Adaptive Mask-Based Interpretable Convolutional Neural Network (AMI-CNN) for Modulation Format Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- This paper proposes an Adaptive Mask-Based Interpretable Convolutional Neural Network (AMI-CNN) for MFI. The model improves discriminative capability and interpretability by using adaptive masks to highlight relevant features and suppress irrelevant ones. Furthermore, adaptive masks automatically adjust during model training, and can directly interpret features after training without additional interpretative techniques.
- (2)
- We propose two metrics to evaluate the performance of the model interpretability. To our knowledge, in modulation format recognition, existing interpretability evaluations primarily rely on qualitative analysis alone. Our study employs quantitative metrics to provide a more accurate assessment of model interpretability.
2. Background and Literature Review
2.1. MFI
2.2. Explainable Artificial Intelligence
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Experimental System
3.2. Dataset Collection and Preprocessing
3.2.1. PSD Dataset
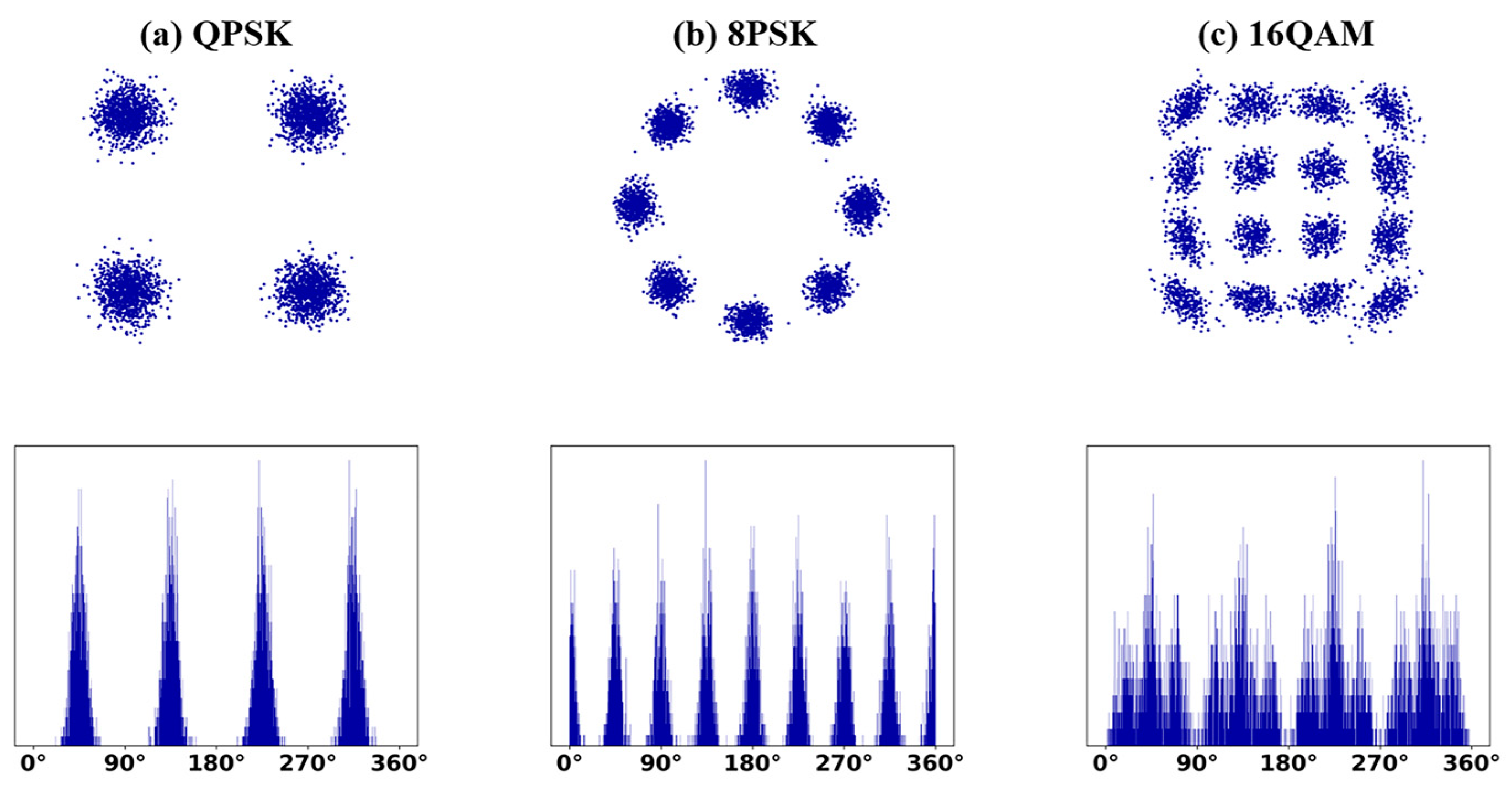
3.2.2. Constellation Phase Histogram Dataset
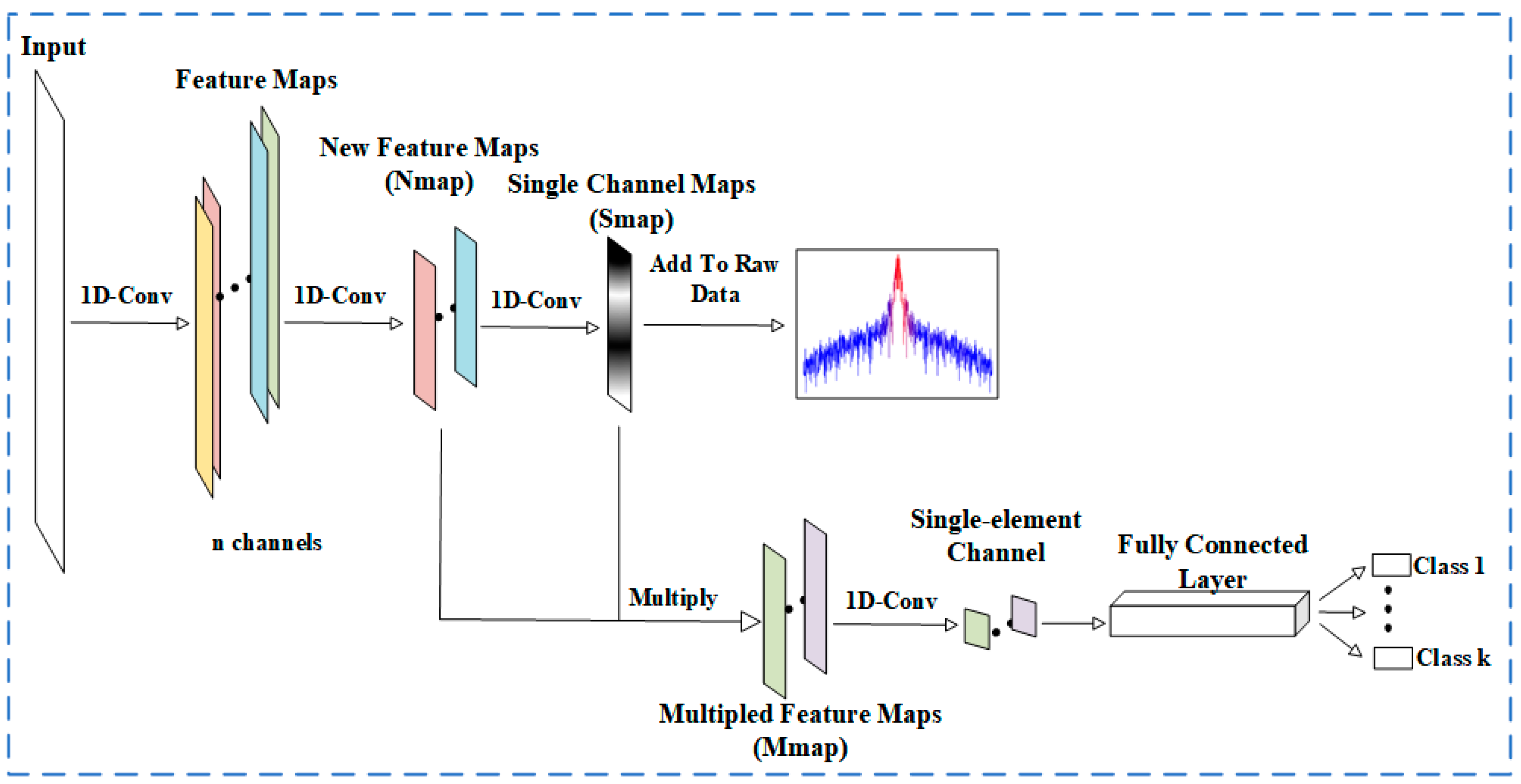
3.3. AMI-CNN Model Structure
3.3.1. Feature Extraction
3.3.2. Adaptive Mask
3.3.3. Classifier
3.3.4. Interpretability Reflected by Masking Techniques
4. Results
4.1. Baseline Model Selection
4.2. Qualitative Analysis of Model Interpretability
4.2.1. Interpretability of Models on the PSD Dataset
4.2.2. Interpretability of Models on the Constellation Phase Histogram Dataset
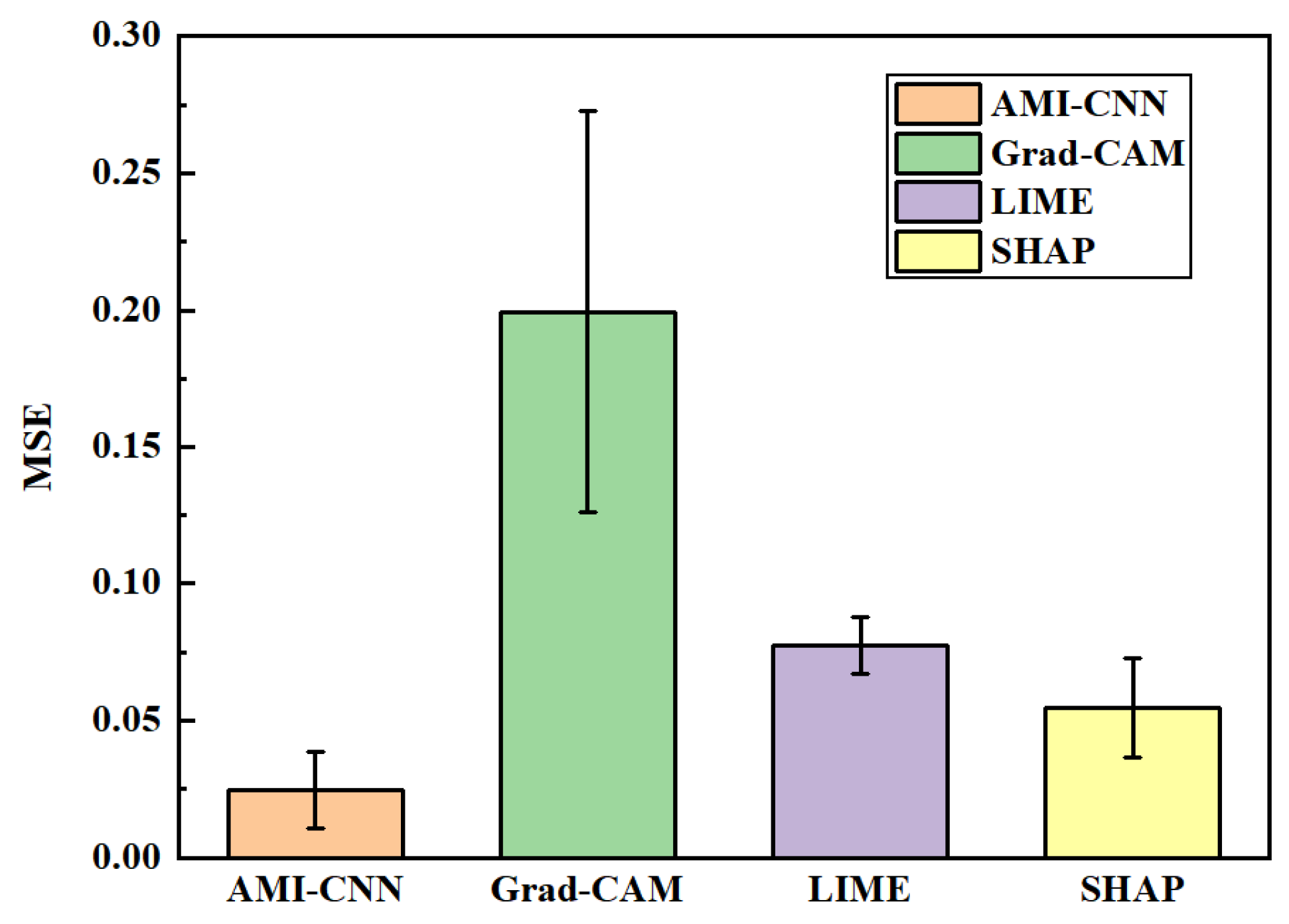
4.3. Quantitative Analysis of Model Interpretability
4.3.1. MSE
4.3.2. PG-Acc
5. Conclusions
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, Y.; Fu, S.; Tang, M.; Liu, D. Multi-Task Deep Neural Network (MT-DNN) Enabled Optical Performance Monitoring from Directly Detected PDM-QAM Signals. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 19062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, M.; He, W.; Jiang, X.; Liang, S.; Jin, W.; Chen, L.; Tang, J. Modulation Format Identification Based on Multi-Dimensional Amplitude Features for Elastic Optical Networks. Photonics 2024, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hao, M.; Yan, L.; Jiang, L.; Xiong, X. Blind and Low-Complexity Modulation Format Identification Based on Signal Envelope Flatness for Autonomous Digital Coherent Receivers. