Unsupervised Segmentation of Muscle Precursor Cell Images In Situ
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
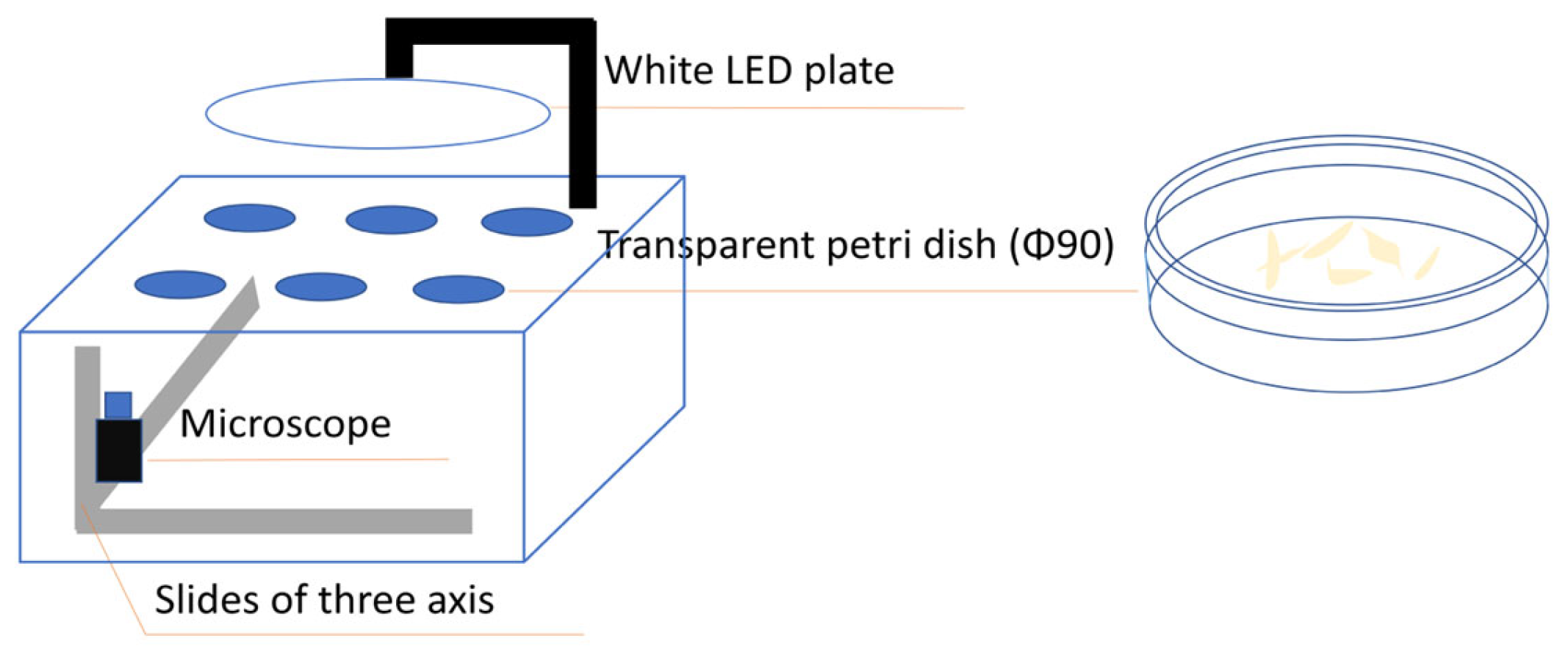
2.1. Cell Culture and Image Acquisition
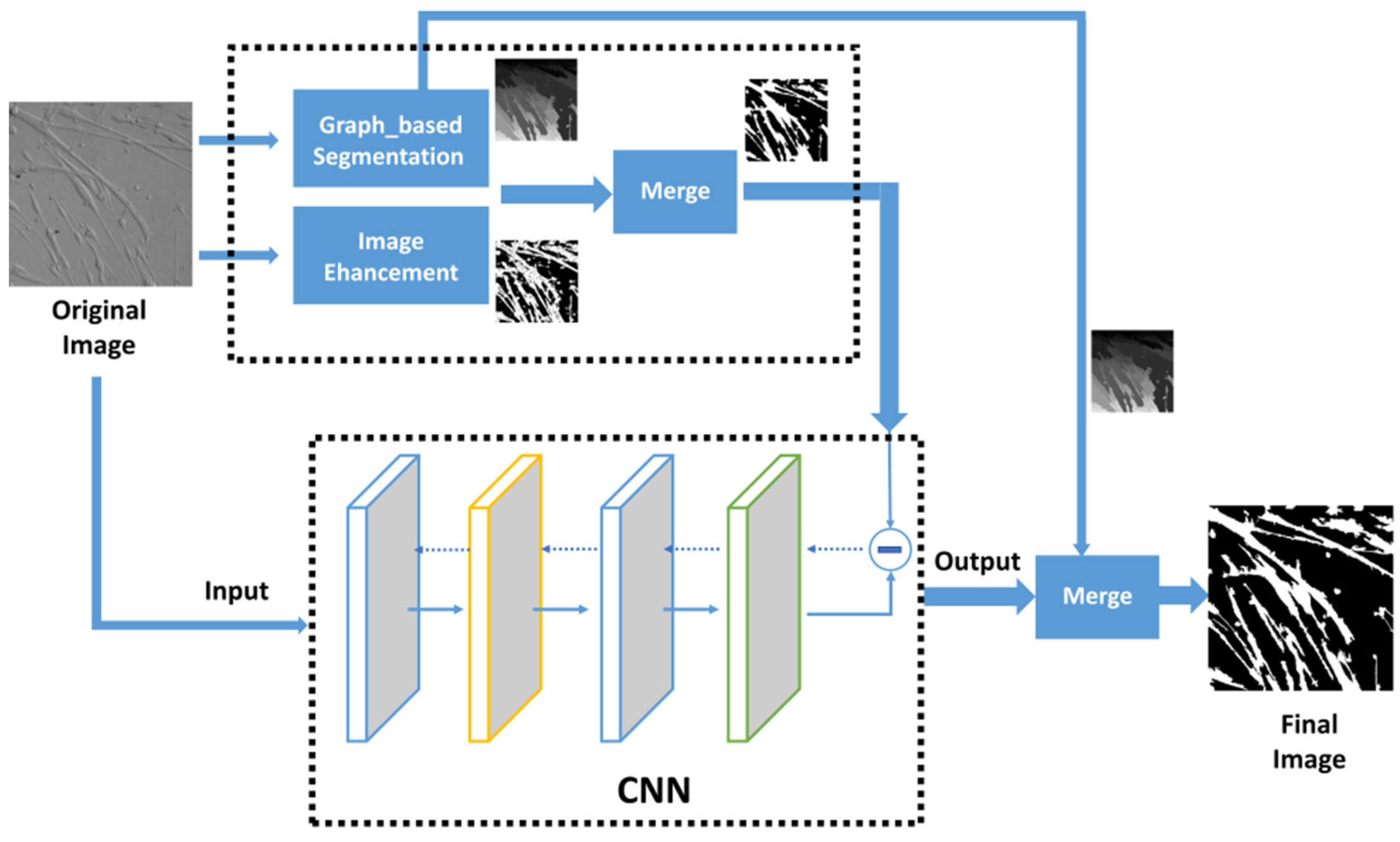
2.2. Image Segmentation
3. Experiment and Results
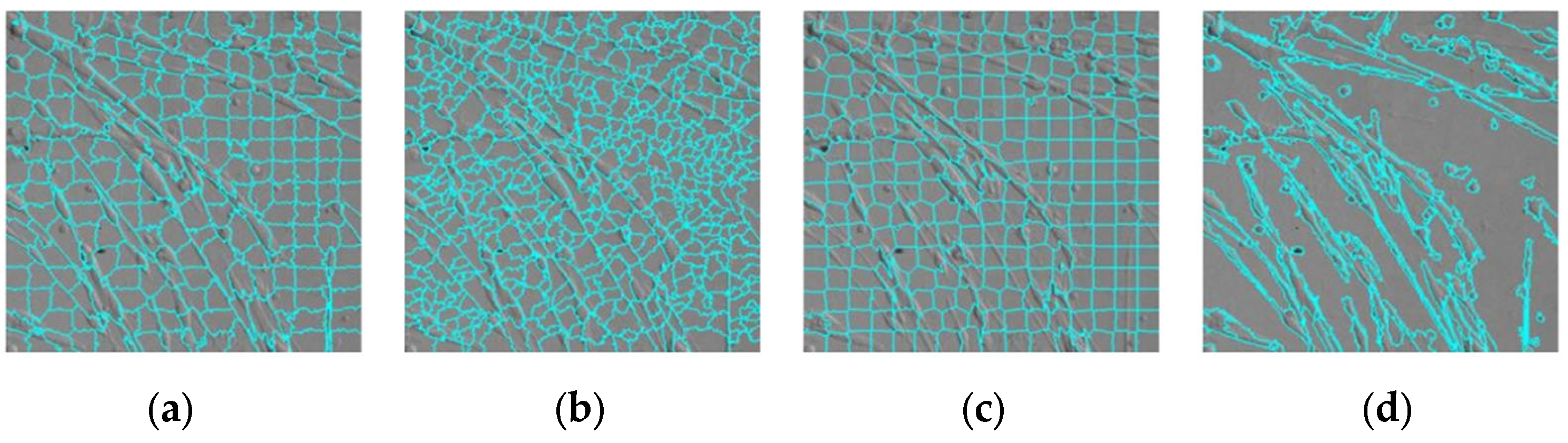
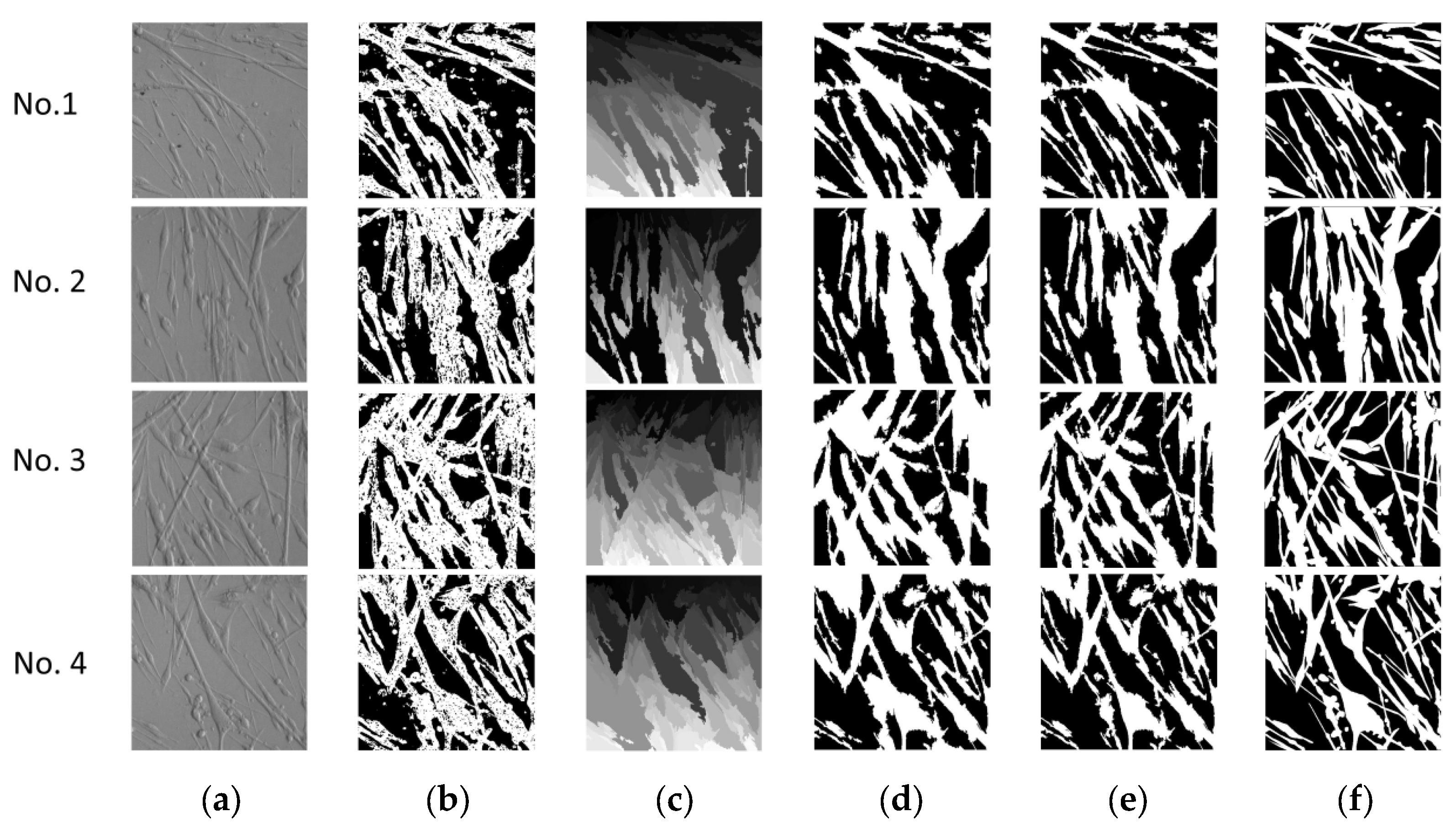
3.1. Superpixel
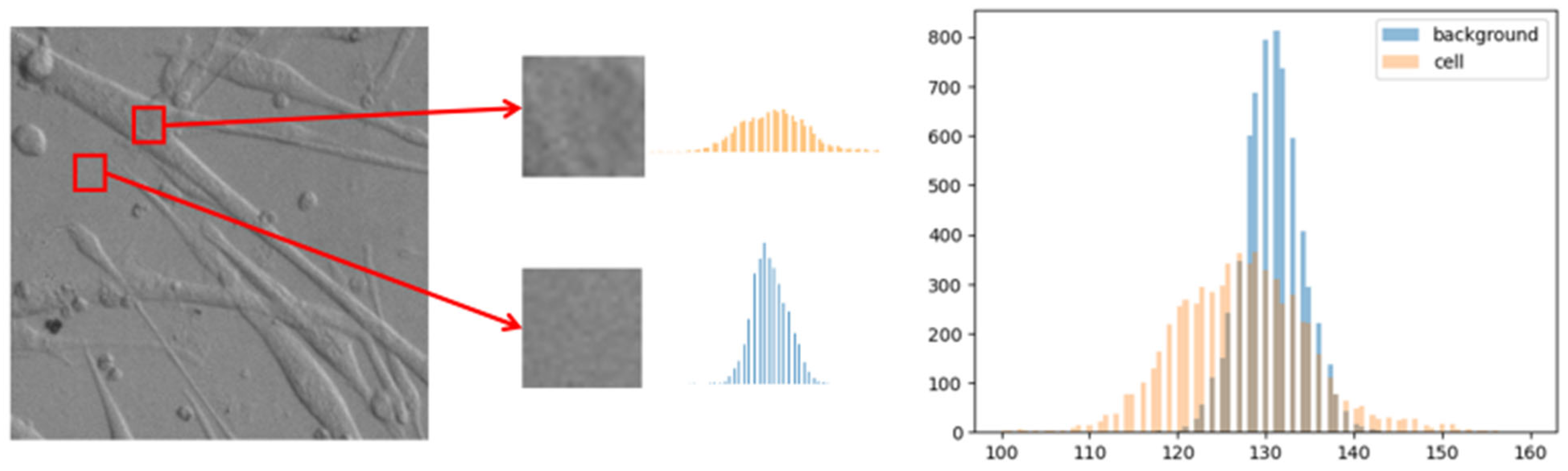
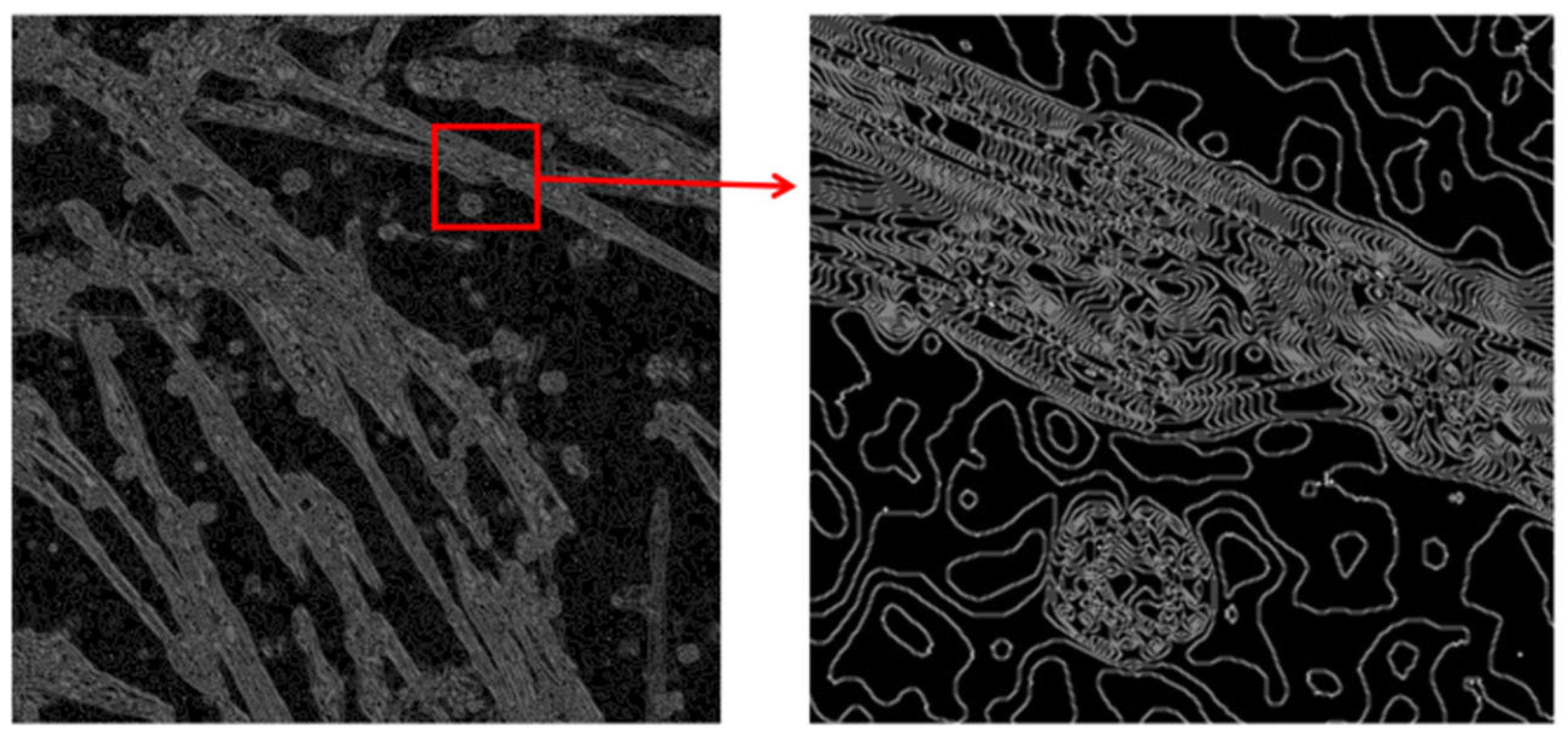
3.2. Image Enhancement
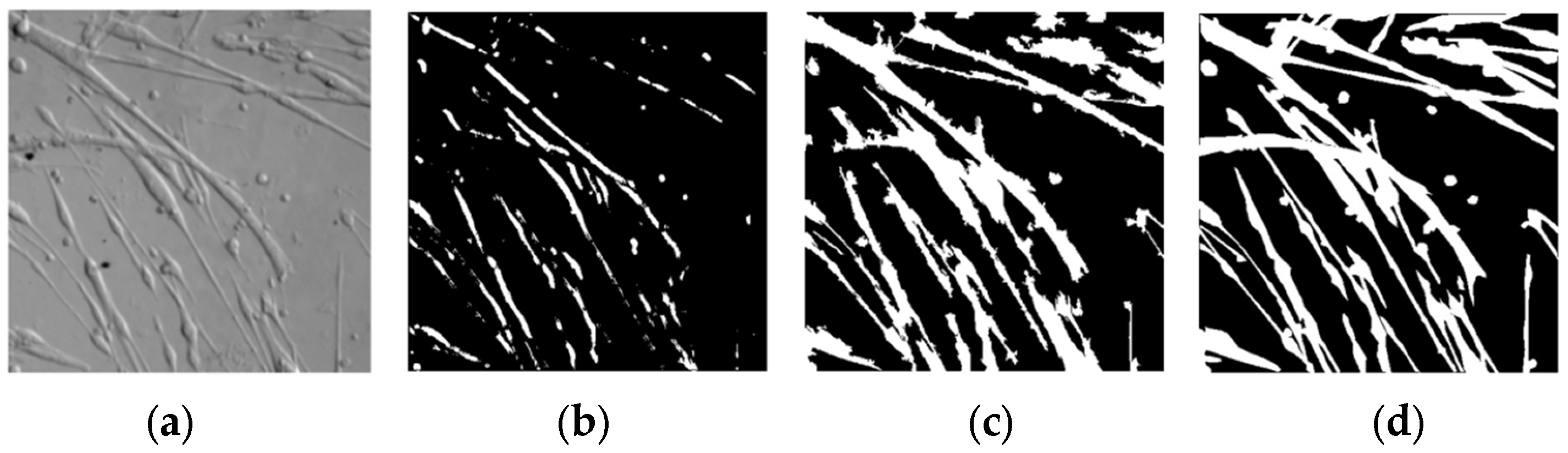
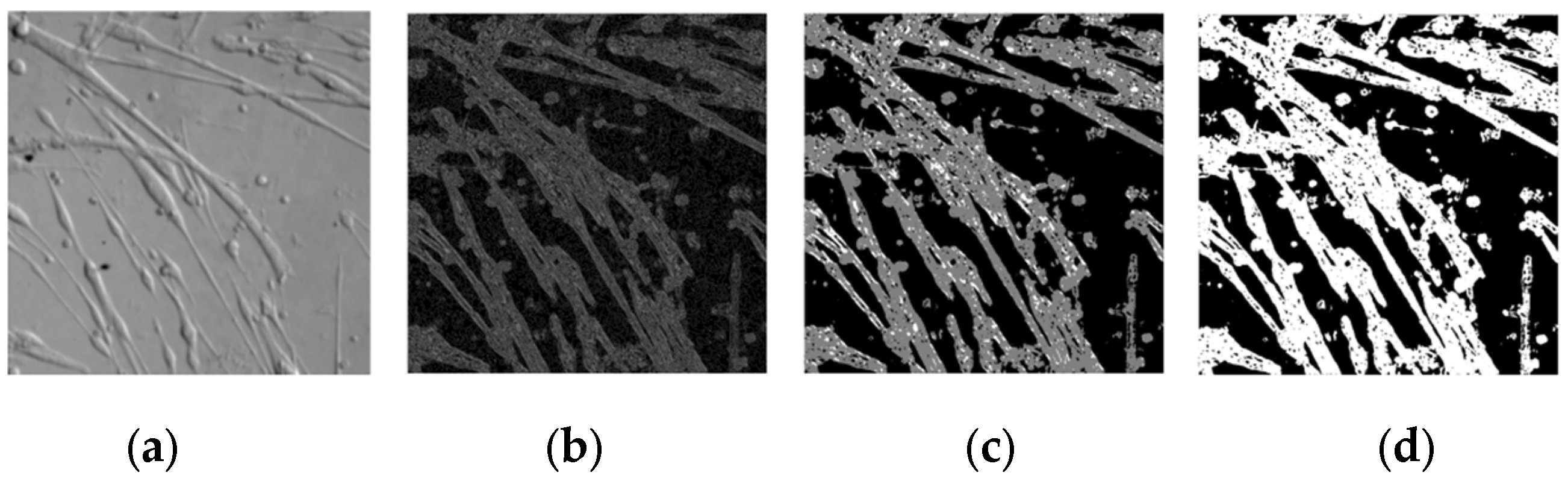
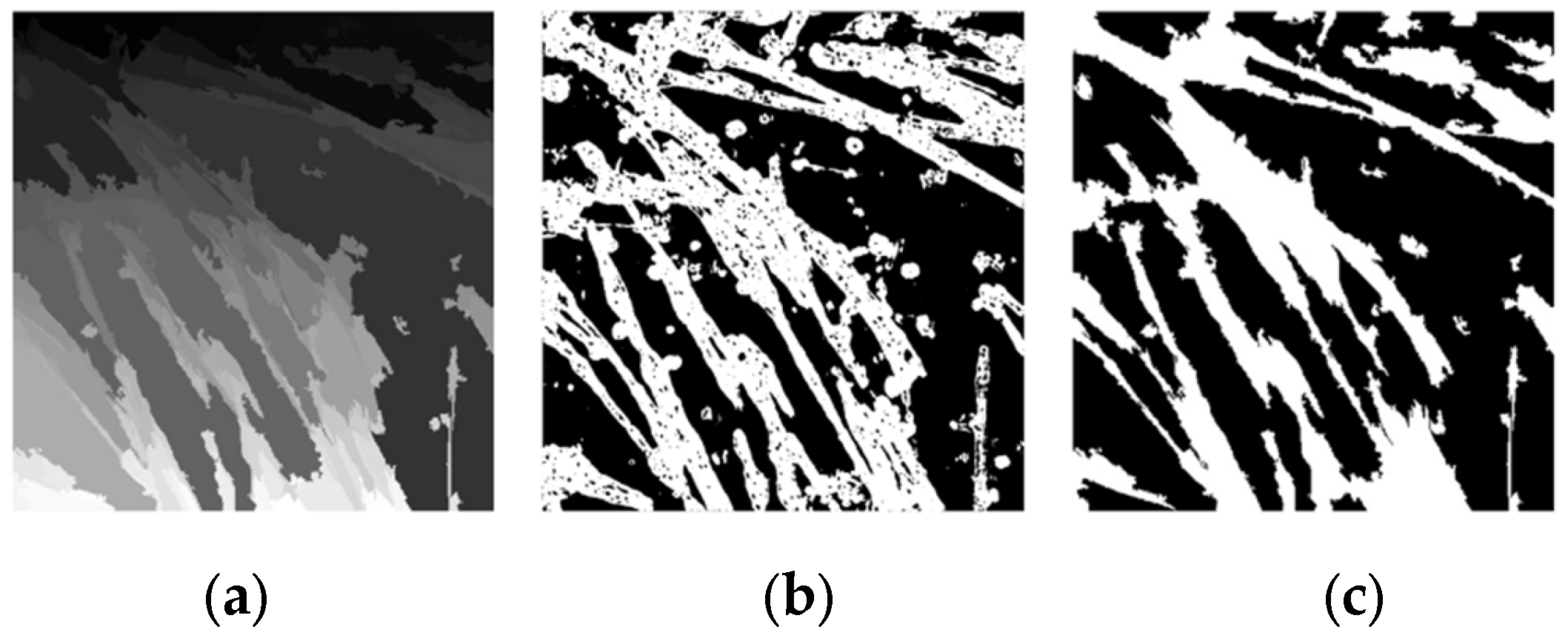
3.3. Image Merging
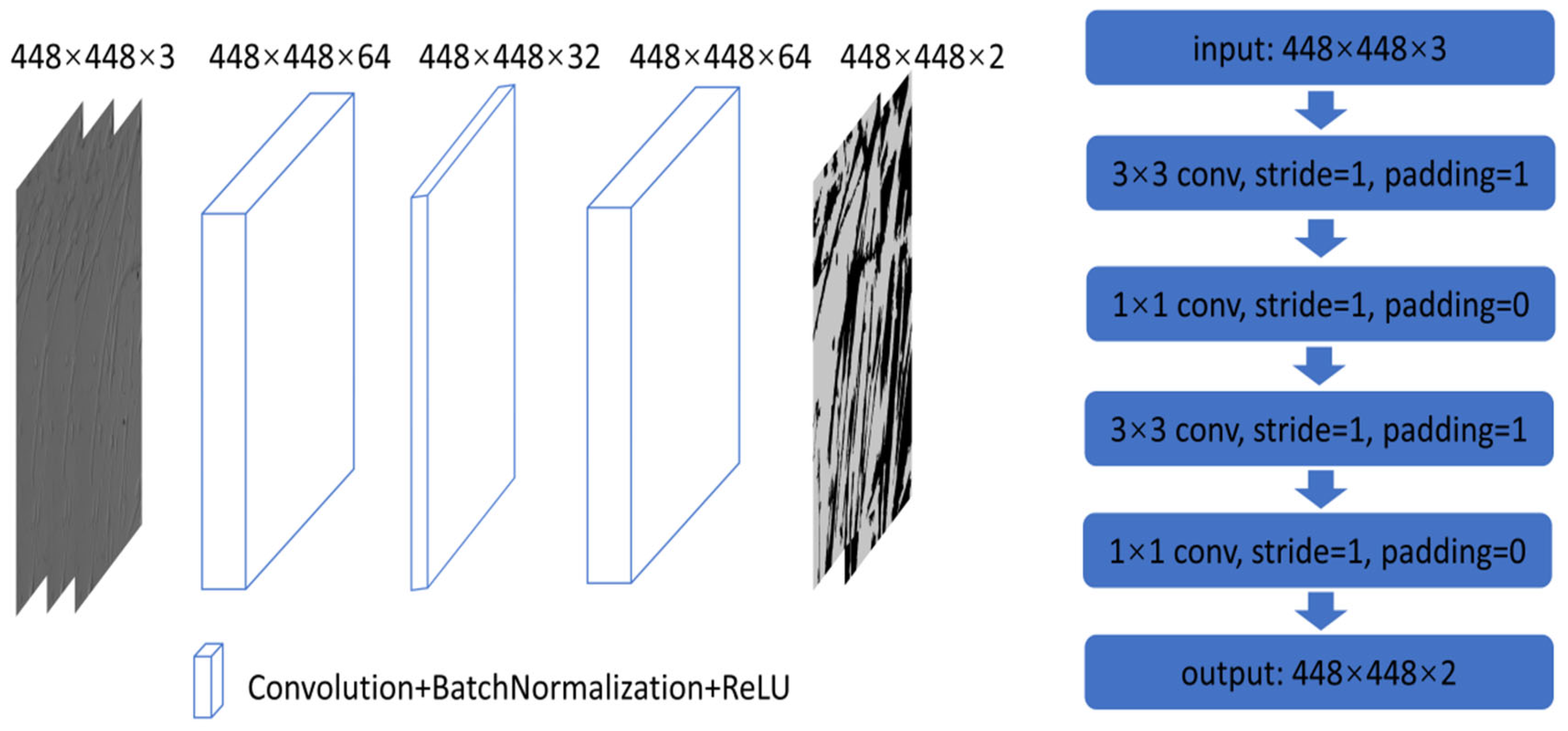
3.4. Convolutional Neural Network
3.5. Results and Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Witherick, J.; Brady, S. Update on muscle disease. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incitti, T.; Magli, A.; Darabi, R.; Yuan, C.; Lin, K.; Arpke, R.W.; Azzag, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Stewart, R.; Thomson, J.A.; et al. Pluripotent stem