Discrete-Event Simulation Integrates an Improved NEH Algorithm for Practical Flowshop Scheduling Problems in the Satellite Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
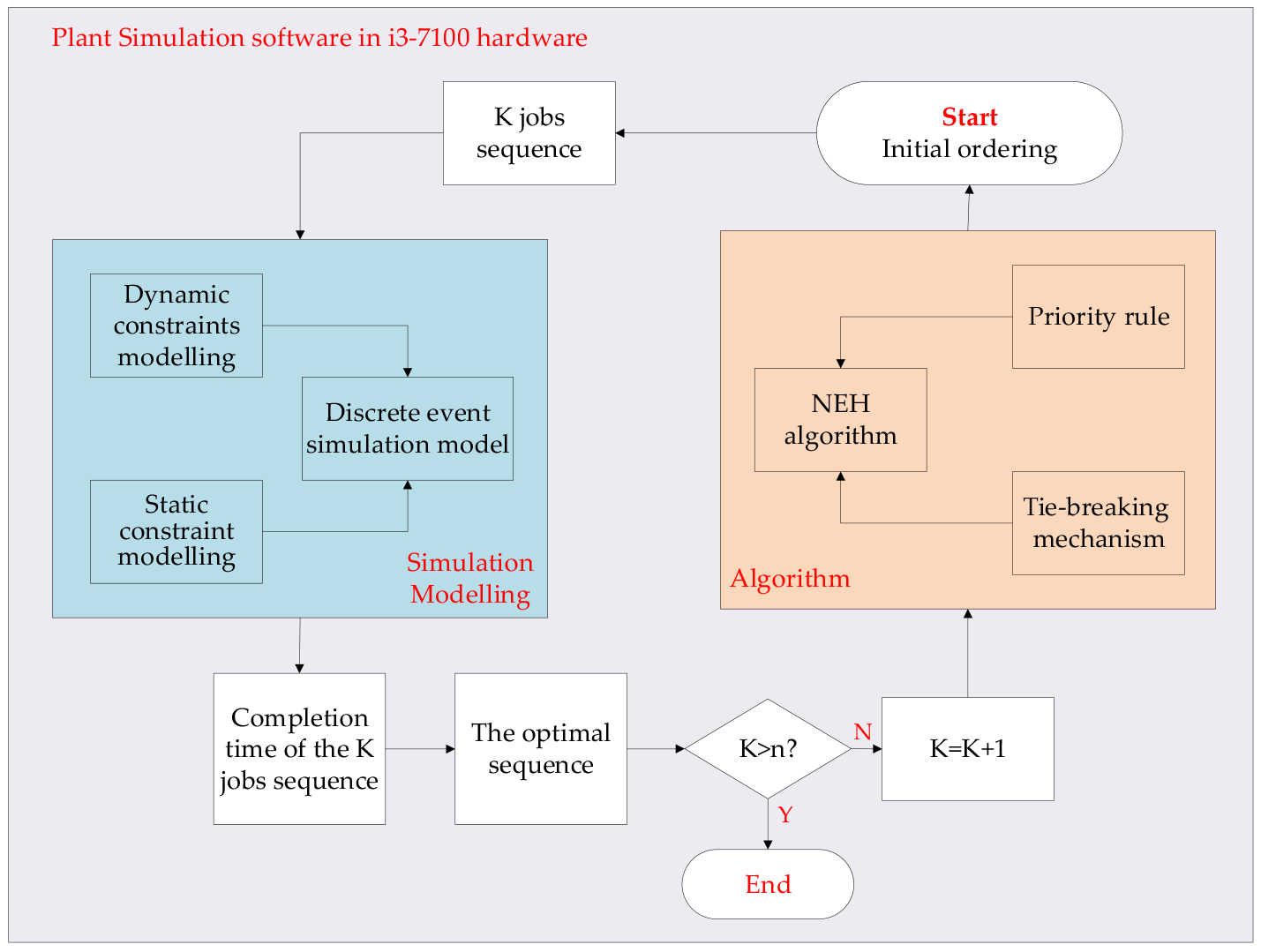
2. Discrete-Event-Simulation-Based Method
2.1. Research Methodology
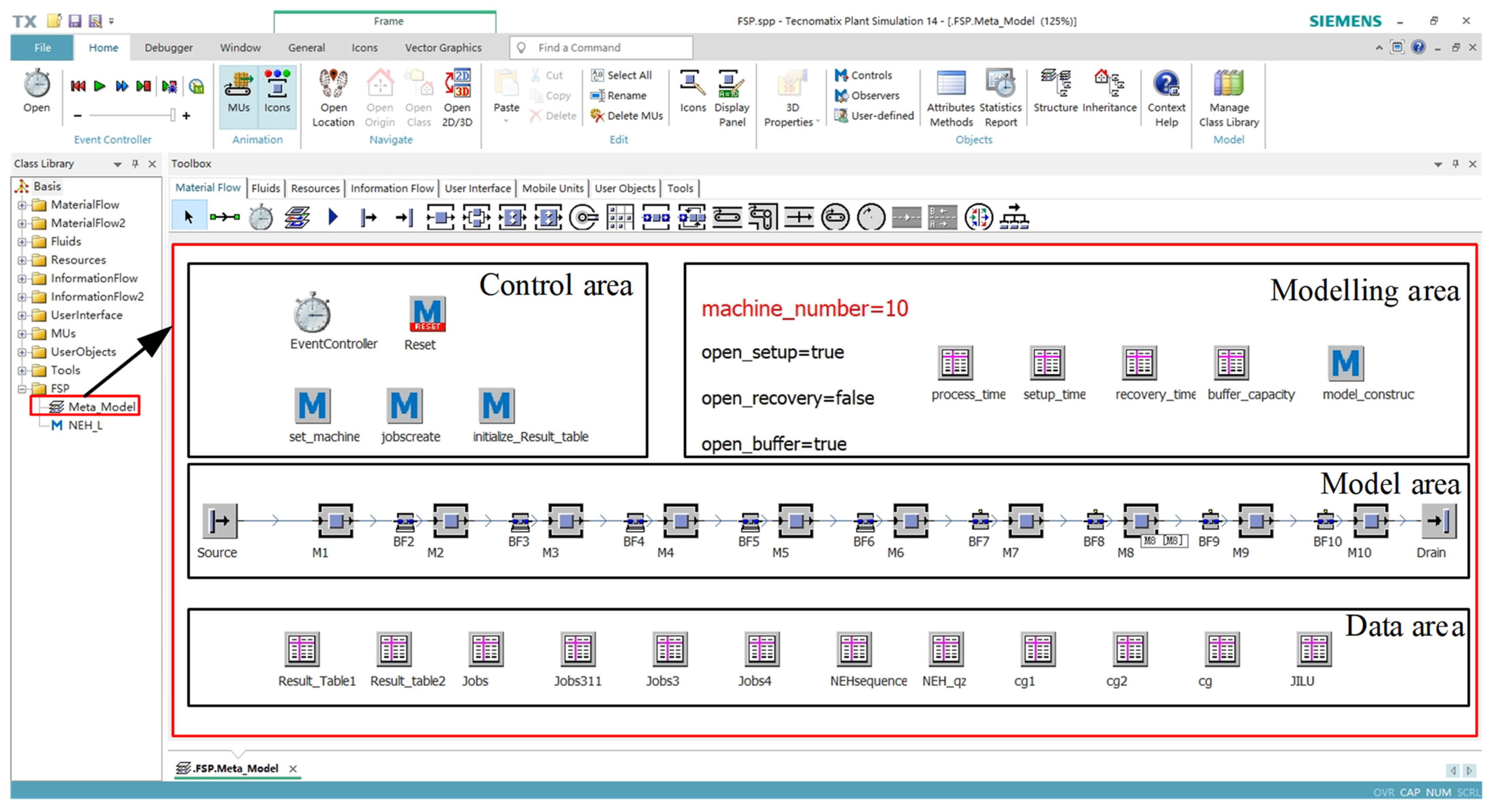
2.2. Flexible Simulation Modelling Approach
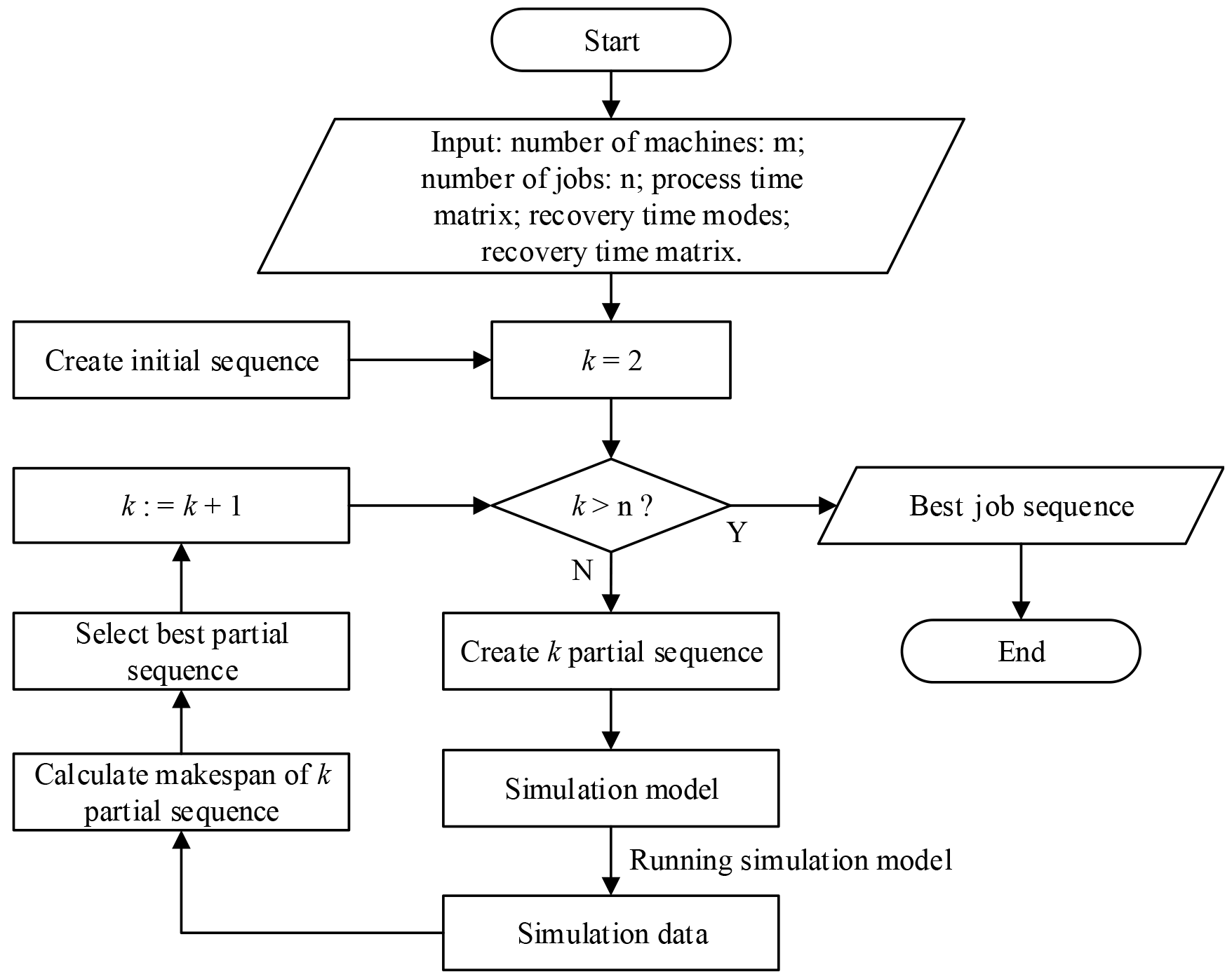
2.3. An Improved NEH Algorithm
2.4. Interaction Mechanism Between the Simulation Model and NEH
3. Computational Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NEH | Three initials: Nawaz, M., Jr.; E.E.E.; and Ham, I.A. |
| PFSP | Permutation flowshop scheduling problem |
| AVG | Average processing time |
| STD | Standard deviation |
| SKE | Skewness |
| KUR | Kurtosis |
| RPD | Relative percentage deviation |
| ACT | Average CPU time |
References
- Jiang, Y.H.; Li, Q.; Li, W.K.; Li, F. Improvement of leak detection technology for small satellite mass production. Spacecr. Environ. Eng. 2020, 37, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q. Analysis on construction and influence of large-scale LEO constellation. Aerosp. China 2019, 42, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.; Yang, H.; Zeng, C. Research on construction of batch intelligent production line for micro/nano satellite. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Networking and Computers, Guiyang, China, 13–16 August 2019; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2020; pp. 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, G.P. Study of the Benefits and Applications of LEO (Low Earth Orbit) for Communications and Definition of Space New Business Models: Oneweb Case. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, C.; Ji, J. A Full Lifecycle-Oriented Flexible Method for Satellite Design. In Proceedings of the Wireless and Satellite Systems: 12th EAI International Conference, Harbin, China, 31 July–2 August 2021; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, L. Study on the Application of Robot-Assisted Assembly in Satellite Board Assembly. