Abstract
Regular exercise plays a crucial role in promoting overall well-being in today’s lifestyle. However, individuals often find it challenging to properly execute exercises, including maintaining correct postures and appropriate movement speeds. Robotic companions have emerged as potential solutions to assist and motivate users during exercise sessions. This research paper proposes a novel robot companion designed for exercise scenarios using a reconfigurable robot. In contrast to existing non-reconfigurable robotic companions, the use of a reconfigurable robot provides added flexibility in generating emotions. The system incorporates a module that utilizes fuzzy logic to evaluate the correctness of exercise performance based on posture variations and movement speeds. The robot generates emotions and provides feedback to users based on the exercise correctness score. The robot expresses emotions through reconfigurations, motion patterns, and variations in robot speed. This emotion-based feedback could be helpful for creating engaging and interactive exercise experiences. Apart from emotion generation, the robot utilizes vocal cues as feedback. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of the proposed system in evaluating exercise correctness and demonstrating meaningful emotion transitions. The findings of this work contribute to the development of innovative robotic companions for improving exercise adherence and overall well-being.
1. Introduction
Regular exercise offers numerous benefits for physical and mental health [1]. With the rise in office jobs and sedentary lifestyles, people spend extended periods sitting and working on laptops, leading to weight gain and obesity. Therefore, incorporating daily exercise is essential. Exercising offers a broad range of benefits, such as disease prevention, increased energy levels, enhanced cognitive function, and stress relief [2]. Many social media platforms provide videos and tips to conduct exercises, such as on YouTube and Instagram. However, it is crucial to note that while people may engage in exercise, they often require proper guidance and motivation to perform exercises correctly, maximizing their impacts on the body. The introduction of robots as exercise trainers becomes impactful in this context.
Robots have emerged as invaluable tools for guiding and motivating individuals during their exercise routines, offering significant advantages over traditional methods of exercise guidance [3,4,5]. One key advantage is their ability to provide consistent and precise instructions, ensuring that individuals perform exercises accurately, thereby minimizing the risk of injury and maximizing the effectiveness of each movement. Furthermore, robots can offer real-time feedback on form and technique, enabling individuals to maintain proper posture and alignment throughout their workouts.
Social assistive robots have emerged as valuable exercise companions, encouraging users to engage in regular physical activity [6]. A robot that monitors user engagement and heart rate while performing upper body exercise has been proposed in [6]. This robot generated appropriate emotions based on user engagement and heart rate using an nth order Markov chain. Another study investigated the effects of exercising alone, receiving instructions from a robot, and exercising conjunctively with the robot [7]. The findings revealed that exercising in conjunction with a humanoid robot increased user motivation and led to longer exercise durations. The impact of different levels of automation on personalizing socially assistive robots in exercise scenarios was explored in a study [8]. The results demonstrated that adaptive robots were perceived as more competent and trustworthy than adaptable robots. A study comparing acknowledgment–feedback versus non-acknowledgment–feedback for a robot exercise instructor and companion has been introduced in [9]. The outcomes indicated that users who exercised co-actively with the robot exhibited significant performance improvements compared to those who were instructed by the robot or exercised alone. These studies highlight the positive influence of social assistive robots in exercise contexts, emphasizing the benefits of companion robots in increasing motivation, personalization, and performance during physical activity.
Furthermore, as the global elderly population grows, promoting active and engaged lifestyles becomes increasingly important for their overall well-being. Recognizing this need, numerous research studies have focused on developing exercising companions specifically tailored for elderly individuals [10,11]. The work [12] introduced a diverse range of human–robot interactive games specifically designed to engage both the elderly and young adults. These interactive games serve as effective tools to encourage physical activity and foster healthy lifestyles across different age groups. Particularly, the use of robot companions for rehabilitation purposes has emerged as an intriguing application in this context [13,14,15]. Integrating robotics in rehabilitation programs showcases the potential of exercise-focused robot companions to aid in the recovery and enhancement of physical well-being in disabled individuals. To personalize the interaction with humans while engaging in the exercises, robotic platforms have been introduced [16]. Furthermore, studies have been conducted to enhance the social interaction in physical training using robots [17].
The existing research discussed above primarily focuses on developing fixed-shape robots as exercise companions. However, there is an unexploited potential for introducing reconfigurable robots for this purpose. Reconfigurable robots have the capability of changing their shape based on the context in which they operate [18,19]. The unique capabilities, applications, and challenges of reconfigurable robots have been introduced in [20]. These robots have been extensively studied in various applications such as cleaning [21], exploration [22], and inspection [23], which demand area coverage. Their use as exercise companions remains limited despite their unique capabilities. Reconfigurable robots present an intriguing opportunity for human–robot interaction in the domain of robotic exercise companions. Through morphology transformation, reconfigurable robots can represent expressions in a more detailed, convincing manner. Their shape-changing abilities can be leveraged to display a wide range of emotions and generate diverse motion patterns, making them highly suitable for assisting in exercise activities.
Motivated by this potential, this paper proposes the development of a reconfigurable exercising companion designed to provide emotional support during exercise scenarios. The novelty of this paper lies in the robot’s ability to adjust its physical configuration and provide emotional feedback based on how well the exercises are performed, aiming to motivate users to improve. The use of reconfigurability for this new application is the major contribution compared to the state of the art, where only non-reconfigurable robots have been used up to now. In this proposed system, the robot delivers exercise instructions while an external laptop displays exercise-related videos for the user. The user’s exercise performance is monitored using the external laptop, and a fuzzy inference system is developed to evaluate the correctness of their movements. Based on the assessed exercise correctness, the robot generates appropriate emotions and motions to enhance the exercise experience. By capitalizing on the reconfigurable nature of the robot, this proposed system aims to create a versatile and interactive exercising companion that can adapt to different exercises and provide personalized emotional support. The incorporation of a fuzzy inference system enables real-time evaluation of the user’s exercise correctness, allowing the robot to generate suitable emotional responses and motion patterns accordingly.
