Abstract
This study analyzes the fractal aspects of the structures of S100 proteins to better understand their structural complexity. We take into account 33 solution structures and 18 crystal structures corresponding to human S100 proteins for the calculation of mass and surface fractal dimensions. The mass fractal dimension value is calculated as Dm = 1.54, confirming the extended conformation of the dimers of these proteins. The mean value of the surface fractal dimension is Ds = 2.35 ± 0.09 when computed using solution structures and Ds = 2.23 ± 0.05 when computed using crystal structures, revealing the surface irregularities of S100 proteins. Changes in surface fractal dimensions have been recorded for S100 proteins due to the changes in the pH of the environment, due to mutations in their sequences that alter how the protein folds, and/or due to their interactions with ions and/or ligands that reflect the structural rearrangements that occur upon binding. These changes can significantly influence the biological activity of the protein, making the fractal dimension of the surface a valuable parameter in studying protein functions, interactions, and potential therapeutic targeting.
1. Introduction
In living organisms, calcium is a cation that has both a structural and a functional role in most cellular processes. One of the most important roles of calcium is as a second messenger in a cell, a role that is dependent on the existence of calcium-binding proteins (CaBPs), proteins that have the ability to form a complex with calcium under various conditions. CaBPs have different cellular and tissue distributions and are involved in specific functions. These proteins typically contain specific domains or motifs that have a high affinity for calcium, allowing them to modulate intracellular calcium levels and mediate calcium signaling [1].
CaBPs can have both intracellular and extracellular localization. Intracellular CaBPs contain or lack the EF-hand structural domain (a helix–loop–helix structure), which is the most common calcium-binding (sometimes magnesium-binding) domain and binds ions with high affinity and specificity [2]. In the case of EF-hand CaBPs, their structures comprise two domains, with each domain containing two EF-hand motifs [3]. Intracellular CaBPs containing the EF-hand motif have been grouped into two functional categories [4]: (i) calcium buffer, proteins that bind calcium to transport or regulate its concentration; and (ii) calcium sensors, proteins that bind calcium to decode its signal by interacting with other target proteins. The two functional categories of EF-hand motif-containing CaBPs also differ in their overall structure, with calcium buffers typically presenting a compact spatial structure and calcium sensors typically exhibiting an extended dumbbell-like spatial structure [4,5]. Data from the literature indicate that the overall extended or compact structures of EF-hand CaBPs depend on the protonation of several acidic residues [6] and the hydrophilicity of the residues linking the two domains [7].
S100 proteins are a large family of CaBPs containing EF-hand motifs and are involved in a wide range of intracellular and extracellular functions, playing critical roles in regulating cellular processes and disease pathology. Importantly, S100 proteins are expressed exclusively in vertebrates and have other functions complemented by their calcium-binding ability [8]. S100 proteins typically contain two EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. The first is called the pseudo-EF-hand motif, a loop that contains 14 residues that chelate calcium via backbone carbonyls, resulting in a weaker calcium-binding affinity. The second EF-hand calcium-binding motif contains a loop of 12 residues that bind calcium via sidechain carboxylates or carbonyls, resulting in a higher calcium-binding affinity [9]. Most S100 proteins form dimers, the dimerization being essential for their functional roles and interactions with target proteins [10]. Figure 1 presents the spatial structure of the dimer of S100A1 protein (model 1), retrieved from Protein Data Bank (PDB) [11] (PDB ID 2LLS) and visualized using Chimera 1.16 software [12].
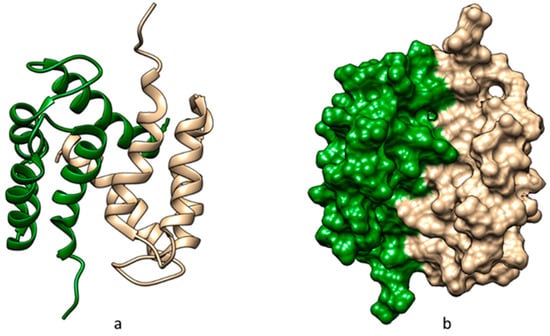
Figure 1.
Spatial structure of human apo S100A1 dimer (chain A is colored brown and chain B is colored forest green): (a) ribbon structures and (b) solid surfaces.
