Abstract
The pet food industry’s growth, driven by increased demand for premium options, emphasizes the popularity of canned dog foods due to their palatability and convenience. This study evaluates the nutritional and microbiological quality of canned dog food for puppies and adult dogs, with and without grains, immediately after opening and following 24 h of incubation simulating home storage conditions. The grain-free products exhibited higher protein and energy levels, while the grain-included products contained more ether extract, crude ash, and nitrogen-free extract. Age-specific differences revealed higher ether extract, crude ash, crude fiber, and energy in growing dog foods and more nitrogen-free extract in adult dog foods. Discrepancies between labeled nutrient values and laboratory results indicated overstatements for ether extract and underestimations for protein and crude ash. A microbiological analysis showed that the canned dog foods were generally safe when opened, but after 24 h, 85% exhibited bacterial presence, emphasizing the need for rigorous evaluation. A statistical analysis did not confirm associations between grain presence or age group and microbiological contamination. This study underscores the importance of accurate labeling for nutritional value and emphasizes the need for microbiological safety evaluations, especially in regions lacking specific regulatory standards, to ensure pet food safety and nutritional adequacy.
1. Introduction
In recent years, veterinary services have demonstrated a positive impact on animal population demographics, health, and the overall well-being of pets, potentially affecting human welfare [1]. It can be said that pets hold a significant place in the lives of people who regard their pets as “members of the family” [2,3,4]. The increase in the pet population has contributed to substantial growth in the pet food industry, driven by an increasing demand for premium and nutritious options to meet the dietary requirements of canine companions. Canned dog foods, characterized by their palatability, moisture content, and convenience, have gained considerable popularity among pet caregivers seeking the optimal nutrition for their pets. Although canned foods are the most expensive model of dog nutrition in terms of maintenance per day and per 1000 kcal of metabolizable energy [5], they offer a compromise for those seeking less processed nutrition (compared to extruded food) for their dogs. Canned dog foods provide an alternative between the time-consuming preparation of homemade wet meals by the caregiver and commercially processed dry food. To ensure the safety and nutritional adequacy of these moist formulations, a rigorous evaluation of their microbial quality and nutrient profiles is imperative.
The presence of pathogenic microorganisms in pet food can pose a substantial health risk to dogs and potentially impact public health [6,7,8]. Therefore, a thorough assessment of the microbiological quality of canned pet food is vital to maintaining the well-being of canine companions. This is particularly noteworthy considering that, dog food, even in its raw form, undergoes no additional thermal processing before serving, unlike human ready-to-cook food, which is subject to thermal processing that has the potential to eliminate any pathogens present in the product [9]. Microbial contamination is a potential concern in pet food, and it can manifest at multiple stages, spanning from the acquisition of raw materials to processing, packaging, and storage. Furthermore, the final handling of pet food before consumption is recognized as a critical hazard, making consumers, retailers, distributors, and manufacturers jointly responsible for safeguarding the nutritional integrity and safety of these food products [10,11]. Microorganisms such as Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli, Campylobacter spp., and Listeria monocytogenes are of particular concern, as they have the potential to cause severe infections in both animals and humans [7,12,13,14]. Salmonella is the most important biological risk in animal nutrition, and there have been several reported instances of Salmonella contamination in pet food and treats in recent years [6,8,15,16,17]. Reports indicate that pet food may harbor additional microbial pathogens, including Listeria, Enterobacteriaceae, and Campylobacter [13,18,19,20,21]. Dogs can become carriers of these pathogens, leading to zoonotic transmission [22], underscoring the significance of the regular monitoring and evaluation of canned pet food.
Moreover, the presence of spoilage microorganisms in canned pet food can result in the degradation of its nutritional value, taste, and texture. Bacterial species, such as Pseudomonas, Enterobacter, and Clostridium, are known to contribute to food spoilage by producing enzymes, toxins, and off-odors [23,24,25]. The growth of these spoilage organisms is influenced by factors like water activity, pH, temperature, and packaging conditions [26,27]. Good microbiological quality of foods can be particularly important among groups of animals with reduced immunity. Among dogs, for example, these may include sick animals and canine seniors, but also puppies. Thus, the microbiological composition of the food, which includes the presence of potential pathogens or microorganisms causing food spoilage, determines the product’s quality and its shelf life.
In addition to microbial quality, nutritional adequacy is a critical aspect of dog foods, considering the distinct dietary requirements between adult dogs and growing puppies. Puppy feeding is a demanding period in dogs’ lives, full of challenges for their caregivers. The goal of a feeding plan for puppies is to create a healthy adult. The specific objectives of a good puppy feeding plan are to achieve healthy growth, meaning the progressive development of physical, cognitive, and behavioral attributes in a balanced manner, as well as to optimize trainability and immune function and minimize obesity and developmental orthopedic disease. Growth is a complex process involving interactions between genetics, nutrition, and other environmental influences. Nutrition plays a role in the health and development of growing dogs. Their need for energy is greater than at any other stage of a dog’s life, with the exception of lactation [28]. A mismatch in the amount of protein and energy in the diet may result in relative protein deficiency, which can cause immune problems and carbohydrate intolerance later in life [29]. Therefore, tailoring puppy foods to meet their specific protein and energy requirements is critical for ensuring the optimal size, form, and health in adult dogs.
The objective of this study was to assess the nutritional value and microbiological safety of canned food for puppies and adult dogs, categorized into grain-included and grain-free products, and to compare the findings with the information provided in the nutritional guidelines and on the product labels.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
For the experiment, various types of canned dog food available on the European market were selected, based on a database of all products intended for standard maintenance, as well as products specifically formulated for puppies and growing dogs. Additionally, the selection was based on the presence or absence of grains in the composition. A total of 20 commercial canned dog foods were included in the research material, comprising 10 canned foods for adult dogs (A, of which 5 included grains, GI, and 5 were grain-free, GF) and 10 canned foods for puppies and growing dogs (P, including 5 GI and 5 GF).
The canned dog food products were chosen from a mix of 6 international brands and 4 local brands, purchased locally from various commercial suppliers and pet food supermarkets. The size of the cans/jars varied, ranging from 380 g to 800 g.
The key nutritional information provided on the labels of the canned dog foods was recorded, including the macronutrient content. The country of origin and batch number of each product were also documented. The composition of the main ingredients of the canned dog foods is shown in the Supplementary Material (Table S1).
For a chemical analysis, representative samples were collected. Three units from the same batch were acquired for each food. In the laboratory, the three cans of the same diet were pooled, mixed thoroughly, and used for the analysis. The samples were weighed and dried in an oven at 65 °C for 48 h, then reweighed to measure their moisture content. Subsequently, the samples were ground into a powder using a laboratory mill (KNIFETEC 1095, Foss Tecator, Höganäs, Sweden), passed through a 1 mm sieve, and transferred to sterile containers labeled with consecutive symbols (samples 1–20). To avoid cross-contamination, the laboratory mill was thoroughly cleaned and vacuumed between processing different samples. Approximately 200 g of each milled sample was utilized for the chemical analysis, and three measurement replications were conducted for each sample to ensure accuracy and reliability.
