Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: Clinical Perspectives, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. History of Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO)
4. Etiology of NMO
5. Symptoms of NMOSD
5.1. Imaging and Diagnosis of NMOSD
5.2. Metabolomic Studies to Differentiate NMOSD and Other Related Disorders
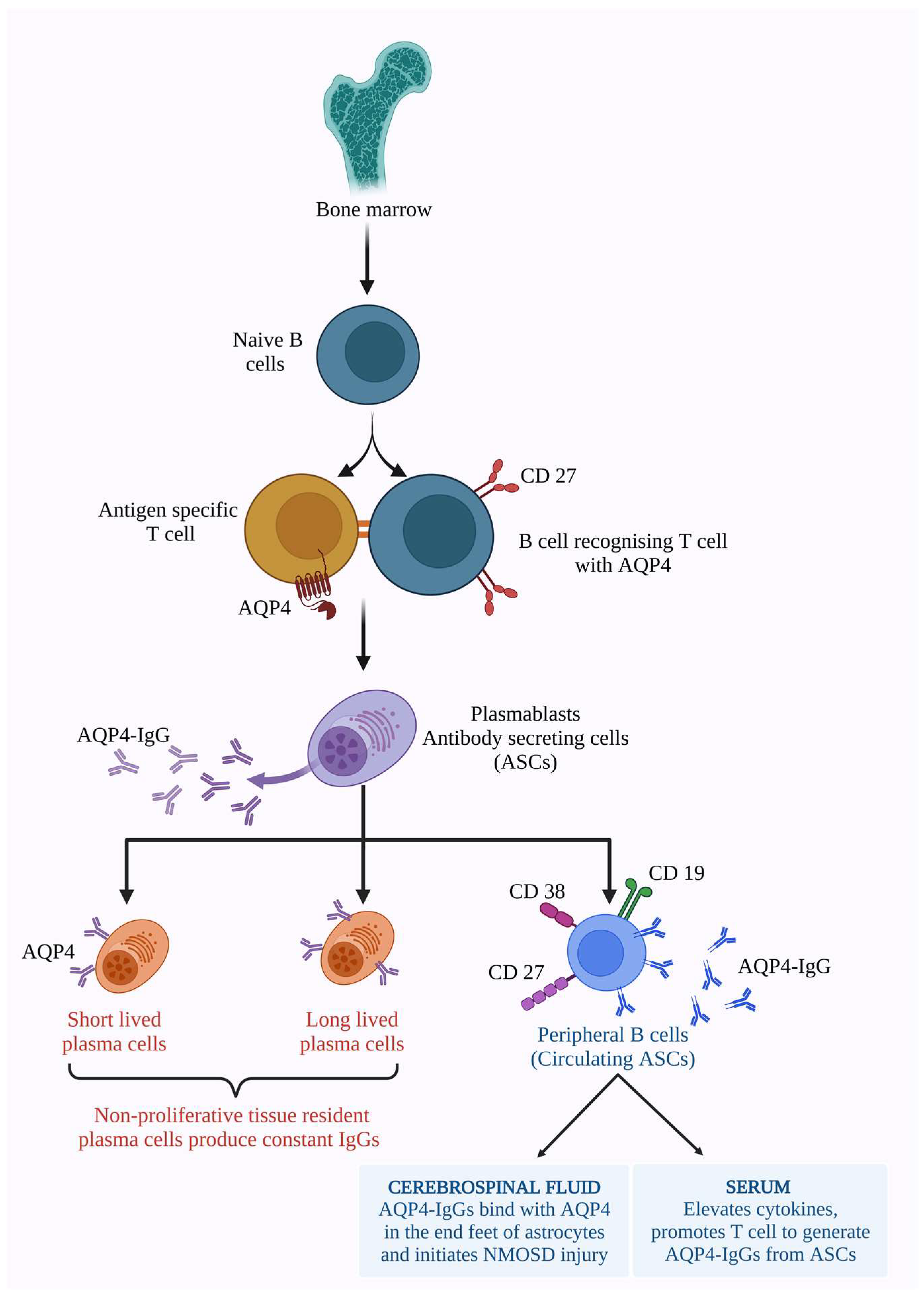
6. Molecular Mechanism of NMOSD
6.1. AQP4 Dependent Pathology
6.2. MOG-IgG-Dependent Pathology
6.3. IL-6 Pathophysiology
6.4. Complement-Mediated Pathology
6.5. Involvement of Gut Microbiome and NMOSD
6.6. Models of NMOSD Study
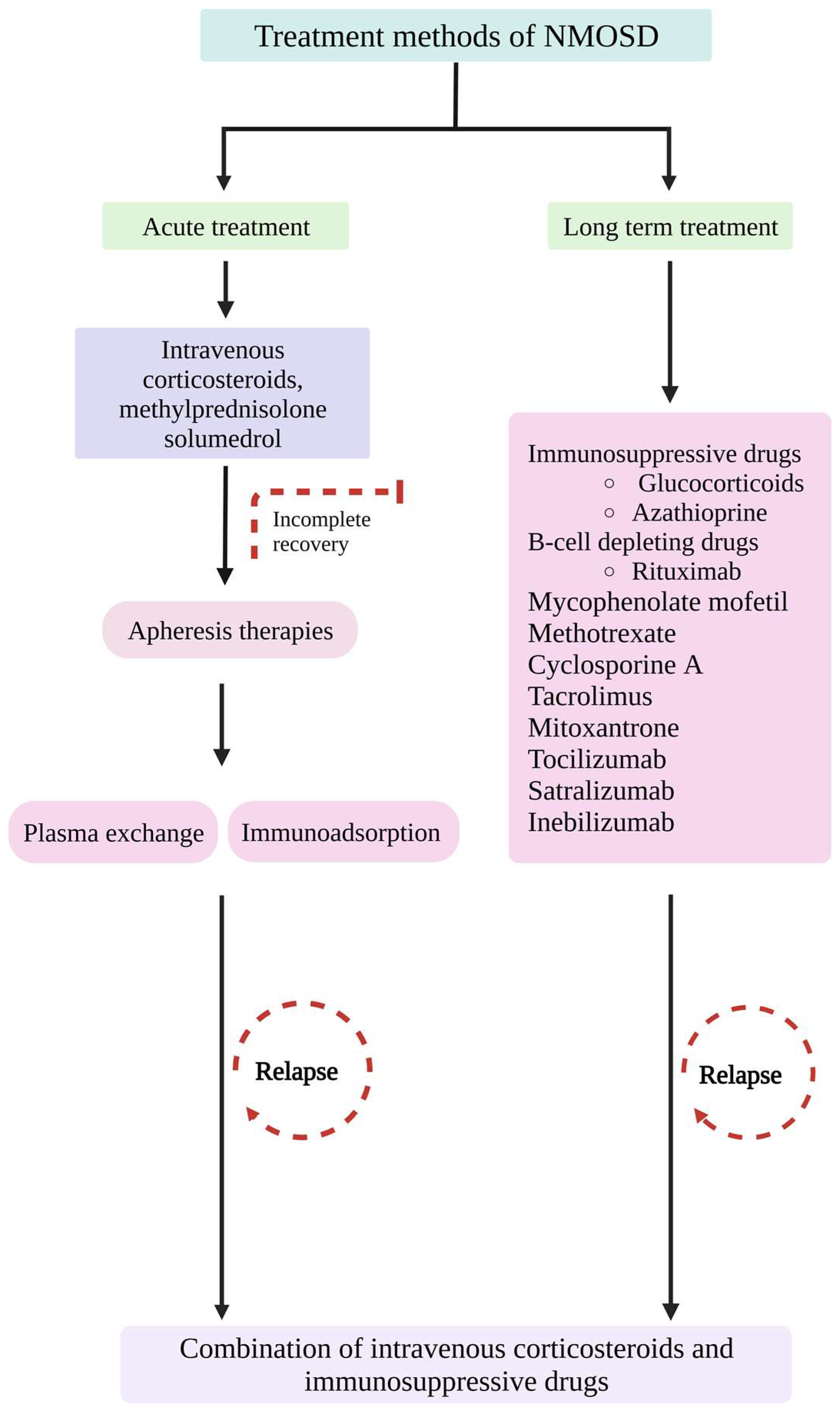
7. Treatment Methods
7.1. Immunosuppressive Treatment Methods
7.2. Blocking and Inactivation of AQP4, IL-6, and Complement Factors
7.3. Stem Cell Therapy
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NMO | Neuromyelitis optica |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| PNS | Peripheral nervous system |
| ON | Optic neuritis |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| AQP4 | Aquaporin 4 |
| AQP4-ab | Aquaporin 4- antibody |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| CDC | Complement dependent cytotoxicity |
| ADCC | Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity |
| MAC | Membrane attack complex |
| AD | Autoimmune diseases |
| NAD | Neurological autoimmune diseases |
| ADEM | Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis |
| LTEM | Longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| GBS | Guillain-Barré syndrome |
| MG | Myasthenia gravis |
| SS | Sjogren’s syndrome |
| NMOSD | Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder |
| Tfh | T follicular helper cells |
| MOGAD | Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-associated disorders |
| CXCR5 | Chemokine C-X-C receptor 5 |
| CXCL13 | C-X-C motif ligand 13 |
| OAP | Orthogonal array proteins |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| ASC | Antibody secreting cell |
| NK | Natural killer cell |
| IL | Interleukin |
| JAK/STAT3 | Janus kinase/Signal transducer and activator of the transcription 3 protein |
| NFkB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| INF γ | Interferon-gamma |
| TNF α | Tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| Th17 | T helper cell 17 |
| Treg | Regulatory T cell |
| P2R | Purinergic receptors |
| GM | Gut microbiota |
| ABC-TP | Adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter permease |
| EAE | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| IVMP | Intravenous methylprednisolone |
| PLEX | Plasma exchange |
| IA | Immunoadsorption |
| IVIg | Intravenous immunoglobulins |
| AZA | Azathioprine |
| RTX | Rituiximab |
| MTX | Mitoxantrone |
| TCZ | Tocilizumab |
| MMF | Mycophenolate mofetil |
| DHFR | Dihydrofolate reductase |
| FcRn | Neonatal Fc receptor |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| AHSCT | Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| P13k | Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase |
References
- Anaya, J.M.; Ramirez-Santana, C.; Alzate, M.A.; Molano-Gonzalez, N.; Rojas-Villarraga, A. The Autoimmune Ecology. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Ramírez-Santana, C. Identifying the culprits in neurological autoimmune diseases. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2019, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny, C.; Souberbielle, J.C. Vitamin D and multiple sclerosis: An update. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2017, 14, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, D.B.; Batra, A.; Vaitkevicius, H.; Vodopivec, I. Autoimmune Neurologic Disorders. Am. J. Med. 2018, 131, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawachi, I.; Lassmann, H. Neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Lennon, V.A.; Parisi, J.E.; Popescu, B.; Vasquez, C.; Pittock, S.J.; Howe, C.L.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Spectrum of sub lytic astrocytopathy in neuromyelitis optica. Brain 2022, 145, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero Contentti, E.; Correale, J. Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: From pathophysiology to therapeutic strategies. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin 4 and Neuromyelitis Optica. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Lee, C.Y. Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M. Neuromyelitis optica: New findings on pathogenesis. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 79, 665–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jarius, S.; Wildemann, B. The history of neuromyelitis optica. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lennon, V.A.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Pittock, S.J.; Weinshenker, B.G. The spectrum of neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, V.A.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Kryzer, T.J.; Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Fujihara, K.; Nakashima, I.; Weinshenker, B.G. A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: Distinction from multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2004, 364, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, V.A.; Kryzer, T.J.; Pittock, S.J.; Verkman, A.S. Hinson SR. IgG marker of optic-spinal multiple sclerosis binds to the aquaporin-4 water channel. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Passos, G.R.; Oliveira, L.M.; da Costa, B.K.; Apostolos-Pereira, S.L.; Callegaro, D.; Fujihara, K.; Sato, D.K. MOG-IgG-Associated Optic Neuritis, Encephalitis, and Myelitis: Lessons Learned From Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiezia, A.L.; Carotenuto, A.; Iovino, A.; Moccia, M.; Gastaldi, M.; Iodice, R.; Tedeschi, E.; Petracca, M.; Lavorgna, L.; d’Ambrosio, A.; et al. AQP4-MOG Double-Positive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: Case Report with Central and Peripheral Nervous System Involvement and Review of Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; de Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsattari, S.M.; Johnston, J.B.; McKenna, R.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Orr, P.; Ross, R.T.; Power, C. Aboriginals with multiple sclerosis: HLA types and predominance of neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2001, 56, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontika, M.P.; Anagnostouli, M.C. Human leukocyte antigens-immunogenetics of neuromyelitis optica or Devic’s disease and the impact on the immunopathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment: A critical review. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 1, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, D.G.; Barreira, A.A.; dos Santos, A.C.; Kaimen-Maciel, D.R.; Matiello, M.; Costa, R.M.; Deghaide, N.H.; Costa, L.S.; Louzada-Junior, P.; Diniz, P.R.; et al. HLA-DRB association in neuromyelitis optica is different from that observed in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2010, 16, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, R.; Paturel, L.; Jeannin, S.; Chausson, N.; Olindo, S.; Béra, O.; Bellance, R.; Smadja, D.; Césaire, D.; Cabre, P. Different HLA class II (DRB1 and DQB1) alleles determine either susceptibility or resistance to NMO and multiple sclerosis among the French Afro-Caribbean population. Mult. Scler. 2011, 17, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collongues, N.; Marignier, R.; Zéphir, H.; Papeix, C.; Blanc, F.; Ritleng, C.; Tchikviladzé, M.; Outteryck, O.; Vukusic, S.; Fleury, M. Neuromyelitis optica in France: A multicenter study of 125 patients. Neurology 2010, 74, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, S.; Isobe, N.; Yonekawa, T.; Matsushita, T.; Masaki, K.; Sato, S.; Kawano, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Kira, J. South Japan Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium. Genetic and infectious profiles of Japanese multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, N.; Oksenberg, J.R. Genetic studies of multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica: Current status in European, African American and Asian populations. Clin. Exp. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 5, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Chang, Y.; Rui, L.; Caixia, L.; Long, Y.; Huang, J.; Mai, W.; Sun, X.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; et al. Human aquaporin 4 gene polymorphisms in Chinese patients with neuromyelitis optica. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 274, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, X.; Wang, K.; Qiu, W.; Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Hu, X. Interleukin 17 gene polymorphism is associated with anti-aquaporin 4 antibody-positive neuromyelitis optica in the Southern Han Chinese–A case control study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 314, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, N.; Nielsen, C.; Stenager, E.; Kyvik, K.O.; Lillevang, S.T. HLA, PTPN22 and PD-1 associations as markers of autoimmunity in neuromyelitis optica. Mult. Scler. 2012, 18, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, F.; Gao, C.; Ma, X.; Peng, X.; Kong, D.; Hao, J. Microarray Analysis of lncRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles in Patients With Neuromyelitis Optica. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaknin-Dembinsky, A.; Charbit, H.; Brill, L.; Abramsky, O.; Gur-Wahnon, D.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Lavon, I. Circulating microRNAs as Biomarkers for Rituximab Therapy, in Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO). J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoman, M.E.; McKarns, S.C. Metabolomic Profiling in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Biomarker Discovery. Metabolites 2020, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Shen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhong, X.; Chang, Y.; Kermode, A.G.; Qiu, W. Gut Microbiome and Bile Acid Metabolism Induced the Activation of CXCR5+ CD4+ T Follicular Helper Cells to Participate in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Recurrence. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 827865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, X.; Jin, T. Circulating Memory T Follicular Helper Cells in Patients with Neuromyelitis Optica/Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 3678152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Ruan, Y.; Qiu, W. Potential role of the gut microbiota in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: Implication for intervention. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 82, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, L.; Cox, L.M.; Malli, C.; D’Cunha, A.; Rooney, T.; Lokhande, H.; Willocq, V.; Saxena, S.; Chitnis, T. Clostridium bolteae is elevated in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in India and shares sequence similarity with AQP4. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 8, e907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roemer, S.F.; Parisi, J.E.; Lennon, V.A.; Benarroch, E.E.; Lassmann, H.; Bruck, W.; Mandler, R.N.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Pittock, S.J.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; et al. Pattern-Specific Loss of Aquaporin-4 Immunoreactivity Distinguishes Neuromyelitis Optica from Multiple Sclerosis. Brain 2007, 130, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Binder, D.K. Aquaporin-4 water channels and synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, T.; Saikali, P.; Cayrol, R.; Roth, A.D.; Bar-Or, A.; Prat, A.; Antel, J.P. Functional consequences of neuromyelitis optica-IgG astrocyte interactions on blood-brain barrier permeability and granulocyte recruitment. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5730–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asavapanumas, N.; Ratelade, J.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Bennett, J.L.; Levin, M.H.; Verkman, A.S. Experimental Mouse Model of Optic Neuritis with Inflammatory Demyelination Produced by Passive Transfer of Neuromyelitis Optica-Immunoglobulin, G. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiello, M.; Schaefer-Klein, J.; Sun, D.; Weinshenker, B.G. Aquaporin 4 Expression and Tissue Susceptibility to Neuromyelitis Optica. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Yasui, M. Aquaporin-4 in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: A Target of Autoimmunity in the Central Nervous System. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckeon, A.; Lennon, V.A.; Lotze, T.; Tenenbaum, S.; Ness, J.M.; Rensel, M.; Kuntz, N.L.; Fryer, J.P.; Homburger, H.; Hunter, J.; et al. CNS Aquaporin-4 Autoimmunity in Children. Neurology 2008, 71, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuan, P.W.; Ratelade, J.; Rossi, A.; Tradtrantip, L.; Verkman, A.S. Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity in Neuromyelitis Optica Requires Aquaporin-4 Protein Assembly in Orthogonal Arrays. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13829–13839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiello, M.; Schaefer-Klein, J.L.; Hebrink, D.D.; Kingsbury, D.J.; Atkinson, E.J.; Weinshenker, B.G. NMO Genetics Collaborators. Genetic analysis of aquaporin-4 in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2011, 77, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, S.R.; Romero, M.F.; Popescu, B.F.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Fryer, J.P.; Wolburg, H.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Noell, S.; Lennon, V.A. Molecular Outcomes of Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO)-IgG Binding to Aquaporin-4 in Astrocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 124–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, J.; Obayashi, S.; Misawa, T.; Tabunoki, H.; Yamamura, T.; Arima, K.; Konno, H. Neuromyelitis Optica/Devic’s Disease: Gene Expression Profiling of Brain Lesions. Neuropathology 2008, 28, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostásy, K.; Mader, S.; Hennes, E.M.; Schanda, K.; Gredler, V.; Guenther, A.; Blaschek, A.; Korenke, C.; Pritsch, M.; Pohl, D. Persisting myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies in aquaporin-4 antibody negative pediatric neuromyelitis optica. Mult. Scler. 2013, 19, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppe, S.; Robertson, N.P. MOG-IgG in neuromyelitis optica. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höftberger, R.; Guo, Y.; Flanagan, E.P.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Endmayr, V.; Hochmeister, S.; Joldic, D.; Pittock, S.J.; Tillema, J.M.; Gorman, M.; et al. The pathology of central nervous system inflammatory demyelinating disease accompanying myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein autoantibody. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 875–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, S.; Gredler, V.; Schanda, K.; Rostasy, K.; Dujmovic, I.; Pfaller, K.; Lutterotti, A.; Jarius, S.; Di Pauli, F.; Kuenz, B.; et al. Complement activating antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in neuromyelitis optica and related disorders. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Gaviria, R.; Baracaldo, I.; Castañeda, C.; Ruiz-Patiño, A.; Acosta-Hernandez, A.; Rosselli, D. Specificity and sensitivity of aquaporin 4 antibody detection tests in patients with neuromyelitis optica: A meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Dis. 2015, 4, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittam, D.; Wilson, M.; Hamid, S.; Keir, G.; Bhojak, M.; Jacob, A. What’s new in neuromyelitis optica? A short review for the clinical neurologist. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 2330–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Mutch, K.; Elsone, L.; Nurmikko, T.; Jacob, A. Neuropathic pain in neuromyelitis optica affects activities of daily living and quality of life. Mult. Scler. 2014, 20, 1658–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsone, L.; Townsend, T.; Mutch, K.; Das, K.; Boggild, M.; Nurmikko, T.; Jacob, A. Neuropathic pruritis (itch) in neuromyelitis optica. Mult. Scler. 2012, 19, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Go, M.J.; Sung, J.J.; Park, K.S.; Lee, K.W. Painful tonic spasm in neuromyelitis optica: Incidence, diagnostic utility, and clinical characteristics. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, D.; Fukihara, K. Atypical presentations of neuromyelitis optica. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2011, 69, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Nakashima, I.; Kanbayashi, T.; Konno, M.; Takahashi, T.; Fujihara, K.; Misu, T.; Takeda, A.; Shiga, Y.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Narcolepsy as an initial manifestation of neuromyelitis optica with antiaquaporin-4 antibody. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.; Methley, A.; Pollard, C.; Mutch, K.; Hamid, S.; Elsone, L.; Jacob, A. Cognitive and psychiatric comorbidities in neuromyelitis optica. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 360, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Xu, J.; Pan, C.; Cheng, J.; Hu, Y.; Hong, Y.; Shen, Y.; Dai, H. Cognitive dysfunction in adult patients with neuromyelitis optica: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekeridou, A.; Lennon, V.A. Aquaporin-4 autoimmunity. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 2, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, W.L.; Reiche, E.M.; Kallaur, A.P.; Kaimen-Maciel, D.R. Epidemiological, clinical, and immunological characteristics of neuromyelitis optica: A review. J. Neurol Sci. 2015, 355, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfueller, C.F.; Paul, F. Imaging the visual pathway in neuromyelitis optica. Mult. Scler. Int. 2011, 2011, 869814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Chien, C.; Lu, A.; Paul, F.; Zimmermann, H.G. Retinal optical coherence tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders and MOG-antibody associated disorders: An updated review. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 1101–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Sharma, A.; Huecker, J.; Gordon, M.; Naismith, R.T.; Van Stavern, G.P. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Optic Neuritis in Patients with Neuromyelitis Optica Versus Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuro. Ophthalmol. 2012, 32, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, J.M.; Tajima, M.; Verkman, A.S. Live-cell imaging of aquaporin-4 diffusion and interactions in orthogonal arrays of particles. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youl, B.D.; Turano, G.; Miller, D.H.; Towell, A.D.; MacManus, D.G.; Moore, S.G.; Jones, S.J.; Barrett, G.; Kendall, B.E.; Moseley, I.F.; et al. The pathophysiology of acute optic neuritis. An association of gadolinium leakage with clinical and electrophysiological deficits. Brain 1991, 114, 2437–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, P.; Sonni, S.; Kister, I.; Loh, J.P.; Lui, Y.W. Pencil-thin ependymal enhancement in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Mult. Scler. 2012, 18, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Mori, M.; Makino, T.; Hayakawa, S.; Kuwabara, S. ‘Cloud-like enhancement’ is a magnetic resonance imaging abnormality specific to neuromyelitis optica. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youl, B.D.; Turano, G.; Towell, A.D.; Barrett, G.; MacManus, D.G.; Moore, S.G.; Miller, D.H.; Jones, S.J.; du Boulay, E.P.; Kendall, B.E.; et al. Optic neuritis: Swelling and atrophy. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Suppl. 1996, 46, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fadda, G.; Flanagan, E.P.; Cacciaguerra, L.; Jitprapaikulsan, J.; Solla, P.; Zara, P.; Sechi, E. Myelitis features and outcomes in CNS demyelinating disorders: Comparison between multiple sclerosis, MOGAD, and AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1011579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayzenberg, I.; Richter, D.; Henke, E.; Asseyer, S.; Paul, F.; Trebst, C.; Hümmert, M.W.; Havla, J.; Kümpfel, T.; Ringelstein, M.; et al. Pain, depression, and quality of life in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: A crosssectional study of 166 AQP4 antibody-seropositive patients. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao-Fleming, H.H.; Valencia Sanchez, C.; Sechi, E.; Inbarasu, J.; Wijdicks, E.F.; Pittock, S.J.; Chen, J.J.; Wingerchuk, D.M.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Lopez-Chiriboga, S.; et al. CNS demyelinating attacks requiring ventilatory support with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein or aquaporin-4 antibodies. Neurology 2021, 97, e1351–e1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, R.; Messina, S.; Kumar, K.; Kuker, W.; Leite, M.I.; Palace, J. Comparison of clinical outcomes of transverse myelitis among adults with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody vs. aquaporin-4 antibody disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1912732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Lennon, V.A.; Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Weinshenker, B.G. Revised diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2006, 66, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, E.; Cacciaguerra, L.; Chen, J.J.; Mariotto, S.; Fadda, G.; Dinoto, A.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Pittock, S.J.; Flanagan, E.P. Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody-Associated Disease (MOGAD): A Review of Clinical and MRI Features, Diagnosis, and Management. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 885218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Flanagan, E.P.; Jitprapaikulsan, J.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.S.; Fryer, J.P.; Leavitt, J.A.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Mckeon, A.; Tillema, J.M.; Lennon, V.A.; et al. Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody-Positive Optic Neuritis: Clinical Characteristics, Radiologic Clues, and Outcome. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 195, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mealy, M.A.; Whetstone, A.; Orman, G.; Izbudak, I.; Calabresi, P.A.; Levy, M. Longitudinally extensive optic neuritis as an MRI biomarker distinguishes neuromyelitis optica from multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 355, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo-Calvo, A.; Ruiz, A.; Maillart, E.; Audoin, B.; Zephir, H.; Bourre, B.; Ciron, J.; Collongues, N.; Brassat, D.; Cotton, F. Clinical spectrum and prognostic value of CNS MOG autoimmunity in adults: The MOGADOR study. Neurology 2018, 90, e1858–e1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Ruprecht, K.; Kleiter, I.; Borisow, N.; Asgari, N.; Pitarokoili, K.; Pache, F.; Stich, O.; Beume, L.A.; Hümmert, M.W. MOG-IgG in NMO and related disorders: A multicenter study of 50 patients. Part 2: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, radiological and laboratory features, treatment responses, and long-term outcome. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurynczyk, M.; Geraldes, R.; Probert, F.; Woodhall, M.R.; Waters, P.; Tackley, G.; DeLuca, G.; Chandratre, S.; Leite, M.I.; Vincent, A.; et al. Distinct brain imaging characteristics of autoantibody-mediated CNS conditions and multiple sclerosis. Brain 2017, 140, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, S.; Khan, M.; Shanechi, A.; Levy, M.; Izbudak, I. MRI differences between MOG antibody disease and AQP4 NMOSD. Mult. Scler. 2020, 26, 1854–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Jia, D.; Fan, M.; Li, T.; Tian, D.C.; Liu, Y.; Shi, F.D. The Occurrence of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibodies in Aquaporin-4-Antibody Seronegative Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disor. 2021, 53, 103030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulut, E.; Karakaya, J.; Salama, S.; Levy, M.; Huisman, T.A.G.M.; Izbudak, I. Brain MRI Findings in Pediatric-Onset Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder: Challenges in Differentiation from Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, A.; Zhang, B.; Chen, S.; Men, X.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Z. Comparison of deep gray matter lesions on magnetic resonance imaging among adults with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, multiple sclerosis, and neuromyelitis optica. Mult. Scler. 2014, 20, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarangaiah, A.; Sehgal, R.; Epperla, N. Sjögren’s syndrome and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD)-a case report and review of literature. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Waters, P.; Vincent, A.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, Y.H.; Park, K.S.; Min, J.H.; Sung, J.J.; Lee, K.W. Sjogren’s syndrome myelopathy: Spinal cord involvement in Sjogren’s syndrome might be a manifestation of neuromyelitis optica. Mult. Scler. 2009, 15, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kuroda, H.; Palace, J.; Fujihara, K. Differential diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2017, 10, 265–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarius, S.; Paul, F.; Aktas, O.; Asgari, N.; Dale, R.C.; de Seze, J.; Franciotta, D.; Fujihara, K.; Jacob, A.; Kim, H.J. MOG encephalomyelitis: International recommendations on diagnosis and antibody testing. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Chiriboga, A.S.; Majed, M.; Fryer, J.; Dubey, D.; McKeon, A.; Flanagan, E.P.; Jitprapaikulsan, J.; Kothapalli, N.; Tillema, J.M.; Chen, J. Association of MOG-IgG serostatus with relapse after acute disseminated encephalomyelitis and proposed diagnostic criteria for MOG-IgG-associated disorders. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, S.; Khan, M.; Pardo, S.; Izbudak, I.; Levy, M. MOG antibody-associated encephalomyelitis/encephalitis. Mult. Scler. 2019, 25, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenembaum, S.N. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 112, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, D.; Alper, G.; Van Haren, K.; Kornberg, A.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Tenembaum, S.; Belman, A.L. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: Updates on an inflammatory CNS syndrome. Neurology 2016, 87, S38–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Fujihara, K.; Nakashima, I.; Misu, T.; Miyazawa, I.; Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, S.; Shiga, Y.; Kanaoka, C.; Fujimori, J.; et al. Anti-Aquaporin-4 Antibody Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of NMO: A Study on Antibody Titre. Brain 2007, 130, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmetzer, O.; Lakin, E.; Roediger, B.; Duchow, A.; Asseyer, S.; Paul, F.; Siebert, N. Anti-Aquaporin 4 IgG Is Not Associated with Any Clinical Disease Characteristics in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 635419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrpour, M.; Kyani, A.; Tafazzoli, M.; Fathi, F.; Joghataie, M.T. A metabonomics investigation of multiple sclerosis by nuclear magnetic resonance. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2013, 51, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villoslada, P.; Alonso, C.; Agirrezabal, I.; Kotelnikova, E.; Zubizarreta, I.; Pulido-Valdeolivas, I.; Saiz, A.; Comabella, M.; Montalban, X.; Villar, L.; et al. Metabolomic signatures associated with disease severity in multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Boccio, P.; Rossi, C.; di Ioia, M.; Cicalini, I.; Sacchetta, P.; Pieragostino, D. Integration of metabolomics and proteomics in multiple sclerosis: From biomarkers discovery to personalized medicine. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieragostino, D.; D’Alessandro, M.; di Ioia, M.; Rossi, C.; Zucchelli, M.; Urbani, A.; Di Ilio, C.; Lugaresi, A.; Sacchetta, P.; Del Boccio, P. An integrated metabolomics approach for the research of new cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of multiple sclerosis. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurynczyk, M.; Probert, F.; Yeo, T.; Tackley, G.; Claridge, T.D.W.; Cavey, A.; Woodhall, M.R.; Arora, S.; Winkler, T.; Schiffer, E.; et al. Metabolomics reveals distinct, antibody-independent, molecular signatures of MS, AQP4-antibody and MOG-antibody disease. Acta. Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussallieh, F.M.; Elbayed, K.; Chanson, J.B.; Rudolf, G.; Piotto, M.; De Seze, J.; Namer, I.J. Serum analysis by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: A new tool for distinguishing neuromyelitis optica from multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2014, 20, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregiworgis, T.; Nielsen, H.H.; Massilamany, C.; Gangaplara, A.; Reddy, J.; Illes, Z.; Powers, R. A Urinary Metabolic Signature for Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Jeong, I.H.; Kong, B.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, H.J. Disease Type- and Status-Specific Alteration of CSF Metabolome Coordinated with Clinical Parameters in Inflammatory Demyelinating Diseases of CNS. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowarik, M.C.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Wemlinger, S.; Ritchie, A.M.; Hemmer, B.; Owens, G.P.; Bennett, J.L. The cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulin transcriptome and proteome in neuromyelitis optica reveals central nervous system-specific B cell populations. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchinetti, C.F.; Guo, Y.; Popescu, B.F.G.; Fujihara, K.; Itoyama, Y.; Misu, T. The Pathology of an Autoimmune Astrocytopathy: Lessons Learned from Neuromyelitis Optica. Brain. Pathol. 2014, 24, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittock, S.J.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Neuromyelitis optica and the evolving spectrum of autoimmune aquaporin-4 channelopathies: A decade later. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1366, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, B.; Lennon, V.A.; Parisi, J.E.; Howe, C.L.; Weigand, S.D.; Cabrera-Gomez, J.A.; Newell, K.; Mandler, R.N.; Pittock, S.J.; Weinshenker, B.G.; et al. Neuromyelitis optica unique area postrema lesions: Nausea, vomiting, and pathogenic implications. Neurology 2011, 76, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoozi, S.; Rao, S.B.; Skauli, N.; Froehner, S.C.; Ottersen, O.P.; Adams, M.E.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M. Functional specialization of retinal Müller cell endfeet depends on an interplay between two syntrophin isoforms. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, R.; Misu, T.; Takahashi, T.; Sato, S.; Fujihara, K.; Itoyama, Y. Astrocytic damage is far more severe than demyelination in NMO: A clinical CSF biomarker study. Neurology 2010, 75, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storoni, M.; Verbeek, M.M.; Illes, Z.; Marignier, R.; Teunissen, C.E.; Grabowska, M.; Confavreux, C.; Plant, G.T.; Petzold, A. Serum GFAP levels in optic neuropathies. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 317, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; McKeon, A.; Hinson, S.R.; Kryzer, T.J.; Pittock, S.J.; Aksamit, A.J.; Lennon, V.A. Autoimmune glial fibrillary acidic protein astrocytopathy: A novel meningo encephalomyelitis. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Aboul-Enein, F.; Waters, P.; Kuenz, B.; Hauser, A.; Berger, T.; Lang, W.; Reindl, M.; Vincent, A.; Kristoferitsch, W. Antibody to aquaporin-4 in the long-term course of neuromyelitis optica. Brain 2008, 131, 3072–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.D.; Yeh, R.; Sandstrom, A.; Chorny, I.; Harries, W.E.; Robbins, R.A.; Miercke, L.J.; Stroud, R.M. Crystal structure of human aquaporin 4 at 1.8 a and its mechanism of conductance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7437–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Xiao, M.; Li, S.; Yang, B. Aquaporins in Nervous System. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 969, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.S.; Bhat, R.V.; Preston, G.M.; Guggino, W.B.; Baraban, J.M.; Agre, P. Molecular characterization of an aquaporin cDNA from brain: Candidate osmoreceptor and regulator of water balance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 13052–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shang, D.; Shi, H.; Teng, W.; Tian, L. Function of Astrocytes in Neuroprotection and Repair after Ischemic Stroke. Eur. Neurol. 2021, 84, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szu, J.I.; Binder, D.K. The Role of Astrocytic Aquaporin-4 in Synaptic Plasticity and Learning and Memory. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2016, 24, 10:18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Verkman, A.S. Greatly attenuated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in aquaporin-4 knockout mice. BMC Neurosci. 2009, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netti, V.; Fernández, J.; Melamud, L.; Garcia-Miranda, P.; Di Giusto, G.; Ford, P.; Echevarría, M.; Capurro, C. Aquaporin-4 Removal from the Plasma Membrane of Human Müller Cells by AQP4-IgG from patients with neuromyelitis optica induces changes in cell volume homeostasis: The first step of retinal injury? Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 5178–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Wildemann, B.; Paul, F. Neuromyelitis optica: Clinical features, immunopathogenesis and treatment. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 176, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C. B cells as therapeutic targets in autoimmune neurological disorders. Nat. Clin. Pract. 2008, 4, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, N.; Aranami, T.; Sato, W.; Miyazaki, Y.; Miyake, S.; Okamoto, T.; Ogawa, M.; Toda, T.; Yamamura, T. Interleukin 6 signaling promotes anti-aquaporin 4 autoantibody production from plasmoblasts in neuromyelitis optica. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3701–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Makuch, M.; Kienzler, A.K.; Varley, J.; Taylor, J.; Woodhall, M.; Palace, J.; Leite, M.I.; Waters, P.; Irani, S.R. Condition-dependent generation of aquaporin-4 antibodies from circulating B cells in neuromyelitis optica. Brain 2018, 141, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBien, T.W.; Tedder, T.F. B lymphocytes: How they develop and function. Blood 2008, 112, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinson, S.R.; Roemer, S.F.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Fryer, J.P.; Kryzer, T.J.; Chamberlain, J.L.; Howe, C.L.; Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A. Aquaporin-4-binding autoantibodies in patients with neuromyelitis optica impair glutamate transport by down-regulating EAAT2. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2473–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marignier, R.; Nicolle, A.; Watrin, C.; Touret, M.; Cavagna, S.; Varrin-Doyer, M.; Cavillon, G.; Rogemond, V.; Confavreux, C.; Honnorat, J.; et al. Oligodendrocytes are damaged by neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G via astrocyte injury. Brain 2010, 133, 2578–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, C.L.; Kaptzan, T.; Magaña, S.M.; Ayers-Ringler, J.R.; LaFrance-Corey, R.G.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Neuromyelitis optica IgG stimulates an immunological response in rat astrocyte cultures. Glia 2014, 62, 692–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Verkman, A.S. Eosinophil pathogenicity mechanisms and therapeutics in neuromyelitis optica. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Yao, X.; Su, T.; Smith, A.J.; Verkman, A.S. Bystander mechanism for complement-initiated early oligodendrocyte injury in neuromyelitis optica. Acta. Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Smith, A.J.; Verkman, A.S. Complement-dependent bystander injury to neurons in AQP4-IgG seropositive neuromyelitis optica. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, T.G.; Bernard, C.A.C. The structure and function of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. J. Neurochem. 2002, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lott, L.B.; Bennett, J.L.; Costello, F. The Changing Landscape of Optic Neuritis: A Narrative Review. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrikowski, L.; Reinehr, S.; Haupeltshofer, S.; Deppe, L.; Graz, F.; Kleiter, I.; Dick, H.B.; Gold, R.; Faissner, S.; Joachim, S.C. Progressive Retinal and Optic Nerve Damage in a Mouse Model of Spontaneous Opticospinal Encephalomyelitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 759389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Hashimoto, B.; Izaki, S.; Oji, S.; Fukaura, H.; Nomura, K. Clinical and Immunological Differences between Mog Associated Disease and Anti Aqp4 Antibody-Positive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown and Peripheral Plasmablasts. Mult. Scler. Rela. Disord. 2020, 41, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataie-Kachoie, P.; Pourgholami, M.H.; Morris, D.L. Inhibition of the IL-6 signaling pathway: A strategy to combat chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wagoner, N.J.; Benveniste, E.N. Interleukin-6 expression and regulation in astrocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 1999, 100, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, K.; Bennett, J.L.; de Seze, J.; Haramura, M.; Kleiter, I.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Kang, D.; Mughal, T.; Yamamura, T. Interleukin-6 in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder pathophysiology. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chang, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Cong, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Yin, L. NMO-IgG Induce Interleukin-6 Release via Activation of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Astrocytes. Neuroscience 2022, 496, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Zhong, X.; Dai, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wu, A.; Hu, X. Notable increased cerebrospinal fluid levels of soluble interleukin-6 receptors in neuromyelitis optica. Neuroimmunomodulation 2012, 19, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Chang, H.; Xu, W.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yin, L.; Zhang, X. Effect of NMO-IgG on the interleukin-6 cascade in astrocytes via activation of the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Heink, S.; Korn, T.