Fractals are geometric shapes exhibiting self-similarity across different scales, and this concept can be extended to biological macromolecules such as proteins. The concepts of fractal geometry can be applied to protein sequences and structures leading to a deeper understanding of their complexity and self-similar patterns. Data from the literature show that proteins have fractal aspects of their sequences and structures. Protein sequences can exhibit patterns in which certain motifs or domains repeat at different scales that can be considered self-similar structures because they occur at different locations in the sequence and contribute to the overall function and stability of the protein. There have been intensive studies on the correlation properties of protein sequences that have used both statistical methods (such as correlation function, random walk, and power spectrum) and nonlinear dynamics theory, which is a powerful method for identifying determinism or randomness of irregular systems. There are numerous studies on the correlation of physicochemical properties of amino acids in protein sequences that reflect the complex nature of protein folding, structure, and function. These studies have revealed statistical dependencies or patterns that occur over long distances along the protein sequence [13,14,15]. In addition, long-range correlation was observed in some residue physicochemical properties, dipole moment, and amino acid hydrophobicity, and anti-correlation was observed in amino acid electrical charge [16,17,18,19,20]. Long-range correlations in protein sequences usually contribute to the stability of the protein’s three-dimensional structure, and functional sites are often constructed by residues that are distant in the sequence but come close in the folded structure.
Similarly, there are published data revealing that protein structures exhibit fractal properties in terms of protein backbones, surfaces, and their overall spatial structures. In terms of fractality, the protein backbone reveals at least two fractal dimensions, one associated with local folding and the other with global folding. The fractal dimensions associated with local folding are almost the same for all proteins investigated, with an average value of 1.38, and the fractal dimensions associated with global folding are distinct for different classes of proteins [21,22,23,24,25]. This highlights that the rules for the local folding of proteins are similar, but not for their global folding. The fractal dimension of the protein surface is a quantitative measure of protein surface roughness, an important structural property associated with protein–protein and ligand–protein binding interfaces. Literature data contain studies revealing fractal aspects of the surfaces of both individual proteins and classes of proteins [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33].
Last but not least, proteins have been described in terms of mass fractals, providing a unique insight into their structural complexity. Proteins as mass fractals are characterized by a scaling relationship between their mass (or number of residues) and the size of the structure, usually the radius of gyration [21]. This relationship can reveal information about how proteins occupy space and how their structures scale at different levels of magnification. Published data reveal that many proteins can be described as mass fractals, with their mass fractal dimensions being associated with a measure of their compactness [25,34,35,36,37,38,39].
The aim of this study is to reveal the fractal features of human S100 protein structures and to correlate these features with the biological function of these proteins.
2. Materials and Methods
In this study, human S100 proteins containing the EF-Hand motif and possessing three-dimensional dimer structures determined using crystallographic and/or NMR techniques were considered: S100A1, S100A2, S100A3, S100A4, S100A5, S100A6, S100A7, S100A8, S100A9, D100A10, S100A11, S100A12, S100A13, S100A14, S100A16, S100B, and S100P (Supplementary Table S1). As dimerization is essential for the functional roles of S100 proteins, only structures containing dimers have been considered in the present study. For S100A13, structures having the PDB IDs 2KI4 and 2KI6 are perfectly similar (Supplementary Table S2) and we only considered the structural file 2KI4 in our analysis. The sequences of these proteins were extracted from the UniProt database [40] and their spatial structures were extracted from the Protein Data Bank [11]. In the case of NMR structures, only model 1 was analyzed for each dimer structure, as this model is often considered more accurate because it has the lowest overall energy or best satisfies the experimental constraints. The UniProt and PDB IDs of the investigated proteins are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
The Clustal Omega tool [41] was considered to perform multiple sequence alignment of the investigated proteins and the Chimera tool [12] was used for structure analysis and superimposition.
The mass fractal dimension, Dm, and surface fractal dimension, Ds, associated with each protein considered were calculated using the methods described by Dewey [21]. The mass of a protein (M), or its amino acid number (N) scales with its mean radius, R, as
with Dm being the mass fractal dimension. Consequently, the mass fractal dimension may be computed from the slope of the line obtained when plotting the number of amino acids or the molecular mass versus the mean radius in a double logarithmical plot. To compute the mean radius of every investigated protein, the Protein Dipole Moments Server (https://dipole.proteopedia.org/—accessed on 2 August 2024) [42] was considered. This server has been also used to assess the overall conformation of the investigated structures.
Computation of the accessible surface area (ASA) of the protein involves the use of a sphere with a given radius, R, which is rolled onto the surface of the protein maintaining contact with the van der Waals surface and gives
where N(R) is the number of spheres required to cover the surface. As the radius is higher, fewer spheres are required to cover the surface
resulting in
where Ds is the fractal dimension of the protein surface that can be further computed from the slope of the line obtained when plotting ASA versus R in a double logarithmical plot [21]. For the investigated proteins, the accessible surface areas for spheres with radii of 1.0, 1.4, 1.8, 2.2, 2.6, and 3.0 Å, respectively, were computed using GetArea online tool (https://curie.utmb.edu/getarea.html—accessed on 26 July 2024) [43]. This tool has been also used to compute the apolar surface areas of investigated proteins, the sphere radius used in this case being 1.4 Å.
