Tunable 60 GHz Multiwavelength Brillouin Erbium Fiber Laser
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
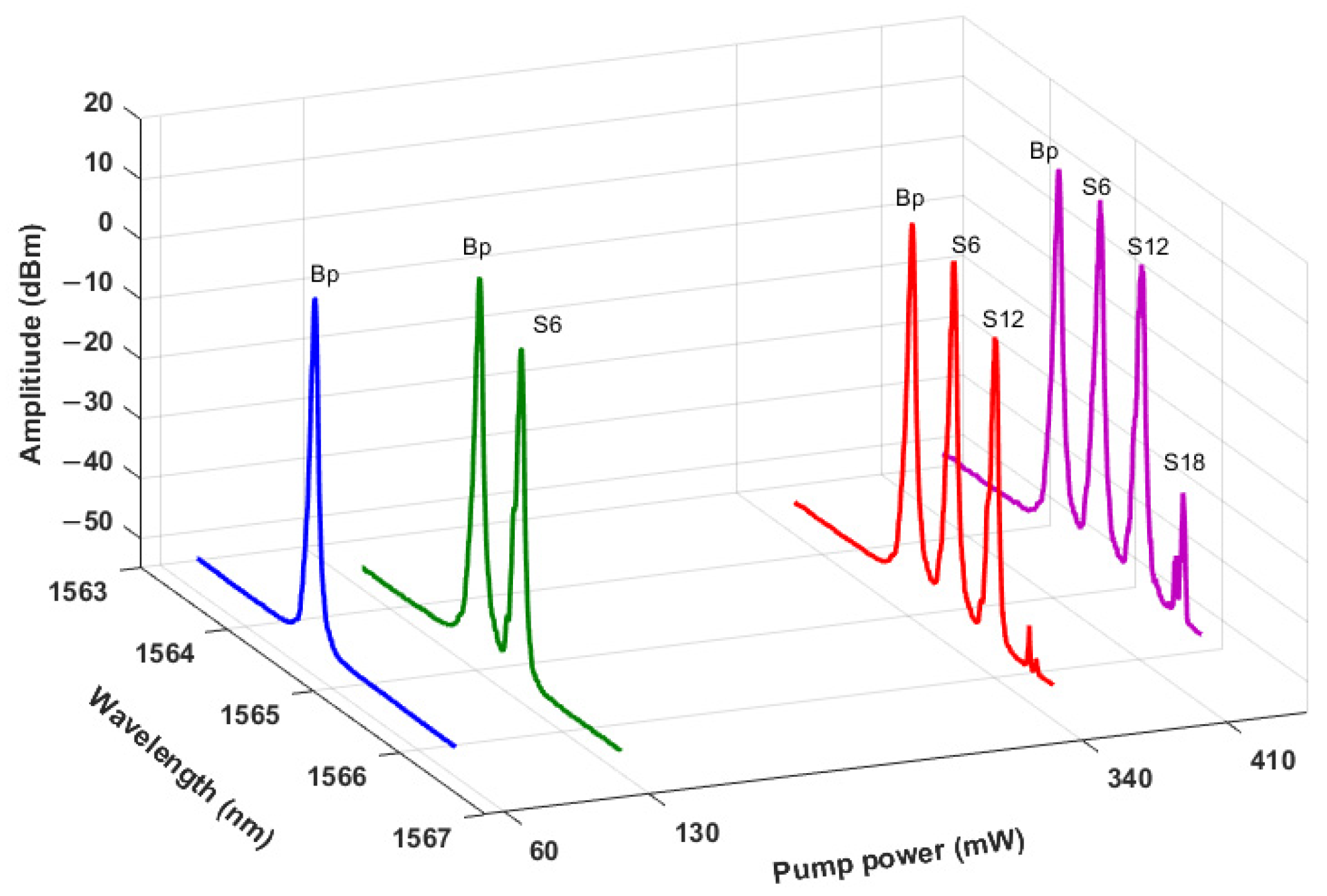
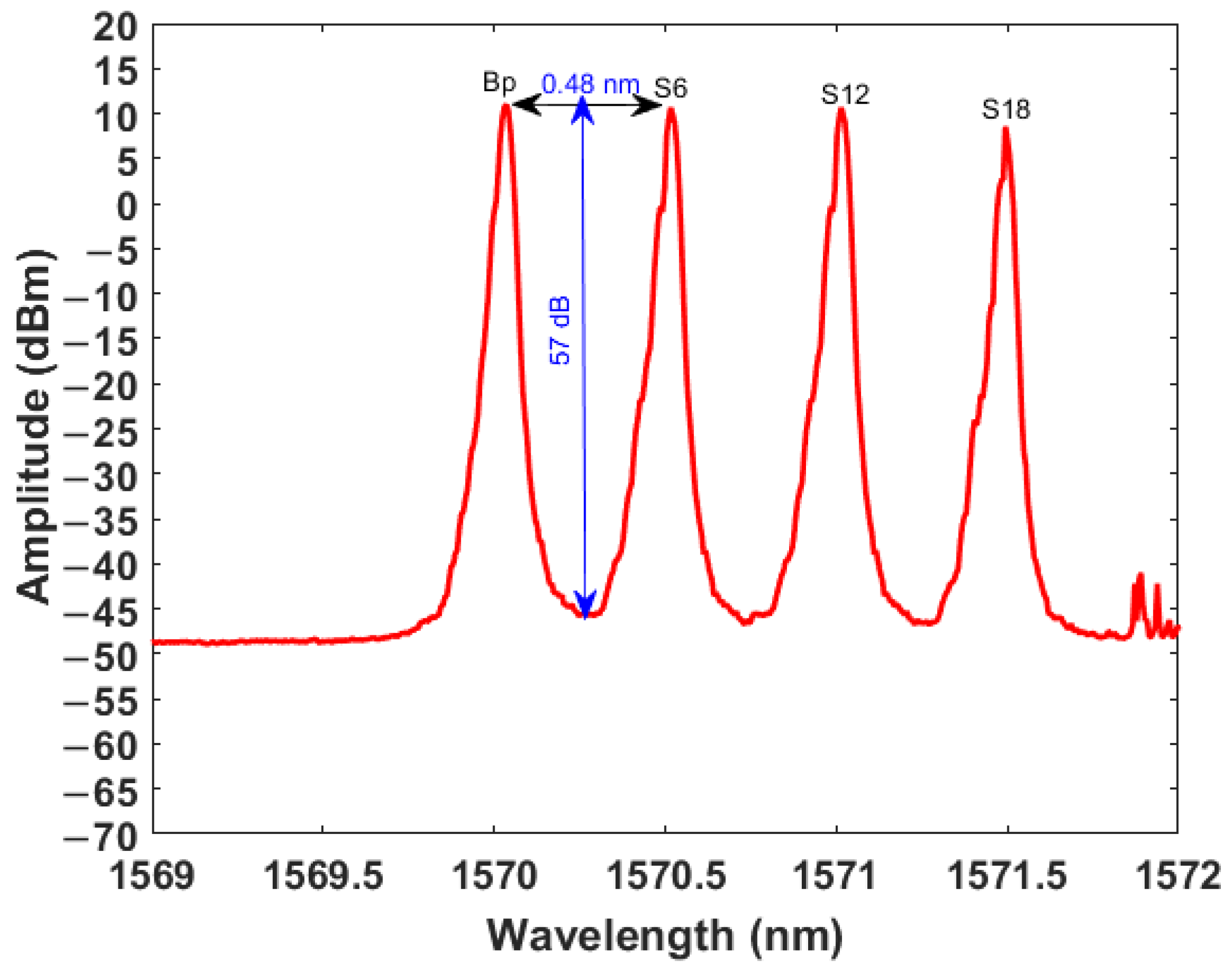
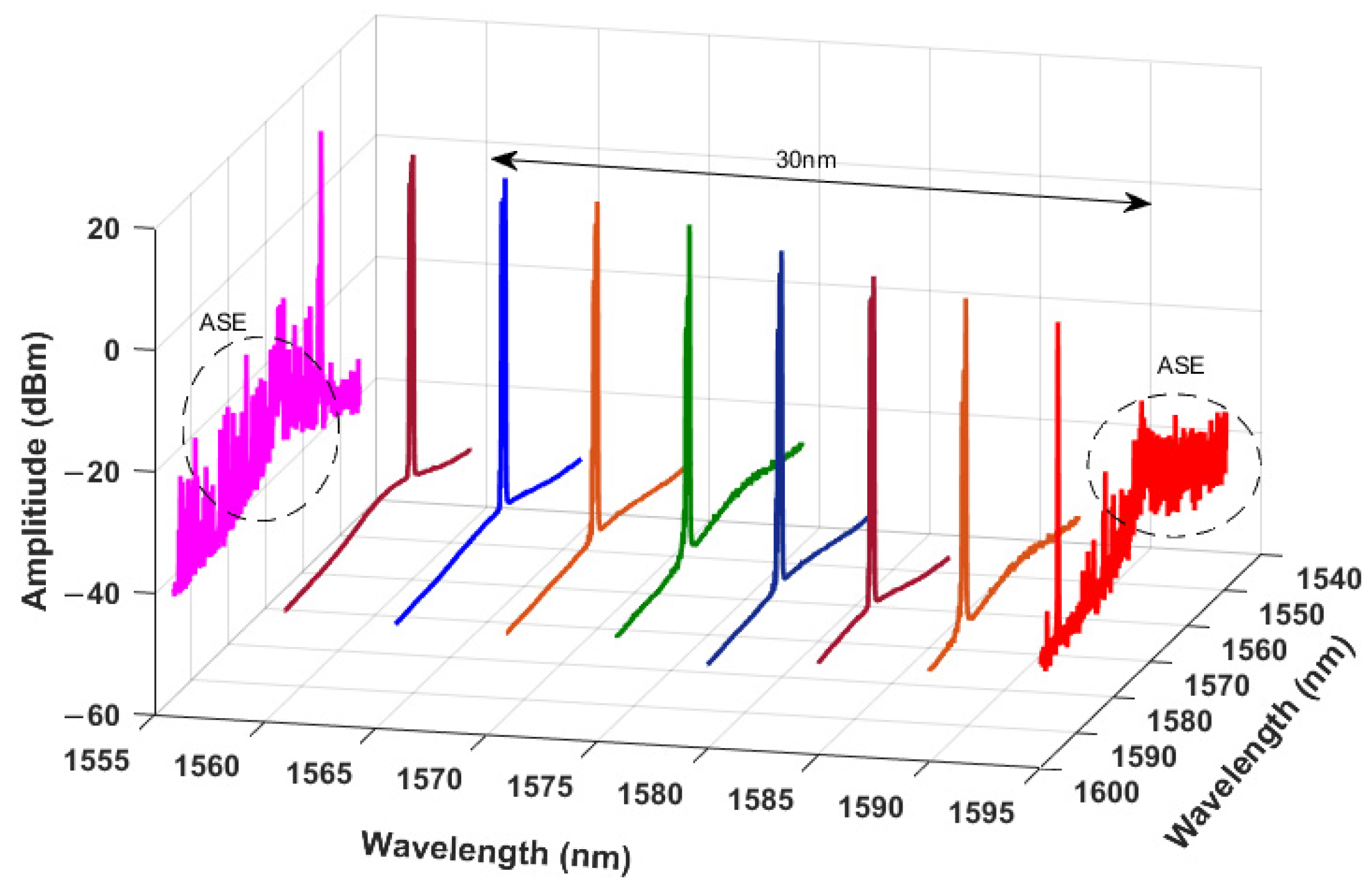
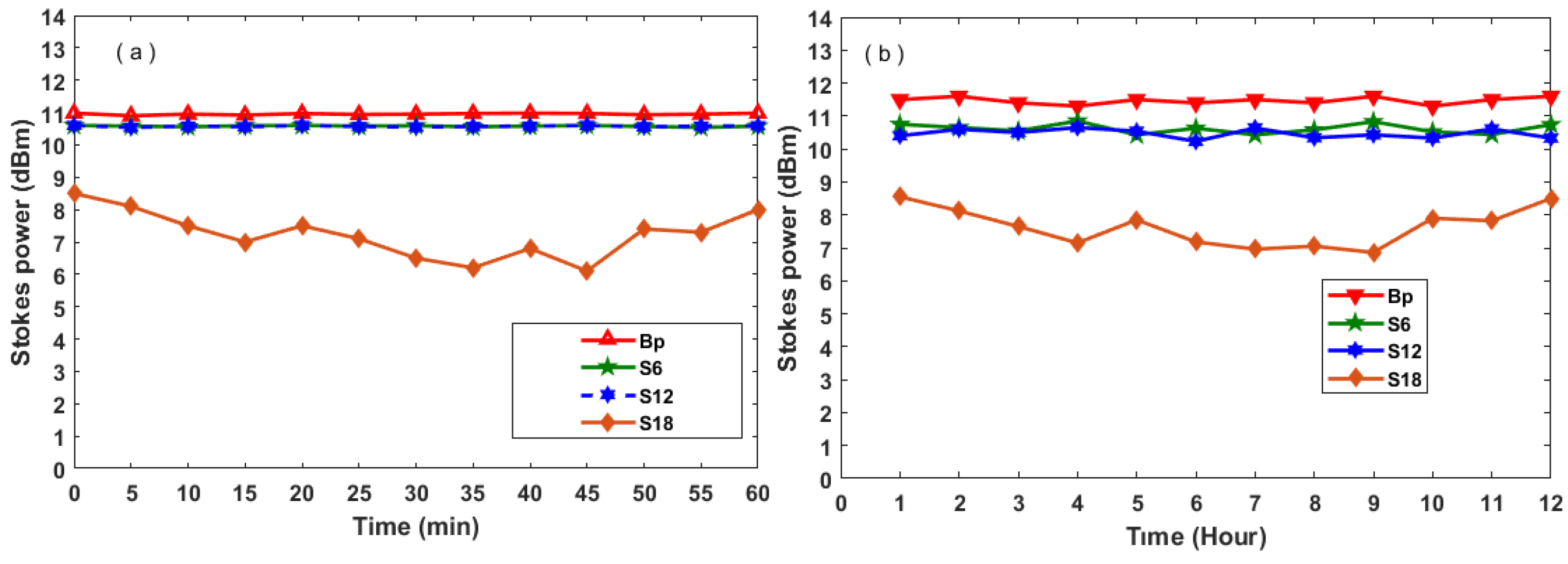
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdullah, M.K. Power Division Analysis of Optical Single Mode Branching Waveguides. J. Kejuruter. 1995, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, G.; Johnstone, W.; Arsad, N.; Duffin, K. Tunable diode and fibre laser spectroscopy in the near-IR for measurement of gas parameters. Opt. Sens. 2008, 7003, 700319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsad, N.; Stewart, G. Stable, tunable, and single-mode operation of an erbium-doped fibre laser system using a saturable absorber for gas spectroscopy applications. Fiber Lasers VI Technol. Syst. Appl. 2009, 7195, 719525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, M.; Mokhtar, M.H.H.; Azeman, N.H.; Hashim, F.H.; Arsad, N.; Abushagur, A.A.G.; Bakar, A.A.A. Phase-interrogated surface plasmon resonance sensor based on laser feedback interferometry. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 141, 106564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeman, N.H.; Arsad, N.; Bakar, A.A.A. Polysaccharides as the sensing material for metal ion detection-based optical sensor applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassa-Baghdouche, L. Optical properties of a point-defect nanocavity-based elliptical-hole photonic crystal for mid-infrared liquid sensing. Phys. Scr. 2019, 95, 15502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa-Baghdouche, L.; Cassan, E. Mid-infrared gas sensor based on high-Q/V point-defect photonic crystal nanocavities. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2020, 52, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.N.A.; Arsad, N.; Zulkipli, N.F.; Rosol, A.H.A.; Paul, M.C.; Yasin, M.; Harun, S.W. kHz pulse generation with Brillouin erbium fiber laser. Laser Phys. 2022, 33, 15102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G.K.W.; Yeo, K.S.; Adikan, F.R.M.; Shee, Y.G. Four-wave-mixing-assisted Brillouin fiber laser with double-Brillouin-frequency spacing. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2015, 21, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, M.H.; Mahdi, M.A. Multiwavelength L-band brillouin-erbium comb fiber laser utilizing nonlinear amplifying loop mirror. J. Light. Technol. 2009, 27, 5038–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, R.; Arof, H.; Ali, N.M.; Ahmad, H.; Harun, S.W. 0.16 nm spaced multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser in a figure-of-eight configuration. Opt. Laser Technol. 2011, 43, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashhadani, T.F.; Al-Mansoori, M.H.; Jamaludin, M.Z.; Abdullah, F.; Abass, A.K. Influence of a bidirectional recycling residual pump on the Stokes signal characteristics of a linear cavity Brillouin fiber laser. Laser Phys. 2013, 23, 85111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, M.H.; Bouzid, B.; Ali, B.M.; Abdullah, M.K.; Mahdi, M.A. Multi-wavelength Brillouin-Erbium fibre laser in a linear cavity. Opt. Commun. 