Condition Monitoring of a Three-Phase AC Asynchronous Motor Based on the Analysis of the Instantaneous Active Electrical Power in No-Load Tests
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
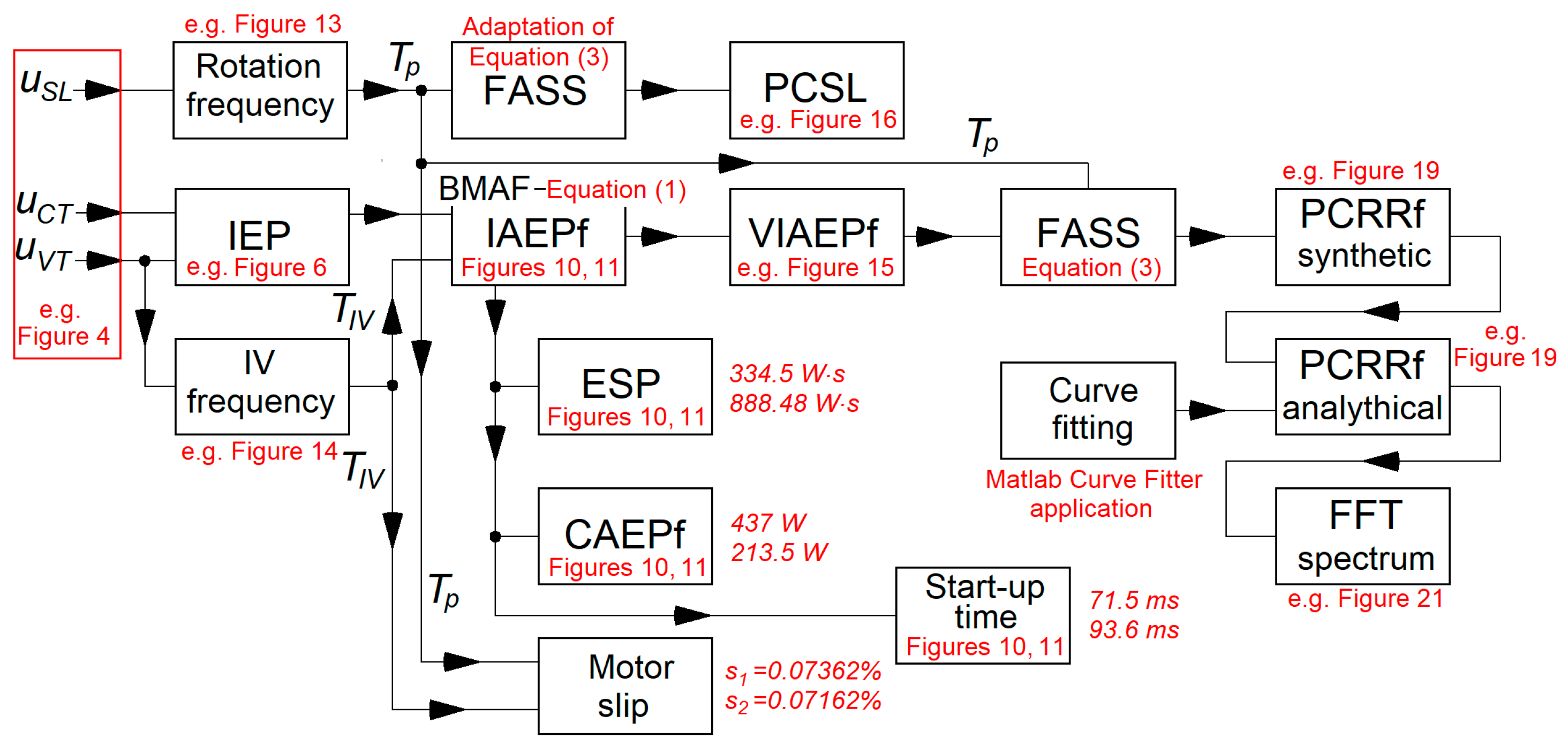
2. Materials and Methods
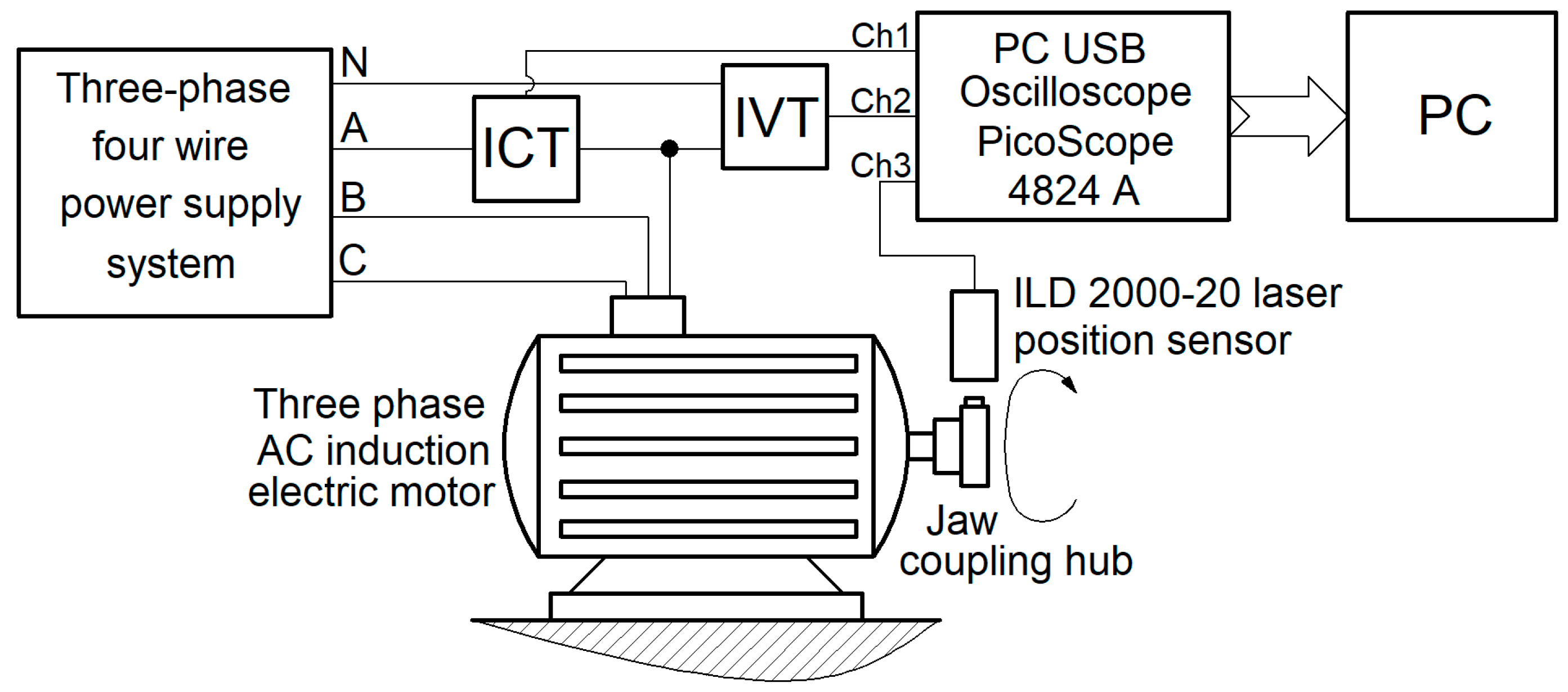
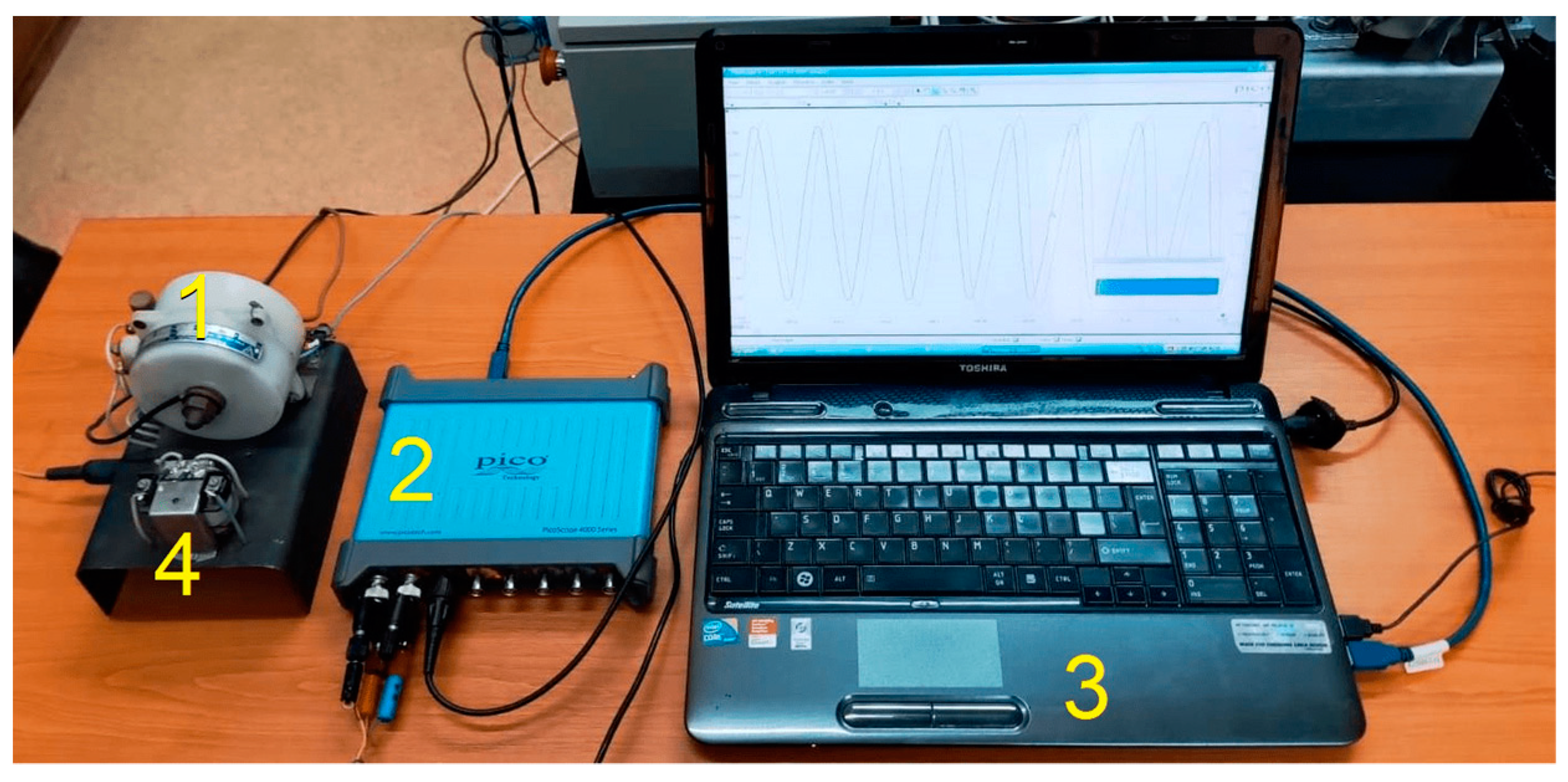
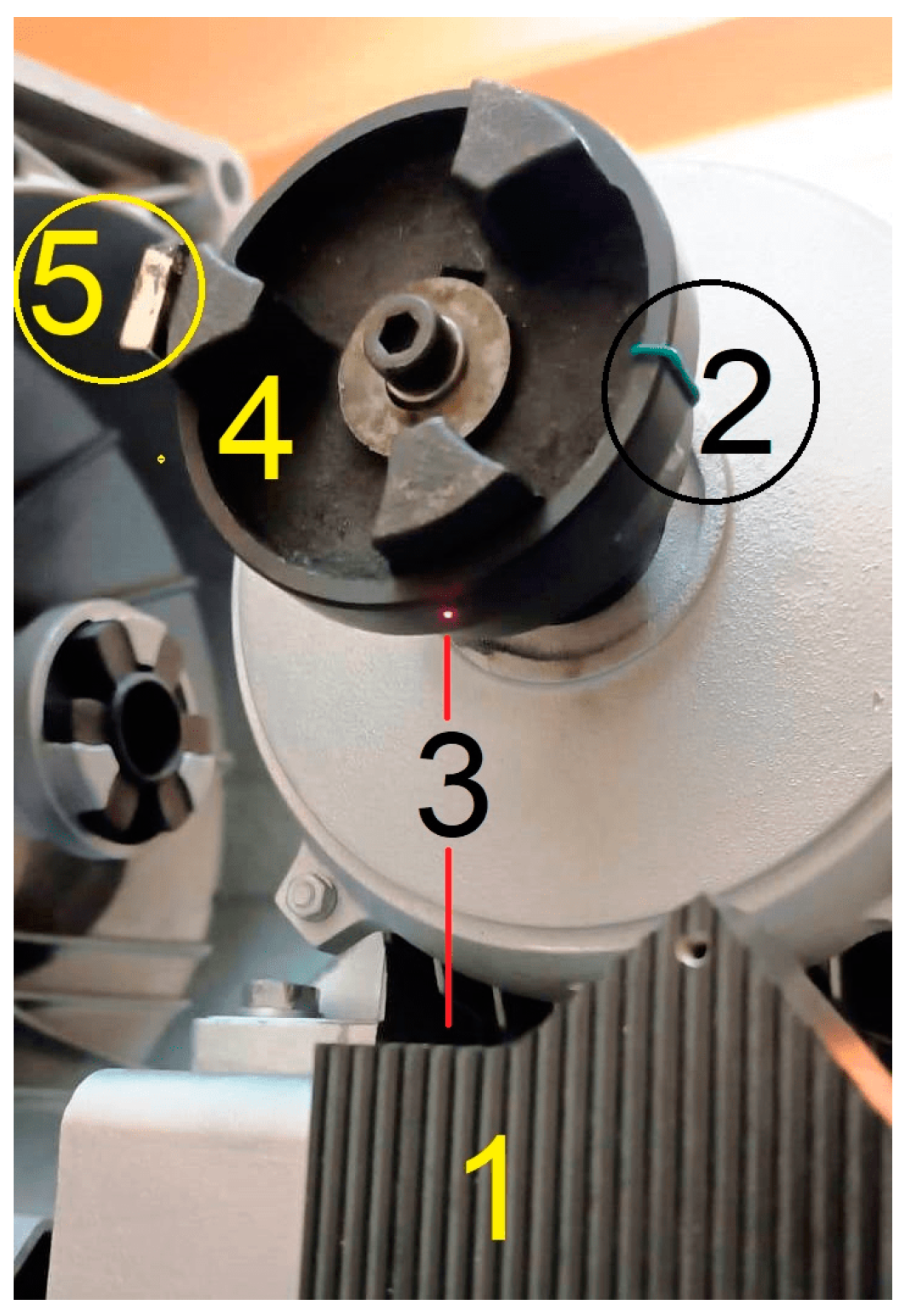
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. The Description of the Instantaneous Electrical Power
2.3. A Description of the Instantaneous Active Electrical Power
