Dense-FG: A Fusion GAN Model by Using Densely Connected Blocks to Fuse Infrared and Visible Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A generator network structure and discriminator network structure with dense connection blocks were designed so that there are paths connecting all layers of the network, enabling feature reuse and improving computational efficiency.
- (2)
- A content loss function was constructed using four losses, an infrared gradient, visible intensity, infrared intensity, and a visible gradient, to maintain a balance between infrared radiation information and visible texture details, and to achieve an ideal fusion image.
- (3)
- By updating the 8-direction gradient operator template and optimizing the design of the loss function, the fusion image details were made richer.
- (4)
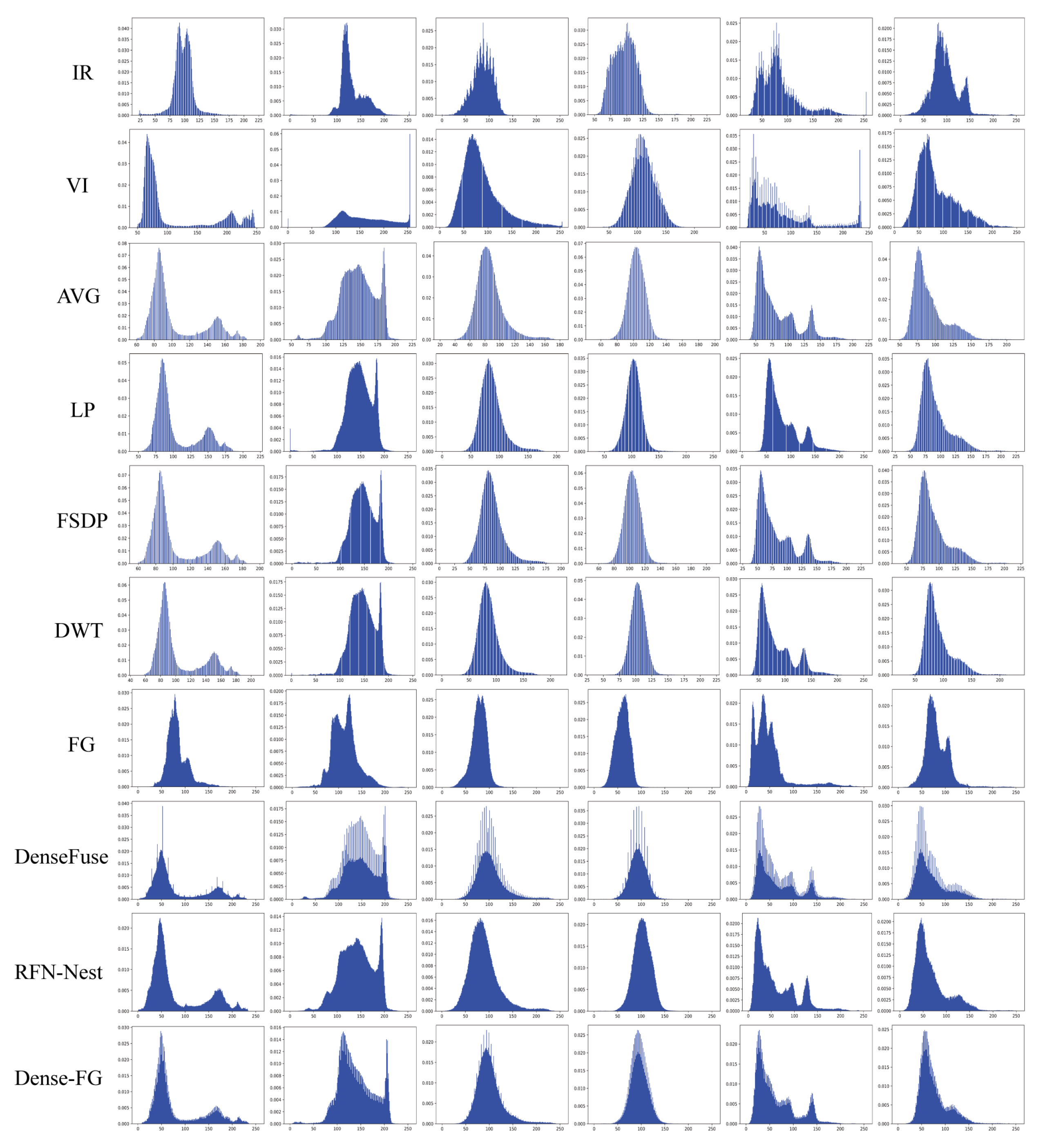
- Histogram comparison was used to demonstrate the fusion ability of eight fusion methods in a clear and intuitive way, providing a reference for the development and improvement of fusion image methods in the future.