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: Designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzawa, A.; Mori, M.; Ito, M.; Uchida, T.; Hayakawa, S.; Masuda, S.; Kuwabara, S. Markedly increased CSF interleukin-6 levels in neuromyelitis optica, but not in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2009, 256, 2082–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzawa, A.; Mori, M.; Arai, K.; Sato, Y.; Hayakawa, S.; Masuda, S.; Taniguchi, J.; Kuwabara, S. Cytokine and Chemokine Profiles in Neuromyelitis Optica: Significance of Interleukin-6. Mult. Scler. 2010, 16, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipfel, P.F.; Skerka, C. Complement regulators and inhibitory proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pache, F.; Ringelstein, M.; Aktas, O.; Kleiter, I.; Jarius, S.; Siebert, N.; Bellmann-Strobl, J.; Paul, F.; Ruprecht, K. C3 and C4 complement levels in AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD and in MOGAD. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 360, 577699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciak, K.; Pietrasik, S.; Dziedzic, A.; Redlicka, J.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M.; Włodarczyk, T.; Miller, E. Th17-Related Cytokines as Potential Discriminatory Markers between Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic’s Disease) and Multiple Sclerosis—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzawa, A.; Mori, M.; Kuwabara, S. Cytokines and chemokines in neuromyelitis optica: Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications. Brain Pathol. 2014, 24, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.M.; Li, Y.F.; He, L.L.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.X.; Li, X.Y. Proportions of Th17 Cells and Th17-Related Cytokines in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 75, 105793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nytrova, P.; Potlukova, E.; Kemlink, D.; Woodhall, M.; Horakova, D.; Waters, P.; Havrdova, E.; Zivorova, D.; Vincent, A.; Trendelenburg, M. Complement activation in patients with neuromyelitis optica. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 274, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asavapanumas, N.; Tradtrantip, L.; Verkman, A.S. Targeting the complement system in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltys, J.; Liu, Y.; Ritchie, A.; Wemlinger, S.; Schaller, K.; Schumann, H.; Owens, G.P.; Bennett, J.L. Membrane assembly of aquaporin-4 autoantibodies regulates classical complement activation in neuromyelitis optica. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2000–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Verkman, A.S. Complement regulator CD59 prevents peripheral organ injury in rats made seropositive for neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G. Acta. Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, S.R.; Srivastava, R.; Kenet, S.; Tanti, G.K.; Dornmair, K.; Bennett, J.L.; Misgeld, T.; Hemmer, B.; Wyss, M.T.; Herwerth, M. P2R Inhibitors Prevent Antibody-Mediated Complement Activation in an Animal Model of Neuromyelitis Optica: P2R Inhibitors Prevent Autoantibody Injury. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittock, S.J.; Lennon, V.A.; McKeon, A.; Mandrekar, J.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; O’Toole, O.; Wingerchuk, D.M. Eculizumab in AQP4-IgG-positive relapsing neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: An open-label pilot study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.L.; Lam, C.; Kalluri, S.R.; Saikali, P.; Bautista, K.; Dupree, C.; Glogowska, M.; Case, D.; Antel, J.P.; Owens, G.P.; et al. Intrathecal pathogenic antiaquaporin-4 antibodies in early neuromyelitis optica. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klos, A.; Tenner, A.J.; Johswich, K.O.; Ager, R.R.; Reis, E.S.; Kohl, J. The role of the anaphylatoxins in health and disease. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2753–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangaleela, S.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Bharathi, M.; Chaiyasut, C. Role of the Gut-Brain Axis, Gut Microbial Composition, Diet, and Probiotic Intervention in Parkinson’s Disease. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, I.I.; Atarashi, K.; Manel, N.; Brodie, E.L.; Shima, T.; Karaoz, U.; Wei, D.; Goldfarb, K.C.; Santee, C.A.; Lynch, S.V.; et al. Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented filamentous bacteria. Cell 2009, 139, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrin-Doyer, M.; Spencer, C.M.; Schulze-Topphoff, U.; Nelson, P.A.; Stroud, R.M.; Cree, B.A.; Zamvil, S.S. Aquaporin 4-specific T cells in neuromyelitis optica exhibit a Th17 bias and recognize Clostridium ABC transporter. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamvil, S.S.; Spencer, C.M.; Baranzini, S.E.; Cree, B.A.C. The Gut Microbiome in Neuromyelitis Optica. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cree, B.A.; Spencer, C.M.; Varrin-Doyer, M.; Baranzini, S.E.; Zamvil, S.S. Gut microbiome analysis in neuromyelitis optica reveals overabundance of Clostridium perfringens. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.F.; Wu, L.; Li, H.F.; Wu, Z.Y. Characteristic of gut microbiota in southeastern Chinese patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disor. 2020, 44, 102217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarius, S.; Wandinger, K.P.; Platzer, S.; Wildemann, B. Homology between Klebsiella pneumoniae and human aquaporin-4: No evidence for cross-reactivity in neuromyelitis optica. A study on 114 patients. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Qiu, W.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, A.; Bao, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Lack of short-chain fatty acids and overgrowth of opportunistic pathogens define dysbiosis of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: A Chinese pilot study. Mult. Scler. 2019, 25, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, S.I.; Zhu, Y.; Ntranos, A.; Clemente, J.C.; Cekanaviciute, E.; Brandstadter, R.; Crabtree-Hartman, E.; Singh, S.; Bencosme, Y.; Debelius, J.; et al. Disease-modifying therapies alter gut microbial composition in MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 6, e517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, R.; Takeda, K. Maintenance of intestinal homeostasis by mucosal barriers. Inflamm. Regen. 2018, 38, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Yadav, H. Bacterial Translocation from the Gut to the Distant Organs: An Overview. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 71, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Liu, C.; Han, J.; Lang, W.; Gao, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, S.; Hou, S.; Zheng, N. Blood brain barrier permeability could be a biomarker to predict severity of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: A retrospective analysis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, H.; Barmeyer, C.; Fromm, M.; Runkel, N.; Foss, H.D.; Bentzel, C.J.; Riecken, E.O.; Schulzke, J.D. Altered tight junction structure contributes to the impaired epithelial barrier function in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterlin, D.; Larsen, M.; Fadlallah, J.; Parizot, C.; Vignes, M.; Autaa, G.; Dorgham, K.; Juste, C.; Lepage, P.; Aboab, J.; et al. Perturbed microbiota/immune homeostasis in multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asavapanumas, N.; Verkman, A.S. Neuromyelitis optica pathology in rats following intraperitoneal injection of NMO-IgG and intracerebral needle injury. Acta. Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, M.; Nakatsuji, Y.; Kimura, T.; Moriya, M.; Takata, K.; Okuno, T.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kajiyama, K.; Yoshikawa, H.; Sakoda, S. Neuromyelitis optica: Passive transfer to rats by human immunoglobulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, H.; Rifkin, R.; Gorelik, M.; Huang, H.; Ferguson, Z.; Jones, M.V.; Levy, M. Passively transferred human NMO-IgG exacerbates demyelination in mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. BMC Neurol. 