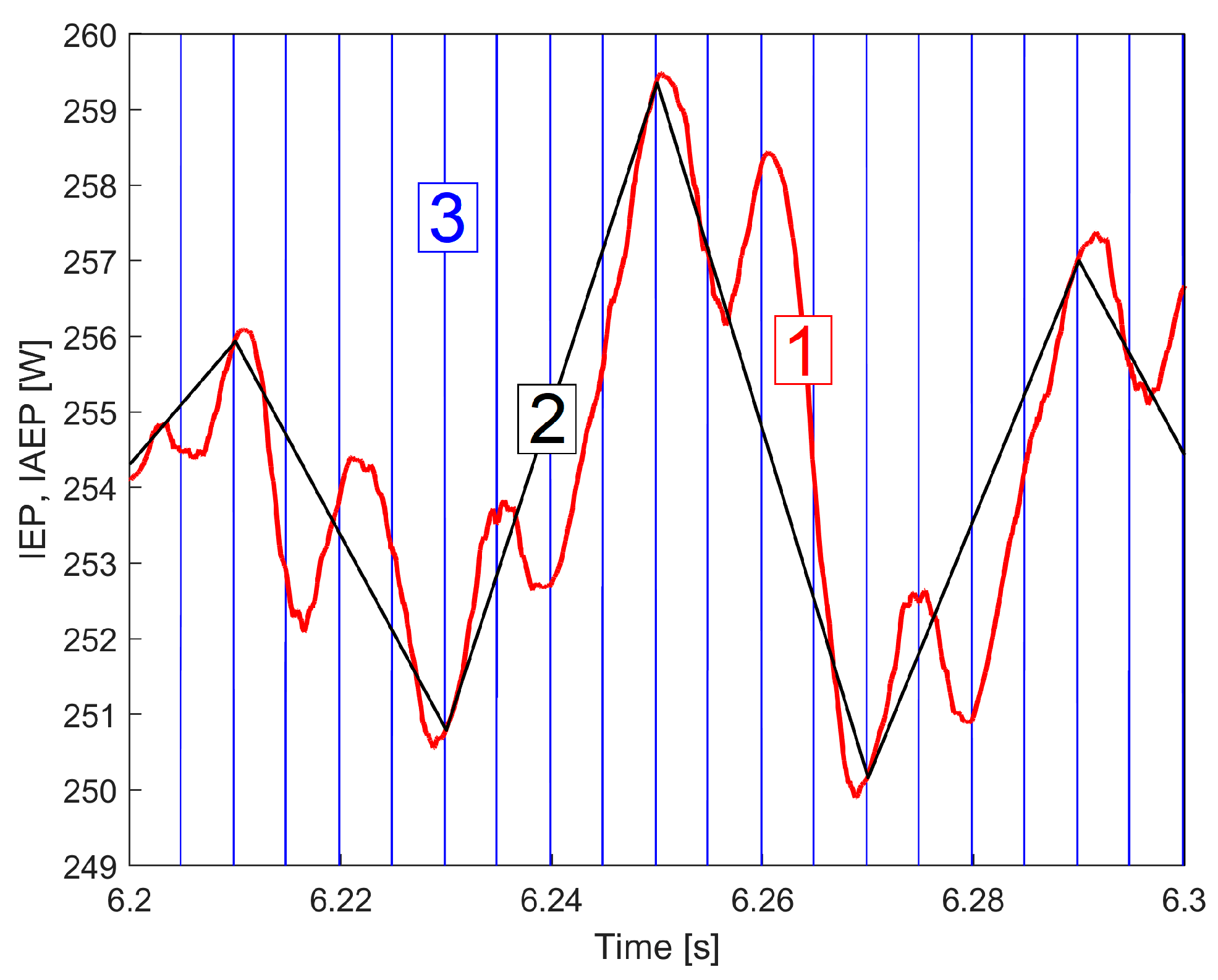
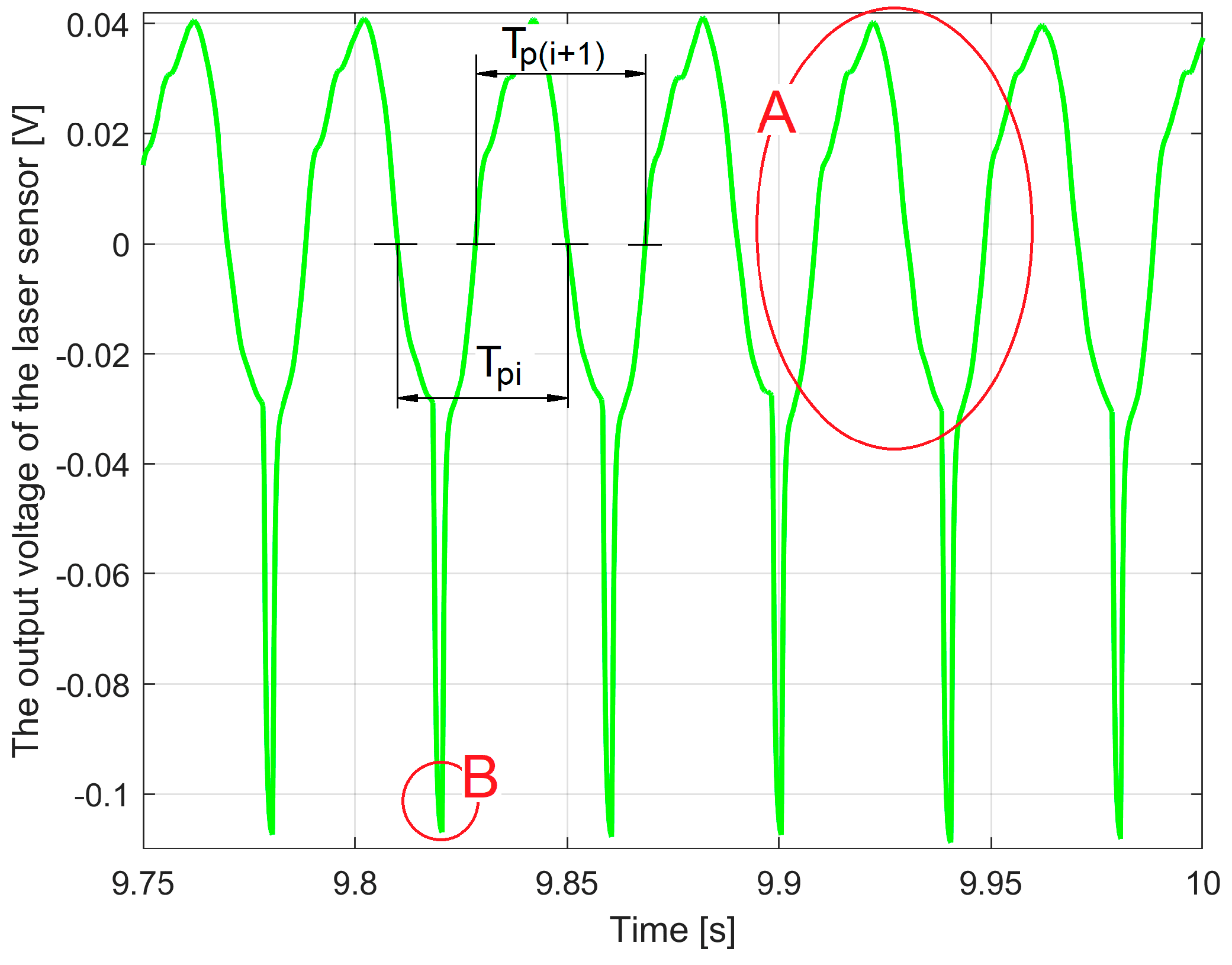
2.4. A Method of Determining a Pattern in IAEPf Variation over Time Useful in Motor Condition Characterisation
- -
- The exact determination of the value of Tp, and n, with . Of course, Tp is the period of a complete rotation of the rotor;
- -
- The exact determination of a moment of time when the angular mark placed on the rotating rotor (2 in Figure 3) passes through the angular origin (when k = 1). This moment of time should preferably be chosen at the very beginning of the VIAEPf signal.