The rest of this paper is outlined as follows. A system overview of the proposed method is given in Section 2. Emotion-based feedback in relation to the performance of exercise is provided in Section 3. Detailed information regarding experimental validation is presented in Section 4. Section 5 provides concluding remarks.
2. System Overview
A functional overview of the proposed system is shown in Figure 1. The proposed system analyzes and evaluates the correctness of an exercise performed by a user and gives verbal and emotion-based feedback to interact with the user. The system extracts dynamic characteristics information related to body movement in order to evaluate performance. The Body Joint Extraction unit gathers vision data as an RGB image through a monocular camera. It outputs the skeletal information as a set of 2D coordinate points representing the specific joints/landmarks of the body. The necessary parameters, such as joint angles and speed, are calculated by the exercise parameter calculation unit based on data points. The set of body joints used for the calculation varies according to the specific exercise the user performs. All the references for each body landmark corresponding to each exercise are stacked in the exercises posture reference database. Calculated parameters are then fed to the exercise correction evaluation unit. This unit uses fuzzy logic to analyze the correctness of an excise based on the incoming parameters. This module is implemented in such a way that it can adapt to different exercises. The parameters required for adapting to different exercises are stored in the parameter reference database. The system evaluates each complete exercise cycle and assigns a correctness score accordingly. The emotion output generation unit determines the type of emotion with its level based on the history of the exercise correctness score. This emotion is then fed to the action manager. The overall coordination of the system is managed by the action manager (AM). It triggers voice responses through the voice response generation unit based on the exercise correctness score. The voice response generation unit is a text-to-speech converter with a set of predefined responses. Furthermore, the AM enables playing a reference video of the exercise at the beginning of the exercise for the user to follow. Up to this level, the whole process is executed inside a PC.
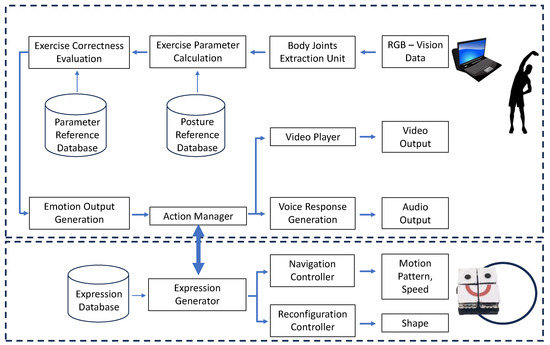
Figure 1.
Overview of the system.
The AM communicates the expression generator in the robot through a wireless link. The expression generator acts upon the requested emotion levels and determines the motion cues and shape changes. The predefined robot shape configurations mapped to a particular emotion with the motion profile to follow stored in the expression database are used in this regard. The reconfiguration controller executes the shape-shifting part of the robot based on the input from the expression generator. The navigation controller handles the maneuvering of the robot according to the given motion profile.
Reconfigurable Robot Platform
The proposed system utilizes the reconfigurable robot Smorphi for emotion expression. Smorphi (www.wefaarobotics.com, accessed on 15 June 2024) is a reconfigurable mobile robot platform consisting of four modules that are connected serially through three hinges for allowing intra-reconfigurability (see Figure 2a). Thus, all four modules act as a single platform. Reconfigurability of the robot is achieved by rotating modules around the hinges to create different shape configurations. This robot can create seven shapes in total, as shown in Figure 2b. Each robot block has a mecanum drive locomotion system to perform holonomic movements required for reconfiguration and navigation.
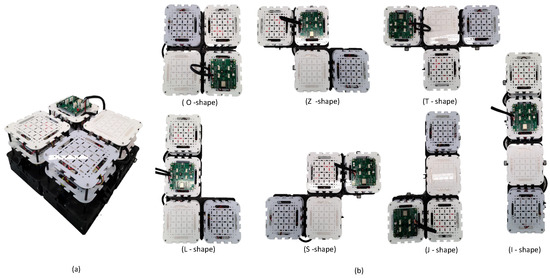
Figure 2.
(a) Smorphi robot platform. (b) Robot shape configurations.
3. Emotion-Based Feedback per Performance of Exercise
3.1. Perceiving Exercises
The correctness of an exercise depends on several parameters. Each exercise requires the movements of a unique set of body joints in predefined ranges. Not achieving or exceeding these ranges tends to reduce the overall outcome expected from the exercise. This scenario can be used as a measure to evaluate the correctness of an exercise. For example, a situation of a person doing an exercise involved with hand movements can be considered. This exercise mainly involves two body joints (i.e., shoulder and elbow joints). Monitoring the movements of these joints can give an idea of how correct the exercise is. There should be a method to extract the information related to the body joint movement for the proposed system to evaluate the correctness of an exercise. In this regard, the proposed system utilizes a monocular camera to capture the movements of body joints. The locations of the body joints are extracted from 2D image frames using MediaPipe Pose framework (https://ai.google.dev/edge/mediapipe/solutions/vision/pose_landmarker accessed on 15 May 2024).