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Networking and Computers, Xi’ning, China, July 2022; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalczynski, P.J.; Kamburowski, J. An empirical analysis of the optimality rate of flow shop heuristics. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 198, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jin, Y.; Price, M. A new improved neh heuristic for permutation flowshop scheduling problems. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 193, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjana, V.; Sridharan, R.; Kumar, P.N.R. Metaheuristics for solving a multi-objective flow shop scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup times. J. Sched. 2020, 23, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Croce, F.; Grosso, A.; Salassa, F. Minimizing total completion time in the two-machine no-idle no-wait flow shop problem. J. Heuristics 2019, 27, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, E.-D.; Wang, L. An improved multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition for energy-efficient permutation flow shop scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup time. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 57, 1756–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thürer, M.; Ma, L.; Stevenson, M. Workload Control order release in general and pure flow shops with limited buffer size induced blocking: An assessment by simulation. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 59, 2558–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benda, F.; Braune, R.; Doerner, K.F.; Hartl, R.F. A machine learning approach for flow shop scheduling problems with alternative resources, sequence-dependent setup times, and blocking. OR Spectr. 2019, 41, 871–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laribi, I.; Yalaoui, F.; Belkaid, F.; Sari, Z. Heuristics for solving flow shop scheduling problem under resources constraints. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa Junior, W.; Barra Montevechi, J.A.; de Carvalho Miranda, R.; Teberga Campos, A.T. Discrete simulation-based optimization methods for industrial engineering problems: A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 128, 526–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, F.; Nawawi, A. Optimization of Permutation Flowshop Schedulling Problem (PFSP) using First Sequence Artificial Bee Colony (FSABC) Algorithm. Prog. Eng. Appl. Technol. 2024, 5, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Qiao, F.; Zhu, G. Solving a many-objective PFSP with reinforcement cumulative prospect theory in low-volume PCB manufacturing. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 20403–20422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajsek, B.; Marolt, J.; Rupnik, B.; Lerher, T.; Sternad, M. Using maturity model and discrete-event simulation for industry 4.0 implementation. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2019, 18, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.; Natário, D.; Costa, A.; Barros, J.-P.; Campos-Rebelo, R. Event-Based Modeling of Input Signal Behaviors for Discrete-Event Controllers. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, J. Assembly transport optimization for a reconfigurable flow shop based on a discrete event simulation. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2020, 15, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Cui, F.; Cheng, H. A simulation-based approach for plant layout design and production planning. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2019, 10, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.; Li, G. Resource allocation methodology based on object-oriented discrete event simulation: A production logistics system case study. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, G.A.; Lopes, L.A.S.; Junior, O.S.S. Discrete event-based railway simulation model for eco-efficiency evaluation. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2020, 19, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Bai, X.; Ren, Z. Bottleneck identification and alleviation in a blocked serial production line with discrete event simulation: A case study. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2020, 15, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Xin, L.; Xu, Z. Verification of intelligent scheduling based on deep reinforcement learning for distributed workshops via discrete event simulation. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2023, 17, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenczyk, D. Deep Reinforcement Learning and Discrete Simulation-Based Digital Twin for Cyber–Physical Production Systems. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.I.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Adhikari, N.; Li, H.; Liu, Z. Evaluating Electrification of Fossil-Fuel-Fired Boilers for Decarbonization Using Discrete-Event Simulation. Energies 2024, 17, 2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S. Simulation Modeling in Supply Chain Management Research of Ethanol: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.T.; Chen, M.; Jiang, W.G. Simulation of flow shop sequence-dependent group scheduling problem. Light Ind. Mach. 2015, 33, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.; Enscore, E.E.; Ham, I. A heuristic algorithm for the m-machine, n-job flow-shop sequencing problem. Omega 1983, 11, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.P. Simulation of Production System; Electronic Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ištoković, D.; Perinić, M.; Doboviček, S.; Bazina, T. Simulation framework for determining the order and size of the product batches in the flow shop: A case study. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2019, 14, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaoui, H.; Artiba, A. Integrating simulation and optimization to schedule a hybrid flow shop with maintenance constraints. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2004, 47, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Huang, H.; Chen, P. An improved neh-based heuristic for the permutation flowshop problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2008, 35, 3962–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Viagas, V.; Framinan, J.M. On insertion tie-breaking rules in heuristics for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 45, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallada, E.; Ruiz, R.; Framinan, J.M. New hard benchmark for flowshop scheduling problems minimising makespan. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 240, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




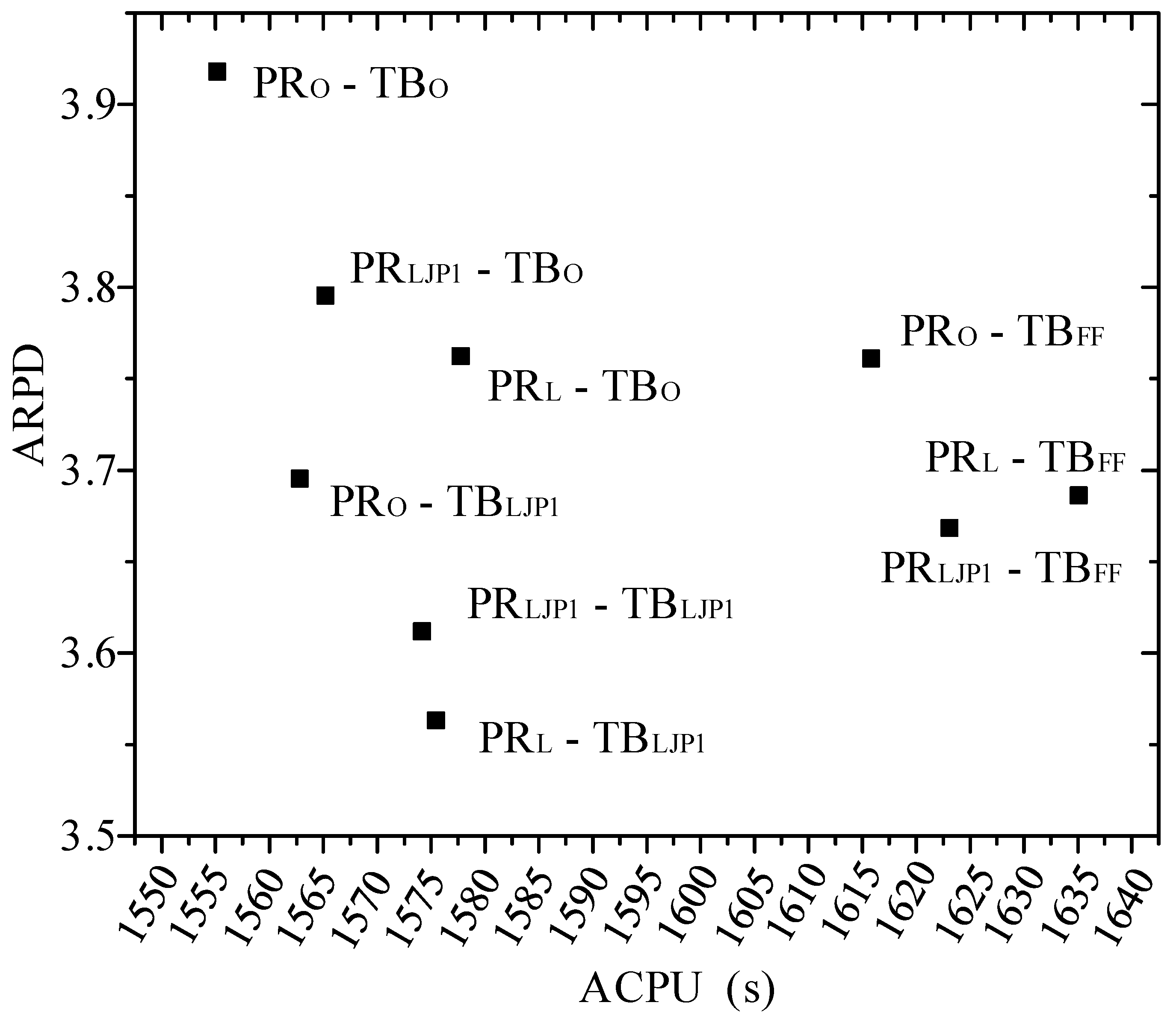
| PRO | PRLJP1 | PRL | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBO | TBFF | TBLJP1 | TBO | TBFF | TBLJP1 | TBO | TBFF | TBLJP1 | |
| 10*5 | 2.18 | 2.47 | 2.09 | 1.51 | 1.69 | 1.39 | 1.51 | 1.47 | 1.39 |
| 10*10 | 1.91 | 2.15 | 1.74 | 1.58 | 2.02 | 1.69 | 1.58 | 2.02 | 1.69 |
| 10*15 | 1.53 | 1.31 | 1.51 | 2.27 | 2.22 | 2.33 | 2.14 | 2.13 | 2.14 |
| 10*20 | 1.99 | 1.99 | 1.97 | 1.62 | 1.76 | 1.78 | 1.62 | 1.76 | 1.78 |
| 20*5 | 1.51 | 1.31 | 1.84 | 2.82 | 2.7 | 2.35 | 2.77 | 2.65 | 2.35 |
| 20*10 | 4.82 | 4.79 | 3.81 | 4.8 | 5.05 | 4.59 | 4.8 | 5.05 | 4.59 |
| 20*15 | 4.33 | 4.04 | 4.08 | 3.89 | 3.74 | 3.62 | 3.39 | 3.29 | 3.38 |