cell-derived myogenic progenitors remodel their molecular signature upon in vivo engraftment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4346–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nance, M.E.; Shi, R.; Hakim, C.H.; Wasala, N.B.; Yue, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Robinson, C.A.; Duan, S.X.; Yao, G.; et al. AAV9 Edits Muscle Stem Cells in Normal and Dystrophic Adult Mice. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1568–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Xiao, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yin, J.; Sun, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Combination of inflammation-related cytokines promotes long-term muscle stem cell expansion. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1082–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Ma, X.; Cen, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, C.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yue, L.; et al. In Vitro Expansion of Primary Human Hepatocytes with Efficient Liver Repopulation Capacity. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 806–819.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.C.; Logan, C.Y.; Fish, M.; Anbarchian, T.; Aguisanda, F.; Álvarez-Varela, A.; Wu, P.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, B.; et al. Inflammatory Cytokine TNFα Promotes the Long-Term Expansion of Primary Hepatocytes in 3D Culture. Cell 2018, 175, 1607–1619.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, S.; Yang, Z. An image processing pipeline to detect and segment nuclei in muscle fiber microscopic images. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2014, 77, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xia, S. A computational approach to detect and segment cytoplasm in muscle fiber images. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2015, 78, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.E.; Jones, T.R.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Clarke, C.; Kang, I.H.; Friman, O.; Guertin, D.A.; Chang, J.H.; Lindquist, R.A.; Moffat, J.; et al. CellProfiler: Image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; Dezonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech, E.; Aksoy, B.A.; Aksoy, P.; Hammerbacher, J. Cytokit: A single-cell analysis toolkit for high dimensional fluorescent microscopy imaging. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kofahi, Y.; Lassoued, W.; Lee, W.; Roysam, B. Improved Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Cell Nuclei in Histopathology Images. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 57, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoshima, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Hirose, O.; Kanamori, M.; Teramoto, T.; Jang, M.S.; Kuge, S.; Ishihara, T.; Yoshida, R.; Iino, Y. Accurate Automatic Detection of Densely Distributed Cell Nuclei in 3D Space. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruszczycki, B.; Pels, K.K.; Walczak, A.; Zamłyńska, K.; Such, M.; Szczepankiewicz, A.A.; Hall, M.H.; Magalska, A.; Magnowska, M.; Wolny, A.; et al. Three-Dimensional Segmentation and Reconstruction of Neuronal Nuclei in Confocal Microscopic Images. Front. Neuroanat. 2019, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec, M.; Piórkowski, A.; Gertych, A. Efficient automatic 3D segmentation of cell nuclei for high-content screening. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari Taghanaki, S.; Abhishek, K.; Cohen, J.P.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Hamarneh, G. Deep semantic segmentation of natural and medical images: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 137–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuoka, Y.; Yamada, T.G.; Mashiko, D.; Ikeda, Z.; Hiroi, N.F.; Kobayashi, T.J.; Yamagata, K.; Funahashi, A. 3D convolutional neural networks-based segmentation to acquire quantitative criteria of the nucleus during mouse embryogenesis. npj Syst. Biol. Appl. 2020, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1961, 9, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Grand, F.; Rudnicki, M.A. Skeletal muscle satellite cells and adult myogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Malik, J. Learning a classification model for segmentation. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA; pp. 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felzenszwalb, P.F.; Huttenlocher, D.P. Efficient graph-based image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 59, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jitendra Malik, J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 888–905. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, A.P.; Prince, S.J.D.; Warrell, J.; Mohammed, U.; Jones, G. Superpixel lattices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, P.; Protzel, P. Compact Watershed and Preemptive SLIC: On Improving Trade-offs of Superpixel Segmentation Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedaldi, A.; Soatto, S. Quick shift and kernel methods for mode seeking. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P. Sabine Susstrunk.SLIC-Superpixels Compared to State-of-the-art Superpixel Methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Lu, J.; Peng, Z. Recent Research Progress of Superpixel Segmentation and Evaluation. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2019, 56, 090005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezaki, A. Unsupervised Image Segmentation by Backpropagation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 1543–1547. [Google Scholar]


| Camera Type | Magnification | Resolution (Pixel) | Size (cm) | Number of Culture Dish | Pixel Size (µm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Basler-aca 2500 | 10× | 2592 × 1944 | W45 × L45 × H30 | 6 | 2.2 × 2.2 |
| No. 1 | No. 2 | No. 3 | No. 4 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enhancement | Reference | CNN | Enhancement | Reference | CNN | Enhancement | Reference | CNN | Enhancement | Reference | CNN | |
| PA | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.87 | 0.90 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.85 | 0.88 |
| mIOU | 0.65 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.78 | 0.81 | 0.63 | 0.72 | 0.78 | 0.66 | 0.74 | 0.77 |
| PA | mIOU | Param | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asako Kanezak’s | 0.62 | 0.35 | 103.6 k |
| The proposed | 0.89 | 0.78 | 22.8 k |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruan, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, T. Unsupervised Segmentation of Muscle Precursor Cell Images In Situ. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5314. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095314
Ruan L, Yuan Y, Zhang T. Unsupervised Segmentation of Muscle Precursor Cell Images In Situ. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(9):5314. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095314
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuan, Lihua, Yongchun Yuan, and Tao Zhang. 2023. "Unsupervised Segmentation of Muscle Precursor Cell Images In Situ" Applied Sciences 13, no. 9: 5314. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095314
APA StyleRuan, L., Yuan, Y., & Zhang, T. (2023). Unsupervised Segmentation of Muscle Precursor Cell Images In Situ. Applied Sciences, 13(9), 5314. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095314