The remaining milled samples were then stored in individual sealed containers at 4 °C until they were required for further microbial evaluation. The microbiological evaluation was performed within two weeks after purchase, immediately after opening the food.
2.2. Nutritional Value
2.2.1. Proximate Analysis
Dry matter (DM), crude protein (CP), crude fiber (CF), ether extract (EE), and crude ash (CA) were measured to assess the nutritional quality of the tested pet food. All tests were performed using ISO 17025 [30] accredited methods based on AOAC [31]. To determine dry matter, the samples were dried at 105 °C to a constant weight (method 945.15). Crude protein (N × 6.25) (method 945.18) was identified via the Kjeldahl method, using a Büchi Scrubber B414 unit and a Büchi 324 distillation set (Büchi Labortechnik AG, Flawil, Switzerland). Ether extract was identified via the traditional Soxhlet extraction method with diethyl ether (method 2003.06). Crude fiber was determined as residue after sequential treatment with 1.25% H2SO4 and with 1.25% NaOH using an ANKOM220 Fiber Analyser (ANKOM Technology, New York, NY, USA). Crude ash was measured by burning in a muffle furnace at 580 °C for 8 h (method 920.153). Nitrogen-free extract (NFE) was calculated as follows [32]:
The results are expressed as g per 100 g of DM. The levels of CP and EE were compared with the recommended amounts of these nutrients for adult dogs determined by FEDIAF [33]. The demand for nutrients recommended by the nutritional guidelines is expressed in a unit per 100 g of DM, assuming an energy density of 400 kcal.
2.2.2. Energy Value
Based on the identified chemical composition, the metabolizable energy (ME, kcal/100 g DM) of the foods was calculated, according to the predictive equation by the National Research Council [34], using a 4-step calculation.
2.3. Microbiological Analysis
The canned dog food samples were examined according to the requirements for microbiological examinations of food and animal feeding stuffs (ISO 7218:2007/Amd 1:2013) [35]. The preparation of samples and dilutions was performed according to the European standard for meat and meat products (ISO 6887-2:2017) [36]. The microbiological analyses were performed immediately after opening the can and included: the detection and enumeration of aerobic mesophilic bacteria (TAMBC, ISO 4833-2:2013) [37], Enterobacteriaceae (ISO 21528-1:2017) [38], Escherichia coli (ISO 7251:2005) [39], Salmonella spp. (ISO 6579-1:2017) [40], coagulase-positive staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus and other CPS species, ISO 6888-3:2003) [41], Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria spp. (ISO 11290-1:2017) [42], Clostridium perfringens (ISO 7937:2004) [43], Bacillus cereus (ISO 7932:2004) [44], Pseudomonas spp. (ISO 13720:2010) [45], and yeasts and molds (ISO 21527-1:2008) [46].
If the number of colonies was between 3 and 1, the result was calculated using the formula CFU/g of dog food.
However, if no colony of microorganisms was isolated, the result was calculated according to the formula CFU/g of dog food, where:
- d—sample dilution
- V—volume of the inoculum (mL).
To simulate home storage conditions, after opening, the cans of food were incubated at room temperature (20 °C) for 24 h. Next, the microbiological analyses were performed using the same ISO standards. In the case of the isolation of microorganisms after 24 h of incubation simulating home storage conditions, regardless of the number of colonies grown on appropriate media, the results were interpreted as the presence of microorganisms (D—detected). However, the lack of growth of microorganisms on the media despite the 24 h incubation of food samples was interpreted as an undetected microorganism (ND—not detected).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
A one-factorial analysis of variance (ANOVA) and principal component analysis (PCA) were carried out using the STATISTICA v13.3 software (TIBCO Software [47] Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference (HSD) at p = 0.05 was used to find the differences between means. The means denoted by different letters differed statistically.
To compare the nutritional value of the dog foods, we determined their compositions (CP, EE, CF, CA, NFE, and ME). The percentage of a given nutrient and metabolic energy in the profile is expressed by an arithmetic mean converted into units on a 9-point scale. For a profile comparison, Cohen’s profile similarity coefficient rc was used, calculated based on the following formula [48]:
where:
- Ai and Bi—unitarized values of traits included in the compared profiles A and B;
- n—number of traits in the profile;
- m—midpoint of the ranking scale.
This coefficient value was measured in the range from −1.00 to 1.00, and its interpretation depends on the value: x ≥ +0.75 (high similarity); + 0.75 > x > +0.30 (moderate similarity); + 0.30 ≥ x ≥ −0.30 (no similarity); −0.30 > x > −0.75 (moderate dissimilarity); and x ≤ −0.75 (high dissimilarity). The closer the values of rc were to the boundary values (1/−1), the stronger the evaluated similarity/dissimilarity was. An inter-profile analysis was conducted using MS Office 2017.
3. Results
3.1. Nutritional Value and Compliance with the Label
Significant differences were discovered in the amounts of the evaluated nutrients, depending on the food (Table 1).

Table 1.
Chemical composition (g/100 g DM) and energy value (kcal/100 g DM) of the analyzed commercial wet dog food 1.
Significantly greater amounts of protein and energy were found in the grain-free products than in the grain-included foods (with average values of 54.82 g of CP and 462.1 kcal versus 40.73 g of CP and 455.2 kcal in 100 g DM, respectively). Of all the foods analyzed, significantly more protein was found in the grain-free food for adult dogs 9_A_GF (74.71 g/100 g DM). The lowest levels of protein were in the grain-included foods 5_A_GI and 12_P_GI (30.78 and 31.67 g/100 g DM). Based on the FEDIAF [33] daily requirements, all 20 canned foods presented higher protein concentrations than the recommended minimum levels (18 g/100 g DM for adults considering an energy intake of 110 kcal/kg BW0.75 for dogs with moderate activity and 25 or 20 g/100 g DM for growing dogs, early and late growth, respectively) (Table 1).
