Evaluation of Artifacts and Misinterpretation in 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography Caused by Three-Dimensional Resistive Structures of Regular or Irregular Shapes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Electrical Resistivity Tomography, Forward Modeling and Inversion
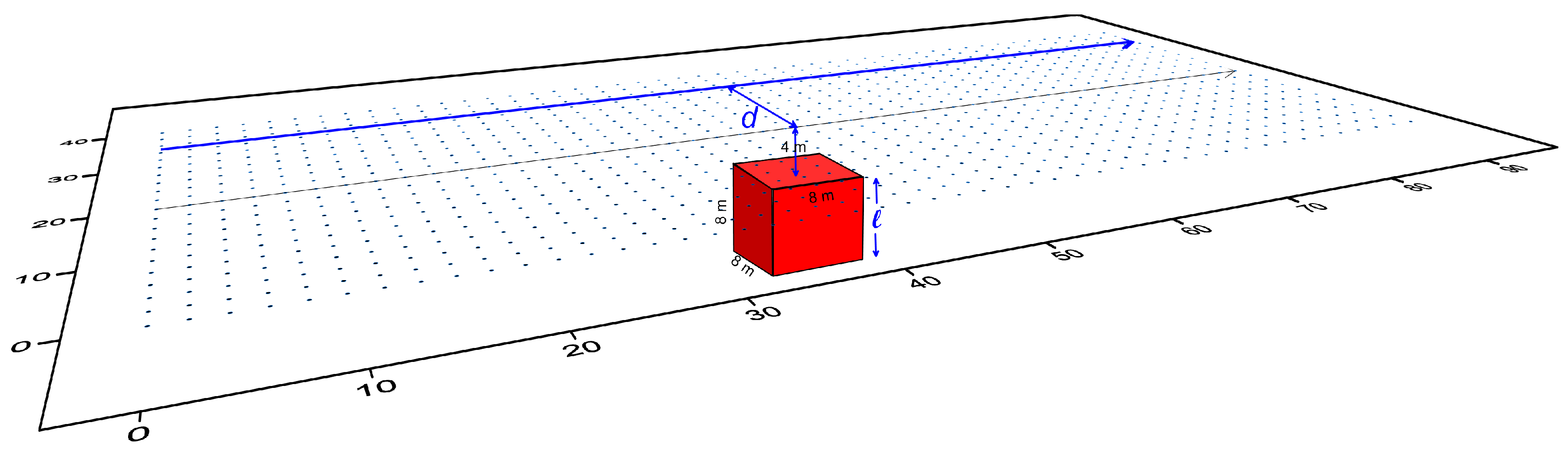
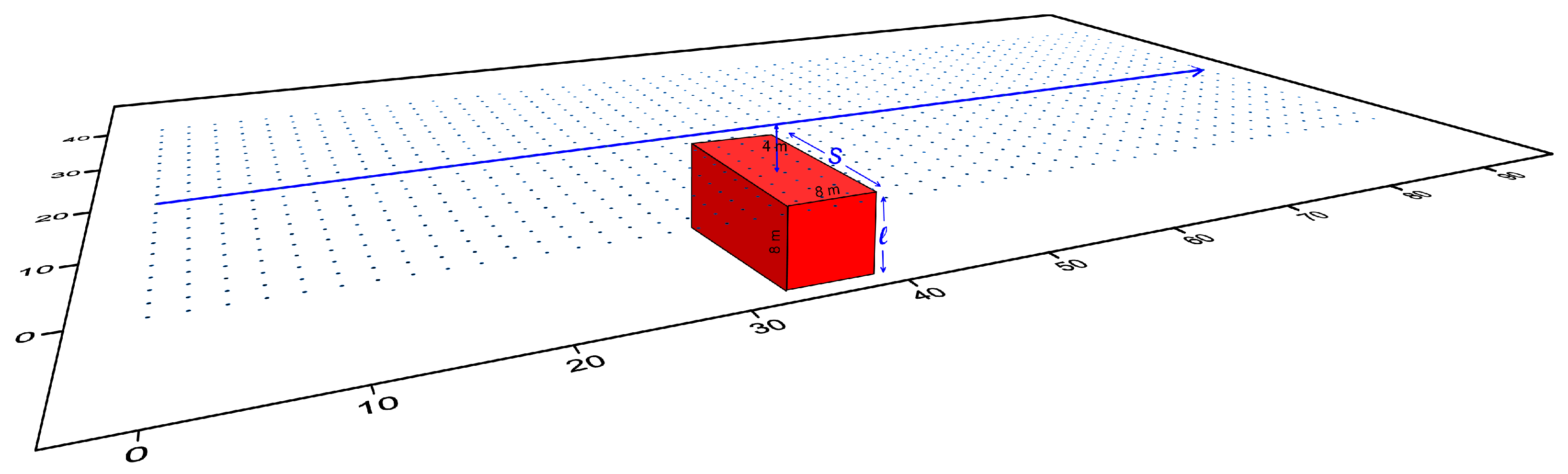
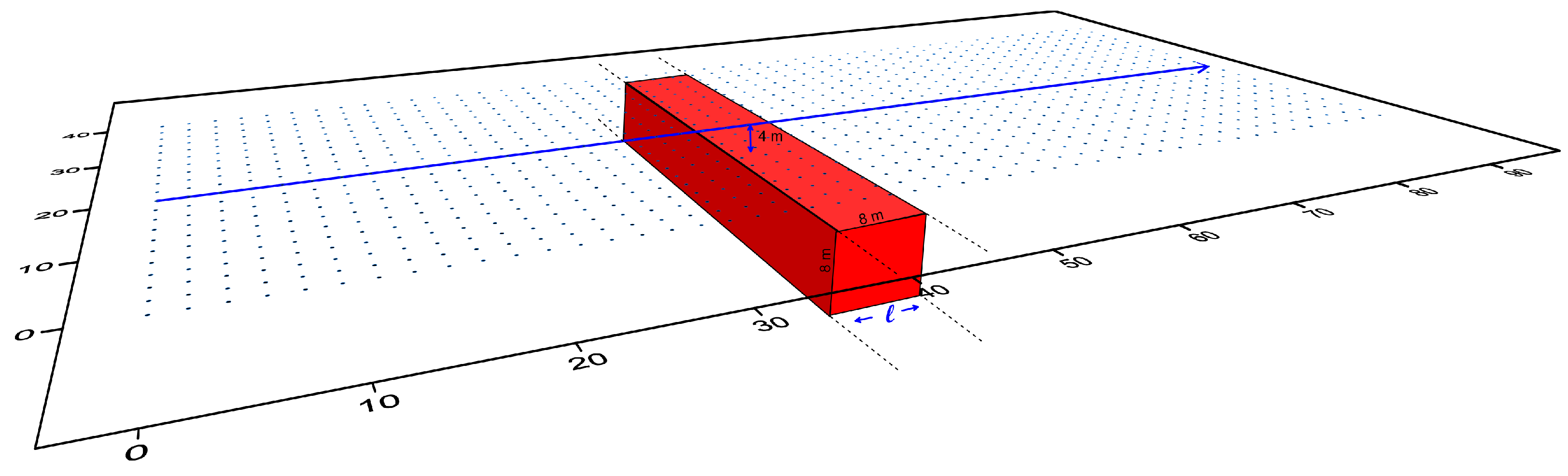
2.2. Design of Synthetic Models
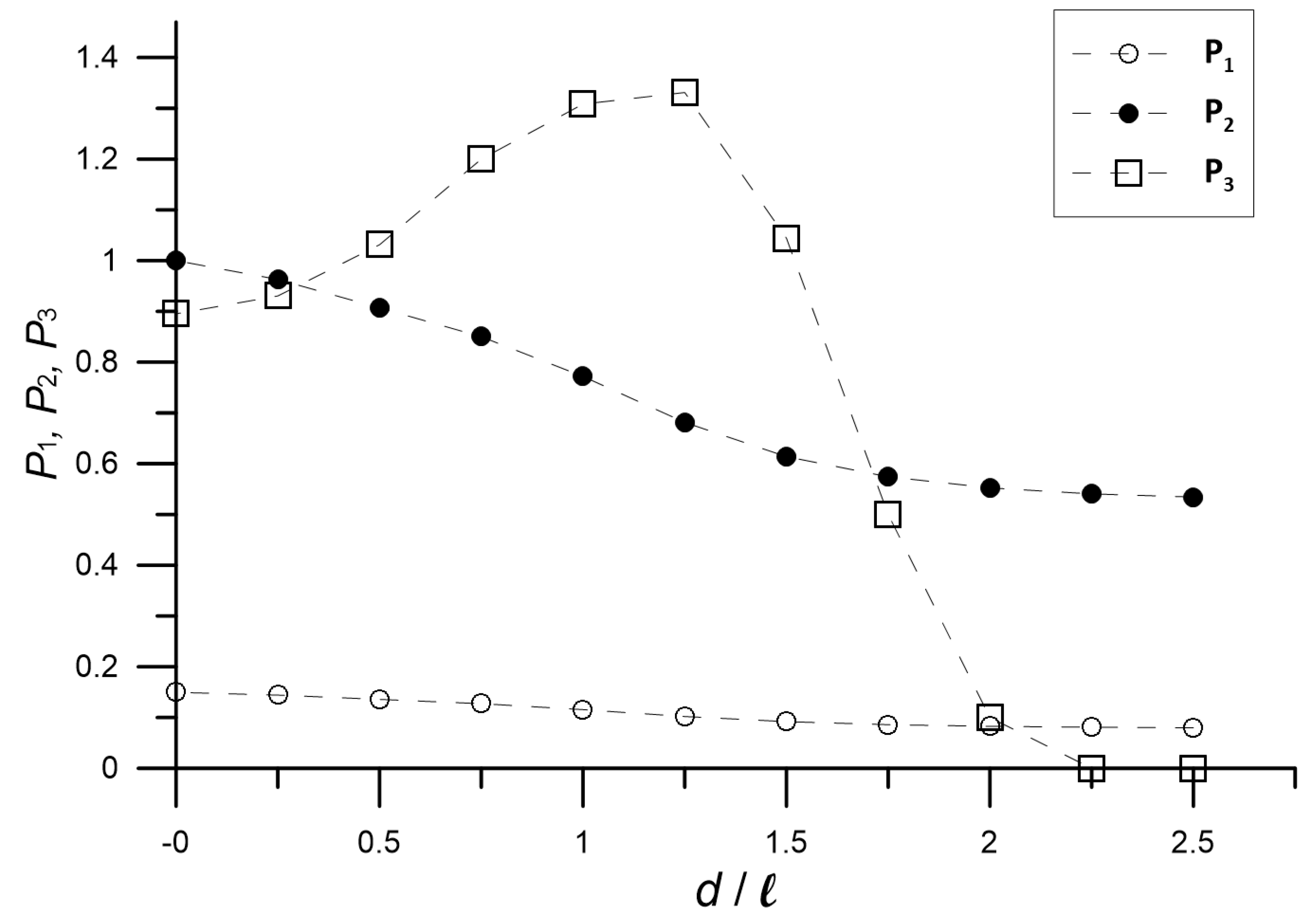
2.3. Parameters to Estimate the Inversion Reliability
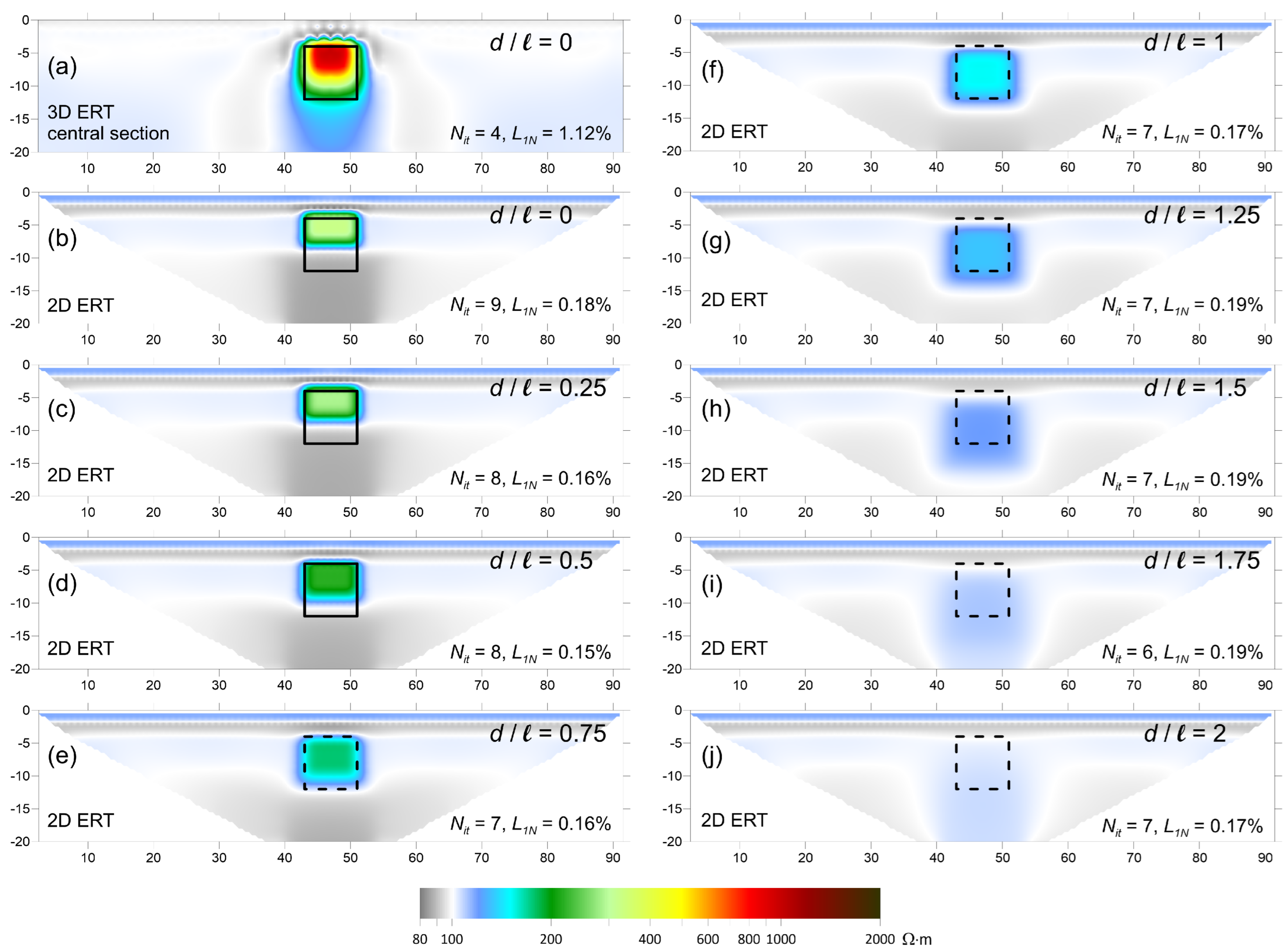
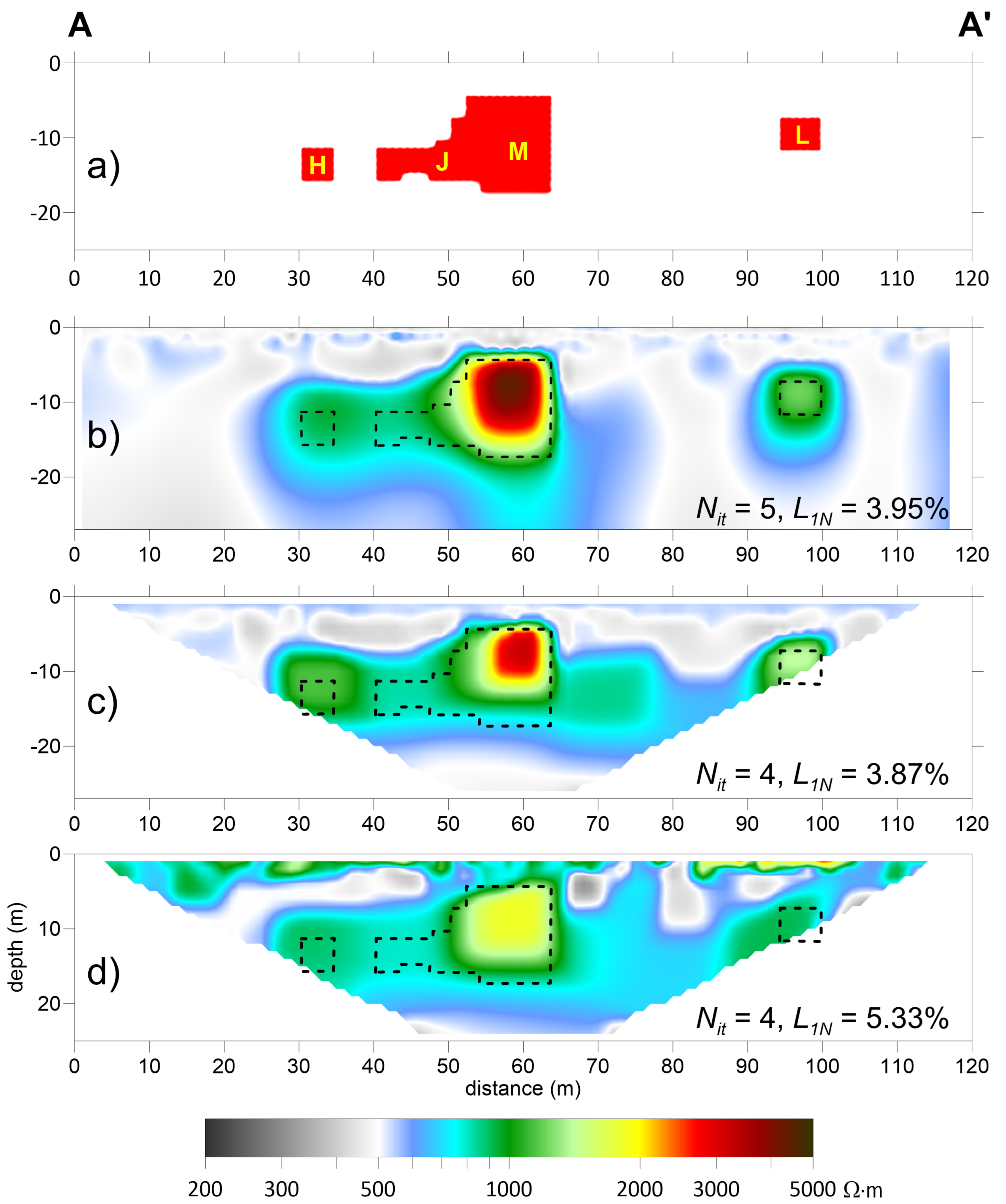
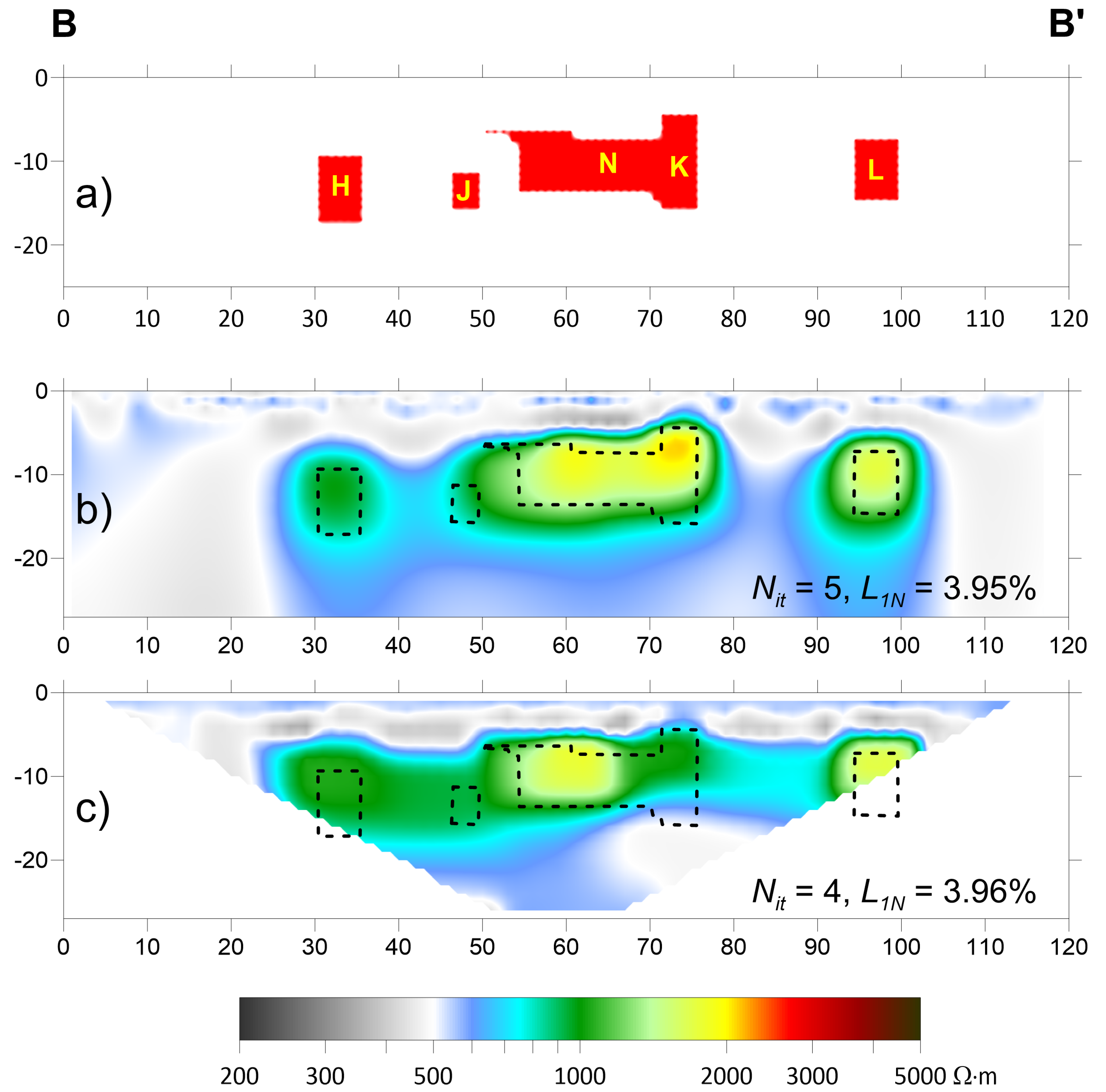
3. Results: Discussion and Comparison
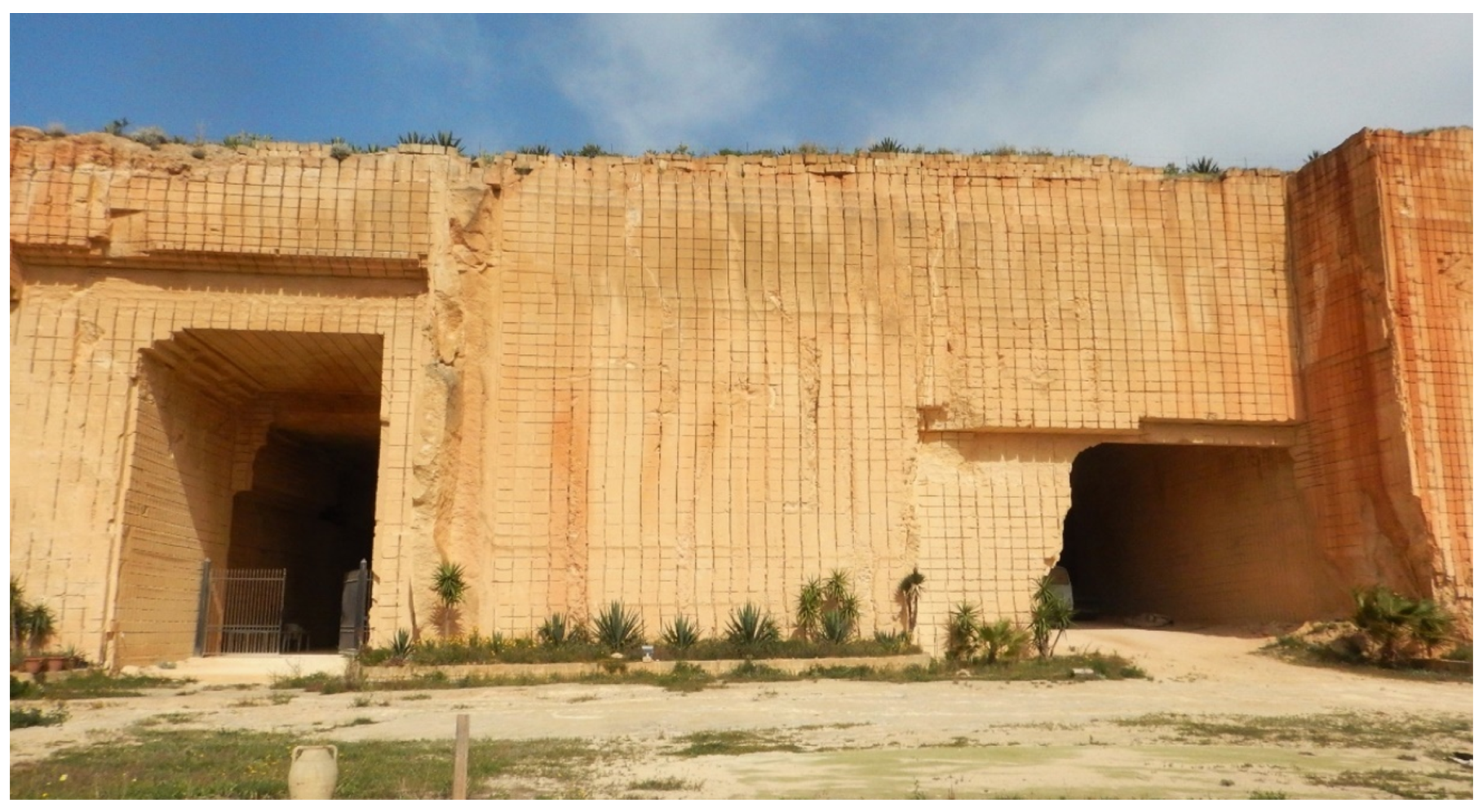
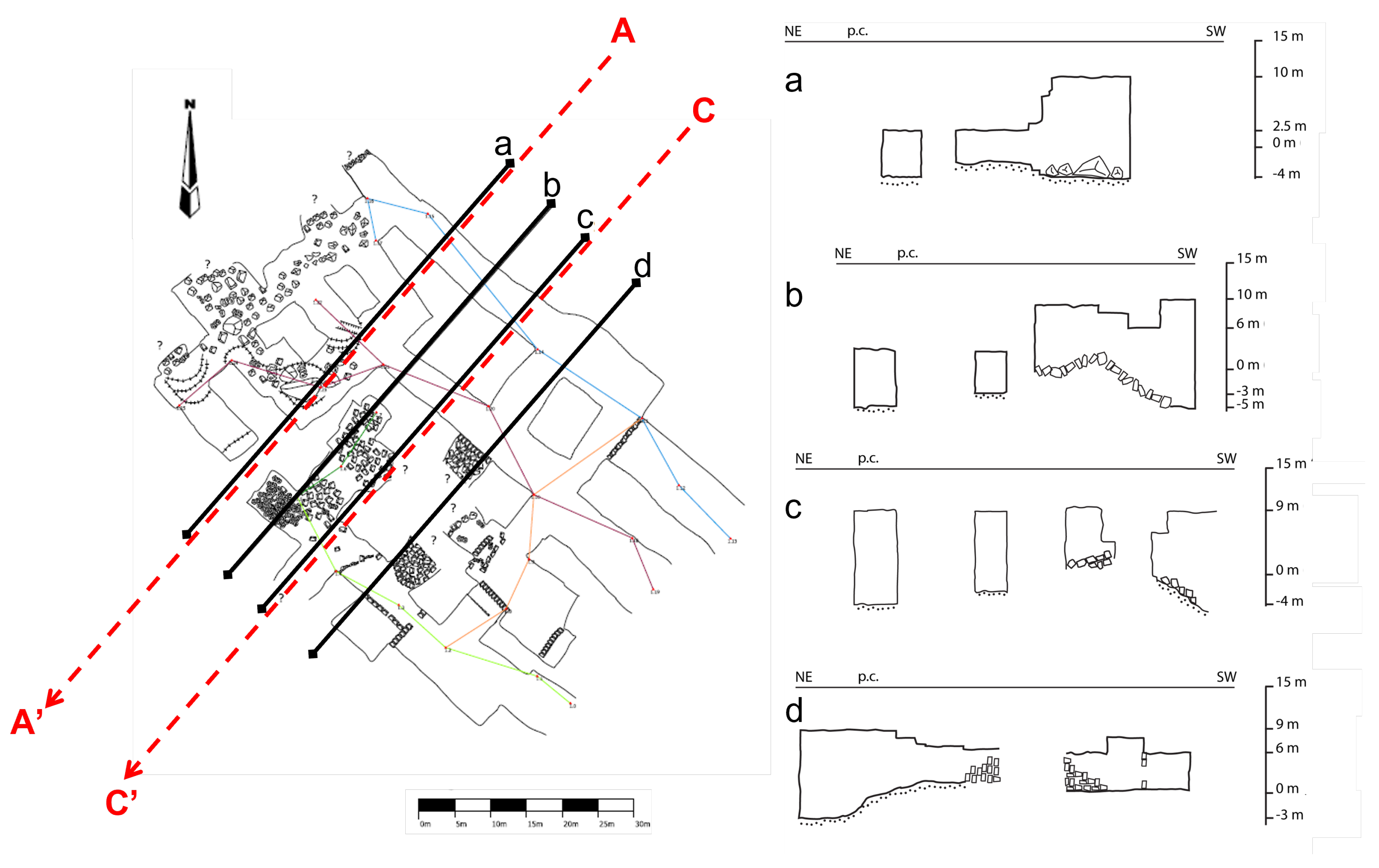
4. Field Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loke, M.; Chambers, J.; Rucker, D.; Kuras, O.; Wilkinson, P. Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 95, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.E.; Kuras, O.; Meldrum, P.I.; Ogilvy, R.D.; Hollands, J. Electrical resistivity tomography applied to geologic, hydrogeologic, and engineering investigations at a former waste-disposal site. Geophysics 2006, 71, B231–B239. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, T.; Zhou, B. Multiple-gradient array measurements for multichannel 2D resistivity imaging. Near Surf. Geophys. 2006, 4, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiandaca, G.; Martorana, R.; Messina, P.; Cosentino, P. The MYG methodology to carry out 3D electrical resistivity tomography on media covered by vulnerable surfaces of artistic value. Il Nuovo C. B 2010, 125, 711–718. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, T.C.; Versteeg, R.J.; Ward, A.; Day-Lewis, F.D.; Revil, A. Improved hydrogeophysical characterization and monitoring through parallel modeling and inversion of time-domain resistivity andinduced-polarization data. Geophysics 2010, 75, WA27–WA41. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M.; Wilkinson, P.; Uhlemann, S.; Chambers, J.; Oxby, L. Computation of optimized arrays for 3-D electrical imaging surveys. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 199, 1751–1764. [Google Scholar]
- Martorana, R.; Capizzi, P.; D’Alessandro, A.; Luzio, D. Comparison of different sets of array configurations for multichannel 2D ERT acquisition. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 137, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, A.; Cosentino, P.L.; Fiandaca, G.; Himi, M.; Macias, J.M.; Martorana, R.; Muñoz, A.; Rivero, L.; Sala, R.; Teixell, I. Non-invasive geophysical surveys in search of the Roman Temple of Augustus under the Cathedral of Tarragona (Catalonia, Spain): A case study. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 39, 1107–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, F.M.; Loke, M.; Nawawi, M.; Abdullah, K. Assessing the reliability and performance of optimized and conventional resistivity arrays for shallow subsurface investigations. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 155, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizebeokhai, A.; Olayinka, A. Anomaly effects of arrays for 3d geoelectrical resistivity imaging using orthogonal or parallel 2d profiles. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 446–454. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, T.; Wisén, R.; Zhang, D. 3D effects on 2D resistivity imaging–modelling and field surveying results. In Proceedings of the Near Surface 2007-13th EAGE European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Istanbul, Turkey, 3–5 September 2007; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gharibi, M.; Bentley, L.R. Resolution of 3-D electrical resistivity images from inversions of 2-D orthogonal lines. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2005, 10, 339–349. [Google Scholar]