| 20*20 | 4.12 | 3.9 | 4 | 3.51 | 3.38 | 3.59 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 3.47 |
| 30*5 | 1.43 | 1.22 | 1.3 | 1.54 | 0.9 | 1.67 | 1.55 | 0.96 | 1.81 |
| 30*10 | 5.26 | 5.44 | 5 | 4.73 | 4.59 | 4.69 | 4.71 | 4.66 | 4.62 |
| 30*15 | 5.83 | 5.32 | 5.73 | 5.24 | 5.26 | 4.9 | 5.51 | 5.21 | 4.77 |
| 30*20 | 5.41 | 5.3 | 5.32 | 5.57 | 5.31 | 5.23 | 5.3 | 5.38 | 5.08 |
| 40*5 | 1.09 | 0.72 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.81 | 1.04 | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.89 |
| 40*10 | 4.97 | 4.38 | 4.52 | 4.13 | 4.1 | 4.25 | 4.79 | 4.41 | 4.15 |
| 40*15 | 6.05 | 5.54 | 5.95 | 5.74 | 5.73 | 5.23 | 5.77 | 5.83 | 5.54 |
| 40*20 | 5.14 | 5.25 | 4.86 | 5.38 | 5.23 | 5.34 | 4.7 | 5.23 | 4.92 |
| 50*5 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.75 | 0.8 | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.63 |
| 50*10 | 4.58 | 4.62 | 3.78 | 4.26 | 4.02 | 3.38 | 4.53 | 4.11 | 4.08 |
| 50*15 | 6.52 | 6.2 | 6.16 | 6.21 | 6.3 | 6.01 | 6.21 | 6.48 | 5.5 |
| 50*20 | 5.96 | 6.2 | 5.8 | 5.7 | 5.74 | 5.51 | 5.78 | 5.63 | 5.67 |
| 60*5 | 0.89 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 0.74 |
| 60*10 | 3.96 | 4.03 | 4.05 | 4.39 | 3.64 | 3.61 | 4.01 | 3.8 | 3.88 |
| 60*15 | 5.79 | 5.15 | 5.7 | 5.95 | 5.62 | 5.85 | 5.91 | 5.39 | 5.63 |
| 60*20 | 6.45 | 6.5 | 6.09 | 6.57 | 6.13 | 6.24 | 5.83 | 6.09 | 5.67 |
| 100*20 | 5.71 | 5.67 | 5.12 | 5.44 | 5.29 | 5.55 | 5.62 | 5.56 | 5.34 |
| 100*40 | 5.47 | 5.07 | 5.2 | 5.25 | 5.31 | 5.32 | 5.37 | 5.36 | 5.16 |
| 100*60 | 4.95 | 4.77 | 4.85 | 4.7 | 4.67 | 4.5 | 4.68 | 4.88 | 4.75 |
| 200*20 | 4.23 | 4.04 | 3.87 | 4.13 | 4.06 | 3.92 | 4.17 | 3.78 | 3.79 |
| 200*40 | 4.71 | 4.53 | 4.56 | 4.56 | 4.3 | 4.29 | 4.67 | 4.45 | 4.49 |
| 200*60 | 4.55 | 4.24 | 4.37 | 4.45 | 4.18 | 4.2 | 4.49 | 4.3 | 4.28 |
| 300*20 | 3 | 2.88 | 2.64 | 3 | 2.72 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.49 |