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Yu, Z.; Shu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K. Intelligent Optical Performance Monitor Using Multi-Task Learning Based Artificial Neural Network. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.E.-D.N.; Al-Makhlasawy, R.M.; Khalaf, A.A.M.; Dessouky, M.I.; Abd El-Samie, F.E. Modulation Format Recognition Based on Constellation Diagrams and the Hough Transform. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X. Modulation Format Recognition and OSNR Estimation Using CNN-Based Deep Learning. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2017, 29, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Xu, T. Optical Performance Monitoring in Transparent Fiber-Optic Networks Using Neural Networks and Asynchronous Amplitude Histograms. Opt. Commun. 2022, 517, 128305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhou, X.; Huo, J.; Yuan, J. Joint OSNR Monitoring and Modulation Format Identification on Signal Amplitude Histograms Using Convolutional Neural Network. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 61, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, H.; Luo, R. Enhancing the Generalization Ability of Deep Learning Model for Radio Signal Modulation Recognition. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 18758–18774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Lu, Y. Fast Adaptation of Multi-Task Meta-Learning for Optical Performance Monitoring. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 23183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, L.; Ren, F.; Xie, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhangsun, T.; Chen, W.; Wang, J. Feature Fusion-Based Multi-Task ConvNet for Simultaneous Optical Performance Monitoring and Bit-Rate/Modulation Format Identification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 126709–126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, J.; Zeng, X.; Luo, M. Modulation Format Identification and OSNR Monitoring Based on Multi-Feature Fusion Network. Photonics 2023, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Cimr, D.; Fujita, H.; Cimler, R. Interpretable Synthetic Signals for Explainable One-Class Time-Series Classification. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 131, 107716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adadi, A.; Berrada, M. Peeking Inside the Black-Box: A Survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access 2018, 6, 52138–52160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Xu, K.