- Aizebeokhai, A.; Olayinka, A.; Singh, V.; Uhuegbu, C. Effectiveness of 3D geoelectrical resistivity imaging using parallel 2D profiles. Curr. Sci. 2011, 101, 1036–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, K.; Nakazato, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Sugimoto, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Yoshisako, H.; Konno, M.; Shoda, D. Investigation of the line arrangement of 2D resistivity surveys for 3D inversion. Explor. Geophys. 2018, 49, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Cardarelli, E.; Fischanger, F. 2D data modelling by electrical resistivity tomography for complex subsurface geology. Geophys. Prospect. 2006, 54, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, T. 2D resistivity surveying for environmental and engineering applications. First Break. 1996, 14, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lagmanson, M. Comparison of 2D and 3D electrical resistivity imaging methods. In Proceedings of the Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems, Seattle, DC, USA, 2–6 April 2006; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2006; pp. 585–594. [Google Scholar]
- Sjödahl, P.; Dahlin, T.; Zhou, B. 2.5 D resistivity modeling of embankment dams to assess influence from geometry and material properties. Geophysics 2006, 71, G107–G114. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlemann, S.; Chambers, J.; Falck, W.E.; Tirado Alonso, A.; Fernández González, J.L.; Espín de Gea, A. Applying electrical resistivity tomography in ornamental stone mining: Challenges and solutions. Minerals 2018, 8, 491. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, T.; Loke, M.H. Resolution of 2D Wenner resistivity imaging as assessed by numerical modelling. J. Appl. Geophys. 1998, 38, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, T.; Loke, M. Quasi-3D resistivity imaging-mapping of three dimensional structures using two dimensional DC resistivity techniques. In Proceedings of the 3rd EEGS Meeting. European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, Aarhus, Denmark, 9–11 August 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Martorana, R.; Capizzi, P.; Carollo, A. Misinterpretation caused by 3D effects on 2d electrical resistivity tomography-tests on simple models. In Proceedings of the 24th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Porto, Portugal, 9–12 September 2018; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 2018, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.P.; Hung, Y.C.; Wu, P.L.; Yu, Z.H. Performance of 2-D ERT in investigation of abnormal seepage: A case study at the Hsin-Shan earth dam in Taiwan. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2014, 19, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.K.; Ha, I.S.; Kim, K.S.; Ahn, H.Y.; Lee, S.; Kang, H.J. 3D effects on 2D resistivity monitoring in earth-fill dams. Near Surf. Geophys. 2014, 12, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Arosio, D.; Hojat, A.; Ivanov, V.; Loke, M.; Longoni, L.; Papini, M.; Tresoldi, G.; Zanzi, L. A laboratory experience to assess the 3D effects on 2D ERT monitoring of river levees. In Proceedings of the 24th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics Porto, Portugal, 9–12 September 2018; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 2018, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hojat, A.; Arosio, D.; Ivanov, V.I.; Loke, M.H.; Longoni, L.; Papini, M.; Tresoldi, G.; Zanzi, L. Quantifying seasonal 3D effects for a permanent electrical resistivity tomography monitoring system along the embankment of an irrigation canal. Near Surf. Geophys. 2020, 18, 427–443. [Google Scholar]
