three improvements on YOLOv5s, and in order to verify the effectiveness of each module, ablation experiments were conducted on the same dataset. As shown in Table 3, the use of Mosaic9 data augmentation can increase the mAP of the model by 0.7%, indicating that by augmenting the number of small targets, the method can enhance the detection ability of the model. In addition, the replacement of traditional convolutions with deformable convolution in the feature extraction network (Backbone) can increase the mAP of the model by 0.3%, indicating that deformable convolution can contribute to flexible sampling positions, thereby further improving the model’s modeling ability for irregular objects. Furthermore, the introduction of adaptive spatial feature fusion into the Head increased the mAP of the model by 0.7%, despite a small increase in model parameters and computational complexity, indicating that the module can adaptively learn weight fusion between different features, fully utilize features of different scales, and enhance the model’s feature extraction capability. Compared to traditional YOLOv5s, the improved YOLOv5DA can achieve better detection performance, whose mAP was increased by 1.7% and reached 86.8%, indicating that the above three optimizations are effective and can further improve the robustness of the model.

Table 3.
Ablation experiments of YOLOv5DA on pig posture dataset.
3.3. Results and Analysis of Comparative Experiments
To validate the efficacy of YOLOv5DA, we conducted a comparative experiment with several mainstream object detection algorithms, including Faster-RCNN, YOLOv4, YOLOv5, FCOS [48], and CenterNet on the same pig posture dataset. As shown in Table 4, compared to other models, YOLOv5s achieves higher accuracy while utilizing fewer model parameters and FLOPs. Consequently, we chose YOLOv5s as the benchmark model for further enhancement. The enhanced model, YOLOv5DA, can accurately recognize the standing, prone-lying, and side-lying postures of pigs with an AP of 99.4%, 99.1%, and 99.1%, respectively. Compared with YOLOv5s, despite a slight increase in computational complexity, YOLOv5DA exhibited a notable 1.7% improvement in mAP, resulting in superior detection performance. Furthermore, when compared with other mainstream object detection algorithms, YOLOv5DA demonstrated the ability to attain the highest detection accuracy while utilizing the fewest model Params and FLOPs. This further supports the effectiveness of YOLOv5DA for accurately identifying various postures of pigs.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of different object detection models on pig posture.
To further verify the detection effect of YOLOv5DA, we selected two images to compare YOLOv5DA and YOLOv5s. It can be observed that the mutual occlusion of live pigs poses a challenge for YOLOv5s, leading to missed detections (represented by red dashed boxes in Figure 9a,c); however, YOLOv5DA can effectively identify the missed targets (Figure 9b,d). In addition, the pig with the side-lying posture at the top of Figure 9c was incorrectly identified as a prone-lying pig (indicated by the red arrow) by YOLOv5s; however, YOLOv5DA can accurately identify the posture category (Figure 9d). Figure 9 revealed that YOLOv5 exhibited omissions in detecting two pigs and misclassification in identifying one pig. These results also demonstrated that YOLOv5DA can effectively deal with missed or false detection and can be used to continuously monitor the growth of pigs and better protect animal welfare.
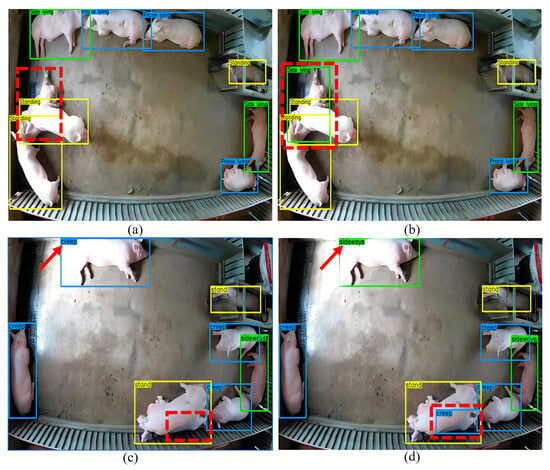

Figure 9.
