Implementation of COGNIVITRA, an Information- and Communications-Technology-Based Solution for Dual-Task Training, in Patients at Risk of Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
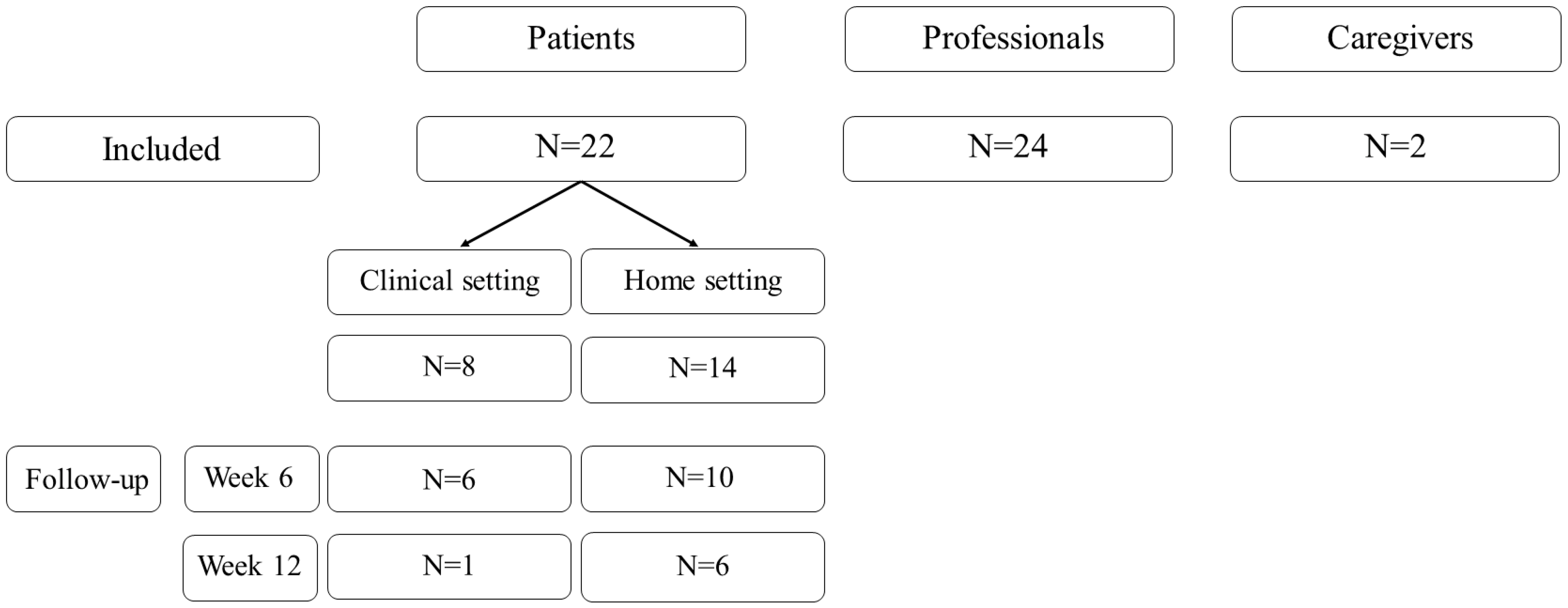
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Variables and Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
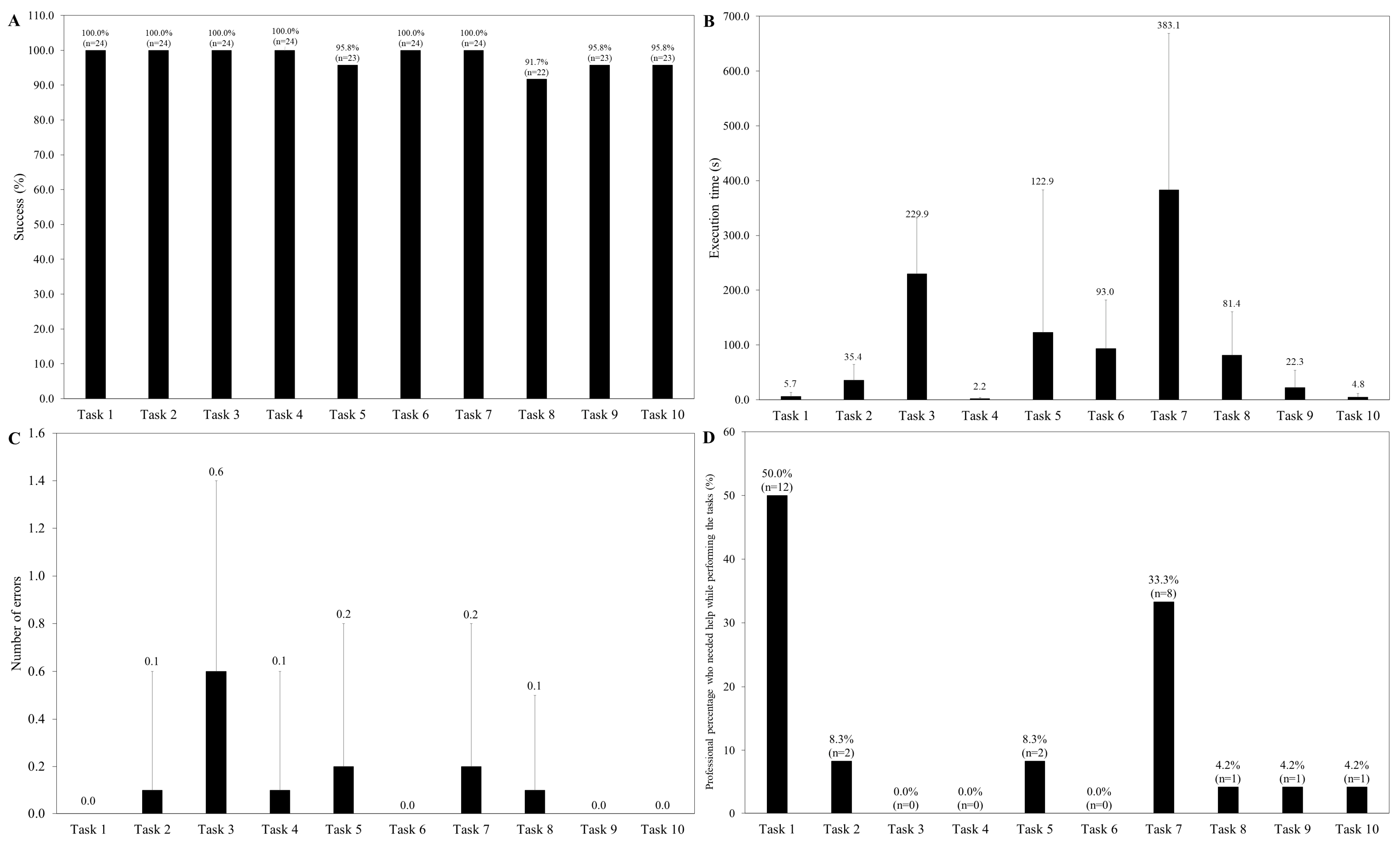
3.1. Usability and User Experience Evaluation
3.2. Satisfaction
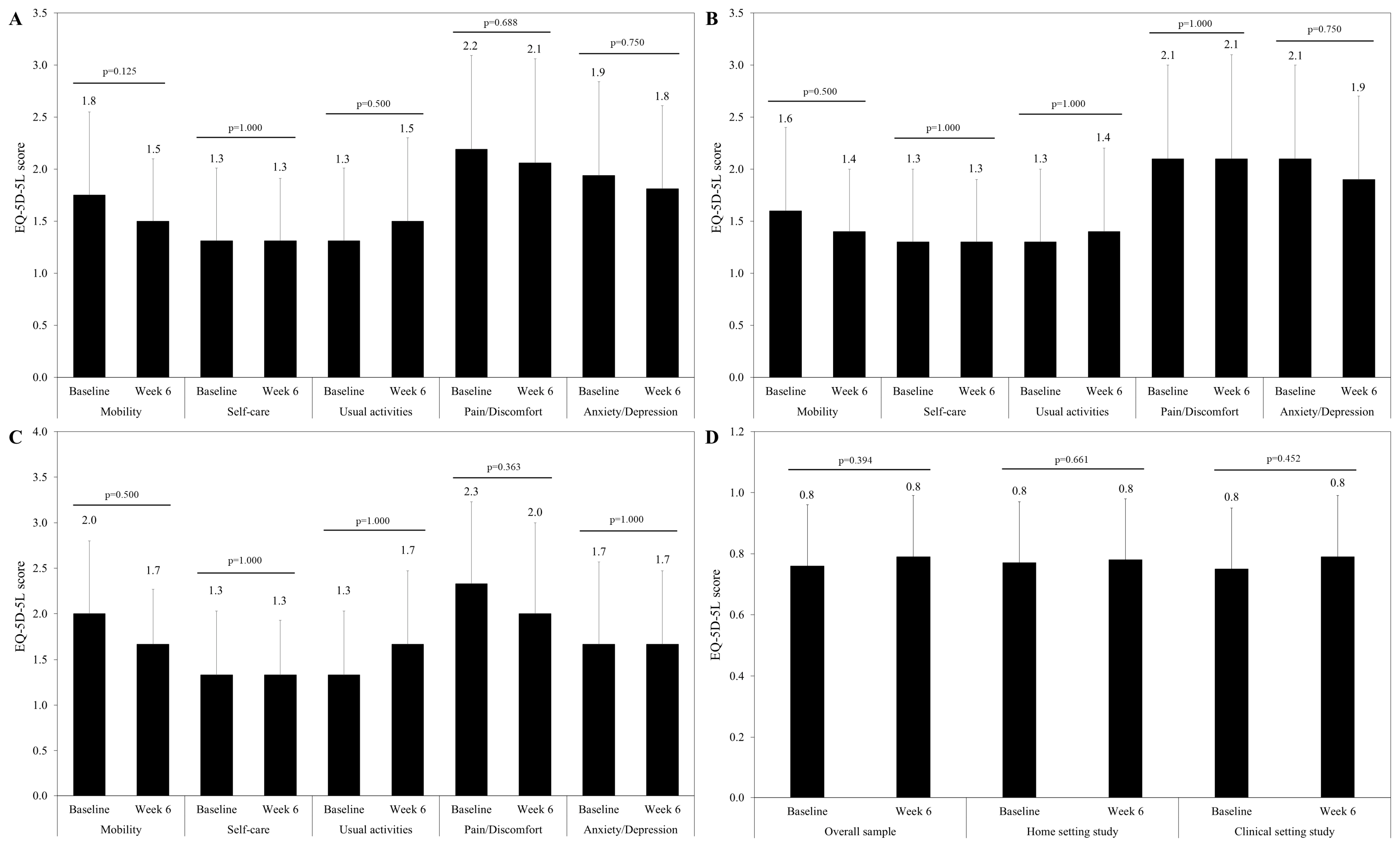
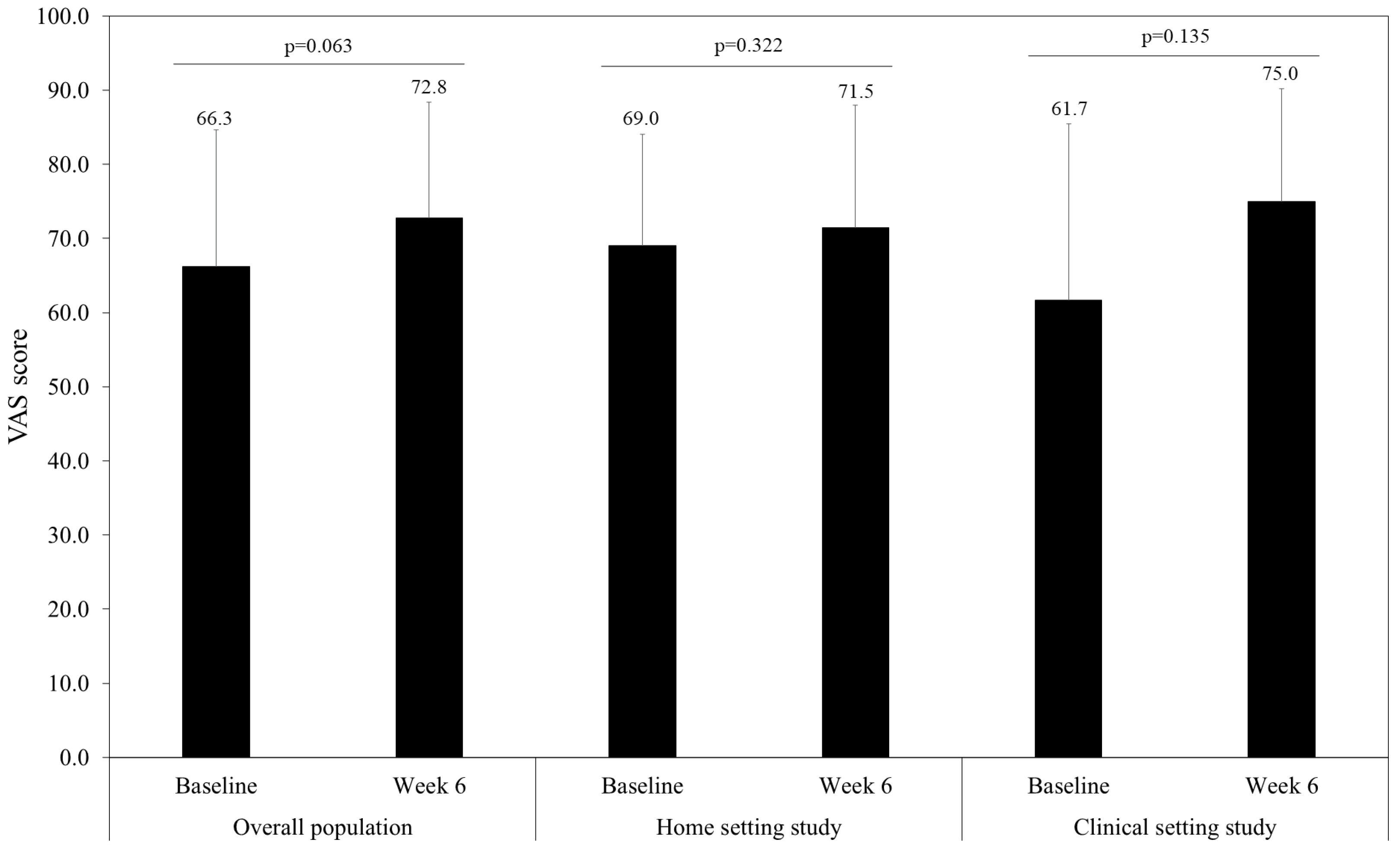
3.3. Effectiveness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5TM, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, S.T.; Mungas, D.; Reed, B.R.; Harvey, D.; DeCarli, C. Progression of mild cognitive impairment to dementia in clinic- vs. community-based cohorts. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.; Arrighi, H.M.; Michels, S.; Cedarbaum, J.M. Mild cognitive impairment: Disparity of incidence and prevalence estimates. Alzheimers Dement. 2012, 8, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Sun, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhou, L.; Liang, R.; He, R.; Yu, H. Risk factors of transition from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease and death: A cohort study. Compr. Psychiatry 2017, 78, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, N.L.; Unverzagt, F.; LaMantia, M.A.; Khan, B.A.; Boustani, M.A. Risk factors for the progression of mild cognitive impairment to dementia. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2013, 29, 873–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langa, K.M.; Levine, D.A. The diagnosis and management of mild cognitive impairment: A clinical review. JAMA 2014, 312, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanford, A.M. Mild Cognitive Impairment. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2017, 33, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugo, J.; Ganguli, M. Dementia and cognitive impairment: Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2014, 30, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demurtas, J.; Schoene, D.; Torbahn, G.; Marengoni, A.; Grande, G.; Zou, L.; Petrovic, M.; Maggi, S.; Cesari, M.; Lamb, S.; et al. Physical Activity and Exercise in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: An Umbrella Review of Intervention and Observational Studies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 1415–1422.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, B.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wan, Q.; Yu, F. Comparative efficacy of various exercise interventions on cognitive function in patients with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Sport Health Sci. 2022, 11, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.I.; Quintas, J.; Neves, L.; Sousa, S.; Cruz, V.T.; Pais, J.; Benhsain, D.; Callén, A.; Rocha, N.P. Cognivitra: An Information Technology-Based Solution to Support Cognitive and Physical Training at Home. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Software Development and Technologies for Enhancing Accessibility and Fighting Info-Exclusion (DSAI ’20), Online, Portugal, 2–4 December 2021; pp. 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Quintas, J.; Pais, J.; Martins, A.; Santos, H.; Neves, L.; Sousa, S.; Benhsain, D.; Dierick, F.; Callén, A.; Cunha, A.; et al. CogniViTra, a Digital Solution to Support Dual-Task Rehabilitation Training. Electronics 2021, 10, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, X.; He, S.; Zhu, H.; Lam, F.M.H.; Pang, M.Y.C. The effect of dual-task training on cognitive ability, physical function, and dual-task performance in people with dementia or mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2024, 38, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COGWEB®. Available online: https://www.cogweb.com/?lang=en (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Brooke, J. SUS: A retrospective. J. Usability Stud. 2013, 8, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, A.I.; Rosa, A.F.; Queirós, A.; Silva, A.; Rocha, N.P. Definition and Validation of the ICF—Usability Scale. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 67, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.I.; Queirós, A.; Silva, A.G.; Rocha, N.P. ICF based Usability Scale: Evaluating usability according to the evaluators’ perspective about the users’ performance. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Software Development and Technologies for Enhancing Accessibility and Fighting Info-Exclusion, Vila Real, Portugal, 1–3 December 2016; pp. 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.; Davis, G.; Davis, F. User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, G.; Garin, O.; Dima, A.L.; Pont, A.; Martí Pastor, M.; Alonso, J.; Van Ganse, E.; Laforest, L.; de Bruin, M.; Mayoral, K.; et al. EuroQol (EQ-5D-5L) Validity in Assessing the Quality of Life in Adults with Asthma: Cross-Sectional Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e10178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motl, R.W.; Cohen, J.A.; Benedict, R.; Phillips, G.; LaRocca, N.; Hudson, L.D.; Rudick, R. Multiple Sclerosis Outcome Assessments Consortium Validity of the timed 25-foot walk as an ambulatory performance outcome measure for multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, N.; Leach, L.; Murphy, K.J. A re-examination of Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) cutoff scores. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2018, 33, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, L.; Maselli, M.; Esposito, R.; Castro, E.; Mancioppi, G.; Cecchi, F.; Laschi, C.; Ottino, S.; Rossi, C.; Pinori, F.; et al. Foot Inertial Sensing for Combined Cognitive-Motor Exercise of the Sustained Attention Domain. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 2413–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callisaya, M.L.; Jayakody, O.; Vaidya, A.; Srikanth, V.; Farrow, M.; Delbaere, K. A novel cognitive-motor exercise program delivered via a tablet to improve mobility in older people with cognitive impairment—StandingTall Cognition and Mobility. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 152, 111434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Mishra, R.K.; York, M.K.; Enriquez, A.; Lindsay, A.; Barchard, G.; Vaziri, A.; Najafi, B. Tele-Medicine Based and Self-Administered Interactive Exercise Program (Tele-Exergame) to Improve Cognition in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment or Dementia: A Feasibility, Acceptability, and Proof-of-Concept Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.; Ho, S.H.; Bae, Y.-H.; Lee, M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J. Digital Health Equity and Tailored Health Care Service for People with Disability: User-Centered Design and Usability Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e50029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Evaluation Phase/ Timeline | Participants | Instruments | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline/First contact with COGNIVITRA | Patients | Informed consent, Study information sheet, Checklist of conditions for participation in home study, Sociodemographic questionnaire, Session script, MMSE, SUS, Overall satisfaction rating question, Weekly registration forms, MoCA, EQ-5D-5L, T25-FW, ICF-US I and II, Log files, Critical incident log sheet, and Observation grid | Collect baseline data on participants’ demographics, initial usability impressions, and system interaction. |
| Professionals | Informed consent, Study Information sheet, Sociodemographic questionnaire, Session script, Observation grid, Log files, and Critical incident log sheet | ||
| Weeks 1–12/Every week throughout the study | Patients | Log files, and Weekly registration forms | Monitor continuous usage, track performance, and document any issues or patterns in system interaction. |
| Week 6/Midpoint of the study | Patients | SUS, Overall satisfaction rating question, MoCA, EQ-5D-5L, T25-FW, Log files, Critical incident log sheet, and Weekly registration forms | Evaluate mid-term usability, user satisfaction, and overall experience with the COGNIVITRA system. |
| Week 12/End of the study | Patients | Overall satisfaction rating question, MoCA, EQ-5D-5L, T25-FW, Log files | Assess final usability, user satisfaction, impact on cognitive function, physical health, and overall quality of life. |
| Professionals | SUS, UTAUT, ICF-US I and II, Log files, Overall Satisfaction rating question | ||