3. Results
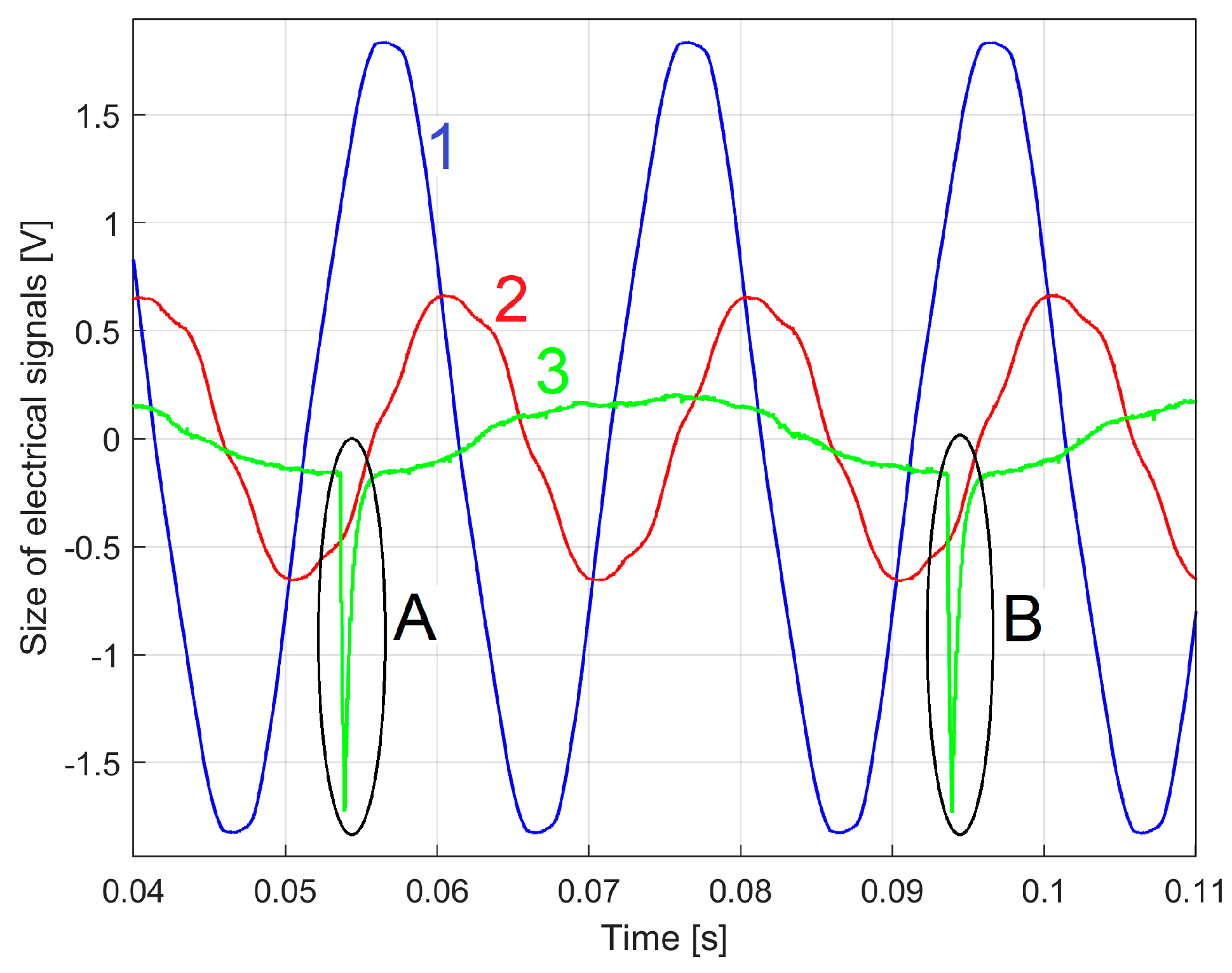
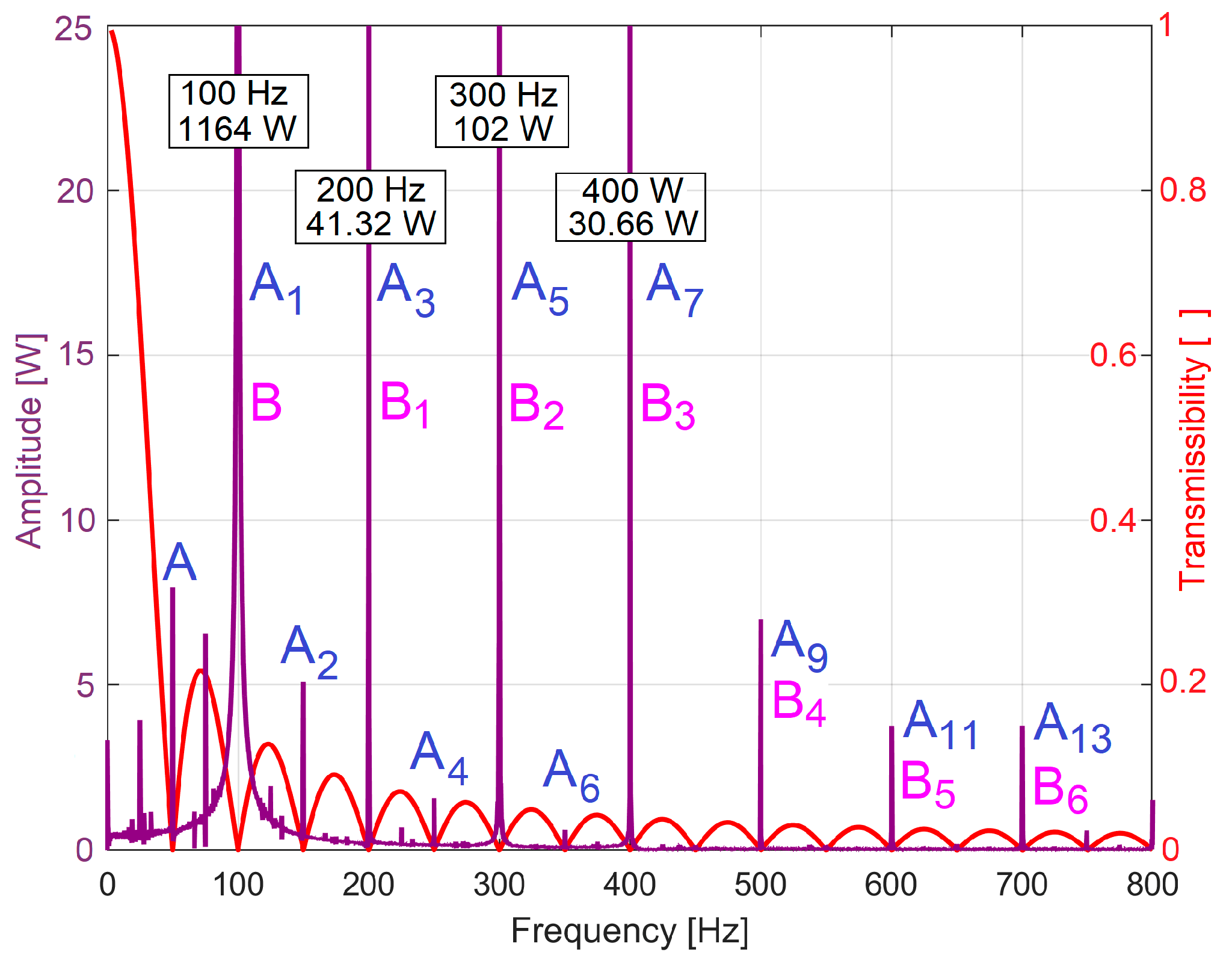
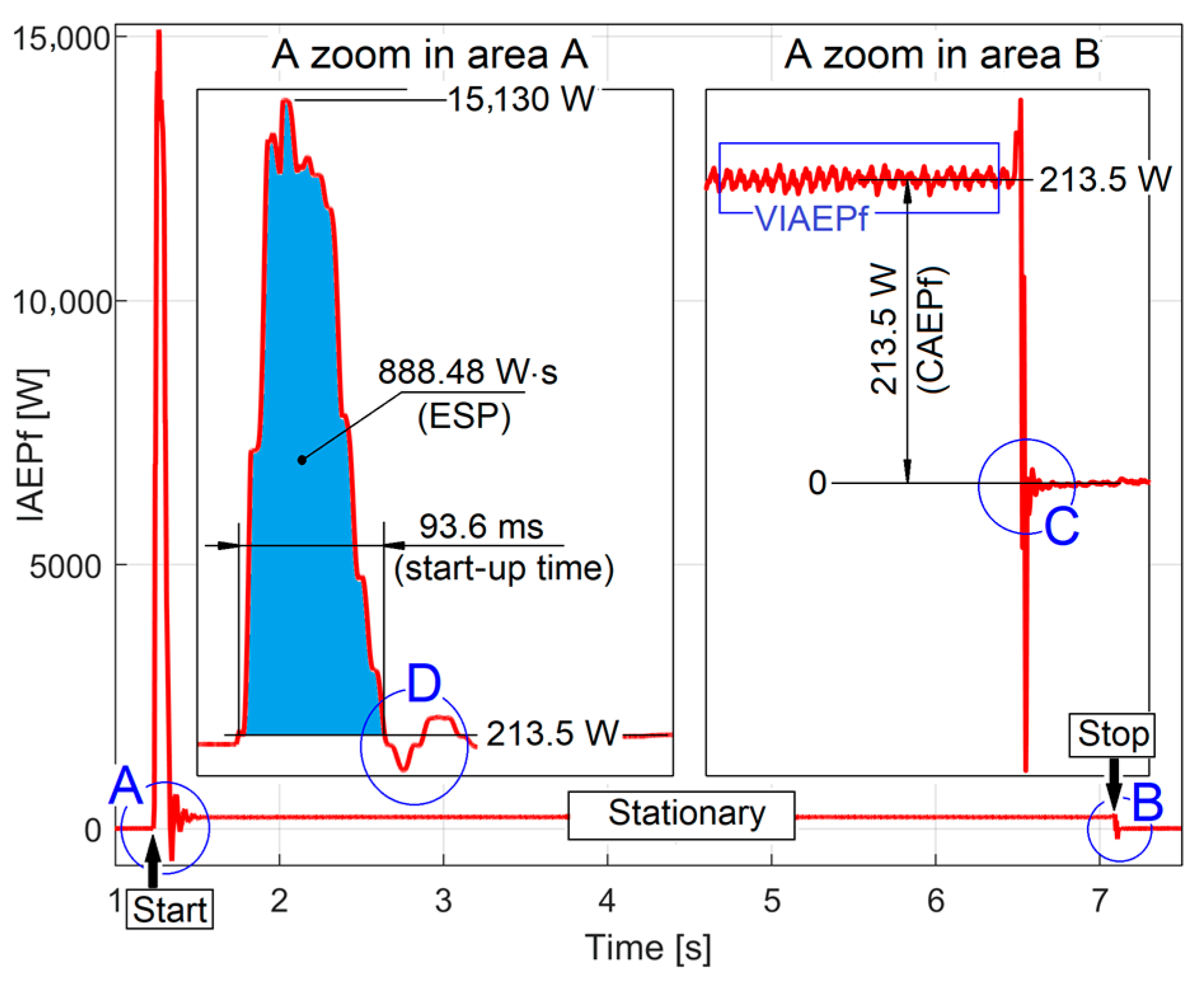
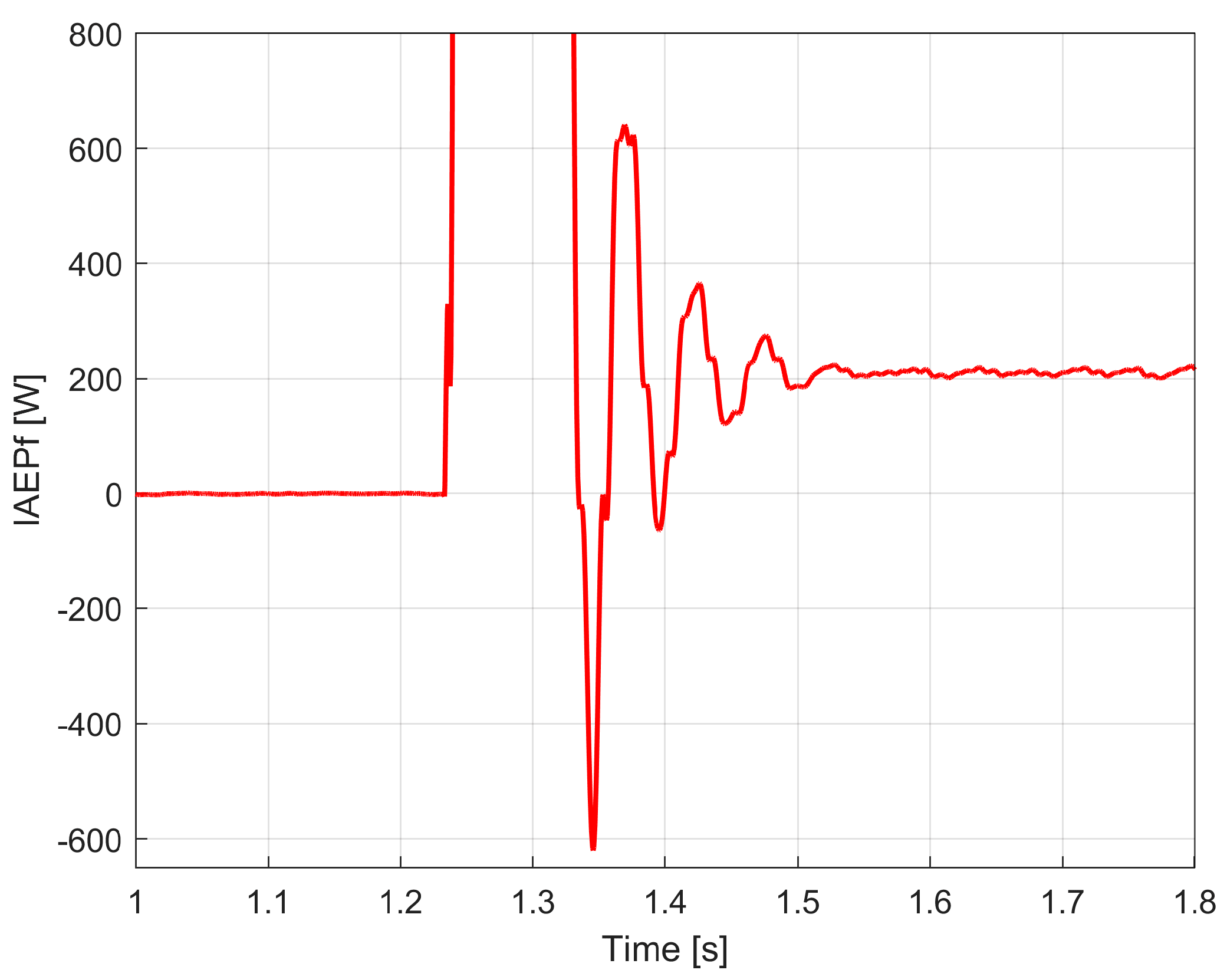
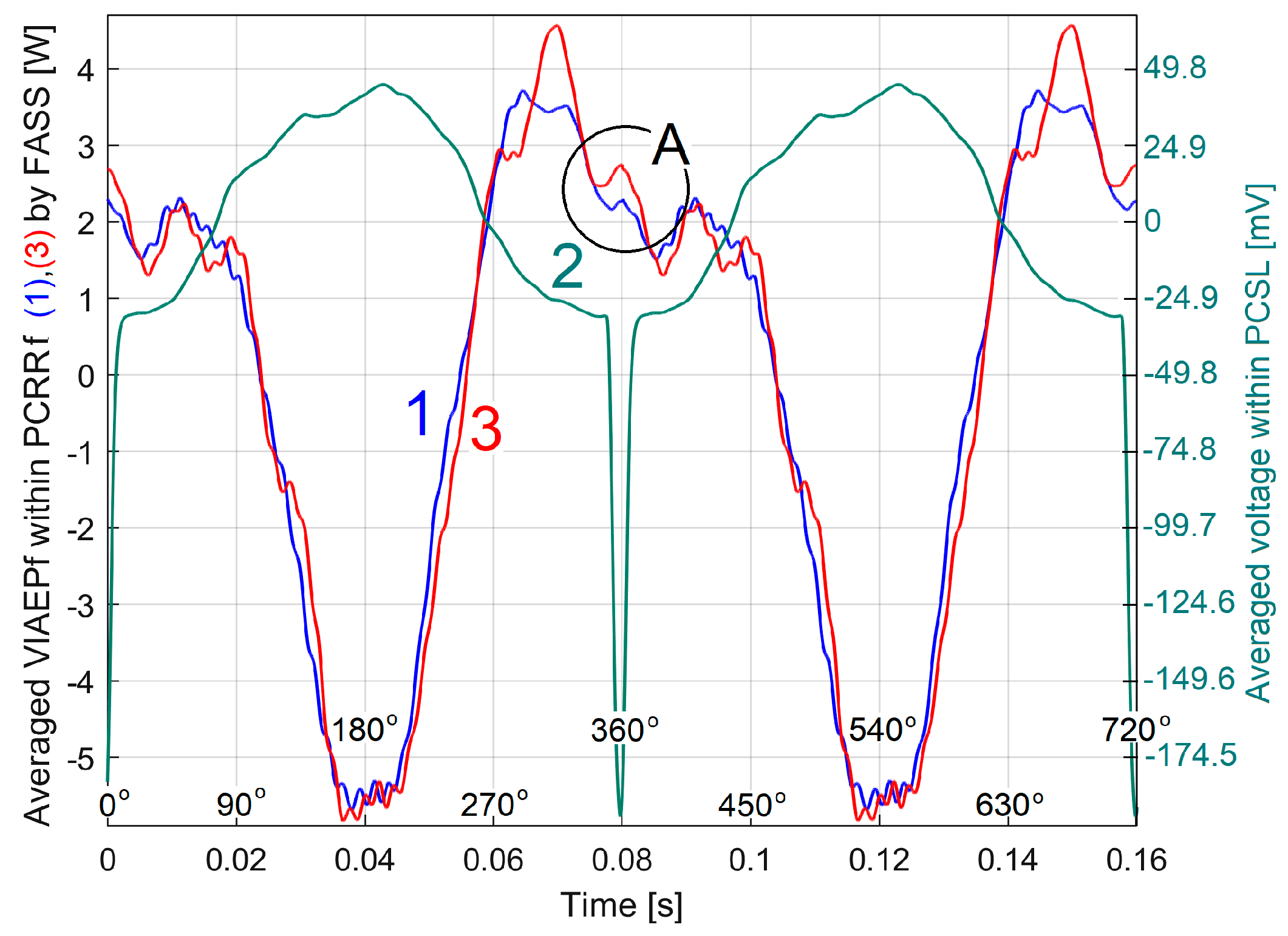
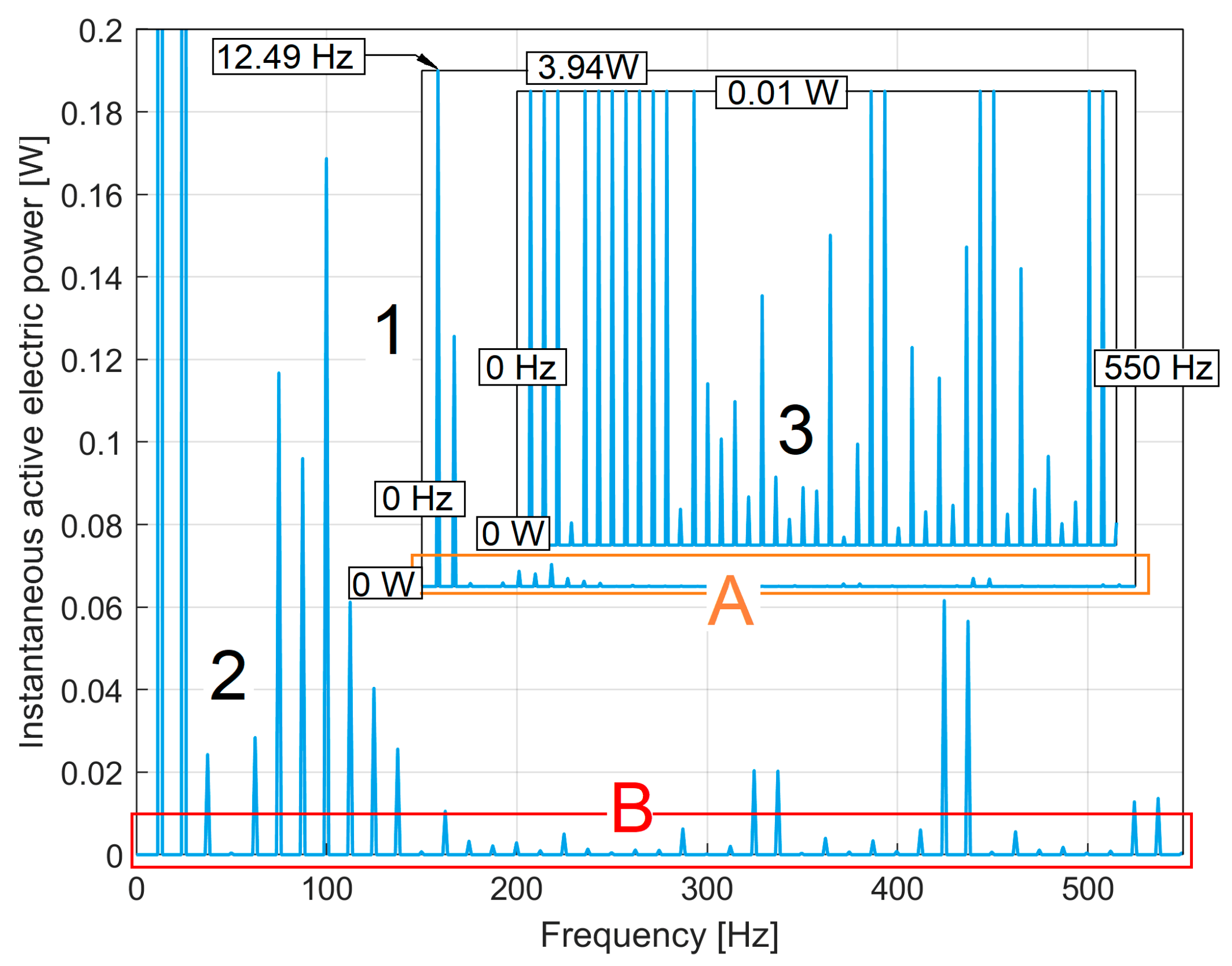
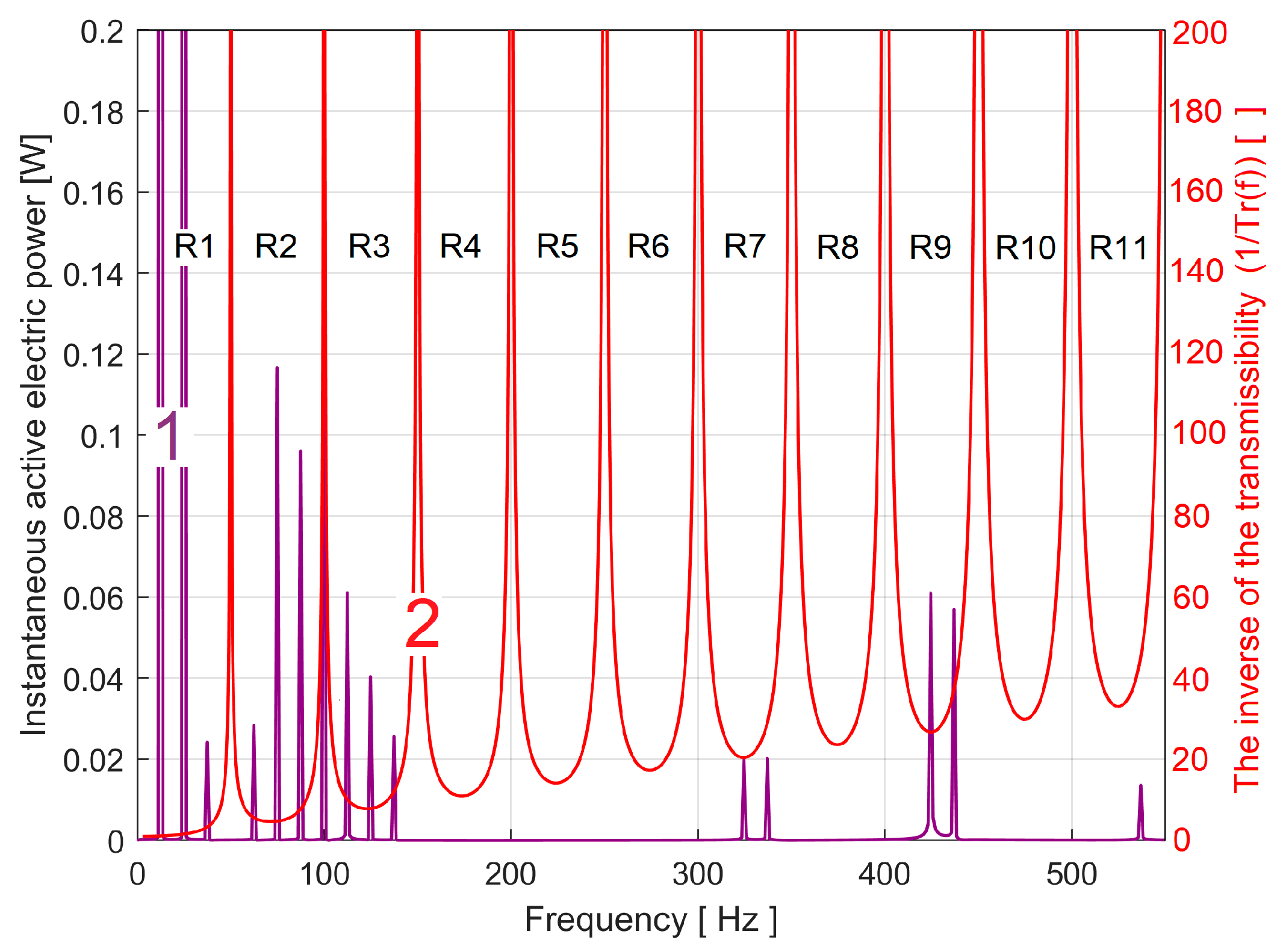
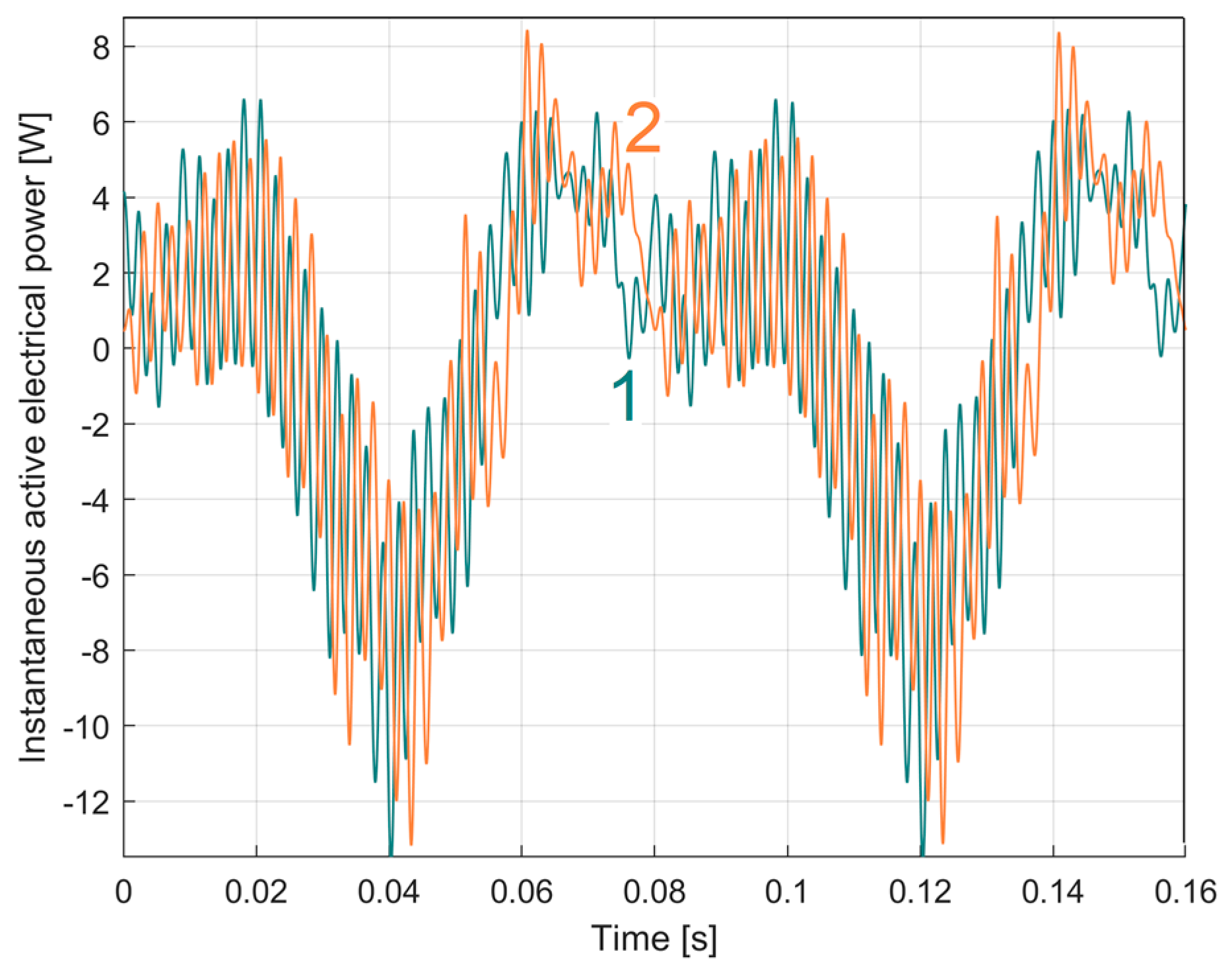
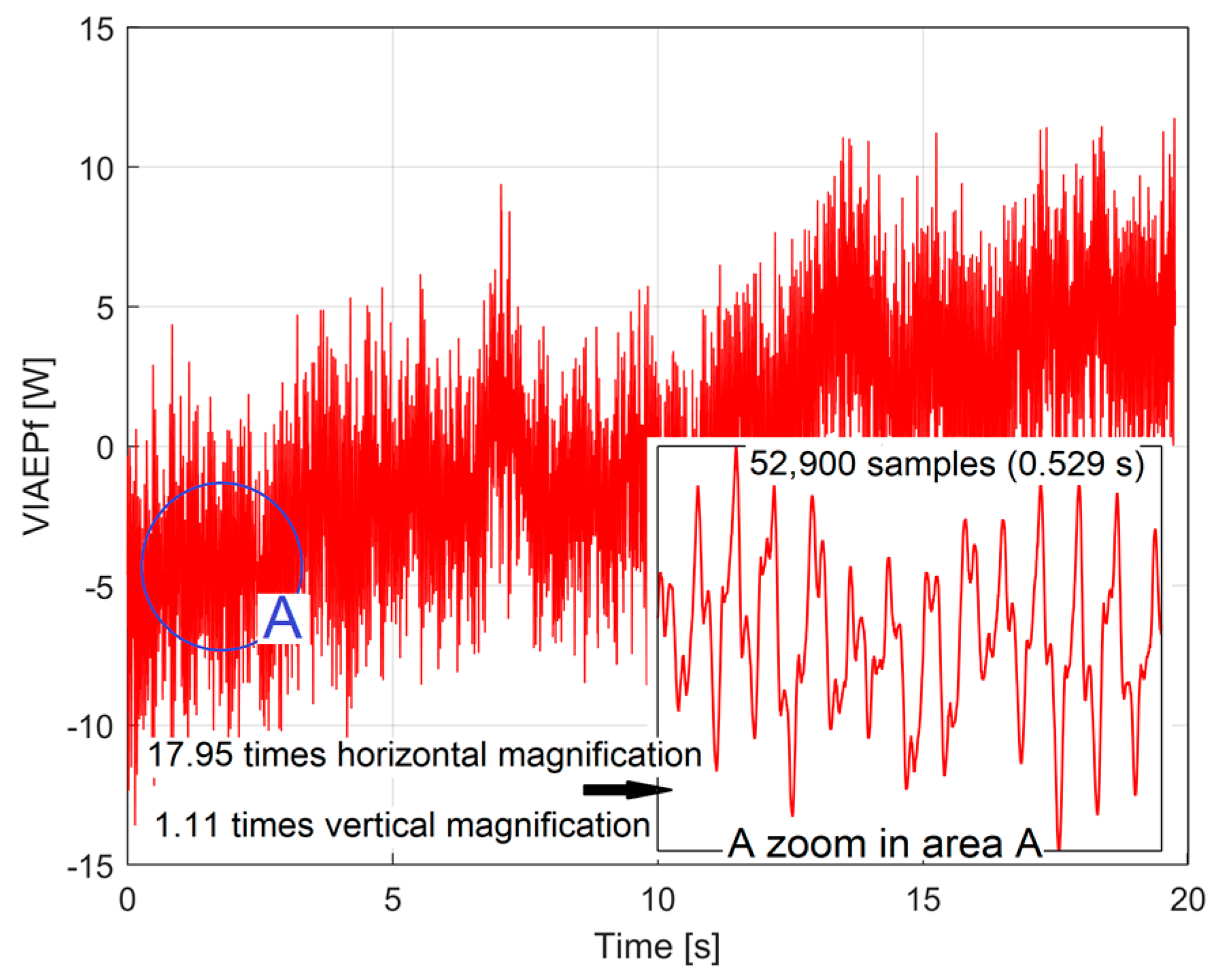
3.1. Some Resources Related to IAEPf, ESP and CAEPf in Motor Condition Monitoring Experimentally Revealed
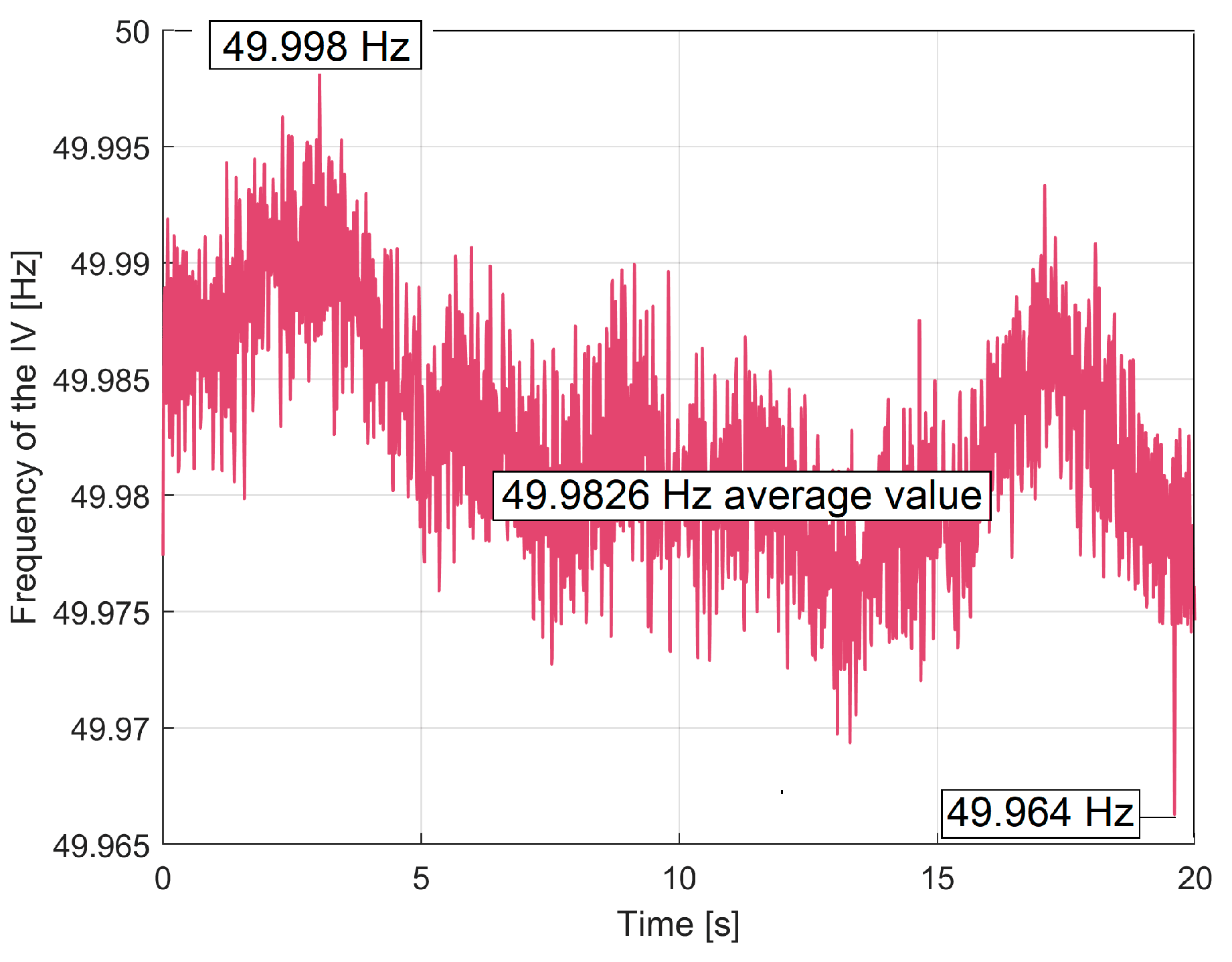
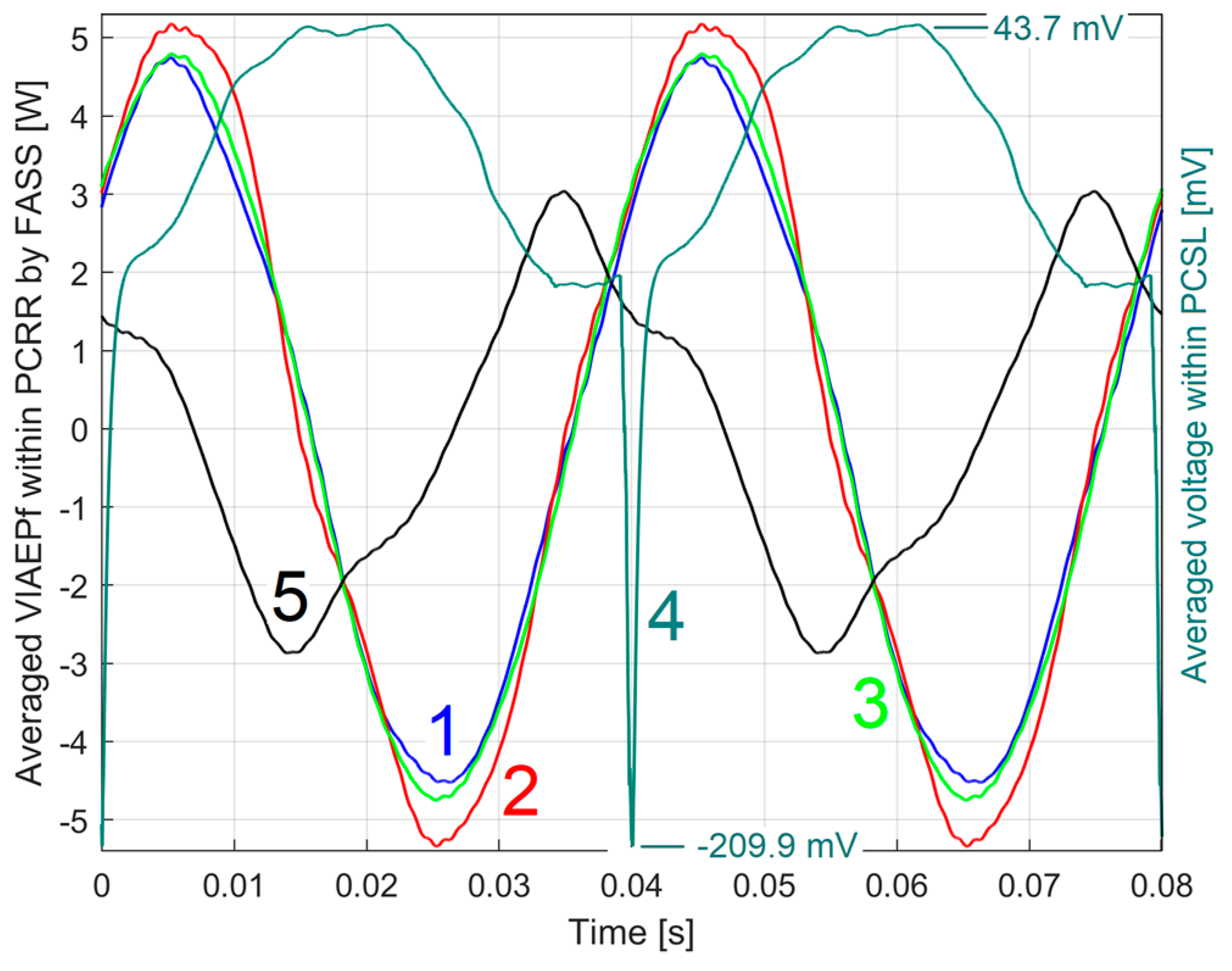
3.2. The Detection of PCRRf Patterns
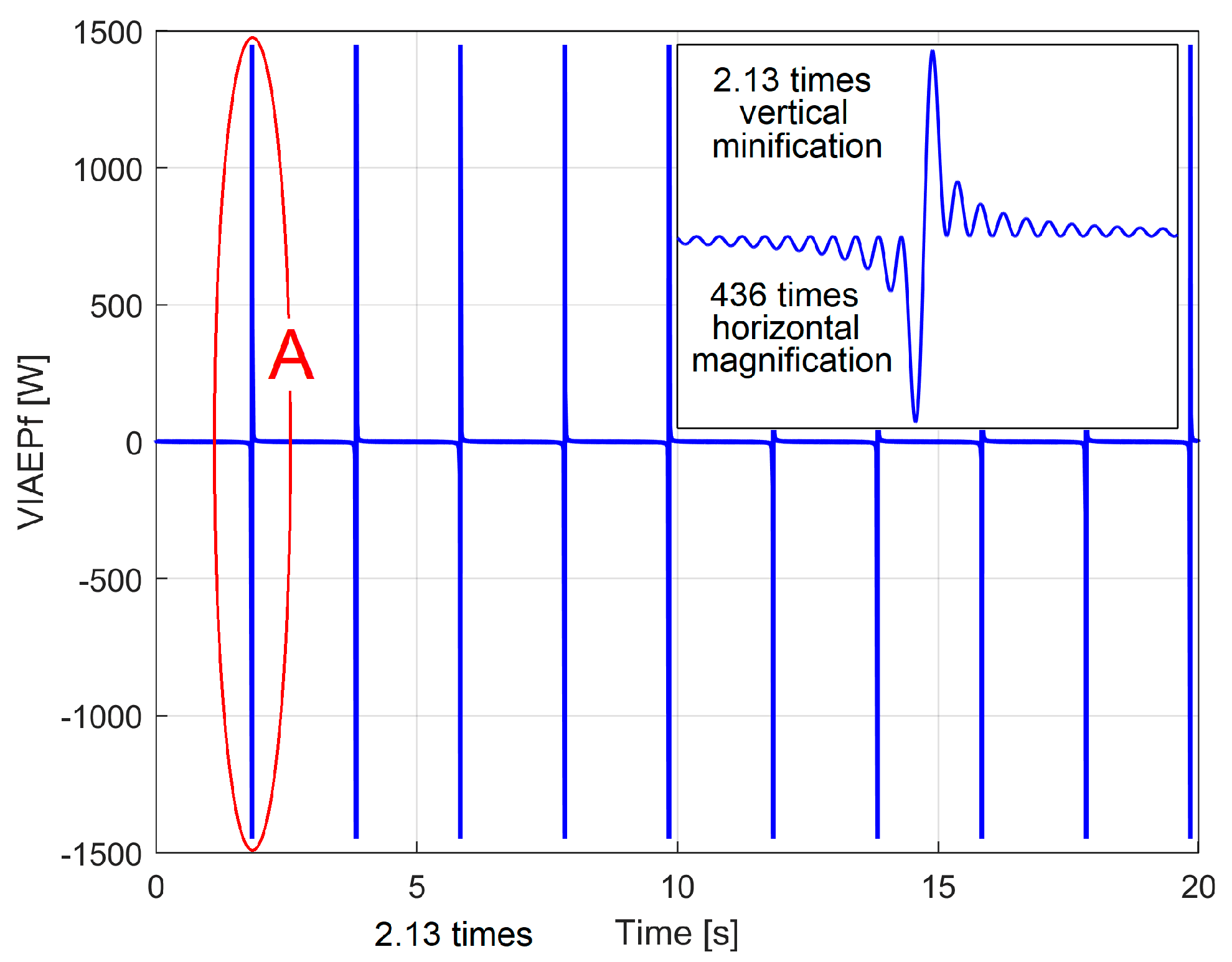
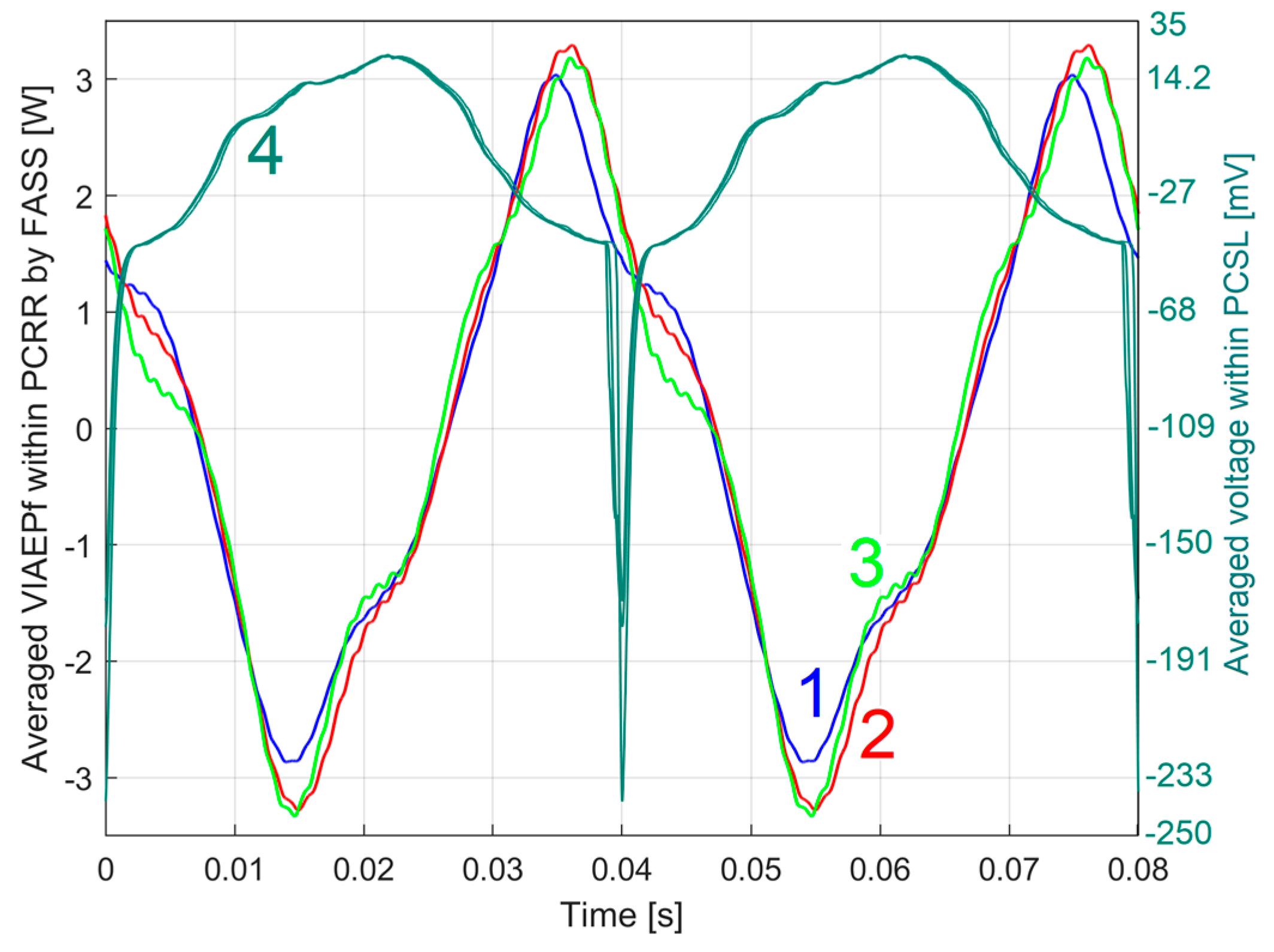
3.2.1. The Extraction of the PCRRf1 Patterns
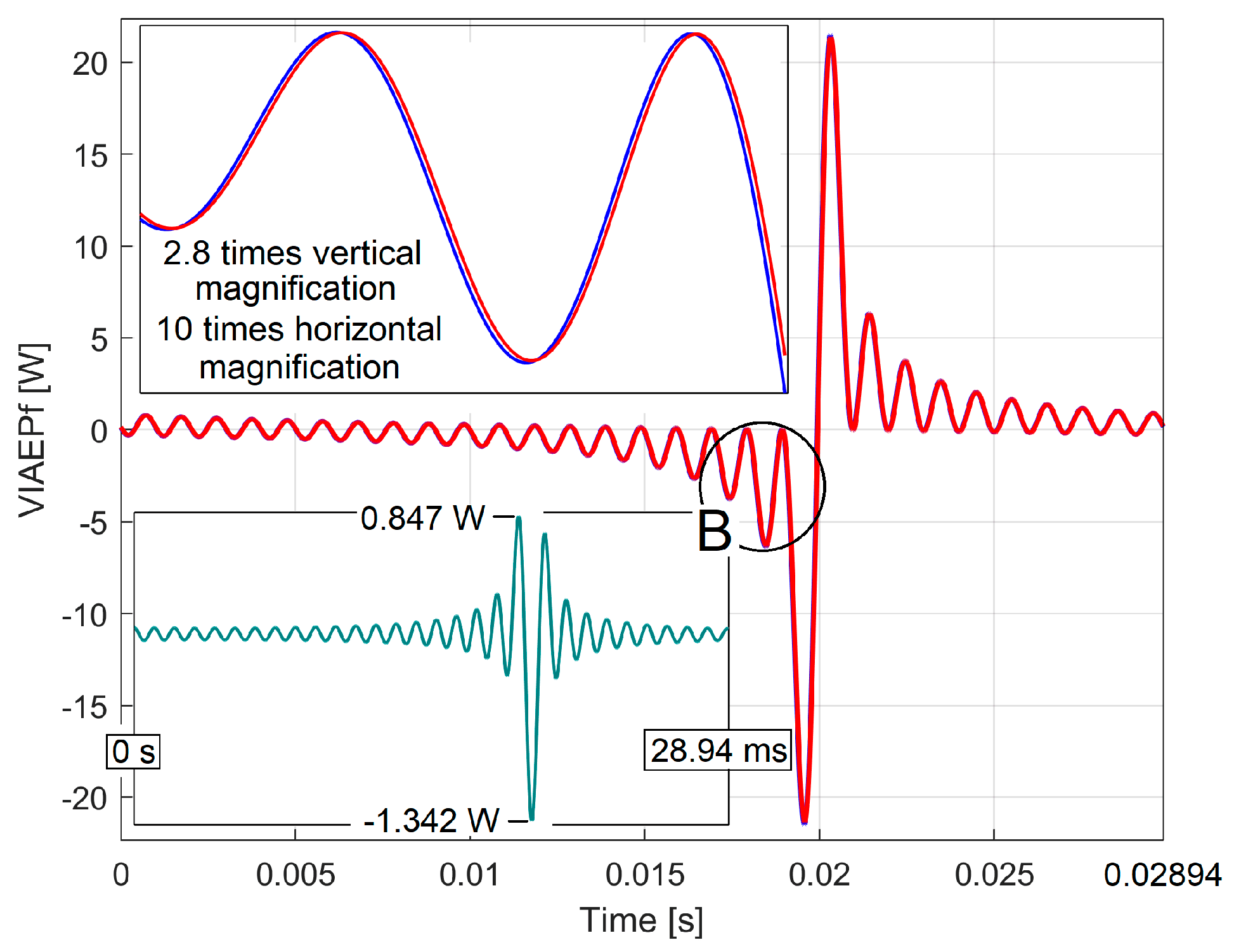
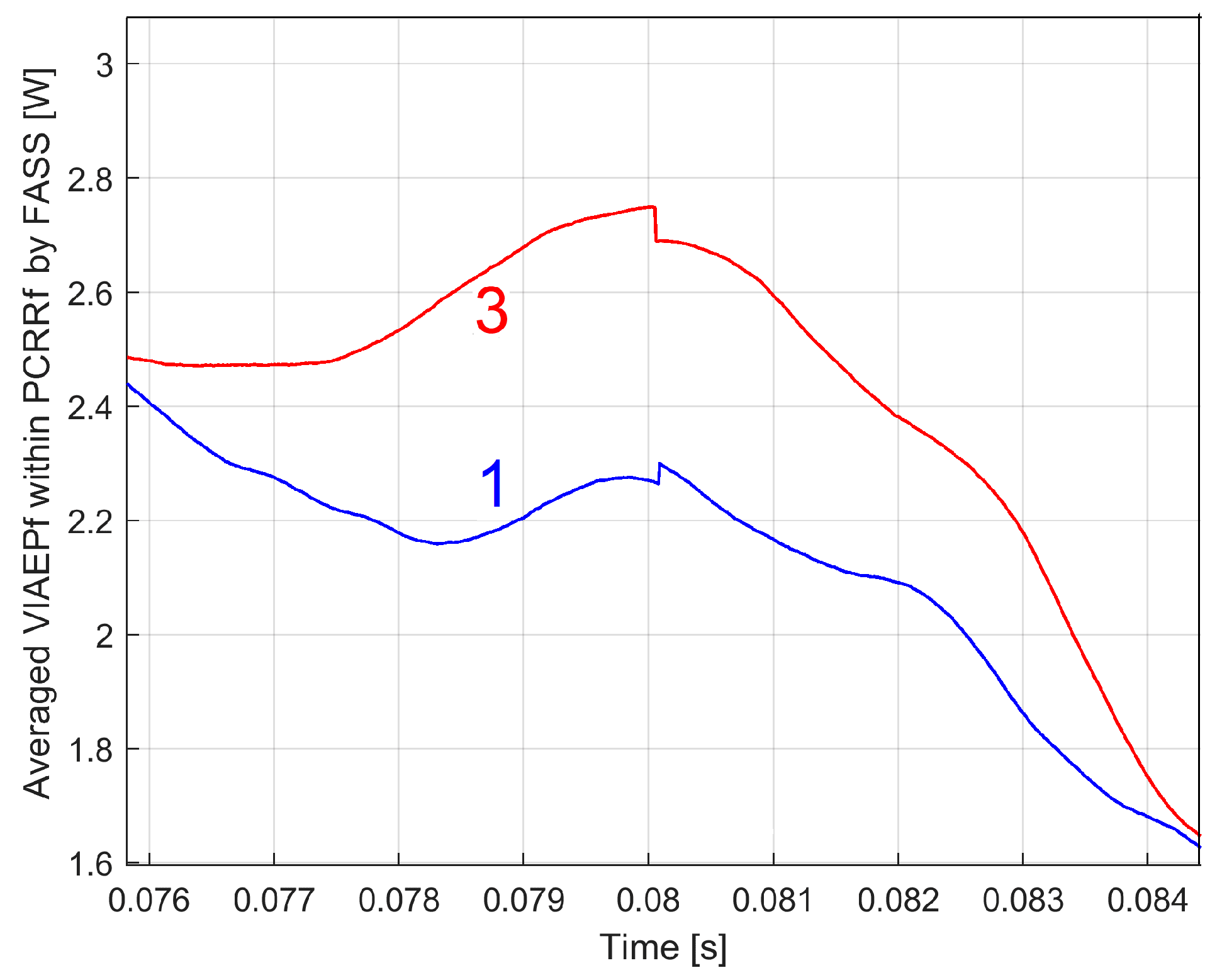
The Analysis of the PCRRf1a Pattern
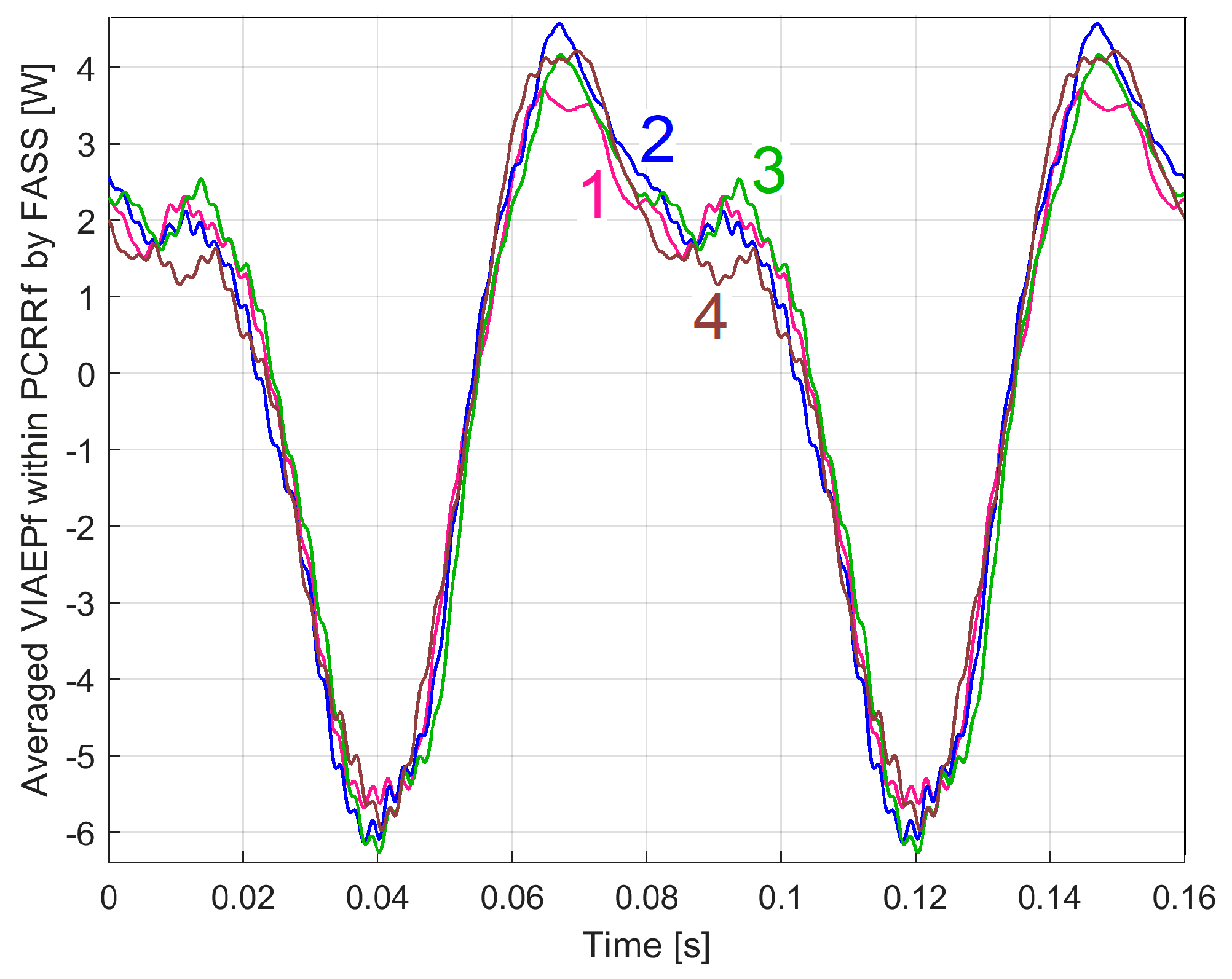
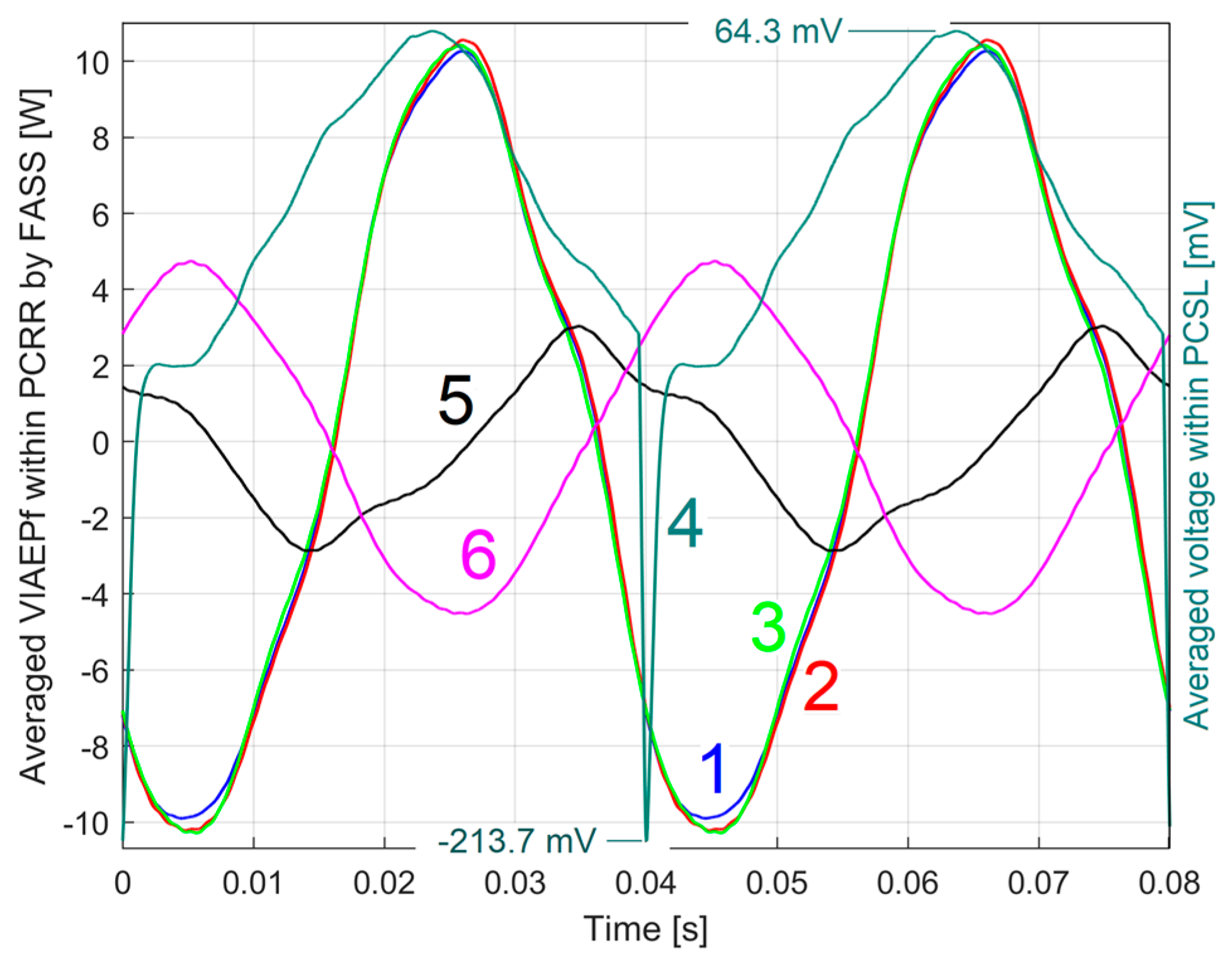
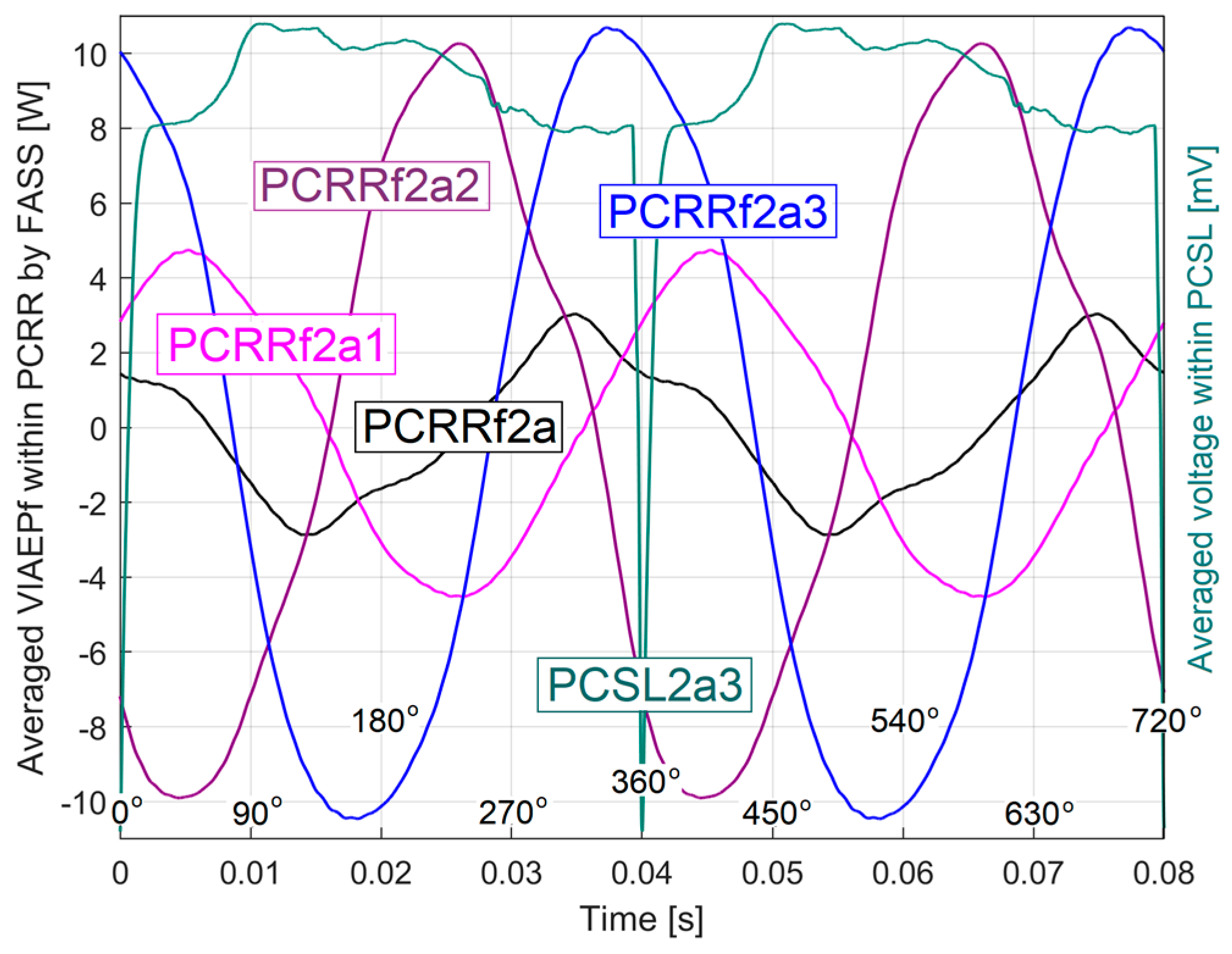
3.2.2. The Extraction and the Analysis of the PCRRf2 Patterns
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Shi, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhen, D.; Gu, F.; Ball, A.D. Early Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis in Induction Motors Based on On-Rotor Sensing Vibrations. Measurement 2023, 222, 113614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Rajpurohit, B.S. Condition Monitoring of Permanent Magnet AC Machines for All-Electric Transportation Systems: State of the Art. IET Energy Syst. Integr. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-C.; Jheng, Y.-M.; Kuo, C.-C.; Hsueh, Y.-M. Induction Motors Condition Monitoring System with Fault Diagnosis Using a Hybrid Approach. Energies 2019, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Gao, R.S.; Sun, C.; Yan, R. Induction Motor Condition Monitoring for Sustainable Manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 33, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibrete, F.; Woldemichael, D.E.; Gebremedhen, H.S. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion in Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machines: A Comprehensive Review. Measurement 2024, 232, 114658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.C.; Righi, R.R.; Crovato, C.D.P. On Proposing a Non-Intrusive Device and Methodology to Monitor Motor Degradation. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2023, 35, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Sun, E.; Zhou, S.; Shang, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Q. Research on Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor Fault Diagnosis Based on Multiscale Weibull Dispersion Entropy. Entropy 2023, 25, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangsar, P.; Tiwari, R. Signal Based Condition Monitoring Techniques for Fault Detection and Diagnosis of Induction Motors: A State-Of-The-Art Review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 144, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhni, M.F.; Cauet, S.; Sakout, A.; Assoum, H.; Etien, E.; Rambault, L.; El-Gohary, M. Variable Speed Induction Motors’ Fault Detection Based on Transient Motor Current Signatures Analysis: A Review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 184, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, E.T.; Wang, S.; Sundararajan, V. Multisensor Wireless System for Eccentricity and Bearing Fault Detection in Induction Motors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, A.; Han, G.A. Deep-Learning-Based Fault Diagnosis Method of Industrial Bearings Using Multi-Source Information. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mechefske, C.K. Detection of Induction Motor Faults: A Comparison of Stator Current, Vibration and Acoustic Methods. J. Vib. Control 2006, 12, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seera, M.; Lim, C.P.; Nahavandi, S.; Loo, C.K. Condition Monitoring of Induction Motors: A Review and an Application of an Ensemble of Hybrid Intelligent Models. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 4891–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Calva, T.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Fernandez-Cavero, V.; Romero-Troncoso, R. Early Detection of Faults in Induction Motors-A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 7855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juez-Gil, M.; Saucedo-Dorantes, J.S.; Arnaiz-González, A.; López-Nozal, C.; García-Osorio, C.; Lowe, D. Early and Extremely Early Multi-Label Fault Diagnosis in Induction Motors. ISA Trans. 2020, 106, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalel, D.; Singh, R.R. Iot Integrated Adaptive Fault Tolerant Control for Induction Motor Based Critical Load Applications. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2024, 51, 101585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-C.; Jheng, Y.-M.; Kuo, C.-C.; Huang, L.-B. On-Line Motor Condition Monitoring System for Abnormality Detection. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2016, 51, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultekin, M.A.; Bazzi, A. Review of Fault Detection and Diagnosis Techniques for AC Motor Drives. Energies 2023, 16, 5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Xu, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W. Analysis of Equivalent Inertia of Induction Motors and Its Influencing Factors. Electr. Pow. Syst. Res. 2023, 225, 109820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.M.; Etemadrezaei, M.; Faiz, J. Dynamic Eccentricity Fault Diagnosis in Round Rotor Synchronous Motors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 2092–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horodinca, M.; Ciurdea, I.; Chitariu, D.; Munteanu, A.; Boca, M. Some Approaches on Instantaneous Angular Speed Measurement Using a Two-phase n Poles AC Generator as Sensor. Measurement 2020, 157, 107636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShorman, O.; Irfan, M.; Abdelrahman, R.B.; Masadeh, M.; Alshorman, A.; Shekh, M.A.; Saad, N.; Rahman, S. Advancements in Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery: A Comprehensive Review of Image-Based Intelligent Techniques for Induction Motors. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 130, 107724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, G.; Werneck, M.M. A Magnetostrictive-Fiber Bragg Grating Sensor for Induction Motor Health Monitoring. Measurement 2018, 122, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-Ramirez, I.; Osornio-Rios, R.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Smart Sensor for Fault Detection in Induction Motors Based on the Combined Analysis of Stray-Flux and Current Signals: A Flexible, Robust Approach. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2022, 28, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Saad, N.; Ibrahim, R.; Asirvadam, V.S. An On-line Condition Monitoring System for Induction Motors via Instantaneous Power Analysis. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Goyal, D.; Shimi, S.L.; Akula, A. Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motors: A Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almounajjed, A.; Sahoo, A.K.; Kumar, M.K. Diagnosis of Stator Fault Severity in Induction Motor Based on Discrete Wavelet Analysis. Measurement 2021, 182, 109780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamira, N.; Dekhane, A.; Kerfali, S.; Bouras, A.; Reffas, O. Experimental Investigation of The Combined Fault: Mechanical and Electrical Unbalances in Induction Motors Based on Stator Currents Monitoring. Instrum. Mes. Metrol. 2022, 21, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, K.; Lv, H.; He, S.; Xu, E. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Machines with Small & Imbalanced Data: A State-Of-The-Art Review and Possible Extensions. ISA Trans. 2022, 119, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo Guajardo, L.A.; Platas Garza, M.A.; Rodríguez Maldonado, J.; González Vázquez, M.A.; Rodríguez Alfaro, L.H.; Salinas Salinas, F. Prony Method Estimation for Motor Current Signal Analysis Diagnostics in Rotor Cage Induction Motors. Energies 2022, 15, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyono, B.; Prasetyo, Y.; Winarno, B.; Wicaksono, H.H. Electrical Motor Interference Monitoring Based on Current Characteristics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1845, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-Ramírez, I.; Osornio-Ríos, R.A.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Triaxial Smart Sensor Based on the Advanced Analysis of Stray Flux and Currents for the Reliable Fault Detection in Induction Motors. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (IEEE ECCE), Detroit, MI, USA, 23 September–15 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita, M.; Kameyama, H.; Ikeboh, Y.; Morimoto, S. Sine-Wave Drive for PM Motor Controlling Phase Difference Between Voltage and Current by Detecting Inverter Bus Current. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Saad, N.; Ibrahim, R.; Asirvadam, V.S. Condition monitoring of induction motors via instantaneous power analysis. J. Intell. Manuf. 2017, 28, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzoug, Y.; Sahraoui, M.; Pusca, R.; Ameid, T.; Romary, R.; Cardoso, A.J.M. Current Sensors Fault Detection and Tolerant Control Strategy for Three-phase Induction Motor Drives. Electr. Eng. 2021, 103, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianov, A.; Anuchin, A. Phase Loss Detection Using Voltage Signals and Motor Models: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 26488–26502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konar, P.; Chattopadhyay, P. Multi-class fault diagnosis of induction motor using Hilbert and Wavelet Transform. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2015, 30, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irgat, E.; Çinar, E.; Ünsal, A.; Ãœnsal, A.; Yazici, A. An IoT-Based Monitoring System for Induction Motor Faults Utilizing Deep Learning Models. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2023, 11, 3579–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bazzi, A.M. A Review and Comparison of Fault Detection and Diagnosis Methods for Squirrel-Cage Induction Motors: State of the Art. ISA Trans. 2017, 70, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Iwnicki, S.D.; Zhao, Y. Application of Power Spectrum, Cepstrum, Higher Order Spectrum and Neural Network Analyses for Induction Motor Fault Diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 39, 342–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, R.S.; Kral, C.; Pirker, F.; Schagginger, M. The Vienna induction machine Monitoring Method; On the impact of the Field Oriented Control structure on real operational behaviour of a faulty machine. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial-Electronics-Society, Aachen, Germany, 31 August–4 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Horodinca, M.; Bumbu, N.-E.; Chitariu, D.-F.; Munteanu, A.; Dumitras, C.-G.; Negoescu, F.; Mihai, C.-G. On the Behaviour of an AC Induction Motor as Sensor for Condition Monitoring of Driven Rotary Machines. Sensors 2023, 23, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PicoScope® 4000A Series. High-Resolution Deep-Memory Oscilloscopes (Pico Technology, UK). Available online: https://www.picotech.com/oscilloscope/4000/picoscope-4000-specifications (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Sowidan, H. ECE 330 Power Circuits and Electromechanics. Lecture 2: Active, Reactive, and Complex Power. Available online: https://courses.engr.illinois.edu/ece330/fa2017/lectures/Lecture%202.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Bumbu, N.E.; Horodinca, M. A Study on the Dynamics of an AC Induction Motor Rotor Based on the Analysis of Free Response at Impulse Excitation. Bull. Polytech. Inst. Iași Mach. Constr. Sect. 2022, 68, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Correia, P.; Wu, R.; Song, S.; Trintis, I.