Detection results of pig posture by YOLOv5s and YOLOv5DA. (a,c) represent the detection results of YOLOv5s; (b,d) represent the detection results of YOLOv5DA; the yellow bounding box represents the standing pig, the green bounding box represents the side-lying pig, and the light blue bounding box represents the prone-lying pig.
3.4. Posture Distribution
The postures of pigs in a pen (7 to 14 September 2021) were detected using YOLOv5DA, with three periods monitored each day: approximately 7:00–8:30 in the morning, 12:00–13:30 at noon, and 16:00–17:30 in the afternoon. Figure 10a shows the proportion of postures over three periods of eight days, and the results indicated that the standing posture was mainly concentrated in the morning and afternoon and was the least common at noon. Figure 10b shows the average proportion of postures over three periods of eight days, and the proportion of standing postures was 47.38% in the morning, 37.18% in the afternoon, and 16.84% at noon. In the morning and afternoon, the proportion of side lying posture was 27.48% and 24.57% lower than those of the prone-lying posture, respectively. However, the proportion of side-lying posture was predominant at noon, surpassing the proportion of prone-lying posture by 29.92% and reaching 59.54%.
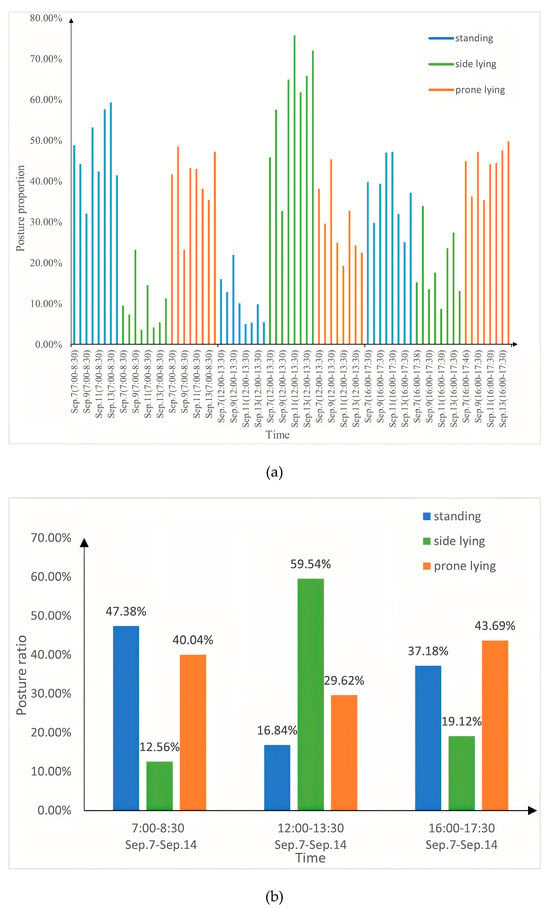
Figure 10.
(a) The proportions of pig postures for three periods from September 7 to 14. (b) The average proportions of pig postures over three periods of eight days. The blue bar depicts the proportion of standing postures, the green bar depicts the proportion of side-lying postures, and the orange bar depicts the proportion of prone-lying postures.
This study detected the posture of pigs in a pen over 8 days, focusing on three specific periods. The results proved the standing posture was predominantly focused in the morning and afternoon, which showed that the pigs are typically more active in the morning and afternoon. The reason may be that the posture of the pigs is influenced by temperature: as the temperature rises, pigs spend less time standing to facilitate faster heat dissipation [49]. When the temperature is highest at noon, pigs choose to lie down instead of standing. The proportion of side-lying postures exceeded the proportion of prone-lying postures by 29.92%, reaching a maximum of 59.54% at noon. The temperature is likely highest at noon, so the pigs adopt the side-lying posture to maximize their body surface contacting the cooler floor, facilitating the dispersion of excess body heat resulting from the elevated ambient temperature [50].