- Nimmer, R.E.; Osiensky, J.L.; Binley, A.M.; Williams, B.C. Three-dimensional effects causing artifacts in two-dimensional, cross-borehole, electrical imaging. J. Hydrol. 2008, 359, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.s.; Dai, Q.w.; Bo, X. Contrast between 2D inversion and 3D inversion based on 2D high-density resistivity data. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.C.; Lin, C.P.; Lee, C.T.; Weng, K.W. 3D and boundary effects on 2D electrical resistivity tomography. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2963. [Google Scholar]
- Koefoed, O. Geosounding Principles, 1. Resistivity Sounding Measurements. In Methods in Geochemistry and Geophysics; Elsevier Scientific: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; Volume 14A, 276p. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, T.; Zhou, B. A numerical comparison of 2D resistivity imaging with 10 electrode arrays. Geophys. Prospect. 2004, 52, 379–398. [Google Scholar]
- Szalai, S.; Szarka, L. On the classification of surface geoelectric arrays. Geophys. Prospect. 2008, 56, 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Martorana, R.; Fiandaca, G.; Casas Ponsati, A.; Cosentino, P. Comparative tests on different multi-electrode arrays using models in near-surface geophysics. J. Geophys. Eng. 2009, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Morrison, H. Resistivity modelling for arbitrarily shaped two-dimensional structures. Geophys. Prospect. 1979, 27, 106–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Morrison, H.F. Resistivity modeling for arbitrarily shaped three-dimensional structures. Geophysics 1979, 44, 753–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidlisecky, A.; Haber, E.; Knight, R. RESINVM3D: A 3D resistivity inversion package. Geophysics 2007, 72, H1–H10. [Google Scholar]
