A Systemic Model for Resilience and Time Management in Healthcare Academia: Application in a Dental University Setting
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of the System’s Theoretical Base
2.1. Time Management Approaches and Techniques in Academia
2.2. The Timebooster Approach in Academic Time Management
3. Methodology of the Systemic Design of the Model
3.1. Modeling and Simulation
- The number of academic dentists embracing time management practices;
- The initial count of dentists integrating time management practices;
- The anticipated progression of dental personnel maturation, representing an increasing percentage of the total potential users of the time management philosophy;
- The average time needed for an academic professional to mature and adopt new time management practices.
- -
- Determining the timeframe for the complete dissemination of time management practices in academia;
- -
- Assessing the number of dentists within each subcategory, aiding in the planning of tailored educational support activities;
- -
- Identifying weaknesses in the dissemination of knowledge about time management;
- -
- Identifying and exploring factors influencing the spread of the Timebooster approach to time management.
3.2. Model Simulation
3.3. Model Execution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldsby, E.; Goldsby, M.; Neck, C.B.; Neck, C.P. Under Pressure: Time Management, Self-Leadership, and the Nurse Manager. Adm. Sci. 2020, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluck, W.F.; Kaufman, P.S.; Walleck, S. Strategic Management for Competitive Advantage. Harvard Business Review. July 1980. Available online: https://hbr.org/1980/07/strategic-management-for-competitive-advantage (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Symonds, M. The World Is VUCA—How Are You Going To Deal With It? Forbes. 1 March 2023. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/mattsymonds/2023/03/01/the-world-is-vuca--how-are-you-going-to-deal-with-it/?sh=4867982f255a (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Baldwin, S. Living in a VUCA World. 29 March 2022. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/living-vuca-world-scottbaldwin?trk=articles_directory (accessed on 30 March 2024).
- Hambrick, D.C.; Finkelstein, S.; Mooney, A. Executive Job Demands: New Insights for Explaining Strategic Decisions and Leader Behaviors. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2005, 30, 472–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.W. The Nature of Leadership: Introductory Considerations; Leadership Studies Program, Independent Sector: Washington, DC, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Judge, T.A.; Thoresen, C.J.; Bon, J.E.; Patton, G.K. The job satisfaction, job performance relationship a qualitative and quantitative review. Psychol. Bull. 2001, 127, 376–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, T.D.; Jackson, P.R.; Mullarkey, S.; Parker, S. The Demand-Control Model of Job Strain: A More Specific Test. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 1996, 69, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theorell, T.; Karasek, R.A. Current Issues Relating to Psychosocial Job Strain and Cardiovascular Disease. Res. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 1996, 1, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniadou, M. Leadership and Managerial Skills in Dentistry: Characteristics and Challenges Based on a Preliminary Case Study. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, M. Quality of Life and Satisfaction from Career and Work–Life Integration of Greek Dentists before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraio, C.; Bonaccorsi, A.; Simar, L. Rankings and University Performance: A Conditional Multidimensional Approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 244, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z.; Ahmad, S. An Empirical Study of Quality in Higher Education in Relation to Stakeholders’ Perspectives. J. Am. Sci. 2013, 9, 387–401. [Google Scholar]