| Patients, caregivers, and professionals | Focus Group | Gather qualitative feedback on the system’s utility, its impact on daily activities, and any suggestions for improvement. |
| Overall (n = 22) | Home Study (n = 14) | Clinical Setting Study (n = 8) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | |||
| Age, mean years (SD) | 63.4 (10.2) | 63.4 (9.9) | 63.4 (11.4) |
| Digital literacy, n (%) | |||
| Use of internet | 17 (77.3) | 12 (85.7) | 5 (62.5) |
| Computer | 14 (63.6) | 10 (71.4) | 4 (50.0) |
| Smartphone | 21 (95.5) | 14 (100.0) | 7 (87.5) |
| Tablet | 7 (31.8) | 4 (28.6) | 3 (37.5) |
| TV | 19 (86.4) | 13 (92.9) | 6 (75.0) |
| Education, mean years completed (SD) | 11.8 (4.0) | 12.0 (4.0) | 11.4 (4.3) |
| Retired, n (%) | 10 (45.5) | 6 (42.9) | 4 (50.0) |
| Retirement age, mean years (SD) | 56.7 (14.0) | 60.9 (6.4) | 49.5 (21.4) |
| MMSE, mean score (SD) | 28.6 (1.4) | 29.1 (1.1) | 27.9 (1.5) |
| EQ-5D-5L, mean score (SD) | |||
| Mobility | 1.7 (0.8) | 1.4 (0.7) | 2.0 (0.9) |
| Self-care | 1.2 (0.6) | 1.2 (0.6) | 1.3 (0.7) |
| Usual activities | 1.3 (0.6) | 1.3 (0.6) | 1.3 (0.7) |
| Pain/discomfort | 2.0 (0.9) | 1.9 (0.9) | 2.1 (0.8) |
| Anxiety/depression | 1.8 (0.9) | 1.9 (0.9) | 1.6 (0.7) |
| General health (VAS scale) | 68.6 (17.5) | 71.1 (15.5) | 64.4 (21.1) |
| Index value | 0.8 (0.2) | 0.8 (0.2) | 0.8 (0.1) |
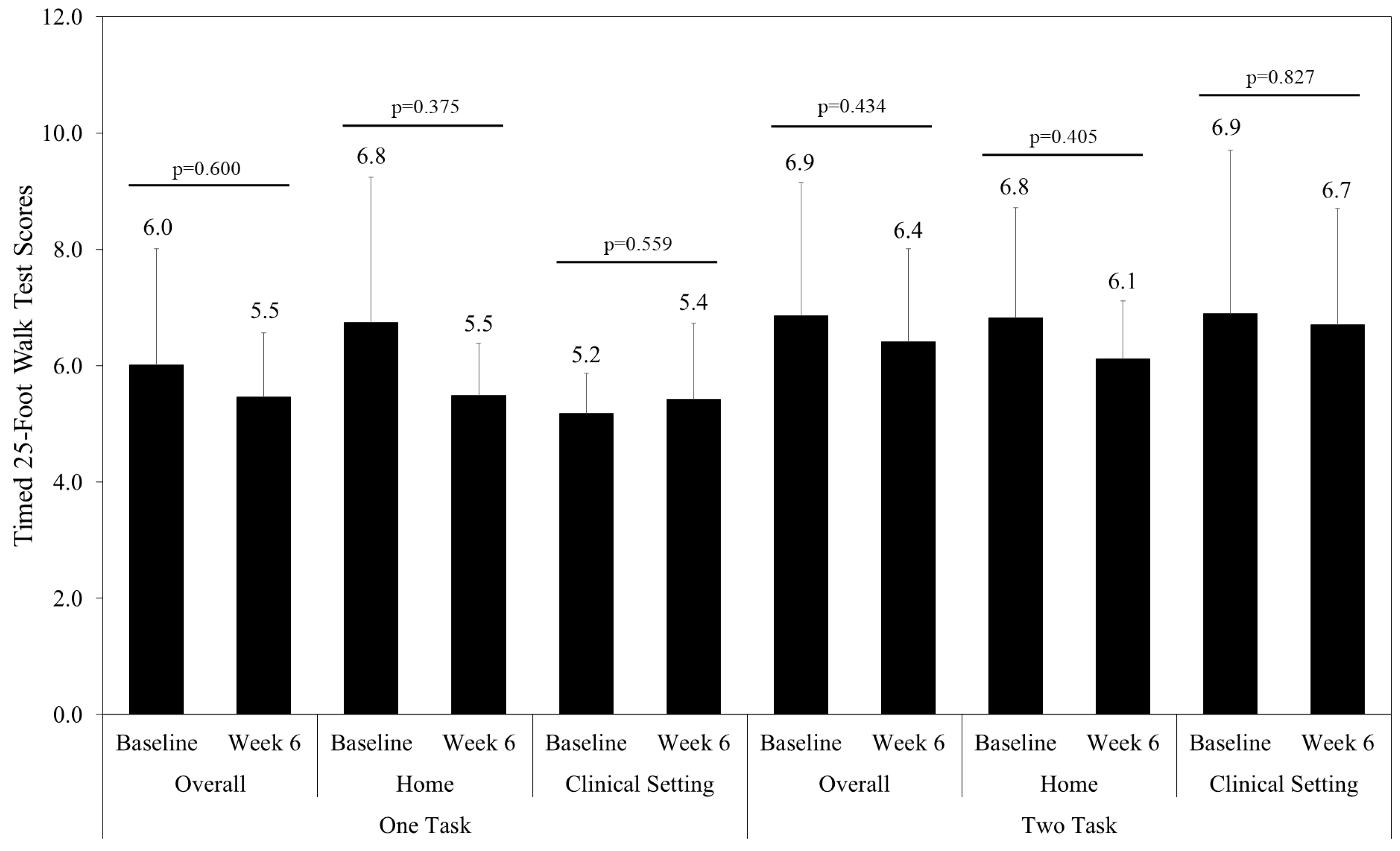
| Timed 25-Foot Walk, mean seconds (SD) | |||
| One task | 6.5 (2.2) | 7.1 (2.7) | 5.8 (1.3) |
| Two tasks | 7.7 (3.2) | 6.7 (1.8) | 8.6 (4.0) |
| MoCA, mean score (SD) | 24.1 (3.2) | 25.0 (2.9) | 23.1 (3.4) |
| Overall (n = 16) | Home Study (n = 10) | Clinical Setting Study (n = 6) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | p | Mean (SD) | p | Mean (SD) | p | |
| I think that I would like to use this website frequently | ||||||
| Baseline | 4.1 (1.0) | 0.494 | 4.0 (1.2) | 0.716 | 4.2 (0.8) | 0.289 |
| Week 6 | 3.6 (1.2) | 3.8 (1.1) | 3.3 (1.4) | |||
| I found this product unnecessarily complex | ||||||
| Baseline | 2.4 (1.3) | 0.508 | 2.2 (1.3) | 0.063 | 2.7 (1.2) | 0.363 |
| Week 6 | 2.2 (1.3) | 1.7 (1.1) | 3.0 (1.4) | |||
| I thought this product was easy to use | ||||||
| Baseline | 2.9 (1.5) | 0.041 * | 2.2 (1.2) | 0.004 * | 4.0 (1.1) | 0.611 |
| Week 6 | 3.9 (1.0) | 4.0 (0.9) | 3.7 (1.0) | |||
| I think that I would need assistance to be able to use this product | ||||||
| Baseline | 2.6 (1.5) | 0.133 | 2.2 (1.5) | 0.125 | 3.3 (1.5) | 0.403 |
| Week 6 | 2.0 (1.3) | 1.8 (1.1) | 2.3 (1.5) | |||
| I found the various functions in this product were well integrated | ||||||
| Baseline | 4.3 (0.9) | 0.391 | 4.4 (0.8) | 1.000 | 4.2 (1.2) | 0.203 |
| Week 6 | 3.9 (1.3) | 4.4 (0.7) | 3.2 (1.8) | |||
| I thought there was too much inconsistency in this product | ||||||
| Baseline | 2.4 (1.3) | 0.828 | 2.9 (1.4) | 0.125 | 1.5 (0.5) | 0.224 |
| Week 6 | 2.3 (1.3) | 2.2 (1.4) | 2.3 (1.2) | |||
| I would imagine that most people could learn to use this product very quickly | ||||||
| Baseline | 3.4 (1.2) | 0.388 | 3.3 (1.3) | 0.138 | 3.5 (1.0) | 0.771 |
| Week 6 | 3.6 (1.1) | 3.8 (1.1) | 3.3 (1.0) | |||
| I found this product very cumbersome/awkward to use | ||||||
| Baseline | 2.1 (1.3) | 0.795 | 2.3 (1.6) | 0.438 | 1.8 (0.4) | 0.444 |
| Week 6 | 2.0 (1.4) | 1.7 (1.3) | 2.5 (1.6) | |||
| I felt very confident using this product | ||||||
| Baseline | 3.6 (1.2) | 0.375 | 3.5 (1.4) | 0.125 | 3.7 (1.0) | 0.842 |
| Week 6 | 4.0 (1.2) | 4.3 (0.8) | 3.5 (1.5) | |||
| I needed to learn a lot of things before I could get going with this product | ||||||
| Baseline | 2.3 (1.1) | 0.125 | 1.8 (0.6) | 0.138 | 3.0 (1.4) | 0.501 |
| Week 6 | 1.7 (0.9) | 1.3 (0.7) | 2.3 (1.0) | |||
| System Usability Scale total | ||||||
| Baseline | 66.1 (12.2) | 0.061 | 65.0 (14.9) | 0.001 * | 67.9 (6.6) | 0.545 |
| Week 6 | 72.3 (17.2) | 79.0 (10.9) | 61.3 (20.8) | |||
| n | Mean (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| I think that I would like to use this website frequently | 24 | 4.1 (0.8) |
| I found this product unnecessarily complex | 24 | 2.4 (1.0) |
| I thought this product was easy to use | 24 | 3.7 (1.3) |
| I think that I would need assistance to be able to use this product | 24 | 2.5 (1.2) |
| I found the various functions in this product were well integrated | 24 | 4.5 (0.7) |
