Shipbuilding 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Industry 4.0 and Shipbuilding
1.2. Related Work and Literature
1.3. Research Questions
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Quality Assessment Criteria
2.2. Content and Research Type Classification
2.3. Research Protocol
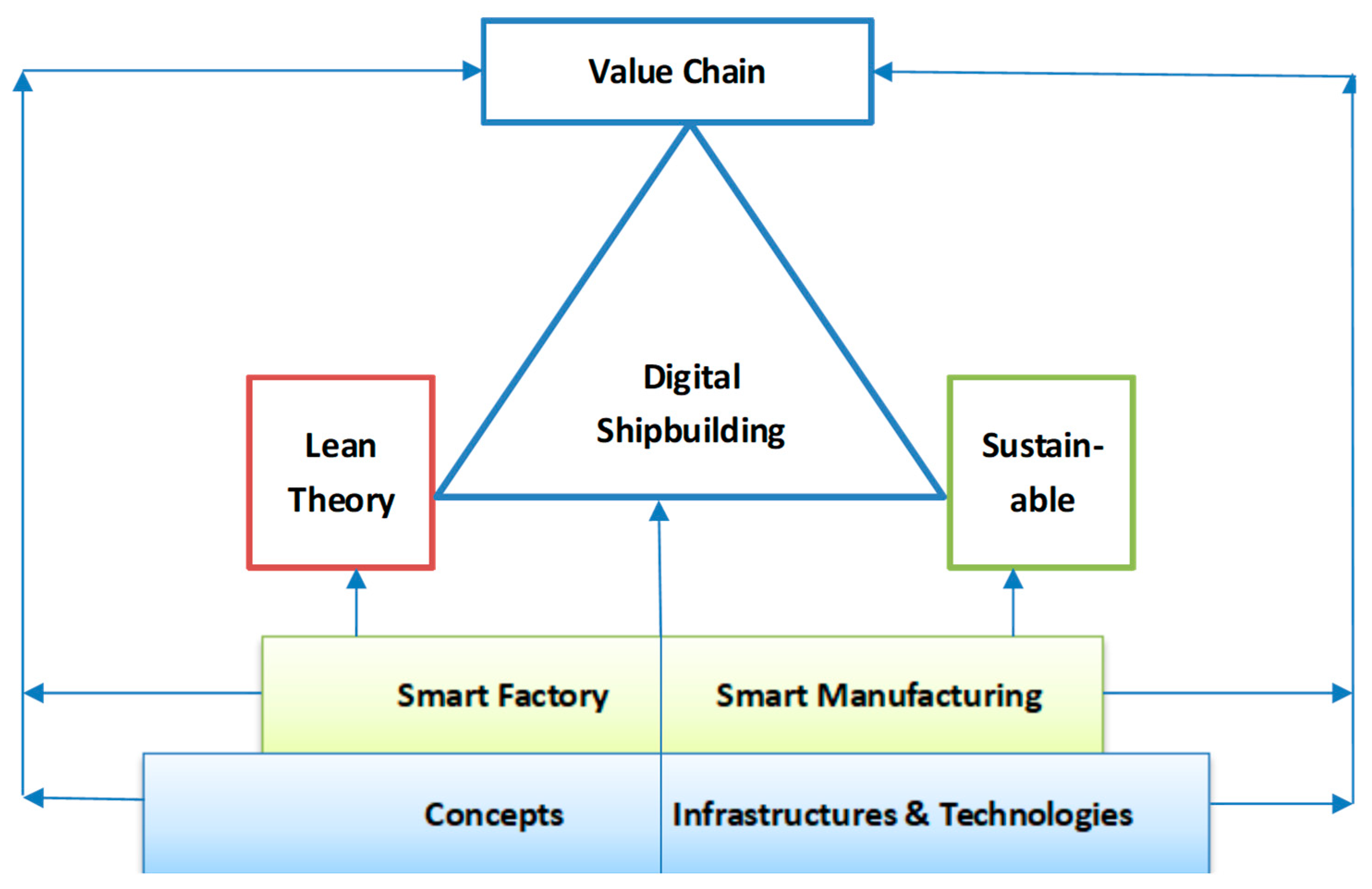
3. Current State of the Art
3.1. Concepts
3.2. Value Chain
3.3. Smart Factory
3.4. Smart Manufacturing
3.5. Infrastructure and Technologies
4. Results
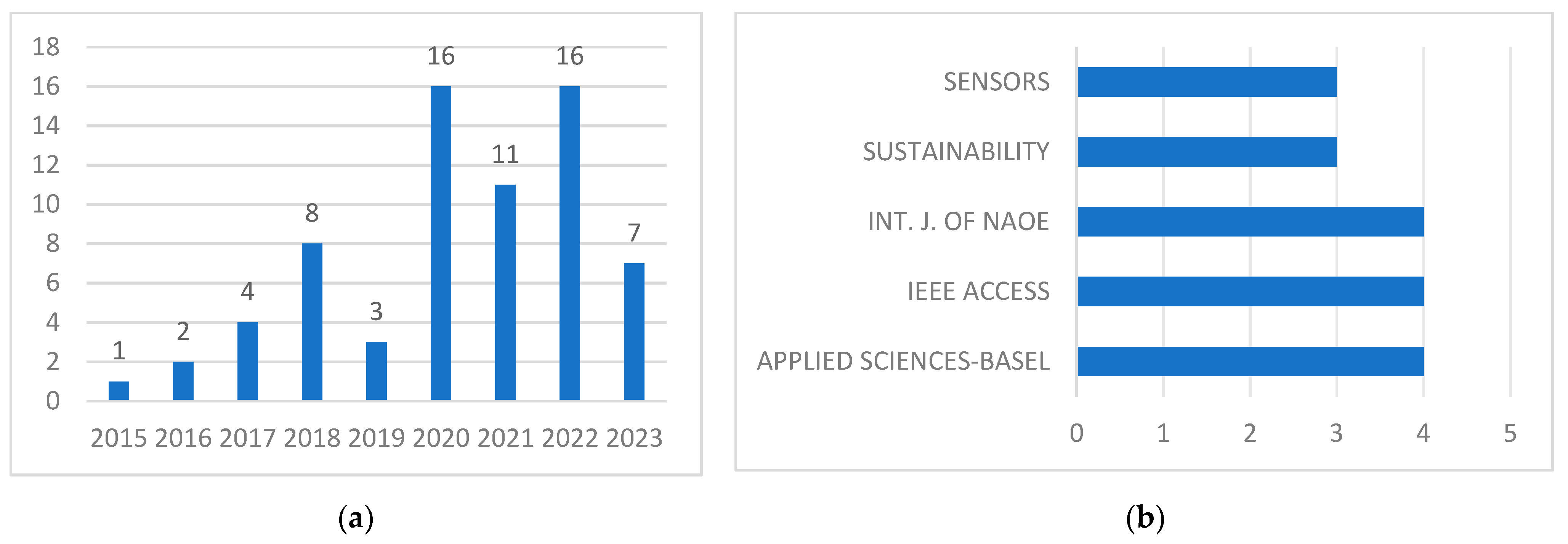
4.1. Year of Publication
4.2. Journals
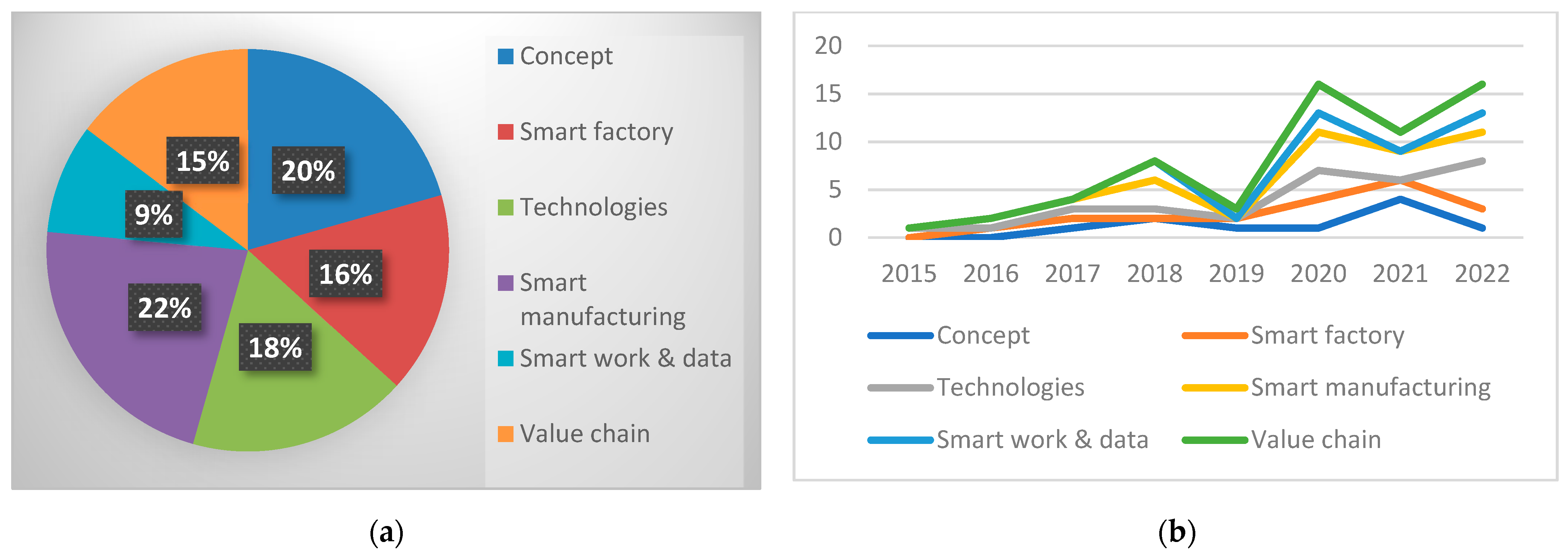
4.3. Content Categories of Publications
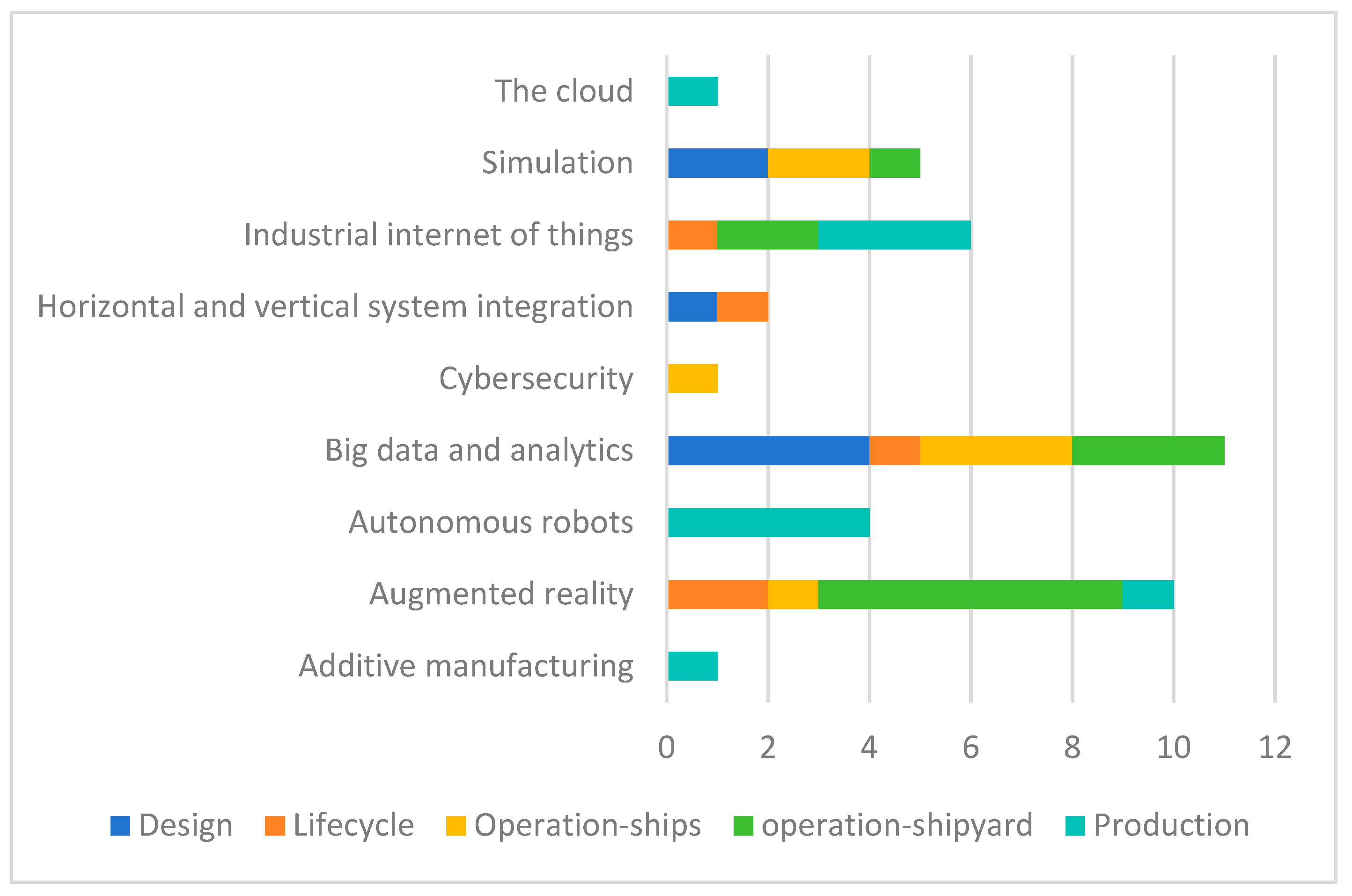
4.4. Life Cycle and Technology Categorization of Publications
4.5. Research Approach Categories of Publications
4.6. Keyword Statistics
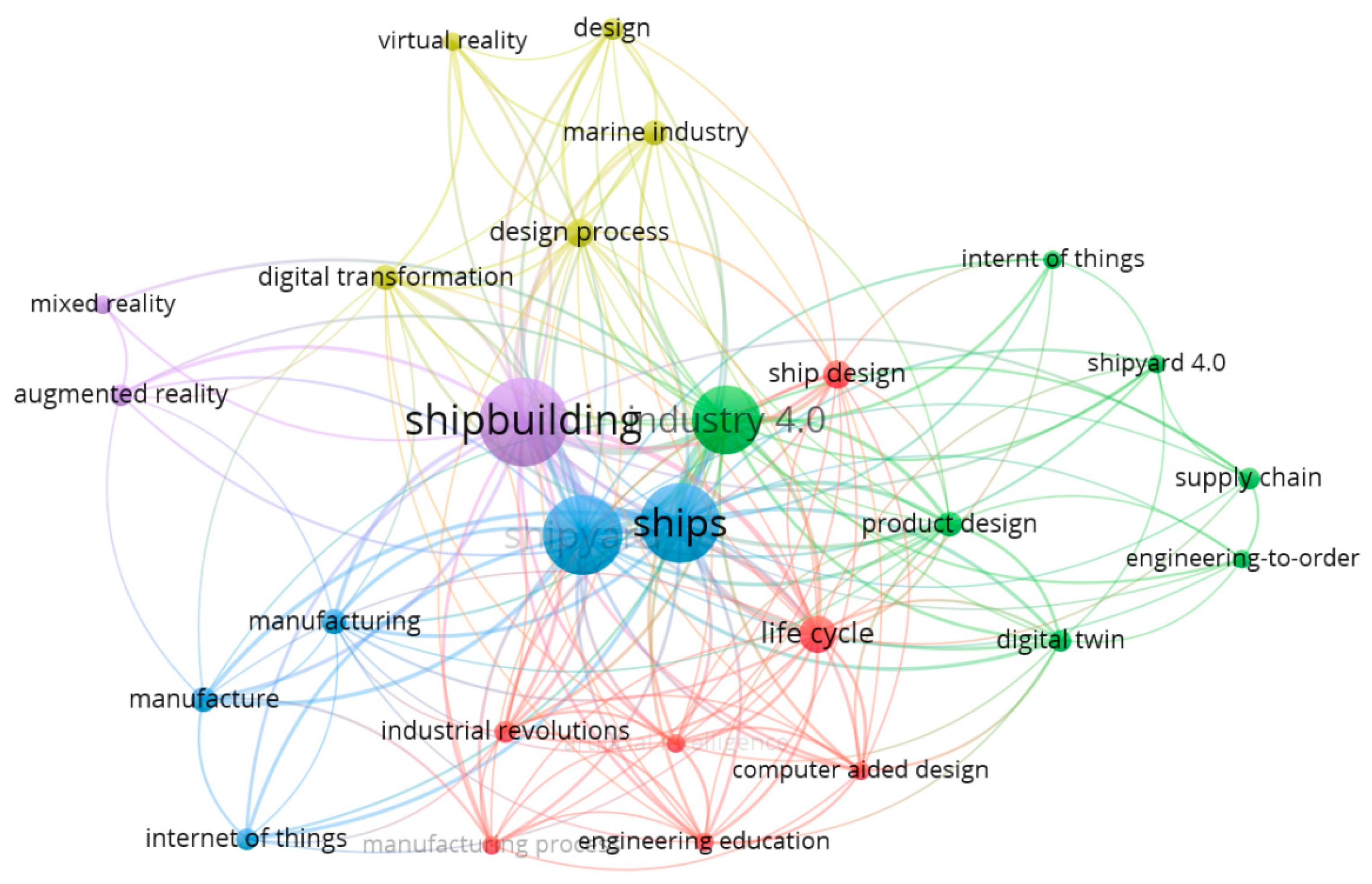
4.7. Keyword Co-Occurrence
4.8. Clusters Found from Keywords Co-Occurrence Networks
5. Proposed Framework and Research Agenda
5.1. Concept
5.1.1. Shipbuilding 4.0
5.1.2. Digital Twin and Digital Thread
5.1.3. Digital Shipyard
5.1.4. Digital Shipbuilding and Lean Application
5.1.5. Competence and Others
5.2. Value Chain
5.2.1. Supply Chain
5.2.2. Sustainability of Shipbuilding
5.2.3. Digital Supply Chain
5.2.4. Horizontal Integration
5.3. Smart Factory
5.3.1. Product Structure and Data Fusion
5.3.2. Smart Design and Engineering
5.3.3. Planning System
5.3.4. Smart Product and Autonomous Ship
5.3.5. End-to-End Integration
5.4. Smart Manufacturing
5.4.1. Robotic Welding System and Pipe Workshop
5.4.2. Pre-Outfitting Workshop
5.4.3. Manufacturing Support
5.4.4. Vertical Integration
5.5. Smart Infrastructure and Technologies
5.5.1. Augmented Reality
5.5.2. Big Data
5.5.3. Simulation and Optimization
5.5.4. Other Core Technologies
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoretical and Managerial Contribution
6.2. Limitations and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Four Studies as Notable Exemplars
| Authors | Year | Title | Abstract |
| Ramirez-Pena, Magdalena; Abad Fraga, Francisco J.; Salguero, Jorge; Batista, Moises | 2020 | Assessing sustainability in the shipbuilding supply chain 4.0: A systematic review | This article aims to gain a comprehensive understanding of the current state of the art in shipbuilding that is compatible with the key enabling technologies of I4.0. This is achieved through a detailed examination of each technology, utilizing a systematic review of the scientific literature to categorize these technologies [11]. |
| Vargas, D.G.M.; Vijayan, K. K.; Mork, O. J. | 2020 | Augmented reality for future research opportunities and challenges in the shipbuilding industry: A literature review | This paper seeks to analyze the most recent research and the most advanced industrial AR applications within the shipbuilding and maritime sectors. The objective is to ascertain how these advancements can foster new research opportunities and contribute to the concurrent development of the learning factory concept at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) in Ålesund [12]. |
| Ziółkowski, M.; Dyl, T. | 2020 | Possible applications of additive manufacturing technologies in shipbuilding: A review | This paper offers insights into ongoing R&D efforts related to the integration of AM in the shipbuilding industry. It explores the potential benefits, opportunities, and associated threats associated with the implementation of AM technology [13]. |
