Improved CycleGAN for Mixed Noise Removal in Infrared Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
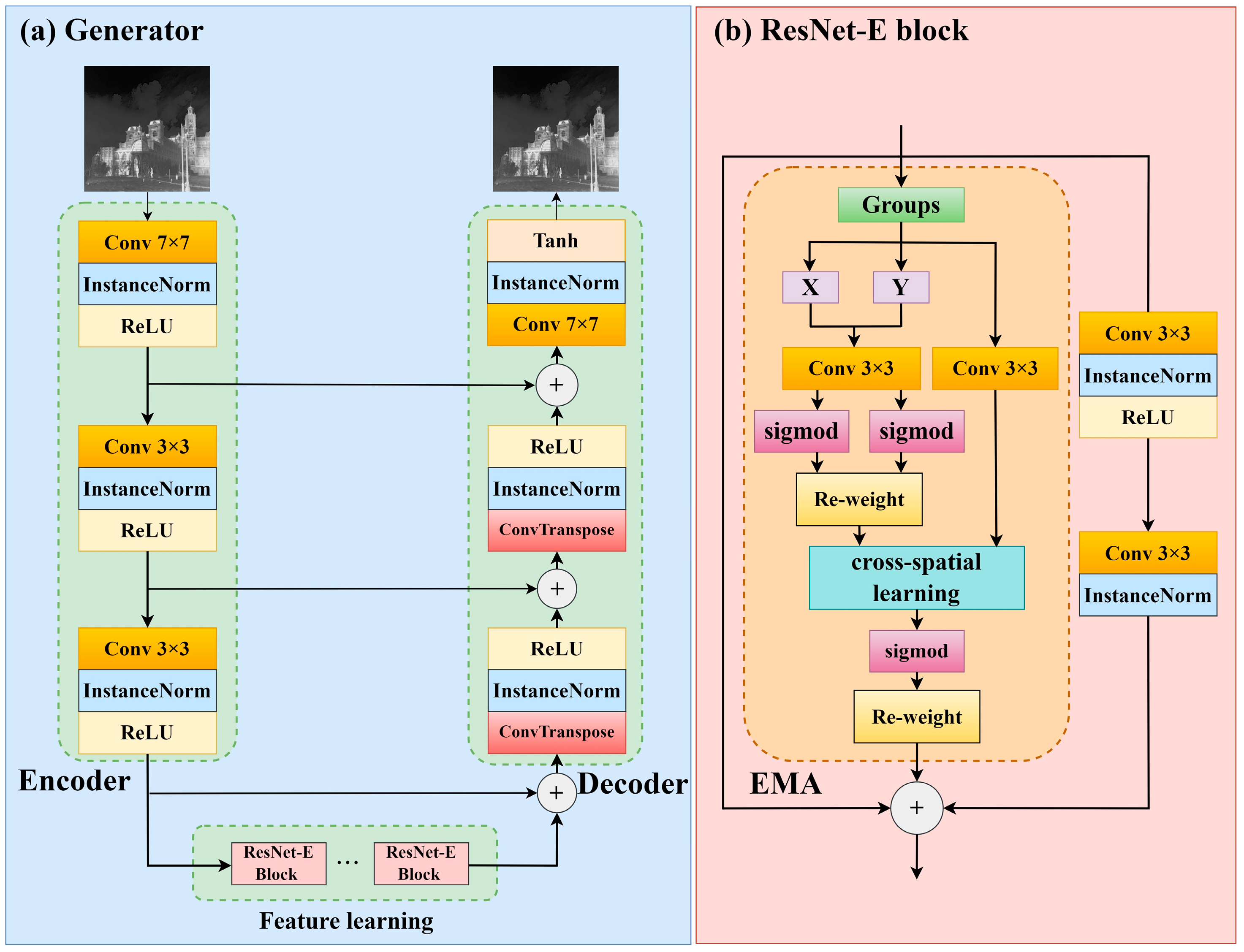
- By adding the EMA attention mechanism to the traditional residual module structure, a Resnet-E feature extraction module is proposed, and a generator is designed based on this module using the skip-connection structure, which improves the denoising performance of the network for mixed noises.