4. Conclusions
This study introduced a posture detection model called YOLOv5DA based on YOLOv5s, which utilizes 2D camera video to identify three postures (standing, side lying, and prone lying) in grouped pigs that may cause the problems of missed or false detection. The experimental results demonstrated that YOLOv5DA achieved an average accuracy of 99.4%, 99.1%, and 99.1% in identifying standing, prone-lying and side-lying pig postures, respectively. Compared to other mainstream object detection algorithms, YOLOv5DA achieves both high accuracy and low FLOPs. By analyzing changes in pig postures over three eight-day periods using YOLOv5DA, our study inferred the variations in pig postures that are associated with changes in environmental temperature, which can improve animal health and welfare. Our work demonstrated that YOLOv5DA, a low-cost, accurate, and stress-free model, is effective and can be used for accurate posture detection in complex scenarios to reduce missed or false detections. This study could be used to monitor the health and well-being status of pigs and prevent animal diseases. Moreover, this study lays the foundation for the sustainable development of intelligent techniques for pig breeding.
Author Contributions
W.S.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Model building, Experiment, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. W.S. and X.W. contributed equally to this work. X.W.: Data acquisition, Experiment, Investigation, Resources, Project administration, Writing—original draft. X.L. (Xuan Li): Equipment setup, Investigation, Resources, Data acquisition, Y.F.: Investigation, Validation, Data analysis. X.L. (Xiaolei Liu): Methodology, Data acquisition. H.W.: Conceptualization, Project administration, Validation, Review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFF1000500, 2022YFD1601903), the HZAU-AGIS Cooperation Fund (SZYJY2022034, SZYJY2022031), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (2662023PY008, 2662022XXYJ009).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available at https://drive.google.com/drive/my-drive, accessed on 1 August 2024. Our study has been previously released as a preprint, and it can be accessed via the following DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3262083/v1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors do not have conflicts of interest.
References
- Larsen, M.L.; Wang, M.; Norton, T. Information technologies for welfare monitoring in pigs and their relation to Welfare Quality®. Sustainability 2021, 13, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, G. Using floor cooling as an approach to improve the thermal environment in the sleep area in an open pig house. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 93, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, H. A Review of Posture Detection Methods for Pigs Using Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, S.; Xu, A.; Ye, J.; Zhao, A. Automatic scoring of postures in grouped pigs using depth image and CNN-SVM. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 194, 106746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.; Matheson, S.M.; Plötz, T.; Edwards, S.A.; Kyriazakis, I. Porcine lie detectors: Automatic quantification of posture state and transitions in sows using inertial sensors. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 127, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassinari, P.; Bovo, M.; Benni, S.; Franzoni, S.; Poggi, M.; Mammi, L.M.E.; Mattoccia, S.; Di Stefano, L.; Bonora, F.; Barbaresi, A.; et al. A computer vision approach based on deep learning for the detection of dairy cows in free stall barn. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 182, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Jing, T.; Sun, D.; Gao, P.; Wang, W.; Lu, J.; Yetan, R.; et al. Litchi Detection in a Complex Natural Environment Using the YOLOv5-Litchi Model. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Zong, C.; Yang, T.; Peng, S.; Zhu, P.; Wang, H.; Teng, G.; Du, X. Detection and analysis of sow targets based on image vision. Agriculture 2022, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonderland, J.J.; van Riel, J.W.; Bracke, M.B.; Kemp, B.; den Hartog, L.A.; Spoolder, H.A. Tail posture predicts tail damage among weaned piglets. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 121, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugmann, K.L.; Mieloch, F.J.; Krieter, J.; Czycholl, I. Can Tail and Ear Postures Be Suitable to Capture the Affective State of Growing Pigs? J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2021, 24, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Liu, Z.; Cui, Q. Multi-target detection based on feature pyramid attention and deep convolution network for pigs. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2020, 36, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Q.; Cai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Application of deep learning in sheep behaviors recognition and influence analysis of training data characteristics on the recognition effect. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Song, Z.; Yan, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Tian, F. Teat detection of dairy cows based on deep learning neural network FS-YOLOv4 model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirahmadi, A.; Sturm, B.; Edwards, S.; Jeppsson, K.-H.; Olsson, A.-C.; Müller, S.; Hensel, O. Deep learning and machine vision approaches for posture detection of individual pigs. Sensors 2019, 19, 3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Zhu, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Tu, S.; Xue, Y. Automatic recognition of lactating sow postures from depth images by deep learning detector. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 147, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekert, M.; Klein, A.; Adrion, F.; Hoffmann, C.; Gallmann, E. Automatically detecting pig position and posture by 2D camera imaging and deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Tan, Z.; Liu, K.; Chen, M. An Improved Pig Counting Algorithm Based on YOLOv5 and DeepSORT Model. Sensors 2023, 23, 6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, J.-H.; Gómez, J.M. Introducing a new Workflow for Pig Posture Classification based on a combination of YOLO and EfficientNet. In Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Honolulu, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zou, Z.; Huang, P. Efficient Detection Method of Pig-Posture Behavior Based on Multiple Attention Mechanism. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1759542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Yu, J.; Lao, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Teng, G. Automatic position detection and posture recognition of grouped pigs based on deep learning. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultralytics. YOLOv5 2020. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Learning spatial fusion for single-shot object detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.09516. [Google Scholar]
- Torralba, A.; Russell, B.C.; Yuen, J. Labelme: Online image annotation and applications. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1467–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Ergu, D.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Ma, B. A Review of Yolo algorithm developments. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 199, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, E.; Liang, Z. Apple detection during different growth stages in orchards using the improved YOLO-V3 model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, W. Faster-YOLO: An accurate and faster object detection method. Digit. Signal Process. 2020, 102, 102756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Farhadi, A.; Redmon, J. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 1804, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wangm, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Uzar, M.; Öztürk, Ş.; Bayrak, O.C.; Arda, T.; Öcalan, N.T. Performance analysis of YOLO versions for automatic vehicle detection from UAV images. Adv. Remote Sens. 2021, 1, 16–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Li, T.; Shi, P. A smoke detection model based on improved YOLOv5. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacal, I.; Karaboga, D. A robust real-time deep learning based automatic polyp detection system. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, S.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Shi, C.; Li, D.; Zhao, R. A lightweight dead fish detection method based on deformable convolution and YOLOV4. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yan, J.; Chen, M.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, L. A multi-scale deformable convolution network model for text recognition. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Graphics and Image Processing (ICGIP 2021), Kunming, China, 18–20 August 2021; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; Volume 12083. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chen, H. Attention-based fusion factor in FPN for object detection. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 15547–15556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yu, J. RetinaNet with difference channel attention and adaptively spatial feature fusion for steel surface defect detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 2503911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Guo, Y.; He, D. Cattle body detection based on YOLOv5-ASFF for precision livestock farming. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 204, 107579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, P.; Kukreja, V.; Manoharan, P.; Kaur, A.; Kamruzzaman, M.M.; Ben Dhaou, I.; Iwendi, C. A novel deep learning model for detection of severity level of the disease in citrus fruits. Electronics 2022, 11, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, G.; Tan, C.; Huang, L.; Sun, Y.; Kong, J. Semantic segmentation for multiscale target based on object recognition using the improved Faster-RCNN model. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 123, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fan, Y.; Cai, T.; Liu, W.; Hu, Z.; Wang, N.; Wu, M. OTL-classifier: Towards imaging processing for future un-manned overhead transmission line maintenance. Electronics 2019, 8, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Fan, S.; Song, R.; Jin, J. Object Detection Based on YOLOv5 and GhostNet for Orchard Pests. Information 2022, 13, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadosey, P.K.; Li, Y.; Agyekum, E.A.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.; Yamak, P.T.; Essaf, F. SD-UNET: Stripped down U-net for seg-mentation of biomedical images on platforms with low computational budgets. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Spoolder, H.A.; Aarnink, A.A.; Vermeer, H.M.; van Riel, J.; Edwards, S.A. Effect of increasing temperature on space requirements of group housed finishing pigs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 138, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.; Aarnink, A.; Gerrits, W.; Heetkamp, M.; Canh, T.; Spoolder, H.; Kemp, B.; Verstegen, M. Thermal behaviour of growing pigs in response to high temperature and humidity. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2005, 91, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).