Abstract
This paper presents a procedure for estimating the motion capabilities of an omnidirectional mobile platform with three omni wheels arbitrarily distributed and oriented. This procedure is based on the analysis of the bidirectionality compliance between the inverse and forward kinematics of a mobile platform for a wide set of discrete motion commands. This procedure has been applied to analyze eleven alternative mobile platform configurations with three omni wheels. The estimation of the omnidirectional motion capabilities of these platforms agrees with state-of-the-art methods while providing new differentiated information on the translational capabilities of each platform. The procedure can be applied in the design stage of new omnidirectional mobile platforms in order to verify the motion capabilities of new designs with omni wheels.
1. Introduction
An omnidirectional mobile platform is characterized by its capability to simultaneously translate and rotate in any direction without kinematic constraints [1,2,3]. Omnidirectional wheels have free rollers on their perimeters [4] to combine rotation around the wheel axis and translation in the rotation direction of the rollers. The angular orientation of the free rolling direction of the rollers relative to the wheel hub () determines the type of omnidirectional wheel. The most commonly used are Mecanum () [5,6,7] and omni wheels () [8,9,10]. Omnidirectional wheels are implemented in a significant number of robot applications [11,12,13]. Compared with conventional wheels, their main disadvantages are the generation of vibrations and the susceptibility to slippage.
The combination of several omnidirectional wheels in a system does not ensure omnidirectional motion; only when wheel placement and orientation is adequate, the platform can achieve three degrees of freedom (DOF). Proposals of omnidirectional mobile robots with different wheel configurations are presented in the scientific literature [14,15,16]; their selection depends on the field of application. The most frequent omnidirectional platforms are based on symmetric designs [17,18] with three omni wheels [19,20] or four Mecanum wheels [21,22,23]. Less common implementations include asymmetric distributions [17,24] and systems with six [25,26,27] or eight wheels [28]. Specific approaches such as navigation within tunnels to inspect nuclear sites rely on compact designs [29] or systems with joints to change the alignment of the Mecanum wheels [30]. Other designs include omnidirectional wheels on a bending platform so that robots can climb and inspect ferromagnetic structures such as walls and circular constructions [31]. Hybrid mobile robots combining legs and Mecanum wheels are convenient in heterogeneous environments with irregular terrains [32], and proposals such as the collinear Mecanum drive are interesting omnidirectional alternatives to typical two-wheeled inverted-pendulum robots [33]. Similarly, hybrid quadruped spherical robots combine the structure of spherical robots and four legged robots [34]. Other omnidirectional proposals extend the operation sceneries to terrain and water by implementing oloid-like paddlewheels based on Schatz linkages [35].
The analysis of omnidirectional mobile platforms is often addressed with the aim of refining their design and operability [36]. For example, Almasri et al. [18] proposed a model for systems with symmetrical distributions of N omni wheels to optimize robot trajectories, Barreto et al. [37] presented a model predictive control to compensate for frictional effects on trajectories, and Manzl et al. [38] considered orthotropic friction to model roller-ground contact of Mecanum wheels and developed an efficient wheel model. With respect to their constructive characteristics, Zhang et al. [39] analyzed the effect of the angles of the rollers on motion performances, Tagliavini et al. [40] presented an overview of three-wheeled omnidirectional motion strategies, and Hijikata et al. [41] proposed an alternative wheel arrangement of four omni wheels in a mobile robot, suggesting that wheel arrangement changes the effect of imperfect control on the motion. Reconfigurable and asymmetric wheel arrangements are useful in case of motor failure [24,42]. In this context, Leng and Cao [43] studied the maximum velocity of omnidirectional robots with arbitrary wheel arrangements, and Mohanraj et al. [19] analyzed the front and back movement of a three-wheeled omnidirectional robot by varying the angles between its wheels.
Several authors have analyzed the omnidirectional mobility of a system on the principle that if the Jacobian matrix of the inverse kinematics model is full rank, the system has three DOF [44]. Li et al. [17] proposed an alternative approach to determine if a mobile platform based on omnidirectional wheels is omnidirectional or not. Their proposal analyzes the intersections of the axes of the rollers in contact with the ground. They validated their method by analyzing a set of platforms with Mecanum wheels under different configurations and comparing the results with the bottom-roller axles approach and the column rank of the Jacobian matrix. When the number of intersections determines that the system is omnidirectional, verifications on dynamics are required to formulate restrictions on the position and orientation of wheels and rollers and guarantee operability and omnidirectionality [45]. Configurations to be avoided include wheels with their axes parallel to the axes of the rollers and distributions with the axes of the rollers coinciding in the center of the platform.
The aforementioned variety of approaches to omnidirectionality analysis manifests that the design of mobile platforms requires a procedure focused on the analysis of the configuration of the wheels to ensure omnidirectional motion without affecting system performance [44].
New Contribution
This paper presents a procedure for estimating the motion capabilities of mobile platforms with three omni wheels arranged in arbitrary locations and orientations. This procedure is based on the analysis of the bidirectionality compliance between the inverse and forward kinematics of a mobile platforms for a wide set of discrete motion commands. The procedure provides a differentiated estimation of the omnidirectional capabilities and of the translational capabilities mobile platforms. This information enables the comparison between diverse implementation alternatives to satisfy the requirements and constraints of an intended application [46]. This approach has been applied to analyze the motion performances of a set of mobile platform configurations. The results of the estimation of the motion capabilities agree with state-of-the-art methods and have been validated using simulations.
2. Materials and Methods
The materials and methods used are the kinematics of a general omnidirectional mobile platform, and a set of omnidirectional mobile platforms configurations.