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. Accelerated Degradation Testing and Failure Mechanism Analysis of Metallized Film Capacitors for AC Filtering. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 6256–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Lin, C.; Xie, D.; Acuna, P.; Liu, W. A Counter-Based Open-Circuit Switch Fault Diagnostic Method for a Single-Phase Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron 2024, 39, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horodinca, M.; Chifan, F.; Paduraru, E.; Dumitras, C.G.; Munteanu, A.; Chitariu, D.-F. A Study of 2D Roughness Periodical Profiles on a Flat Surface Generated by Milling with a Ball Nose End Mill. Materials 2024, 17, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Sensors | Output sensors | Vibration | [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12] |
| Temperature | [2,3,4,5,6,10,13,14,15,16,17,18] | ||
| Instantaneous rotation speed Acoustic | [6,9,14,16,18,19,20,21] [5,8,11,12,14] | ||
| Magnetic field | [20,22,23] | ||
| Stray flux | [6,24] | ||
| Input sensors | Instantaneous current | [2,4,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,17,18,20,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35] | |
| Instantaneous voltage | [2,13,26,36] | ||
| Instantaneous (active) electrical power | [13,19,21,25,34] | ||
| Phase shift (power factor) | [6,13,17,30,33,37] | ||
| Processing techniques and methods for monitoring | Fast Fourier Transform | [2,6,8,9,17,21,34] | |
| Wavelet transform | [2,8,9,13,14,17,18,20,26,27,28,37,38,39] | ||
| Neural networks | [2,5,11,13,18,26,38,40] | ||
| Machine learning | [3,5,8,10,14,29,36] | ||
| Support vector machine | [2,13] | ||
| Deep learning | [11] | ||
| Vienna monitoring method | [41] | ||
| Early detection | [1,4,10,14,15,41] | ||
| Online | [8,9,17] | ||
| IoT | [16,38] | ||
| Detectable failures | Bearing condition | [1,2,3,4,5,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,17,22,25,26,32,34,38,39] | |
| Rotor mechanical imbalance/eccentricity | [4,6,9,10,13,14,15,17,20,22,28,37,39] | ||
| Broken bars in squirrel-cage rotor | [2,4,7,8,9,12,14,15,17,22,23,24,26,30,32,37,39,40] | ||
| Stator winding faults | [5,8,13,14,17,22,27,32,37,39,40] | ||
| Magnetic asymmetries in stator/rotor | [2,22,23] | ||
| Current imbalance | [3,8,9,14,22,28,37] | ||
| Phase loss | [9,36] | ||
| i | Afai [W] | Bfai [Hz] | Cfai [rad] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.945 | 12.4857 = 1/Tp1a = Bfa1 | Fundamental | 1.725 |
| 2 | 1.913 | 24.9714 = 2·Bfa1 | 1st harmonic | −1.747 |
| 3 | 0.02436 | 37.4491 = 2.9993·Bfa1 | 2nd harmonic | 1.059 |
| 4 | 0.02832 | 62.4364 = 5.0006·Bfa1 | 4th harmonic | −2.031 |
| 5 | 0.1168 | 74.9142 = 6·Bfa1 | 5th harmonic | 2.07 |
| 6 | 0.09591 | 87.4078 = 7·Bfa1 | 6th harmonic | −1.45 |
| 7 | 0.1688 | 99.8856 = 8·Bfa1 | 7th harmonic | 0.9121 |
| 8 | 0.06114 | 112.3474 = 8.9980·Bfa1 | 8th harmonic | 1.169 |