3. Results
The multiple sequence alignment of the investigated S100 proteins is shown in Figure 2 and the corresponding percent identity matrix is shown in Figure 3. Both figures reveal a low sequence identity of the investigated proteins.

Figure 2.
Multiple sequence alignments of S100 EF-hand calcium-binding proteins considered in the present study. Conserved residues are marked by “*”, residues with strongly similar physicochemical properties are marked by “:” and residues with weakly similar properties are marked by “.”.
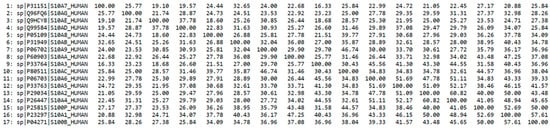
Figure 3.
Percent identity matrix for the multiple sequence alignments of S100 EF-hand calcium-binding proteins considered in the present study.
Superimposition of the structural files for the investigated proteins reveals low structural similarity (Supplementary Table S2). As expected, the values of root mean square deviations (RMSD), obtained by superimposing the structures of every family of S100 proteins, are lower for crystallographic structures due to the reduced conformational flexibility in the crystal compared to the inherent flexibility existent in the solution state. The low sequence identity added to low structural similarity emphasizes that the fractal aspects were not assessed for similar structures. Moreover, the differences in the structures of the same protein in apo- and loaded forms emphasize the conformational change undergone by the protein upon interaction with ions, substrate/ligand, or other proteins.
Figure 4 shows the scatterplot of the double-log values for the number of amino acids of the protein versus the protein mean radius for the investigated proteins considering both solution (Figure 4a) and crystal (Figure 4b) structures. The linear fit of the data presented in Figure 4 leads to a mass fractal dimension Dm = 1.540 ± 0.07 (R2 = 0.680) for solution structures and Dm = 1.538 ± 0.14 (R2 = 0.628) for crystal structures, suggesting that they adopt extended global conformations. It is in good correlation with outcomes of the Protein Dipole Moments Server for the great majority of investigated structures (Table 1). The extended shape of S100 proteins, in conjunction with their calcium-binding ability, allows them to function as calcium sensors. Upon calcium binding, the proteins undergo conformational changes that expose previously hidden interaction surfaces, enabling them to regulate diverse biological processes such as cytoskeletal dynamics, cell migration, inflammation, and apoptosis.
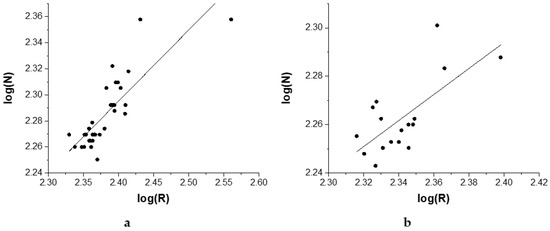
Figure 4.
Determination of the mass fractal dimension for S100 proteins as the slope of the line when plotting the number of residues (N) versus the mean radius (R) of the proteins in a double logarithmical scale: (a) solution structures; (b) crystal structures.

Table 1.
Values of the surface fractal dimensions (Ds) for the investigated structures, their global conformation, and polar and apolar surface areas. Crystallographic structures are marked with asterisks (*). E—elongated conformation, S—spherical conformation.
The values obtained for the surface fractal dimensions, the overall conformations, and the polar and apolar surface areas for the investigated proteins are presented in Table 1. The values of polar and apolar areas are computed using a sphere radius of 1.4 Å.