Significantly more ether extract, crude ash, and NFE were found in the grain-included products. The greatest amount of ether extract was found in grain-free adult dog food no 6 (43.46 g/100 g DM, Table 1), and the lowest amount in grain-free adult dog food no 9 (18.18 g/100 g DM). All the tested canned foods presented higher ether extract concentrations than the recommended minimum levels (5.50 g/100 g DM for adults and 8.5 g/100 g DM for growing dogs). Dog food for puppies without grains (18_P_GF) had the highest level of crude ash (13.707 g/100 g DM, Table 1), and dog food for adults with grains (5_A_GI) had the highest level of NFE (38.721 g/100 g DM). The lowest amount of NFE was in the grain-free dog food for puppies at the level of less than 2% of DM (17_P_GF, 1.635 g/100 g DM, Table 1). The grain-free and grain-included foods did not differ in their mean levels of DM and crude fiber. In the case of the age division of dog foods, the growing dog foods contained significantly more ether extract, crude ash, crude fiber, and energy, and the foods for adult dogs contained significantly more NFE.
To avoid assessing individual differences in the levels of individual ingredients, we performed a comparative analysis of the nutritional profiles of the tested foods (Cohen’s profile similarity coefficient), which included the basic composition and metabolic energy of the foods. The number of comparisons of nutrient profiles for the grain-free foods was 45, and their differences prove a clear variation (Table 2). A lack of similarity (lack of color) was found 20 times, and dissimilarity coefficients (dissimilarity—red color) were found 8 times. This means that the remaining Cohen’s profile similarity coefficients (17) were above 0.3 (green) and reflected the similarity, i.e., graded conformity (shades of green) of the nutrient profiles in terms of nutrient content and energy value. In this group of foods (10 grain-free dog foods), the composition profile of 9_A_GF exhibited similarities with the profiles of as many as six other dog foods. However, the profile of this particular dog food significantly deviated from the profiles of the 6_A_GF and 18_P_GF foods (Table 2). This observed distinctiveness was further confirmed by the PCA analysis (Figure 1), as these dog foods are situated on opposite sides in the coordinate system (quadrants II and IV). While the differentiation between 9_A_GF and 18_P_GF is understandable, considering that these dog foods are designed for animals of different ages, the substantial dissimilarity of the profiles between 9_A_GF and 6_A_GF is surprising, given that both are intended for adult dogs. Food 9_A_GF is notably lower in energy and contains less EE and CA. Examining Figure 1, it is challenging to identify a clear differentiation between dog foods containing grains and those that are grain-free.

Table 2.
Comparative analysis of the nutritional profile (Cohen’s profile similarity coefficient) for grain-free (GF) and grain-included (GI) wet foods for adult dogs (A) and puppies (P).
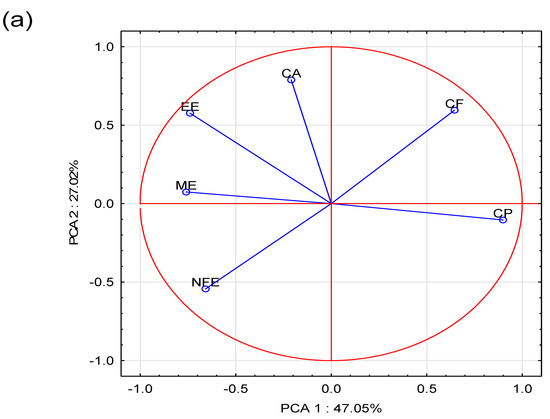
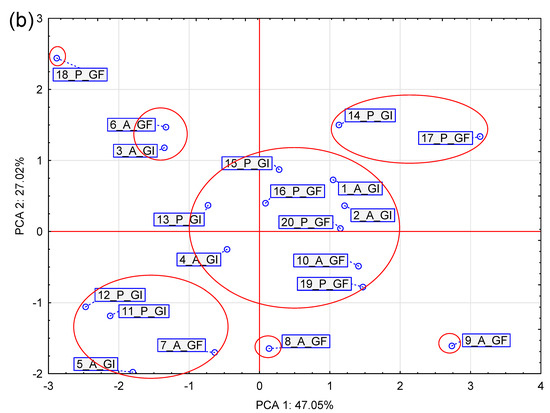
Figure 1.
Biplot based on first two principal component axes for nutritional value and metabolic energy of dog foods (a) and distribution of 20 commercial dog foods based on the first two components obtained from principal component analysis (b) (DM—dry matter; CP—crude protein; EE—ether extract; CF—crude fiber; CA—crude ash; NFE—nitrogen free extract; ME—metabolizable energy; A—food for adults dogs; P—food for puppies and growing dogs; GI—grain included; and GF—grain-free).
Within the GI dog foods, 18 dog foods showed dissimilarity (no color), 7 showed dissimilarity, and 20 dog foods showed similarity in their composition profiles. Within the puppy dog foods, out of 10 profile comparisons, as many as 7 rc values indicated a lack of similarity in the basic composition profiles. This signifies significant variation in these profiles, as only three rc values confirmed profile similarities, with the highest being observed between the dog foods 1_A_GI and 2_A_GI (0.947). In the P_GI group of dog foods, the differentiation appears even greater than that in the P_GF group, as dissimilarity in composition profiles was found between the dog food 14_P_GI and the dog foods 11 and 12_P_GI (−0.706 and −0.696, respectively). The compositional dissimilarity of these dog foods was confirmed by the PCA analysis (Figure 1), as these dog foods are located in opposite quadrants of the coordinate system (quadrants I and III). This variation in composition profiles between P_GI and A_GI was expected, but within the 25 comparisons, as many as 13 rc values confirmed the similarity of the basic composition profiles, and only 5 indicated the dissimilarity of these profiles (Table 2).
Within the puppy dog foods, only fourteen pairs of dog foods showed similarity (rc > 0.3) and eight showed dissimilarity (rc < 0.3). The remaining 23 coefficients confirmed the lack of similarity of the compared pairs of dog foods. Somewhat surprisingly, the dog foods 14_P_GI and 17_P_GF exhibited a high similarity in their composition profiles (rc = 0.832), as evident in the PCA analysis, which located these dog foods in the first quadrant of the coordinate system (Table 2). Despite their significant difference in composition (GI/GF), both dog foods had a higher CF content (Figure 1).
The adult dog foods appeared even more differentiated than the puppy dog foods, as 28 Cohen’s coefficients indicated no similarity, 6 indicated dissimilarity, and only 11 pairs of dog foods showed similarity. Similarities appeared between the A_GF and A_GI dog foods, with, for example, the 6_A_GF and 3_A_GI dog foods being situated close to each other in the second quadrant of the coordinate system. Strongly dissimilar from the other dog foods in this group were the foods 8_A_GF and 9_A_GF, situated at the bottom of the fourth quadrant of the coordinate system (Figure 1). They are characterized by a lower energy value and lower EE and CA contents compared to the other tested dog foods.
