Emulsions Stabilized with an Electrostatic Complex of Quaternized Cellulose Nanofiber and Octanoyl Gelatin and the Effect of pH Value on Their Stability
Abstract
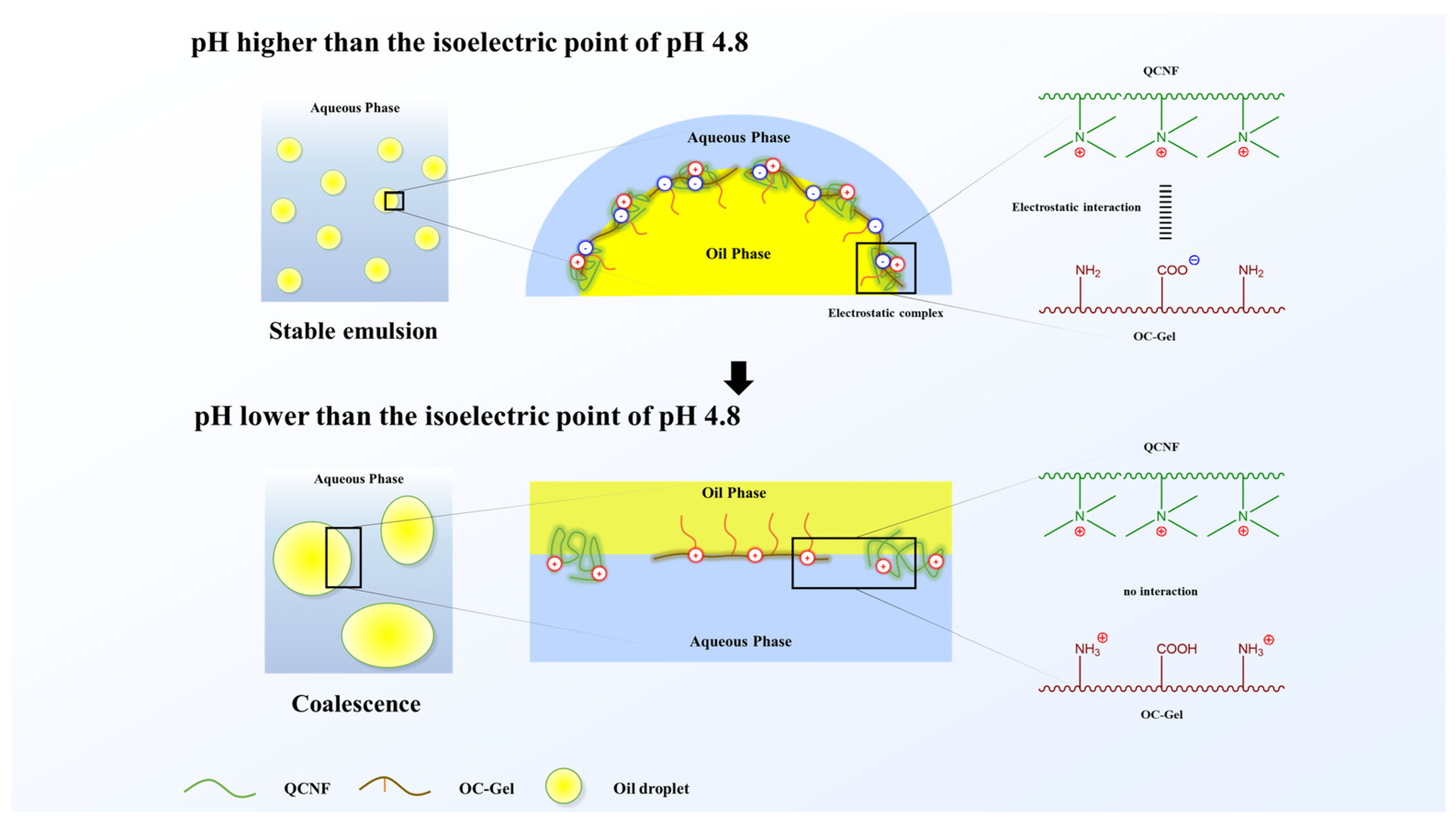
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Hydrophobicised Gelatin
2.3. 1H NMR Spectroscopy
2.4. Measurement of Air/Water Interface Tension
2.5. Measurement of QCNF/HpGel Complexation Degree
2.6. FT−IR Spectroscopy
2.7. X−ray Diffractometry
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.9. Preparation of Emulsion Stabilized with QCNF and OC−Gel
2.10. Measurement of Size and Stability of Oil Droplets of Em(OC−Gel), Em(QCNF), and Em(QCNF/OC−Gel) by Microscopic Observation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. 1H NMR Spectroscopy
3.2. Measurement of Air/Water Interface Tension
3.3. Measurement of QCNF/HpGel Complexation Degree
3.4. FT−IR Spectroscopy
3.5. X−ray Diffractometry
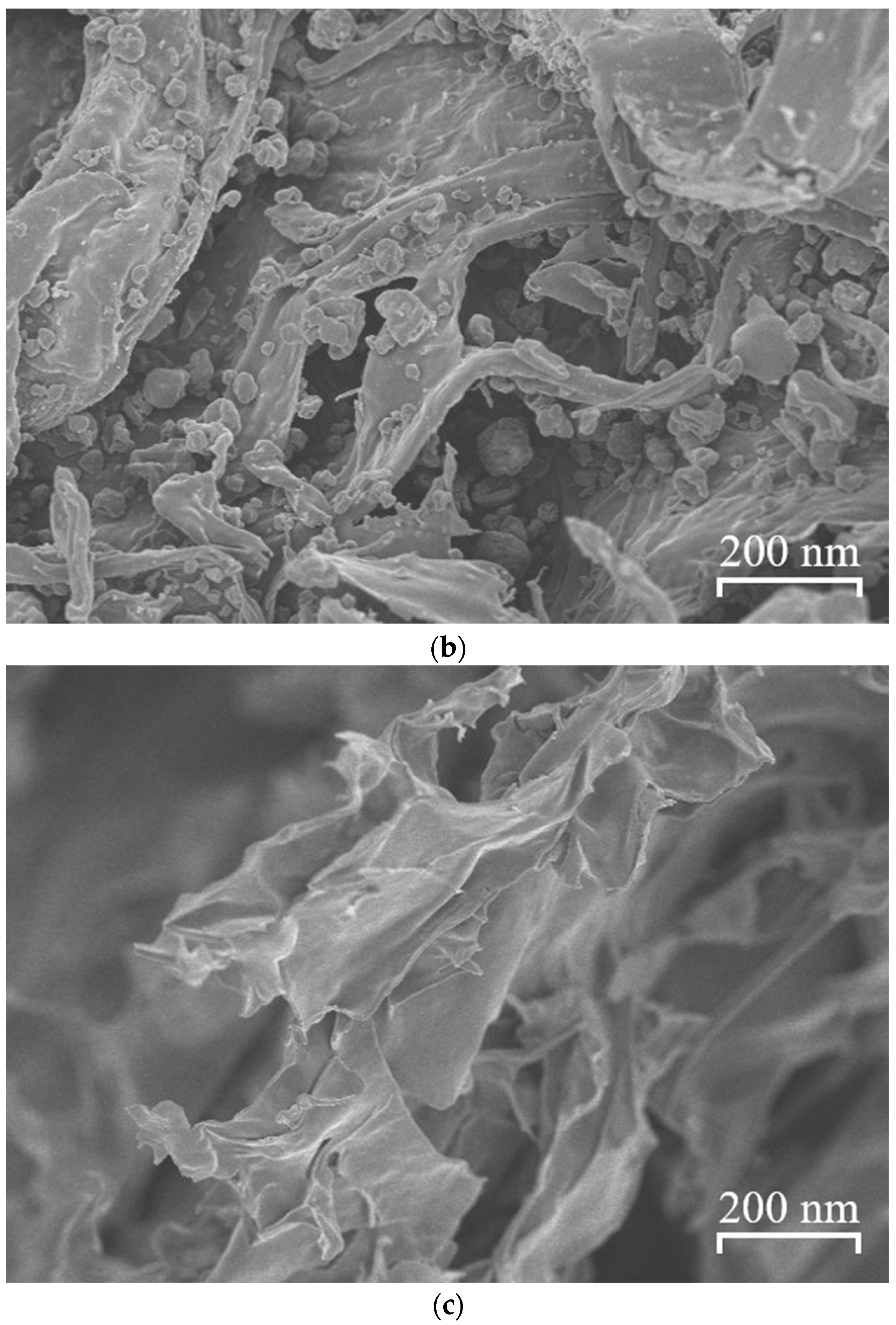
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.7. Measurement of Size and Stability of Oil Droplets of Em(OC−Gel), Em(QCNF), and Em(QCNF/OC−Gel) by Microscopic Observation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amine, C.; Dreher, J.; Helgason, T.; Tadros, T. Investigation of emulsifying properties and emulsion stability of plant and milk proteins using interfacial tension and interfacial elasticity. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Hydrocolloids as emulsifiers and emulsion stabilizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterenko, A.; Drelich, A.; Lu, H.; Clausse, D.; Pezron, I. Influence of a mixed particle/surfactant emulsifier system on water-in-oil emulsion stability. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, H.T.; Akoh, C.C. Effect of emulsifier type, droplet size, and oil concentration on lipid oxidation in structured lipid-based oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2004, 84, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Ugarte, G.A.; Ramírez-Corona, N.; López-Malo, A.; Palou, E.; Martín-González, M.F.S.; Jiménez-Munguía, M.T. Modeling phase separation and droplet size of W/O emulsions with oregano essential oil as a function of its formulation and homogenization conditions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushikubo, F.Y.; Cunha, R.L. Stability mechanisms of liquid water-in-oil emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 34, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capek, I. Degradation of kinetically-stable o/w emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 107, 125–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardhono, E.Y.; Zafimahova-Ratisbonne, A.; Saleh, K.; Clausse, D.; Lanoiselle, J.-L. W/O Emulsion Destabilization and Release of a Polysaccharide Entrapped in the Droplets. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Díaz, C.; Wandersleben, T.; Marqués, A.M.; Rubilar, M. Multilayer emulsions stabilized by vegetable proteins and polysaccharides. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 25, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, C.; Zeeb, B.; Weiss, J. Investigations into aggregate formation with oppositely charged oil-in-water emulsions at different pH values. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobin, M.