This joint extraction model returns a total of 33 human body joints as depicted in Figure 3a. Here, each joint has a unique Identity (ID), which is useful for tracking. This information is then used to derive the joint angles that can be used to determine the correctness of the posture during an exercise [24]. Apart from varying the posture, the speed of the movements should be within certain limits for a specific exercise where the movement speed should not be too slow or too fast [25]. Therefore, posture correctness and movement speed are considered to evaluate the correctness of an exercise. The posture correctness is measured as the deviation from the required posture movement range.
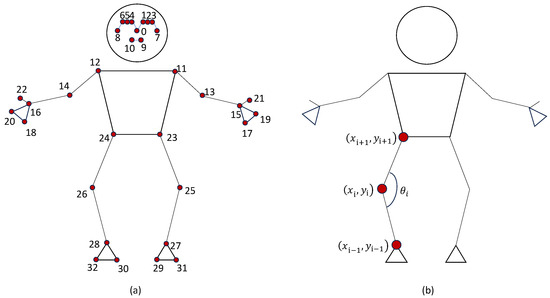
Figure 3.
Human body joint extraction: (a) 33 joint positions identified by Mediapipe Pose, and (b) body joints corresponding to derive .
Given the 2D body joint coordinates for considered exercise, joint angles can be derived. For a predefined set of exercises, the required joint angles to be calculated are stored in a database with a given reference ID to each joint angle. Let set A consist of the exercises . The eth exercise consists of an array of joint angles IDs to be measured. Equation (1) explains how each exercise data point with relevant angles is stored in the database A. The required angles can be derived using this database for a known exercise.
A specific joint angle can be calculated using another database that stores a stack of body joint IDs required to form a specific joint angle. Let B be the set of the joint angle identities for the eth exercises such that . Each joint angle ID points to a set of body joint IDs where ith joint angle can be measured using the locations of the joints . The mapping of joint IDs to each joint in database B is explained in (2).
The joint angle can be calculated as in (3), where is the extracted joint coordinates (see Figure 3b).
such that relevant body joint angles are calculated for each captured image frame at time t. Calculation of the joint angle deviation becomes complex if each captured frame is considered, since there should be a database of correct joint angle values for each frame, which is challenging to implement. Instead, the deviation between maximum and minimum values of joint angles acquired per an exercise cycle is considered. In this case, the only requirement is to have a database with possible maximum and minimum joint angles for each joint involved in each exercise. Consider that the minimum and maximum angles of the ith joint of the exercise are and , respectively.
Let the database F consist of reference minimum and maximum values for joint angle data for each considered exercise . Then, (4) shows how the data are stored in the database F.
Using the reference minimum and maximum joint angles (i.e., ), the posture deviation for the eth exercises at time t, D can be calculated as in (5). Mean square error is utilized as the joint deviation since deviations can be negative and positive.
The second parameter to evaluate the correctness of an exercise is the movement speed per cycle (defined as S). Let the image frame indicate the initiation of one exercise cycle, which is acquired at time . Then, frame represents the end of that cycle at . Then, the speed per cycle S can be calculated as in (6). The frames corresponding to the minimum and maximum joint angles are used to identify the initiation and completion frames of an exercise cycle.
Finally, calculated posture deviation (i.e., D) and the movement speed (i.e., S) are used to evaluate the exercise correctness in each cycle.
3.2. Exercise Correctness Score
The goal of this module is to evaluate the correctness of an exercise performed by a user. Although the mathematical modeling of the relationship between perceived parameters (i.e., posture deviation, D and movement speed, S) and exercise correctness is challenging, linguistic explanations based on expert knowledge can provide insights. In this context, fuzzy logic can be employed to model this process, which involves unknown dynamics and linguistic relationships [26]. Fuzzy logic is a universal approximator that can map the nonlinear relationship between input and output spaces through linguistic expressions [27,28]. Additionally, the user parameters perceived by the robot may contain noise due to limitations in the vision-based detection of human body joints. In contrast, fuzzy logic effectively handles imprecise sensory information [29]. Furthermore, the relationships between input parameters and exercise correctness should be adapted to each exercise. Fuzzy logic possesses adaptive abilities, making it well-suited for evaluating exercise correctness based on the perceived information. Hence, fuzzy logic is utilized to develop the module to evaluate the correctness of an exercise performed by a user based on the perceived information.
The inputs of the fuzzy logic module are the posture deviation, D, and movement speed, S. Figure 4a,b depict the corresponding input fuzzy membership functions. Non-singleton fuzzy sets have been chosen to cope with the uncertainties in the inputs. The membership function for D has been defined with the three triangular fuzzy sets; L: Low, M: Medium, and H: High. The membership function for S has been defined with the three triangular fuzzy sets; S: Slow, G: Good, and F: Fast. The ranges D and S should be varied with the exercise a user is conducting since the amount of variation in body joint angles and the expected speed differ from one exercise to another. The ranges of the input membership functions are adapted with and to facilitate the adaptation of the fuzzy logic module for different exercises. The parameters and define the possible posture deviation and the speed range for the eth exercise. These range parameter values are derived by analyzing a set of typical series of exercise cycles, and obtaining the average for each selected parameter. These data are pre-stored in the database and retrieved when they are required.
