A Conceptual Model for Depicting the Relationships between Toluene Degradation and Fe(III) Reduction with Different Fe(III) Phases as Terminal Electron Acceptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Fe(III) Oxide
2.2. Inoculum Source
2.3. Anaerobic Incubation with Different Iron Oxides
2.4. Analytical Method
2.5. Data Statistical Processing
3. Results
3.1. The Relationship of Toluene over Time under Different Iron Mineral Conditions
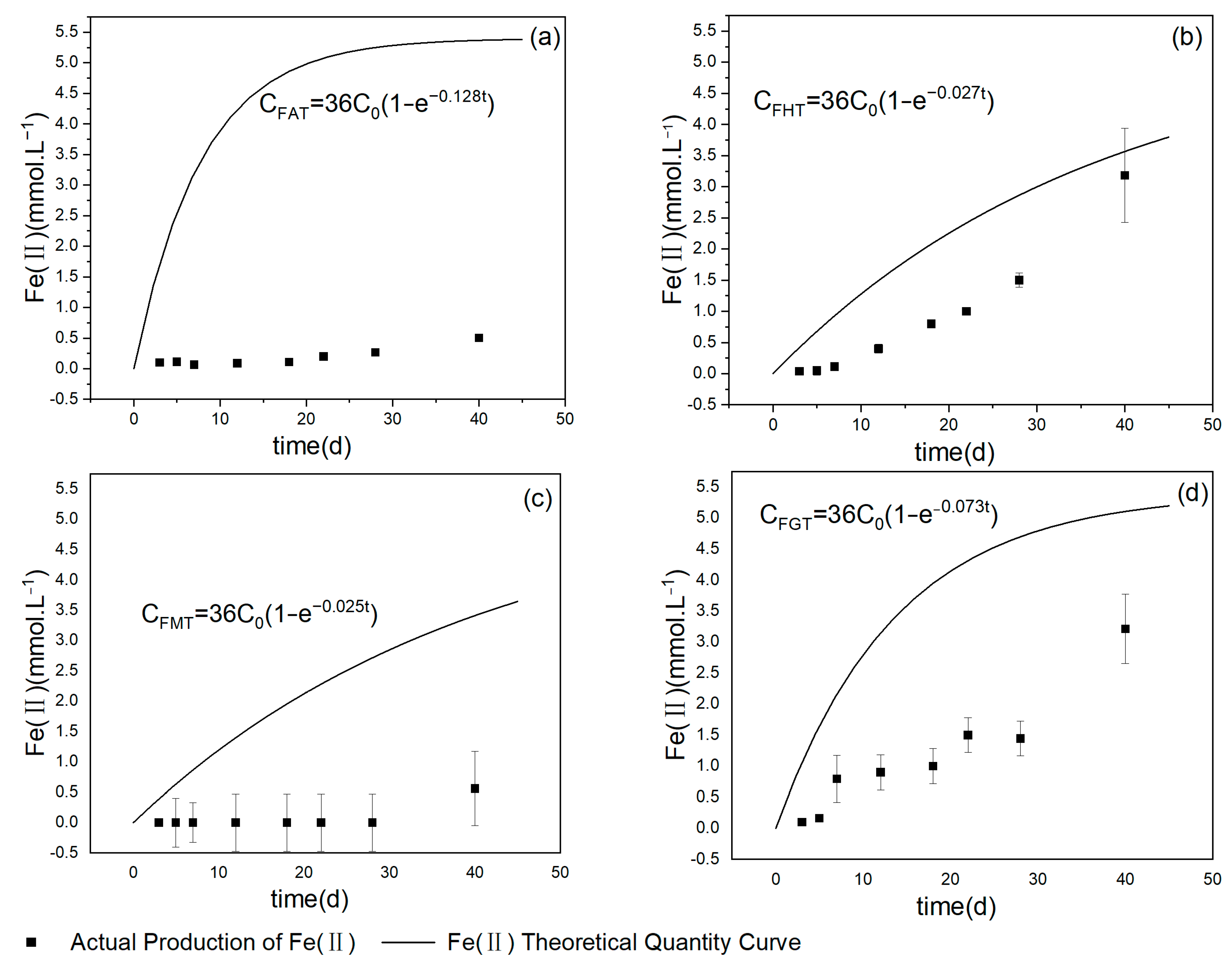
3.2. The Relationship of Ferrous Products over Time under Different Iron Mineral Conditions
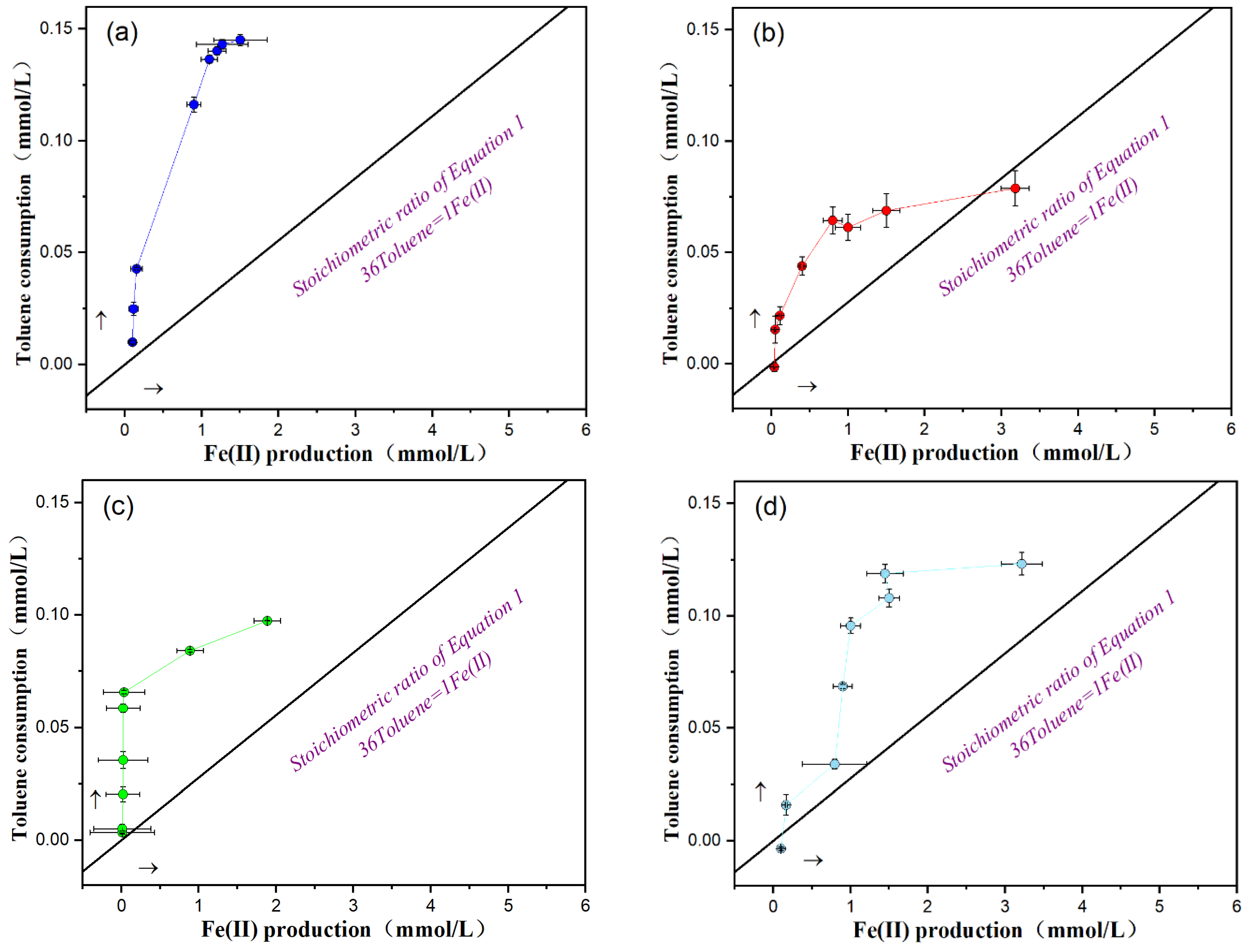
3.3. The Relationship between Toluene and Ferrous Products under Different Iron Mineral Conditions
4. Discussion
4.1. Toluene Degradation under Different Iron Mineral Conditions
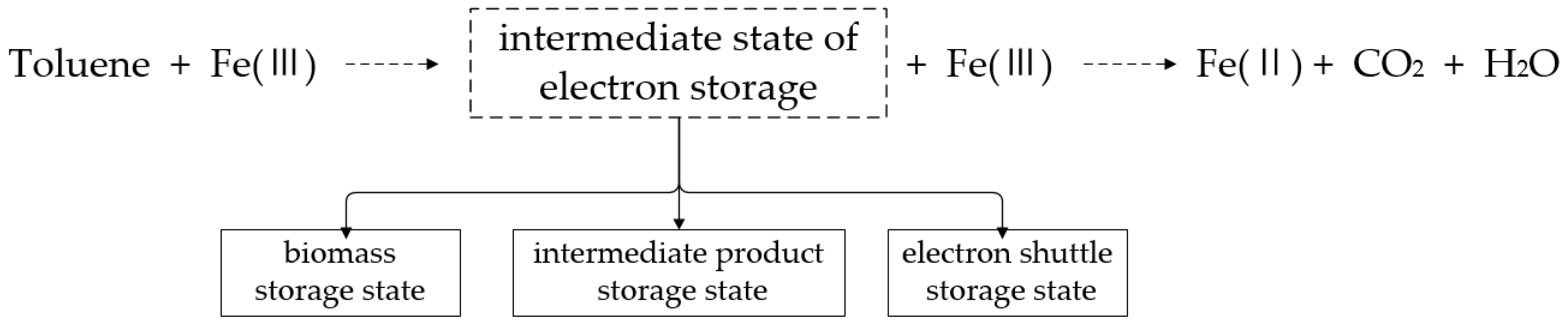
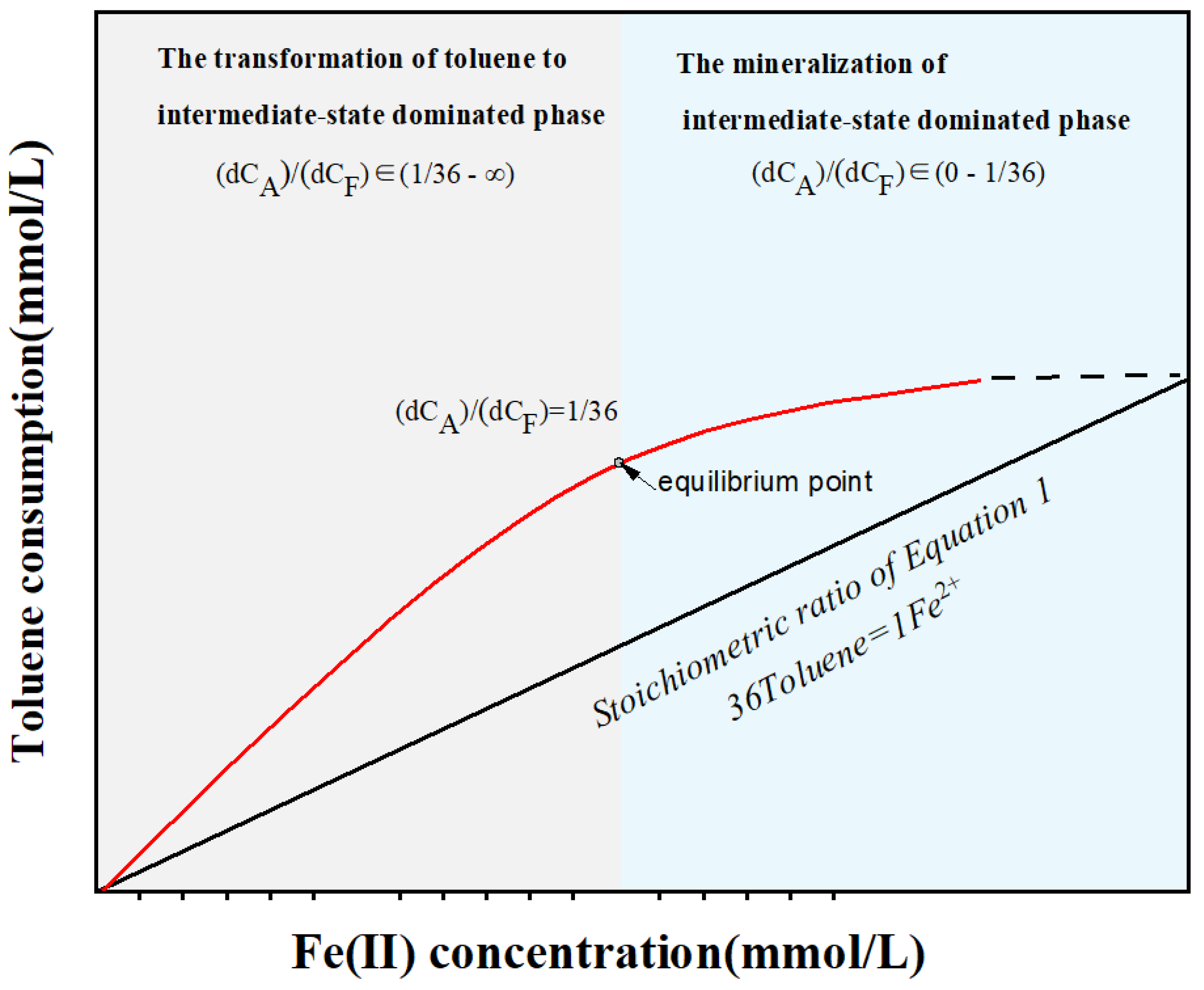
4.2. The Conceptual Model of the Interrelationship between Toluene Degradation and Iron Reduction Processes
4.3. Implication
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Chen, H.; He, J.; Liu, F.; Shen, Z.; Han, B.; Sun, J. Health-based risk assessment of contaminated sites: Principles and methods. Earth Sci. Front. 2006, 13, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. Analytical integration procedures for the derivation of risk-based generic assessment criteria for soil. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2010, 16, 1295–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, J.; Luo, F. Risk assessment of soil and groundwater for an organic chemical contaminated site. Soil 2013, 45, 933–939. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Zhang, J.; Luo, F. Health risk assessment of soil and groundwater for a typical organic chemical contaminated site in Southern China. Soils 2015, 47, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; He, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Yin, M.; Ning, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhen, S. Application research of enhanced in-situ micro-ecological remediation of petroleum contaminated soil. J. Groundwater Sci. Eng. 2016, 4, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhou, J.; Liang, P.; Su, Y. Characteristics-based classification research on typical petroleum contaminants of groundwater. J. Groundwater Sci. Eng. 2014, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.H.; Kjeldsen, P.; Bjerg, P.L.; Jensen, D.L.; Christensen, J.B.; Baun, A.; Albrechtsen, H.-J.; Heron, G. Biogeochemistry of landfill leachate plumes. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 659–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, P.J.J.; Illman, W.A. Bioremediation and Natural Attenuation: Process Fundamentals and Mathematical Models; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Spormann, A.M.; Widdel, F. Metabolism of alkylbenzenes, alkanes, and other hydrocarbons in anaerobic bacteria. Biodegradation 2000, 11, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdel, F.; Rabus, R. Anaerobic biodegradation of saturated and aromatic hydrocarbons. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Coates, J. Anaerobic degradation of monoaromatic hydrocarbons. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zeng, Q.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Yu, G.; Kappler, A. Coupled iron cycling and organic matter transformation across redox interfaces. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.; Schnell, S. Microbial Reduction Capacity of Various Iron Oxides in Pure Culture Experiment. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2001, 41, 745–749. [Google Scholar]
- Weelink, S.A.; Van Doesburg, W.; Saia, F.T.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Röling, W.F.; Smidt, H.; Stams, A.J. A strictly anaerobic betaproteobacterium Georgfuchsia toluolica gen. nov., sp. nov. degrades aromatic compounds with Fe (III), Mn (IV) or nitrate as an electron acceptor. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 70, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botton, S.; Van Harmelen, M.; Braster, M.; Parsons, J.R.; Röling, W.F. Dominance of Geobacteraceae in BTX-degrading enrichments from an iron-reducing aquifer. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 62, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, S.R.; Beller, H.R.; Legler, T.C.; Anderson, R.T. Biochemical and genetic evidence of benzylsuccinate synthase intoluene-degrading, ferric iron-reducing Geobacter metallireducens. Biodegradation 2002, 13, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zachara, J.M.; Wang, Z.; Shi, L.; Fredrickson, J.K. Reductive dissolution of goethite and hematite by reduced flavins. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 121, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pearce, C.I.; Shi, L.