| I thought there was too much inconsistency in this product | 24 | 3.3 (1.1) |
| I would imagine that most people could learn to use this product very quickly | 24 | 3.6 (1.1) |
| I found this product very cumbersome/awkward to use | 23 | 1.8 (0.9) |
| I felt very confident using this product | 24 | 3.6 (1.1) |
| I needed to learn a lot of things before I could get going with this product | 24 | 2.6 (1.4) |
| System Usability Scale total | 23 | 68.9 (12.2) |
| Patients | Professionals (n = 24) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall (n = 22) | Home Study (n = 14) | Clinical Setting Study (n = 8) | ||
| Ease of use | 1.3 (1.2) | 1.1 (1.4) | 1.6 (0.7) | 1.4 (1.2) |
| Satisfaction with its use | 1.9 (0.8) | 1.7 (0.8) | 2.3 (0.7) | 1.7 (1.2) |
| Learning ease | 1.8 (1.1) | 1.9 (0.5) | 1.6 (1.8) | 1.5 (0.9) |
| Achievement of expected results (e.g., wanted to write a text and did it) | 1.7 (1.4) | 2.0 (1.2) | 1.3 (1.6) | 1.5 (1.1) |
| Similarity in the operation mode in the different tasks (such the way to confirm an action always being the same) | 1.6 (1.1) | 1.5 (1.1) | 1.7 (1.3) | 0.8 (1.6) |
| Possibility of interacting in various ways (e.g., keyboard, touch, or voice) | 0.7 (1.8) | 0.7 (1.8) | 0.6 (1.9) | 1.4 (1.4) |
| Understanding of the messages presented (e.g., written or sound) | 1.5 (1.4) | 1.6 (1.1) | 1.4 (2.0) | 0.6 (1.6) |
| The application’s responsiveness to your actions | 1.8 (1.1) | 1.8 (1.4) | 1.9 (0.6) | 1.5 (1.3) |
| Knowledge of what was happening in the application during use | 1.5 (1.5) | 1.5 (1.0) | 1.5 (2.3) | 1.6 (0.5) |
| Overall satisfaction | 1.8 (1.2) | 1.9 (0.7) | 1.5 (1.7) | 1.8 (0.8) |
| Total ICF-US I | 15.5 (9.3) | 15.5 (7.3) | 15.4 (12.8) | 13.4 (7.1) |
| Overall (n = 22) | Home Study (n = 14) | Clinical Setting Study (n = 8) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||
| Training weeks, n (SD) | 8.1 (3.7) | 8.8 (4.2) | 6.9 (2.5) |
| Percentage of completed weeks, % (SD) | 60.9 (23.4) | 55.5 (19.6) | 70.23 (27.7) |
| Total accesses completed, n (SD) | 14.5 (11.9) | 17.4 (14.0) | 9.5 (4.4) |
| Total accesses completed/week, n (SD) | 1.7 (0.9) | 1.9 (1.0) | 1.4 (0.4) |
| Patients with more than 2 accesses/week, n (%) | 4 (18.2) | 4 (28.6) | 0 (0.0) |
| Total time realized (min) | 296.6 (244.7) | 318.3 (304.5) | 258.7 (70.0) |
| Time realized (min/week) | 36.4 (18.4) | 34.9 (22.4) | 39.0 (8.6) |
| % patients with >40 min/week | 7 (31.8) | 5 (35.7) | 2 (25.0) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 172.1 (126.7) | 185.3 (155.1) | 148.9 (50.0) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 32.9 (22.7) | 33.7 (24.6) | 31.50 (20.6) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| By cognitive area and exercise (duringthe entirestudy) | |||
| Attention | |||
| Attention | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 66.5 (46.7) | 71.8 (56.5) | 57.1 (21.5) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 44.2 (27.0) | 48.29 (33.2) | 37.00 (7.7) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 5.7 (5.7) | 5.9 (6.7) | 5.5 (3.6) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.4 (0.3) | 0.3 (0.3) | 0.5 (0.3) |
| Equal or different v1 | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 11.4 (7.7) | 11.0 (9.3) | 12.3 (2.8) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 9.9 (5.6) | 10.4 (6.6) | 9.3 (3.8) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 0.5 (1.3) | 0.0 (0.0) | 1.3 (2.0) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.0 (0.1) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.1 (0.2) |
| Equal or different v2 | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 16.9 (12.8) | 16.7 (14.0) | 17.4 (11.4) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 14.8 (6.9) | 15.3 (7.8) | 14.0 (5.6) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.4 (1.9) | 1.2 (1.8) | 1.9 (2.1) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Equal or different v3 | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 15.8 (17.0) | 16.9 (18.3) | 14.1 (15.9) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 14.7 (7.9) | 16.9 (9.5) | 11.6 (3.9) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.7 (2.9) | 2.4 (3.6) | 0.6 (0.9) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.0 (0.0) |