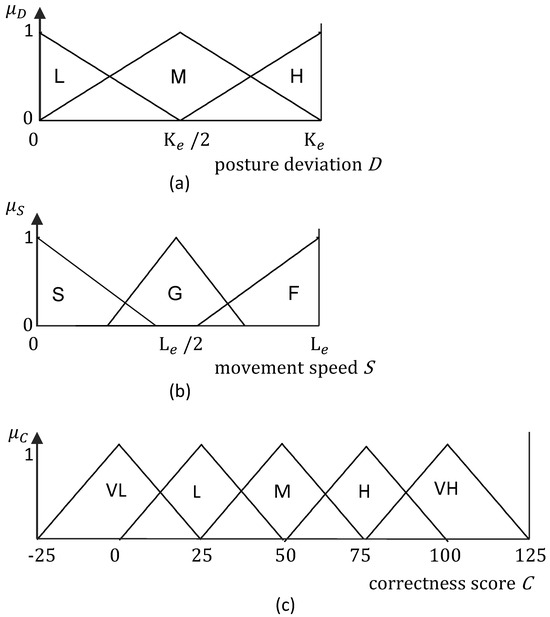
Figure 4.
Membership function of the fuzzy logic module developed for evaluating the correctness of exercises. (a): the input membership function for D, (b): the input membership function for S, and (c): the output membership function.
The output of this fuzzy logic module is the correctness score of an exercise performed by a user (defined by C). The output membership function is given in Figure 4c. The output membership function has five triangular fuzzy sets; VL: Very Low, L: Low, M: Medium, H: High, and VH: Very High. The fuzzy rule base given in Table 1 maps the input fuzzy sets with the output fuzzy sets. There is a particular speed that is most effective for a specific exercise, and performing it too fast or too slow would not be as impactful. Similarly, deviation in the postures should be minimized to make the exercise perfect. These facts were considered in formulating the rule base based on expert knowledge. The fuzzy sets in the output membership function are defined by equivalently dividing the output range in such a way that the minimum and the maximum output are in the range . The fuzzy logic module is considered to be a Mamdani-type system with the center of area method for the defuzzification. A C value closer to 100 indicates that the exercise is performed flawlessly, while 0 indicates that the exercise is not performed at a satisfactory level.

Table 1.
Rule base of the fuzzy logic module.
3.3. Emotion Generation
Expressing emotions through non-humanoid robots can be challenging [30]. Therefore, adopting a systematic approach to generate emotions effectively is crucial. One effective method is utilizing an emotion space model to represent and assess emotions. Various options are available in this context, ranging from 1D to 4D emotion space models [31]. The application and the desired number of emotions should be accounted for to determine the most suitable model.
In the proposed system, the exercises evaluation unit generates a correctness score in the range for each exercise cycle. Emotions can be mapped by setting threshold values at specific positions along the continuum of correctness values, which spans from 0 to 100. This enables the mapping of multiple emotions by defining distinct regions. However, due to the dynamic nature of the scenario and the limitations of the hardware setup, incorporating multiple emotions may result in a less smooth emotion transformation.
Existing literature based on emotion space models reveals various approaches to express emotions using non-humanoid robots such as movement path, speed, color indications, and sound [32,33]. Using multiple unique techniques allows for distinguishing between emotions easily. Thus, the proposed system uses three different methods to express an individual emotion with its level. Those are movement pattern, movement speed, and reconfiguration-based visual indication. As one emotion is the opposite of the other, making the transition recognizable while being smooth is vital. The proposed emotion model is inspired by the valence–arousal model [34]. Valence discriminates between positive and negative emotions, while arousal stands for the energy level of each emotion. Happiness refers to high valence, high arousal expression, whereas sadness refers to low valence, low arousal expression. According to the work [34], movement patterns can be used to represent the valence where jerky motion indicates the negative and a smoother motion pattern is used for the positive expression. Furthermore, speed can be used to indicate the level of energy, which is arousal. Apart from that, the proposed system uses one more technique to distinguish emotions in view of valence. Visual indication of the emotion is a highly efficient way to represent it such that a user can easily understand the expression well. The proposed system uses a sticker arrangement placed on top of the robot to indicate emotion as a facial expression similar to a human. This sticker placement is aligned in such a way that the reconfiguration can produce a unique human-like visual aid. Reconfiguration is a unique feature of Smorphi, the mobile robot that is used in the proposed system. Figure 5 shows the emotion model used in the proposed system. It also shows how the expression modalities are mapped to specific emotions.
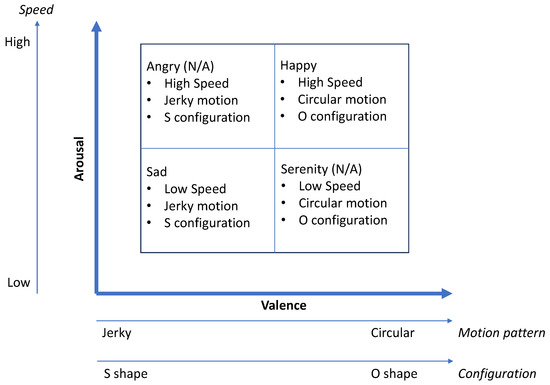
Figure 5.
Emotion space model configured for the proposed system.
The proposed system uses O-shape and S-shape configurations for the emotion expression through reconfiguration based visual aid. Figure 6 shows the reconfiguration-based emotions that can be generated by the robot.
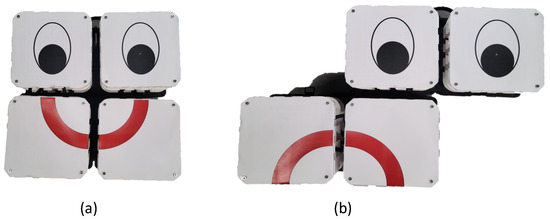
Figure 6.