2004, 242, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashhadani, T.F. Erbium gain effects on Stokes signal performance in a Fabry–Perot Brillouin Erbium fiber laser. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2019, 51, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiya, M.; Mahdi, M.A.; Al-Mansoori, M.H.; Mokhtar, M.; Hitam, S. Directivity influence of signals propagation through EDFA gain medium of Brillouin-erbium fiber laser. Opt. Commun. 2009, 282, 4266–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiu, Z.C.; Aidit, S.N.; Hassan, N.A.; Bin Ismail, M.F.; Ahmad, H. Single and Double Brillouin Frequency Spacing Multi-Wavelength Brillouin Erbium Fiber Laser with Micro-Air Gap Cavity. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2016, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alimi, A.W.; Cholan, N.A.; Yaacob, M.H.; Abas, A.F.; Alresheedi, M.T.; Mahdi, M.A. Wide bandwidth and flat multiwavelength Brillouin-erbium fiber laser. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 19382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shee, Y.G.; Al-Mansoori, M.H.; Ismail, A.; Hitam, S.; Mahdi, M.A. Double Brillouin frequency shift through circulation of odd-order Stokes signal. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 3956–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zou, H.; Xiong, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y. Multiwavelength generation by using a novel Brillouin-erbium fiber laser with double linear-cavity based on a double-pass Brillouin Pump (BP) amplification technique. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 117, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Sun, J.; Chen, T.; Zhou, Y. A stable optical comb with double-Brillouin-frequency spacing assisted by multiple four-wave mixing processes. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2011, 17, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashhadani, T.F.; Al-Mashhadani, M.K.S.; Yucel, M.; Goktas, H.H. Influence of bidirectional cavity structure on the Brillouin Stokes signal characteristics in ring BFL. Optik (Stuttg.) 2019, 185, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shee, Y.G.; Al-Mansoori, M.H.; Yaakob, S.; Man, A.; Zamzuri, A.K.; Adikan, F.R.; Mahdi, M.A. Millimeter wave carrier generation based on a double-Brillouin-frequency spaced fiber laser. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 13402–13408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abass, A.K.; Al-Mansoori, M.H.; Jamaludin, M.Z.; Abdullah, F.; Al-Mashhadani, T.F.; Ali, M.H. L-band multi-wavelength brillouin-raman fiber laser with 20-GHz channel spacing. Fiber Integr. Opt. 2014, 33, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Fen, D.; Xie, H.; Sun, J. A novel tunable multi-wavelength Brillouin fiber laser with switchable frequency spacing. Opt. Commun. 2015, 340, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, M.; Wei, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, G.; Bi, M.; Li, Q. Multi-Wavelength Brillouin Fiber Laser with Triple Brillouin Frequency Spacing. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 2379–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gu, Y.; Yao, Y. Frequency spacing switchable multiwavelength Brillouin erbium fiber laser utilizing cascaded Brillouin gain fibers. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, M.H.; Al-Sheriyani, A.; Al-Nassri, S.; Hasoon, F.N. Generation of efficient 33 GHz optical combs using cascaded stimulated Brillouin scattering effects in optical fiber. Laser Phys. 2017, 27, 65112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Jia, Q.; Ma, W.; Su, Q.; Zhang, P. Triple Brillouin frequency spacing multiwavelength fiber laser with double Brillouin cavities and its application in microwave signal generation. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, M.H.; Al-Sheriyani, A.; Younis, M.A.A.; Mahdi, M.A. Widely tunable multiwavelength Brillouin-erbium fiber laser with triple Brillouin-shift wavelength spacing. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2018, 41, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashhadani, T.F.; Al-Mashhadani, M.K.S.; Goktas, H.H.; Yucel, M.; Celebi, F.V. Widely triple Brillouin frequency shift multiwavelength Brillouin erbium fiber laser. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2020, 52, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Bo, B. 40 GHz narrow linewidth frequency-switched microwave signal generation based on a single-longitudinal-mode double-Brillouin-frequency spaced Brillouin fiber laser. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mashhadani, M.K.S.; Al-Mashhadani, T.F.; Goktas, H.H. Broadly tunable 40 GHz Brillouin frequency spacing multiwavelength Brillouin–Erbium fiber laser for DWDM. Opt. Commun. 2019, 451, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mashhadani, M.K.S.; Al-Mashhadani, T.F.; Goktas, H.H. Tunable 50 GHz laser comb generation of multiwavelength Brillouin erbium fiber laser. Opt. Commun. 2020, 464, 125542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ref. No. | No. of Stokes | Tuning Range (nm) | Channel Spacing GHz | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | 2 | 22 | 30 |