| Stanic, Venesa; Hadjina, Marko; Fafandjel, Niksa; Matulja, Tin | 2018 | Toward Shipbuilding 4.0—An Industry 4.0 changing the face of the shipbuilding industry | The objective of this article is to conduct a comprehensive review of the current academic and industrial advancements in what is known as the Shipbuilding 4.0 (or Shipping 4.0, Maritime 4.0, Shipyard 4.0) wave within the shipbuilding sector. The analyzed publications were assessed across various topics and their impact on the industrial aspects of society [10]. |
Appendix B. Research Protocol
| 1. Databases | Scopus and WoS | ||
| 2. Search Criteria and Screening | WoS | Scopus | |
| 2.1 Search Terms | (industry 4.0 OR Smart manufacturing or smart factory) and (Shipbuilding or shipyard) | 232 | 131 |
| 2.2 Year of Publication | 2010 to 2023 | 207 | 129 |
| 2.3 Language | English | 190 | 126 |
| 2.4 Subject Area(s) | Engineering, computer science, science technology other topics | ||
| 2.5 Document Type(s) | Articles, meeting, reviews, book chapters | ||
| 2.6 Date of Search | 17 November 2023 | 137 | 120 |
| 3. Exclusion Criteria | 3.1 Total after elimination of duplicate records | 178 | |
| 3.2 Article does not address I4.0 issues in shipbuilding (scope) after reading title and keywords | 152 | ||
| 4. Selection | 4.1 After first reading according to quality index | 68 | |
| 5. Analysis | 5.1 Descriptive analysis | ||
| 5.2 Content analysis (second reading) | |||
| 6.Classification | |||
| 6.1 Research content | Concept | ||
| Technology | |||
| Value chain | |||
| Smart factory | |||
| Smart manufacturing | |||
| Smart work and data, etc. | |||
| 6.2 Research approach | Review | ||
| Conceptual | |||
| Empirical: | |||
| Case study | |||
| Simulation | |||
| Prototypes | |||
| Experimentation | |||
| Survey | |||
| 6.3 Pillars of Technology of I4.0 | Big data and analytics | ||
| Autonomous robots | |||
| Simulation | |||
| Horizontal and vertical system integration | |||
| The industrial IoT | |||
| Cybersecurity | |||
| The cloud | |||
| AM | |||
| AR | |||
| 6.2 Life cycle phase | Design | ||
| Production/manufacturing | |||
| Operation—shipyard | |||
| Operation—ships | |||
| Retirement | |||
| Life cycle | |||
References
- Ramirez-Peña, M.; Sánchez Sotano, A.J.; Pérez-Fernandez, V.; Abad, F.J.; Batista, M. Achieving a sustainable shipbuilding supply chain under I4.0 perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Gawankar, S.A. Sustainable Industry 4.0 framework: A systematic literature review identifying the current trends and future perspectives. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 117, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zutin, G.C.; Barbosa, G.F.; de Barros, P.C.; Tiburtino, E.B.; Kawano, F.L.F.; Shiki, S.B. Readiness levels of Industry 4.0 technologies applied to aircraft manufacturing-a review, challenges and trends. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterreich, T.D.; Teuteberg, F. Understanding the implications of digitisation and automation in the context of Industry 4.0: A triangulation approach and elements of a research agenda for the construction industry. Comput. Ind. 2016, 83, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, L.R.; Mariscal, A.M.; Alvarez, E.P.; Mas, F. A Process-Oriented Approach for Shipbuilding Industrial Design Using Advanced PLM Tools. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Product Lifecycle Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, J.H.; Zhu, H.; Lee, D.K.; Chung, H.; Jeong, Y. Assessment Framework of Smart Shipyard Maturity Level via Data Envelopment Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Xu, J.; Zheng, M. Industry 4.0: Review and proposal for implementing a smart factory. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 133, 1331–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Vogel-Heuser, B.; Wang, L. Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0—Inception, conception and perception. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 61, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelhaus, S.; Grosse, E.H. Logistics 4.0: A systematic review towards a new logistics system. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanić, V.; Hadjina, M.; Fafandjel, N.; Matulja, T. Toward Shipbuilding 4.0—An Industry 4.0 Changing the Face of the Shipbuilding Industry. Brodogradnja 2018, 69, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Peña, M.; Abad Fraga, F.J.; Salguero, J.; Batista, M. Assessing Sustainability in the Shipbuilding Supply Chain 4.0: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina Vargas, D.G.; Vijayan, K.K.; Mork, O.J. Augmented Reality for Future Research Opportunities and Challenges in the Shipbuilding Industry: A Literature Review. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 45, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziółkowski, M.; Dyl, T. Possible Applications of Additive Manufacturing Technologies in Shipbuilding: A Review. Machines 2020, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Khan, M.A.; Romero, D.; Wuest, T. A critical review of smart manufacturing & Industry 4.0 maturity models: Implications for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). J. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 49, 194–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, F.; Kana, A.A. Digital twin for ship life-cycle: A critical systematic review. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 269, 113479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemstra, M.A.M.S.; de Mesquita, M.A. Industry 4.0: A tertiary literature review. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 186, 122204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosalska, K.; Piątek, Z.M.; Mazurek, G.; Rządca, R. Industry 4.0: Coherent definition framework with technological and organizational interdependencies. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2020, 31, 837–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepasepp, T.K.; Hurst, W. A Systematic Literature Review of Industry 4.0 Technologies within Medical Device Manufacturing. Future Internet 2021, 13, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüßmann, M.; Lorenz, M.; Gerbert, P.; Waldner, M.; Engel, P.; Harnisch, M.; Justus, J. Industry 4.0: The Future of Productivity and Growth in Manufacturing Industries. BCG Global [Online], April 9. 2015. Available online: https://www.bcg.com/publications/2015/engineered_products_project_business_industry_4_future_productivity_growth_manufacturing_industries (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- Dolz, M.; Martinez, X.; Sá, D.; Silva, J.; Jurado, A. Composite materials, technologies and manufacturing: Current scenario of European Union shipyards. Ships Offshore Struct. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, J.; Goh, C.; Saldivar, A.; Li, Y. Energy-Efficient Through-Life Smart Design, Manufacturing and Operation of Ships in an Industry 4.0 Environment. Energies 2017, 10, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwańkowicz, R.; Rutkowski, R. Digital Twin of Shipbuilding Process in Shipyard 4.0. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkera, Z.; Opetuk, T.; Hadžić, N.; Tošanović, N. Using Digital Twin in a Shipbuilding Project. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, L.C.; Magalhães, L.C.; Ramos, J.B.; Moura, L.R.; de Moraes, R.E.N.; Gonçalves, J.B.; Hisatugu, W.H.; Souza, M.T.; de Lacalle, L.N.L.; Ferreira, J.C.E. Conceiving a Digital Twin for a Flexible Manufacturing System. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagusch, K.; Sender, J.; Jericho, D.; Flügge, W. Digital thread in shipbuilding as a prerequisite for the digital twin. Procedia CIRP 2021, 104, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T.Y.; Pelaez Restrepo, J.D.; Cheng, C.-T.; Yasin, A.; Lim, H.; Miletic, M. Developing a Digital Twin and Digital Thread Framework for an ‘Industry 4.0’ Shipyard. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, F.; Dallasega, P. Lean and Industry 4.0 mitigating common losses in Engineer-to-Order theory and practice: An exploratory study. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2023, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Mi, S.; Tong, T.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J. Intelligent initial model and case design analysis of smart factory for shipyard in China. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centobelli, P.; Cerchione, R.; Maglietta, A.; Oropallo, E. Sailing through a digital and resilient shipbuilding supply chain: An empirical investigation. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 158, 113686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Peña, M.; Mayuet, P.F.; Vazquez-Martinez, J.M.; Batista, M. Sustainability in the Aerospace, Naval, and Automotive Supply Chain 4.0: Descriptive Review. Materials 2020, 13, 5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandhagen, J.W.; Buer, S.-V.; Semini, M.; Alfnes, E.; Strandhagen, J.O. Sustainability challenges and how Industry 4.0 technologies can address them: A case study of a shipbuilding supply chain. Prod. Plan. Control. 2022, 33, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.; Pérez, V.; Gómez, A.; Montaño, R.; Batista, M. Supply chain production planning of a manufacturing project system 4.0: Case study: Shipbuilding. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1193, 12051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.; Smith, K.; Acero, B.; Longo, F.; Padovano, A. Developing an Artificial Intelligence Framework to Assess Shipbuilding and Repair Sub-Tier Supply Chains Risk. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 180, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarinha-Matos, L.M.; Fornasiero, R.; Ramezani, J.; Ferrada, F. Collaborative Networks: A Pillar of Digital Transformation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Huh, J.-H. Study on PLM and Big Data Collection for the Digital Transformation of the Shipbuilding Industry. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, I.; Shin, D.; Jeong, J. Components for Smart Autonomous Ship Architecture Based on Intelligent Information Technology. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 134, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Im, N.-K.; Zhongyu, D.; Meijuan, Z. Review on the Research of Ship Automatic Berthing Control. In Offshore Robotics; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 87–109. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, M.; Park, J.; Woo, J. Development of HHI’s Advanced Navigation Assistance System for Safe Voyage. IFAC-Pap. 2019, 52, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Lee, J.M.; Woo, J.H. Development of production planning system for shipbuilding using component-based development framework. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 13, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.G.; Ju, S.; Woo, J.H. Simulation-based planning system for shipbuilding. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 33, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, W.; Yang, B.; Chen, L.; Dong, R.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H. Modeling of Digital Twin Workshop in Planning via a Graph Neural Network: The Case of an Ocean Engineering Manufacturing Intelligent Workshop. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, J.H.; Goh, C.; Jirafe, V.P.; Li, Y. Efficient Hull Form Design Optimisation Using Hybrid Evolutionary Algorithm and Morphing Approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Applications in Shipbuilding, Singapore, 26–28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, J.H.; Goh, C.; Choo, C.T.; Lee, Z.M.; Jirafe, V.P.; Li, Y. Evolutionary Computation Automated Design of Ship Hull Forms for the Industry 4.0 Era. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Wellington, New Zealand, 10–13 June 2019; pp. 2347–2354. [Google Scholar]
- Son, Y.-B.; Nam, J.-H. Creation of hierarchical structure for computerized ship block model based on interconnection relationship of structural members and shipyard environment. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 14, 100455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilen, U.; Helvacioglu, S. Data Driven Performance Evaluation in Shipbuilding. Brodogr. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. Res. Dev. 2020, 71, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Lee, J.M.; Woo, J.H. (Eds.) Ship Design with a Morphing Evolutionary Algorithm: 2020 conference proceedings. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gianni, M.; Bucci, V.; Marinò, A. System simulation as decision support tool in ship design. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 180, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, P.L.; Morgado-Estévez, A.; Aparicio, J.L.; Bárcena, G.; Soto-Núñez, J.A.; Chavera, P.; Abad Fraga, F.J. Development of a Customized Interface for a Robotic Welding Application at Navantia Shipbuilding Company. In Iberian Robotics Conference; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Morgado-Estevez, A.; Galindo, P.L.; Aparicio-Rodriguez, J.-L.; Diaz-Cano, I.; Rioja-del-Rio, C.; Soto-Nuñez, J.A.; Chavera, P.; Abad-Fraga, F.J. Towards Automated Welding in Big Shipbuilding Assisted by Programed Robotic Arm Using a Measuring Arm. In Robot 2017. Volume 2: Third Iberian Robotics Conference; Ollero, A., Sanfeliu, A., Montaño, L., Lau, N., Cardeira, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 53–63. ISBN 978-3-319-70835-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Noceda-Davila, D.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Díaz-Bouza, M.A.; Vilar-Montesinos, M. Smart Pipe System for a Shipyard 4.0. Sensors 2016, 16, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Fernandez-Carames, T.M.; Noceda-Davila, D.; Diaz-Bouza, M.A.; Castedo, L. Enabling automatic event detection for the pipe workshop of the shipyard 4.0. In Proceedings of the 2017 56th FITCE Congress, Madrid, Spain, 14–15 September 2017; pp. 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Munín-Doce, A.; Díaz-Casás, V.; Trueba, P.; Ferreno-González, S.; Vilar-Montesinos, M. Industrial Internet of Things in the production environment of a Shipyard 4.0. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, K.; Yotsuzuka, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Tanabe, Y. “Monitoring Platform” of Monitoring and Visualizing System for Shipyard: Application to Cutting and Subassembly Processes. In Practical Design of Ships and Other Floating Structures; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 321–337. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Lee, S. Smart System to Detect Painting Defects in Shipyards: Vision AI and a Deep-Learning Approach. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.-H.; Park, H.-S.; Nguyen, Q.-V.; Hoang, T.-D. Development of a Smart Cyber-Physical Manufacturing System in the Industry 4.0 Context. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, K.; Sipsas, K.; Xanthakis, E.; Makris, S.; Mourtzis, D. An industrial Internet of things based platform for context-aware information services in manufacturing. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2018, 31, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharaki, N.; Dimitropoulos, N.; Makris, S. Challenges in human-robot collaborative assembly in shipbuilding and ship maintenance, repair and conversion (SMRC) industry. Procedia CIRP 2022, 106, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Varela-Barbeito, J.; Fernandez-Carames, T.M. Next Generation Auto-Identification and Traceability Technologies for Industry 5.0: A Methodology and Practical Use Case for the Shipbuilding Industry. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 140700–140730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Seo, Y. A Real-Time Physical Progress Measurement Method for Schedule Performance Control Using Vision, an AR Marker and Machine Learning in a Ship Block Assembly Process. Sensors 2020, 20, 5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, Z.; Byun, Y.-C. Smart Manufacturing Real-Time Analysis Based on Blockchain and Machine Learning Approaches. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.; Budjac, R.; Tanuska, P.; Gaspar, G.; Schreiber, P. Identification Overview of Industry 4.0 Essential Attributes and Resource-Limited Embedded Artificial-Intelligence-of-Things Devices for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Novoa, O.; Fernandez-Carames, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P.; Vilar-Montesinos, M.A. A Practical Evaluation of Commercial Industrial Augmented Reality Systems in an Industry 4.0 Shipyard. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 8201–8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P.; Suárez-Albela, M.; Vilar-Montesinos, M. A Fog Computing and Cloudlet Based Augmented Reality System for the Industry 4.0 Shipyard. Sensors 2018, 18, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Fernandez-Carames, T.M.; Blanco-Novoa, O.; Vilar-Montesinos, M.A. A Review on Industrial Augmented Reality Systems for the Industry 4.0 Shipyard. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 13358–13375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Balea, A.; Blanco-Novoa, O.; Fraga-Lamas, P.; Vilar-Montesinos, M.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. Creating Collaborative Augmented Reality Experiences for Industry 4.0 Training and Assistance Applications: Performance Evaluation in the Shipyard of the Future. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Balea, A.; Blanco-Novoa, O.; Fraga-Lamas, P.; Vilar-Montesinos, M.