-F.; Michel, V.; Martini, M.-C. Study of formulation and stability of emulsions with polymeric emulsifiers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 152, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, F.-P.; Tang, C.-H. Whether ovalbumin performs as a particulate or polymeric emulsifier is largely determined by pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.K.; Kim, J.-C. Preparations and temperature- and pH-dependent release property of ethylcellulose microcapsules containing N-isopropylacrylamide copolymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, S.; Nasirpour, A.; Fathi, M. Effect of Polymer Concentration and Acidification Time on Olive Oil Microcapsules Obtained by Complex Coacervation. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2016, 3, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loxley, A.; Vincent, B. Preparation of Poly(methylmethacrylate) Microcapsules with Liquid Cores. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 208, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghbashlo, M.; Mobli, H.; Madadlou, A.; Rafiee, S. The correlation of wall material composition with flow characteristics and encapsulation behavior of fish oil emulsion. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.-C. Oxidation–Responsive Emulsions Stabilized with Poly(Vinyl Pyrrolidone-co-allyl Phenyl Sulfide). Polymers 2020, 12, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Quinlan, P.J.; Tam, K.C. Stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsions: Recent advances and potential applications. Soft Matter. 2015, 11, 3512–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugger, B.; Richtering, W. Magnetic, Thermosensitive Microgels as Stimuli-Responsive Emulsifiers Allowing for Remote Control of Separability and Stability of Oil in Water-Emulsions. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2973–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Gurram, S.R.; Basavaraj, M.G. Doubly pH Responsive Emulsions by Exploiting Aggregation of Oppositely Charged Nanoparticles and Polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 2018, 34, 5060–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.-C. Thermo- and pH-Responsiveness of Emulsions Stabilized with Acidic Thermosentive Polymers. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.R.; Kim, J.-C. Emulsions Stabilized with poly(Hydroxyethyl Acrylate-co-Coumaryl Acrylate-co-2-Ethylhexyl acrylate). J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2013, 50, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.; Kim, J.-C. Emulsion stabilized with disulfide proteinoid and its stability in reducing condition. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.-C. Oil-in-gold nanoparticle solution emulsion stabilized with amphiphilic polymers and its stability under NIR irradiation. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, K.; Taguchi, T. Bonding behavior of hydrophobically modified gelatin films on the intestinal surface. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2014, 29, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mizuta, R.; Fukata, N.; Taguchi, T. Design of bio-inspired adhesive surface composed of hexanoyl group-modified gelatin and silicon nanowire. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 178, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledano, O.; Magdassi, S. Emulsification and Foaming Properties of Hydrophobically Modified Gelatin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 200, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zou, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, L.; Fan, Y. Comparison of Cellulose and Chitin Nanofibers on Pickering Emulsion Stability—Investigation of Size and Surface Wettability Contribution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.-H.; Chen, K.-M. Preparation and surface activity of gelatin derivative surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 272, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Zhong, J. Gelatins as emulsifiers for oil-in-water emulsions: Extraction, chemical composition, molecular structure, and molecular modification. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auweter, H.; André, V.; Horn, D.; Lüddecke, E. The function of gelatin in controlled precipitation processes of nanosize particles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1998, 19, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewald, L.; Claaßen, C.; Götz, T.; Claaßen, M.H.; Truffault, V.; Tovar, G.E.M.; Southan, A.; Borchers, K. Beyond the Modification Degree: Impact of Raw Material on Physicochemical Properties of Gelatin Type A and Type B Methacryloyls. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, 1800168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, F.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B. Effects of Relative Molecular Weight Distribution and Isoelectric Point on the Swelling Behavior of Gelatin Films. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 857976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Shi, B. Physicochemical properties of collagen, gelatin and collagen hydrolysate derived from bovine limed split wastes. J. Soc. Leather Technol. Chem. 2006, 90, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Zhao, F.; Park, S.C.; Kim, J.C. Gelatin-Loaded Cubosomes Stabilized with Hydrophobically Modified Quaternized Cellulose Nanofiber and Their PH-Dependent Release Property. J. Biomater. Appl. 2021, 35, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Khalid, N.; Shu, G.; Neves, M.A.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M. Complex Coacervates from Gelatin and Octenyl Succinic Anhydride Modified Kudzu Starch: Insights of Formulation and Characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 86, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Yang, Y.; Tu, P.; Chen, J.Y. Value-Added Utilization of Wheat Straw: From Cellulose and Cellulose Nanofiber to All-Cellulose Nanocomposite Film. Membranes 2022, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y. Eects of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Cellulose Nanofibers on the Structure and Properties of Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanocomposites. Polymers 2019, 11, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Montero, P.; Fernández-Martín, F.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Physico-chemical and film-forming properties of bovine-hide and tuna-skin gelatin: A comparative study. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.S.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T. Effect of heat treatment of film-forming solution on the properties of film from cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) skin gelatin. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Fu, Y.; He, J. Preparation and physical properties of soy protein isolate and gelatin composite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goi, Y.; Fujisawa, S.; Saito, T.; Yamane, K.; Kuroda, K.; Isogai, A. Dual Functions of TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibers in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: A Pickering Emulsifier and a Unique Dispersion Stabilizer. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10920–10926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.L.R.; Gomes, A.; Tibolla, H.; Menegalli, F.C.; Cunha, R.L. Cellulose nanofibers from banana peels as a Pickering emulsifier: High-energy emulsification processes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 194, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Jia, H.; Gao, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Using Cellulose Nanofibers and Its Palm Oil Pickering Emulsion as Fat Substitutes in Emulsified Sausage. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanpichai, S.; Biswas, S.K.; Witayakran, S.; Yano, H. Optically transparent tough nanocomposites with a hierarchical structure of cellulose nanofiber networks prepared by the Pickering emulsion method. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 132, 105811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, S.M.; Rao, C.M. The role of surface charge in the desolvation process of gelatin: Implications in nanoparticle synthesis and modulation of drug release. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-Y.; Lu, P.-L.; Chen, K.-H.; Tabata, Y.; Hsiue, G.-H. Effect of Charge and Molecular Weight on the Functionality of Gelatin Carriers for Corneal Endothelial Cell Therapy. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, H.K.; Park, S.C.; Kim, J.-C. Emulsions Stabilized with an Electrostatic Complex of Quaternized Cellulose Nanofiber and Octanoyl Gelatin and the Effect of pH Value on Their Stability. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104122
Son HK, Park SC, Kim J-C. Emulsions Stabilized with an Electrostatic Complex of Quaternized Cellulose Nanofiber and Octanoyl Gelatin and the Effect of pH Value on Their Stability. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(10):4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104122
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Hyeon Ki, Soo Chan Park, and Jin-Chul Kim. 2024. "Emulsions Stabilized with an Electrostatic Complex of Quaternized Cellulose Nanofiber and Octanoyl Gelatin and the Effect of pH Value on Their Stability" Applied Sciences 14, no. 10: 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104122
APA StyleSon, H. K., Park, S. C., & Kim, J.-C. (2024). Emulsions Stabilized with an Electrostatic Complex of Quaternized Cellulose Nanofiber and Octanoyl Gelatin and the Effect of pH Value on Their Stability. Applied Sciences, 14(10), 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104122