- Condon, W.; Iverson, E.R.; Manduca, C.A.; Rutz, C.; Willett, G. Faculty Development and Student Learning: Assessing the Connections; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.; Kurzweil, M. Instructional Quality, Student Outcomes, and Institutional Finances; American Council on Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Available online: https://www.acenet.edu/Documents/Instructional-Quality-Student-Outcomes-and-Institutional-Finances.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Gewin, V. Has the ‘Great Resignation’ Hit Academia? 31 May 2022. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-022-01512-6 (accessed on 30 March 2024).
- Bass, R.; Eynon, B.; Gambino, L.M. The New Learning Compact: A Framework for Professional Learning and Educational Change. Every Learner Everywhere. 2019. Available online: https://www.everylearnersolve.com/asset/YAhR8dclZb0mzn4v2zXh (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Roy, S.; Edwards, M.A. NSF Fellows’ perceptions about incentives, research misconduct, and scientific integrity in STEM academia. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralka, S. Stochastic Frontier Analysis in Higher Education: A Systematic Review; CEPIE Working Papers 05/18; Technische Universität Dresden, Center of Public and International Economics (CEPIE): Dresden, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Aeon, B.; Faber, A.; Panaccio, A. Does time management work? A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ailamaki, A.; Gehrke, J. Time Management for New Faculty. Sigmod Rec. 2003, 32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillestad, S.G.; Berkowitz, E.N. Health Care Market Strategy: From Planning to Action; Jones and Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, P.; Sundheim, D. The 25 Best Time Management Tools and Techniques: How to Get More Done without Driving Yourself Crazy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniadou, M.; Mangoulia, P.; Myrianthefs, P. Quality of Life and Wellbeing Parameters of Academic Dental and Nursing Personnel vs. Quality of Services. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnadieu, G. L’Approche Systémique: De Quoi S’agit-il? Synthèse des Travaux du Groupe AFSCET; Diffusion de la pensée systémique; 2003; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ackoff, R.L.; Emery, F.E. On Purposeful Systems; Tavistock Publications: London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, E. Evaluating Research and Innovation Policy: A Systems World Needs Systems Evaluations’. Res. Eval. 2004, 13, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre, E.M.; Casani, F.; Sagarra, M. Defining Typologies of Universities through a DEA-MDS Analysis: An Institutional Characterization for Formative Evaluation Purposes. Res. Eval. 2018, 27, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.M. Complexity: The Emerging Science at the Edge of Order and Chaos; Simon and Schuster Paperbacks: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.C. Fifty Years of Systems Thinking for Management. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2009, 60, S24–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, A.J.; Hekkert, M.P. Systemic Instruments for Systemic Innovation Problems: A Framework for Policy Makers and Innovation Scholars. Sci. Public Policy 2012, 39, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagefors, C.; Lantz, B.; Rosén, P. Creating Short-Term Volume Flexibility in Healthcare Capacity Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covey, S. The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People; Fireside; Simon & Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J. Time Management 100 Success Secrets: The 100 Most Asked Questions on Skills, Tips, Training, Tools and Techniques for Effective Time Management; Lulu Publications: Morrisville, NC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Laredo, P. Revisiting the Third Mission of Universities: Toward a Renewed Categorization of University Activities? High. Educ. Policy 2007, 20, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterman, R. Attitudes count “soft skills” top list of what area employer’s desire. Sacramento Bee, 23 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemiparast, M.; Negarandeh, R.; Theofanidis, D. Exploring the barriers of utilizing theoretical knowledge in clinical settings: A qualitative study. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2019, 6, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizeshfar, F.; Rakhshan, M.; Shirazi, F.; Dokoohaki, R. The effect of time management education on critical care nurses’ prioritization: A randomized clinical trial. Acute Crit. Care 2022, 37, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metty, P.; Maglaras, L.; Amine Ferrag, M.; Almomani, I. Digitization of healthcare sector: A study on privacy and security concerns. ICT Express 2023, 9, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlongo, S.; Mbatha, K.; Ramatsetse, B.; Dlamini, R. Challenges, opportunities, and prospects of adopting and using smart digital technologies in learning environments: An iterative review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, T. Effective Time Management; The New Jersey Lawyer, Inc.: Trenton, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 14, p. A6. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, R.; Holmes, L. Business Faculty time management: Lessons learned from the trenches. Am. J. Bus. Educ. 2009, 2, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobis, M.; Tobis, I. Managing Multiple Projects; McGraw-Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, D. Who has time for success? Manag. Online 2005, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Borrás, S.; Edquist, C. Holistic Innovation Policy: Theoretical Foundations, Policy Problems, and Instrument Choices; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rigby, D.; Sutherland, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Embracing Agile. Harvard Business Review. May 2016. Available online: https://hbr.org/2016/05/embracing-agile (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Buljac-Samardzic, M.; Doekhie, K.D.; van Wijngaarden, J.D.H. Interventions to improve team effectiveness within health care: A systematic review of the past decade. Hum. Resour. Health 2020, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collie, R.; Holliman, A.; Martin, A. Adaptability, engagement and academic achievement at university. Educ. Psychol. 2016, 37, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, I. The Time Management Pocketbook, 6th ed.; Management Pocketbooks: Alresford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Acuity Training. 2022. Available online: https://www.acuitytraining.co.uk/news-tips/time-management-statistics-2022-research/ (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Porta, C.R.; Anderson, M.R.; Steele, S.R. Effective time management: Surgery, research, service, travel, fitness, and family. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2013, 26, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asana Team. The Eisenhower Matrix: How to Prioritize Your To-Do List. 29 January 2024. Available online: https://asana.com/resources/eisenhower-matrix (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Kennedy, D.R.; Porter, A.L. The Illusion of Urgency. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2022, 86, 8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, A.; Kane, M.J. Toward a Holistic Approach to Reducing Academic Procrastination With Classroom Interventions. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2022, 31, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, T. Management by Objectives, 2nd ed.; Jossey-Bass/Pfeiffer; The Pfeiffer Library, 1998; Volume 20, Available online: http://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://home.snu.edu/~jsmith/library/body/v20.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Coito, T.; Firme, B.; Martins, M.S.E.; Vieira, S.M.; Figueiredo, J.; Sousa, J.M.C. Intelligent Sensors for Real-Time Decision-Making. Automation 2021, 2, 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, S. Time Management for Academics—Forget about the Eisenhower Method. 2022. Available online: https://kamounlab.medium.com/time-management-for-academics-forgetabout-the-eisenhower-method-15b380ade0a8 (accessed on 20 March 2024). [CrossRef]