It is also interesting to examine the counts of Cohen’s coefficients comparing the puppy and adult dog foods and the grain-containing and grain-free dog foods. In the case of the first group of comparisons (puppy/adult), out of 100 pairs of comparisons, 37 had coefficients confirming similarity, and there were only 22 confirming dissimilarity between the pairs of compared dog foods. The frequencies of Cohen’s coefficients in the GI and GF comparison group were slightly more favorable. In this case, out of 100 coefficients, 25 confirmed similarity and 21 confirmed dissimilarity. The large number of similarity coefficients between dog foods that, due to different compositions (GI/GF) or age targets (puppy/adult), should have differed, indicates the limited validity of such divisions in the analyzed set of dog foods.
3.2. Compliance with Dog Food Label Declarations
In terms of the percentage distribution of the tested canned foods, based on the disparities between the declared data and laboratory analysis results, it was found that almost half of the tested samples contained a higher ether extract content (40% of samples) than what the manufacturer had declared on the label. The largest excess for ether extract was observed in the 18_P_GF sample by more than 36% above the maximum allowable tolerance level (Table 3). In six canned dog foods (30% of samples), the manufacturers overstated the amount of ether extract on the label relative to the results of our analysis.

Table 3.
Percentage non-compliance with label declarations: comparison of the obtained results of the analytical composition with tolerances for analytical constituents [49].
An underestimation of the amounts of protein and crude ash on the food label occurred in seven foods (35% of the samples). Our analyses showed over 88% more crude ash above the tolerance range in the food 2_A_GI and over 50% more crude protein in the food 8_A_GF than the labels of these products declared. Higher amounts of crude ash on the label than in our analysis were detected in two foods for growing dogs (10% of samples), and for crude protein, in three foods (15%, including two for adult dogs and one for puppies). Three pet foods were found to have label irregularities for all of the nutrients analyzed, and only two foods were fully compliant with their label claims (in terms of tolerability), (Table 3).
3.3. Microbiological Safety
In 2 out of 20 (10%) samples of canned dog food, levels lower than 4 × 101 CFU/g of dog food of aerobic mesophilic bacteria were detected (Table 4). No Enterobacteriaceae family, including E. coli and Salmonella spp., and CPS, Listeria spp., Clostridium spp., Bacillus spp., Pseudomonas spp., as well as yeasts or molds, were detected in analyzed canned dog food samples (<1 × 101 CFU/g of dog food, Table 4).

Table 4.
Microbiological analysis of the canned dog foods—in accordance with ISO standards 1.
In turn, after storing open cans of dog food for 24 h, the presence of aerobic mesophilic bacteria was confirmed in two samples (dog food 6_A_GF and 12_P_GI, Table 4 and Table 5). Moreover, after this 24 h of incubation, bacteria were isolated from 17 (85%) foods samples (Table 5). In only one sample (5%), despite 24 h of incubation, no microorganisms were detected (Table 5).

Table 5.
Microbiological analysis of the canned dog foods—after 24 h incubation.
Furthermore, after 24 h of incubation for the open canned dog food (Table 5), the Enterobacteriaceae were found in six (30%) samples, although Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. were not identified. In turn, CPS were detected in six (30%) samples, although Staphylococcus aureus was not confirmed. Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas spp. were isolated from six (30%) and five (25%) samples of canned dog food, respectively. None of the samples of food from the open cans contained Listeria spp., Clostridium perfringens, yeast, or molds (Table 5).
The highest microbiological diversity was observed in one (5%) sample of canned dog food (18_P_GF), from which Enterobacteriaceae, CPS, and Pseudomonas spp. were isolated (Table 5).
The conducted statistical analyses aimed at determining the relationship between the frequency of microbiological contamination within the examined types of canned dog food (GF/GI and puppy/adult) do not allow for the confirmation of such a relationship (Table 5).
4. Discussion
Regulatory compliance for labelling is required for commercial pet foods marked as complete. Pet food labels offer valuable insights into product details and serve as a crucial resource for pet owners when determining how to nourish their pets. However, studies analyzing the use of pet food labels have indicated that fewer than 40% of pet caregivers consistently review these labels when making feeding decisions [50], although this may have changed in recent years as consumers have become increasingly aware. While, in our study, all the tested canned dog foods were in line with the recommended levels of macronutrients stated in the nutritional guidelines [33], significant discrepancies were observed between the manufacturer’s label declarations and the results of the chemical analysis. Among the analytical constituents, discrepancies in ether extract and crude protein contents were the most prevalent in the canned dog foods evaluated in this study (70% and 50% of the tested canned dog foods were inconsistent with the manufacturer’s claims for EE and CP, respectively). More specifically, in 40% of the products, the measured ether extract content was found to be higher than that declared. While the FEDIAF guidelines do not specify a maximum recommended fat intake, the NRC [34] suggests a safe upper limit (SUL) of 82.5 g fat/1000 kcal for dogs. This recommendation is based on evidence indicating a potential association between high-fat diets and the development of acute pancreatitis in dogs [51,52]. It is important to note that this relationship has not been definitively established [53]. Nevertheless, it is advised to avoid feeding commercial high-fat diets to dogs at a heightened risk of developing acute pancreatitis or those with altered lipid profiles, such as obese dogs [54]. Alarmingly, among the canned dog foods evaluated in this study, one dog food intended for growth (18_P_GF) provided significantly less crude protein (−15.4%) while containing more ether extract (+36.9%) than what the manufacturer stated on the label. Feeding dogs a high-fat, high-energy, low-protein diet can lead to insufficient protein (and amino acid) intake or an excess of energy [55]. Providing such food to a puppy can be harmful to their growth and may have lasting consequences on their future adult lives. Research conducted on rats [56] has demonstrated that a high-fat, low-protein diet may elicit significant physiological, metabolic, and histological changes in rat models, and these alterations appeared to be associated with the development of metabolic syndrome and the potential disruption of cognitive functions in female rats. Fortunately, some previous assessments have confirmed compliance with regulations in the case of pet food, resulting in relatively favorable outcomes. For instance, in the United States, the variation between the protein content indicated on labels and the actual analyzed protein content in pet food was considered to be acceptable [57]. However, in Canada, 11% of dry pet food samples fell below the lower tolerance threshold for protein content [58], while, in our study, three canned dog foods (15%) exhibited protein content below the lower tolerance threshold (Table 3). In these products, the protein content on the label was overestimated by an average of 7.7%. In turn, a similar study conducted in Brazil [59] on canned dog foods found an overestimation of the composition declared on the label compared to the actual content, with the following discrepancies: total protein by 2.6%, ether extract by 1.2%, crude fiber by 3.7%, and crude ash by 6.4%. In our study, for the amount of ether extract, there was an overestimation of the composition declared on the label compared to the actual content in six canned dog foods (by an average of 9.1%) and an underestimation in eight canned dog foods (by an average of 12.0%). We posit that the disparities observed between the label data and the analysis results do not indicate intentional data falsification by the manufacturer. It is essential to underscore that our study involved the analysis of only three batches of a particular product, recognizing the potential for variations among batches. However, despite this limitation, we assert that this report will serve as an impetus for manufacturers to enhance and rigorously monitor the nutritional value of both their raw materials and finished products, aiming to mitigate the occurrence of such discrepancies in the future.
