Adaptive Suppression Method of LiDAR Background Noise Based on Threshold Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
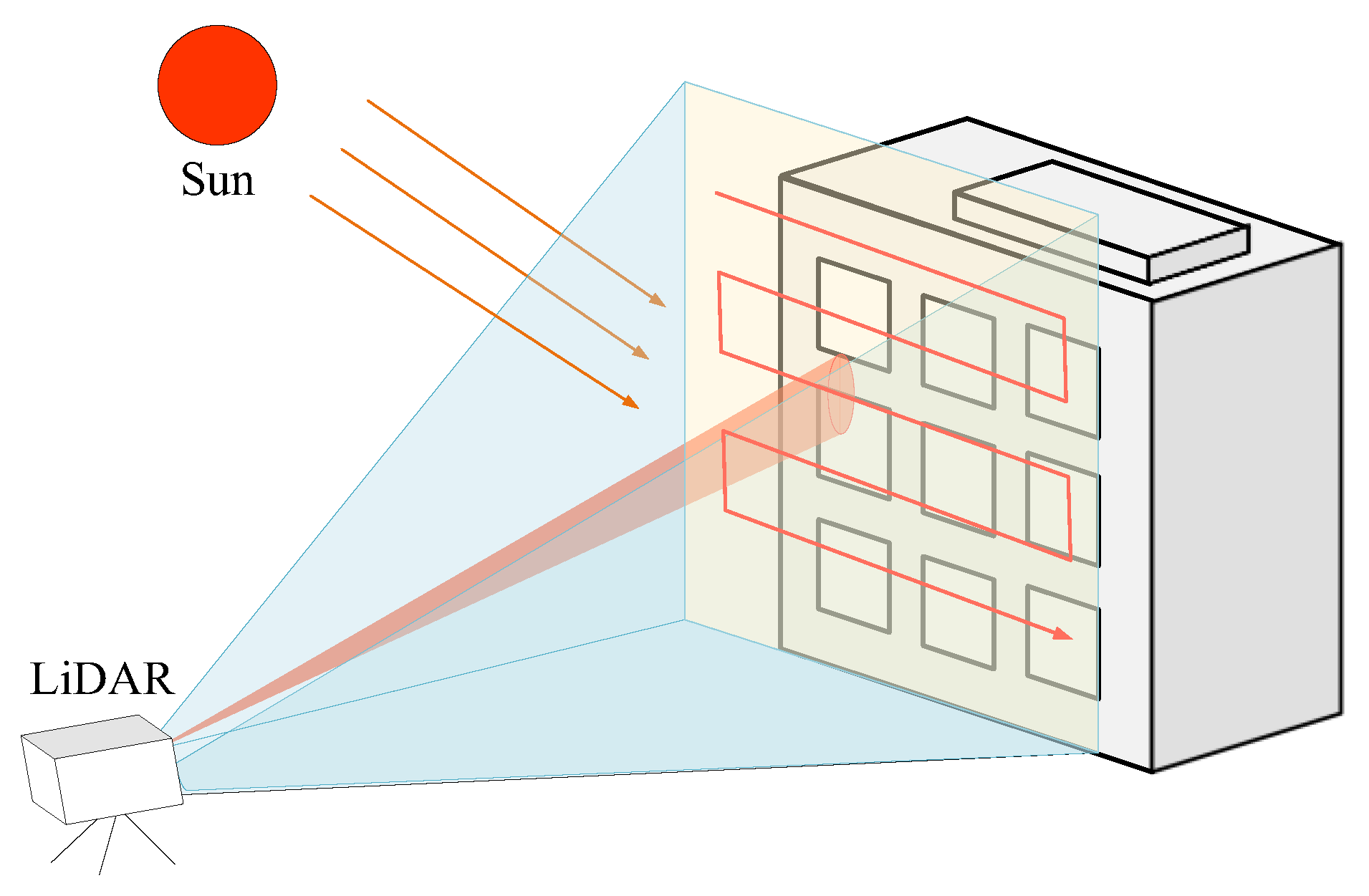
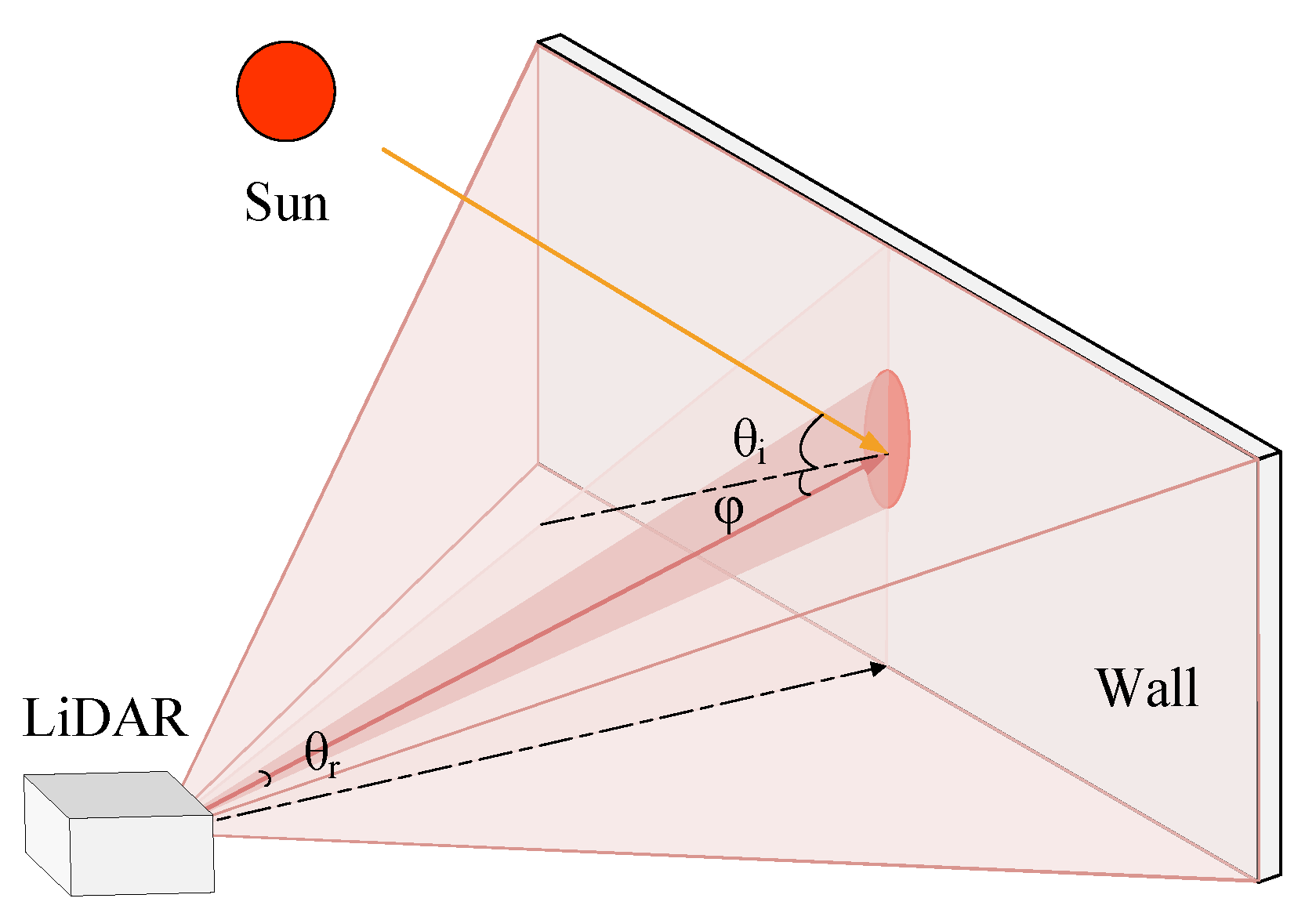
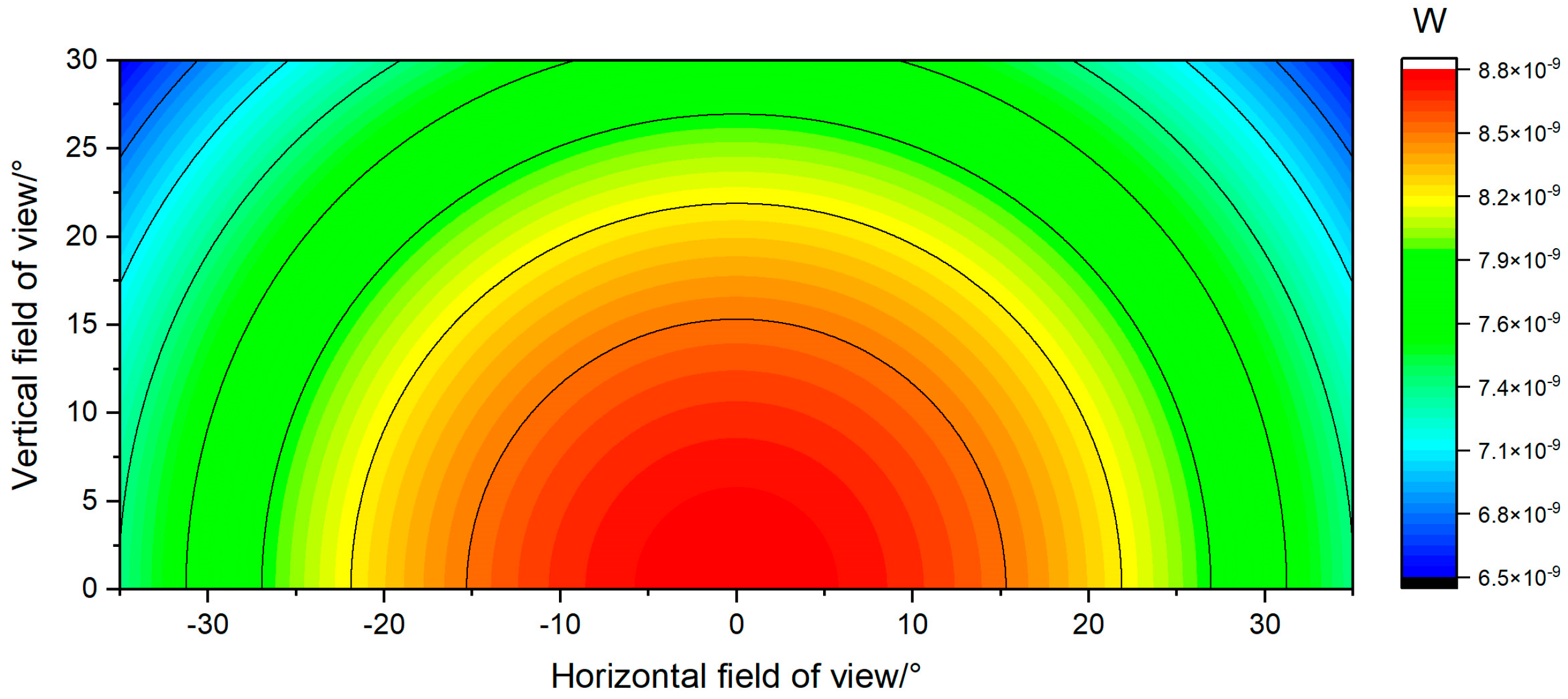
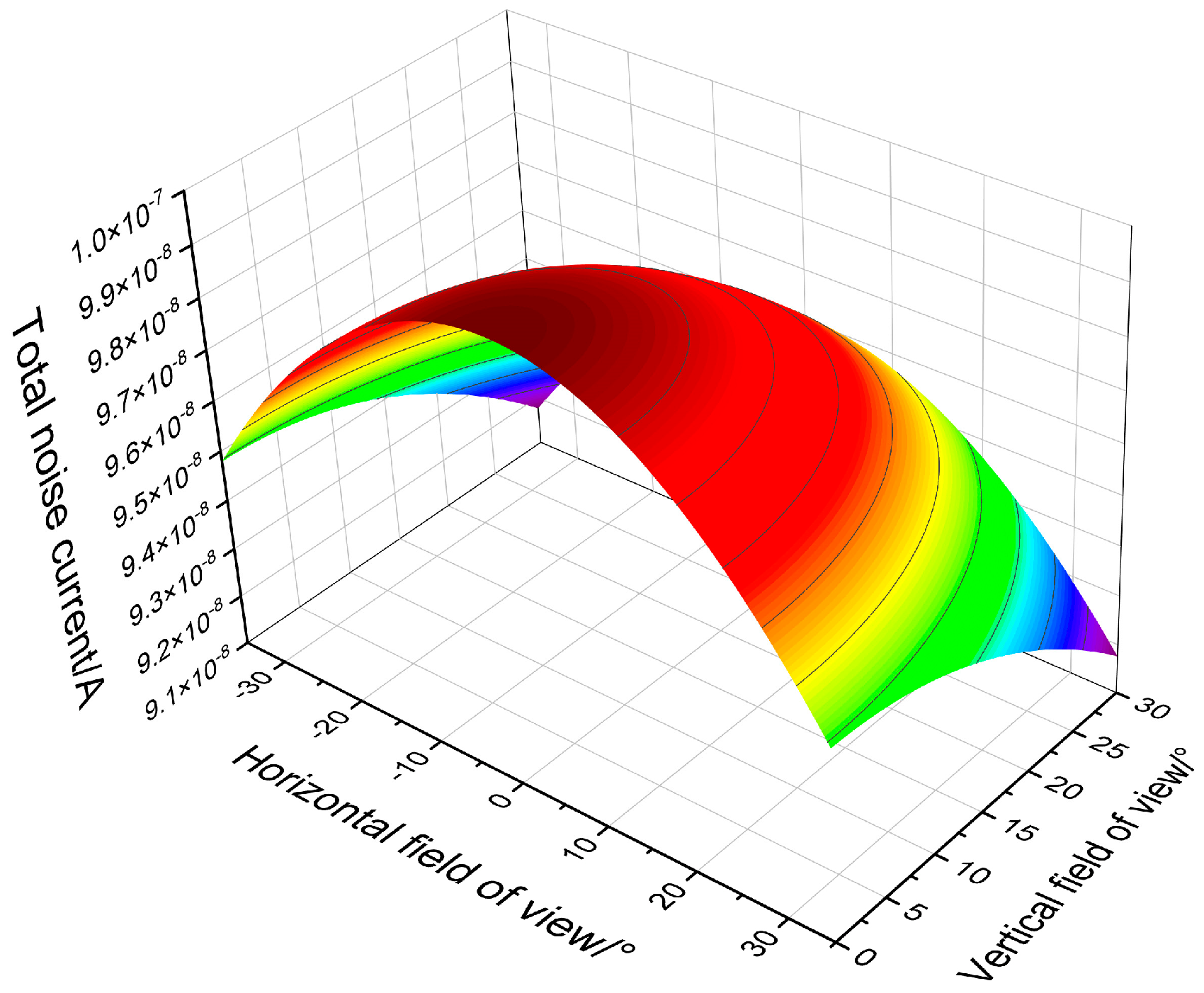
2. Influence of Background Noise
3. Adaptive Suppression Method of Background Noise
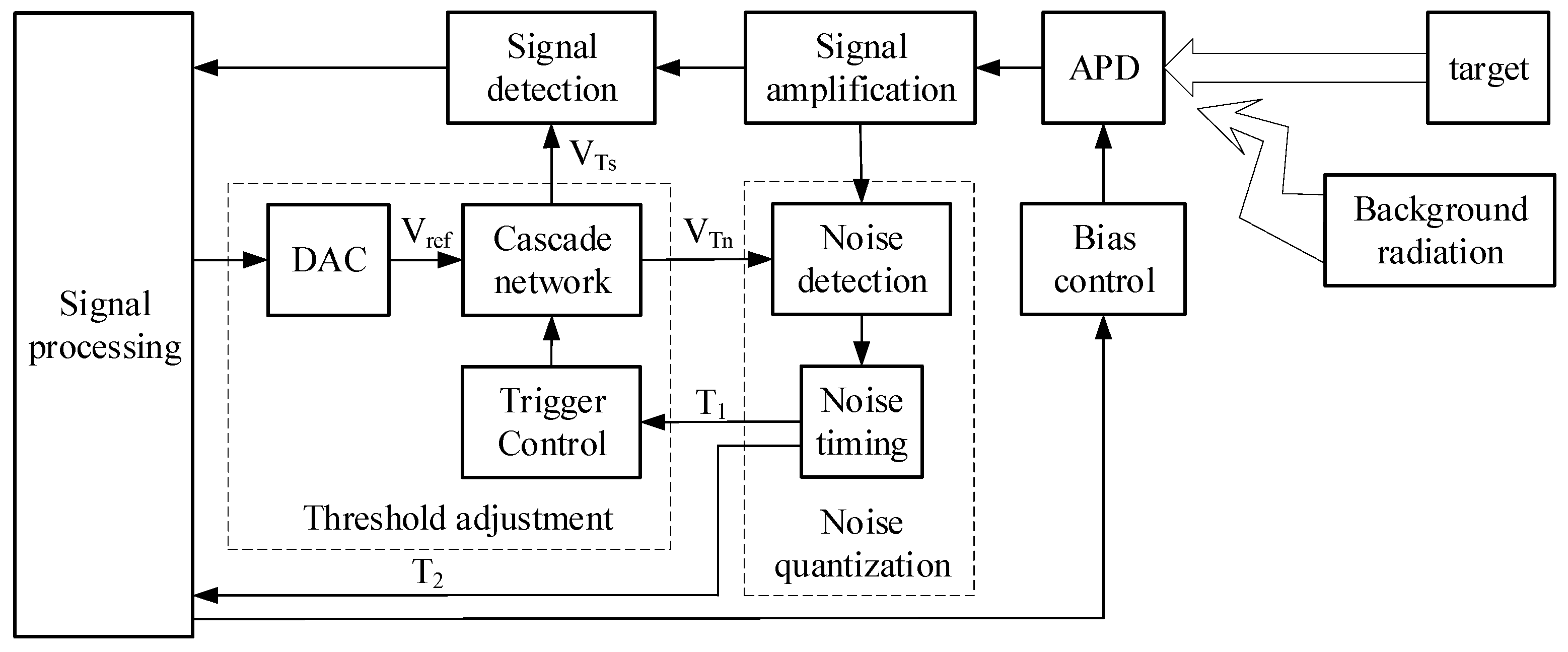
3.1. Structure and Implementation
3.2. Critical Modules Implementation
3.2.1. Noise Detection
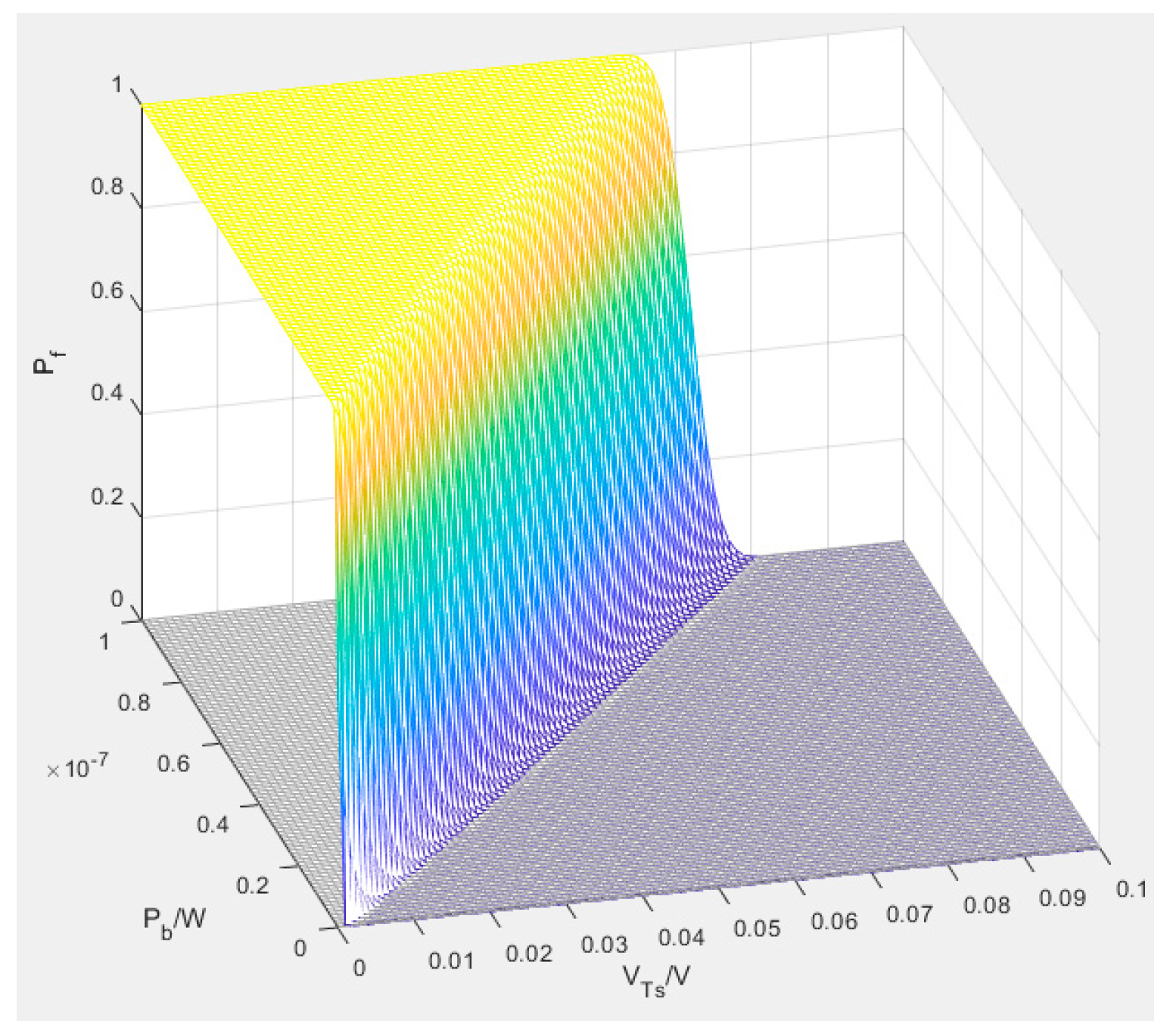
3.2.2. Threshold Adjustment
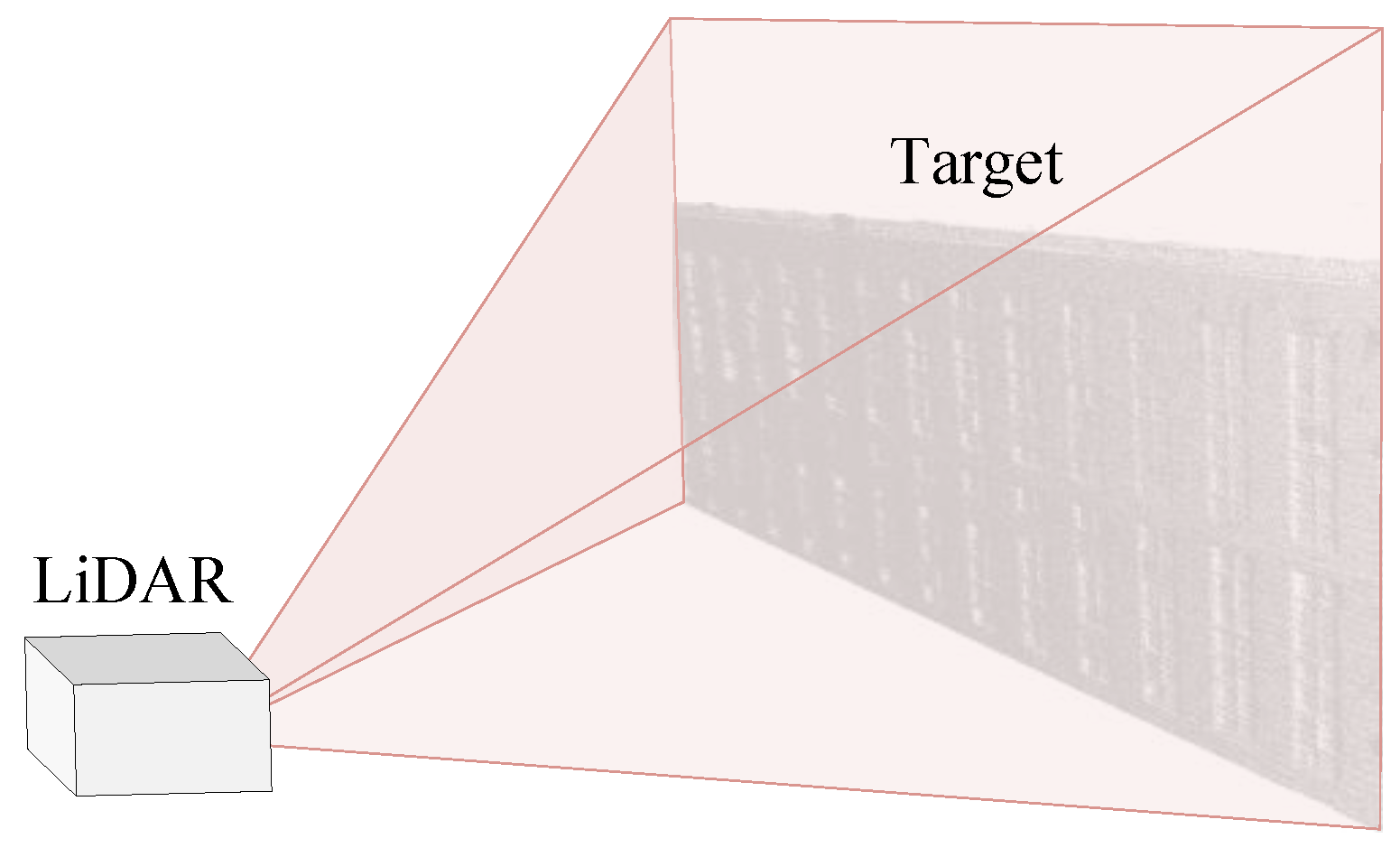
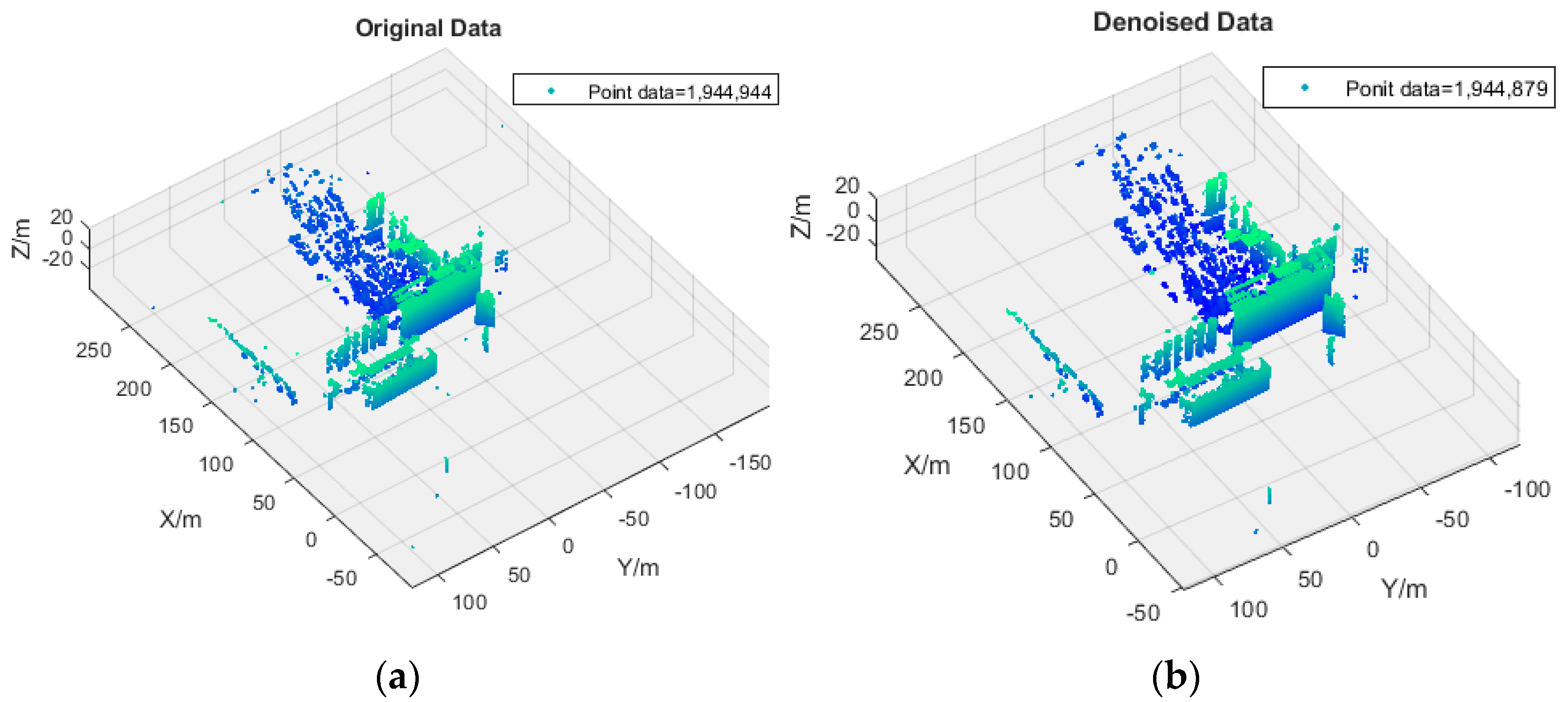
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Category | Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| APD | Responsivity | Rp | 30 A/W |
| Bandwidth | B | 150 MHz | |
| Gain | M | 100 | |
| Total Dark Current | Id | 50 nA | |
| Excess noise factor | F | 3.9 | |
| Equivalent load resistance | RL | 1 kΩ | |
| Amplifier | Integrated input current noise (rms) | iNa | 20 nA |

Appendix B
| Category | Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser | Wavelength | λ | 1064 nm |
| Repetition frequency | f | 100 KHz | |
| Average transmitted laser power | Pt | 1 W | |