- Coggon, J. Electromagnetic and electrical modeling by the finite element method. Geophysics 1971, 36, 132–155. [Google Scholar]
- Inman, J.R. Resistivity inversion with ridge regression. Geophysics 1975, 40, 798–817. [Google Scholar]
- Lines, L.; Treitel, S. A review of least-squares inversion and its application to geophysical problems. Geophys. Prospect. 1984, 32, 159–186. [Google Scholar]
- deGroot Hedlin, C.; Constable, S. Occam’s inversion to generate smooth, two-dimensional models from magnetotelluric data. Geophysics 1990, 55, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, Y. Resolution of resistivity tomography inferred from numerical simulation. Geophys. Prospect. 1992, 40, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, S.C.; Parker, R.L.; Constable, C.G. Occam’s inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data. Geophysics 1987, 52, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, R.; Oldenburg, D. Applied geophysical inversion. Geophys. J. Int. 1994, 116, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H.; Rucker, D.; Chambers, J.; Wilkinson, P.; Kuras, O. Electrical resistivity surveys and data interpretation. In Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Farquharson, C.G.; Oldenburg, D.W. Non-linear inversion using general measures of data misfit and model structure. Geophys. J. Int. 1998, 134, 213–227. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M.H.; Acworth, I.; Dahlin, T. A comparison of smooth and blocky inversion methods in 2D electrical imaging surveys. Explor. Geophys. 