| 300*40 | 4.08 | 3.79 | 3.86 | 3.97 | 3.68 | 3.6 | 3.88 | 3.84 | 3.52 |
| 300*60 | 3.93 | 3.94 | 3.83 | 3.85 | 3.73 | 3.9 | 3.89 | 3.92 | 3.62 |
| 400*20 | 2.56 | 2.22 | 2.17 | 2.44 | 2.14 | 2.22 | 2.36 | 2.06 | 2.09 |
| 400*40 | 3.66 | 3.43 | 3.21 | 3.57 | 3.35 | 3.17 | 3.53 | 3.37 | 3.08 |
| 400*60 | 3.56 | 3.45 | 3.34 | 3.36 | 3.25 | 3.23 | 3.46 | 3.23 | 3.08 |
| 500*20 | 2.27 | 1.87 | 1.78 | 2 | 1.86 | 1.67 | 2.14 | 1.87 | 1.75 |
| AVG | 3.92 | 3.76 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.67 | 3.61 | 3.76 | 3.69 | 3.56 |
| Tie-Breaking | PRO | PRLJP1 | PRL |
|---|---|---|---|
| TBO | 1555.15 | 1565.20 | 1577.75 |
| TBFF | 1615.86 | 1623.12 | 1635.08 |
| TBLJP1 | 1562.80 | 1574.15 | 1575.48 |
| Mean | 1577.94 | 1587.49 | 1596.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Zhang, L. Discrete-Event Simulation Integrates an Improved NEH Algorithm for Practical Flowshop Scheduling Problems in the Satellite Industry. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9755. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219755
Li G, Zhang L. Discrete-Event Simulation Integrates an Improved NEH Algorithm for Practical Flowshop Scheduling Problems in the Satellite Industry. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(21):9755. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219755
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guangzhen, and Lei Zhang. 2024. "Discrete-Event Simulation Integrates an Improved NEH Algorithm for Practical Flowshop Scheduling Problems in the Satellite Industry" Applied Sciences 14, no. 21: 9755. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219755
APA StyleLi, G., & Zhang, L. (2024). Discrete-Event Simulation Integrates an Improved NEH Algorithm for Practical Flowshop Scheduling Problems in the Satellite Industry. Applied Sciences, 14(21), 9755. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219755