Smorphi configurations with labeled top for emotion expression. (a): happy expression with O shape and (b): sad expression with S shape.
After receiving the exercise’s correctness score at cycle t (i.e., ), the average correctness score at cycle t (defined as ) is calculated as in (7) considering the correctness scores received for the immediate past three cycles. This average calculation is performed every three cycles to avoid the high variations in emotion output that could not be handled by reconfiguration as well as to account for the history of exercise performance by a user. Two threshold values are introduced to define the emotion regions based on the range of . Algorithm 1 shows the flow of the emotion generation based on the average correctness score. According to the output emotion, the robot motion profile is derived. The robot moves on a jerky path for the sad emotion expression, and for the happy emotion, it follows a smooth circular path. Furthermore, the robot’s movement speed is calculated based on the degree of each emotion level. This process is given in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 1 Emotion derivation |
|
| Algorithm 2 Motion pattern, robot speed calculation |
|
The robot is commanded to follow the motion profile and the speed determined by the algorithms. These motion cues are predefined for both cases of emotions. The navigation controller of the robot derives linear velocity components of the robot in x and y directions at time t (defined by ). Here, the robot’s movement is holonomic. Hence the angular displacement of the robot is not required for circular loop motions.
Let the motion pattern be circular with a fixed radius and speed is at time t. Let be the current position on the path. Thus, directional linear velocity components of the robot can be calculated according to (8). The directional velocity components are derived according to (9) for the jerky motion. Here, is a constant that controls the amount of jerkiness. The wheel angular velocities corresponding to the linear velocity components are calculated based on the kinematic model of the robot. The motors are commanded to follow the derived wheel velocities.
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
Normal squats and sumo squats were considered for the experiments (see Figure 7b,c). These two exercises were often conducted in domestic environments and are essential to verify the correctness of body joint movements. The user maintained a distance from the laptop in such a way that the camera captured the whole body’s joints. The robot was placed in front of the user in order to perform the emotional expression. The experiment setup is depicted in Figure 7a. The setup consisted of a laptop computer that handles the vision-based perception and processing. The built-in front camera of the laptop was used to capture the video. No additional data collection or training was performed as the detection processing module uses pre-trained models. The robot was initiated with the happy configuration without movements. The experiments commenced with a warm greeting and then provided a video guide to follow the specific exercise by the computer. The user then performed the exercise, referring to a guide video on the computer screen. In order to observe and verify the transition of emotions, the user was instructed to perform the exercise incorporating correct and incorrect posture variations. This process allowed for the examination of emotional changes in response to different performance scenarios. The important variables of the system were recorded for each time step throughout the experiment.
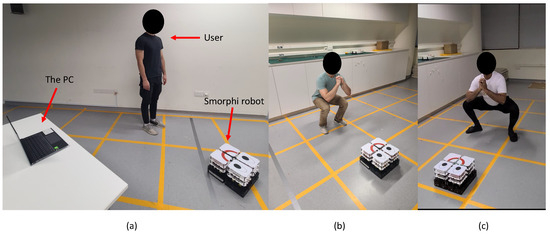
Figure 7.
Experimental setup. (a): Hardware setup with a user. (b): A user performing normal squats. (c): A user performing sumo squats.
4.2. Results and Discussion
The results obtained with respect to the normal squat exercise are displayed in Figure 8. The variations in the emotions and the robot speed with the average correctness score during this experiment are depicted in Figure 9. Table 2 represents the results for the first 15 cycles of normal squat exercise performance. The variation in the parameters during the second cycle is considered for the explanation. Knee and hip flexion are the movements that are required to be monitored during the squat exercises. Therefore, variations in knee and hip angles are considered in evaluating the exercise’s correctness. These were identified from the pre-stored data in the posture reference database. The posture variation captured by the camera during the second cycle is shown in Figure 10.
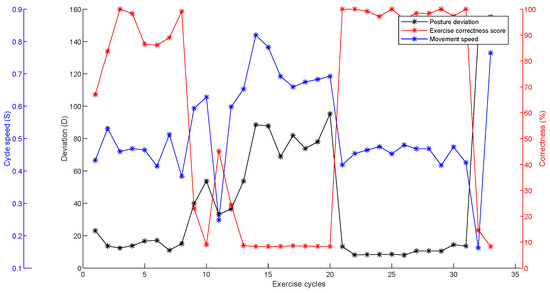
Figure 8.
Normal squat experiment correctness evaluation results.
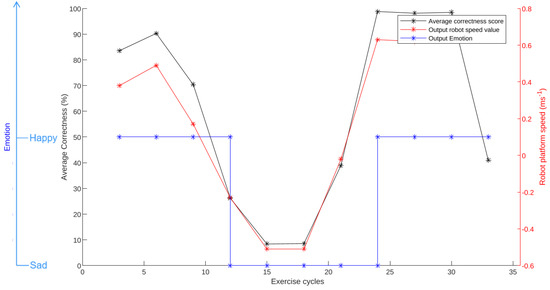
Figure 9.
Normal squat experiment emotion expression results.

Table 2.
Normal squat performance results.
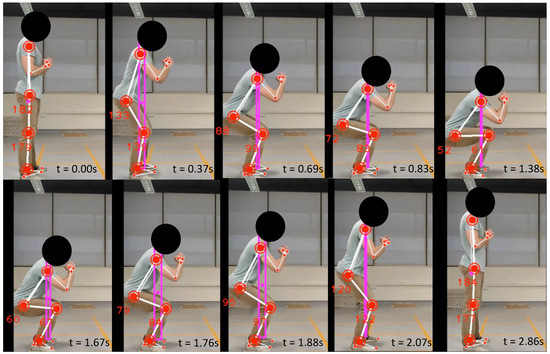
Figure 10.