|
| [25] | 10 | 35 | 30 |
|
| [26] | 4 | not covered | 30 |
|
| [28] | 9 | only at the center wavelength | 30 |
|
| [29] | 3 | 40 | 30 |
|
| [26] | 3 | not covered | 40 |
|
| [31] | 1 | not covered | 40 |
|
| [32] | 4 | 60 | 40 |
|
| [33] | 4 | 40 | 50 |
|
| our work | 4 | 30 | 60 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Awsaj, M.K.; Al-Mashhadani, T.F.; Al-Mashhadani, M.K.S.; Hammudi, R.N.; Ali, A.y.; Zan, M.S.D.; Arsad, N. Tunable 60 GHz Multiwavelength Brillouin Erbium Fiber Laser. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053275
Awsaj MK, Al-Mashhadani TF, Al-Mashhadani MKS, Hammudi RN, Ali Ay, Zan MSD, Arsad N. Tunable 60 GHz Multiwavelength Brillouin Erbium Fiber Laser. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(5):3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053275
Chicago/Turabian StyleAwsaj, Mohammed K., Thamer Fahad Al-Mashhadani, Mohammed Kamil Salh Al-Mashhadani, Rabi Noori Hammudi, Ali yaseen Ali, Mohad Saiful Dzulkefly Zan, and Norhana Arsad. 2023. "Tunable 60 GHz Multiwavelength Brillouin Erbium Fiber Laser" Applied Sciences 13, no. 5: 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053275
APA StyleAwsaj, M. K., Al-Mashhadani, T. F., Al-Mashhadani, M. K. S., Hammudi, R. N., Ali, A. y., Zan, M. S. D., & Arsad, N. (2023). Tunable 60 GHz Multiwavelength Brillouin Erbium Fiber Laser. Applied Sciences, 13(5), 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053275