4. Discussion
The mass fractal dimension obtained from the investigated S100 proteins is Dm = 1.54, this value being obtained for both solution and crystal structures. This result is not unexpected because the fractal dimension primarily reflects how mass is distributed at different scales, being less sensitive to the fine details of flexibility or the ordered nature of crystals. Solution structures capture a more dynamic and flexible state, but they maintain a fractal-like distribution of mass at larger scales. Crystal structures capture a more rigid and static form of the proteins, but the internal fold complexity is similar and the overall fractal nature of molecular mass distribution in proteins remains similar. It is known that for fully extended polymers Dm = 1.67, and for ideal compact polymers, Dm = 2 [21]. Proteins are complex macromolecules that fold into specific three-dimensional structures dictated by their amino acid sequences. Due to this folding process, proteins do not behave as ideal polymers and their scaling properties differ from those of ideal polymers. The value of the mass fractal dimension obtained for the dimers of S100 proteins suggests that they have extended global conformations in good correlation with outcomes of the Protein Dipole Moments Server for the great majority of investigated proteins, as presented in Table 1. This extended conformation results from their EF-hand calcium-binding motifs, dimerization, and their ability to undergo calcium-induced conformational changes [44,45]. These structural properties allow S100 proteins to engage in diverse biological processes such as calcium signaling, immune response, and protein regulation, making the extended shape critical for their functional versatility. In another study regarding the mass fractal dimensions of CaBPs containing EF-hand regions, the mass fractal dimensions for CaBPs with extended structures were calculated as Dm = 1.38, and Dm = 1.43 for CaBPs with compact structures [25]. The difference between the value obtained in this study when compared to that obtained in the previous one could be explained by the fact that in the present study, the dimers of S100 proteins are considered, whereas the previous study involved only monomers of other families of CaBPs.
The values of the surface fractal dimensions of S100 proteins obtained in this study, Ds = 2.35 ± 0.09 for solution structures and Ds = 2.23 ± 0.05 for crystal structures, are quite similar to the values of surface fractal dimension obtained for the other extended CaBPs presented in the study of Pitulice and coworkers [25]. The surface fractal dimension is related to the roughness or complexity of the surface of a structure, and a higher surface fractal dimension indicates a more irregular and complex surface. When comparing protein structures obtained from NMR and X-ray crystallography, NMR structures generally have larger surface fractal dimensions than crystallographic structures, due to the nature of the environments in which these structures are determined [46]. In solution, proteins are in a dynamic, flexible state, leading to more irregular surface topologies.
There are small differences in the values of surface fractal dimensions obtained for the structures of the same protein in apo- and calcium- or -sodium loaded form, respectively, for the structures of protein complexes with different ligands (Table 1). In addition, there are also differences between the surface fractal dimension values for the structures corresponding to the native protein and its mutants, underscoring the role of mutations in altering protein structures and modulating responses to calcium fluctuations (Table 1). Changes in the structures of the investigated S100 proteins due to calcium and/or ligand binding, respectively, due to mutations in the protein sequences are also highlighted by superimposing the structures (Supplementary Table S2).
In cases of S100A1, S100A2, S100A5, and S100A13, the proteins adopt more compact or smoother conformations in the presence of calcium or of the ligand, resulting in a decrease in the surface fractal dimension. In the case of the S100A1 protein, its surface fractal dimension decreases from 2.404 in apo-form (PDB ID 2L0P) to 2.324 in calcium-loaded form (PDB ID 2LP2). This is in good correlation with structural data revealing that after calcium binding, S100A1 undergoes an important conformational change, resulting in the exposure of a large hydrophobic cleft that binds to target proteins [47]. For S100A2, there is a decrease in the surface fractal dimension from 2.293, obtained for the sodium-loaded structure (PDB ID 2RGI), to 2.259 for the calcium-loaded structure (PDB ID 4DUQ), revealing the influence of the cation type. For the S100A5 protein, the surface fractal dimension decreases from 2.264 in apo-form (PDB ID 2KAX) to 2.181 in calcium-loaded form (PDB ID 2KAY). The 2KAX and 2KAY structural files, corresponding to S100A5 in apo- and calcium-loaded forms, respectively, reveal structural differences resulting from calcium binding, leading to a change in the overall shape of the protein from spherical to extended (Table 1) and changes in the distribution of hydrophobic and charged residues of the S100A5 homodimer [48]. For S100A12, the surface fractal dimension increases from 2.215 for the sodium-loaded structure (PDB ID 2WCE) to 2.184 for the calcium-loaded structure (PDB ID 1E8A), also revealing the influence of the type of ion bound on the surface properties. In the case of the S100A13 protein, its surface fractal dimension decreases from 2.288 (PDB ID 1YUS) in apo-form to 2.251 in calcium-loaded form (PDB ID 1YUU). Structural data for the S100 protein also show that the binding of two calcium ions per monomer generates key conformational changes [49]. All these changes reveal that these protein surfaces become more ordered upon calcium binding and that there are differences in the effects of various ions binding on the surface properties.