| Pages | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 17.3 (16.0) | 22.0 (19.3) | 10.2 (4.3) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 11.7 (8.4) | 14.8 (9.5) | 7.0 (3.1) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 2.2 (2.8) | 2.3 (3.3) | 1.9 (1.9) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.3) |
| Tiles | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 11.0 (12.7) | 12.0 (13.9) | 8.6 (10.1) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 7.2 (5.2) | 7.5 (5.9) | 6.3 (1.2) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.9 (2.4) | 2.1 (2.7) | 1.3 (0.6) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.3) | 0.2 (0.4) | 0.1 (0.0) |
| Calculations | |||
| Calculous | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 56.8 (53.2) | 58.7 (66.1) | 53.6 (19.0) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 30.2 (24.8) | 31.3 (29.3) | 28.3 (15.6) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 6.2 (4.9) | 6.1 (4.0) | 6.3 (6.5) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.5 (0.3) | 0.5 (0.3) | 0.5 (0.5) |
| Math | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 12.0 (12.9) | 9.7 (13.2) | 16.6 (11.9) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 10.8 (5.1) | 10.0 (6.4) | 12.0 (2.4) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.0 (1.5) | 1.0 (1.4) | 1.0 (1.7) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Compare the results | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 18.6 (20.3) | 21.3 (24.4) | 13.8 (9.3) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 9.6 (8.6) | 11.2 (10.3) | 6.7 (3.0) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 2.4 (2.5) | 2.9 (2.5) | 1.6 (2.6) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.2) |
| Complete the math | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 13.7 (11.0) | 12.8 (12.5) | 15.0 (9.1) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 8.2 (3.3) | 8.0 (2.7) | 8.4 (4.3) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 2.0 (3.0) | 1.5 (2.8) | 2.6 (3.4) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.2) |
| Complete the equation | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 13.5 (17.8) | 17.1 (21.2) | 7.6 (8.3) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 12.9 (9.5) | 15.4 (10.8) | 8.4 (4.6) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 2.8 (2.5) | 3.0 (2.2) | 2.4 (3.2) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.2) |
| Find out the result | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 8.2 (9.1) | 6.4 (11.0) | 11.4 (1.3) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 7.1 (5.1) | 9.0 (7.7) | 5.8 (2.6) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.5 (1.2) | 1.5 (0.6) | 1.5 (1.5) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Executivefunctioning | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 25.0 (17.4) | 23.5 (19.7) | 27.7 (13.1) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 18.7 (11.4) | 17.9 (13.0) | 20.0 (8.8) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.7 (2.3) | 1.5 (2.1) | 1.9 (2.7) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Executive functioning | |||
| Logical mind | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 15.4 (14.2) | 14.6 (14.7) | 16.8 (14.3) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 12.5 (9.4) | 11.8 (9.4) | 13.7 (9.9) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.1 (1.6) | 1.2 (1.9) | 0.9 (1.1) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Match the color | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 10.1 (8.5) | 8.9 (9.6) | 12.5 (5.5) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 10.3 (4.6) | 11.4 (4.5) | 9.1 (4.8) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.0 (1.6) | 0.8 (1.0) | 1.3 (2.1) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Language | |||
| Language | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 24.7 (20.6) | 26.8 (25.2) | 20.9 (8.2) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 20.5 (11.5) | 23.6 (13.5) | 15.3 (5.7) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 2.7 (2.2) | 3.6 (2.5) | 1.6 (1.1) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Antonyms | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 10.2 (10.2) | 11.7 (12.3) | 7.8 (5.6) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 10.9 (6.3) | 12.2 (8.0) | 9.0 (1.8) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.1 (1.9) | 1.4 (2.4) | 0.7 (1.0) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Commands | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 15.7 (12.4) | 16.0 (15.1) | 15.0 (4.7) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 12.1 (6.3) | 13.6 (7.6) | 9.7 (2.1) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 1.9 (2.0) | 2.4 (2.5) | 1.3 (1.0) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Memory | |||