2.1. Kinematics of an Omnidirectional Mobile Platform
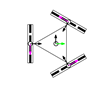
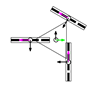
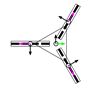
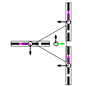
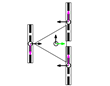
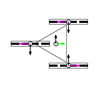
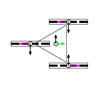
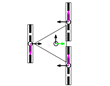
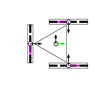
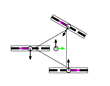
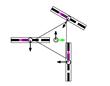
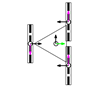
This section describes the general kinematic model of a platform with omni wheels, which is used to estimate its translation and rotation performances. Figure 1 shows the system definition of a mobile platform. The system is defined in a static frame . The mobile platform has its own body-attached frame , and each wheel also has its corresponding frame , being the identifying number the wheel. The position of the platform is defined by its frame coordinates and orientation relative to the world frame . Likewise, the position of each wheel is defined by its frame coordinates and orientation relative to the body frame . In the scientific literature, the orientation of the wheels () is usually referenced as (Figure 1a) [47]. In this paper we propose an alternative representation that emphasizes the relative orientation of the wheels (), referenced to the perpendicular of the centerline, joining the centroids of the platform and each wheel (Figure 1b).
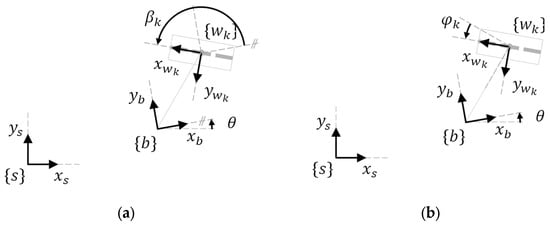
Figure 1.
System definition of a mobile platform (top view): (a) description generally used in the scientific literature, with the orientation of the wheels referenced to the platform frame ; (b) description proposed in this paper, with the orientation of the wheels referenced to the centerline joining the platform frame and the wheel frame . In both cases the wheels represented are omni wheels with passive rollers with .
The direction of the axis in the platform frame defines the positive direction of translation (forwards), and the positive rotation of the platform is counterclockwise. In each wheel, coincides with the wheel plane, and is collinear with the wheel hub.
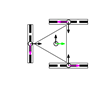
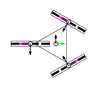
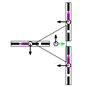
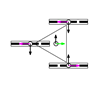
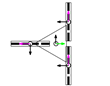
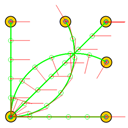
Figure 2 shows a top view of the definition of the wheels in an omnidirectional platform. The axes of the rollers are represented in grey, with thicker lines to depict the rollers in contact with the ground.
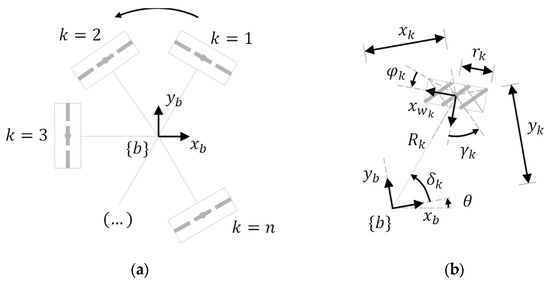
Figure 2.
Wheels definition (top view): (a) enumeration of the wheels of a platform (the wheels represented are omni wheels with ); (b) generic dimensional parameters (the wheel represented is of the Mecanum type with ).
Figure 2a shows how wheels are enumerated: the first one is the closest to in the first quadrant of the platform frame and the others are defined in the counterclockwise direction. Figure 2b shows the dimensional parameters: is the radius of the wheel , measured from the center of the wheel to the ground; is the centerline joining the centroids of the platform and wheel ; and are the distances between the centroids of the platform and wheel in the and directions; is the angular distribution of wheel , measured between the axis and the centerline ; is the angular orientation of wheel , measured between the perpendicular of the centerline and the axis; is the angular orientation of the rollers of wheel , measured as the angle of the free rolling direction relative to the axis.
The target velocity of the omnidirectional motion is defined in the platform frame by the motion command , where is the norm of the translational velocity of the motion, is the angular orientation of the translational velocity, and is the angular velocity of the platform. The components of this command can be decomposed in the platform frame as :
The velocity of the platform must be expressed in the wheel frame as by first translating () and then rotating (), the velocity vector in the platform frame:
where the translation matrix from the platform centroid to the wheel centroid is (4), the rotation from the platform to the wheel frame is , and the rotation matrix is (5):
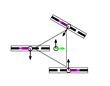
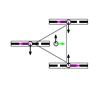
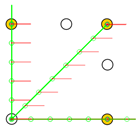
The velocity of the platform in the wheel frame is then decomposed in the drive direction (translation in the direction of the wheel plane) and slide direction (free sliding in the direction of the rollers), as in Figure 3. The direction of coincides with the drive direction, so it is labelled as . The components of are labelled as in the drive direction and in the slide direction. The resulting velocity in the drive direction is
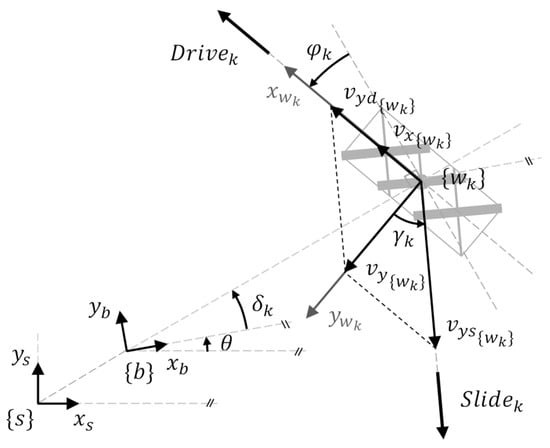
Figure 3.
Velocity of the platform in the wheel frame decomposed into the drive and slide directions (top view). The wheel represented is a Mecanum wheel with . The slide direction is perpendicular to the axes of the rollers.
The angular velocities of the wheels are obtained from the translational velocity in the drive direction, assuming there is no skidding ():
Equation (7) is expressed in a matrix form for wheel and as a function of the target velocity defined in the platform frame as:
which can be written in a compact form as:
In the case with wheels (), the inverse kinematics of the mobile platform can be described as
where the matrix containing the vectors is the Jacobian matrix of the inverse kinematics of the mobile platform.
Finally, the forward kinematics expression to compute the velocity of the platform from the velocity of its wheels is
where is the Moore–Penrose generalized inverse matrix which, in case the Jacobian matrix is full rank, corresponds with the inverse of the Jacobian matrix, .