In some cases, calcium binding may induce a conformational shift that exposes hydrophobic regions or binding sites for other ligands leading to an increase in surface complexity, as the protein might expose additional binding sites or undergo conformational changes that create a more rugged surface [50]. These changes are important for protein function because they modulate its ability to interact with target molecules. For the S100 proteins analyzed, calcium binding produces an increase in the surface fractal dimension for S100A16 from 2.312 for the apo-form (PDB ID 2L50) to 2.471 for the calcium-loaded form (PDB ID 2L51). Structural data reveal that, by comparison to most S100 proteins, the conformational rearrangement of S100A16 upon calcium binding is minor and the change in the surface fractal dimension should mainly be due to the increased hydrophobic interactions between the third and fourth helices of S100A16 [51]. There also is an increase in the surface fractal dimension for S100P from 2.177 for apo-form (PDB ID 1OZO) to 2.225 for the calcium-loaded S100P in complex with RAGE (PDB ID 2MJW).
The binding of ligands and of calcium and/or sodium ions can significantly alter protein conformation and surface properties. Complexations of these proteins with ligands and/or ions modulate their surface properties by altering surface charge, exposing hydrophobic regions, and/or influencing metal ion specificity, all these resulting in conformational changes. These modifications are crucial for the functional versatility of S100 proteins, allowing them to participate in a variety of cellular processes through dynamic interactions with other biomolecules.
Changes in surface fractal dimensions are also recorded when comparing native structures with mutant structures. In the case of S100A1, the CYS85MET mutation leads to a decrease in the surface fractal dimension from 2.404 for the native protein (PDB ID 2L0P) to 2.297 for the mutant (PDB ID 2LLS). The conformational change produced by the CYS85MET mutation in S100A1 was found to be similar to that caused by CYS85 thionylation [47]. It was also revealed that post-translational modifications of S100A1 at CYS85 lead to conformational changes that disrupt the apo-state folding by increasing the solvent exposure of the protein target binding domain (the hydrophobic patch). This increases the calcium sensitivity of binding targets and thus modulates the corresponding signaling pathways [52]. This is consistent with the critical role of cysteine residues in the structural and functional properties of the protein, these residues being usually involved in disulfide bond formation, which contributes to protein stability. The substitution of cysteine with the non-polar amino acid methionine can disrupt disulfide bridges, affecting the tertiary or quaternary structure of the protein. Methionine is bulkier than cysteine, and the resulting structural change could alter the conformation of the calcium-binding domains in S100A1, which may impair the protein’s ability to bind calcium and, consequently, its biological function. Consequently, the CYS85MET mutation in S100A1 is likely to impair its structural integrity, calcium-binding capacity, interaction with target proteins, and redox sensitivity. This mutation could potentially contribute to diseases involving muscle dysfunction or altered calcium homeostasis, especially in the heart and skeletal muscles.
In the case of the S100A4 protein, the four mutations (CYS3SER, CYS76SER, CYS81SER, and CYS86SER) result in the stabilization of the solution structure [53], and the surface fractal dimension changes slightly from 2.313 for the native protein (PDB ID 2LNK) to 2.308 for the mutant (PDB ID 2MRD). The decrease in the surface fractal dimension from 2.218 in the case of native S100A4 (PDB ID 4ETO) to 2.173 for the CYS3SER, CYS81SER, CYS86SER, and PHE45TRP mutants (PDB ID 4CFR) has also been noticed when using crystal structures. A cysteine-to-serine substitution results in the loss of the thiol group, which is critical for forming disulfide bonds. The absence of these bonds can lead to changes in the protein’s tertiary or quaternary structure, making it less stable or altering its conformation. Also, these mutations in S100A4 could have profound effects on the structural integrity, calcium-binding properties, and protein–protein interactions of S100A4. These changes could result in altered cellular functions, particularly in processes like cell motility, invasion, and metastasis, making them potentially relevant for understanding cancer progression.
For the S100A9 protein, the surface fractal dimension obtained for the CYS3SER mutant (PDB ID 5I8N), 2.282, decreases to 2.2510 for the CYS3SER and MET67PHE mutant structure (PDB ID 7UI5). Methionine is a flexible, non-polar amino acid with a sulfur-containing side chain, while phenylalanine is a bulkier, aromatic amino acid. MET67PHE substitution, due to the aromatic ring of phenylalanine, introduces a more rigid structure and could have a significant impact on the protein’s structure, dimerization with S100A8, and its role in calcium and zinc binding [54]. These changes are likely to affect its inflammatory signaling and antimicrobial functions, with potential consequences for diseases involving chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
It may be noticed from Table 1 that, in the case of the S100B protein, the change in the pH also affects the surface characteristics as the surface fractal dimension slightly decreases from 2.296 at pH 6.5 (PDB ID 3D0Y) to 2.234 at pH 10 (PDB ID 3d10). Protein surface charges are determined by the ionizable amino acid residues that are exposed on the protein’s surface. These charges depend on the pH of the environment, which affects the protonation or deprotonation of these residues. This highlights that the surface fractal dimension of proteins can be used to assess the effects of the characteristics of the environment in which the protein is found, particularly pH, as pH affects protein conformation, interactions, and aggregation behavior, which in turn modifies the surface complexity of the protein structures.