2. Literature Survey
2.1. Research Status of Traditional Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
2.2. Research Status of Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Deep Learning
3. Proposed Method
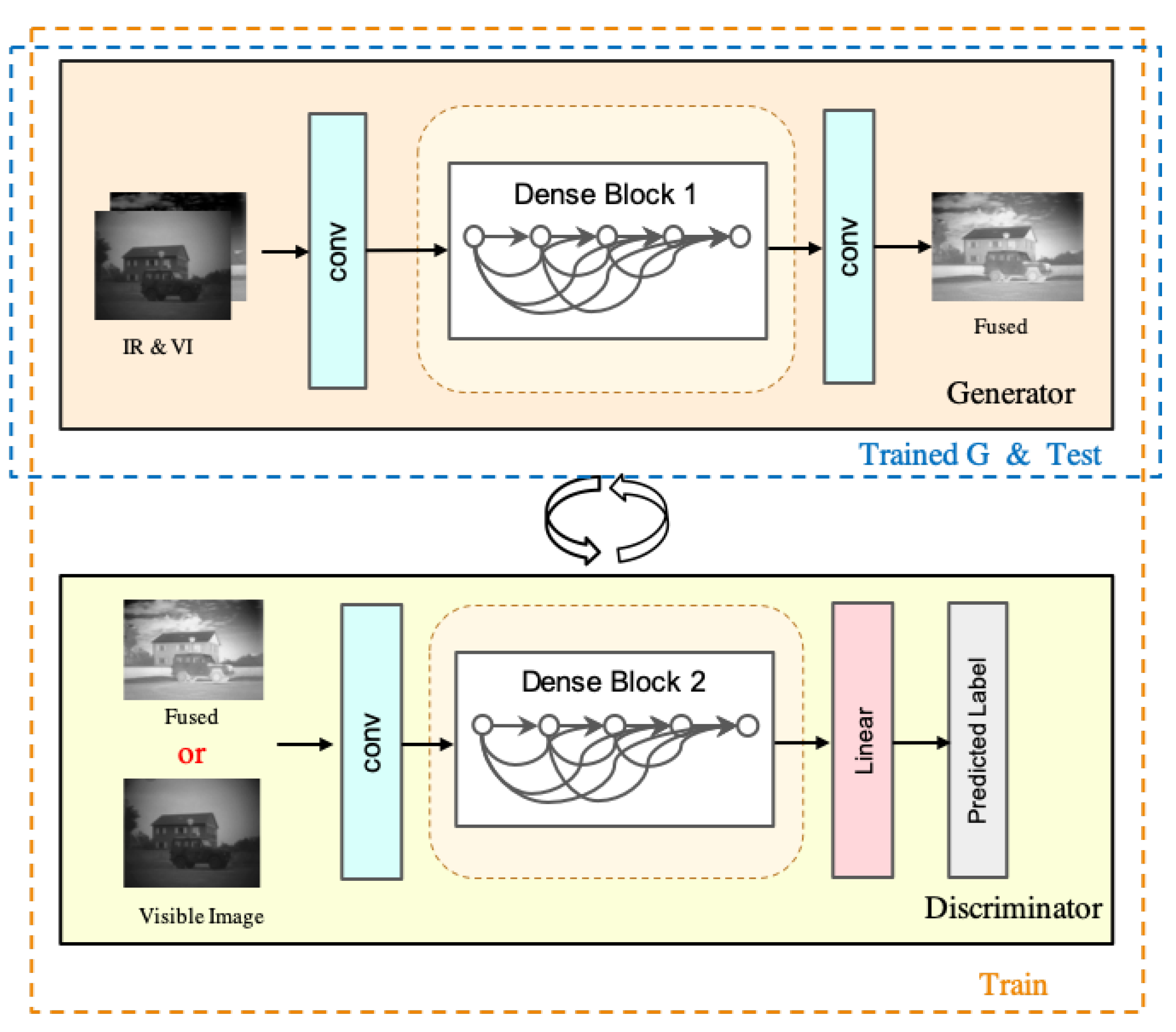
3.1. Network Architecture Design
3.1.1. Generator Network Architecture
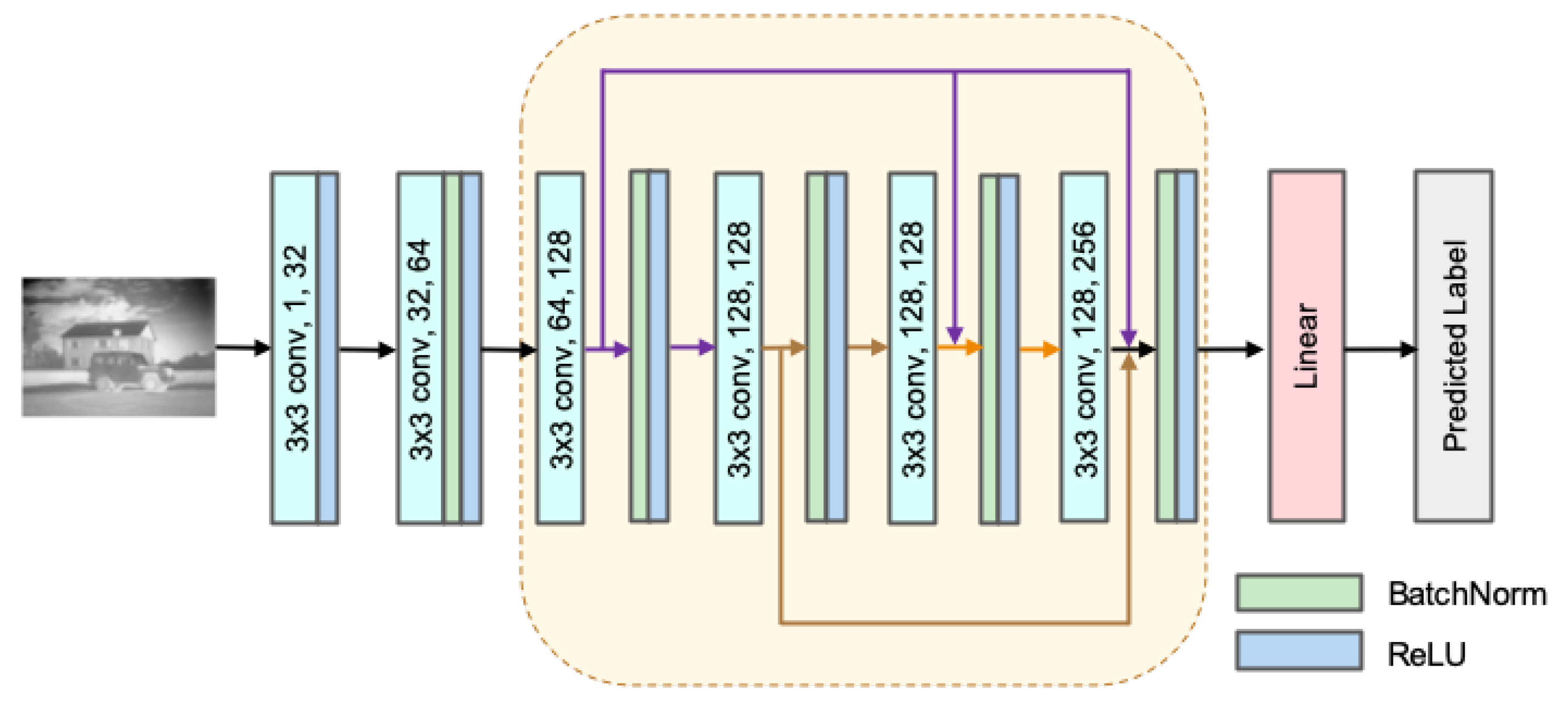
3.1.2. Discriminator Network Architecture
3.2. Loss Function Design
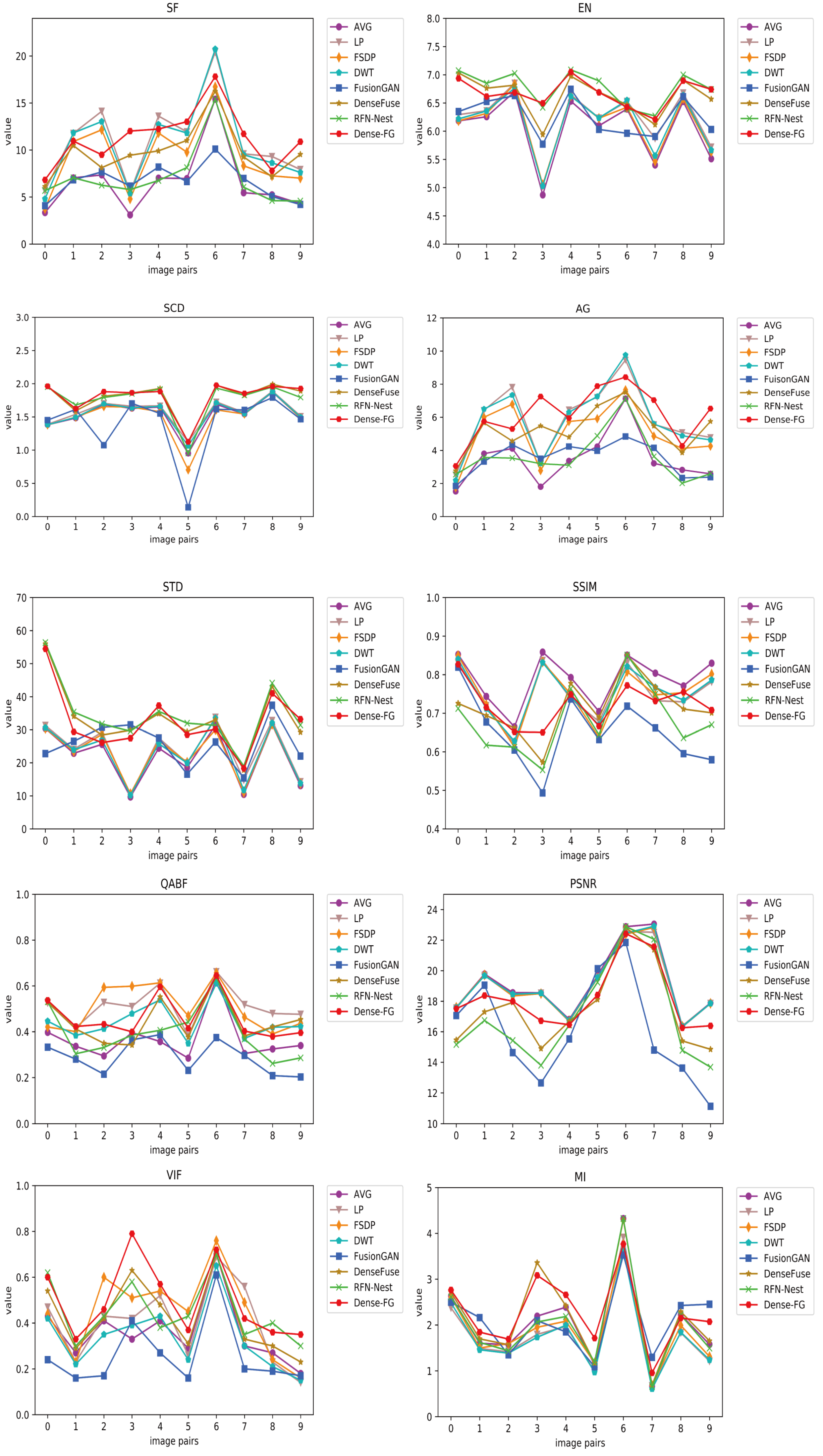
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Design and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Comparative Experiment
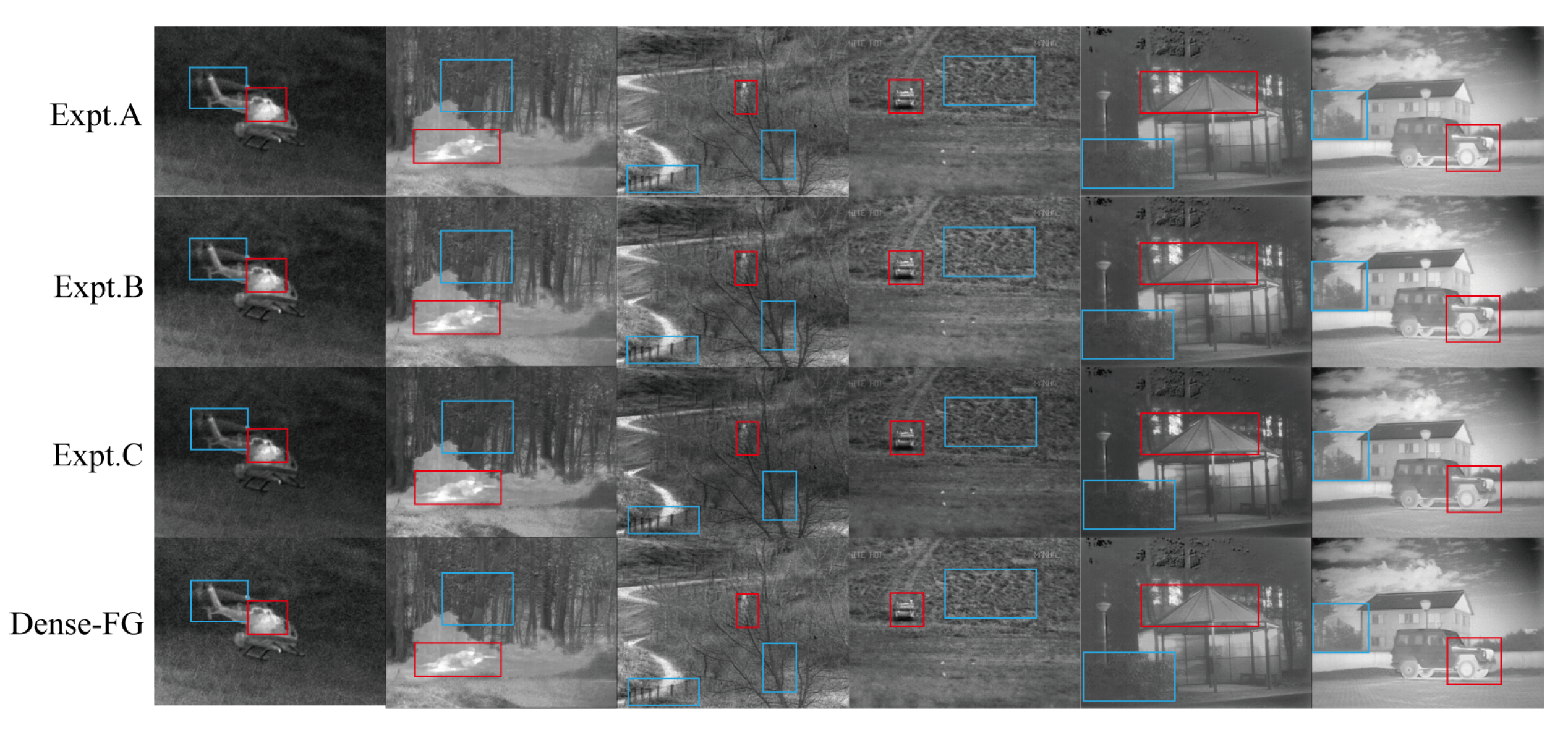
4.3. Ablation Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Ziou, D.; Armenakis, C.; Li, D.; Li, Q. A comparative analysis of image fusion methods. IEEE Trans. Geoence Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Multimodal medical image fusion based on IHS and PCA. Procedia Eng. 2010, 7, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion with a Generative Adversarial Network and a Residual Network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, G.; Farina, A.; Morabito, F.C.; Serpico, S.B.; Bruzzone, L. Image fusion techniques for remote sensing applications. Inf. Fusion 2002, 3, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, N. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Techniques Based on Deep Learning: A Review. Electronics 2020, 9, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Nasrin, S.; Darabi, N.; Gomes, W.; Trivedi, A.R. MC-CIM: Compute-in-Memory With Monte-Carlo Dropouts for Bayesian Edge Intelligence. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2022, 70, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekman, T.; Abolfathi, M.; Jafarian, H.; Biswas, A.; Banaei-Kashani, F.; Das, K. Practical Black Box Model Inversion Attacks Against Neural Nets. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases: International Workshops of ECML PKDD 2021, Virtual Event, 13–17 September 2021; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejatishahidin, N.; Fayyazsanavi, P.; Košecka, J. Object pose estimation using mid-level visual representations. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 13105–13111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, B.; Hu, J. Performance comparison of different multi-resolution transforms for image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2011, 12, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, T.; Ni, G. Contrast-based image fusion using the discrete wavelet transform. Opt. Eng. 2000, 39, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, P.J.; Adelson, E.H. The Laplacian Pyramid as a Compact Image Code. Readings Comput. Vis. 1987, 31, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, B.l. Multifocus image fusion using the nonsubsampled contourlet transform. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tong, S.; Huang, S.; Lin, P. Multifocus Image Fusion Based on NSCT and Focused Area Detection. IEEE Sensors J. 2015, 15, 2824–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, W. Multiscale contrast-pyramid-based image fusion scheme and its performance evaluation. Acta Optica Sinica 2021, 21, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencini, F.; Garzelli, A.; Baronti, S.; Alparone, L. Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, B.; Agrawal, S.; Panda, R.; Abraham, A. A survey on region based image fusion methods. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathaki, T. Image Fusion: Algorithms and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ghassemian, H. A review of remote sensing image fusion methods. Inf. Fusion 2016, 32, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogervorst, M.A.; Toet, A. Fast natural color mapping for night-time imagery. Inf. Fusion 2010, 11, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J. DenseFuse: A Fusion Approach to Infrared and Visible Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.j.; Durrani, T.S. Infrared and visible image fusion with ResNet and zero-phase component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Infrared and visible image fusion with convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolution Inf. Process. 