Normal squat correct posture variation.
The maximum knee and hip joint angles captured by the system were 179° and 182°, while the minimum knee and hip angles were recorded as 52° and 61°, respectively. The maximum reference angle defined for knee and hip angles was 180°, while the minimum reference angle was 65° for both. Thus, the posture deviation was observed as 13.78°. According to the fuzzy membership functions that correspond to this exercise, this value has a higher degree of membership for the Low deviation region and a trivial degree of membership for the Medium deviation region. The movement speed was recorded as 0.53, slightly higher than the reference movement speed corresponding to the exercise (reference speed is 0.38). Thus, a correctness score of 83.71 was received for this cycle, suggesting that the user is correctly performing the exercise. Here, the user performed the exercise correctly, and the proposed system successfully interpreted it.
The user intentionally performed some segments of the exercise incorrectly to validate the system’s ability to identify such situations. For example, the user performed the exercise during cycle 15 while having deviated posture movements. Figure 11 depicts the body joint observation recorded in the system. During this cycle, minimum angles of 131° and 122° were observed for hip and knee flexion, respectively. Consequently, the deviation value was calculated as 87.8°. In addition, the observed movement speed was 0.6 m s−1 indicating a too-fast movement speed. As a result, the fuzzy logic system returned a correctness score of 8.33, suggesting that the user was performing the exercise incorrectly.
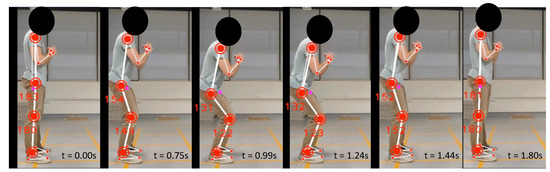
Figure 11.
Normal squat wrong posture variation.
The variations in the average correctness score and the corresponding emotions of the robot is given in Figure 9. The average correctness value at the end of the third cycle was 83.57. Since the average value is higher than the threshold value of 60, the robot started to express a happy emotion with a circular movement. The movement speed was 0.38 m s−1. The user performed the exercise correctly in the subsequent three cycles, and the average correctness score observed at the end of the sixth cycle was 90.31. As a result of the increased happiness level, the robot speed was raised to 0.49 m s−1 to express that the user is performing well.
At the end of the 9th cycle, the average correctness score was 70.4. This value was higher than the predefined upper threshold, and the robot’s emotion output was happy. However, the robot speed was lowered to 0.3 m s−1 since the average correctness score dropped. According to these parameter values, the robot’s configuration was an O-shape, and it was moving on a circular path with a speed of 0.3 m s−1. The same emotion with the same speed was observed for the subsequent three cycles.
At the end of the 12th cycle, the average correctness was 26.15, which is below the lower threshold of the average correctness score considered for sad emotion transition (i.e., 40). So, the robot reconfigured itself to an S-shape to express a sad emotion. After reconfiguration was performed, the robot moved on a jerky path with a speed of 0.23 m s−1. The robot remained in this shape configuration and motion expression until the end of the 24th cycle. At the end of the 24th cycle, the robot’s emotion changed to happy, and the robot was moving in a circular path in the O-shape. This behavior continued until the end of the first experiment. These observations related to emotion variation suggest that the proposed system is capable of varying the emotion as planned to give feedback to the user.
The second experiment was carried out considering a sumo squat exercise. Similar to the previous experiments, the user performed both correct and wrong exercise cycles to analyze the behavior of the system. Only the knee angle was considered for evaluating the correctness of this exercise since it was the factor defined in the database. Figure 12 shows a cycle of a user accurately performing sumo squats. The third cycle is considered here. The maximum knee flexion has been recorded as 180°, where the leg is fully stretched. As for the minimum angle, 95° was observed. The reference minimum for the knee flexion angle was defined as 100° for this exercise.
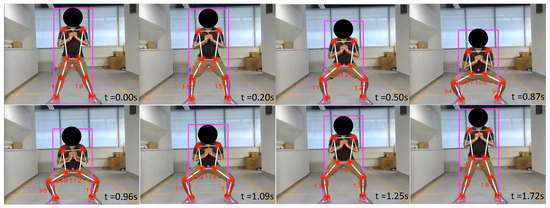
Figure 12.
Sumo squat correct posture variation.
Hence, the posture deviation was observed as 7.87°, which has a higher degree of membership for the low category in the fuzzy membership function. The movement speed was observed as 0.73 m s−1, which is closer to the expected speed level for this exercise. Thus, the exercise correctness score received a value of 100. The system has correctly identified the perfectness of the exercise being performed by the user. Figure 13 shows the variation in the exercise correctness score during the second exercise. The cycle number 20 represents a situation where the user incorrectly performed the exercises. The posture deviation was 29.53°, and the movement speed was observed as 0.37 m s−1. These parameters were way off from the expectation. Thus, a correctness score of 13.78 was received, indicating that the user was performing the exercise incorrectly.