Changes in the values of the surface fractal dimensions are usually accompanied by changes in polar and apolar surface areas. There is no direct correlation between polar/apolar surface area and surface fractal dimension, but it is reasonable to expect that increased surface complexity and polar character can influence each other in specific contexts. A protein with a complex surface may have a larger number of polar residues exposed to the solvent, potentially increasing the polar surface area, but a complex surface could also result in increased exposure of hydrophobic residues, small pockets on the surface might expose regions that would otherwise be buried in a smoother structure. Changes in polar/apolar surface area may affect protein folding, as hydrophobic residues tend to be buried inside the protein to minimize exposure to the aqueous environment, and are also important for understanding how proteins interact with hydrophobic/hydrophilic environments. This underlines that the polar/apolar surface area and surface fractal dimension of proteins are measures that provide insights into protein structure, surface complexity, and behavior in biological systems, but they describe different aspects of protein surfaces.
Changes in surface fractal dimension can directly affect protein function. These structural changes of S100 proteins are crucial for their role as calcium sensors and signal transducers, modulating interactions with other proteins based on calcium levels. By analyzing how the surface fractal dimension changes due to different factors, details can be obtained about the nature of the binding interaction, such as its strength, the degree of induced conformational change, and potential biological implications. All these results highlight the existence of different conformational changes undergone by the investigated proteins upon mutations, changes in the pH of the environment, calcium binding, and/or interactions with ligands that could influence the efficiency and sensitivity of calcium signaling pathways potentially leading to disease states or changes in protein activity. Therefore, the surface fractal dimension is a valuable parameter for understanding the functional implications of both the wild-type and mutant forms of S100 proteins.
All these data reveal that changes in the surface fractal dimension of a protein can provide valuable insights into how the environment and/or mutations affect the protein’s structure and surface properties in correlation with the protein’s biological function, and that surface fractal dimension can be used to assess the structural changes in proteins caused by various factors.
Even if fractal analysis can reveal patterns and scaling laws in proteins, it has limitations when applied to biological systems. Further experimental analysis is needed to obtain a complete understanding of how fractal properties influence the biological functions of proteins.
5. Conclusions
This study shows that human S100 proteins reveal fractal aspects of their structures and are in good correlation with the identified fractal aspects of other calcium-binding proteins. The mass fractal dimension of S100 proteins is Dm = 1.54, indicating that these proteins adopt an extended conformation. The extended dimeric structure provides a large surface area for interaction with other proteins or receptors, which is essential for the multifunctional nature of S100 proteins. The mean value of the surface fractal dimension of S100 proteins, Ds = 2.35 when computed for solution structures and Ds = 2.23 when computed for crystal structures, indicates a moderately complex surface, which could correlate with functional properties. The moderate complexity suggested by this fractal dimension may support the ability of S100 proteins to bind calcium and undergo conformational changes that expose or hide specific binding sites. This value illustrates that the S100 protein surfaces are well-suited for multi-partner interactions and offers insights into how structural properties of the protein could relate to its biological function, including interactions with other molecules, regulatory roles, and cellular signaling. The structural complexity of these proteins might facilitate their role in dynamic cellular environments, where they need to interact with multiple targets depending on calcium concentration. Since S100 proteins are involved in a variety of critical processes, such as calcium signaling, immune responses, and inflammation, understanding their fractal dimension can help elucidate how their structure influences their activity. The fractal properties of S100 proteins may allow them to adapt to the complex, multi-scale environment of the cell. This adaptability could be important for their diverse functions, from modulating inflammation to influencing cell motility and proliferation. Understanding the fractality of the S100 protein structures could lead to new therapeutic strategies, especially in diseases where S100 proteins are dysregulated.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app14209540/s1, Table S1: Structural files considered in the present study, their accession codes in UniProt (UniProt ID) and Protein Data Bank (PDB ID) and short description of the content of structural files. With an asterisk (*) are highlighted the crystallographic files; Table S2: Results of the superimposition of investigated structures. With an asterisk (*) are highlighted the crystallographic files.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.I.; Methodology, A.I.; Validation, A.I.; Formal Analysis, D.E.P.; Investigation, D.E.P.; Data Curation, A.I.