| 9 | 0.04019 | 124.8570 = 10·Bfa1 | 9th harmonic | 0.5538 |
| 10 | 0.02553 | 137.3507 = 11·Bfa1 | 10th harmonic | 1.596 |
| 11 | 0.02038 | 324.6760 = 26·Bfa1 | 25th harmonic | 2.634 |
| 12 | 0.02024 | 337.0901 = 26.9980·Bfa1 | 26th harmonic | 1.23 |
| 13 | 0.06175 | 424.6253 = 34.0089·Bfa1 | 33rd harmonic | −2.366 |
| 14 | 0.05657 | 437.0394 = 35.0032·Bfa1 | 34th harmonic | 1.26 |
| 15 | 0.01367 | 536.8296 = 42.9955·Bfa1 | 42nd harmonic | −0.5324 |
| i | Afai [W] | 1/Tr(Bfai) | Aai = Afai·1/Tr(Bfai) [W] | Bai [Hz] | Cai [rad] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.945 | 1.103 | 4.351 | 12.4857 | Fundamental | 1.725 |
| 2 | 1.913 | 1.568 | 2.999 | 24.9714 | 1st harmonic | −1.747 |
| 3 | 0.02436 | 3.311 | 0.0807 | 37.4491 | 2nd harmonic | 1.059 |
| 4 | 0.02832 | 5.578 | 0.1580 | 62.4364 | 4th harmonic | −2.031 + π = 1.105 |
| 5 | 0.1168 | 4.704 | 0.5494 | 74.9142 | 5th harmonic | 2.07 + π = 5.2115 |
| 6 | 0.09591 | 7.697 | 0.7382 | 87.4078 | 6th harmonic | −1.45 + π = 1.6915 |
| 7 | 0.1688 | 608 | 102.6304 | 99.8856 | 7th harmonic | 0.9121 |
| 8 | 0.06114 | 10.111 | 0.6182 | 112.3474 | 8th harmonic | 1.169 |
| 9 | 0.04019 | 7.841 | 0.3151 | 124.8570 | 9th harmonic | 0.5538 |
| 10 | 0.02553 | 12.035 | 0.3073 | 137.3507 | 10th harmonic | 1.596 |
| 11 | 0.02038 | 20.398 | 0.4157 | 324.6760 | 25th harmonic | 2.634 |
| 12 | 0.02024 | 28.90 | 0.5849 | 337.0901 | 26th harmonic | 1.23 |
| 13 | 0.06175 | 26.684 | 1.6477 | 424.6253 | 33rd harmonic | −2.366 |
| 14 | 0.05657 | 37.25 | 2.1072 | 437.0394 | 34th harmonic | 1.26 |
| 15 | 0.01367 | 45.09 | 0.6164 | 536.8296 | 42nd harmonic | −0.5324 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chitariu, D.-F.; Horodinca, M.; Mihai, C.-G.; Bumbu, N.-E.; Dumitras, C.G.; Seghedin, N.-E.; Edutanu, F.-D. Condition Monitoring of a Three-Phase AC Asynchronous Motor Based on the Analysis of the Instantaneous Active Electrical Power in No-Load Tests. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146124
Chitariu D-F, Horodinca M, Mihai C-G, Bumbu N-E, Dumitras CG, Seghedin N-E, Edutanu F-D. Condition Monitoring of a Three-Phase AC Asynchronous Motor Based on the Analysis of the Instantaneous Active Electrical Power in No-Load Tests. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146124
Chicago/Turabian StyleChitariu, Dragos-Florin, Mihaita Horodinca, Constantin-Gheorghe Mihai, Neculai-Eduard Bumbu, Catalin Gabriel Dumitras, Neculai-Eugen Seghedin, and Florin-Daniel Edutanu. 2024. "Condition Monitoring of a Three-Phase AC Asynchronous Motor Based on the Analysis of the Instantaneous Active Electrical Power in No-Load Tests" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146124
APA StyleChitariu, D.-F., Horodinca, M., Mihai, C.-G., Bumbu, N.-E., Dumitras, C. G., Seghedin, N.-E., & Edutanu, F.-D. (2024). Condition Monitoring of a Three-Phase AC Asynchronous Motor Based on the Analysis of the Instantaneous Active Electrical Power in No-Load Tests. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146124