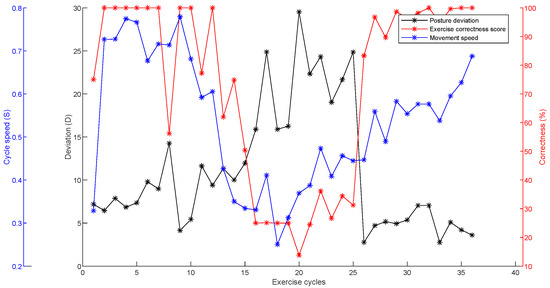
Figure 13.
Sumo squat experiment correctness evaluation results.
Figure 14 shows the variations in robot emotion and average correctness score. Referring to the figure, an emotion transition happened at the 27th cycle. The previous average, calculated at the 24th cycle, was beneath the lower threshold; hence the robot expressed sad emotion with an S-shape configuration while moving in a jerky path with a speed of 0.1 . In the 27th cycle, the average correctness score climbed above the upper threshold, and the emotion output transformed from sad to happy as in Figure 14. The robot reconfigured from S-shape to O-shape in this regard. The robot’s speed also varied accordingly.
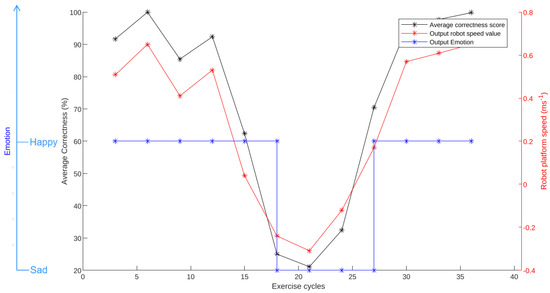
Figure 14.
Sumo squat experiment emotion expression results.
The observation from the two experiments confirms that the system is effective in evaluating the correctness of an exercise being performed by a user. The results also validated that the robot is capable of expressing emotions based on the variation in the exercise correctness. Furthermore, the robot configuration, movement path, and speed are effectively varied for expressing the required emotion.
5. Conclusions
A reconfigurable robotic system that can evaluate the correctness of an exercise being performed by a user and gives emotion-based feedback to the user has been proposed. The system consists of two segments, one for exercise correctness evaluation and another for robot emotion generation.
The exercise correctness evaluation module implemented using fuzzy logic determines the correctness of an exercise based on a set of parameters derived from the skeletal information. A monocular vision-based system is used to acquire skeletal information about a user during an exercise scenario. The posture deviation and the movement speed are considered for evaluating the correctness. The system has been developed in such a way that it can be adapted to various exercises by defining the reference values corresponding to exercises of interest.
The robot’s reconfiguration, movement pattern, and speed varied per the correctness of the exercise to generate robot emotions. The major leap of the proposed system over the existing approaches in emotion expression is its unique emotion generation with the aid of reconfiguration. The system also provides predefined voice feedback to the user, revealing an idea about the correctness of the exercise.
In order to evaluate the performance of the proposed system, experiments have been carried out considering a mixture of correct and wrong exercise scenarios. The experimental results validated the effectiveness of the proposed system in determining the exercise correctness and the transition of emotions per the variation in the exercise correctness. Therefore, the proposed system would be useful as an exercise companion that could interact and provide feedback to a user to improve exercise performance, as it provides interactive emotional feedback that encourages the users to correct their postures.
Currently, the proposed system is only capable of evaluating one target at a time, and the robot may fail to adapt to an environment with more than one human. The positioning of the user is highly important as the vision system should be able to capture the whole body of the user to generate skeletal information. As future work, it is expected that the system will be improved to solve these limitations. Furthermore, the current system has been implemented to express only two emotions, happy and sad, which can be further improved to have more emotional feedback.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app14167249/s1, Video S1: Experiment results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M.B.P.S. and M.A.V.J.M.; Methodology, W.K.R.S., I.D.W. and M.A.V.J.M.; Software, W.K.R.S. and I.D.W.; Validation, W.K.R.S. and I.D.W.; Formal analysis: S.M.B.P.S. and M.R.E.; Writing—original draft preparation, W.K.R.S. and I.D.W.; Writing—review and editing, S.M.B.P.S. and M.A.V.J.M.; Supervision, M.R.E.; Project administration, M.R.E.; Funding acquisition, M.R.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Robotics Programme under its National Robotics Programme (NRP) BAU, Ermine III: Deployable Reconfigurable Robots, Award No. M22NBK0054 and also supported by A*STAR under its “RIE2025 IAF-PP Advanced ROS2-native Platform Technologies for Cross-sectorial Robotics Adoption (M21K1a0104)” programme.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Mikkelsen, K.; Stojanovska, L.; Polenakovic, M.; Bosevski, M.; Apostolopoulos, V. Exercise and mental health. Maturitas 2017, 106, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatriain-Fernández, S.; Murillo-Rodríguez, E.S.; Gronwald, T.; Machado, S.; Budde, H. Benefits of physical activity and physical exercise in the time of pandemic. Psychol. Trauma Theory Res. Pract. Policy 2020, 12, S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, A.; Langensiepen, C.; Yahaya, S.W. Socially assistive robotics: Robot exercise trainer for older adults. Technologies 2018, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.; Rocha, R.P. Promotion of active ageing through interactive artificial agents in a smart environment. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, W.F. GEC-HR: Gamification exercise companion for home robot with IoT. In Proceedings of the HCI International 2019-Posters: 21st International Conference, HCII 2019, Orlando, FL, USA, 26–31 July 2019; Proceedings, Part II 21. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, M.; Alves, S.F.D.R.; Ismail, O.; Zhang, X.; Nejat, G.; Benhabib, B. You are doing great! only one rep left: An affect-aware social robot for exercising. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 3811–3817. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.; Kümmert, F. Exercising with a humanoid companion is more effective than exercising alone. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE-RAS 16th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Cancun, Mexico, 15–17 November 2016; pp. 495–501. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.; Kummert, F. Comparing robot and human guided personalization: Adaptive exercise robots are perceived as more competent and trustworthy. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2021, 13, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Kummert, F. Motivational effects of acknowledging feedback from a socially assistive robot. In Proceedings of the Social Robotics: 8th International Conference, ICSR 2016, Kansas City, MO, USA, 1–3 November 2016; Proceedings 8. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 870–879. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Martin, E.; Cazorla, M. A socially assistive robot for elderly exercise promotion. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 75515–75529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Kanda, T.; Yamada, S.; Suzuki, T. The effects of assistive walking robots for health care support on older persons: A preliminary field experiment in an elder care facility. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2021, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitter, N.T.; Mohan, M.; Kuchenbecker, K.J.; Johnson, M.J. Exercising with Baxter: Preliminary support for assistive social-physical human-robot interaction. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, A. Human-robot interaction in rehabilitation and assistance: A review. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2020, 1, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Raju, R.; Amitha, M.; Hashim, M.; Jose, J.; George, R. TOYBOT: An Interactive exercise companion for rehabilitation of sedentary geriatric and obese children. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 6th Conference on Information and Communication Technology (CICT), Gwalior, India, 18–20 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Casas, J.; Cespedes, N.; Múnera, M.; Cifuentes, C.A. Human-robot interaction for rehabilitation scenarios. In Control Systems Design of Bio-Robotics and Bio-Mechatronics with Advanced Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Maroto-Gómez, M.; Carrasco-Martínez, S.; Marqués-Villarroya, S.; Malfaz, M.; Castro-González, A.; Salichs, M.A. Bio-inspired Cognitive Decision-making to Personalize the Interaction and the Selection of Exercises of Social Assistive Robots in Elderly Care. In Proceedings of the 2023 32nd IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Busan, Republic of Korea, 28–31 August 2023; pp. 2380–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Kim, J.; Kang, J.H. Robot social skills for enhancing social interaction in physical training. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), Christchurch, New Zealand, 7–10 March 2016; pp. 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, S.B.P.; Muthugala, M.V.J.; Elara, M.R. Toward obstacle-specific morphology for a reconfigurable tiling robot. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattas, R.J.; Patel, S.; Sobh, T.M. Evolutionary modular robotics: Survey and analysis. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2019, 95, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, M.; Shen, W.M.; Salemi, B.; Rus, D.; Moll, M.; Lipson, H.; Klavins, E.; Chirikjian, G.S. Modular self-reconfigurable robot systems [grand challenges of robotics]. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2007, 14, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijegunawardana, I.D.; Muthugala, M.A.V.J.; Samarakoon, S.M.B.P.; Hua, O.J.; Padmanabha, S.G.A.; Elara, M.R. Insights from autonomy trials of a self-reconfigurable floor-cleaning robot in a public food court. J. Field Robot. 2024, 41, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daudelin, J.; Jing, G.; Tosun, T.; Yim, M.; Kress-Gazit, H.; Campbell, M. An integrated system for perception-driven autonomy with modular robots. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Park, S.; Yim, M.; Seo, T. Polygon-based random tree search algorithm for a size-changing robot. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 7, 8100–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsali, M.; Sheikhhoseini, R.; Sayyadi, P.; Hides, J.A.; Dadfar, M.; Piri, H. Association between physical activity and body posture: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, M.; Zajac, A.; Tufano, J.J. The influence of movement tempo during resistance training on muscular strength and hypertrophy responses: A review. Sport. Med. 2021, 51, 1629–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, S.M.B.P.; Muthugala, M.A.V.J.; Jayasekara, A.G.B.P.; Elara, M.R. Adapting approaching proxemics of a service robot based on physical user behavior and user feedback. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. 2022, 33, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Walker, C.L.; Walker, E.A. A First Course in Fuzzy Logic; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra, L.; Webb, C. Advantages of fuzzy control while dealing with complex/unknown model dynamics: A quadcopter example. New Appl. Artif. Intell 2016, 31, 93–121. [Google Scholar]
- Pourabdollah, A.; Wagner, C.; Aladi, J.H.; Garibaldi, J.M. Improved uncertainty capture for nonsingleton fuzzy systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 24, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthugala, M.A.V.J.; Vengadesh, A.; Wu, X.; Elara, M.R.; Iwase, M.; Sun, L.; Hao, J. Expressing attention requirement of a floor cleaning robot through interactive lights. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 103015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Iliyasu, A.M.; Hirota, K. Emotion space modelling for social robots. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 100, 104178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollinger, G.A.; Georgiev, Y.; Manfredi, A.; Maxwell, B.A.; Pezzementi, Z.A.; Mitchell, B. Design of a Social Mobile Robot Using Emotion-Based Decision Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Beijing, China, 9–15 October 2006; pp. 3093–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoggenmüller, M.; Chen, J.; Hespanhol, L. Emotional Expressions of Non-Humanoid Urban Robots: The Role of Contextual Aspects on Interpretations. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM International Symposium on Pervasive Displays, Manchester, UK, 4–5 June 2020; pp. 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.H.H.; Hutzler, G.; Hoppenot, P. Mobile robot emotion expression with motion based on MACE-GRACE model. In Proceedings of the 2011 15th International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR), Tallinn, Estonia, 20–23 June 2011; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).