It is worth noting that our study, surprisingly, showed that the intended age of use for the dog food (puppy/adult) and the presence or absence of grains in the formula did not highly differentiate these groups of foods from each other. Although puppy foods contained, on average, more ether extract, crude fiber, crude ash, and energy than adult dog foods, and grain-free foods contained more crude protein and energy than grain-included dog foods (Table 1), Cohen’s similarity analysis (Table 2) revealed a large number of similarity coefficients between these groups of foods, indicating the limited validity of such divisions in the analyzed set of canned dog foods. This confirms other studies on cat foods in which the inclusion or exclusion of cereals in the formulation and the categorization of foods by life stage did not significantly impact the crude protein content of the pet foods [60]. However, it is essential to note that this does not imply interchangeability between puppy and adult dog food. Our study only analyzed basic nutrients (macronutrients), and variations in individual amino acids, minerals, and fatty acids, specific to each age category, were not considered. These parameters, unexplored in this study, can significantly influence product differentiation. Additionally, although not conclusively demonstrated in our study, the presence or absence of grains can indeed influence the nutritional value of the final product, as suggested by earlier research [61,62]. In our previous investigation [62], the addition of grains to dog food notably impacted the quantity of carbohydrates in the diet, concurrently reducing the average contents of protein, fat, and ash. The grain-free trend in the pet food sector has gained substantial attention [63], underscoring the significance of taking these factors into account when choosing dog food.
Pet food is subjected to strict regulations to ensure the highest standards of hygiene, safety, and quality. European pet food manufacturers are obligated to comply with a series of regulations that cover the entire production process, from the selection of raw materials to the sale of the final products [33]. However, there is a lack of strict regulations regarding the maximum limits for individual biological contaminants in pet food. Under EU regulations, it is stipulated that “the feed business is primarily responsible for feed safety” [64]. Nevertheless, numerous publications have highlighted concerns related to the quality and safety of pet food [21,65]. In recent years, the most attention in scientific research on commercial pet foods has been focused on the relatively new raw dog and cat foods in the market (raw-meat-based diets, RMBDs). On the one hand, they have gained popularity among pet caregivers seeking a more natural feeding option than conventional, processed pet food. On the other hand, these products have raised significant concerns about their microbiological quality and safety. These diets remain unprocessed, making them susceptible to pathogenic bacterial contamination, which can pose significant risks to pets’ health. Numerous studies have reported the adverse consequences of feeding RMBDs to dogs, including bacterial diseases, parasitic diseases, and nutrient imbalances [19,20,66,67,68,69,70,71,72].
The microbiological quality of canned dog foods is less frequently addressed in scientific research. Canned pet foods undergo a heat treatment process to attain commercial sterility, effectively removing heat-sensitive pathogens. Consequently, they are generally considered to be safe and reliable products. On the other hand, pet food recalls have been reported due to, e.g., contamination with mycotoxins [73]. In our prior investigation examining the microbiological quality of dry dog foods [74], molds, which may be responsible for mycotoxin presence, were identified in nearly 20% of the tested dog foods. Notably, the presence of mold was found to be correlated with the inclusion of cereals in the dog food composition. The presence of mold was correlated with the presence of grains in the composition of the dog food, since yeast and mold presence was more common in grain-included dog foods (six out of seven positive results applied to grain foods, 86%). In a study assessing the microbiological safety of dry and canned pet food marketed in Lebanon, the results showed that a number of dry pet food samples had higher bacterial contamination than canned samples [75]. However, the same study showed that canned pet food products may also harbor food-borne pathogens such as Salmonella, Listeria, and Enterobacteriaceae (in 26%, 54%, and 8% of canned tested samples, respectively). In turn, in research assessing the microbiological quality of feed mixtures used in Poland in 2007–2010 [76], the results showed that the highest level of Enterobacteriaceae contamination was found in wet pet foods.
Although measures taken during production, distribution, and usage significantly influence the quality and safety of pet foods, the importance of consumer habits in maintaining these aspects seems to be largely overlooked. Improper handling and storage practices by pet caregivers can compromise the quality of dry and canned commercial pet foods, thereby posing risks to both humans and animals. Such contaminated foods can adversely affect the well-being and health of animals, necessitating careful preservation of their sensory profile, nutritional value, and microbiological safety until consumption [74,77,78]. Canned pet foods undergo heat treatment to achieve commercial sterility by eliminating heat-sensitive pathogens, ensuring that these products are free from pathogens when opened. This fact was confirmed by our research, which indicated the good microbiological quality of the cans in the microbiological analyses (Table 4). However, the presence of pathogens after an additional 24 h of incubation simulating home storage conditions was observed (Table 5). In our study, 24 h of incubation showed the presence of bacteria in 85% of the tested dog foods (Table 5). Interestingly, statistical analyses indicated that the presence of a grain component in canned dog food does not have a confirmed association with an elevated risk of microbiological contamination by Enterobacteriaceae, CPS, Bacillus cereus, or Pseudomonas spp. Likewise, the analyses conducted do not permit the conclusion that canned dog food designed for various age groups exhibits variations in microbiological purity. The presence of Enterobacteriaceae, coagulase-positive staphylococci, Bacillus cereus, and Pseudomonas spp. were observed in few tested dog foods. The contamination of Enterobacteriaceae can be associated with the presence of fecal or intestinal content, suggesting inadequate hygiene practices at the slaughterhouse or improper storage methods [79]. In this study, Enterobacteriaceae were found after 24 h of incubation simulating home storage conditions in six samples of dog food (30%), although the presence of Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. was excluded.
Pseudomonas spp. are a group of aerobic, Gram-negative bacteria that are commonly found in food-processing environments and are recognized as major food spoilage microorganisms [80]. In our study, Pseudomonas spp. were isolated after 24 h of incubation from five (25%) samples of canned dog food. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this marks the first instance of Pseudomonas bacteria being detected in pet food. The sample with the highest bacterial diversity was the dog food sample 18_P_GF, from which Enterobacteriaceae, CPS, and Pseudomonas spp. were isolated (Table 5). This discovery raises a considerable concern, especially considering that this particular food is intended for puppies, a group of dogs with immature immune systems. It is essential to highlight that puppy dog foods do not adhere to higher microbial control standards. This lack of stringent standards in microbial control for puppy food poses an increased risk, given the vulnerability of puppies to potential health issues. Therefore, this emphasizes the need for heightened attention to quality control measures and microbial safety in the production of dog food, particularly that designed for puppies.