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Arenholz, E.; Rosso, K.M. Particle size effect and the mechanism of hematite reduction by the outer membrane cytochrome OmcA of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 193, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihe, S.H.; Mangayayam, M.; Sand, K.K.; Tobler, D.J. Hematite crystallization in the presence of organic matter: Impact on crystal properties and bacterial dissolution. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkadapu, R.K.; Zachara, J.M.; Smith, S.C.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Liu, C. Dissimilatory bacterial reduction of Al-substituted goethite in subsurface sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2913–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, A.R.; Yoshimura, M.; LaRowe, D.E.; Bird, L.J.; Amend, J.P.; Hashimoto, K.; Nealson, K.H.; Okamoto, A. In situ electrochemical enrichment and isolation of a magnetite-reducing bacterium from a high pH serpentinizing spring. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2272–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botton, S.; Parsons, J.R. Degradation of BTX by dissimilatory iron-reducing cultures. Biodegradation 2007, 18, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villatoro-Monzón, W.; Mesta-Howard, A.; Razo-Flores, E. Anaerobic biodegradation of BTEX using Mn (IV) and Fe (III) as alternative electron acceptors. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, S.J.; Cha, I.T.; Min, D.; Kim, J.S.; Chung, W.H.; Chae, J.C.; Jeon, C.O.; Rhee, S.K. Metabolic versatility of toluene-degrading, iron-reducing bacteria in tidal flat sediment, characterized by stable isotope probing-based metagenomic analysis. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankel, R.B.; Bazylinski, D.A. Biologically induced mineralization by bacteria. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2003, 54, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilloni, G.; von Netzer, F.; Engel, M.; Lueders, T. Electron acceptor-dependent identification of key anaerobic toluene degraders at a tar-oil-contaminated aquifer by Pyro-SIP. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, T.; Müller, A.; Igarashi, Y.; Conrad, R.; Friedrich, M.W. Identification of iron-reducing microorganisms in anoxic rice paddy soil by 13C-acetate probing. ISME J. 2010, 4, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobler, N.B.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Schwarzenbach, R.P. Carbon and hydrogen isotope fractionation during anaerobic toluene oxidation by Geobacter metallireducens with different Fe (III) phases as terminal electron acceptors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7786–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenhoff, A.A.M.