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Chen, H. Data-Driven Fiber Model Based on the Deep Neural Network with Multi-Head Attention Mechanism. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 46626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhen, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T. The Performance Analysis of Signal Recognition Using Attention Based CNN Method. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 214915–214922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, T.; Du, J. Low-Complexity and Nonlinearity-Tolerant Modulation Format Identification Using Random Forest. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2019, 31, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrane, J.; Wass, J.; Piels, M.; Diniz, J.C.M.; Jones, R.; Zibar, D. Machine Learning Techniques for Optical Performance Monitoring From Directly Detected PDM-QAM Signals. J. Light. Technol. 2017, 35, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tang, M.; Chen, X.; Feng, Z.; Wu, Q.; Fu, S.; Liu, D. Fractal Dimension Aided Modulation Formats Identification Based on Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the 43RD European Conference on Optical Communication (ECOC 2017), Gothenburg, Sweden, 17–21 September 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.N.; Zhou, Y.; Lau, A.P.T.; Lu, C. Modulation Format Identification in Heterogeneous Fiber-Optic Networks Using Artificial Neural Networks. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 12422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.N.; Shen, T.S.R.; Zhou, Y.; Lau, A.P.T.; Lu, C. Optical Performance Monitoring Using Artificial Neural Networks Trained With Empirical Moments of Asynchronously Sampled Signal Amplitudes. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2012, 24, 982–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z.; Sun, X. Modulation Format Identification Based on an Improved RBF Neural Network Trained With Asynchronous Amplitude Histogram. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 59524–59532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, M.A.; Ayad, J.; Abdulkareem, H.J. Modulation Scheme Identification Based on Artificial Neural Network Algorithms for Optical Communication System. J. ICT Res. Appl. 2020, 14, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.N.; Fan, Q.; Lu, C.; Lau, A.P.T. An Optical Communication’s Perspective on Machine Learning and Its Applications. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 493–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerappa, M.; Anneken, M.; Burkart, N.; Huber, M.F. Validation of XAI Explanations for Multivariate Time Series Classification in the Maritime Domain. J. Comput. Sci. 2022, 58, 101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Fan, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Jain, S.; Liu, Y.; Jain, A.; Tang, J. Trustworthy AI: A Computational Perspective. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2023, 14, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Velden, B.H.M.; Kuijf, H.J.; Gilhuijs, K.G.A.; Viergever, M.A. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in Deep Learning-Based Medical Image Analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdoch, W.J.; Singh, C.; Kumbier, K.; Abbasi-Asl, R.; Yu, B. Definitions, Methods, and Applications in Interpretable Machine Learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22071–22080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igor, I.; Berk, G.; Mucahit, C.; Gökçe, B.M. Explainable Boosted Linear Regression for Time Series Forecasting. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 120, 108144. [Google Scholar]
- Sagi, O.; Rokach, L. Explainable Decision Forest: Transforming a Decision Forest into an Interpretable Tree. Inf. Fusion 2020, 61, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civit-Masot, J.; Bañuls-Beaterio, A.; Domínguez-Morales, M.; Rivas-Pérez, M.; Muñoz-Saavedra, L.; Corral, J.M.R. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis Aid with Histopathological Images Using Explainable Deep Learning Techniques. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 226, 107108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?”: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS): La Jolla, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep Inside Convolutional Networks: Visualising Image Classification Models and Saliency Maps. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6034. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_53 (accessed on 15 September 2014).