| Memory | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 97.4 (97.5) | 107.5 (121.5) | 79.8 (23.8) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 45.6 (45.3) | 50.7 (55.9) | 36.5 (14.8) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 12.1 (11.8) | 12.5 (13.3) | 11.5 (9.7) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.8 (0.8) | 0.7 (0.4) | 1.0 (1.2) |
| Remember the words | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 10.2 (8.4) | 9.7 (10.3) | 11.1 (0.8) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 8.5 (3.7) | 10.4 (3.7) | 6.3 (2.3) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 0.8 (1.3) | 0.7 (1.1) | 0.8 (1.6) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.0 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Frames | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 9.1 (12.9) | 7.7 (14.5) | 12.0 (9.5) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 7.3 (4.2) | 7.4 (5.2) | 7.2 (3.7) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 0.7 (1.6) | 0.2 (0.5) | 1.2 (2.2) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.6) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.4 (0.8) |
| Colored letters | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 11.6 (16.8) | 13.4 (20.8) | 8.6 (5.6) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 7.9 (9.0) | 9.9 (11.8) | 5.3 (1.4) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 3.1 (2.3) | 4.4 (2.1) | 1.3 (1.0) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.1) |
| Colored squares | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 18.2 (21.2) | 19.5 (26.4) | 16.3 (10.9) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 9.6 (8.6) | 10.9 (10.8) | 7.7 (4.1) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 2.8 (3.0) | 2.9 (3.1) | 2.7 (3.2) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.3) | 0.2 (0.4) | 0.1 (0.2) |
| Canvas | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 19.1 (21.4) | 25.4 (24.6) | 9.7 (11.3) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 13.2 (13.0) | 16.4 (14.9) | 6.8 (3.7) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 2.3 (2.2) | 2.1 (1.8) | 2.8 (3.0) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.3) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.4 (0.6) |
| Windows | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 18.3 (13.6) | 23.2 (15.3) | 11.3 (6.9) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 9.1 (6.0) | 11.2 (6.7) | 5.7 (2.4) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 2.8 (3.0) | 3.1 (3.4) | 2.3 (2.4) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.2) |
| Trees | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 13.5 (15.0) | 16.0 (17.5) | 8.9 (7.8) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 9.4 (6.0) | 10.6 (7.0) | 7.0 (2.9) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 2.7 (3.7) | 3.1 (4.3) | 1.8 (2.1) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.1 (0.2) |
| Mixed letters | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 15.1 (14.1) | 15.1 (16.4) | 15.1 (10.3) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 7.9 (3.9) | 8.5 (5.1) | 7.2 (2.3) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 4.3 (3.5) | 4.7 (3.8) | 3.8 (3.6) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.2 (0.2) |
| Perception | |||
| Perception | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 28.8 (31.0) | 34.9 (38.1) | 19.6 (13.2) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 20.7 (20.8) | 27.8 (24.9) | 11.9 (9.8) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 6.0 (4.3) | 7.0 (4.3) | 4.8 (4.3) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.4 (0.3) | 0.4 (0.3) | 0.4 (0.4) |