2.2. Set of Mobile Platform Configurations Assessed
This section describes eleven mobile platform configurations whose omnidirectional capabilities are analyzed in the paper. All of them have three identical omni wheels with the same radius (), roller orientation (), and distance from the centroid of the mobile platform (), but they have different wheel distributions () and relative orientations (). Table 1 shows the configurations assessed, providing an identification name, a top-view schematic representation of the distribution and orientation of the three omni wheels, and the angular distribution of each wheel () and its relative orientation (). The axes of the platform frame are represented with green () and black () arrows, and the axes of the wheel frames are represented with pink () and black () arrows.

Table 1.
Mobile platforms analyzed.
3. Procedure for Omnidirectionality Analysis
This section describes the procedure proposed to analyze the omnidirectional capabilities of a mobile platform with three omni wheels. The procedure is based on the hypothesis that the analysis of the bidirectionality compliance between the inverse and forward kinematics can be used to evaluate the omnidirectionality of a motion system. That is, given a set of target motion commands, the result of the sequential computation of the inverse and forward kinematics for each command is coincidental with its corresponding target motion command as long as the system is omnidirectional.
3.1. Bidirectionality Error
The bidirectionality error is computed from the execution of a specific motion command. It is defined as the difference between the motion command applied to the mobile platform and the motion estimated from its kinematics. The bidirectionality error is computed in two steps. Firstly, the target motion command applied to the mobile platform , expressed as , is used to compute the angular velocities of the wheels using inverse kinematics (10). Secondly, the angular velocities of the wheels obtained in the first step are used to compute the motion of the mobile platform using direct kinematics (11). Thirdly, the computed motion of the mobile platform, expressed as , is compared with the target motion command to obtain the bidirectionality errors using
These errors are zero or numerical noise if the computed motion is equal to the original target motion command applied to the mobile platform, which means that the bidirectionality compliance is satisfied for this motion command.
Figure 4 shows the flowchart of the procedure used to estimate the bidirectionality error associated with one specific target motion command for a mobile platform with three omni wheels. The inputs of the procedure are the platform model (see Figure 2, Table 1), and a target motion command expressed in the platform base . The outputs of the process are the bidirectionality error for each variable of the motion command, . For the sake of comparison, this procedure is executed in 0.522 ms on a testbench computer.
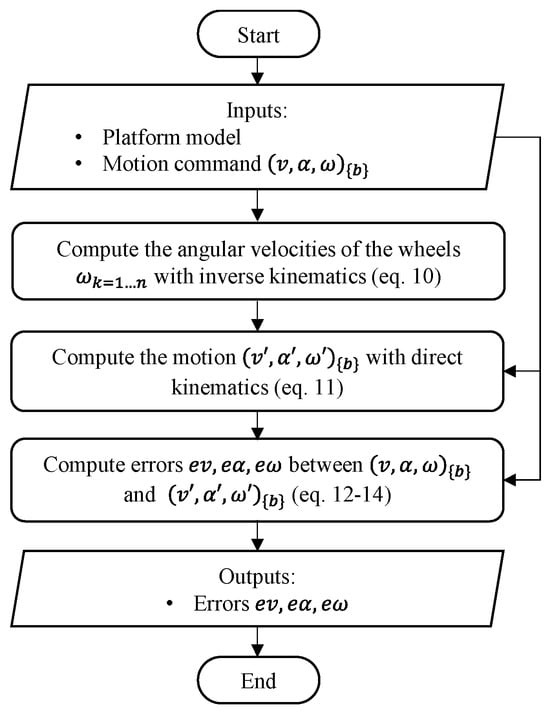
Figure 4.
Flowchart of the procedure proposed to estimate the bidirectionality error associated with one specific target motion command for a mobile platform with three omni wheels.
3.2. Omnidirectionality Analysis
The complete procedure proposed to evaluate the omnidirectional capabilities of a mobile platform is based on the assessment of the kinematics bidirectionality compliance for a whole set of motion commands. This requires the computation of the bidirectional errors for a range of motion commands explored to analyze under which motion commands the bidirectionality compliance is satisfied.
The selection of the set of motion commands to be evaluated consists of the definition of a feasible constant norm for the translational velocity , and the definition of a feasible set of values for the angular orientation of the translational velocity and for the angular velocity , with and . The values are and , with being the maximum angular velocity analyzed. In this procedure, the translational velocity is not explored as a set of values because there is a linear relationship between the angular velocity of the wheels () and the translational velocity that makes it unnecessary to assess its influence in the computation. This linear relationship is described in Equation (8).
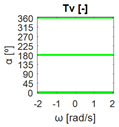
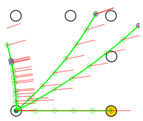
Figure 5 shows the diagram of the process used to assess the omnidirectionality of a mobile platform. The inputs of the process are the platform model and the range of motion commands expressed in the platform base. Specifically, the set of motion commands explore, for each value of the angular velocity (), the whole set of angular orientations () of the linear velocity of the platform.
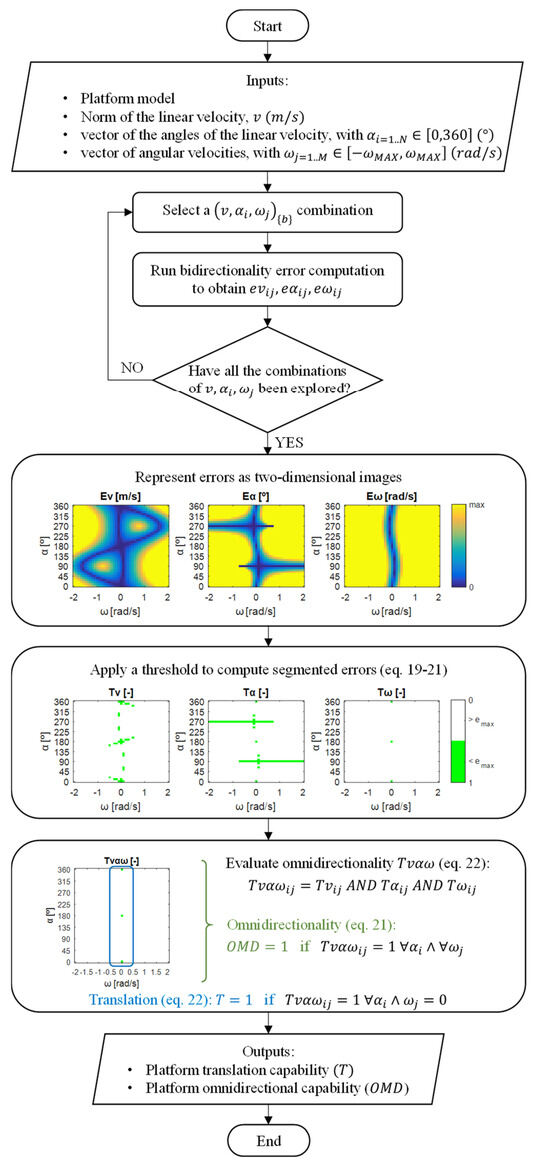
Figure 5.