2003, 34, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M. 3-D Resistivity and Ip Forward Modeling Using the Finite-Difference and Finite-Element Methods. Instruction Manual for RES3DMOD Ver. 2.14 and RES3DMODx64 Ver. 3.04; Geotomosoft Solutions: Gelugor, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Capizzi, P.; Martorana, R.; Carollo, A.; Vattano, M. Cluster analysis for cavity detection using seismic refraction and electrical resistivity tomography. In Proceedings of the 23rd European meeting of environmental and engineering geophysics, Malmö, Sweden, 3–7 September 2017; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands, 2017; Volune 2017, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Carollo, A.; Capizzi, P.; Martorana, R. Joint interpretation of seismic refraction tomography and electrical resistivity tomography by cluster analysis to detect buried cavities. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 178, 104069. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M. Rapid 2D Resistivity forward Modeling Using the Finite Difference and Finite Element Methods. Instruction Manual for RES2DMOD ver. 3.03; Geotomosoft Solutions: Gelugor, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M. Rapid 2-D Resistivity and IP Inversion Using the Least-Squares Method. Instruction Manual for RES2DINVx64 Ver. 4.07; Geotomosoft Solutions: Gelugor, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M. Rapid 3-D Resistivity and IP Inversion Using the Least-Squares Method. Instruction Manual for RES3DINVx64 Ver. 3.13; Geotomosoft Solutions: Gelugor, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bonamini, M.; Di Maggio, C.; Lollino, P.; Madonia, G.; Parise, M.; Vattano, M. Study of anthropogenic sinkholes in the Marsala area (western Sicily) through numerical analyses of instability processes in underground quarries. In Proceedings of the GeoItalia 2011, VIII