| Mirroredcolors | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 8.7 (12.9) | 11.3 (15.2) | 4.7 (7.7) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 11.6 (10.5) | 14.3 (11.9) | 6.8 (6.2) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 3.1 (3.4) | 3.7 (3.8) | 2.0 (2.5) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.3 (0.3) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.4 (0.4) |
| Mirroredsymbols | |||
| Time realized, min (SD) | 21.2 (20.9) | 23.6 (26.2) | 17.0 (4.8) |
| Total games played, n (SD) | 15.4 (12.7) | 19.8 (15.4) | 9.7 (4.6) |
| Total errors, n (SD) | 4.6 (3.2) | 4.9 (3.6) | 4.3 (2.9) |
| Errors/min, n (SD) | 0.3 (0.3) | 0.3 (0.3) | 0.3 (0.2) |
| n | Mean (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| Performance expectancy | ||
| I would find the COGNIVITRA system useful for my job | 24 | 5.3 (1.4) |
| Using the COGNIVITRA system would enable me to accomplish tasks more quickly | 24 | 4.4 (1.8) |
| Using the COGNIVITRA system would increase my productivity | 24 | 4.5 (1.9) |
| If I use the COGNIVITRA system, I will have a better chance of progressing in my career | 24 | 4.1 (1.8) |
| Effort expectancy | ||
| I believe that my interaction with the COGNIVITRA system would be clear and understandable | 24 | 5.6 (1.3) |
| It would be easy for me to develop the skills necessary to use the COGNIVITRA system | 23 | 6.0 (1.5) |
| I believe that the COGNIVITRA system would be easy to use | 24 | 5.5 (1.6) |
| It would be easy to learn how to use the COGNIVITRA system | 24 | 5.8 (1.6) |
| Social influence | ||
| The people who influence my work feel that I should use the COGNIVITRA system | 23 | 4.0 (2.0) |
| The people important to me think that I should use the COGNIVITRA system | 23 | 3.8 (1.9) |
| The management of my organization would support the use of the COGNIVITRA system | 23 | 5.6 (1.3) |
| In general, I believe that my organization would support the use of the COGNIVITRA system | 23 | 5.7 (1.3) |
| Facilitating conditions | ||
| I would have the necessary resources to use the COGNIVITRA system (e.g., Wi-Fi; computer) | 24 | 6.5 (0.9) |
| I would have the necessary knowledge to use the COGNIVITRA system | 24 | 6.3 (1.3) |
| The COGNIVITRA system would be compatible with my usual work dynamics | 24 | 4.8 (2.1) |
| A person (or group) would be available to support me in using the COGNIVITRA system in case of difficulties | 24 | 5.3 (1.3) |
| Attitude toward using technology | ||
| Using the COGNIVITRA system would be a good idea | 24 | 6.4 (1.0) |
| The COGNIVITRA system would make my work more interesting | 24 | 5.6 (1.4) |
| Working with the COGNIVITRA system would be enjoyable | 24 | 6.0 (1.0) |
| I would like to use the COGNIVITRA system | 24 | 6.0 (1.3) |
| Self-efficacy | ||
| I would be able to complete a task using the COGNIVITRA system even if no one told me what to do | 24 | 4.8 (1.5) |
| I would be able to complete a task using the COGNIVITRA system if I could call someone to help me if I was blocked | 24 | 5.8 (1.5) |
| I would be able to complete a task using the COGNIVITRA system if I had a lot of time to complete it | 24 | 5.7 (1.6) |
| I would be able to complete a task using the COGNIVITRA system if someone showed me how to use it first | 24 | 6.1 (1.4) |
| Anxiety/behavioral intentions to use the system | ||
| I feel apprehensive about using the COGNIVITRA system | 24 | 2.8 (1.9) |
| It scares me to think that I could lose a lot of information using the COGNIVITRA system if I performed a wrong action | 24 | 2.8 (1.7) |
| I would hesitate to use the COGNIVITRA system for fear of making mistakes that I could not correct | 24 | 2.7 (1.9) |
| The COGNIVITRA system is somewhat intimidating to me | 24 | 1.9 (1.4) |
| Security | ||
| I would hesitate to use the COGNIVITRA system when I know that all the data I enter would be visible to my peers/managers | 24 | 2.5 (1.8) |
| It scares me to think that using the COGNIVITRA system would make my workflow more consultable by my peers | 24 | 2.0 (1.6) |
| Information sharing | ||
| I believe that the COGNIVITRA system is a secure system | 24 | 6.2 (1.0) |
| n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Patients | |
| How was your experience with the COGNIVITRA system in an individual context? | |
| Positive | 11 (91.7) |
| Negative | 5 (41.7) |
| Do you believe the system is an added value to your life? | |
| Yes | 8 (66.7) |
| No | 4 (33.3) |