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. A Collaborative Industrial Augmented Reality Digital Twin: Developing the Future of Shipyard 4.0. In International Summit Smart City 360°; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 104–120. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Mehtab, R.; Mohan, S.; Mohd Shah, M.K. Augmented reality—An important aspect of Industry 4.0. Ind. Robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. Appl. 2022, 49, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P. Augmented and Mixed Reality for Shipbuilding. In Springer Handbook of Augmented Reality; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 643–667. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.-P.; Ham, S.-H.; Ku, N.; Jo, A.; Suh, H.-W. Development of offshore drilling platform simulation for virtual onboard experience. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 14, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.H.; Cho, Y.I.; Choe, S.W.; Kwon, H.J.; Woo, J.H. Optimization of long-term planning with a constraint satisfaction problem algorithm with a machine learning. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 14, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J. A hypernetwork-based context-aware approach for design lesson-learned knowledge proactive feedback in design for manufacturing. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 54, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, I.; Pazouki, K.; Norman, R.; Younessi, S.; Coleman, S. Challenges and Opportunities of Big Data Analytics for Upcoming Regulations and Future Transformation of the Shipping Industry. Procedia Eng. 2017, 194, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavallieratos, G.; Katsikas, S. Managing Cyber Security Risks of the Cyber-Enabled Ship. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladysz, B.; Tran, T.; Romero, D.; van Erp, T.; Abonyi, J.; Ruppert, T. Current development on the Operator 4.0 and transition towards the Operator 5.0: A systematic literature review in light of Industry 5.0. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 70, 160–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.G.; Dalenogare, L.S.; Ayala, N.F. Industry 4.0 technologies: Implementation patterns in manufacturing companies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 210, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apilioğulları, L. Digital transformation in project-based manufacturing: Developing the ISA-95 model for vertical integration. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2022, 245, 108413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cil, I.; Arisoy, F.; Kilinc, H.; Ozgurbuz, E.; Cil, A.Y.; Uysal, E. Challenges and Trends in Shipbuilding Industry: Digitization of SEDEF Shipyard in Turkey. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2021 5th International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 21–23 October 2021; pp. 799–804. [Google Scholar]
- Beifert, A.; Gerlitz, L.; Prause, G. Industry 4.0—For Sustainable Development of Lean Manufacturing Companies in the Shipbuilding Sector. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication, Riga, Latvia, 18–21 October 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 563–573. [Google Scholar]