Forum Italiano di Scienze della Terra. IT, Torino, Italy, 19–23 September 2011; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Capizzi, P.; Martorana, R. Integration of constrained electrical and seismic tomographies to study the landslide affecting the cathedral of Agrigento. J. Geophys. Eng. 2014, 11, 045009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinea, A.; Bicknell, J.; Cox, N.; Swan, H.; Simmons, N. Characterization of legacy landfills with electrical resistivity tomography; A comparative study. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 203, 104716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martorana, R.; Capizzi, P. Evaluation of Artifacts and Misinterpretation in 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography Caused by Three-Dimensional Resistive Structures of Regular or Irregular Shapes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13032015
Martorana R, Capizzi P. Evaluation of Artifacts and Misinterpretation in 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography Caused by Three-Dimensional Resistive Structures of Regular or Irregular Shapes. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13032015
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartorana, Raffaele, and Patrizia Capizzi. 2023. "Evaluation of Artifacts and Misinterpretation in 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography Caused by Three-Dimensional Resistive Structures of Regular or Irregular Shapes" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13032015
APA StyleMartorana, R., & Capizzi, P. (2023). Evaluation of Artifacts and Misinterpretation in 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography Caused by Three-Dimensional Resistive Structures of Regular or Irregular Shapes. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13032015