2013, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillebrand, S.; Schanda, K.; Nigritinou, M.; Tsymala, I.; Böhm, D.; Peschl, P.; Takai, Y.; Fukihara, K.; Nakashima, I.; Misu, T. Circulated AQP4-specific auto-antibodies alone can induce neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in the rat. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, S.; Waters, P.; Bell, B.A.; Vincent, A.; Verkman, A.S.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Intra-cerebral injection of neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G and human complement produces neuromyelitis optica lesions in mice. Brain 2010, 133, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Xie, C.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y. Experimental mouse model of NMOSD produced by facilitated brain delivery of NMO-IgG by microbubble-enhanced low-frequency ultrasound in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis mice. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disor. 2020, 46, 102473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Verkman, A.S. Experimental animal models of aquaporin-4-IgG-seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: Progress and shortcomings. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, J.M.; Lam, C.; Rossi, A.; Gupta, T.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Binding affinity and specificity of neuromyelitis optica autoantibodies to aquaporin-4 M1/M23 isoforms and orthogonal arrays. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 16516–16524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geis, C.; Ritter, C.; Ruschil, C.; Weishaupt, A.; Grunewald, B.; Stoll, G.; Holmoy, T.; Misu, T.; Fujihara, K.; Hemmer, B.; et al. The intrinsic pathogenic role of autoantibodies to aquaporin 4 mediating spinal cord disease in a rat passive-transfer model. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 265, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marignier, R.; Ruiz, A.; Cavagna, S.; Nicole, A.; Watrin, C.; Touret, M.; Parrot, S.; Malleret, G.; Peyron, C.; Benetollo, C. Neuromyelitis optica study model based on chronic infusion of autoantibodies in rat cerebrospinal fluid. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, C.M.; Levin, M.H.; Verkman, A.S. Complement-independent retinal pathology produced by intravitreal injection of neuromyelitis optica immunoglobulin G. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Ex vivo spinal cord slice model of neuromyelitis optica reveals novel immunopathogenic mechanisms. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Nakazawa, T.; Doi, H.; Hariya, T.; Omodaka, K.; Misu, T.; Takahashi, T.; Fujihara, K.; Nishida, K. Early high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone is effective in preserving retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with neuromyelitis optica. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2010, 248, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Stiebel-Kalish, H.; Hellmann, M.A.; Mimouni, M.; Paul, F.; Bialer, O.; Bach, M.; Lotan, I. Does time equal vision in the acute treatment of a cohort of AQP4 and MOG optic neuritis? Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflam. 2019, 6, e572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimbrough, D.; Fujihara, K.; Jacob, A.; Lana-Peixoto, M.A.; Leite, M.I.; Levy, M.; Marignier, R.; Nakashima, I.; Palace, J.; de Seze, J.; et al. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica: Review and recommendations. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2012, 1, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingele, M.; Allmendinger, C.; Thieme, S.; Baerens, L.; Fliser, D.; Jan, B. Therapeutic apheresis within immune-mediated neurological disorders: Dosing and its effectiveness. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, H.M.; Winters, J.L. The mechanisms of action of plasma exchange. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.A.; Mealy, M.A.; Levy, M. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: Acute, preventative, and symptomatic. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2016, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnan, M.; Valentino, R.; Olindo, S.; Mehdaoui, H.; Smadja, D.; Cabre, P. Plasma exchange in severe spinal attacks associated with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Mult. Scler. 2009, 15, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, H.; Olindo, S.; Jeannin, S.; Valentino, R.; Mehdaoui, H.; Cabot, F.; Donnio, A.; Hage, R.; Richer, R.; Smadja, D.; et al. Treatment of Optic Neuritis by Plasma Exchange (Add-On) in Neuromyelitis Optica. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, N.; Risler, T. Immunoadsorption as a Tool for the Immunomodulation of the Humoral and Cellular Immune System in Autoimmune Disease. Ther. Apher. 1999, 3, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiter, I.; Gahlen, A.; Borisow, N.; Fischer, K.; Wernecke, K.D.; Hellwig, K.; Pache, F.; Ruprecht, K.; Havla, J.; Kümpfel, T. Apheresis therapies for NMOSD attacks: A retrospective study of 207 therapeutic interventions. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 5, e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiter, I.; Gahlen, A.; Borisow, N.; Fischer, K.; Wernecke, K.-D.; Wegner, B.; Hellwig, K.; Pache, F.; Ruprecht, K.; Havla, J.; et al. Neuromyelitis optica: Evaluation of 871 attacks and 1153 treatment courses. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, B.L.; Choudhary, R.; Sharma, C.M.; Jain, D.; Hiremath, A. Plasma Exchange as a First Line Therapy in Acute Attacks of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2019, 22, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, R.; Pedapati, R.; Chopra, S. Plasmapheresis for NMOSD: Not a Rescue Therapy Anymore!? Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2019, 22, 371–372. [Google Scholar]
- Lunemann, J.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Dalakas, M.C. Intravenous immunoglobulin in neurology—Mode of action and clinical efficacy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lennon, V.A. Mechanism of intravenous immune globulin therapy in antibody-mediated autoimmune diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, K.; Matsushita, T.; Kira, J.; Tsuji, S. B-cell activating factor of the TNF family is upregulated in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2012, 74, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunrende, B.; Akdal, G.; Bajin, M.S.; Yaman, A.; Kocaslan, M.; Nalbantoğlu, M.; Ertaşoğlu, H.; Akman, G. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Treatment for Recurrent Optic Neuritis. Noro. Psikiyatr. Ars. 2019, 56, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Chu, F.; Jin, T.; Zhu, J. Progress in treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD): Novel insights into therapeutic possibilities in NMOSD. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, J.; Mares, J.; Barnett, M.; Aktas, O.; Albrecht, P.; Zamvil, S.S.; Hartung, H.P. Targeting B cells to modify MS, NMOSD, and MOGAD: Part 1. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, W.