- Kunkera, Z.; Tošanović, N.; Štefanić, N. Improving the Shipbuilding Sales Process by Selected Lean Management Tool. Machines 2022, 10, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosteczko, J.P.; Smith, K.; Johnson, J.; Diaz, R. Virginia Digital Shipbuilding Program (VDSP): Building an Agile Modern Workforce to Improve Performance in the Shipbuilding and Ship Repair Industry. In Proceedings of the 2020 ASEE Virtual Annual Conference Content Access, Virtual, 22–26 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, R.P. How the industry 4.0 could affect the shipbuilding world. J. Marit. Res. 2020, 17, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ellingsen, O.; Aasland, K.E. Digitalizing the maritime industry: A case study of technology acquisition and enabling advanced manufacturing technology. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2019, 54, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Peña, M.; Abad Fraga, F.J.; Sánchez Sotano, A.J.; Batista, M. Shipbuilding 4.0 Index Approaching Supply Chain. Materials 2019, 12, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordin, N.; Salleh, Z. Green Shipbuilding Technology for Boustead Naval Shipyard Sdn Bhd Towards Sustainable Shipbuilding Development. In Advanced Maritime Technologies and Applications; Ismail, A., Dahalan, W.M., Öchsner, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 99–110. ISBN 978-3-030-89991-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, J.H.; Goh, C.; Li, Y. Smart design for ships in a smart product through-life and industry 4.0 environment. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 5301–5308. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Jun, S.; Chang, T.-W.; Park, J. A Smartness Assessment Framework for Smart Factories Using Analytic Network Process. Sustainability 2017, 9, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Celaya-Echarri, M.; Blanco-Novoa, O.; Azpilicueta, L.; Varela-Barbeito, J.; Falcone, F.; Fernandez-Carames, T.M. Design and Empirical Validation of a Bluetooth 5 Fog Computing Based Industrial CPS Architecture for Intelligent Industry 4.0 Shipyard Workshops. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 45496–45511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallanza, A.; Aiello, G.; Marannano, G.; Nigrelli, V. Industry 4.0: Smart test bench for shipbuilding industry. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2020, 14, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cil, İ.; Arisoy, F.; Özgürbüz, E.; Cil, A.Y.; Kılınç, H. Indoor Positioning Technology Selection Using a Combined AHP and PROMETHEE Method at SEDEF Shipyard. J. ETA Marit. Sci. 2022, 10, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, Q.; Liu, J. Digital Twin-Driven Approach for Process Management and Traceability towards Ship Industry. Processes 2022, 10, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Reference Type | Title |
|---|---|
| Book | 2 |
| Collected work | 1 |
| Conference proceedings | 1 |
| Contribution in… | 18 |
| Journal article | 46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Chen, D. Shipbuilding 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6363. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146363
Zhang X, Chen D. Shipbuilding 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6363. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146363
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaowei, and Daoyi Chen. 2024. "Shipbuilding 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6363. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146363
APA StyleZhang, X., & Chen, D. (2024). Shipbuilding 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6363. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146363