| Beam divergence angle | θt | 1 mrad | |
| Pulse width | tp | 5 ns | |
| APD | Responsivity | Rp | 36 A/W |
| Receiving aperture | Dr | 30 mm | |
| Rise Time | tr | 2 ns | |
| Gain | M | 100 | |
| Total Dark Current | Id | 50 nA | |
| Filter bandwidth | ∆λ | 10 nm | |
| Optics | Optical efficiency of the receiving system | ηr | 0.7 |
| Optical efficiency of the transmitting system | ηt | 0.95 | |
| Receiving field angle | θr | 2 mrad | |
| Horizontal scanning field angle | θH | 70° | |
| Vertical scanning field angle | θV | 30° |
References
- Alain, Q.; Olivier, M.; Xavier, S. Analytic Model for Optimizing a Long-range Pulsed LiDAR Scanner for Small Object Detection. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 5496. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Tang, W.; Xu, S.Y. Real-time and High-precision Ranging Method for Large Dynamic Range of Imaging LiDAR. Infrared Laser Eng. 2020, 49, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Wang, C.; Qi, B. Application of DMLF in Pulse Ranging LiDAR System. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Q.; Zhu, J.G.; Xie, T.P. Research progress on security LiDAR. Laser Optoelectron. Progress. 2021, 58, 28–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, T.; Roriz, R.; Cunha, L.; Ganal, A.; Soares, N.; Araújo, T.; Monteiro, J. Evaluation and Testing System for Automotive LiDAR Sensors. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 13003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chang, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, G. LiDAR-Based Dense Pedestrian Detection and Tracking. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candan, C.; Tiken, M.; Berberoglu, H.; Orhan, E.; Yeniay, A. An Experimental Study on Km-Range Long-Distance Measurement Using Silicon Photomultiplier Sensor with Low Peak Power Laser Pulse. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtti, S.; Baharmast, A.; Jansson, J.P. A Low-noise and Wide Dynamic Range 15MHz CMOS Receiver for Pulsed Time-of-Flight Laser Ranging. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 22944–22955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.B.; Wang, Z.Z.; Liu, D. Comparison of De-noising Methods of LiDAR Signal. Acta Opt. Sin. 2021, 41, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, J.F.; Fan, Z.G.; Li, S.N.; Lu, W. Research on Detection Performance Improvement of Polarization GM-APD LiDAR with Adaptive Adjustment of Aperture Diameter and Spatial Correlation Method. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 155, 108400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, T.A.; Wu, H.M. Analysis of Land Cover Classification Using Multi-Wavelength LiDAR System. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.L.; Wu, B.H. Application of Kalman Filter to Improve 3D LiDAR Signals of Autonomous Vehicles in Adverse Weather. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zheng, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Xu, Z. Three-Dimensional Imaging via Time-Correlated Single-Photon Counting. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, G.; Vignesh, R.; Sandeep, K. A strip line technique based 1 Gb/s, 70-dB linear dynamic range transimpedance amplifier towards LiDAR unmanned vehicle application. Microelectron. J. 2022, 126, 105477. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, P.; Mao, Z.; Pan, D. Polarization Properties of Reflection and Transmission for Oceanographic LiDAR Propagating through Rough Sea Surfaces. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Wang, R. Application of Avalanche Photodiode Constant False Alarm Rate Control in Laser Imaging System. Infrared Laser Eng. 2002, 31, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Carrara, L.; Fiergolski, A. An Optical Interference Suppression Scheme for TCSPC Flash LiDAR. Imagers. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravil, A.; Barry, G.; Fred, M.; Alexander, G.; Ahmed, S. Simple approach to predict APD/PMT lidar detector performance under sky background using dimensionless parametrization. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2006, 44, 779–796. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Cheng, C.H.; Liu, D.G.; Le, M.H. Improvement of Accuracy and Precision of the LiDAR System Working in High Background Light Conditions. Electronics 2022, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, A.S.; Williams, G.M.; Lee, A.O. Modeling False Alarm Rate and Related Characteristics of Laser Ranging and LiDAR Avalanche Photodiode Photoreceivers. Opt. Eng. 2018, 57, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, H.X.; He, X. Effect of background radiation on APD multiplication factor under the compensation of constant false alarm Rate. Acta Photonica Sin. 2018, 47, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.F.; Lang, J.H. Design of Receiving Circuit in Long-distance Laser Range Finding Based on Variable Background-adaptation. Electro-Opt. Tech Appl. 2018, 33, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, J.H.; Huang, G.H.; Chen, P.F. Study of Constant False Alarm Rate Controlling Technique based on FPGA in LiDAR. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2009, 28, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, B.; Stefan, H.; Roman, B. Analytical Evaluation of Signal-to-noise Ratios for Avalanche- and Single-photon Avalanche Diodes. Sensors 2021, 21, 2887. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.J. Lidar Technology; Publishing House of Electronics Industry (PHEI): Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 193–195. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.R.; Li, P.; Chen, H.M. Interference from Scattered Sunlight on Photodetector Posed in Different Angles. J. Detect. Control 2009, 31, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Bu, X.Z.; Han, W. Design of Pulsed Laser Rangefinder Under Background Light Noise. Foreign Electron Meas. Techno. 2017, 36, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.B.; Luo, Y.; He, Y. The Short-Range, High-accuracy Compact Pulsed Laser Ranging System. Sensors 2022, 22, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.H.; Ouyang, J.H.; Shu, R. Influence of Background Radiant Power on the Signal-to-noise Ratio of Space-borne Laser Altimeter. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2009, 28, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, L.R. Multiple-scattering LiDAR Equation. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 6449–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.W. Suppression of Background Radiance of Airborne Laser Radar. Electron. Opt. Control 2009, 16, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.G.; Sun, X.Q. Principles and Applications of Laser Antagonism; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 212–214. [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik, M.I. Introduction to Radar Systems, 3rd ed.; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Cui, J.Y.; Li, G. A Three-dimensional Point Cloud Denoising Method Based on Adaptive Threshold. Acta Photonica Sin. 2022, 51, 0212003. [Google Scholar]






| Time/a.m. | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar altitude/° | 13.3 | 22.6 | 30.2 | 35.3 | 37.1 |
| Illuminance/lux | 6387 | 12,960 | 22,120 | 27,010 | 32,550 |
| Name | Noise Reduction Percentage | Processing Time Per Point | Implementation Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bunny radius filtering method | 83.9% | 238 us | software |
| Dragon radius filtering method | 82.8% | 261 us | software |
| Piecewise adaptive threshold method | 96.5% | 289 us | software |
| This work | 80.1% | 10 us | hardware |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, C.; Xie, T.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y. Adaptive Suppression Method of LiDAR Background Noise Based on Threshold Detection. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063772
Jiang Y, Zhu J, Jiang C, Xie T, Liu R, Wang Y. Adaptive Suppression Method of LiDAR Background Noise Based on Threshold Detection. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(6):3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063772
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yan, Jingguo Zhu, Chenghao Jiang, Tianpeng Xie, Ruqing Liu, and Yu Wang. 2023. "Adaptive Suppression Method of LiDAR Background Noise Based on Threshold Detection" Applied Sciences 13, no. 6: 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063772
APA StyleJiang, Y., Zhu, J., Jiang, C., Xie, T., Liu, R., & Wang, Y. (2023). Adaptive Suppression Method of LiDAR Background Noise Based on Threshold Detection. Applied Sciences, 13(6), 3772. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063772










