Wobble Board Performance: A Practical and Useful Quantification in Balance Assessment
Abstract
Featured application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Data Handling
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DiStefano, L.J.; Clark, M.A.; Padua, D.A. Evidence supporting balance training in healthy individuals: A systemic review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 2718–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachman, A.; Kamieniarz, A.; Michalska, J.; Pawłowski, M.; Słomka, K.J.; Juras, G. Balance training programs in athletes–A systematic review. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 58, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nnodim, J.O.; Yung, R.L. Balance and its clinical assessment in older adults—A review. J. Geriatr. Med. Gerontol. 2015, 1, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim-Chiplis, P.K.; Talbot, L.A. Defining and measuring balance in adults. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2000, 1, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, C.A. Is there a clinical standing balance measurement appropriate for use in sports medicine? A review of the literature. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2003, 6, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanenko, Y.; Gurfinkel, V.S. Human postural control. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, G.C.; Fong, S.S.; Chung, J.W.; Chung, L.M.; Ma, A.W.; Macfarlane, D.J. Determinants of sport-specific postural control strategy and balance performance of amateur rugby players. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, V.; Burkett, B.; McKean, M. Six weeks of unsupervised WiiFit game play improves balance and gait speed in independent older adults aged 65–84 years. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2013, 16, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Noronha, M.; França, L.C.; Haupenthal, A.; Nunes, G.S. Intrinsic predictive factors for ankle sprain in active university students: A prospective study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 23, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, R.; Bahr, A. Incidence of acute volleyball injuries: A prospective cohort study of injury mechanisms and risk factors. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 1997, 7, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochefort, C.; Walters-Stewart, C.; Aglipay, M.; Barrowman, N.; Zemek, R.; Sveistrup, H. Self-reported balance status is not a reliable indicator of balance performance in adolescents at one-month post-concussion. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2017, 20, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontos, A.P.; Monti, K.; Eagle, S.R.; Thomasma, E.; Holland, C.L.; Thomas, D.; Bitzer, H.B.; Mucha, A.; Collins, M.W. Test–retest reliability of the Vestibular Ocular Motor Screening (VOMS) tool and modified Balance Error Scoring System (mBESS) in US military personnel. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2021, 24, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhe, A.; Fejer, R.; Walker, B. The test–retest reliability of centre of pressure measures in bipedal static task conditions–a systematic review of the literature. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muehlbauer, T.; Roth, R.; Mueller, S.; Granacher, U. Intra and intersession reliability of balance measures during one-leg standing in young adults. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 2228–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinzey, S.J.; Armstrong, C.W. The reliability of the star-excursion test in assessing dynamic balance. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1998, 27, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribble, P.A.; Hertel, J.; Plisky, P. Using the Star Excursion Balance Test to assess dynamic postural-control deficits and outcomes in lower extremity injury: A literature and systematic review. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 47, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, A.; Giancotti, G.F.; Fuchs, P.X.; Wagner, H.; Varalda, C.; Capranica, L.; Cortis, C. Dynamic balance evaluation: Reliability and validity of a computerized wobble board. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, A.; Fuchs, P.X.; De Maio, M.; Wagner, H.; Cortis, C. A novel approach to measuring wobble board performance in individuals with chronic ankle instability. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, A.; Hübscher, M.; Vogt, L.; Banzer, W.; Hänsel, F.; Pfeifer, K. Balance training for neuromuscular control and performance enhancement: A systematic review. J. Athl. Train. 2010, 45, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Mentiplay, B.F.; Pua, Y.H.; Bower, K.J. Reliability and validity of the Wii Balance Board for assessment of standing balance: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2018, 61, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Bentman, S. An investigation into the reliability and variability of wobble board performance in a healthy population using the SMARTwobble instrumented wobble board. Phys. Ther. Sport. 2014, 15, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.D.; Boser, Q.A.; Kumawat, A.S.; Agarwal, K.; Rouhani, H.; Vette, A.H. Design and evaluation of an instrumented wobble board for assessing and training dynamic seated balance. J. Biomech. Eng. 2018, 140, 041006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Brito Silva, P.; Oliveira, A.S.; Mrachacz-Kersting, N.; Laessoe, U.; Kersting, U.G. Strategies for equilibrium maintenance during single leg standing on a wobble board. Gait Posture 2016, 44, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizovska, L.; Janura, M.; Svoboda, Z.; Cerny, M.; Krohova, J.; Smondrk, M. Intra-and inter-session reliability of traditional and entropy-based variables describing stance on a wobble board. Med. Eng. Phys. 2017, 50, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholes, M.; Stadler, S.; Connell, D.; Barton, C.; Clarke, R.A.; Bryant, A.L.; Malliaras, P. Men with unilateral Achilles tendinopathy have impaired balance on the symptomatic side. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, A.; Giancotti, G.F.; Fuchs, P.X.; Wagner, H.; Varalda, C.; Cortis, C. Wobble board balance assessment in subjects with chronic ankle instability. Gait Posture 2019, 68, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, L.V. The meta-analysis of test validity studies: Some new approaches. In Test Validity, 1st ed.; Wainer, H., Braun, H.I., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; pp. 191–212. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A.P. Correlation. In Discovering Statistics Using SPSS, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2009; pp. 166–196. [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle, D.E.; Wiersma, W.; Jurs, S.G. Correlation: A measure of relationship, chapter 5. In Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences, 6th ed.; Houghton Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, J.; Taylor, P.J.; Hobbs, S.J. Digital filtering of three-dimensional lower extremity kinematics: An assessment. J. Hum. Kinet. 