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.S.; Jia, D.; Zhang, T.X.; Yuan, M.; et al. TANGO Study Investigators. Safety and efficacy of tocilizumab versus azathioprine in highly relapsing neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (TANGO): An open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houssiau, F.A.; D’Cruz, D.; Sangle, S.; Remy, P.; Vasconcelos, C.; Petrovic, R.; Fiehn, C.; de Ramon Garrido, E.; Gilboe, I.M.; Tektonidou, M.; et al. Azathioprine versus mycophenolate mofetil for long-term immunosuppression in lupus nephritis: Results from the maintain nephritis trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poupart, J.; Giovannelli, J.; Deschamps, R.; Audoin, B.; Ciron, J.; Maillart, E.; Papeix, C.; Collongues, N.; Bourre, B.; Cohen, M.; et al. Evaluation of efficacy and tolerability of first-line therapies in NMOSD. Neurology 2020, 94, e1645–e1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Ramanathan, M.; Lincoff, N.; Napoli, S.Q.; Sharma, J.; Feichter, J.; Bakshi, R. Study of mitoxantrone for the treatment of recurrent neuromyelitis optica (Devic’s disease). Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, W.; Park, M.S.; Sohn, E.H.; Li, X.F.; Kim, H.J. Efficacy and safety of mitoxantrone in patients with highly relapsing neuromyelitis optica. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabre, P.; Olindo, S.; Marignier, R.; Jeannin, S.; Merle, H.; Smadja, D. Efficacy of mitoxantrone in neuromyelitis optica spectrum: Clinical and neuroradiological study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitley, J.; Elsone, L.; George, J.; Waters, P.; Woodhall, M.; Vincent, A.; Jacob, A.; Leite, M.I.; Palace, J. Methotrexate is an alternative to azathioprine with aquaporin-4 antibodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.S.; Malhotra, K.; Scott, T. Treatment of neuromyelitis optica/neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders with methotrexate. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, T.; Kleiter, I.; Fujihara, K.; Palace, J.; Greenberg, B.; Zakrzewska-Pniewska, B.; Patti, F.; Tsai, C.P.; Saiz, A.; Yamazaki, H.; et al. Trial of satralizumab in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traboulsee, A.; Greenberg, B.M.; Bennett, J.L.; Szczechowski, L.; Fox, E.; Shkrobot, S.; Yamamura, T.; Terada, Y.; Kawata, Y.; Wright, P.; et al. Safety and efficacy of satralizumab monotherapy in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmøy, T.; Høglund, R.A.; Illes, Z.; Myhr, K.M.; Torkildsen, Ø. Recent progress in maintenance treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. J. Neurol. 2020, 268, 4522–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Zhang, H.; Saadoun, S.; Phuan, P.W.; Lam, C.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Anti-aquaporin-4 monoclonal antibody blocker therapy for neuromyelitis optica. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Zhang, H.; Anderson, M.O.; Saadoun, S.; Phaun, P.W.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Small-molecule inhibitors of NMO-IgG binding to aquaporin-4 reduce astrocyte cytotoxicity in neuromyelitis optica. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2197–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, M.; Olsen, A. Endo S, a novel secreted protein from Streptococcus pyogenes with endoglycosidase activity on human IgG. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3046–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tradtrantip, L.; Asavapanumas, N.; Verkman, A.S. Therapeutic cleavage of anti-aquaporin-4 autoantibody in neuromyelitis optica by an IgG-selective proteinase. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, P.; Lledo-Garcia, R.; Watanabe, S.; Langdon, G.; Tran, D.; Bari, M.; Christodoulou, L.; Jones, E.; Price, G.; Smith, B.; et al. The FcRn inhibitor rozanolixizumab reduces human serum IgG concentration: A randomized phase 1 study. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipphardt, M.; Mühlhausen, J.; Kitze, B.; Heigl, F.; Mauch, E.; Helms, H.J.; Müller, G.A.; Koziolek, M.J. Immunoadsorption or plasma exchange in steroid-refractory multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. J. Clin. Apher. 2019, 34, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faissner, S.; Nikolayczik, J.; Chan, A.; Gold, R.; Yoon, M.S.; Haghikia, A. Immunoadsorption in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2016, 9, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsbernd, P.M.; Hoffman, W.R.; Carter, J.L.; Wingerchuk, D.M. Interleukin-6 inhibition with tocilizumab for relapsing MOG-IgG associated disorder (MOGAD): A case-series and review. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 48, 102696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, D.M. Satralizumab: An interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor antagonist for the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Drugs Today 2021, 57, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enspryng (Satralizumab-Mwge) Injection [Prescribing Information]. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2020. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/761149s000lbl.pdf. (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Kieseier, B.C.; Stüve, O.; Dehmel, T.; Goebels, N.; Leussink, V.I.; Mausberg, A.K.; Ringelstein, M.; Turowski, B.; Aktas, O.; Antoch, G.; et al. Disease amelioration with tocilizumab in a treatment-resistant patient with neuromyelitis optica: Implication for cellular immune responses. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruol, D.L. IL-6 regulation of synaptic function in the CNS. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morizane, A.; Li, J.Y.; Brundin, P. From bench to bed: The potential of stem cells for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Tissue. Res. 2008, 331, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, Y.; Abematsu, M.; Falk, A.; Tsujimura, K.; Sanosaka, T.; Juliandi, B.; Semi, K.; Namihira, M.; Komiya, S.; Smith, A.; et al. Treatment of a mouse model of spinal cord injury by transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived long-term self-renewing neuroepithelial-like stem cells. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Qiu, W.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Huang, R.; Lin, D.; Bao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Bian, L. A preliminary result of treatment of neuromyelitis optica with autologous peripheral hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Neurologist 2010, 16, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, B. Effect of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020, 55, 1928–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, R.K.; Balabanov, R.; Han, X.; Burns, C.; Gastala, J.; Jovanovic, B.; Helenowski, I.; Jitprapaikulsan, J.; Fryer, J.P.; Pittock, S.J. Autologous nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2019, 93, e1732–e1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thangaleela, S.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Radha, A.; Kesika, P.; Chaiyasut, C. Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: Clinical Perspectives, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatments. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085029
Thangaleela S, Sivamaruthi BS, Radha A, Kesika P, Chaiyasut C. Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: Clinical Perspectives, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatments. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(8):5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085029
Chicago/Turabian StyleThangaleela, Subramanian, Bhagavathi Sundaram Sivamaruthi, Arumugam Radha, Periyanaina Kesika, and Chaiyavat Chaiyasut. 2023. "Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: Clinical Perspectives, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatments" Applied Sciences 13, no. 8: 5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085029
APA StyleThangaleela, S., Sivamaruthi, B. S., Radha, A., Kesika, P., & Chaiyasut, C. (2023). Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders: Clinical Perspectives, Molecular Mechanisms, and Treatments. Applied Sciences, 13(8), 5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085029