- Kuh, G.D.; O’Donnell, K.O.; Schneider, C.G. HIPs at ten. Chang. Mag. High. Learn. 2017, 49, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vught, F. Mission Diversity and Reputation in Higher Education. High. Educ. Policy 2008, 21, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, R.D. The Relationship between Self-Directed Informal Learning and the Career Development Process of Technology Users. Walden University ScholarWorks. Ph.D. Thesis, Walden University, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2007. Available online: https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1013&context=hodgkinson (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Kamushadze, T.; Martskvishvili, K.; Mestvirishvili, M.; Odilavadze, M. Does Perfectionism Lead to Well-Being? The Role of Flow and Personality Traits. Eur. J. Psychol. 2021, 17, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, M.M.; Swinson, R.P. When Perfect Isn’t Good Enough, 2nd ed.; New Harbinger: Oakland, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, H.; Firebaugh, C.; Zolnikov, T.; Wardlow, R.; Morgan, S.; Gordon, B. A Systematic Review on the Psychological Effects of Perfectionism and Accompanying Treatment. Psychology 2021, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, S.; Dehghani, M.; Lavasani, F.F.; Ashouri, A.; Mohamadi, L. The effectiveness of short-term dynamic/interpersonal group therapy on perfectionism; assessment of anxiety, depression and interpersonal problems. Res. Psychother. 2022, 25, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhaiem, M. Measurement and Determinants of Academic Research Efficiency: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Scientometrics 2017, 110, 581–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L. Challenges and Resilience-Building: A Narrative Inquiry Study on a Mid-Career Chinese EFL Teacher. Front. Psychol. Sec. Posit. Psychol. 2021, 12, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.A.; Topp, R.; Smith, C.E.; Cohen, M.Z.; Fahrenwald, N.; Zerwic, J.J.; Benefield, L.E.; Anderson, C.M.; Conn, V.S. Time management strategies for research productivity. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2013, 35, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, M. Application of the Humanities and Basic Principles of Coaching in the Health Sciences; Tsotras: Athens, Greece, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cissna, K. Self-Actualized Leadership: Exploring the Intersection of Inclusive Leadership and Workplace Spirituality at a Faith-Based Institution of Higher Education; Pepperdine University: Malibu, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Getman-Eraso, J.; Culkin, K. High-impact catalyst for success: ePortfolio integration in the first-year seminar. In Catalyst in Action: Case Studies of High-Impact ePortfolio Practice; Eynon, B., Gambino, L.M., Eds.; Stylus; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2018; pp. 32–49. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, A. Important Time Management Skills for Workplace Success. 16 December 2021. Available online: https://www.thebalancemoney.com/time-management-skills-2063776 (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Dweck, C. What Having a “Growth Mindset” Actually Means. Harvard Business Review. 13 January 2016. Available online: https://hbr.org/2016/01/what-having-a-growth-mindset-actually-means (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Schuman-Olivier, Z.; Trombka, M.; Lovas, D.A.; Brewer, J.A.; Vago, D.R.; Gawande, R.; Dunne, J.P.; Lazar, S.W.; Loucks, E.B.; Fulwiler, C. Mindfulness and Behavior Change. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2020, 28, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervaiz, S.; Li, G.; He, Q. The mechanism of goal-setting participation’s impact on employees’ proactive behavior, moderated mediation role of power distance. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, C. Fostering a Positive Workplace Culture: Impacts on Performance and Agility [Internet]. Human Resource Management—An Update. IntechOpen. 2023. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/1170791 (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Thorgren, S.; Wincent, J.; Sirén, C. The Influence of Passion and Work–Life Thoughts on Work Satisfaction. Hum. Resour. Dev. Q. 2013, 24, 469–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, S. 9 Ways to Handle Interruptions Like a Pro. 2011. Available online: http://www.lifehack.org/articles/lifehack/9-ways-to-handle-interruptions-like-a-pro.html (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Manz, C.C.; Manz, K.P. Taking time to consider time, work life, and spirituality: A case in point. J. Manag. Spiritual. Relig. 2017, 14, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folabit, N.E.; Reddy, S.; Jita, L.J. Understanding Delegated Administrative Tasks: Beyond Academics’ Professional Identities. Afr. J. Inter/Multidiscip. Stud. 2023, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James Jacob, W.; Xiong, W.; Ye, H. Professional development programmes at world-class universities. Palgrave Commun. 2015, 1, 15002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunder, V.; Mahalingam, S. An empirical investigation of implementing Lean Six Sigma in Higher Education Institutions. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2018, 35, 2157–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, C.; Eversley, S. Practicing the Equitable, Transformative Pedagogy We Preach. Inside Higher Ed. 15 August 2021. Available online: https://www.insidehighered.com/views/2021/08/16/academe-needs-structural-change-toward-more-equitable-pedagogy-opinion (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Kovačič Lukman, R.; Glavič, P. What are the key elements of a sustainable university? Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2007, 9, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.J.; Reingen, P.H. Social ties and word-of-mouth referral behavior. J. Consum. Res. 1987, 14, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.W. Applying diffusion of innovation theory to intervention development. Res. Soc. Work Pract. 2009, 19, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyilasy, G. Word of mouth: What we really know–and what we don’t. In Word of Mouth in the Real World; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 161–184. [Google Scholar]
- Hennig-Thurau, T.; Gwinner, K.P.; Walsh, G.; Gremler, D.D. Electronic word-of-mouth via consumer-opinion platforms: What motivates consumers to articulate themselves on the internet? J. Interact. Mark. 2004, 18, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincaid, L.; Figueroa, M.E.; Storey, D.; Underwood, C. A Socio-Ecological Model of Communication for Social and Behavioral Change. A Brief Summary. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. 2009. Available online: https://breakthroughactionandresearch.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/socio-ecological-model-of-communication-for-sbc.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Kincaid, D.L.; Figueroa, M.E. Communication for participatory development: Dialogue, action, and change. In Routledge Handbook of Applied Communication Research; Frey, L.R., Cissna, K.N., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 506–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.; Habib, R.; Hardisty, D.J. How to SHIFT Consumer Behaviors to be More Sustainable: A Literature Review and Guiding Framework. J. Mark. 2019, 83, 22–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, B.A.; Gelaw, Y.M.; Eyowas, F.A.; Bogale, T.W.; Aynalem, Z.B.; Guadie, H.A. “Time wasted by health professionals is time not invested in patients”: Time management practice and associated factors among