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Schraa, G. Behaviour of toluene, benzene and naphthalene under anaerobic conditions in sediment columns. Biodegradation 1996, 7, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, h.c.U.; Cornell, R.M. Goethite. In Iron Oxides in the Laboratory; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lovley, D. Dissimilatory Fe(III)- and Mn(IV)-Reducing Prokaryotes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q.; Xun, S.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, C. Spectrophotometric Determination of lron Valency States with 1,10-Phenantbroline. Chin. J. Health Lab. Technol. 2000, 10, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borch, T.; Kretzschmar, R.; Kappler, A.; Cappellen, P.V.; Ginder-Vogel, M.; Voegelin, A.; Campbell, K. Biogeochemical redox processes and their impact on contaminant dynamics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlostathis, S.G.; Giraldo-Gomez, E. Kinetics of anaerobic treatment: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 21, 411–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J.D.; Woodward, J.; Allen, J.; Philp, P.; Lovley, D.R. Anaerobic degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and alkanes in petroleum-contaminated marine harbor sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3589–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L. Migration and Transformation of Typical Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics during the Crystal Phase Transformation of Ferrihydrite. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Krieger, C.J.; Beller, H.R.; Reinhard, M.; Spormann, A.M. Initial reactions in anaerobic oxidation of m-xylene by the denitrifying bacterium Azoarcus sp. strain T. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6403–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.-S.; Chen, J.-J.; Cheng, R.-F.; Min, Y.; Yu, H.-Q. Iron Cycle Tuned by Outer-Membrane Cytochromes of Dissimilatory Metal-Reducing Bacteria: Interfacial Dynamics and Mechanisms In Vitro. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 11424–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, S.; Huang, Z.; Liang, J. lmpacts of Soil Nutrients and Stoichiometry on Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency. J. Guangxi Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2022, 40, 376–387. [Google Scholar]