Bacillus cereus is a Gram-positive, spore-forming bacterium that is commonly associated with food poisoning, posing a significant public health concern worldwide [81]. This organism has garnered attention due to its ability to produce toxins that can cause gastrointestinal distress when ingested. These toxins are heat-stable, allowing them to persist in contaminated food items even after cooking. Because of its abundance and the resistance of its spores, B. cereus contaminates nearly all agricultural products and plays a major role in the contamination and spoilage of food products [82,83]. In one of the more recent studies, B. cereus contamination of home products packed in retort pouches and glass jars prepared for sale in Malaysia was assessed [84]. It was found that the B. cereus count of 20% of samples exceeded the acceptable limit (>1 × 104 CFU/g). In our study, B. cereus was isolated from six (30%) samples of wet dog food after 24 h of incubation, two of which were puppy foods, and four products contained cereals in their formulation (Table 5). This represents the first case of B. cereus identification in pet food.
The 24 h incubation of food at 20 °C used in this work was designed to mimic the conditions at home, where a can of dog food is often left open for several, if not dozens of hours. This duration of open-can storage is influenced by the can size and the size of the dog, with larger cans and smaller dogs leading to longer storage times. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize the importance of responsible storage practices to preserve the safety and nutritional integrity of pet food. Caregivers should consistently adhere to the storage recommendations provided by the manufacturer on the label. Once opened, canned wet foods should be stored in the fridge and consumed by a dog within 24 h.
5. Conclusions
In summary, while all the tested foods met the minimum standards set by FEDIAF, certain deviations were noted, including, for example, a reduced protein content and increased ether extract content compared to the declared values on the labels. This is especially unsafe in puppy foods and may lead to an improper energy balance in daily dosages, leading to impaired growth and disease in the dog’s future. This emphasizes the importance of the continued verification of the accuracy of the information provided on dog food labels. Also, comparative analyses revealed that the affiliation of pet food to the group described on the package (adult dog/puppy) is not binding, as demonstrated by the similarity among dog foods that were completely label-separate.
Furthermore, our microbiological analysis indicated that canned dog foods were generally safe upon their initial opening. However, after an additional incubation period, the presence of bacteria, including Enterobacteriaceae, coagulase-positive staphylococci, Bacillus cereus, and Pseudomonas spp., was observed in the majority (85%) of the tested products. Statistical analyses revealed that there was no confirmed association between the presence of a grain component in the canned dog food and an increased risk of microbiological contamination by Enterobacteriaceae, CPS, Bacillus cereus, or Pseudomonas spp. Similarly, the conducted analyses do not allow for the determination that canned dog foods for different age groups differ in microbiological purity. These findings contribute significantly to the existing body of knowledge regarding the microbiological safety of canned pet food. By identifying potential microbial risks and suggesting appropriate control measures, we can ensure that canned pet food for dogs meets the highest standards of safety and quality.
Further research is warranted to comprehensively characterize and identify the microorganisms that may proliferate in canned food following prolonged exposure to ambient conditions, as well as to assess their antibiotic resistance profiles. A deep understanding of these dynamics is essential for ensuring the safety and nutritional quality of pet food, underscoring the need for responsible storage practices. This study also adds to the knowledge database regarding the potential contamination of pet food by microorganisms, as it represents the first report on the contamination of wet dog food by Pseudomonas bacteria and Bacillus cereus.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app14020760/s1, Table S1. Main ingredients of analyzed wet dog foods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K. and W.B.; methodology, K.K., W.B., R.W. and J.K.-K.; software, R.W.; validation, W.B. and R.W.; formal analysis, K.K.; investigation, K.K. and J.K.-K.; resources, K.K. and J.K.-K.; data curation, K.K.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K., W.B., R.W. and J.K.-K.; writing—review and editing, K.K., W.B., R.W. and J.K.-K.; visualization, K.K. and R.W.; supervision, K.K., W.B. and R.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Julia Uhlendorf from the West Pomeranian University of Technology in Szczecin, Poland, for her contributions during isolation of microorganisms.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Baker, T.; Rock, M.; Bondo, K.; Van Der Meer, F.; Kutz, S. 11 Years of Regular Access to Subsidized Veterinary Services Is Associated with Improved Dog Health and Welfare in Remote Northern Communities. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 196, 105471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Morales-Medina, J.C.; Cocco, R.; Palmieri, B.; Pezzuto, F.; Flores, G.; Iannitti, T. Functional Foods in Pet Nutrition: Focus on Dogs and Cats. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 112, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauktis, M.E.; Rose, L.; Chen, Q.; Martone, R.; Martello, A. “Their Pets Are Loved Members of Their Family”: Animal Ownership, Food Insecurity, and the Value of Having Pet Food Available in Food Banks. Anthrozoös 2017, 30, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, A.R.; Lloyd, E.P.; Humphrey, B.T. We Are Family: Viewing Pets as Family Members Improves Wellbeing. Anthrozoös 2019, 32, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramini, T.H.A.; Pedrinelli, V.; Macedo, H.T.; Zafalon, R.V.A.; Risolia, L.W.; Rentas, M.F.; Macegoza, M.V.; Gameiro, A.H.; Brunetto, M.A. Homemade versus Extruded and Wet Commercial Diets for Dogs: Cost Comparison. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behravesh, C.B.; Ferraro, A.; Deasy, M.; Dato, V.; Moll, M.; Sandt, C.; Rea, N.K.; Rickert, R.; Marriott, C.; Warren, K.; et al. Human Salmonella Infections Linked to Contaminated Dry Dog and Cat Food, 2006–2008. Pediatrics 2010, 126, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanishi, M.; Rotstein, D.S.; Reimschuessel, R.; Schwensohn, C.A.; Woody, D.H.; Davis, S.W.; Hunt, A.D.; Arends, K.D.; Achen, M.; Cui, J.; et al. Outbreak of Salmonella Enterica Serotype Infantis Infection in Humans Linked to Dry Dog Food in the United States and Canada, 2012. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 244, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambertini, E.; Buchanan, R.L.; Narrod, C.; Ford, R.M.; Baker, R.C.; Pradhan, A.K. Quantitative Assessment of Human and Pet Exposure to Salmonella Associated with Dry Pet Foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 216, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamimuzzaman; Roy, R.K.; Majumder, T.R.; Barman, N.C.; Lina, N.N.; Hasan, T.; Dash, B.K. Microbial Profile of Some Ready-to-Cook Frozen Food Items Sold in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, G.; Stefanutti, D.; Ricci, R. A Survey among Dog and Cat Owners on Pet Food Storage and Preservation in the Households. Animals 2021, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langiano, E.; Ferrara, M.; Lanni, L.; Viscardi, V.; Abbatecola, A.M.; De Vito, E. Food Safety at Home: Knowledge and Practices of Consumers. J. Public Health 2012, 20, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilung, L.M.; Ulok, V.; Tesfamariam, F.M.; Apun, K. Assessment of Listeria Monocytogenes in Pet Food. Agric Food Secur. 