2018, 16, 1850018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Mei, X.; Zhang, X.P. DDcGAN: A Dual-Discriminator Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Multi-Resolution Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, Y. RXDNFuse: A aggregated residual dense network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2021, 69, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Wan, W.; Wen, W.; Guan, J. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Texture Conditional Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 4771–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Q. AttentionFGAN: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Using Attention-Based Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J. Classification Saliency-Based Rule for Visible and Infrared Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Jin, X.; Hou, J.; Lee, S.J.; Yao, S. Multi-Sensor Image Fusion Based on Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets and Regional Features in Nonsubsampled Shearlet Transform Domain. IEEE Sensors J. 2018, 18, 2494–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A. The TNO multiband image data collection. Data Brief 2017, 15, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.; Sheikh, H.; Simoncelli, E. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.; Bovik, A. Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, C.; Bovik, A.C. Quality Assessment of Deblocked Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Simoncelli, E.P.; Bovik, A.C. Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 9–12 November 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A. A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2002, 9, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xydeas, C.S.; Pv, V. Objective image fusion performance measure. Mil. Tech. Cour. 2000, 56, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F.; Selva, M. Multispectral and Panchromatic Data Fusion Assessment Without Reference. ASPRS J. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
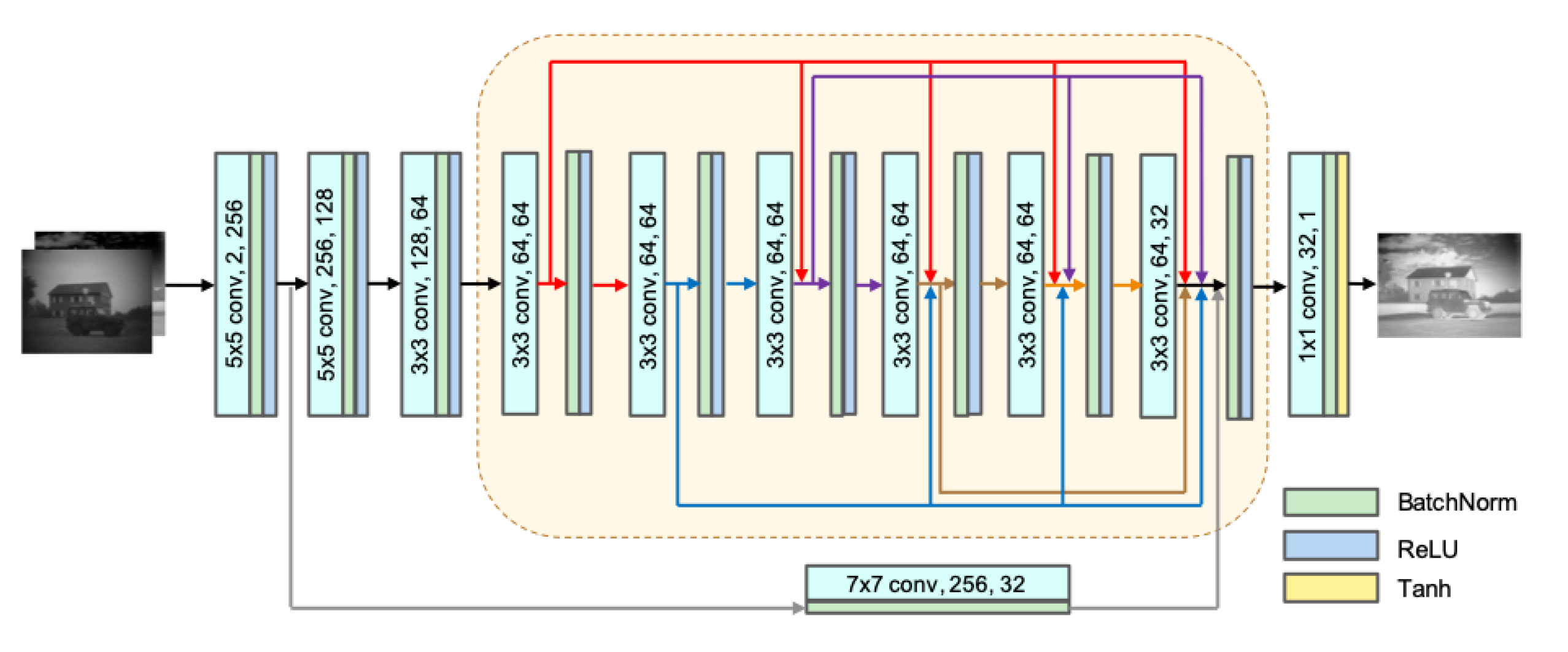

| Name | Layer | K | S | Input | N1 | Output | N2 | Padding | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input layer | Conv1 | 5*5 | 1 | IR+VI | 2 | I1 | 256 | VALID | LReLU |
| Conv layer | Conv2 | 5*5 | 1 | I1 | 256 | I2 | 128 | VALID | LReLU |
| Conv3 | 3*3 | 1 | I2 | 128 | I3 | 64 | VALID | LReLU | |
| Dense layer | Dense1 | 3*3 | 1 | I3 | 64 | I4 | 64 | SAME | LReLU |
| Dense2 | 3*3 | 1 | I4 | 64 | I5 | 64 | SAME | LReLU | |
| Dense3 | 3*3 | 1 | I4+I5 | 64 | I6 | 64 | SAME | LReLU | |
| Dense4 | 3*3 | 1 | I4+I5+I6 | 64 | I7 | 64 | SAME | LReLU | |
| Dense5 | 3*3 | 1 | I4+I5+I6+I7 | 64 | I8 | 64 | SAME | LReLU | |
| Conv layer | Conv1_1 | 7*7 | 1 | I1 | 256 | I1_1 | 64 | VALID | LReLU |
| Dense layer | Dense6 | 3*3 | 1 | I1_1+I4+I5+ I6+I7+I8 | 64 | I9 | 32 | VALID | LReLU |
| Output layer | Conv4 | 1*1 | 1 | I9 | 32 | F | 1 | VALID | Tanh |