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, A.I. and D.E.P.; Writing—Review and Editing, A.I.; Supervision, A.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yáñez, M.; Gil-Longo, J.; Campos-Toimil, M. Calcium Binding Proteins. In Calcium Signaling; Islam, M.d.S., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 461–482. ISBN 978-94-007-2888-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lewit-Bentley, A.; Réty, S. EF-Hand Calcium-Binding Proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000, 10, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.R.; Thulin, E.; Fagan, P.A.; Forsén, S.; Chazin, W.J. The EF-Hand Domain: A Globally Cooperative Structural Unit. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carafoli, E. The Calcium-Signalling Saga: Tap Water and Protein Crystals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchikoga, N.; Takahashi, S.; Ke, R.; Sonoyama, M.; Mitaku, S. Electric Charge Balance Mechanism of Extended Soluble Proteins. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isvoran, A.; Craescu, C.T.; Alexov, E. Electrostatic Control of the Overall Shape of Calmodulin: Numerical Calculations. Eur. Biophys. J. 2007, 36, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouawad, L.; Isvoran, A.; Quiniou, E.; Craescu, C.T. What Determines the Degree of Compactness of a Calcium-Binding Protein? FEBS J. 2009, 276, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R.; Cannon, B.R.; Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Hsu, K.; Weber, D.J.; Geczy, C.L. Functions of S100 Proteins. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 24–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, W.; Kirberger, M.; Lee, H.-W.; Ayalasomayajula, G.; Yang, J.J. Prediction of EF-Hand Calcium-Binding Proteins and Analysis of Bacterial EF-Hand Proteins. Proteins 2006, 65, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R. Functional Roles of S100 Proteins, Calcium-Binding Proteins of the EF-Hand Type. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 1999, 1450, 191–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Huang, Y.; Xu, R.; Xiao, Y. Nonlinear Analysis of Sequence Symmetry of Beta-Trefoil Family Proteins. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2005, 25, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, A.H.; Lyle, N.; Pappu, R.V. Describing Sequence-Ensemble Relationships for Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchi, J.; Galpern, E.A.; Espada, R.; Ferreiro, D.U.; Walczak, A.M.; Mora, T. Size and Structure of the Sequence Space of Repeat Proteins. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, V.S.; Grosberg, A.Y.; Tanaka, T. Nonrandomness in Protein Sequences: Evidence for a Physically Driven Stage of Evolution? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12972–12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, O.; Herzel, H. Correlations in Protein Sequences and Property Codes. J. Theor. Biol. 1998, 190, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Nonlinear Deterministic Structures and the Randomness of Protein Sequences. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2003, 17, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerich, C.; Kim, S. A Study of Residue Correlation within Protein Sequences and Its Application to Sequence Classification. EURASIP J. Bioinform. Syst. Biol. 2007, 2007, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciorsac, A.; Craciun, D.; Ostafe, V.; Isvoran, A. Nonlinear Correlations in the Hydrophobicity and Average Flexibility along the Glycolytic Enzymes Sequences. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2011, 44, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, T.G. Fractals in Molecular Biophysics; Topics in Physical Chemistry Series; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; ISBN 1429404248. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, M.; Baskar, S.; Latha, M.M. Fractal Dimension and Tertiary Structure of Proteins. Phys. Scr. 1999, 60, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isvoran, A. Describing Some Properties of Adenylat Kinase Using Fractal Concepts. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2004, 19, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isvoran, A.; Pitulice, L.; Craescu, C.T.; Chiriac, A. Fractal Aspects of Calcium Binding Protein Structures. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2008, 35, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitulice, L.; Isvoran, A.; Craescu, C.T.; Chiriac, A. Scaling Properties of the Radius of Gyration and Surface Area for EF-Hand Calcium Binding Proteins. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 40, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.; Rees, D.C. Fractal Surfaces of Proteins. Science (1979) 1985, 230, 1163–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, B.A.; Fedorov, B.B.; Schmidt, P.W. An Analysis of the Fractal Properties of the Surfaces of Globular Proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 4076–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, F.K.; Bowie, J.U. Protein Surface Roughness and Small Molecular Binding Sites 1 1Edited by F. Cohen. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczor, A.A.; Guixà-González, R.; Carrió, P.; Obiol-Pardo, C.; Pastor, M.; Selent, J. Fractal Dimension as a Measure of Surface Roughness of G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Implications for Structure and Function. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 4465–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, A.; Navare, C. Fractal Nature of Protein Surface Roughness: A Note on Quantification of Change of Surface Roughness in Active Sites, before and after Binding. J. Mol. Recognit. 