| What has changed in your daily routine with the introduction of COGNIVITRA? | |
| Perceived cognitive improvement (memory, concentration) | 5 (41.7) |
| No changes | 4 (33.3) |
| Performed more cognitive training exercises | 2 (16.7) |
| What are the advantages of the COGNIVITRA system? | |
| Training the mind in different functions (attention, memory) | 5 (41.7) |
| Learning new exercises | 3 (25.0) |
| Including head and body movements to involve coordination | 1 (8.3) |
| Possibility to check the results after the session | 1 (8.3) |
| What are the disadvantages of the COGNIVITRA system? | |
| No possibility to stop the game | 2 (16.7) |
| Wrong movement detection | 2 (16.7) |
| Some exercises can be stressful | 1 (8.3) |
| Connecting the device requires technical knowledge | 1 (8.3) |
| Repetitive exercises | 1 (8.3) |
| Being aware of cognitive functions that the patient should improve | 1 (8.3) |
| Visual impairment difficulties in interacting with the device | 1 (8.3) |
| Including head and body movements to involve coordination | 1 (8.3) |
| What aspects/functionalities do you think should be enhanced to improve COGNIVITRA? | |
| Make it easier to interact with | 4 (33.3) |
| Improve detection of movements | 2 (16.7) |
| Improve the games | 2 (16.7) |
| Provide adaptations to the interface for colorblind people | 1 (8.3) |
| Add examples and clearer instructions regarding how to perform the exercises | 1 (8.3) |
| Patients and caregivers | |
| Would you be willing to pay for COGNIVITRA? If so, how much would you be willing to pay? | |
| No | 3 (25.0) |
| Yes | 9 (75.0) |
| Monthly (EUR 20–100) | 6 (66.7) |
| Per session (EUR 6.5–30) | 3 (33.3) |
| Purchase (EUR 50–200) | 3 (33.3) |
| Professionals | |
| Make the interface and the avatar more friendly (graphic information, adding more colors, etc.) | 11 (64.7) |
| There is a benefit to performing rehabilitation at home | 7 (41.2) |
| Possible application in other fields such as mental health, hospital rooms, etc. | 5 (29.4) |
| Include positive feedback | 4 (23.5) |
| Use gamification | 4 (23.5) |
| Would need some adaptation or training time to use COGNIVITRA | 3 (17.6) |
| Concern regarding the implementation of COGNIVITRA in some patient populations (technology readiness, sociocultural and economic situations, etc.) | 3 (17.6) |
| The device needs to be more portable and easier to carry around | 3 (17.6) |
| Incorporate AI | 2 (11.8) |
| Add the possibility to exercise in groups | 1 (5.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luque, J.L.; Chivite, I.; Serena, M.; Szymanski, C.; Benhsain, D.; Martins, A.I.; Rocha, N.P.; Pais, J.; Cruz, V.T.; Quintas, J.; et al. Implementation of COGNIVITRA, an Information- and Communications-Technology-Based Solution for Dual-Task Training, in Patients at Risk of Cognitive Impairment. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7906. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177906
Luque JL, Chivite I, Serena M, Szymanski C, Benhsain D, Martins AI, Rocha NP, Pais J, Cruz VT, Quintas J, et al. Implementation of COGNIVITRA, an Information- and Communications-Technology-Based Solution for Dual-Task Training, in Patients at Risk of Cognitive Impairment. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7906. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177906
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuque, Judit Lopez, Iñigo Chivite, Marina Serena, Clara Szymanski, David Benhsain, Ana Isabel Martins, Nelson Pacheco Rocha, Joana Pais, Vítor Tedim Cruz, João Quintas, and et al. 2024. "Implementation of COGNIVITRA, an Information- and Communications-Technology-Based Solution for Dual-Task Training, in Patients at Risk of Cognitive Impairment" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7906. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177906
APA StyleLuque, J. L., Chivite, I., Serena, M., Szymanski, C., Benhsain, D., Martins, A. I., Rocha, N. P., Pais, J., Cruz, V. T., Quintas, J., & Callen, A. (2024). Implementation of COGNIVITRA, an Information- and Communications-Technology-Based Solution for Dual-Task Training, in Patients at Risk of Cognitive Impairment. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7906. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177906