- (2)
- A new term containing PSNR loss calculation is added to the original cycle consistency loss function, which better ensures the consistency of the non-noise features between the input image and the output image, and thus improves the network’s ability to retain details when removing noise.
- (3)
- Experimental validation on both synthesized and real infrared noise image data demonstrates that our proposed improved network has excellent denoising effects for mixed noise of different intensities.
2. Methods
2.1. Mixed Noise in Infrared Image
2.2. Introduction of CycleGAN
2.3. Architecture of the Improved Network
2.4. Loss Functions
3. Experiments
3.1. Experiment Settings
3.2. Evaluating Indicator
3.3. Ablation Study
3.4. Comparison Test
3.5. Experiments on Practical Dataset
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, J.; Yang, J. Trends in infrared imaging detecting technology. In Proceedings of the Electro-Optical and Infrared Systems: Technology and Applications X, SPIE, Dresden, Germany, 23–24 September 2013; Volume 8896, pp. 292–304. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T. Analysis of the principle and application of infrared thermal imager. In Proceedings of the 14th Ningxia Young Scientists Forum on Petrochemical Topics, Ningxia, China, 24 July 2018; pp. 323–325. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lv, B.; Wu, J. Review on infrared imaging technology. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, B.; Guo, Z.; He, C.; Luo, S. Mini-infrared thermal imaging system image denoising with multi-head feature fusion and detail enhancement network. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 179, 111311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Luo, S.; He, C.; Wu, W.; Wu, H. Infrared thermal image denoising with symmetric multi-scale sampling network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 134, 104909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, B.; Dogra, A.; Agrawal, S.; Sohi, B.S.; Sharma, A. Image denoising review: From classical to state-of-the-art approaches. Inf. Fusion 2020, 55, 220–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, L.D. Mean, median and mode filtering of images. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2000, 456, 2995–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justusson, B.I. Median filtering: Statistical properties. In Two-Dimensional Digital Signal Prcessing II: Transforms and Median Filters; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 161–196. [Google Scholar]
- D’Haeyer, J.P.F. Gaussian filtering of images: A regularization approach. Signal Process. 1989, 18, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, C.; Manduchi, R. Bilateral filtering for gray and color images. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision (IEEE Cat. No. 98CH36271), Bombay, India, 7 January 1998; pp. 839–846. [Google Scholar]
- McClellan, J.; Parks, T. Eigenvalue and Eigenvector Decomposition of the Discrete Fourier Transform. IEEE Transactions on Audio and Electroacoustics 1972, 20, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisier, F.; Blu, T.; Unser, M. SURE-LET for orthonormal wavelet-domain video denoising. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2010, 20, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimha, M.; Peterson, A. On the computation of the discrete cosine transform. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1978, 26, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zuo, W.; Feng, X. Weighted Nuclear Norm Minimization with Application to Image Denoising. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2862–2869. [Google Scholar]
- Denis, L.; Dalsasso, E.; Tupin, F. A review of deep-learning techniques for SAR image restoration. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 411–414. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, F.; Xiang, W. Single infrared image stripe removal via deep multi-scale dense connection convolutional neural network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 121, 104008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Sui, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Gu, G. Single infrared image enhancement using a deep convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 2019, 332, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Qin, H.; Yuan, S.; Yan, X.; Rahmani, H. DestripeCycleGAN: Stripe Simulation CycleGAN for Unsupervised Infrared Image Destriping. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.09101. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Wu, H.; Cheng, L.; Luo, S. Infrared image denoising via adversarial learning with multi-level feature attention network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 128, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binbin, Y. An improved infrared image processing method based on adaptive threshold denoising. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2019, 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman Chowdhury, M.; Zhang, J.; Qin, J.; Lou, Y. Poisson image denoising based on fractional-order total variation. Inverse Probl. Imaging 2020, 14, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Nichols, E.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Smith, C.; Howard, S. A poisson-gaussian denoising dataset with real fluorescence microscopy images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11710–11718. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Module with Cross-Spatial Learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5802–5811. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Keleş, O.; Yιlmaz, M.A.; Tekalp, A.M.; Korkmaz, C.; Doğan, Z. On the Computation of PSNR for a Set of Images or Video. In Proceedings of the 2021 Picture Coding Symposium (PCS), Bristol, UK, 29 June–2 July 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Starovoytov, V.V.; Eldarova, E.E.; Iskakov, K.T. Comparative analysis of the SSIM index and the pearson coefficient as a criterion for image similarity. Eurasian J. Math. Comput. Appl. 2020, 8, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. FFDNet: Toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4608–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. Toward convolutional blind denoising of real photographs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 5–20 June 2019; pp. 1712–1722. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, S.; Barnes, N. Real image denoising with feature attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3155–3164. [Google Scholar]








| Item | Name |
|---|---|
| operating system | Windows11 |
| CPU | AMD Ryzen 9 5900X |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 |
| RAM | 32G |
| deep learning framework | PyTorch(1.13.1) |
| interpreter | Python(3.10) |
| cuda version | CUDA (11.7) |
| Group | Indicators | 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOL | PSNR | 37.443 | 37.811 | 38.575 | 38.776 |
| SSIM | 0.962 | 0.969 | 0.974 | 0.978 | |
| NOM | PSNR | 36.478 | 36.936 | 37.479 | 37.641 |
| SSIM | 0.952 | 0.958 | 0.967 | 0.973 | |
| NOH | PSNR | 34.431 | 35.182 | 35.818 | 36.026 |
| SSIM | 0.919 | 0.928 | 0.936 | 0.938 |
| Group | Base | Improved G + D | Lcycle | PSNR | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOL | √ | 37.443 | 0.962 | ||
| √ | √ | 38.213 | 0.966 | ||
| √ | √ | 38.006 | 0.968 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 38.575 | 0.974 | |
| NOM | √ | 36.478 | 0.952 | ||
| √ | √ | 37.224 | 0.956 | ||
| √ | √ | 37.107 | 0.961 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 37.479 | 0.967 | |
| NOH | √ | 34.431 | 0.919 | ||
| √ | √ | 35.751 | 0.926 | ||
| √ | √ | 35.632 | 0.931 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 35.818 | 0.936 |
| Algorithm | NOL | NOM | NOH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | |
| BM3D | 37.015 | 0.956 | 35.270 | 0.951 | 34.064 | 0.925 |
| DnCNN | 36.832 | 0.946 | 34.886 | 0.937 | 33.418 | 0.905 |
| FFDNet | 37.241 | 0.967 | 36.439 | 0.954 | 33.955 | 0.921 |
| CBDNet | 37.595 | 0.964 | 36.351 | 0.955 | 34.704 | 0.927 |
| RIDNet | 38.172 | 0.971 | 36.944 | 0.962 | 35.413 | 0.939 |
| Ours | 38.575 | 0.974 | 37.479 | 0.967 | 35.818 | 0.936 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X. Improved CycleGAN for Mixed Noise Removal in Infrared Images. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146122
Wang H, Yang X, Wang Z, Yang H, Wang J, Zhou X. Improved CycleGAN for Mixed Noise Removal in Infrared Images. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146122
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haoyu, Xuetong Yang, Ziming Wang, Haitao Yang, Jinyu Wang, and Xixuan Zhou. 2024. "Improved CycleGAN for Mixed Noise Removal in Infrared Images" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146122
APA StyleWang, H., Yang, X., Wang, Z., Yang, H., Wang, J., & Zhou, X. (2024). Improved CycleGAN for Mixed Noise Removal in Infrared Images. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146122