2013, 39, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.I. A concordance correlation coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.B.; Mrachacz-Kersting, N.; Oliveira, A.S.; Kersting, U.G. Effect of wobble board training on movement strategies to maintain equilibrium on unstable surfaces. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 58, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Rosen, A.B.; Brown, C.N. Functional performance tests identify lateral ankle sprain risk: A prospective pilot study in adolescent soccer players. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 2611–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikstrom, E.A.; Tillman, M.D.; Chmielewski, T.L.; Cauraugh, J.H.; Naugle, K.E.; Borsa, P.A. Dynamic postural control but not mechanical stability differs among those with and without chronic ankle instability. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, e137–e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Son, S.J.; Seeley, M.K.; Hopkins, J.T. Altered movement strategies during jump landing/cutting in patients with chronic ankle instability. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
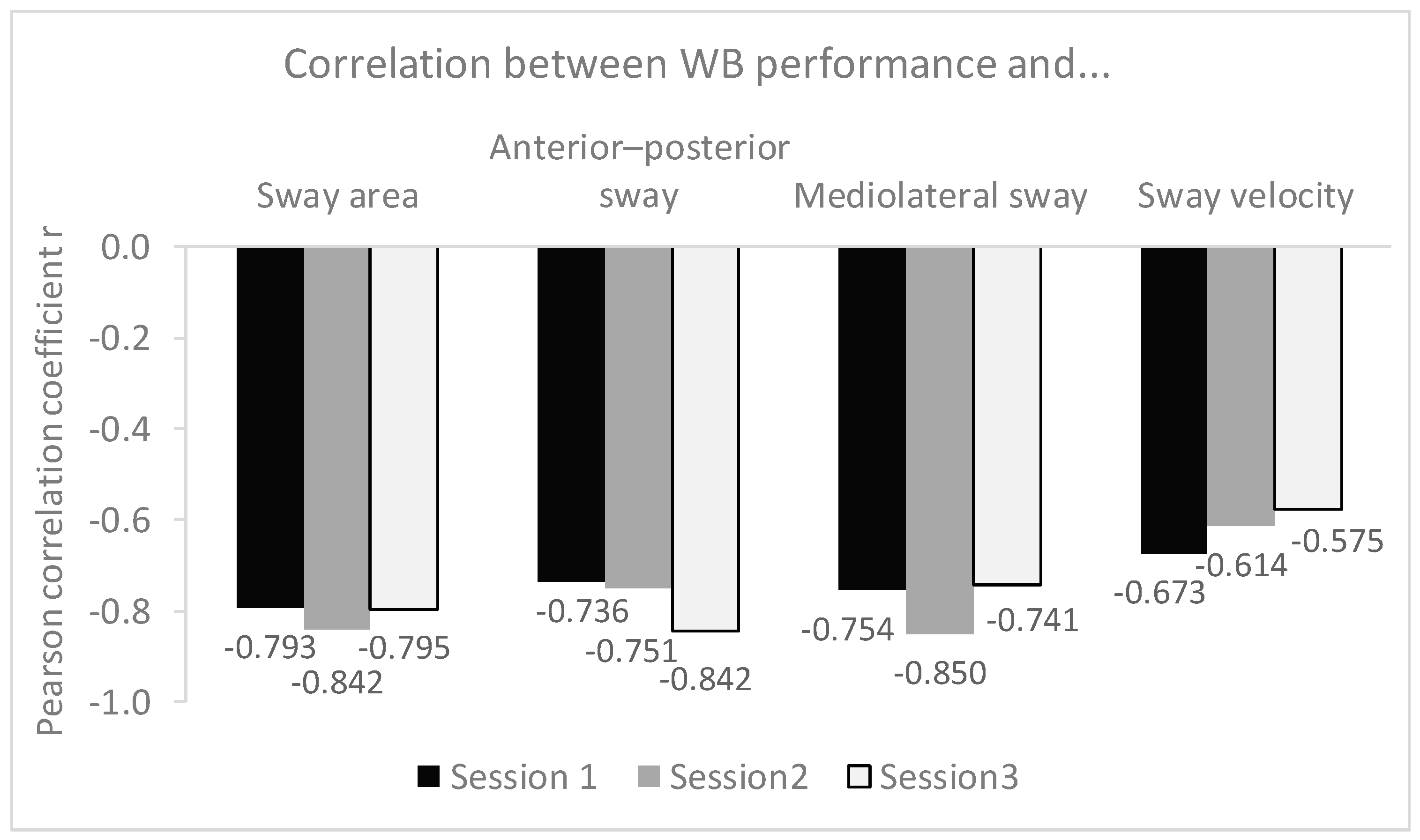

| WB [%] | AP [mm] | ML [mm] | Area [cm2] | V [mm·s−1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean ± SD | 36.58 ± 22.09 | 7.30 ± 1.91 $ 7.47 ± 1.32 # | 5.96 ± 1.11 $ 6.56 ± 0.80 # | 8.43 ± 3.41 $ 8.43 ± 2.74 # | 64.20 ± 9.26 $ 64.08 ± 6.06 # | |
| 95% CI | 23.08–48.08 | 6.22–8.38 $ 6.73–8.21 # | 5.33–6.59 $ 6.11–7.01 # | 6.50–10.36 $ 6.88–9.98 # | 58.96–69.44 $ 60.65–67.51 # | |
| WB | r | 1 | −0.842 | −0.714 | −0.795 | −0.575 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.051 | ||
| AP | r | 1 | 0.836 | 0.941 | 0.515 | |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.087 | |||
| ML | r | 1 | 0.969 | 0.500 | ||
| p | <0.001 | 0.098 | ||||
| Area | r | 1 | 0.510 | |||
| p | 0.090 | |||||
| V | r | 1 | ||||
| p | ||||||
| Polynomial Order | Sway Area | Anterior–Posterior Sway | Mediolateral Sway | Sway Velocity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 2 | 0.738 | 0.778 | 0.683 | 0.496 |
| 3 | 0.753 | 0.778 | 0.699 | 0.572 | |
| 4 | 0.781 | 0.817 | 0.706 | 0.634 | |
| 5 | 0.790 | 0.842 | 0.774 | 0.648 | |
| 6 | 0.802 | 0.843 | 0.799 | 0.648 | |
| Adjusted R2 | 2 | 0.713 | 0.757 | 0.653 | 0.448 |
| 3 | 0.716 | 0.745 | 0.654 | 0.508 | |
| 4 | 0.735 | 0.778 | 0.644 | 0.557 | |
| 5 | 0.731 | 0.798 | 0.711 | 0.550 | |
| 6 | 0.732 | 0.788 | 0.728 | 0.524 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuchs, P.X.; Fusco, A.; Shiang, T.-Y.; Cortis, C.; Wagner, H. Wobble Board Performance: A Practical and Useful Quantification in Balance Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146113
Fuchs PX, Fusco A, Shiang T-Y, Cortis C, Wagner H. Wobble Board Performance: A Practical and Useful Quantification in Balance Assessment. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146113
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuchs, Philip X., Andrea Fusco, Tzyy-Yuang Shiang, Cristina Cortis, and Herbert Wagner. 2024. "Wobble Board Performance: A Practical and Useful Quantification in Balance Assessment" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146113
APA StyleFuchs, P. X., Fusco, A., Shiang, T.-Y., Cortis, C., & Wagner, H. (2024). Wobble Board Performance: A Practical and Useful Quantification in Balance Assessment. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6113. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146113