- Harwood, C.S.; Gerhard, B.; Heidrun, H.; Georg, F. Anaerobic metabolism of aromatic compounds via the benzoyl-CoA pathway. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 22, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, C.; Tang, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhuang, L. Mechanisms and Applications of Electron Shuttle-Mediated Extracellular Electron Transfer. Prog. Chem. 2015, 27, 1833. [Google Scholar]
- Leuthner, B.; Heider, J. Anaerobic toluene catabolism of Thauera aromatica: The bbs operon codes for enzymes of β oxidation of the intermediate benzylsuccinate. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutwein, C.; Heider, J. (R)-Benzylsuccinyl-CoA dehydrogenase of Thauera aromatica, an enzyme of the anaerobic toluene catabolic pathway. Arch. Microbiol. 2002, 178, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Horsten, S.; Lippert, M.L.; Geisselbrecht, Y.; Schühle, K.; Schall, I.; Essen, L.O.; Heider, J. Inactive pseudoenzyme subunits in heterotetrameric BbsCD, a novel short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase involved in anaerobic toluene degradation. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, G.; Boll, M.; Heider, J. Microbial degradation of aromatic compounds—From one strategy to four. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forkan, A.; Hasibullah, M.; Jannatul, F.; Nurul, A.M. Microbial Degradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbon. Bangladesh J. Microbiol. 2010, 27, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Das, N.; Chandran, P. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants: An overview. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 941810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varjani, S.J. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Dong, H.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Ni, S.; Zeng, Q.; Hu, J.; Coffin, E.; Zhao, S.; Sommer, A.J.; McCarrick, R.M.; et al. Lignin-enhanced reduction of structural Fe(III) in nontronite: Dual roles of lignin as electron shuttle and donor. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 307, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.W.; Paula, J.C.D.; Keeler, J. Atkins’ Physical Chemistry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]


| Components | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| Biotin | 2.0 |
| Folic acid | 2.0 |
| Pyridoxine HCL | 10.0 |
| Riboflavin | 5.0 |
| Thiamine | 5.0 |
| Nicotinic acid | 5.0 |
| Pantothenic acid | 5.0 |