| Name | Layer | K | S | Input | N1 | Output | N2 | Padding | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input layer | Conv1 | 3*3 | 2 | VI/F | 1 | I1 | 32 | VALID | LReLU |
| Conv layer | Conv2 | 3*3 | 2 | I1 | 32 | I2 | 64 | VALID | LReLU |
| Dense layer | Dense1 | 3*3 | 2 | I3 | 64 | I4 | 128 | VALID | LReLU |
| Dense2 | 3*3 | 1 | I4 | 128 | I5 | 128 | SAME | LReLU | |
| Dense3 | 3*3 | 1 | I4+I5 | 128 | I6 | 128 | SAME | LReLU | |
| Dense4 | 3*3 | 2 | I4+I5+I6 | 128 | I7 | 256 | VALID | LReLU | |
| Output layer | Line1 | / | / | I7 | 256 | Lable | 1 | / | Matmul |
| Method | SF | EN | SCD | AG | SD | SSIM | PSNR | VIF | MI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVG | 6.522 | 6.084 | 1.5361 | 3.4586 | 21.7940 | 0.7872 | 19.1160 | 0.3672 | 0.3590 | 2.0310 |
| LP | 10.985 | 6.2214 | 1.5774 | 5.8541 | 23.7810 | 0.7496 | 18.9590 | 0.5113 | 0.3950 | 1.7672 |
| FSDP | 9.247 | 6.1346 | 1.4970 | 4.9874 | 22.6290 | 0.7513 | 18.9800 | 0.5045 | 0.4420 | 1.8655 |
| DWT | 10.604 | 6.1636 | 1.5565 | 5.7666 | 22.8310 | 0.7530 | 19.0090 | 0.4435 | 0.3360 | 1.7352 |
| Fusion-GAN | 6.592 | 6.2567 | 1.4009 | 3.4929 | 25.6690 | 0.6519 | 16.0430 | 0.2893 | 0.2580 | 2.0750 |
| Dense-Fuse | 9.729 | 6.6278 | 1.7955 | 5.2541 | 33.5800 | 0.7150 | 17.4820 | 0.4465 | 0.4230 | 2.1868 |
| RFN-Nest | 7.033 | 6.7754 | 1.7646 | 3.6195 | 34.6520 | 0.6808 | 17.021 | 0.3951 | 0.4490 | 1.9810 |
| Dense-FG | 11.276 | 6.6750 | 1.8053 | 6.1461 | 32.5990 | 0.7227 | 18.2110 | 0.4627 | 0.4970 | 2.2712 |