health professionals at public hospitals in Bahir Dar, Ethiopia: A multicenter mixed method study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1159275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restivo, V.; Minutolo, G.; Battaglini, A.; Carli, A.; Capraro, M.; Gaeta, M.; Odone, A.; Trucchi, C.; Favaretti, C.; Vitale, F.; et al. Leadership Effectiveness in Healthcare Settings: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cross-Sectional and Before-After Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirinhos, G.; Cardoso, A.; Neves, M.; Silva, R.; Rêgo, R. Leadership Styles, Motivation, Communication and Reward Systems in Business Performance. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2023, 16, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benneworth, P.; Pinheiro, R.; Sánchez-Barrioluengo, M. One Size Does Not Fit All! New Perspectives on the University in the Social Knowledge Economy. Sci. Public Policy 2016, 43, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Mustric, F. Can I Have 5 Minutes of Your Time? Morgan James Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Macan, T.H. Time management training: Effects on time behaviours, attitudes, and job performance. J. Psychol. 1996, 130, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolthuis, R.K.; Lankhuizen, M.; Gilsing, V. A System Failure Framework for Innovation Policy Design. Technovation 2005, 25, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudatsou, M.; Stavropoulou, A.; Philalithis, A.; Koukouli, S. The Role of Empathy in Health and Social Care Professionals. Healthcare 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, K.T. Systems thinking and project management—Time to reunite. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 1993, 11, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamminga, S.J.; Emal, L.M.; Boschman, J.S.; Levasseur, A.; Thota, A.; Ruotsalainen, J.H.; Schelvis, R.M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, K.; van der Molen, H.F. Individual-level interventions for reducing occupational stress in healthcare workers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 5, CD002892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozeman, B.; Youtie, J.; Jung, J. Robotic Bureaucracy and Administrative Burden: What Are the Effects of Universities’ Computer Automated Research Grants Management Systems? Res. Policy 2020, 49, 103980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensfeldt, A.B.; Rahm, L. Automating Teacher Work? A History of the Politics of Automation and Artificial Intelligence in Education. Postdigit Sci. Educ. 2023, 5, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbuchulem, K.I.; Ogundipe, H.D.; Uwajeh, K. The future is yesterday: Automating the thought process, an impending assault on academic writing. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2023, 21, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bornman, J.; Louw, B. Leadership Development Strategies in Interprofessional Healthcare Collaboration: A Rapid Review. J. Healthc. Leadersh. 2023, 15, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, J.; Yaneth Rodríguez, D.; Zabala-Iturriagagoitia, J.M. The systemic approach as an instrument to evaluate higher education systems: Opportunities and challenges. Res. Eval. 2021, 30, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, T.; Stichweh, R. System theoretical perspectives on higher education policy and governance. In The Palgrave International Handbook of Higher Education Policy and Governance; Huisman, J., de Boer, H., Dill, D., Souto-Otero, M., Eds.; Palgrave MacMillan: London, UK, 2015; pp. 152–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalov, F.; Santandreu Calonge, D.; Gurrib, I. New Era of Artificial Intelligence in Education: Towards a Sustainable Multifaceted Revolution. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
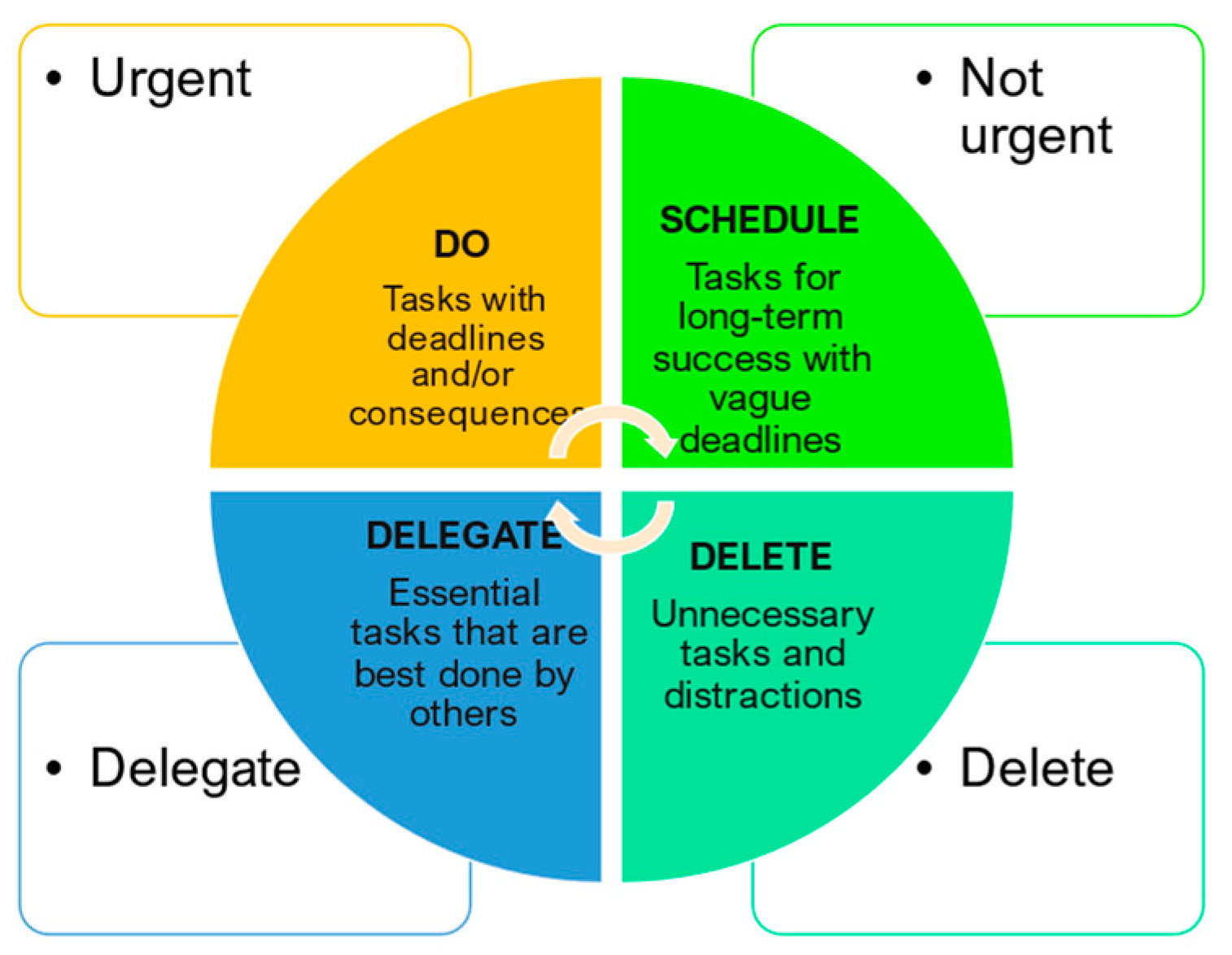
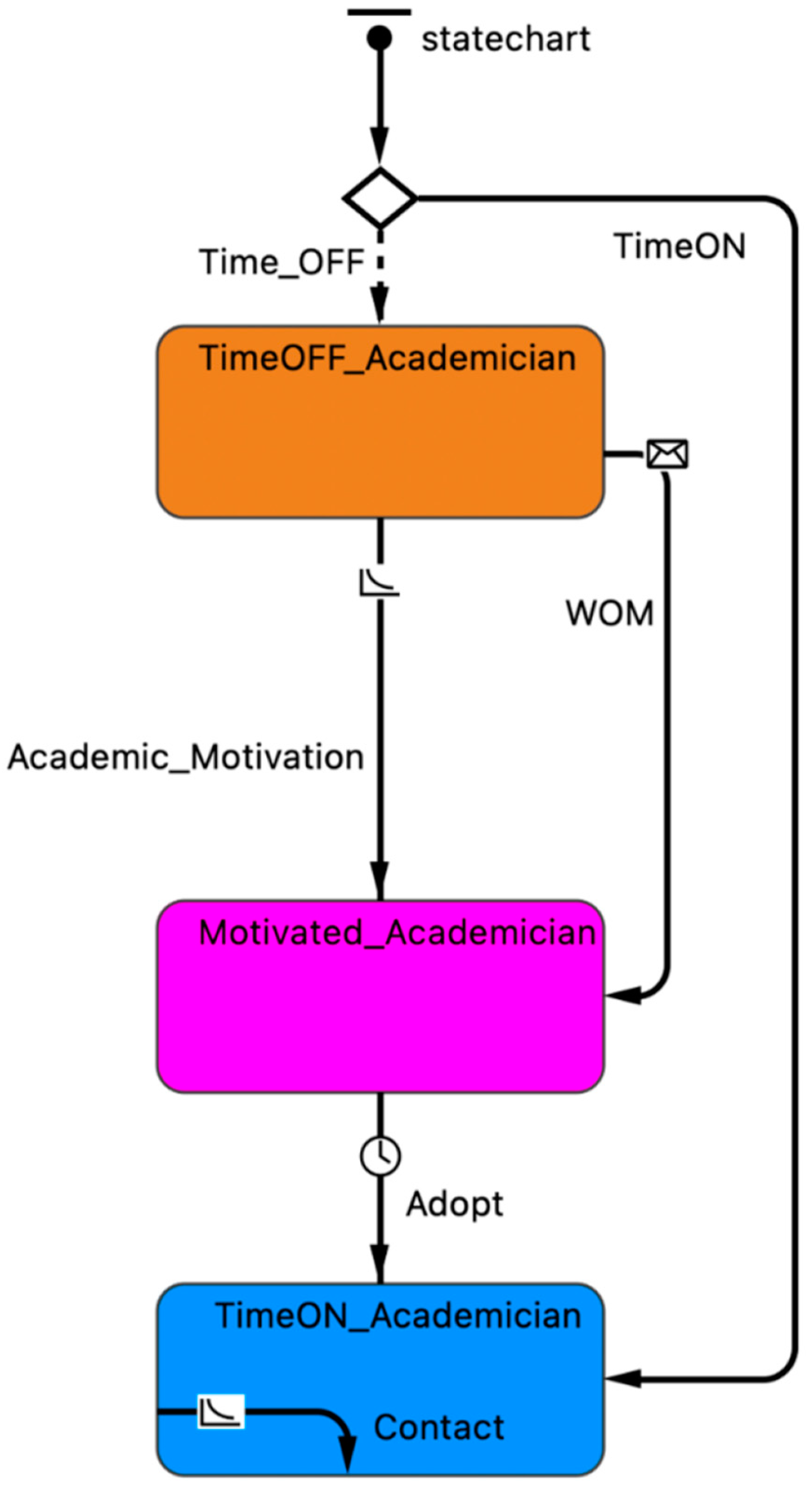

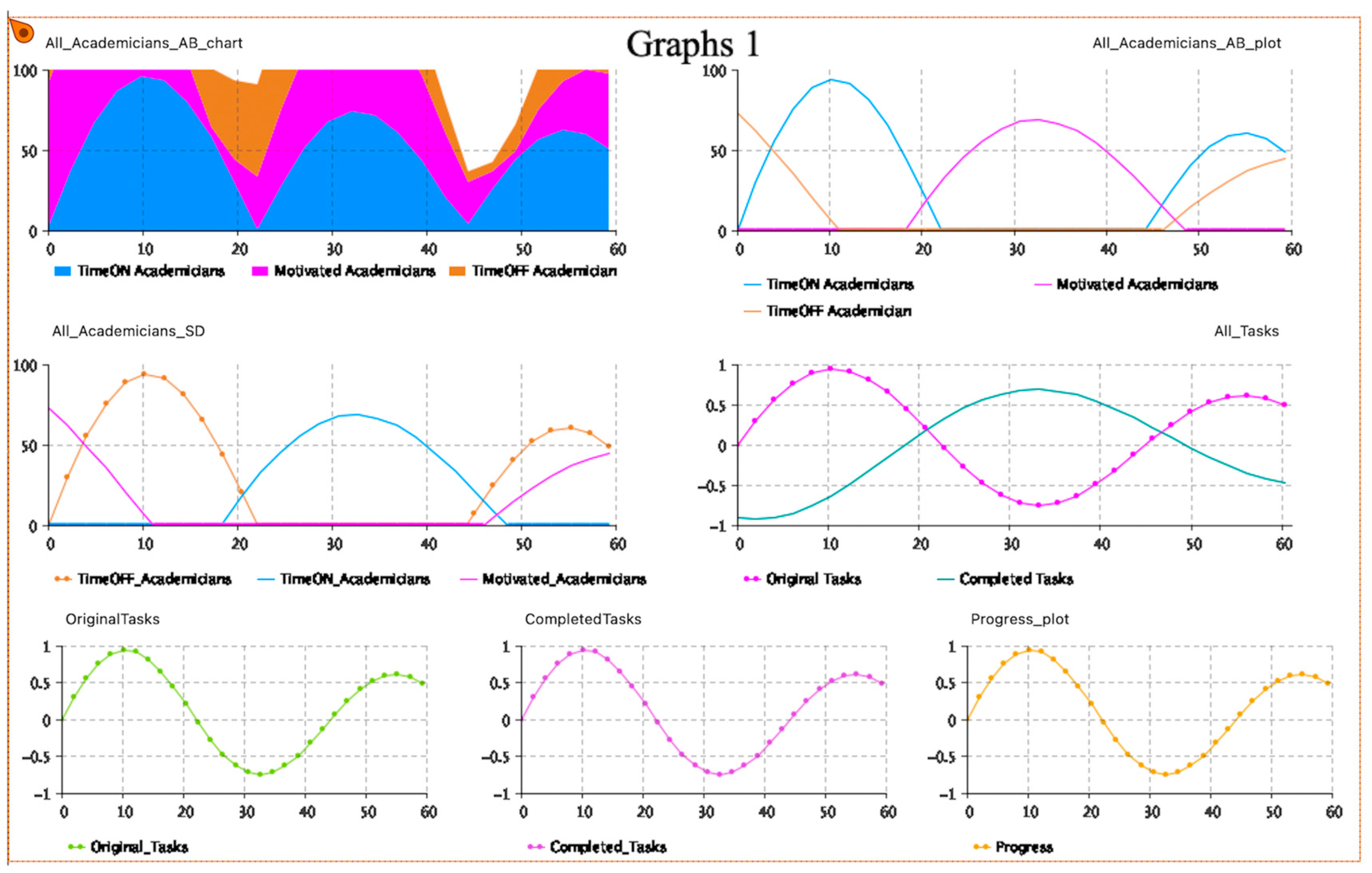
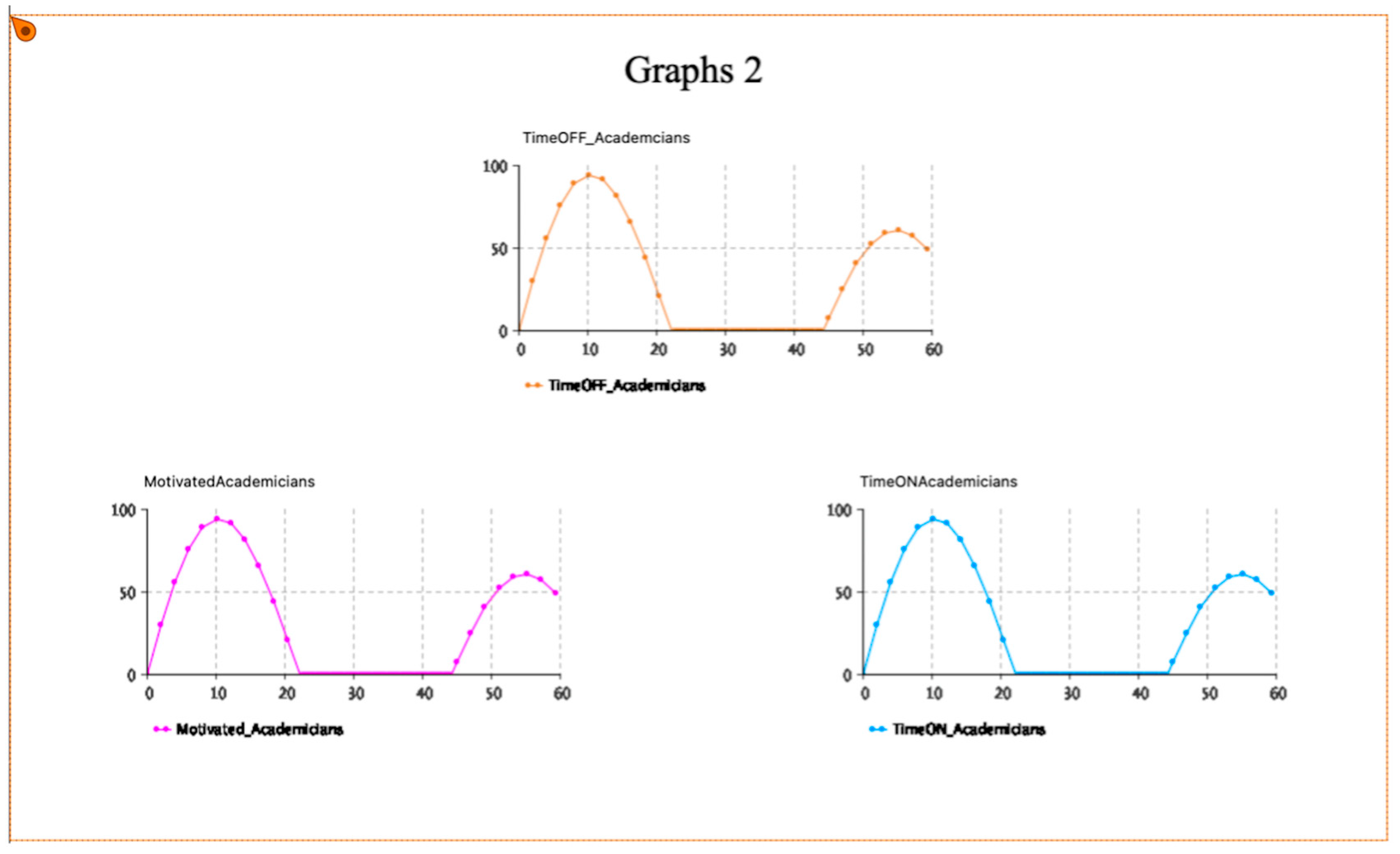