2018, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemser, S.M.; Doran, T.; Grabenstein, M.; McConnell, T.; McGrath, T.; Pamboukian, R.; Smith, A.C.; Achen, M.; Danzeisen, G.; Kim, S.; et al. Investigation of Listeria, Salmonella, and Toxigenic Escherichia Coli in Various Pet Foods. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, B.N.; Porter, C.J.; Ryvar, R.; Stavisky, J.; Williams, N.J.; Pinchbeck, G.L.; Birtles, R.J.; Christley, R.M.; German, A.J.; Radford, A.D.; et al. Prevalence of Campylobacter spp. in a Cross-Sectional Study of Dogs Attending Veterinary Practices in the UK and Risk Indicators Associated with Shedding. Vet. J. 2010, 184, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adley, C.; Dillon, C.; Morris, C.P.; Delappe, N.; Cormican, M. Prevalence of Salmonella in Pig Ear Pet Treats. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, R.; Reid-Smith, R.; Weese, J.S.; Angulo, F.J. Human Health Implications of Salmonella-Contaminated Natural Pet Treats and Raw Pet Food. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Bethune, L.; Jia, Y.; Lovell, R.; Proescholdt, T.; Benz, S.; Schell, T.; Kaplan, G.; McChesney, D. Surveillance of Salmonella Prevalence in Animal Feeds and Characterization of the Salmonella Isolates by Serotyping and Antimicrobial Susceptibility. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, O. Hygiene Quality and Presence of ESBL-Producing Escherichia Coli in Raw Food Diets for Dogs. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 28758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bree, F.P.J.; Bokken, G.C.A.M.; Mineur, R.; Franssen, F.; Opsteegh, M.; van der Giessen, J.W.B.; Lipman, L.J.A.; Overgaauw, P.A.M. Zoonotic Bacteria and Parasites Found in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Cats and Dogs. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellgren, J.; Hästö, L.S.; Wikström, C.; Fernström, L.-L.; Hansson, I. Occurrence of Salmonella, Campylobacter, Clostridium and Enterobacteriaceae in Raw Meat-Based Diets for Dogs. Vet. Rec. 2019, 184, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kępińska-Pacelik, J.; Biel, W.; Witkowicz, R.; Frączek, K.; Bulski, K. Assessment of the Content of Macronutrients and Microbiological Safety of Dry Dog Foods. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 165, 105071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, M.-L.; Nunes, A.; Ancora, M.; Cammà, C.; da Costa, P.M.; Oleastro, M. Campylobacter Jejuni in Different Canine Populations: Characteristics and Zoonotic Potential. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rood, L.; Bowman, J.P.; Ross, T.; Corkrey, R.; Pagnon, J.; Kaur, M.; Kocharunchitt, C. Spoilage Potential of Bacterial Species from Chilled Vacuum-Packed Lamb. Food Microbiol. 2022, 107, 104093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Sun, J.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, T. Unraveling Characterizations of Bacterial Community and Spoilage Profiles Shift in Chilled Pork during Refrigerated Storage. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, e80321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, R.; Luo, X. Microbial Community Dynamics Analysis by High-Throughput Sequencing in Chilled Beef Longissimus Steaks Packaged under Modified Atmospheres. Meat Sci. 2018, 141, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Williams, M.; Bissett, A.; Ross, T.; Bowman, J.P. Effect of Abattoir, Livestock Species and Storage Temperature on Bacterial Community Dynamics and Sensory Properties of Vacuum Packaged Red Meat. Food Microbiol. 2021, 94, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Youssef, M.K.; Gill, C.O.; Badoni, M.; López-Campos, Ó. Effects of Meat pH on Growth of 11 Species of Psychrotolerant Clostridia on Vacuum Packaged Beef and Blown Pack Spoilage of the Product. Food Microbiol. 2014, 39, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, L.P.; Daristotle, L.; Hayek, M.G.; Raasch, M.F. Canine and Feline Nutrition, 3rd ed.; Mosby Elsevier: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-323-06619-8. [Google Scholar]
- Nap, R.C.; Hazewinkel, H.A.; Voorhout, G.; Van den Brom, W.E.; Goedegebuure, S.A.; Van ’T Klooster, A.T. Growth and Skeletal Development in Great Dane Pups Fed Different Levels of Protein Intake. J. Nutr. 1991, 121, S107–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN ISO 17025; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 21st ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pomeranz, Y.; Meloan, C.E. Carbohydrates. In Food Analysis: Theory and Practice; Pomeranz, Y., Meloan, C.E., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 625–677. ISBN 978-1-4615-6998-5. [Google Scholar]
- FEDIAF. Nutritional Guidelines for Complete and Complementary Pet Food for Cats and Dogs; The European Pet Food Industry: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Dogs and Cats; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN ISO 7218; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—General Requirements and Guidance for Microbiological Examinations—Amendment 1. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- PN-EN ISO 6887-2; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Preparation of Test Samples, Initial Suspension and Decimal Dilutions for Microbiological Examination—Part 2: Specific Rules for the Preparation of Meat and Meat Products. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- PN-EN ISO 4833-2; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 2: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Surface Plating Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- PN-EN ISO 21528-1; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Enterobacteriaceae—Part 1: Detection of Enterobacteriaceae. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- PN-EN ISO 7251; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Presumptive Escherichia Coli—Most Probable Number Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- PN-EN ISO 6579; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella Spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- PN-EN ISO 6888-3; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci (Staphylococcus Aureus and Other Species)—Part 3: Detection and MPN Technique for Low Numbers. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- PN-EN ISO 11290; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria Monocytogenes and of Listeria Spp.—Part 1: Detection Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- PN-EN ISO 7937; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Clostridium Perfringens—Colony-Count Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- PN-EN ISO 7932; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Presumptive Bacillus Cereus—Colony-Count Technique at 30 Degrees C. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- PN-EN ISO 13720; Meat and Meat Products—Enumeration of Presumptive Pseudomonas Spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- PN-EN ISO 21527-1; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Yeasts and Moulds—Part 1: Colony Count Technique in Products with Water Activity Greater than 0.95. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; 0.
- TIBCO Software. TIBCO. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/321061529/STATISTICA-Electronic-Manual (accessed on 23 October 2020).
- Cohen, J. rc: A Profile Similarity Coefficient Invariant over Variable Reflection. Psychol. Bull. 1969, 71, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2022/1104 of 1 July 2022 Amending Regulation (EU) No 68/2013 on the Catalogue of Feed Materials; The European Comission: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2022.