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Xing, F.; McGough, M.; Yang, L. MDNet: A Semantically and Visually Interpretable Medical Image Diagnosis Network. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2017), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 3549–3557. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; IEEE: Venice, Italy, 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, Z.; Brandt, J.; Shen, X.; Sclaroff, S. Top-Down Neural Attention by Excitation Backprop. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, PT IV, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing Ag: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9908, pp. 543–559. [Google Scholar]








| Technique | Explanation Scope | Computational Complexity | Theoretical Basis | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIME | Local | Moderate | Linear approximation | Depends on the surrogate model |
| SHAP | Global and local | High | Shapley values (cooperative game theory) | Requires complex calculations |
| Grad-CAM | Local | Moderate | Gradient computation | Can be less precise for small object localization |
| Model Type | LeNet | ResNet18 | VGG19 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Total Parameters | 7.19 × 105 | 8.7 × 106 | 1.19 × 107 |
| Model Type | LeNet | ResNet18 | VGG19 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Total Parameters | 7.19 × 105 | 8.73 × 106 | 1.19 × 107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Cheng, Y.; He, J.; Guo, J. Adaptive Mask-Based Interpretable Convolutional Neural Network (AMI-CNN) for Modulation Format Identification. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6302. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146302
Zhu X, Cheng Y, He J, Guo J. Adaptive Mask-Based Interpretable Convolutional Neural Network (AMI-CNN) for Modulation Format Identification. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6302. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146302
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiyue, Yu Cheng, Jiafeng He, and Juan Guo. 2024. "Adaptive Mask-Based Interpretable Convolutional Neural Network (AMI-CNN) for Modulation Format Identification" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6302. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146302
APA StyleZhu, X., Cheng, Y., He, J., & Guo, J. (2024). Adaptive Mask-Based Interpretable Convolutional Neural Network (AMI-CNN) for Modulation Format Identification. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6302. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146302