2013, 26, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroff, N.; Kunze, J.; Schreuder, H.; Hessler, G.; Baringhaus, K.; Schneider, G. Fractal Dimensions of Macromolecular Structures. Mol. Inform. 2014, 33, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.-Y.; Ren, W.; Wang, J.; Kaneko, K. The Statistical Trends of Protein Evolution: A Lesson from AlphaFold Database. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Qi, W.; Wang, M.; Su, R.; He, Z. Backbone Fractal Dimension and Fractal Hybrid Orbital of Protein Structure. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2013, 18, 3373–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteca, G.A. Scaling Regimes of Molecular Size and Self-Entanglements in Very Compact Proteins. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 51, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Leitner, D.M. Anomalous Diffusion of Vibrational Energy in Proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 12673–12679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M.B.; Leitner, D.M. Mass Fractal Dimension and the Compactness of Proteins. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 11912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, D.; Trewhella, J.; Goldenberg, D.P. Fractal Dimension of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein: Small-angle X-ray Scattering and Computational Study of the Bacteriophage λ N Protein. Protein Sci. 2011, 20, 1955–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Qi, W.; Su, R.; He, Z. Describing Some Characters of Serine Proteinase Using Fractal Analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2012, 45, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendker, F.L.; Lo, Y.K.; Heimerl, T.; Bohn, S.; Persson, L.J.; Mais, C.-N.; Sadowska, W.; Paczia, N.; Nußbaum, E.; del Carmen Sánchez Olmos, M.; et al. Emergence of Fractal Geometries in the Evolution of a Metabolic Enzyme. Nature 2024, 628, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.; Martin, M.-J.; Orchard, S.; Magrane, M.; Ahmad, S.; Alpi, E.; Bowler-Barnett, E.H.; Britto, R.; Bye-A-Jee, H.; Cukura, A.; et al. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 48, 3.13.1–3.13.16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, C.E.; Prilusky, J.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. A Server and Database for Dipole Moments of Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W512–W521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraczkiewicz, R.; Braun, W. Exact and Efficient Analytical Calculation of the Accessible Surface Areas and Their Gradients for Macromolecules. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R. S100: A Multigenic Family of Calcium-Modulated Proteins of the EF-Hand Type with Intracellular and Extracellular Functional Roles. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2001, 33, 637–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deloulme, J.C.; Assard, N.; Mbele, G.O.; Mangin, C.; Kuwano, R.; Baudier, J. S100A6 and S100A11 Are Specific Targets of the Calcium- and Zinc-Binding S100B Protein in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 35302–35310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craciun, D.; Pitulice, L.; Ciorsac, A.; Ostafe, V.; Isvoran, A. Proteins Surface Roughness Analysis. Comparison of Crystallographic and NMR Structures. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2012, 64, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Nowakowski, M.; Ruszczyńska-Bartnik, K.; Budzińska, M.; Jaremko, Ł.; Jaremko, M.; Zdanowski, K.; Bierzyński, A.; Ejchart, A. Impact of Calcium Binding and Thionylation of S100A1 Protein on Its Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Derived Structure and Backbone Dynamics. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertini, I.; Das Gupta, S.; Hu, X.; Karavelas, T.; Luchinat, C.; Parigi, G.; Yuan, J. Solution Structure and Dynamics of S100A5 in the Apo and Ca2+-Bound States. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 14, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnesano, F.; Banci, L.; Bertini, I.; Fantoni, A.; Tenori, L.; Viezzoli, M.S. Structural Interplay between Calcium(II) and Copper(II) Binding to S100A13 Protein. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 6341–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria-Kisiel, L.; Rintala-Dempsey, A.C.; Shaw, G.S. Calcium-Dependent and -Independent Interactions of the S100 Protein Family. Biochem. J. 2006, 396, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babini, E.; Bertini, I.; Borsi, V.; Calderone, V.; Hu, X.; Luchinat, C.; Parigi, G. Structural Characterization of Human S100A16, a Low-Affinity Calcium Binder. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 16, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Kekenes-Huskey, P.M. Molecular Basis of S100A1 Activation and Target Regulation Within Physiological Cytosolic Ca2+ Levels. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.C.; Hung, K.-W.; Gorja, D.R.; Yu, C. The Solution Structure of Human Calcium-Bound S100A4 Mutated at Four Cysteine Loci. J. Biomol. NMR 2015, 62, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, J.L.; Reardon, P.N.; Costello, S.M.; Warren, G.D.; Phillips, S.R.; Connor, P.J.; Marqusee, S.; Harms, M.J. Evolution Avoids a Pathological Stabilizing Interaction in the Immune Protein S100A9. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2208029119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).