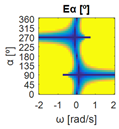
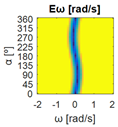
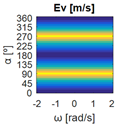
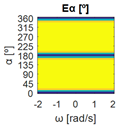
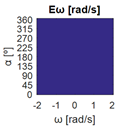
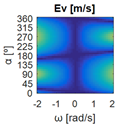
Flowchart of the procedure proposed to evaluate the translation and omnidirectional (translation and rotation) capabilities of a mobile platform using three omni wheels. The images displayed correspond to the platform configuration 2A-1B.
Firstly, for each combination of , , and , the bidirectionality errors , , are computed following the procedure described in Figure 4. The evaluation of the whole set of bidirectionality errors is stored in the matrixes , , and , defined as
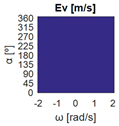
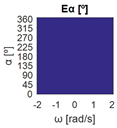
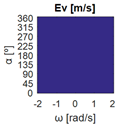
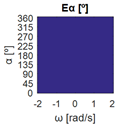
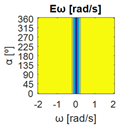
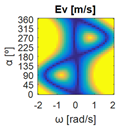
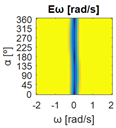
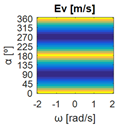
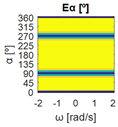
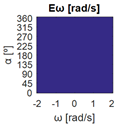
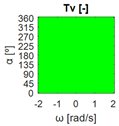
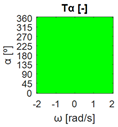
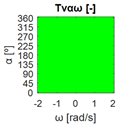
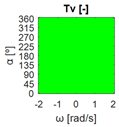
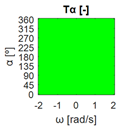
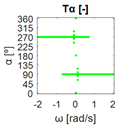
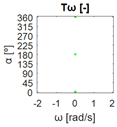
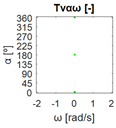
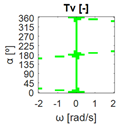
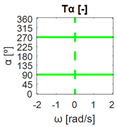
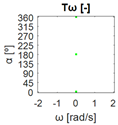
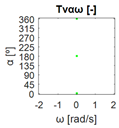
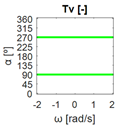
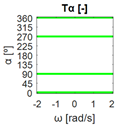
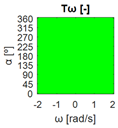
The errors computed in this first step are represented in Figure 5 as a color-scaled image. The X-axis of the image denotes the range of values explored, and the Y-axis denotes the range of values explored. In this case, the bidirectionality errors , and displayed in Figure 5 correspond to the case 2A-1B.
Secondly, three acceptability threshold values are applied to the bidirectionality errors: is the maximum acceptable error allowed in the linear velocity , is the maximum acceptable error allowed in the angular orientation , and is the maximum acceptable error allowed in the angular rotation of the mobile platform . The segmented errors are stored in the matrixes , and , whose elements are defined as follows:
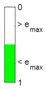
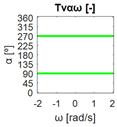
Again, the segmented errors computed in this second step are represented in Figure 5 as a color-scaled image, where white color represents errors above the threshold, and green depicts errors below it. The segmented errors , and displayed in Figure 5 also correspond to the case 2A-1B.
Finally, the bidirectionality compliance associated with a motion command is obtained from the logical conjunction (“AND”) for its corresponding segmented errors , and :
All the logical conjunctions corresponding to each combination of and are stored in the matrix , which is analyzed to determine the omnidirectional capability of the mobile platform. The values in the matrix are represented as a two-dimensional image: the green color represents the errors below the thresholds, and white represents the cases in which at least one of the , , and errors are above the thresholds. If this matrix reveals no errors above the thresholds (the entire matrix has a green color), bidirectionality compliance is satisfied for the whole range of motion commands explored and thus the system is omnidirectional:
where is the binary value that summarizes the omnidirectional capabilities of the mobile platform.
In the specific case with the errors below the threshold only in the whole set of for , translation is possible and controllable in any direction but without rotation.
where is the binary value that summarizes the translational capabilities of the mobile platform.
Figure 5 includes an example representation of the matrix from case 2A-1B. The outputs of the procedure are the platform translation () and omnidirectional () capabilities.
4. Results
4.1. Prediction of the Omnidirectional and Translation Capabilities
This section presents the results obtained from the application of the procedure proposed in this paper. Table 2 and Table 3 show the evaluation of the bidirectionality errors , , and of the mobile platforms assessed in this paper (described in Table 1).

Table 2.
Mobile platform configurations with the same negligible bidirectional errors in , , and . The maximum value in the color scale is 0.3 m/s for , 20° for and 0.3 rad/s for . The schematic representation of the configurations is shown in Table 1.

Table 3.
Mobile platform configurations with different non-negligible bidirectional errors in , , and . The maximum value in the color scale is 0.3 m/s for , 20° for and 0.3 rad/s for .
The results form Table 2 and Table 3 were obtained with the following parameters: , ranging within , and ranging within . These values are inspired by the motion commands used by a humanoid-sized assistance robot with three omni wheels using the 3A configuration [48].