- Lemke, R.J.; Burkholder, W.J.; Conway, C.E.; Lando, A.M.; Valcin, S. An Analysis of Pet Food Label Usage. J. Consum. Aff. 2015, 49, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haig, T.H.B. Experimental pancreatitis intensified by a high fat diet. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1970, 131, 914–918. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, S.; Entenman, C.; Chaikoff, I.L. Pancreatitis accompanying hepatic disease in dogs fed a high fat, low protein diet. Arch. Pathol. 1948, 45, 635–638. [Google Scholar]
- Lem, K.Y.; Fosgate, G.T.; Norby, B.; Steiner, J.M. Associations between Dietary Factors and Pancreatitis in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2008, 233, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, R.S.; Kass, P.H.; Shofer, F.S.; Van Winkle, T.J.; Washabau, R.J. Evaluation of Risk Factors for Fatal Acute Pancreatitis in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1999, 214, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raubenheimer, D.; Machovsky-Capuska, G.E.; Gosby, A.K.; Simpson, S. Nutritional Ecology of Obesity: From Humans to Companion Animals. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, S26–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharavath, R.N.; Arora, S.; Bishnoi, M.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Chopra, K. High Fat-Low Protein Diet Induces Metabolic Alterations and Cognitive Dysfunction in Female Rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.C.; Choate, C.J.; Scott, K.C.; Molenberghs, G. Comparison of the Guaranteed Analysis with the Measured Nutrient Composition of Commercial Pet Foods. Javma 2009, 234, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdett, S.W.; Mansilla, W.D.; Shoveller, A.K. Many Canadian Dog and Cat Foods Fail to Comply with the Guaranteed Analyses Reported on Packages. Can. Vet. J. 2018, 59, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Urrego, M.I.G.; Ernandes, M.C.; Matheus, L.F.D.O.; Santos, K.D.M.; Oba, P.M.; Silva, C.G.P.; Vendramini, T.H.A.; Pedrinelli, V.; Brunetto, M.A. Nutritional Composition and Evaluation of Different Methodologies for Fat Determination in Wet Feed for Dogs and Cats. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2017, 54, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, S.C.; Stockman, J.; Larsen, J.A.; Zhang, L.; Rodriguez, A.S. Evaluation of Phosphorus, Calcium, and Magnesium Content in Commercially Available Foods Formulated for Healthy Cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzali, J.G.; Aldrich, C.G. Effect of Ancient Grains and Grain-Free Carbohydrate Sources on Extrusion Parameters and Nutrient Utilization by Dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 3758–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierska, K.; Biel, W.; Witkowicz, R. Mineral Composition of Cereal and Cereal-Free Dry Dog Foods versus Nutritional Guidelines. Molecules 2020, 25, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meineri, G.; Candellone, A.; Bello, F.D.; Gastaldi, D.; Medana, C.; Peiretti, P.G. Gluten Contamination of Canned and Dry Grain-Free Commercial Pet Foods Determined by HPLC-HRMS. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 19, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament, Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 183/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 January 2005 Laying down Requirements for Feed Hygiene; European Parliament, Council of the European Union: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Witaszak, N.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Bocianowski, J.; Stępień, Ł. Contamination of Pet Food with Mycobiota and Fusarium Mycotoxins—Focus on Dogs and Cats. Toxins 2020, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottari, B.; Bancalari, E.; Barera, A.; Ghidini, S.; Gatti, M. Evaluating the Presence of Human Pathogens in Commercially Frozen, Biologically Appropriate Raw Pet Food Sold in Italy. Vet. Rec. 2020, 187, e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, L.M.; Michel, K.E. Evaluation of Raw Food Diets for Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, B.; Stengel, C.; Neiger, R. Dietary Hyperthyroidism in Dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 53, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, J.; Joffe, D.; Kauffman, M.; Zhang, Y.; LeJeune, J. Perceptions, Practices, and Consequences Associated with Foodborne Pathogens and the Feeding of Raw Meat to Dogs. Can. Vet. J. 2009, 50, 637–643. [Google Scholar]
- Strohmeyer, R.A.; Morley, P.S.; Hyatt, D.R.; Dargatz, D.A.; Scorza, A.V.; Lappin, M.R. Evaluation of Bacterial and Protozoal Contamination of Commercially Available Raw Meat Diets for Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 228, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiato, C.G.; Schwaiger, K.; Biagi, G.; Dobenecker, B. From Nutritional Adequacy to Hygiene Quality: A Detailed Assessment of Commercial Raw Pet-Food for Dogs and Cats. Animals 2022, 12, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, J.S.; Rousseau, J.; Arroyo, L. Bacteriological Evaluation of Commercial Canine and Feline Raw Diets. Can. Vet. J. 2005, 46, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, K.; Rumbeiha, W.K. Pet Food Recalls and Pet Food Contaminants in Small Animals: An Update. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 48, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierska, K.; Biel, W.; Witkowicz, R.; Karakulska, J.; Stachurska, X. Evaluation of Nutritional Value and Microbiological Safety in Commercial Dog Food. Vet. Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, M.; Hadid, M.; Dimassi, H.; Deghel, M.; Hassan, H.F. Microbiological Safety of Commercial Canned and Dry Pet Food Products in Lebanon. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 995184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukier, E.; Goldsztejn, M.; Grenda, T.; Kwiatek, K.; Wasyl, D.; Hoszowski, A. Microbiological Quality of Compound Feed Used in Poland. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2012, 56, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, K.; Głogowski, R. Selected Quality Properties of Lipid Fraction and Oxidative Stability of Dry Dog Foods under Typical Storage Conditions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kępińska-Pacelik, J.; Biel, W. Microbiological Hazards in Dry Dog Chews and Feeds. Animals 2021, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylis, C.L. Enterobacteriaceae. In Food Spoilage Microorganisms; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2006; pp. 624–667. [Google Scholar]
- Møretrø, T.; Langsrud, S. Residential Bacteria on Surfaces in the Food Industry and Their Implications for Food Safety and Quality. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 1022–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeni, J.L.; Lee Wong, A.C. Bacillus Cereus Food Poisoning and Its Toxins. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M.W.; Schraft, H. Chapter 20—Bacillus Cereus Food Poisoning. In Foodborne Diseases, 3rd ed.; Dodd, C.E.R., Aldsworth, T., Stein, R.A., Cliver, D.O., Riemann, H.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 395–405. ISBN 978-0-12-385007-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovic, J.; Ornelis, V.F.M.; Madder, A.; Rajkovic, A. Bacillus Cereus Food Intoxication and Toxicoinfection. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3719–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.A.C.; Jamzuri, M.N.S.; Ahmad, F.; Zamri, A.I.; Chilek, T.Z.T. Bacillus Cereus Contamination in Selected Home-Based Food Products Sold Throughout Malaysia. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2023, 19, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).