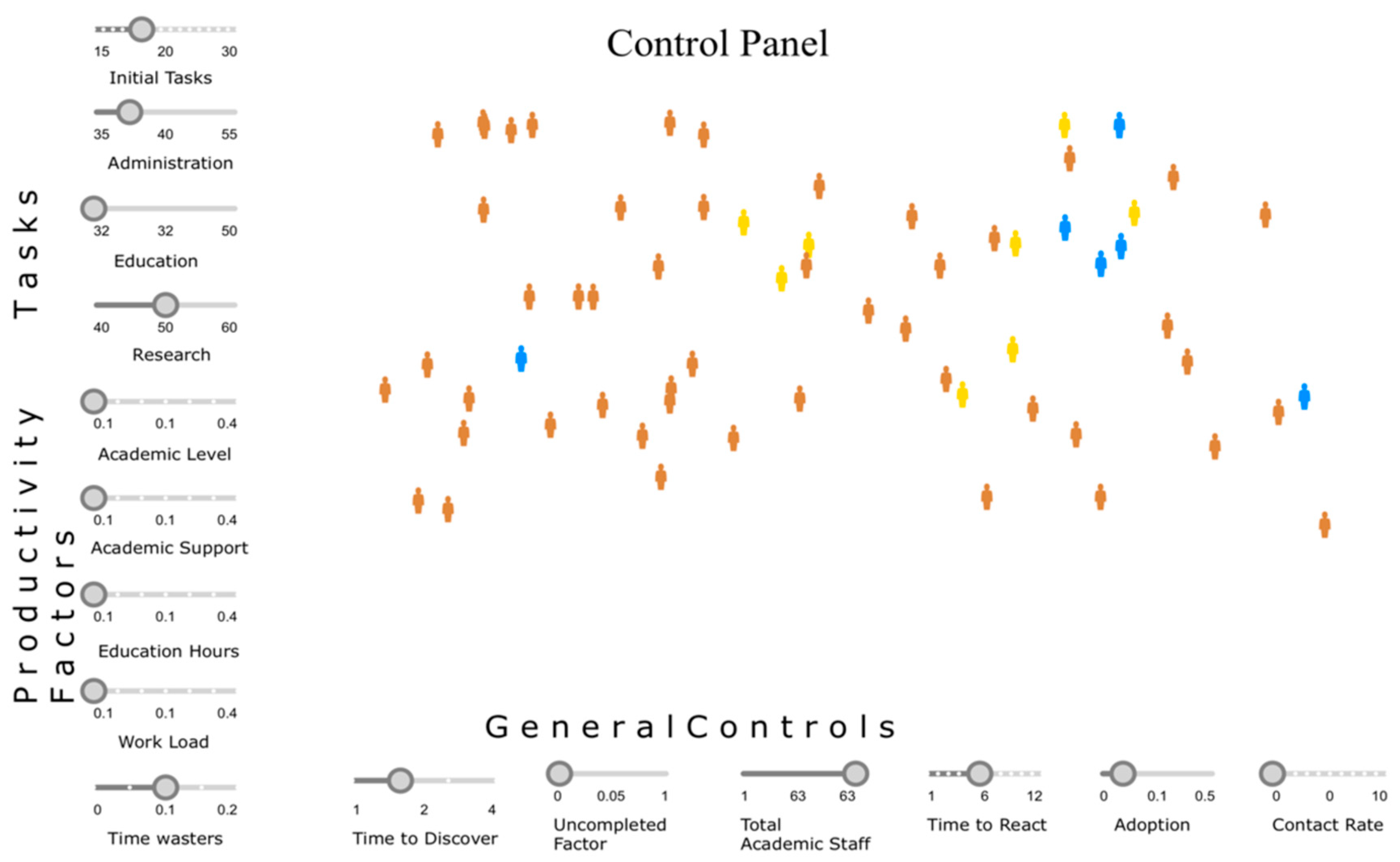
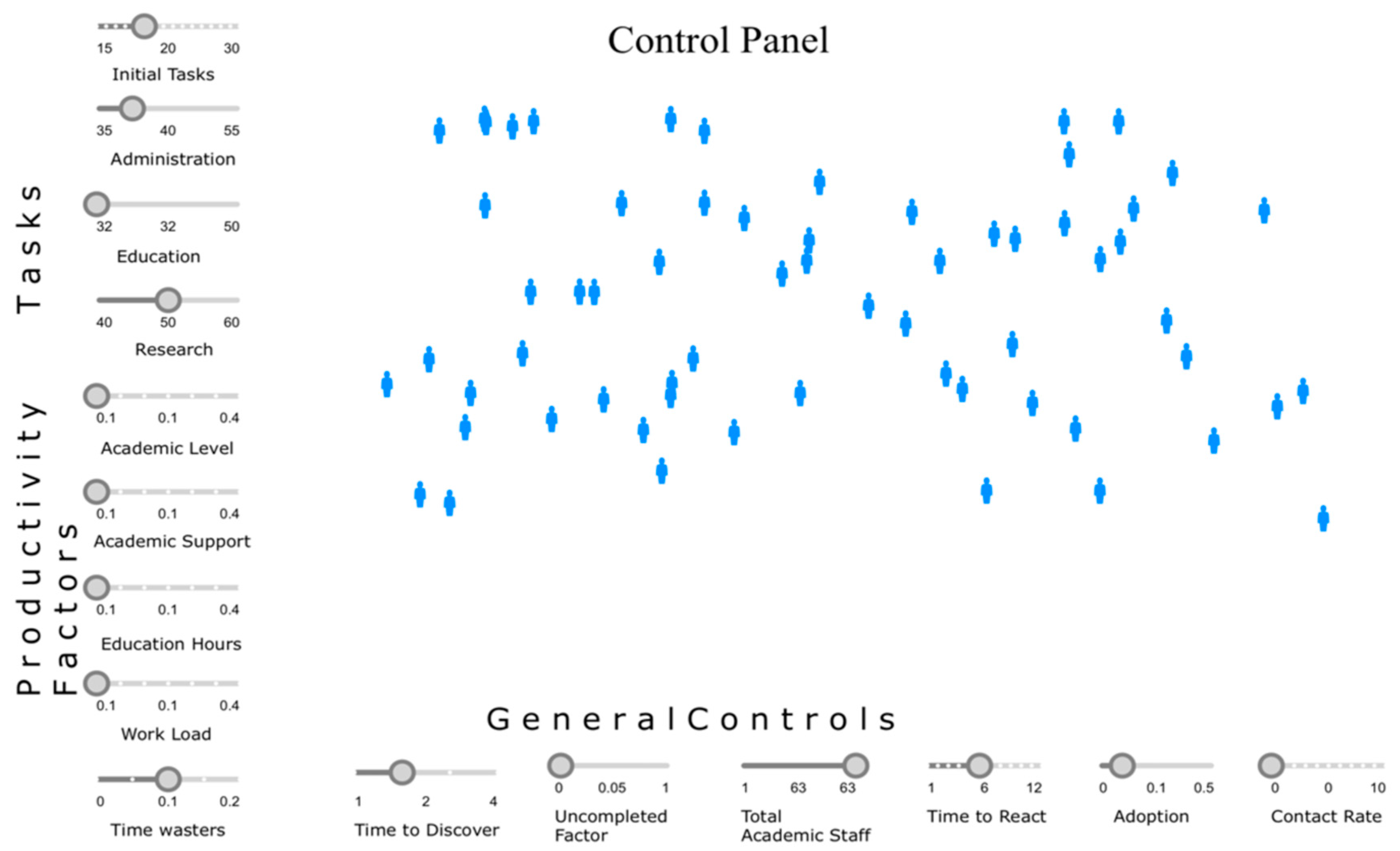
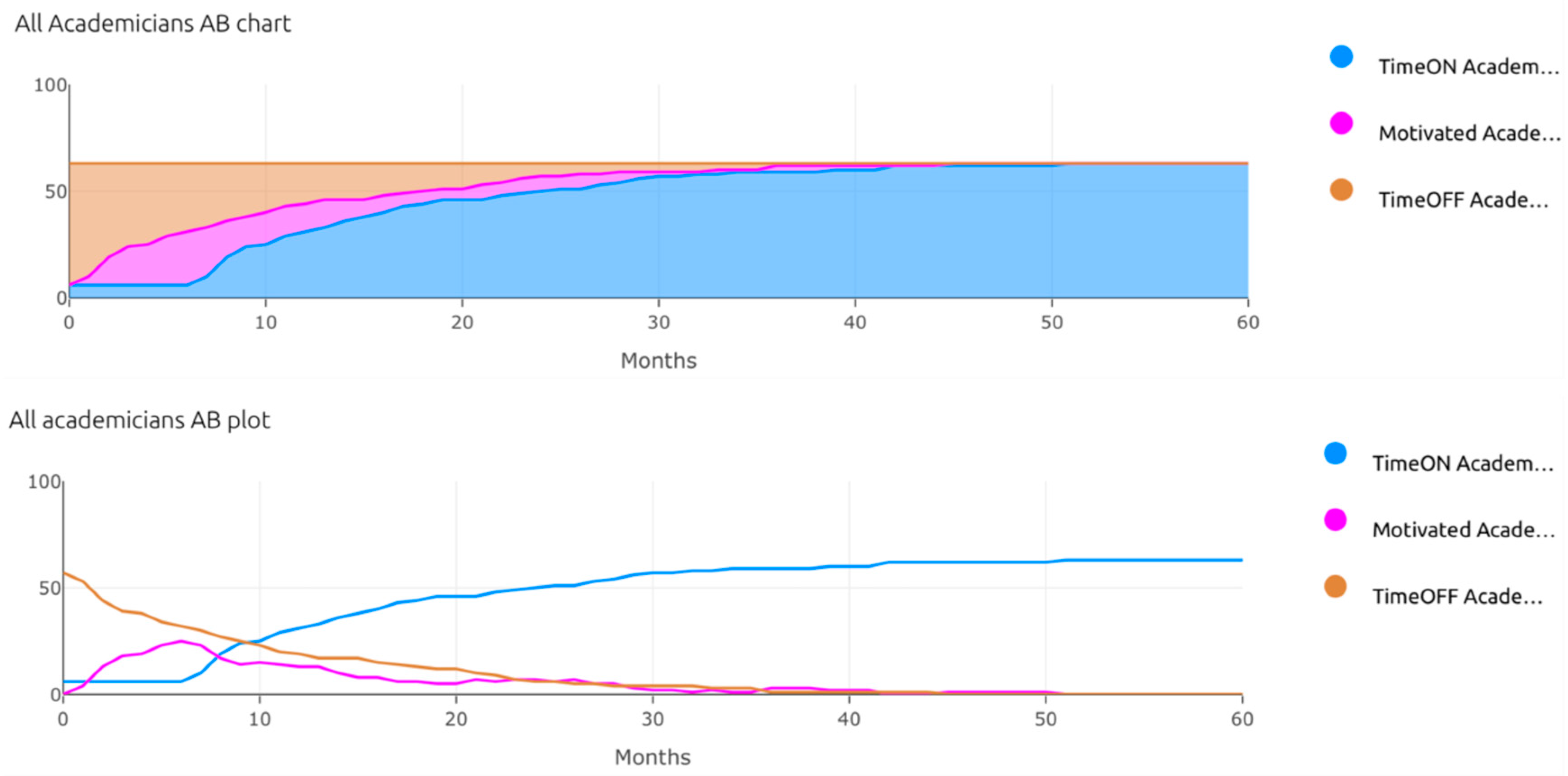
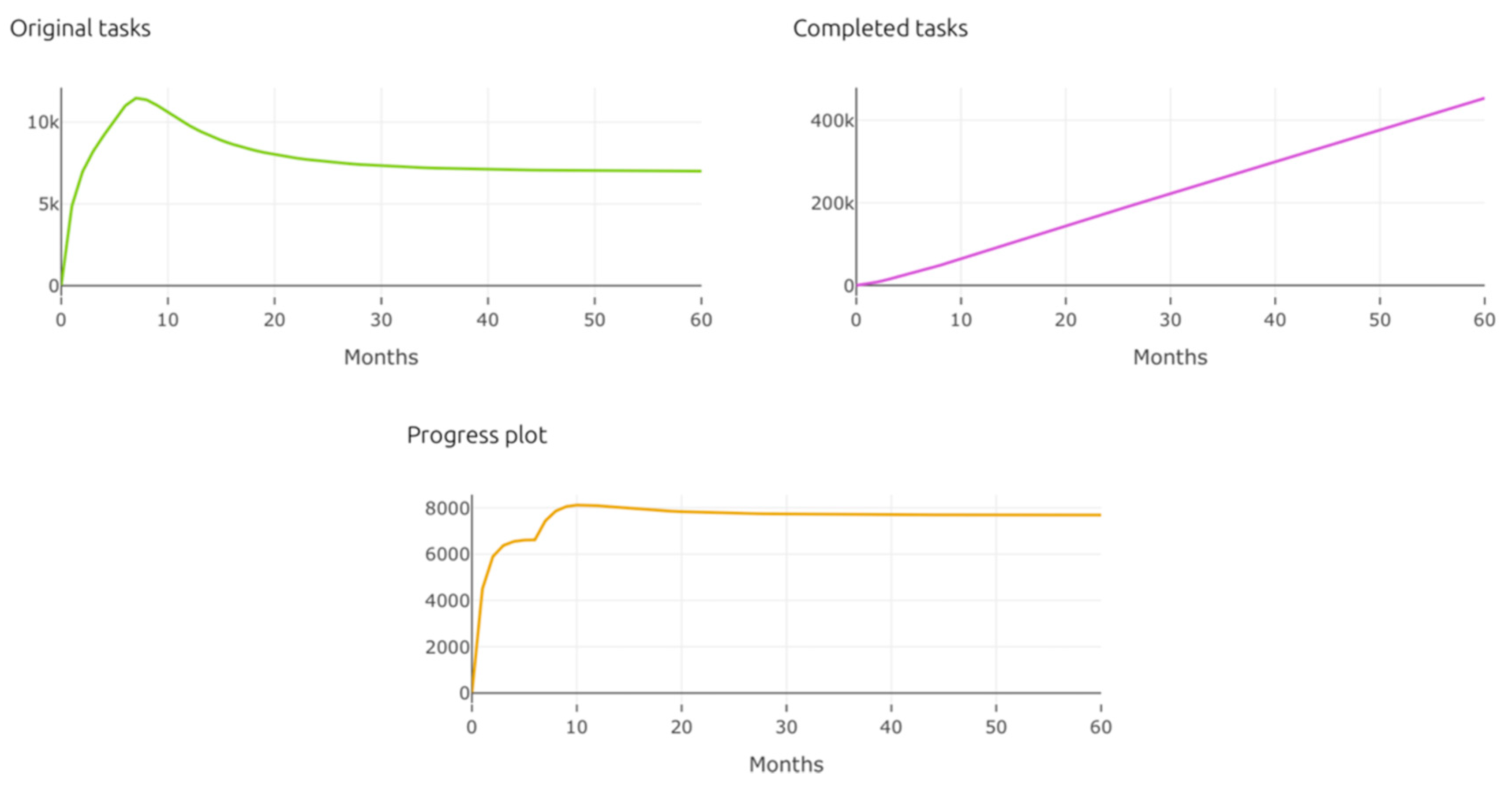
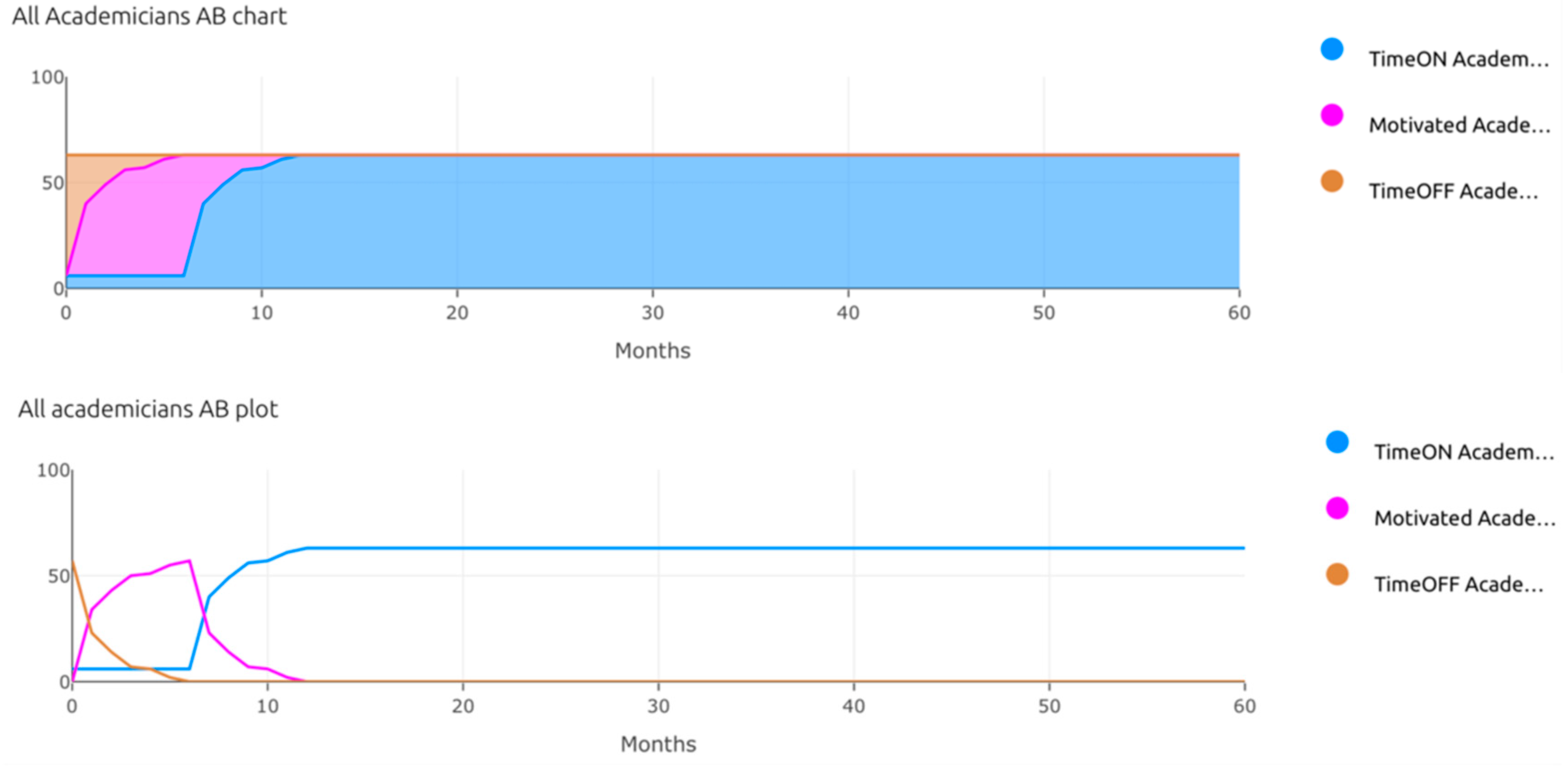
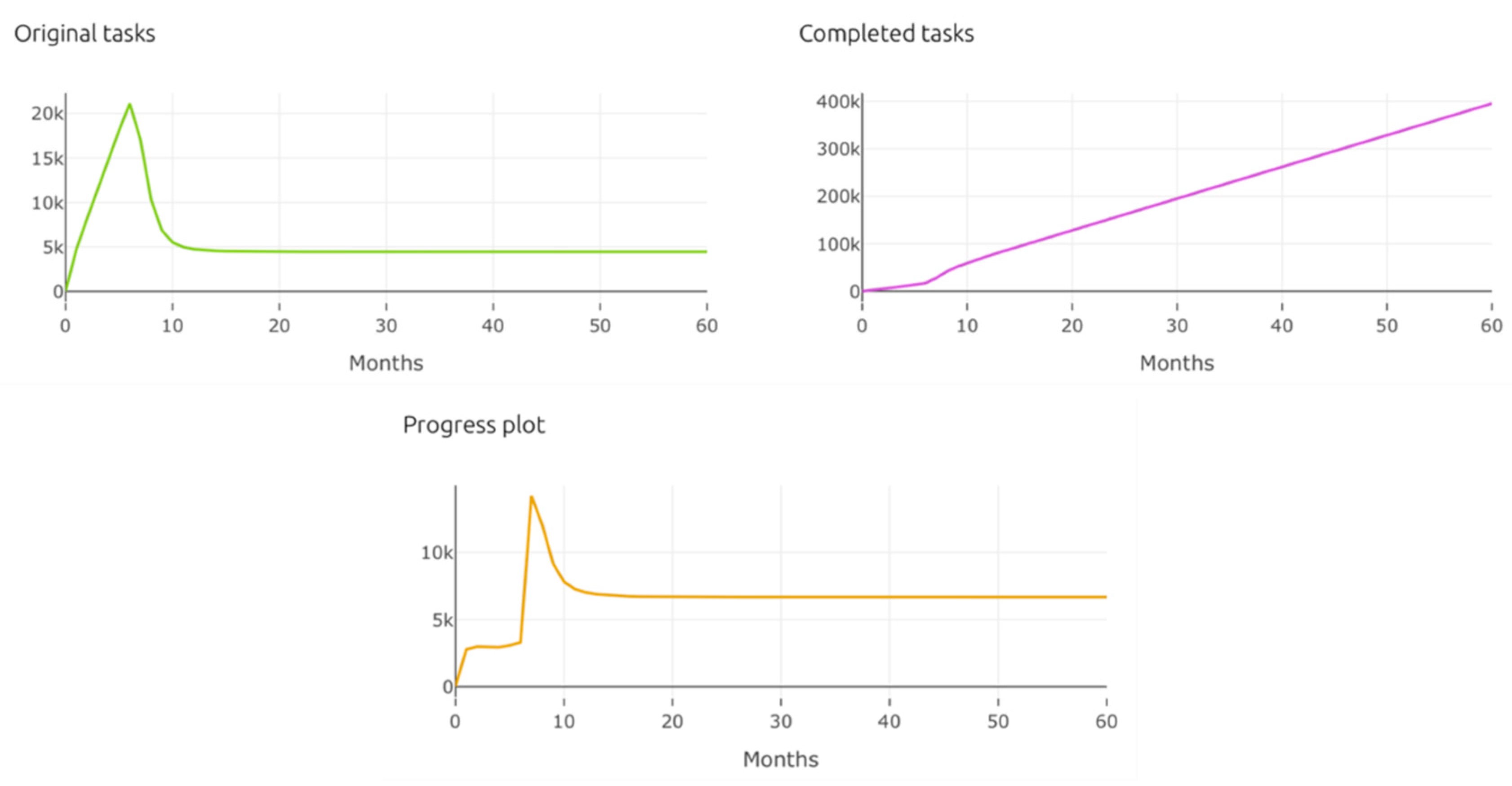
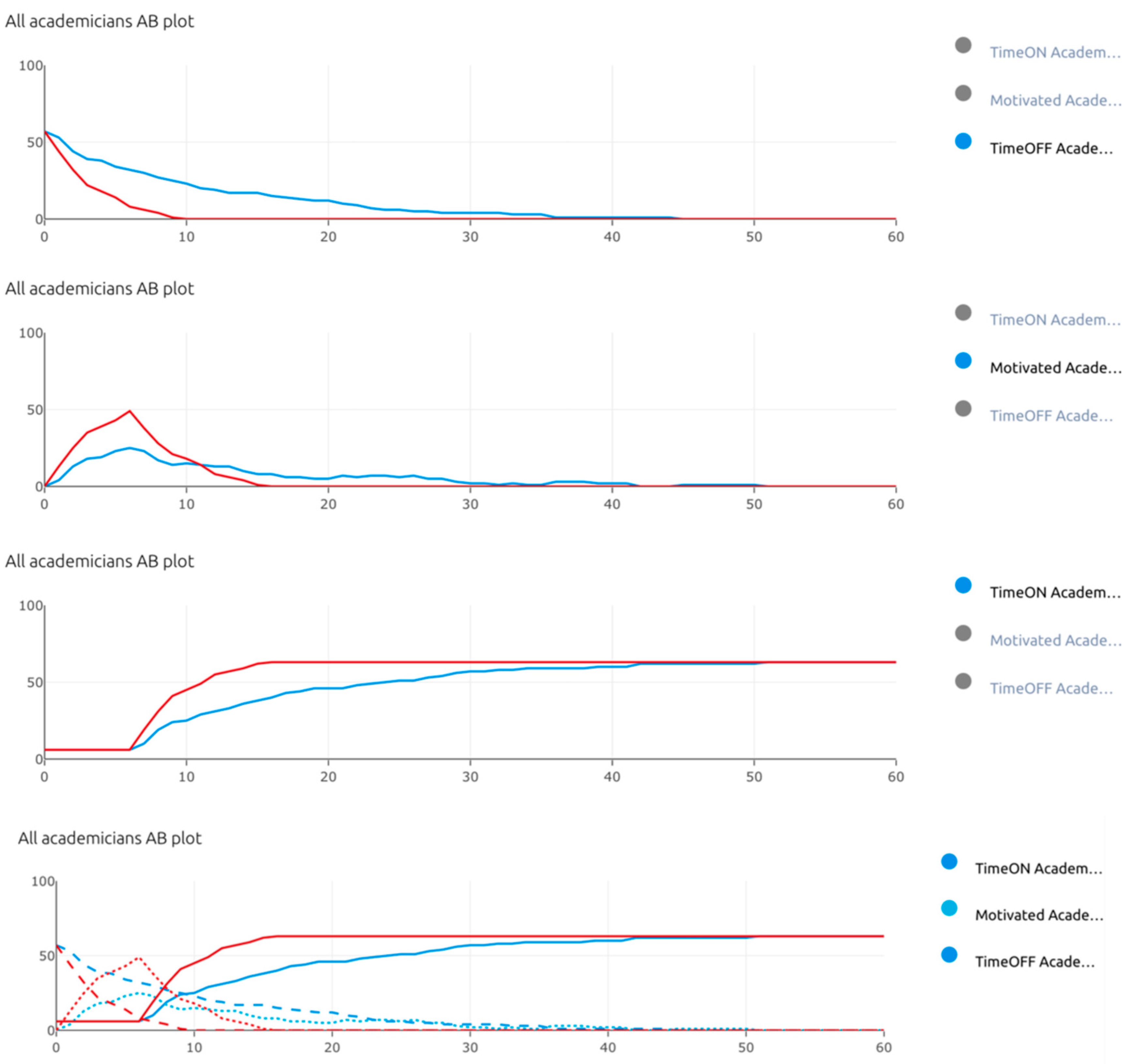
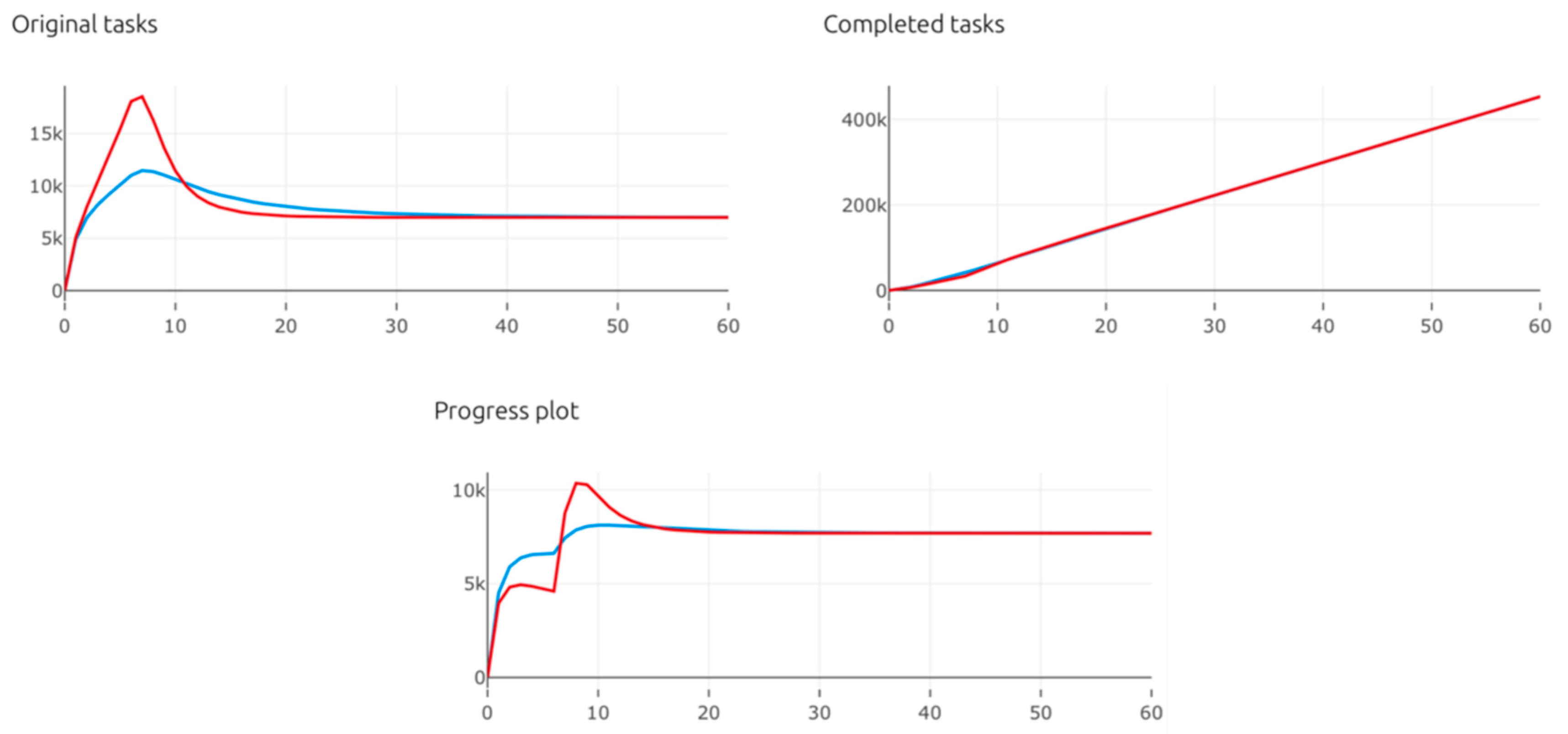
| Pillar | Tools for Time Management |
|---|---|
| Role definition and delegation | Manager–leader role: Academicians adopt a manager–leader mindset, focusing on high-impact tasks and delegating non-expertise tasks to others. Strategic delegation: Use strategic delegation to save time and optimize planning, assigning tasks that do not require specialized skills to support staff [10,72]. |
| Task prioritization | Eisenhower matrix: Use the Eisenhower matrix to categorize tasks as urgent and important, not urgent but important, urgent but not important, and not urgent and not important [54,55]. Career evolution focus: Prioritize tasks that align with career goals and professional development [1,55,73,74,75]. |
| Time management techniques | Time blocking: Allocate specific time blocks for focused work on important tasks, minimizing interruptions [83]. Efficient documentation: Utilize efficient documentation tools to streamline administrative tasks and reduce time spent on paperwork [83]. |
| Motivation and well-being | Incorporate enjoyable tasks: Infuse enjoyable activities into daily routines to sustain motivation and enhance well-being [73,74,75]. Minimize interruptions: Set boundaries for interaction time to preserve personal energy and improve focus [81]. |
| Addressing common timewasters | Perfectionism, procrastination, seeking no help, and keeping control: Recognize and manage perfectionistic tendencies and procrastination, start seeking help, and let go of constant control to enhance productivity [61,62,63,64,82]. Spiritual perspective: bring joy in academic pursuits and detach from results to maintain a healthy work–life balance [82]. |
| Professional development and education | Continuous professional development: Engage in ongoing professional development to stay current and improve skills [83,84,85,86,87]. Time management education: Integrate time management education into academic training programs to propagate efficient practices [83]. |
| Technological integration | Educational technology: Utilize educational technology to streamline teaching and research activities [83]. Collaborative research tools: Employ collaborative tools to facilitate teamwork and enhance research productivity [83,84,85,86,87]. |
| Health and well-being strategies | Mindfulness practices: Incorporate mindfulness practices to reduce stress and improve focus [83,84,85,86,87]. Professional development programs: Implement professional development programs and waste reduction initiatives to foster resilience and well-being [87]. |
| Implementation and evaluation | Process improvement programs: Gradually implement process improvement programs to ensure a balanced approach and maintain educational quality [84]. Regular evaluation: Continuously evaluate and adjust the model based on feedback and changing needs to sustain academic performance and well-being [85,86,87]. |
| Settings and Values | |
| Setting | Value |
| INITIAL TIME | 0 months |
| FINAL TIME | 60 months (simulation time = 5 years) |
| Time Unit | 1 month |
| Stocks and Explanations | |
| Stock | Explanation |
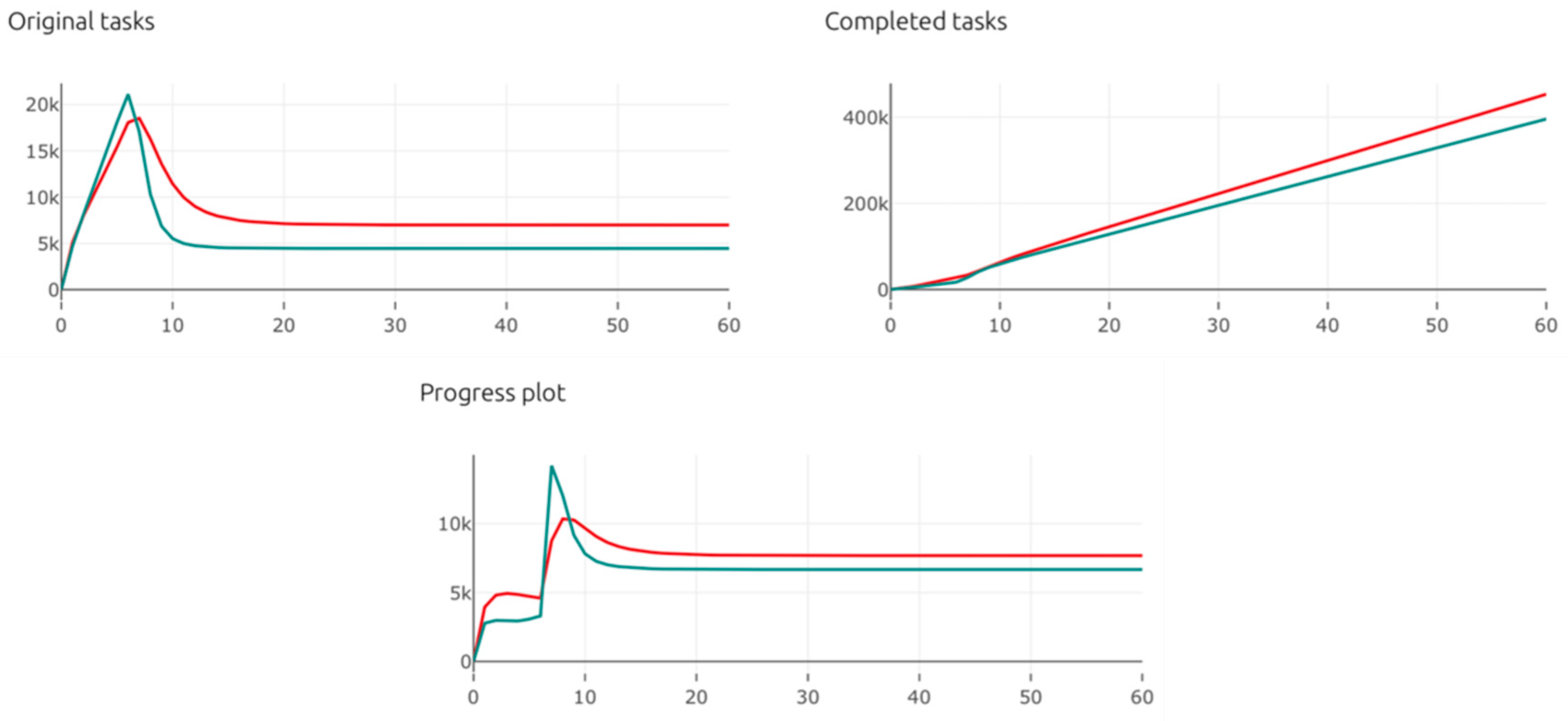
| Original_Tasks | The overall tasks created |
| Rework_to_Do | The tasks that must be redone |
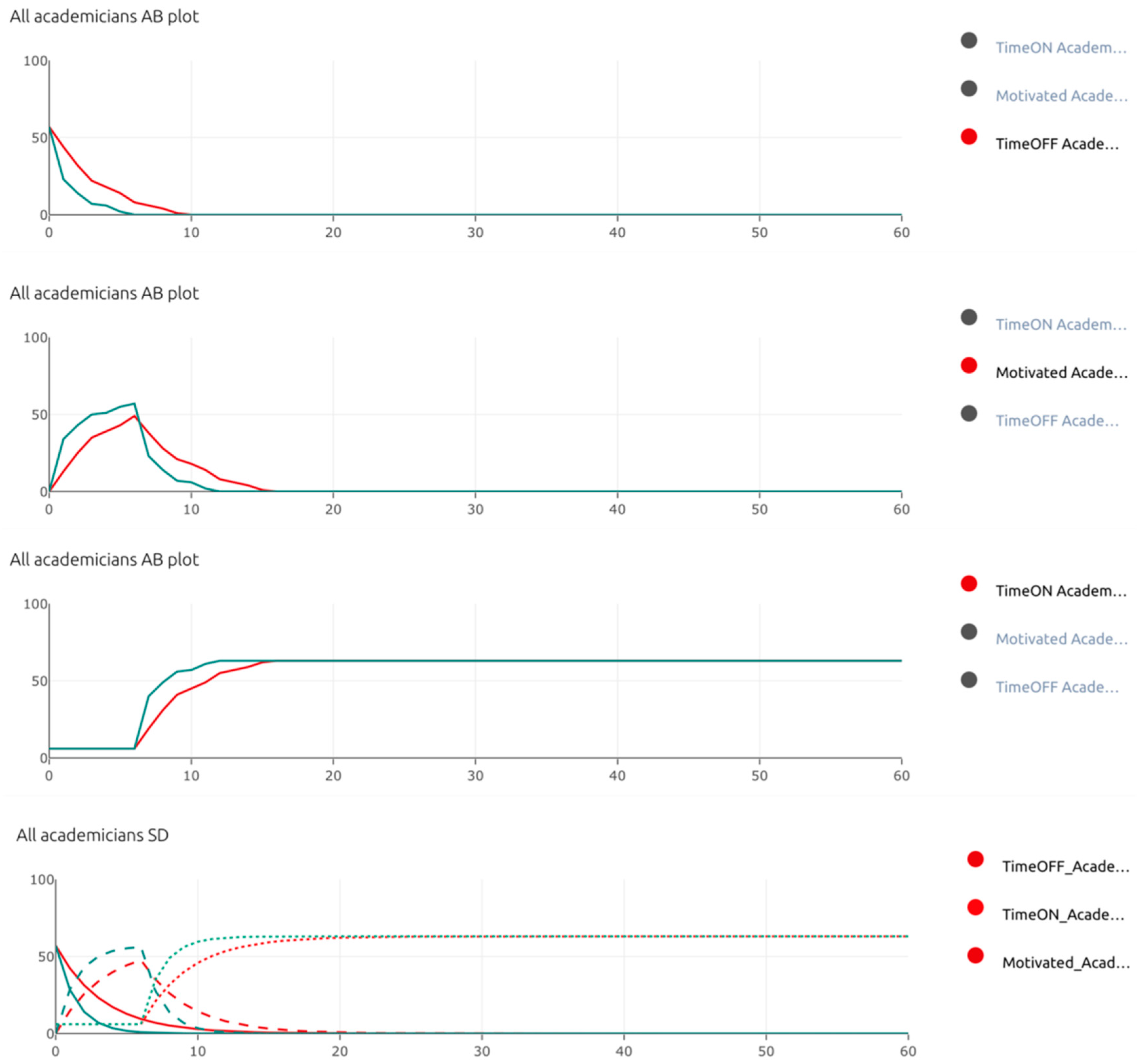
| TimeOFF_Academicians | The number of dentists who do not apply time management |
| TimeON_Academicians | The TimeON academic dentists |
| Completed_Tasks | The overall completed tasks |
| Undiscovered_Rework | The undiscovered tasks to be performed |
| Motivated_Academicians | The motivated academic dentists |
| Dynamic variables and explanations | |
| Dynamic Variable | Explanation |
| Productivity_Factor | The productivity factor |