Table 2 shows the graphical representation of the bidirectionality errors , and of mobile platform configurations 3A, 1A-2B, 1A-2C, 1A-1B-1C, 1A-1B-1D, and 3E. Given that the order of the bidirectionality errors in Table 2 is below 10−14, the errors can be considered numerical noise and are negligible, so they have the same matrixes , and and their representation is the same for all the platform configurations assessed. The color scale used to represent the bidirectionality errors is saturated with maximum values of 0.3 m/s for , 20° for and 0.3 rad/s for . The term in the color scale in Table 2 is a general representation of the saturation values for , and . Similarly, Table 3 shows the graphical representation of the bidirectionality errors of , and of configurations 3B, 2A-2B, 1B-2C, 1B-2D, and 1A-2D, which have non-negligible bidirectionality errors. In these cases, the errors obtained depend on the configuration of the mobile platform assessed and thus the configurations have different matrixes , and . The color scale used in Table 3 is the same as in Table 2.
The bidirectionality errors , , (Table 2 and Table 3) are segmented using the following thresholds: , , and . The images of the segmented errors , , are displayed in Table 4 and Table 5. These tables also display the matrixes storing the logical conjunction “AND” of the segmented errors of each motion command, which are used to evaluate the omnidirectional capabilities of the mobile platform configurations. The green color represents the combinations in which the errors are smaller than their corresponding threshold, and white color represents the combinations in which the errors are greater than their corresponding threshold. The term in the color scale used in Table 4 and Table 5 represents the thresholds for , for and for .

Table 4.
Segmented errors , , and of the mobile platform configurations assessed. The green color depicts that all bidirectionality errors are below the acceptability thresholds.

Table 5.
Segmented errors , , and of the mobile platform configurations assessed. The white color depicts bidirectionality errors above the acceptance thresholds.
Table 4 shows the segmented errors of configurations 3A, 1A-2B, 1A-2C, 1A-1B-1C, 1A-1B-1D, and 3E, which have the bidirectionality errors below the thresholds, thus having the same matrixes , and and the same combination . Table 5 shows the segmented errors of configurations 3B, 2A-2B, 1B-2C, 1B-2D, and 1A-2D, which have bidirectionality errors above the thresholds, thus having different matrixes , and and a different combination .
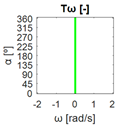
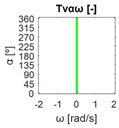
The bidirectionality errors of the mobile platform configurations shown in Table 2 (3A, 1A-2B, 1A-2C, 1A-1B-1C, 1A-1B-1D, 3E) describe negligible numerical noise, which is represented with a uniform color. The application of the error thresholds results in the segmented errors shown in Table 4, which also includes the matrixes with the logical conjunctions that combine the segmented results for each motion command. The results in Table 4 show that the segmented errors are below the thresholds for the whole set of motion commands explored ( is all green), so the bidirectionality compliance is satisfied and the configurations have omnidirectional capabilities. That is to say, all the set of motion commands assessed (all combinations of , , and ) can be executed by the mobile platforms, so they can translate in any direction with or without rotation . In short, configurations 3A, 1A-2B, 1A-2C, 1A-1B-1C, 1A-1B-1D, 3E (Table 1) have been classified as omnidirectional according to the procedure proposed in this paper.
The bidirectionality errors in the mobile platform configurations shown in Table 3 (3B, 2A-2B, 1B-2C, 1B-2D, 1A-2D) are case-dependent and their representations show a non-uniform color distribution that will be analyzed case by case.
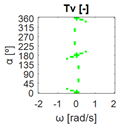
In Table 3, configuration 3B, the bidirectionality errors obtained from comparing the target and calculated linear velocities of the mobile platform () are negligible. Similarly, the bidirectionality errors obtained from comparing the target and calculated angular orientations of the motions () from its kinematics are also negligible. However, the bidirectionality errors obtained from comparing the target and calculated angular speeds of the motions () are negligible only in the set of with , which indicates that the mechanism is uncontrollable with respect to rotation.
Table 5, configuration 3B, shows these errors segmented according to the defined thresholds and the logical conjunction “AND” in . In this case, some points in have bidirectionality errors above the thresholds (represented in white color), which means that bidirectionality compliance is not satisfied and an omnidirectional motion is not possible. Nevertheless, in the cases in the set of with , show bidirectionality errors below the thresholds (represented as a green vertical line), meaning that the mobile platform is able to translate with any angular orientation without rotation. This new information about the translational capabilities of the platform is only provided by the procedure proposed in this paper.
In Table 3, configurations 2A-1B, 1B-2C, 1B-2D, and 1A-2D, the bidirectionality errors , and obtained from comparing the target and calculated motions of each mobile platform (comparing and , and , and and ), have irregular non-zero distributions. After applying the acceptability thresholds, the representations of the combined segmented errors in Table 5 depict the following information. In cases 2A-1B and 1B-2D, the mobile platforms can only translate in the directions of the angular orientations and (forwards and backwards) with , so the applicability of these configurations is very limited. In cases 1B-2C and 1A-2D, the mobile platforms can only move in the direction of two specific angular orientations: or for the case 1B-2C, and or for the case 1A-2D. In both cases, they can rotate with any angular speed while performing these displacements, but their applicability is also limited because only two angular orientations are possible. Finally, Table 6 summarizes the analysis of the motion capabilities of all the set of mobile platform configurations described in Table 1. Table 6 shows that the omnidirectional capability results obtained with the procedure proposed in this paper agree with the state-of-the-art methods while a new differentiated estimation of the translational capabilities is also provided.

Table 6.
Comparative analysis of the omnidirectional capabilities of the platforms obtained with two state-of-the-art methods and the omnidirectional and translation capabilities obtained with the procedure proposed in this paper.