| B-12 | 0.1 |
| p-Aminobenzoic acid | 5.0 |
| Thioctic acid | 5.0 |
| Components | Concentration (g/L) |
|---|---|
| Trisodium nitrilotriacetic acid | 1.5 |
| MgSO4. | 3 |
| MnSO4·H2O | 0.5 |
| NaCl | 1 |
| FeSO4·7H2O | 0.1 |
| CaCl2·2H2O | 0.1 |
| CoCl2·6H2O | 0.1 |
| ZnCl2 | 0.13 |
| CuSO4·5H2O | 0.01 |
| AIK(SO4)2·12H2O | 0.01 |
| H3BO3 | 0.01 |
| Na2MoO4 | 0.025 |
| NiCl2·6H2O | 0.024 |
| Na2WO4·2H2O | 0.025 |
| Group | First-Order Kinetic Equation | R2 | Reaction Rate Constant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amorphous iron hydroxide group | CAT = C0e−0.128t | 0.98 | 0.128 |
| Hematite group | CHT = C0e−0.027t | 0.97 | 0.027 |
| Magnetite group | CMT = C0e−0.025t | 0.99 | 0.025 |
| Goethite group | CGT = C0e−0.073t | 0.99 | 0.073 |
| Group | Time Periods with Slopes Greater than 1/36 | Time Periods with Slopes Approximately Equal to 1/36 | Time Periods with Slopes Less than 1/36 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amorphous iron hydroxide Group | 0–22 | 22–28 | 28–40 |
| Hematite Group | 0–12 | 12–28 | 28–40 |
| Magnetite Group | 0–22 | 22–28 | 28–40 |
| Goethite Needle Group | 0–18 | 18–22 | 22–40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di, H.; Zhang, M.; Ning, Z.; He, Z.; Liu, C.; Song, J. A Conceptual Model for Depicting the Relationships between Toluene Degradation and Fe(III) Reduction with Different Fe(III) Phases as Terminal Electron Acceptors. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125017
Di H, Zhang M, Ning Z, He Z, Liu C, Song J. A Conceptual Model for Depicting the Relationships between Toluene Degradation and Fe(III) Reduction with Different Fe(III) Phases as Terminal Electron Acceptors. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(12):5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125017
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi, He, Min Zhang, Zhuo Ning, Ze He, Changli Liu, and Jiajia Song. 2024. "A Conceptual Model for Depicting the Relationships between Toluene Degradation and Fe(III) Reduction with Different Fe(III) Phases as Terminal Electron Acceptors" Applied Sciences 14, no. 12: 5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125017
APA StyleDi, H., Zhang, M., Ning, Z., He, Z., Liu, C., & Song, J. (2024). A Conceptual Model for Depicting the Relationships between Toluene Degradation and Fe(III) Reduction with Different Fe(III) Phases as Terminal Electron Acceptors. Applied Sciences, 14(12), 5017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125017