| Incoming_Tasks | The tasks to be fulfilled for the total academic staff per time unit |
| Motivation_Rate | Both academic and WOM motivation |
| Adoption_From_WOM | The WOM adoption |
| Motivation | The academic motivation |
| Parameters and explanations | |
| Parameter | Explanation |
| Administration | The administration tasks per time unit |
| Education | The education tasks per time unit |
| Research | The research tasks per time unit |
| Time_to_Discover_Rework | The delay time to discover rework to be done |
| Academic_Support | The level of academic support per time unit |
| Time_Educ_Hours | The level of education hours |
| Academic_Level | The academic level |
| Work_Load | The workload level |
| Timewaster | The timewaster level |
| Adoption_Fraction | The percentage of WOM adoption |
| Contact_Rate | The number of contacts per time unit |
| Initial_TimeOn_Academicians | The number of initial TimeON academic dentists |
| Total_Academic_Staff | The total academic dentist staff |
| Time_to_React | The time taken for motivated academic dentists to become TimeON academic dentists |
| Initial_Tasks | The number of initial tasks |
| Uncompleted_Tasks_Factor | The percentage of uncompleted tasks per time unit |
| Flows and explanations | |
| Flow | Explanation |
| Progress | The completed tasks per time unit |
| Task_Rate | The tasks to be fulfilled of the total academic dentist staff per time unit |
| Rework | The discovered uncompleted tasks to be fulfilled per time unit |
| Uncompleted_Tasks | The uncompleted tasks per time unit |
| Transformation | The TimeOFF academic dentists who become motivated academic dentists per time unit |
| Trans2 | The acceptance of the time management philosophy and the transformation of motivated dentists into TimeON dentists |
| Rework_Discovery | The discovered uncompleted tasks per time unit |
| Name | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Administration | 40 | tasks |
| Education | 32 | tasks |
| Research | 50 | tasks |
| Time to discover rework | 2 | months |
| Academic support | 10% | |
| Time educ hours | 10% | |
| Academic_level | 10% | |
| Workload | 10% | |
| Timewasters | 10% | |
| Adoption fraction | 10% | |
| Contact rate | 0 | persons/month |
| Initial time on academicians | 6 | persons |
| Total academic staff | 63 | persons |
| Time_to_react | 6 | months |
| Initial tasks | 20 | tasks |
| Uncompleted tasks factor | 5% |
| Name | Value B | Value C |
|---|---|---|
| Administration | 40 | 24 |
| Education | 32 | 32 |
| Research | 50 | 50 |
| Time to discover rework | 2 | 2 |
| Academic support | 10% | 20% |
| Time educ hours | 10% | 20% |
| Academic_level | 10% | 20% |
| Workload | 10% | 5% |
| Timewasters | 10% | 5% |
| Adoption fraction | 10% | 10% |
| Contact rate | 2 | 2 |
| Initial time on academicians | 6 | 6 |
| Total academic staff | 63 | 63 |
| Time_to_react | 6 | 6 |
| Initial tasks | 20 | 20 |
| Uncompleted tasks factor | 5% | 5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antoniadou, M.; Antoniadis, R. A Systemic Model for Resilience and Time Management in Healthcare Academia: Application in a Dental University Setting. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4918. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114918
Antoniadou M, Antoniadis R. A Systemic Model for Resilience and Time Management in Healthcare Academia: Application in a Dental University Setting. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(11):4918. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114918
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntoniadou, Maria, and Rallis Antoniadis. 2024. "A Systemic Model for Resilience and Time Management in Healthcare Academia: Application in a Dental University Setting" Applied Sciences 14, no. 11: 4918. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114918
APA StyleAntoniadou, M., & Antoniadis, R. (2024). A Systemic Model for Resilience and Time Management in Healthcare Academia: Application in a Dental University Setting. Applied Sciences, 14(11), 4918. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114918