Specifically, Table 6 presents the configuration name, a schematic representation of each platform configuration, the analysis of its omnidirectional capabilities based on two state-of-the-art methods [49], and the estimation of the omnidirectional and translation capabilities obtained with the procedure proposed in this paper. The first state-of-the-art method is based on computing the rank of the Jacobian matrix of the kinematic model of the mobile platform: if the matrix is full rank, the system is omnidirectional. The second state-of-the-art method is based on the bottom-roller axle intersections approach proposed by Y. Li et al. [17] applied to omni wheels with . This method analyzes the intersections between the axes of the passive rollers in contact with the ground to determine geometrically if a system is omnidirectional: when the axes intersect at two or three points, the platform is omnidirectional, whereas when the axes do not intersect or intersect only at one point, it is non-omnidirectional. As stated before, the results of Table 6 shows that the estimation of the omnidirectional capabilities provided by these state-of-the-art methods agree with the procedure proposed in this paper.
4.2. Validation of the Omnidirectionality and Translation Capabilities
This section presents the experiments conducted to validate the application of the procedure proposed for estimating the omnidirectional and translational capabilities of the mobile platforms described in Table 1. This validation is based on the simulation of the motion of the different omnidirectional platforms assessed. The simulator used in the paper is described in [50]. The simulator uses the information of the configuration of the wheels of the platform and the target velocity assigned to each wheel to compute the trajectory and displacement of the mobile platform. The simulator is limited to indoor conditions and no wheel slippage.
The validation experiments consist of the definition of a set of trajectories and on the implementation of these trajectories by the mobile platforms assessed. The execution of the motion defined in these trajectories requires a combination of translation and rotation capabilities in the mobile platform. Table 7 details the experiments, the target motion command applied to each mobile platform, the translation or rotation capabilities required to execute the motion, and the expected final position of the platform after the motion . In all these experiments, the initial position of the mobile platform in the simulation is the same: (0 m, 0 m, 0°). The last parameter of the motion command is the time defined to execute the motion in order to reach the final position of the motion . Additionally, Figure 6 shows the expected trajectory that must follow the mobile platform in case of executing the motion commands defined in Table 7. Trajectories E1 and E2 only require translational capabilities in the and axes of the world frame. Trajectory E3 requires a combination of translational capabilities in both axes in the world frame. Trajectories E4 and E5 require translation and rotation capabilities. Finally, trajectory E6 only requires rotation capabilities as it depicts a single rotation of approximately 90° to the left side of the mobile platform.

Table 7.
Definition of the motion commands used in the validation experiments.
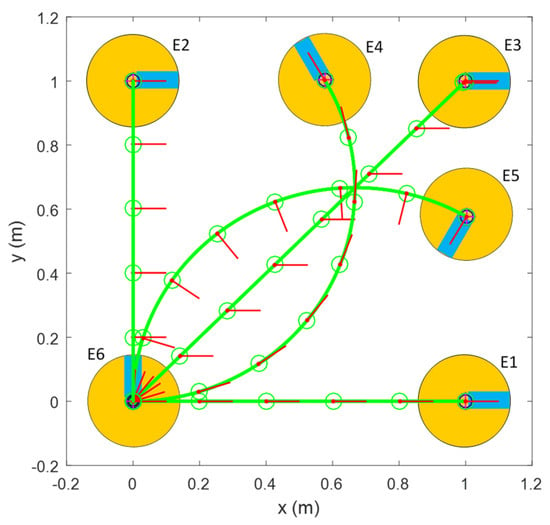
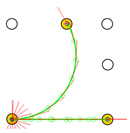
Figure 6.
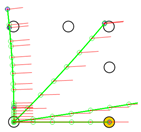
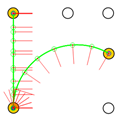
Trajectories of the motion commands defined in Table 7. Yellow circles represent the final positions of the platform after implementing each motion, and blue lines represent the final orientation of the platform. The green circles and the red lines depict intermediate positions of the mobile platform along the trajectory simulated.
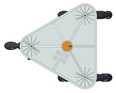
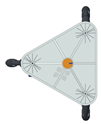
Table 8 and Table 9 summarize the results of the simulation experiments performed with all the mobile platforms assessed. Table 8 shows the results of the mobile platforms identified as omnidirectional in the previous analysis (provided in Table 6), while Table 9 shows the results of the mobile platforms identified as non-omnidirectional. Both tables show a CAD design of the mobile platform and the evaluation of the validation experiments defined in Table 7 and Figure 6. The result of each validation experiment is labeled as OK in the case where the final position reached by the mobile platform differs less than 0.01 m from the expected destination, and as FAILED if it differs more. Additionally, Table 8 and Table 9 provide a summary of the trajectories simulated. In these images, a yellow circle depicts that the mobile platform has reached the expected final position within the distance threshold of 0.01 m while an empty circle depicts that the final position has not been reached. The parameter OMD summarizes the omnidirectional capabilities of the mobile platform obtained by simulation: labeled as YES in the case that the mobile platform is able to successfully execute all trajectories requiring a rotation (E4, E5, and E6), and NO otherwise. Similarly, the parameter T summarizes the translational capabilities of each mobile platform: labeled as YES in the case that the mobile platform is able to successfully execute all trajectories requiring only translation (E1, E2, and E3), and NO otherwise.

Table 8.
Results of the validation experiments of the mobile platforms identified as omnidirectional. OK means that the trajectory has been successfully executed by the platform (it has arrived at the planned destination).

Table 9.
Results of the validation experiments of the mobile platforms identified as non-omnidirectional. OK means that the trajectory has been successfully executed by the platform.
The simulation results displayed in Table 8 show that the mobile platforms identified as omnidirectional by the procedure proposed in this paper are able to execute successfully all the validation trajectories. Alternatively, the simulation results displayed in Table 9 show that the mobile platforms identified as non-omnidirectional are not able to execute successfully all the validation trajectories. Results for the 3B platform indicate that it is not controllable when there is rotation of the platform (), so the system is stable only when translational trajectories without rotation are implemented. Both 2A-1B and 1B-2D platforms are only able to execute the E1 command (move forward without rotation), and do not successfully implement the rest of the commands, including the rotation-only motions. Both 1B-2C and 1A-2D platforms are able to implement specific translation-only trajectories and specific trajectories combining translation and rotation, but other motions requiring the same capabilities fail. Such results indicate that both platforms act like a differential-drive one, with its corresponding motion restrictions. Finally, these results obtained by simulation (Table 9) agree with the motion capabilities predicted in this paper (provided in Table 6).