| Expt. | SF | EN | SCD | AG | SD | SSIM | PSNR | VIF | MI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8.569 | 6.7146 | 1.5124 | 4.7516 | 30.954 | 0.6897 | 15.460 | 0.4247 | 0.436 | 1.8662 |
| B | 8.728 | 6.6034 | 1.7125 | 4.8224 | 31.597 | 0.6863 | 15.630 | 0.4295 | 0.477 | 1.9733 |
| C | 8.489 | 6.8226 | 1.6903 | 4.6403 | 31.308 | 0.6704 | 14.589 | 0.4106 | 0.461 | 1.8960 |
| Dense-FG | 10.355 | 6.756 | 1.8142 | 5.8026 | 31.766 | 0.6804 | 15.959 | 0.4387 | 0.447 | 1.8412 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Shen, Y.; Han, S. Dense-FG: A Fusion GAN Model by Using Densely Connected Blocks to Fuse Infrared and Visible Images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13084684
Xu X, Shen Y, Han S. Dense-FG: A Fusion GAN Model by Using Densely Connected Blocks to Fuse Infrared and Visible Images. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(8):4684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13084684
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaodi, Yan Shen, and Shuai Han. 2023. "Dense-FG: A Fusion GAN Model by Using Densely Connected Blocks to Fuse Infrared and Visible Images" Applied Sciences 13, no. 8: 4684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13084684
APA StyleXu, X., Shen, Y., & Han, S. (2023). Dense-FG: A Fusion GAN Model by Using Densely Connected Blocks to Fuse Infrared and Visible Images. Applied Sciences, 13(8), 4684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13084684