5. Conclusions
This paper presents a procedure for estimating the motion capabilities of mobile platforms with three omni wheels, which is the minimum number of wheels required to achieve omnidirectionality. This procedure is able to differentiate between omnidirectional capabilities and translational capabilities by analyzing the bidirectionality compliance between the inverse and forward kinematics for a wide set of motion commands.
The procedure has been assessed with eleven mobile platforms, each one with different omni wheel configurations. The estimation of the motion capabilities of these platforms agrees with state-of-the-art methods [17] while providing a new specific estimation of the translation capabilities and combined visual information of the motion capabilities of the platforms. These estimations have been validated by simulating the trajectories followed by the mobile platforms while executing a reduced set of motion commands.
Results have shown that the procedure proposed in this paper for estimating the omnidirectionality capabilities is 869-fold faster than performing alternative trajectory simulations. This is because the computation of the bidirectionality error of a motion command requires an average time of 0.522 ms on a testbench computer, as it is based on two matrix operations (see Figure 4). Alternatively, the simulation of the execution of a trajectory by a mobile platform to verify if a motion command can be executed or not requires an average time of 0.454 s on the same testbench computer. This performance allows this procedure to be applied during the design stage of new mobile platforms with three omni wheels to validate their motion performances.
Relative to the related scientific literature [17,18,51], the advantage of this proposal is that it indicates which platform configurations become uncontrollable when the angular velocity of the platform is different from zero, which indirectly conveys specific information on the translational performance of the platform under evaluation. Additionally, the graphical information on the motion capabilities of a mobile platform provides direct visual information about which motions may be successfully executed by the platform.
This proposal has the limitation of not considering dynamic effects in the omnidirectional motion, which will be addressed in future works. Future work will apply the procedure proposed in this paper on the optimal design of translation-only mobile platforms tailored for heavy-duty industrial applications where rotation is not needed during transportation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.P.; formal analysis, J.P.; investigation, E.R.; methodology, E.C.; resources, R.B.; software, E.R., R.B. and E.C.; supervision, J.P.; validation, E.R.; visualization, E.R.; writing—original draft, E.R.; writing—review and editing, J.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was supported by the predoctoral grants from the Departament de Recerca i Universitats de la Generalitat de Catalunya (AGAUR FI SDUR 2022) and the Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (FPU 2022).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Dickerson, S.L.; Lapin, B.D. Control of an Omni-Directional Robotic Vehicle with Mecanum Wheels. In Proceedings of the NTC’91—National Telesystems Conference Proceedings, Atlanta, GA, USA, 26–27 March 1991; pp. 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- Pin, F.G.; Killough, S.M. A New Family of Omnidirectional and Holonomic Wheeled Platforms for Mobile Robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1994, 10, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwin, O.; D’Andrea, R. Trajectory Generation and Control for Four Wheeled Omnidirectional Vehicles. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2006, 54, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroftei, I.; Grosu, V.; Spinu, V. Omnidirectional Mobile Robot—Design and Implementation. In Bioinspiration and Robotics Walking and Climbing Robots; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-3-902613-15-8. [Google Scholar]
- Indiveri, G. Swedish Wheeled Omnidirectional Mobile Robots: Kinematics Analysis and Control. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 25, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilon, B.E. Wheels for a Course Stable Selfpropelling Vehicle Movable in Any Desired Direction on the Ground or Some Other Base. U.S. Patent No. 3,876,255, 8 April 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Diegel, O.; Badve, A.; Bright, G.; Potgieter, J.; Tlale, S. Improved Mecanum Wheel Design for Omni-Directional Robots. In Proceedings of the Australian Conference on Robotics and Automation, Auckland, Australia, 27–29 November 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grabowfecki, J. Vehicle-Wheei. U.S. Patent US1305535A, 3 June 1919. [Google Scholar]
- Blumrich, J. Omnidirectional Wheel. U.S. Patent US3789947A, 5 February 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, J.; Clotet, E.; Lupiañez, R.; Tresanchez, M.; Martínez, D.; Pallejà, T.; Casanovas, J.; Palacín, J. Design, Implementation and Validation of the Three-Wheel Holonomic Motion System of the Assistant Personal Robot (APR). Sensors 2016, 16, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eirale, A.; Martini, M.; Tagliavini, L.; Gandini, D.; Chiaberge, M.; Quaglia, G. Marvin: An Innovative Omni-Directional Robotic Assistant for Domestic Environments. Sensors 2022, 22, 5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, T.; Ni, X.; Wu, C.; Zong, H.; Lu, H.; Lu, Z.; Shen, Y. An Omnidirectional and Movable Palletizing Robot Based on Computer Vision Positing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Safety for Robotics (ISR), Shenyang, China, 24–27 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Samani, H.A.; Abdollahi, A.; Ostadi, H.; Rad, S.Z. Design and Development of a Comprehensive Omni Directional Soccer Player Robot. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2004, 1, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Q.; Chen, H.B.; Du, Y.P.; Wei, L. Design and Development of an Omni-Directional Mobile Robot for Logistics. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 602–605, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levratti, A.; Riggio, G.; Fantuzzi, C.; De Vuono, A.; Secchi, C. TIREBOT: A Collaborative Robot for the Tire Workshop. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2019, 57, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racz, S.-G.; Crenganis, M.; Barsan, A.; Adrian, M. Omnidirectional Autonomous Mobile Robot with Mecanum Wheel. In Proceedings of the International Student Innovation and Scientific Research Exhibition, Sibiu, Romania, 1 April 2019; pp. 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Dai, S.; Zhao, L.; Yan, X.; Shi, Y. Topological Design Methods for Mecanum Wheel Configurations of an Omnidirectional Mobile Robot. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasri, E.; Uyguroğlu, M.K. Modeling and Trajectory Planning Optimization for the Symmetrical Multiwheeled Omnidirectional Mobile Robot. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, A.P.; Elango, A.; Reddy, M.C. Front and Back Movement Analysis of a Triangle-Structured Three-Wheeled Omnidirectional Mobile Robot by Varying the Angles between Two Selected Wheels. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 7612945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Palacín, J.; Rubies, E.; Clotet, E. The Assistant Personal Robot Project: From the APR-01 to the APR-02 Mobile Robot Prototypes. Designs 2022, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y. A New Kind of Wheel-Model All-Directional Moving Mechanism. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2001, 33, 854–857. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Salih, J.E.; Rizon, M.; Yaacob, S.; Adom, A.; Mamat, M. Designing Omni-Directional Mobile Robot with Mecanum Wheel. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 3, 1831–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, R.; Cobano, J.A.; Corzetto, M.; Merino, L.; Alvito, P.; Caballero, F. A Novel Robot Co-Worker System for Paint Factories without the Need of Existing Robotic Infrastructure. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2021, 70, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijikata, M.; Miyagusuku, R.; Ozaki, K. Omni Wheel Arrangement Evaluation Method Using Velocity Moments. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.L.; Flann, N.S. A Six-Wheeled Omnidirectional Autonomous Mobile Robot. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2000, 20, 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, K.L.; Davidson, M.; Bahl, V.; Rich, S.; Jirgal, S. Modelling and Control of a Six-Wheeled Autonomous Robot. In Proceedings of the 2000 American Control Conference. ACC (IEEE Cat. No.00CH36334), Chicago, IL, USA, 28–30 June 2000; Volume 3, pp. 1483–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Meng, R.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X. Practical Obstacle-Overcoming Robot with a Heterogeneous Sensing System: Design and Experiments. Machines 2022, 10, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zhang, J.; Yan, N.M.; Zeng, W. Research on Simulation of Motion Compensation for 8 × 8 Omnidirectional Platform Based on Back Propagation Network. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 299, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados Sesmero, C.; Buonocore, L.R.; Di Castro, M. Omnidirectional Robotic Platform for Surveillance of Particle Accelerator Environments with Limited Space Areas. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, W.; Groves, K.; Martin, H.; Peel, H.; Watson, S.; Marjanovic, O.; Lennox, B. MIRRAX: A Reconfigurable Robot for Limited Access Environments. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Viegas, C.; Marques, L.; Pires, J.N.; de Almeida, A.T. OmniClimbers: Omni-Directional Magnetic Wheeled Climbing Robots for Inspection of Ferromagnetic Structures. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Magdaleno, E.C.; Gómez-Bravo, F.; Castillo-Castañeda, E.; Carbone, G. Evaluation of Locomotion Performances for a Mecanum-Wheeled Hybrid Hexapod Robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.T.; Gladwin, D.T.; Prescott, T.J.; Conran, S.O. Dual-Mode Model Predictive Control of an Omnidirectional Wheeled Inverted Pendulum. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 2964–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboubi, S.; Fakhrabadi, M.M.S.; Ghanbari, A. Design and Implementation of a Novel Hybrid Quadruped Spherical Mobile Robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yao, S.; Liu, R.; Yao, Y. A Schatz-Based Omnidirectional Mobile Mechanism with Oloid-like Paddlewheels. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 189, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, H.; Zhao, C.X. Omnidirectional Mobile Robots, Mechanisms and Navigation Approaches. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 153, 103958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, S.J.C.L.; Conceição, A.G.S.; Dórea, C.E.T.; Martinez, L.; de Pieri, E.R. Design and Implementation of Model-Predictive Control With Friction Compensation on an Omnidirectional Mobile Robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzl, P.; Sereinig, M.; Gerstmayr, J. A Mecanum Wheel Model Based on Orthotropic Friction with Experimental Validation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2024, 193, 105548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Su, Q.; Gao, J. Research on Motion Characteristic of Omnidirectional Robot Based on Mecanum Wheel. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Digital Manufacturing & Automation, Changcha, China, 18–20 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini, L.; Colucci, G.; Botta, A.; Cavallone, P.; Baglieri, L.; Quaglia, G. Wheeled Mobile Robots: State of the Art Overview and Kinematic Comparison Among Three Omnidirectional Locomotion Strategies. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2022, 106, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijikata, M.; Miyagusuku, R.; Ozaki, K. Wheel Arrangement of Four Omni Wheel Mobile Robot for Compactness. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sharma, M.; Mohan, S. Behavioural Fault Tolerant Control of an Omni Directional Mobile Robot with Four Mecanum Wheels. Def. Sci. J. 2019, 69, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Cao, Q. Velocity Analysis of Omnidirectional Mobile Robot and System Implementation. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, Shanghai, China, 8 October 2006; pp. 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Wu, D.; Chen, K.; Liu, F.; Fan, N. Analysis of the Mecanum Wheel Arrangement of an Omnidirectional Vehicle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 233, 5329–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamaev, I.S.; Kilin, A.A.; Karavaev, Y.L.; Shestakov, V.A. Criteria of Motion Without Slipping for an Omnidirectional Mobile Robot. Rus. J. Nonlin. Dyn. 2021, 17, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Long, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Jia, Z. Experimental Characterization and Comparison of Three Typical Omnidirectional Mobile Robots. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics, ICARM 2023, Sanya, China, 8–10 July 2023; pp. 1162–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, K.M.; Park, F.C. Modern Robotics: Mechanics, Planning, and Control; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-107-15630-2. [Google Scholar]
- Palacín, J.; Rubies, E.; Clotet, E.; Martínez, D. Evaluation of the Path-Tracking Accuracy of a Three-Wheeled Omnidirectional Mobile Robot Designed as a Personal Assistant. Sensors 2021, 21, 7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedrzycki, R. Comparison with State-of-the-Art: Traps and Pitfalls. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Kraków, Poland, 28 June–1 July 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 863–870. [Google Scholar]
- Clotet, E.; Rubies, E.; Bitriá, R.; Palacín, J. Simulator for Omnidirectional Robots Equipped with 2D and 3D LiDAR Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 2nd Industrial Electronics Society Annual On-Line Conference (ONCON), Online, 8–10 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Siradjuddin, I.; Azhar, G.A.; Wibowo, S.; Ronilaya, F.; Rahmad, C.; Rohadi, E. A General Inverse Kinematic Formulation and Control Schemes for Omnidirectional Robots. Eng. Lett. 2021, 29, 1344–1358. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).